The Microbiota-Bone-Allergy Interplay
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Osteoporosis
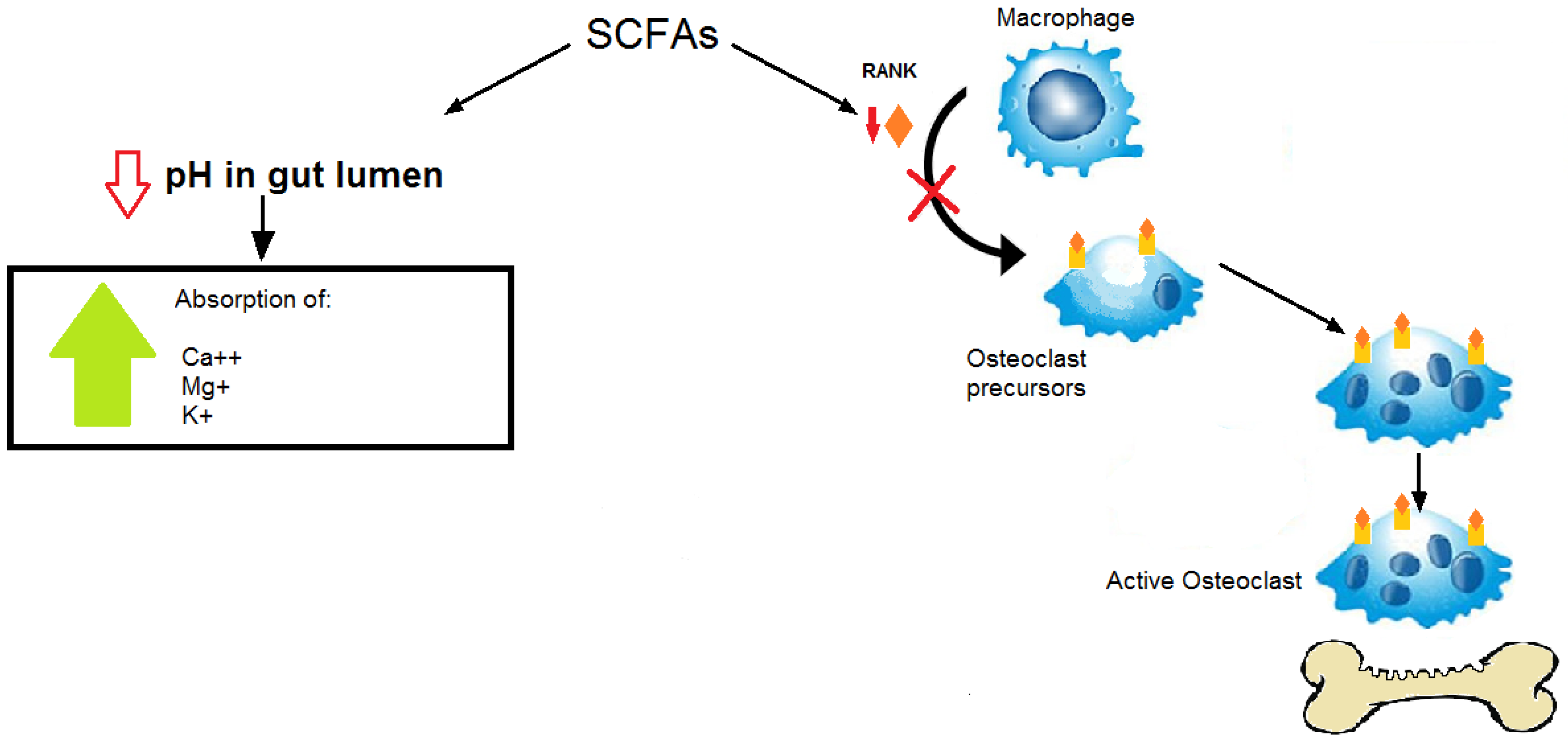
3. Microbiota and Osteoporosis
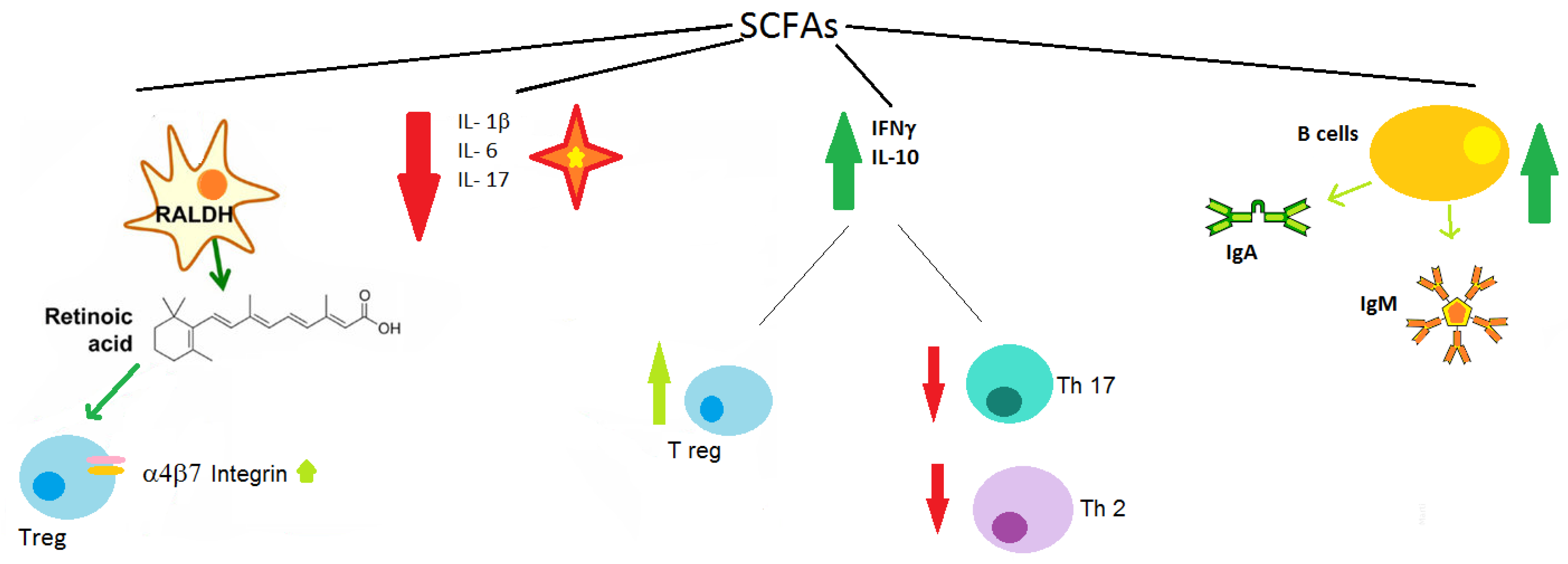
4. Allergy
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nance, C.L.; Deniskin, R.; Diaz, V.C.; Paul, M.; Anvari, S.; Anagnostou, A. The Role of the Microbiome in Food Allergy: A Review. Children 2020, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.Y.; Groer, M.; Dutra, S.V.O.; Sarkar, A.; McSkimming, D.I. Gut Microbiota and Immune System Interactions. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.H.; Song, Y.; Wu, W.; Yu, K.; Zhang, G. The gut microbiota, environmental factors, and links to the development of food allergy. Clin. Mol. Allergy 2020, 18, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Jazwinski, S.M. The Gut Microbiota and Healthy Aging: A Mini-Review. Gerontology 2018, 64, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miqdady, M.; Al Mistarihi, J.; Azaz, A.; Rawat, D. Prebiotics in the Infant Microbiome: The Past, Present, and Future. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2020, 23, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreft, L.; Hoffmann, C.; Ohnmacht, C. Therapeutic Potential of the Intestinal Microbiota for Immunomodulation of Food Allergies. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, N.B.; Bilezikian, J.P.; Camacho, P.M.; Greenspan, S.L.; Harris, S.T.; Hodgson, S.F.; Kleerekoper, M.; Luckey, M.M.; McClung, M.R.; Pollack, R.P.; et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists Medical Guidelines for Clinical Practice for the diagnosis and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Endocr. Pract. 2010, 16, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Mao, Y.; Zhou, F.; Yang, H.; Shi, Q.; Meng, B. Gut microbiome and osteoporosis: A review. Bone Jt. Res. 2020, 9, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irelli, A.; Sirufo, M.M.; Scipioni, T.; De Pietro, F.; Pancotti, A.; Ginaldi, L.; De Martinis, M. mTOR Links Tumor Immunity and Bone Metabolism: What are the Clinical Implications? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Martinis, M.; Sirufo, M.M.; Ginaldi, L. Osteoporosis: Current and Emerging Therapies Targeted to Immunological Checkpoints. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 6356–6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martinis, M.; Sirufo, M.M.; Polsinelli, M.; Placidi, G.; Di Silvestre, D.; Ginaldi, L. Gender Differences in Osteoporosis: A Single-Center Observational Study. World J. Men’s Health 2021, 39, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirufo, M.M.; Ginaldi, L.; De Martinis, M. Bone Health Risks Associated with Finasteride and Dutasteride Long-Term Use. World J. Men’s Health 2021, 39, 389–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofbauer, L.C.; Khosla, S.; Dunstan, C.R.; Lacey, D.L.; Boyle, W.J.; Riggs, B.L. The roles of osteoprotegerin and osteoprotegerin ligand in the paracrine regulation of bone resorption. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2000, 15, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofbauer, L.C.; Khosla, S.; Dunstan, C.R.; Lacey, D.L.; Spelsberg, T.C.; Riggs, B.L. Estrogen stimulates gene expression and protein production of osteoprotegerin in human osteoblastic cells. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 4367–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lochlin, R.M.; Khosla, S.; Turner, R.T.; Riggs, B.L. Mediators of the bisphasic responses of bone to intermittent and continuously administered parathyroid hormone. J. Cell. Biochem. 2003, 89, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofbauer, L.C.; Gori, F.; Riggs, B.L.; Lacey, D.L.; Dunstan, C.R.; Spelsberg, T.C.; Khosla, S. Stimulation of osteoprotegerin ligand and inhibition of osteoprotegerin production by glucocorticoids in human osteoblastic lineage cells. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 4382–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeilschifter, J.; Köditz, R.; Pfohl, M.; Schatz, H. Changes in proinflammatory cytokine activity after menopause. Endocr. Rev. 2002, 23, 90–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bismar, H.; Diel, I.; Ziegler, R.; Pfeilschifter, J. Increased cytokine secretion by human bone marrow cells after menopause or discontinuation of estrogen replacement. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1995, 80, 3351–3355. [Google Scholar]
- D’Amelio, P.; Grimaldi, A.; Di Bella, S.; Brianza, S.Z.M.; Cristofaro, M.A.; Tamone, C.; Giribaldi, G.; Ulliers, D.; Pescarmona, G.P.; Isaia, G. Estrogen deficiency increases osteoclastogenesis up-regulating T cells activity: A key mechanism in osteoporosis. Bone 2008, 43, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitzmann, M.N.; Roggia, C.; Toraldo, G.; Weitzmann, L.; Pacifici, R. Increased production of IL-7 uncouples bone formation from bone resorption during estrogen deficiency. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 1643–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghbali-Fatourechi, G.; Khosla, S.; Sanyal, A.; Boyle, W.J.; Lacey, D.L.; Riggs, B.L. Role of RANK ligand in mediating increased bone resorption in early postmenopausal women. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 1221–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.Y.; Tawfeek, H.; Bedi, B.; Yang, X.; Adams, J.; Gao, K.Y.; Zayzafoon, M.; Weitzmann, M.N.; Pacifici, R. Ovariectomy disregulates osteoblast and osteoclast formation through the T-cell receptor CD40 ligand. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sjögren, K.; Engdahl, C.; Henning, P.; Lerner, U.H.; Tremaroli, V.; Lagerquist, M.K.; Bäckhed, F.; Ohlsson, C. The gut microbiota regulates bone mass in mice. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2012, 27, 1357–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.Y.; Chassaing, B.; Tyagi, A.M.; Vaccaro, C.; Luo, T.; Adams, J.; Darby, T.M.; Weitzmann, M.N.; Mulle, J.G.; Gewirtz, A.T.; et al. Sex steroid deficiency-associated bone loss is microbiota dependent and prevented by probiotics. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 2049–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hernandez, C.J.; Moeller, A.H. The microbiome: A heritable contributor to bone morphology? Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, F.L.; Rios-Arce, N.D.; Schepper, J.D.; Parameswaran, N.; McCabe, L.R. The Potential of Probiotics as a Therapy for Osteoporosis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, Y.; Irie, K.; Fukuhara, D.; Kataoka, K.; Hattori, T.; Ono, M.; Ekuni, D.; Kubota, S.; Morita, M. Commensal Microbiota Enhance Both Osteoclast and Osteoblast Activities. Molecules 2018, 23, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Q.; Wei, X.; Feng, G.; Zhao, M.; Pei, Y.; Zhang, L. Assessing causal relationship from gut microbiota to heel bone mineral density. Bone 2020, 143, 115652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Gao, W.; Wang, B.; Zhao, H.; Zeng, Y.; Ji, Y.; Hao, D. Diversity analysis of gut microbiota in osteoporosis and osteopenia patients. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaughn, A.C.; Cooper, E.M.; DiLorenzo, P.M.; O’Loughlin, L.J.; Konkel, M.E.; Peters, J.H.; Hajnal, A.; Sen, T.; Lee, S.H.; de La Serre, C.B.; et al. Energy-dense diet triggers changes in gut microbiota, reorganization of gut brain vagal communication and increases body fat accumulation. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2017, 77, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rowland, I.; Gibson, G.; Heinken, A.; Scott, K.; Swann, J.; Thiele, I.; Tuohy, K. Gut microbiota functions: Metabolism of nutrients and other food components. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cox, L.M.; Yamanishi, S.; Sohn, J.; Alekseyenko, A.V.; Leung, J.M.; Cho, I.; Kim, S.G.; Li, H.; Gao, Z.; Mahana, D.; et al. Altering the intestinal microbiota during a critical developmental window has lasting metabolic consequences. Cell 2014, 158, 705–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saltzman, J.R.; Russell, R.M. The aging gut: Nutritional issues. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 1998, 27, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, E.M. Gut bacteria in health and disease. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 9, 560–569. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty, D.P.; Mohapatra, S.; Misra, S.; Sahu, P.S. Milk derived bioactive peptides and their impact on human health: A review. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 23, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, G.Q.; Guo, C.; Song, G.H.; Fang, N.; Fan, W.J.; Chen, X.D.; Yuan, L.; Wang, Z.Q. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) promotes osteoclast differentiation and activation by enhancing the MAPK pathway and COX-2 expression in RAW264.7 cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 32, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Itoh, K.; Udagawa, N.; Kobayashi, K.; Suda, K.; Li, X.; Takami, M.; Okahashi, N.; Nishihara, T.; Takahashi, N. Lipopolysaccharide promotes the survival of osteoclasts via Toll-like receptor 4, but cytokine production of osteoclasts in response to lipopolysaccharide is different from that of macrophages. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 3688–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, C.M.; Diet, W.C.M. Diet, gut microbiome, and bone health. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2015, 13, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, S.A.; Griffin, I.J.; Hawthorne, K.M.; Liang, L.; Gunn, S.K.; Darlington, G.; Ellis, K.J. A combination of prebiotic short- and long-chain inulin-type fructans enhances calcium absorption and bone mineralization in young adolescents. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.K.; Balaji, S.; Suresh, P.S.; Liu, X.S.; Lu, X.; Li, Z.; Guo, X.E.; Mann, J.J.; Balapure, A.K.; Gershon, M.D.; et al. Pharmacological inhibition of gut-derived serotonin synthesis is a potential bone anabolic treatment for osteoporosis. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.W.; Suh, J.H.; Kim, A.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, J.B. Histone deacetylase 1-mediated histone modification regulates osteoblast differentiation. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 2432–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katono, T.; Kawato, T.; Tanabe, N.; Suzuki, N.; Iida, T.; Morozumi, A.; Ochiai, K.; Maeno, M. Sodium butyrate stimulates mineralized nodule formation and osteoprotegerin expression by human osteoblasts. Arch. Oral Biol. 2008, 53, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Kukita, A.; Kukita, T.; Shobuike, T.; Nakamura, T.; Kohashi, O. Two histone deacetylase inhibitors, trichostatin A and sodium butyrate, suppress differentiation into osteoclasts but not into macrophages. Blood 2003, 101, 3451–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindels, L.B.; Delzenne, N.M.; Cani, P.D.; Walter, J. Towards a more comprehensive concept for prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Lin, Y.K.; Liu, Y.J.; Chang, K.H.; Chieng, P.U.; Chan, W.P. Prevalence of osteoporosis and low bone mass in older chinese population based on bone mineral density at multiple skeletal sites. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scholz-Ahrens, K.E.; Ade, P.; Marten, B.; Weber, P.; Timm, W.; Acil, Y.; Gluer, C.C.; Schrezenmeir, J. Prebiotics, probiotics, and synbiotics affect mineral absorption, bone mineral content, and bone structure. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 838s–846s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlsson, C.; Engdahl, C.; Fak, F.; Andersson, A.; Windahl, S.H.; Farman, H.H.; Moverare-Skrtic, S.; Islander, U.; Sjogren, K. Probiotics protect mice from ovariectomy-induced cortical bone loss. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Herzog, J.W.; Tsang, K.; Brennan, C.A.; Bower, M.A.; Garrett, W.S.; Sartor, B.R.; Aliprantis, A.O.; Charles, J.F. Gut microbiota induce IGF-1 and promote bone formation and growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E7554–E7563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiang, S.S.; Pan, T.M. Beneficial effects of phytoestrogens and their metabolites produced by intestinal microflora on bone health. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 1489–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, R.; Shi, J.; Fuhrman, B.; Xu, X.; Veenstra, T.D.; Gail, M.H.; Gajer, P.; Ravel, J.; Goedert, J.J. Fecal microbial determinants of fecal and systemic estrogens and estrogen metabolites: A cross-sectional study. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Britton, R.A.; Irwin, R.; Quach, D.; Schaefer, L.; Zhang, J.; Lee, T.; Parameswaran, N.; McCabe, L.R. Probiotic L. reuteri treatment prevents bone loss in a menopausal ovariectomized mouse model. J. Cell. Physiol. 2014, 229, 1822–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Motyl, K.J.; Irwin, R.; MacDougald, O.A.; Britton, R.A.; McCabe, L.R. Loss of bone and Wnt10b expression in male type 1 diabetic mice is blocked by the probiotic L. reuteri. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 3169–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, C.M.; Hong, T.; Van Pijkeren, J.P.; Hemarajata, P.; Trinh, D.V.; Hu, W.; Britton, R.A.; Kalkum, M.; Versalovic, J. Histamine derived from probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri suppresses TNF via modulation of PKA and ERK signaling. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.G.; Lee, E.; Kim, S.H.; Whang, K.Y.; Oh, S.; Imm, J.Y. Effects of a Lactobacillus casei 393 fermented milk product on bone metabolism in ovariectomised rats. Int. Dairy J. 2009, 19, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narva, M.; Halleen, J.; Väänänen, K.; Korpela, R. Effects of Lactobacillus helveticus fermented milk on bone cells in vitro. Life Sci. 2004, 75, 1727–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero-Franco, C.; Keller, K.; Simone, C.; Chadee, K. The VSL # 3 probiotic formula induces mucin gene expression and secretion in colonic epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 292, 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Crittenden, R.G.; Martinez, N.R.; Playne, M.J. Synthesis and utilisation of folate by yoghurt starter cultures and probiotic bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 80, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunachalam, K.D. Role of bifidobacteria in nutrition, medicine and technology. Nutr. Res. 1999, 19, 1559–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.M.; Fahey, G.C.; Wolf, B.W. Selected indigestible oligosaccharides affect large bowel mass, cecal and fecal short-chain fatty acids, pH and microflora in rats. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, L.R.; Irwin, R.; Schaefer, L.; Britton, R.A. Probiotic use decreases intestinal inflammation and increases bone density in healthy male but not female mice. J. Cell. Physiol. 2013, 228, 1793–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collins, F.L.; Irwin, R.; Bierhalter, H.; Schepper, J.; Britton, R.A.; Parameswaran, N.; McCabe, L.R. Lactobacillus reuteri 6475 Increases Bone Density in Intact Females Only under an Inflammatory Setting. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, J.A.; Bernstein, I.L.; Bucchini, L.; Goldman, L.R.; Hamilton, R.G.; Lehrer, S.; Rubin, C.; Sampson, H.A. Clinical and laboratory investigation of allergy to genetically modified foods. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Martinis, M.; Sirufo, M.M.; Viscido, A.; Ginaldi, L. Food Allergies and Ageing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Martinis, M.; Sirufo, M.M.; Viscido, A.; Ginaldi, L. Food Allergy Insights: A Changing Landscape. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2020, 68, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Martinis, M.; Sirufo, M.M.; Ginaldi, L. Allergy and Aging: An Old/New Emerging Health Issue. Aging Dis. 2017, 8, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sicherer, S.H.; Sampson, H.A. Food allergy: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Martinis, M.; Sirufo, M.M.; Suppa, M.; Ginaldi, L. New Perspectives in Food Allergy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sirufo, M.M.; De Pietro, F.; Bassino, E.M.; Ginaldi, L.; De Martinis, M. Osteoporosis in Skin Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muir, A.B.; Benitez, A.J.; Dods, K.; Spergel, J.M.; Fillon, S.A. Microbiome and its impact on gastrointestinal atopy. Allergy 2016, 71, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aitoro, R.; Paparo, L.; Amoroso, A.; Di Costanzo, M.; Cosenza, L.; Granata, V.; Di Scala, C.; Nocerino, R.; Trinchese, G.; Montella, M.; et al. Gut microbiota as a target for preventive and therapeutic intervention against food allergy. Nutrients 2017, 9, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- West, C.E.; Renz, H.; Jenmalm, M.C.; Kozyrskyj, A.L.; Allen, K.; Vuillermin, P.; Prescott, S.L.; MacKay, C.; Salminen, S.; Wong, G.; et al. The gut microbiota and inflammatory noncommunicable diseases: Associations and potentials for gut microbiota therapies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalliomäki, M.; Kirjavainen, P.; Eerola, E.; Kero, P.; Salminen, S.; Isolauri, E. Distinct patterns of neonatal gut microflora in infants in whom atopy was and was not developing. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 107, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunyavanich, S.; Shen, N.; Grishin, A.; Wood, R.; Burks, W.; Dawson, P.; Jones, S.M.; Leung, D.Y.M.; Sampson, H.; Sicherer, S.; et al. Early-life gut microbiome composition and milk allergy resolution. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rachid, R.A.; Gerber, G.; Li, N.; Umetsu, D.T.; Bry, L.; Chatila, T.A. Food allergy in infancy is associated with dysbiosis of the intestinal microbiota. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, J.H.; Lee-Sarwar, K.A.; Sordillo, J.; Bunyavanich, S.; Zhou, Y.; O’Connor, G.; Sandel, M.; Bacharier, L.B.; Zeiger, R.; Sodergren, E.; et al. A prospective microbiome-wide association study of food sensitization and food allergy in early childhood. Allergy 2018, 73, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, M.B.; Konya, T.; Guttman, D.S.; Field, C.J.; Sears, M.R.; HayGlass, K.T.; Mandhane, P.J.; Turvey, S.E.; Subbarao, P.; Becker, A.B.; et al. Infant gut microbiota and food sensitization: Associations in the frst year of life. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2015, 45, 632–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, X.; Goedert, J.J.; Pu, A.; Yu, G.; Shi, J. Allergy associations with the adult fecal microbiota: Analysis of the American Gut Project. EBioMedicine 2016, 3, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inoue, R.; Sawai, T.; Sawai, C.; Nakatani, M.; Romero-Perez, G.A.; Ozeki, M.; Nonomura, K.; Tsukahara, T. A preliminary study of gut dysbiosis in children with food allergy. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2017, 81, 2396–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ling, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Luo, Y.; Tong, X.; Yuan, L.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, L.; et al. Altered fecal microbiota composition associated with food allergy in infants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 2546–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.-C.; Chen, K.-J.; Kong, M.-S.; Chang, H.-J.; Huang, J.-L. Alterations in the gut microbiotas of children with food sensitization in early life. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 27, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazlollahi, M.; Chun, Y.; Grishin, A.; Wood, R.A.; Burks, A.W.; Dawson, P.; Jones, S.M.; Leung, D.Y.M.; Sampson, H.A.; Sicherer, S.H.; et al. Early-life gut microbiome and egg allergy. Allergy 2018, 73, 1515–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, M.; Guadamuro, L.; Espinosa-Martos, I.; Mancabelli, L.; Jimenez, S.; Molinos-Norniella, C.; Perez-Solis, D.; Milani, C.; Rodriguez, J.M.; Ventura, M.; et al. Microbiota and derived parameters in fecal samples of infants with non-IgE cow’s milk protein allergy under a restricted diet. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berni Canani, R.; De Filippis, F.; Nocerino, R.; Paparo, L.; Di Scala, C.; Cosenza, L.; Della Gatta, G.; Calignano, A.; De Caro, C.; Laiola, M.; et al. Gut microbiota composition and butyrate production in children afected by non-IgE-mediated cow’s milk allergy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kourosh, A.; Luna, R.A.; Balderas, M.; Nance, C.; Anagnostou, A.; Devaraj, S.; Davis, C.M. Fecal microbiome signatures are diferent in food-allergic children compared to siblings and healthy children. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 29, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanis, J.M.; Alexeev, E.E.; Curtis, V.F.; Kitzenberg, D.A.; Kao, D.J.; Battista, K.D.; Gerich, M.E.; Glover, L.E.; Kominsky, D.J.; Colgan, S.P. Tryptophan metabolite activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor regulates IL-10 receptor expression on intestinal epithelia. Mucosal. Immunol. 2017, 10, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; McKenzie, C.; Vuillermin, P.J.; Goverse, G.; Vinuesa, C.G.; Mebius, R.E.; Macia, L.; Mackay, C.R. Dietary fiber and bacterial SCFA enhance oral tolerance and protect against food allergy through diverse cellular pathways. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 2809–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiménez-Saiz, R.; Anipindi, V.C.; Galipeau, H.; Ellenbogen, Y.; Chaudhary, R.; Koenig, J.F.; Gordon, M.E.; Walker, T.D.; Mandur, T.S.; Abed, S.; et al. Microbial Regulation of Enteric Eosinophils and Its Impact on Tissue Remodeling and Th2 Immunity. Front Immunol. 2020, 11, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berni Canani, R.; Sangwan, N.; Stefka, A.T.; Nocerino, R.; Paparo, L.; Aitoro, R.; Calignano, A.; Khan, A.A.; Gilbert, J.A.; Nagler, C.R. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG-supplemented formula expands butyrate-producing bacterial strains in food allergic infants. ISME J. 2016, 10, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.L.; Ponsonby, A.L.; Orsini, F.; Tey, D.; Robinson, M.; Su, E.L.; Licciardi, P.; Burks, W.; Donath, S. Administration of a probiotic with peanut oral immunotherapy: A randomized trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuello-Garcia, C.A.; Brozek, J.L.; Fiocchi, A.; Pawankar, R.; Yepes-Nuñez, J.J.; Terracciano, L.; Gandhi, S.; Agarwal, A.; Zhang, Y.; Schünemann, H.J. Probiotics for the prevention of allergy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 952–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, F.; Veysseyre-Balter, C.; Rousset, H.; Descos, L.; André, C. Exogenous oestrogen as an alternative to food allergy in the aetiology of angioneurotic oedema. Toxicology 2003, 185, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, M.; Beser, O.F.; Konukoglu, D.; Cokugras, H.; Erkan, T.; Kutlu, T.; Cokugras, F.C. The utility of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-10 in the diagnosis and/or follow-up food allergy. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2020, 48, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelkopoulou, N.; Taparkou, A.; Agakidis, C.; Mavroudi, A.; Xinias, I.; Farmaki, E. IL-10 receptor expression on lymphocytes and monocytes in children with food allergy. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 32, 1108–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Martinis, M.; Ginaldi, L.; Sirufo, M.M.; Pioggia, G.; Calapai, G.; Gangemi, S.; Mannucci, C. Alarmins in Osteoporosis, RAGE, IL-1, and IL-33 Pathways: A Literature Review. Medicina 2020, 56, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sirufo, M.M.; Suppa, M.; Ginaldi, L.; De Martinis, M. Does Allergy Break Bones? Osteoporosis and Its Connection to Allergy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Martinis, M.; Sirufo, M.M.; Suppa, M.; Ginaldi, L. IL-33/IL-31 Axis in Osteoporosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ginaldi, L.; De Martinis, M.; Saitta, S.; Sirufo, M.M.; Mannucci, C.; Casciaro, M.; Ciccarelli, F.; Gangemi, S. Interleukin-33 serum levels in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narita, S.; Goldblum, R.M.; Watson, C.S.; Brooks, E.G.; Estes, D.M.; Curran, E.M.; Midoro-Horiuti, T. Environmental estrogens induce mast cell degranulation and enhance IgE-mediated release of allergic mediators. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baker, J.M.; Al-Nakkash, L.; Herbst-Kralovetz, M.M. Estrogen–gut microbiome axis: Physiological and clinical implications. Maturitas 2017, 103, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Martinis, M.; Sirufo, M.M.; Nocelli, C.; Fontanella, L.; Ginaldi, L. Hyperhomocysteinemia is Associated with Inflammation, Bone Resorption, Vitamin B12 and Folate Deficiency and MTHFR C677T Polymorphism in Postmenopausal Women with Decreased Bone Mineral Density. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Bonilla-Rosso, G.; Kwong Chung, C.K.C.; Bäriswyl, L.; Rodriguez, M.P.; Kim, B.S.; Engel, P.; Noti, M. High dietary fat intake induces a microbiota signature that promotes food allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 157–170.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, S.; Kubota, N.; Kakiyama, S.; Miyazaki, K.; Sato, K.; Harima-Mizusawa, N. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum YIT 0132 on Japanese cedar pollinosis and regulatory T cells in adults. Allergy 2020, 75, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lowe, K.E.; Mansfield, K.E.; Delmestri, A.; Smeeth, L.; Roberts, A.; Abuabara, K.; Prieto-Alhambra, D.; Langan, S.M. Atopic eczema and fracture risk in adults: A population-based cohort study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 145, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garg, N.; Silverberg, J.I. Association between eczema and increased fracture and bone or joint injury in adults a us population-based study. JAMA Dermatol. 2015, 151, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.W.; Ramsook, A.H.; Coxson, H.O.; Bon, J.; Reid, W.D. Prevalence and Risk Factors for Osteoporosis in Individuals with COPD: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Chest 2019, 156, 1092–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccarelli, F.; De Martinis, M.; Ginaldi, L. Glucocorticoids in Patients with Rheumatic Diseases: Friends or Enemies of Bone? Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Anouti, F.; Taha, Z.; Shamim, S.; Khalaf, K.; Al Kaabi, L.; Alsafar, H. An insight into the paradigms of osteoporosis: From genetics to biomechanics. Bone Rep. 2019, 11, 100216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucci, S.; Incorvaia, C. Allergy as an organ and a systemic disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 153, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrick, B.J.; Jalan, S.; Tollefson, M.M.; Milbrandt, T.A.; Larson, A.N.; Rank, M.A.; Lohse, C.M.; Davis, D.M.R. Associations of self-reported allergic diseases and musculoskeletal problems in children: A US population-based study. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017, 119, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puth, M.T.; Klaschik, M.; Schmid, M.; Weckbecker, K.; Münster, E. Prevalence and comorbidity of osteoporosis- a cross-sectional analysis on 10,660 adults aged 50 years and older in Germany. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2018, 19, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adami, G.; Gatti, D.; Rossini, M.; Giollo, A.; Bertoldo, E.; Viapiana, O.; Olivi, P.; Fassio, A. Factors associated with referral for osteoporosis care in men: A real-life study of a nationwide dataset. Arch. Osteoporos. 2021, 16, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martinis, M.; Ginaldi, L.; Sirufo, M.M.; Bassino, E.M.; De Pietro, F.; Pioggia, G.; Gangemi, S. IL-33/Vitamin D Crosstalk in Psoriasis-Associated Osteoporosis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 604055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardecka-Milewska, I.; Łoś-Rycharska, E.; Gawryjołek, J.; Toporowska-Kowalska, E.; Krogulska, A. Role of FOXP3 Expression and Serum Vitamin D and C Concentrations When Predicting Acquisition of Tolerance in Infants With Cow’s Milk Allergy. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 30, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koplin, J.J.; Suaini, N.H.; Vuillermin, P.; Ellis, J.A.; Panjari, M.; Ponsonby, A.L.; Peters, R.L.; Matheson, M.C.; Martino, D.; Dang, T.; et al. Polymorphisms affecting vitamin D-binding protein modify the relationship between serum vitamin D (25[OH]D3) and food allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 500–506.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vuillermin, P.J.; Ponsonby, A.L.; Kemp, A.S.; Allen, K.J. Potential links between the emerging risk factors for food allergy and vitamin D status. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2013, 43, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirufo, M.M.; Ginaldi, L.; De Martinis, M. Gut microbiota-microRNA interactions in osteoarthritis. Gene 2021, 803, 145887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirufo, M.M.; Ginaldi, L.; De Martinis, M. Microbiota-miRNA interactions: Opportunities in ankylosing spondylitis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirufo, M.; Ginaldi, L.; De Martinis, M. Noncoding RNAs, Osteoarthritis, and the Microbiome: New Therapeutic Targets? Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 2146, Comment on the Article by Wei et al. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.X.; Rothenberg, M.E. MicroRNA. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1202–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sirufo, M.M.; Ginaldi, L.; De Martinis, M. MicroRNAs, bone and microbiota. Bone 2021, 144, 115824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Martinis, M.; Ginaldi, L.; Allegra, A.; Sirufo, M.M.; Pioggia, G.; Tonacci, A.; Gangemi, S. The Osteoporosis/Microbiota Linkage: The Role of miRNA. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davoodvandi, A.; Marzban, H.; Goleij, P.; Sahebkar, A.; Morshedi, K.; Rezaei, S.; Mahjoubin-Tehran, M.; Tarrahimofrad, H.; Hamblin, M.R.; Mirzaei, H. Effects of therapeutic probiotics on modulation of microRNAs. Cell Commun. Signal. 2021, 19, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Food Allergy | Associated Bacteria |
|---|---|
| Cow’s milk | ↓Clostridia, Firmicutes |
| Cow’s milk, egg, peanut | ↑Enterobacteriaceae ↓Bacteroidaceae |
| Peanut | ↓Clostridiales ↑Bacteroidales |
| Egg white, cow’s milk, wheat, peanut, soy bean | ↓Bacteroidetes ↑Firmicutes |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sirufo, M.M.; De Pietro, F.; Catalogna, A.; Ginaldi, L.; De Martinis, M. The Microbiota-Bone-Allergy Interplay. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010282
Sirufo MM, De Pietro F, Catalogna A, Ginaldi L, De Martinis M. The Microbiota-Bone-Allergy Interplay. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(1):282. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010282
Chicago/Turabian StyleSirufo, Maria Maddalena, Francesca De Pietro, Alessandra Catalogna, Lia Ginaldi, and Massimo De Martinis. 2022. "The Microbiota-Bone-Allergy Interplay" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 1: 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010282
APA StyleSirufo, M. M., De Pietro, F., Catalogna, A., Ginaldi, L., & De Martinis, M. (2022). The Microbiota-Bone-Allergy Interplay. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(1), 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010282








