Effect of Mobile-Based Lifestyle Intervention on Body Weight, Glucose and Lipid Metabolism among the Overweight and Obese Elderly Population in China: A Randomized Controlled Trial Protocol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
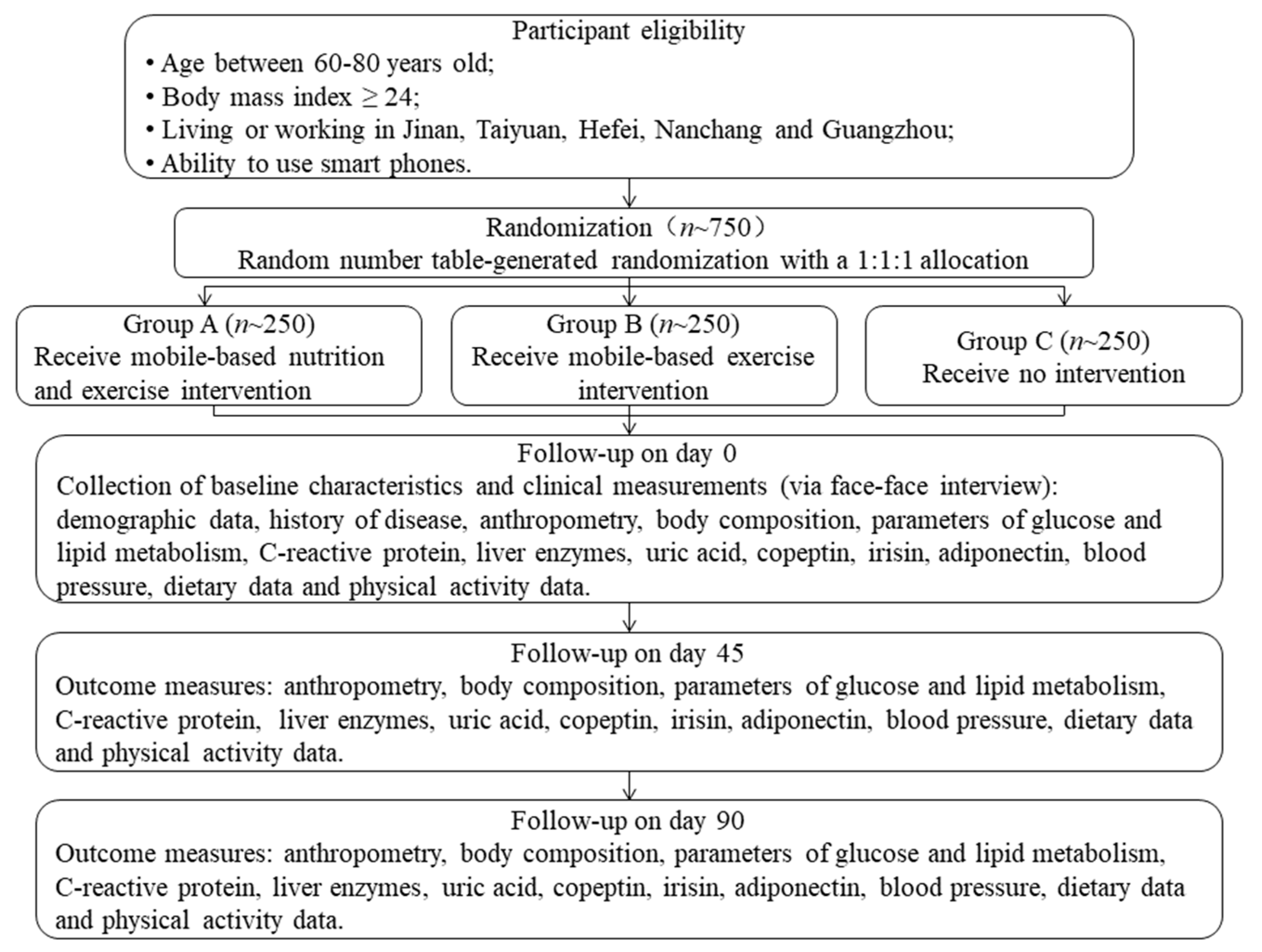
2.1. Sample Selected
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Randomization and Blinding
2.4. Intervention
2.5. Follow-Up
2.6. Procedures
| Time Point | At Enrollment | After Allocation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start (Day 0) | Day 45 | Day 90 | ||
| Enrolment | ||||
| Eligibility screen | √ | |||
| Informed consent | √ | |||
| Collection of basic information | √ | |||
| Randomization | √ | |||
| App and sports bracelet training | √ | |||
| Interventions (day 0-day 90) | √ | √ | √ | |
| Follow-up (day 0-day 90) | √ | √ | √ | |
| Assessments | ||||
| Anthropometry | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Body composition (Inbody measurement) | √ | √ | √ | |
| Blood lipids | √ | √ | √ | |
| Fasting and postprandial blood sugar | √ | √ | √ | |
| Hemoglobin A1C | √ | √ | √ | |
| Blood CRP and insulin | √ | √ | √ | |
| Blood ALT and AST | √ | √ | √ | |
| Blood uric acid | √ | √ | √ | |
| Blood copeptin | √ | √ | √ | |
| Blood irisin | √ | √ | √ | |
| Blood adiponectin | √ | √ | √ | |
| Blood pressure | √ | √ | √ | |
| Dietary data | √ | √ | √ | |
| Physical activity data | √ | √ | √ | |
2.7. Outcomes
2.7.1. Anthropometry
2.7.2. Body Composition
2.7.3. Parameters of Glucose and Lipid Metabolism, C-Reactive Protein, Liver Enzymes, Uric Acid, Copeptin, Irisin and Adiponectin
2.7.4. Blood Pressure (Systolic and Diastolic)
2.7.5. Dietary Data and Physical Activity Data
2.8. Sample Size Calculation
2.9. Statistical Analysis
2.10. Ethics
2.11. Providing Suggestions
2.12. Dissemination
3. Trial Registration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jaacks, L.M.; Vandevijvere, S.; Pan, A.; McGowan, C.J.; Wallace, C.; Imamura, F.; Mozaffarian, D.; Swinburn, B.; Ezzati, M. The Obesity Transition: Stages of the Global Epidemic. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Jiang, C.; Wang, M.; Cai, R.; Zhang, Y.; He, Z.; Wang, H.; Wu, D.; Wang, F.; Liu, X.; et al. BMI, Leisure-Time Physical Activity, and Physical Fitness in Adults in China: Results From a Series of National Surveys, 2000–2014. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016, 4, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fock, K.M.; Khoo, J. Diet and Exercise in Management of Obesity and Overweight. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.M.; Chen, Z.H.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, Z.P.; Huang, Z.J.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Guan, Y.Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.H. Study of the Prevalence and Disease Burden of Chronic Disease in the Elderly in China. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2019, 40, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.B.; Liu, Y.; Willett, W.C. Preventing Chronic Diseases by Promoting Healthy Diet and Lifestyle: Public Policy Implications for China. Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, U.; Kwok, L.L.; Magkidis, A. Efficacy of Lifestyle Interventions in Reducing Diabetes Incidence in Patients with Impaired Glucose Tolerance: A Systematic Re-View of Randomized Controlled Trials. Metabolism 2013, 62, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, B.C.; Kanters, S.; Bandayrel, K.; Wu, P.; Naji, F.; Siemieniuk, R.A.; Ball, G.D.C.; Busse, J.W.; Thorlund, K.; Guyatt, G.; et al. Comparison of Weight Loss Among Named Diet Programs in Overweight and Obese Adults. JAMA 2014, 312, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannu, G.S.; Zaman, M.J.; Gupta, A.; Rehman, H.U.; Myint, P.K. Evidence of Lifestyle Modification in the Management of Hypercholesterolemia. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2013, 9, 2–14. [Google Scholar]
- Lackland, D.T.; Voeks, J.H. Metabolic Syndrome and Hypertension: Regular Exercise as Part of Lifestyle Management. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2014, 16, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Gómez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Trenell, M. Treatment of NAFLD with Diet, Physical Activity and Exercise. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 829–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamaoka, K.; Tango, T. Effects of Lifestyle Modification on Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Med. 2012, 10, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, P.; Mukerji, G.; Desveaux, L.; Ivers, N.M.; Bhattacharyya, O.; Hensel, J.M.; Shaw, J.; Bouck, Z.; Jamieson, T.; Onabajo, N.; et al. Mobile App for Improved Self-Management of Type 2 Diabetes: Multicenter Pragmatic Randomized Controlled Trial. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2019, 7, e10321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindahl, B.; Nilssön, T.K.; Borch-Johnsen, K.; Røder, M.E.; Söderberg, S.; Widman, L.; Johnson, O.; Hallmans, G.; Jansson, J. A Randomized Lifestyle Intervention With 5-Year Follow-up In Subjects With Impaired Glucose Tolerance: Pronounced Short-Term Impact but Long-Term Adherence Problems. Scand. J. Public Health 2009, 37, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Moseson, H.; Uppal, J.; Juusola, J.L. A Diabetes Mobile App With in-App Coaching From a Certified Diabetes Educator Reduces a1c for Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Educ. 2018, 44, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, G.G.; Steinberg, D.; Askew, S.; Levine, E.; Foley, P.; Batch, B.C.; Svetkey, L.P.; Bosworth, H.B.; Puleo, E.M.; Brewer, A.; et al. Effectiveness of an App and Provider Counseling For Obesity Treatment in Primary Care. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2018, 55, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro-Ramos, T.; Lee, D.; Kim, Y.; Michaelides, A.; Oh, T.J.; Kim, K.M.; Jang, H.C.; Lim, S. Effectiveness of a Smartphone Application for the Management of Metabolic Syndrome Components Focusing on Weight Loss: A Preliminary Study. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2017, 15, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godino, J.G.; Merchant, G.; Norman, G.J.; Donohue, M.C.; Marshall, S.J.; Fowler, J.H.; Calfas, K.J.; Huang, J.S.; Rock, C.L.; Griswold, W.G.; et al. Using Social and Mobile Tools for Weight Loss in Overweight and Obese Young Adults (Project Smart): A 2 Year, Parallel-Group, Randomised, Controlled Trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016, 4, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, N.; Liang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, S.; Du, S.; He, H.; Xu, Y.; Cai, H.; et al. The Amounts and Contributions of Total Drinking Fluids and Water from Food to Total Water Intake of Young Adults in Baoding, China. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 2669–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalewski, B.M.; Szajewska, H. Effect of Glucomannan Supplementation on Body Weight in Overweight and Obese Children: Protocol of a Randomised Controlled Trial. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e007244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, H.; Paillard-Borg, S.; Zhu, H.; Qi, X.; Rizzuto, D. Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity among Chinese Adults: Role of Adiposity Indicators and Age. Obes. Facts 2016, 9, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Xu, Y.; He, H.; Cai, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Yan, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, N.; Maddela, R.L.; et al. Effects of a Meal Replacement on Body Composition and Metabolic Parameters Among Subjects With Overweight or Obesity. J. Obes. 2018, 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, X.; Xu, Y.; He, H.; Cai, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Yan, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, N.; Maddela, R.L.; et al. Visceral Fat Reduction Is Positively Associated With Blood Pressure Reduction in Overweight or Obese Males but Not Females: An Observational Study. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 16, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joint Committee Issued Chinese Guideline For The Management of Dyslipidemia in Adults. Chinese Guideline for the Management of Dyslipidemia in Adults. Chin. Circ. J. 2016, 31, 937–953.
- Alberti, K.G.M.M.; Zimmet, P.Z. Definition, Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications. Part 1: Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Provisional Report of a WHO Consultation. Diab. Med. 1998, 15, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multidisciplinary Expert Task Force on Hyperuricemia and Related Diseases. Chinese Multidisciplinary Expert Consensus on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Hyperuricemia and Related Diseases. Chin. Med. J. 2017, 130, 2473–2488. [CrossRef]
- Chobanian, A.V.; Bakris, G.L.; Black, H.R.; Cushman, W.C.; Green, L.A.; Izzo, J.L.; Jones, D.W.; Materson, B.J.; Oparil, S.; Wright, J.T.; et al. Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Hypertension 2003, 42, 1206–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahar, D.; Shai, I.; Vardi, H.; Brener-Azrad, A.; Fraser, D. Development of a Semi-Quantitative Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ) to Assess Dietary Intake of Multiethnic Populations. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 18, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Chinese Food Composition Table; Peking University Medical Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kleist, B.; Wahrburg, U.; Stehle, P.; Schomaker, R.; Greiwing, A.; Stoffel-Wagner, B.; Egert, S. Moderate Walking Enhances the Effects of an Energy-Restricted Diet on Fat Mass Loss and Serum Insulin in Overweight and Obese Adults in a 12-Week Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 1875–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Liu, T.; Teng, Y.Q.; Yao, X.Y.; Zhao, T.T.; Lin, L.Y.; Jin, Q.S.; Jin, Y.J. Effect of a 12-Week Aerobic Exercise Training on Serum Fetuin-A and Adipocytokine Levels in Type 2 Diabetes. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2018, 126, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Liu, K.; Colangelo, L.A.; Yan, L.L.; Klein, L.; Loria, C.M.; Lewis, C.E.; Savage, P. Consistently Stable or Decreased Body Mass Index in Young Adulthood and Longitudinal Changes in Metabolic Syndrome Components. Circulation 2007, 115, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, G.; Kong, L.; Zhao, W.; Wan, X.; Zhai, Y.; Chen, L.C.; Koplan, J.P. Emergence of Chronic Non-Communicable Diseases in China. Lancet 2008, 372, 1697–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, K.; Mathers, C.; Leeder, S.; Beaglehole, R. Preventing Chronic Diseases: How Many Lives Can We Save? Lancet 2005, 366, 1578–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herder, C.; Peltonen, M.; Koenig, W.; Sütfels, K.; Lindström, J.; Martin, S.; Ilanne-Parikka, P.; Eriksson, J.G.; Aunola, S.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Lifestyle Changes in the Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quinn, C.C.; Clough, S.S.; Minor, J.M.; Lender, D.; Okafor, M.C.; Gruber-Baldini, A. WellDoc™ Mobile Diabetes Management Randomized Controlled Trial: Change in Clinical and Behavioral Outcomes and Patient and Physician Satisfaction. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2008, 10, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, J.B.; Yu, X.W.; Yi, X.R.; Wang, C.H.; Tuo, X.P. Epidemiology of Chronic Noncommunicable Diseases and Evaluation of Life Quality in Elderly. Aging Med. 2018, 1, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Outcomes | Assessments |
|---|---|
| Primary outcome | the between-group (three groups) difference in body mass index at the end of intervention |
| Secondary outcomes | parameters of glucose and lipid metabolism, CRP, liver enzymes, uric acid, copeptin, irisin, adiponectin, body composition, blood pressure, dietary data and physical activity data |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhang, N.; Yan, X.; Li, M.; Zhou, M.; He, H.; Li, Y.; Guo, W.; Zhang, M.; et al. Effect of Mobile-Based Lifestyle Intervention on Body Weight, Glucose and Lipid Metabolism among the Overweight and Obese Elderly Population in China: A Randomized Controlled Trial Protocol. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4854. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094854
Zhang Y, Guo X, Zhang N, Yan X, Li M, Zhou M, He H, Li Y, Guo W, Zhang M, et al. Effect of Mobile-Based Lifestyle Intervention on Body Weight, Glucose and Lipid Metabolism among the Overweight and Obese Elderly Population in China: A Randomized Controlled Trial Protocol. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(9):4854. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094854
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yu, Xiaohui Guo, Na Zhang, Xinyu Yan, Muxia Li, Mingzhu Zhou, Hairong He, Yibin Li, Wen Guo, Man Zhang, and et al. 2021. "Effect of Mobile-Based Lifestyle Intervention on Body Weight, Glucose and Lipid Metabolism among the Overweight and Obese Elderly Population in China: A Randomized Controlled Trial Protocol" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 9: 4854. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094854
APA StyleZhang, Y., Guo, X., Zhang, N., Yan, X., Li, M., Zhou, M., He, H., Li, Y., Guo, W., Zhang, M., Zhang, J., & Ma, G. (2021). Effect of Mobile-Based Lifestyle Intervention on Body Weight, Glucose and Lipid Metabolism among the Overweight and Obese Elderly Population in China: A Randomized Controlled Trial Protocol. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(9), 4854. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094854








