Abstract
Phthalates are typical chemical pollutants in kindergarten classrooms since numerous artificial products (e.g., polyvinyl chloride (PVC) floorings, soft polymers and plastic toys) that might contain phthalates are widely distributed in kindergarten classrooms. Although Chinese preschool children spend a considerable amount of their waking hours (>8 h/day) in kindergartens, phthalate exposure in such indoor environment has not been given much attention. In this study, the mass fractions of six phthalates in twenty-six artificial products (fifteen flat decoration materials and eleven plastic toys) commonly found in Chinese kindergarten classrooms were measured. Di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP) was the most predominant compound in all materials. The emission characteristics of the DEHP from these materials were further investigated. The measured emission characteristics were used for predicting multi-phase DEHP concentrations in kindergarten classrooms by applying a mass transfer model. The modeled concentrations were comparable with those measured in the real environment, indicating that these products might be the major sources of DEHP in Chinese kindergarten classrooms. Preschool children’s exposure to DEHP was found to be 0.42 μg/kg/day in kindergartens under baseline conditions, accounting for 18% of the total exposure to DEHP in Chinese indoor environments.
1. Introduction
Phthalates, known as plasticizers, are a group of emerging chemical pollutants in modern indoor environments [1,2]. Indoor phthalates originate from widely distributed source materials, such as soft polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polymers, wallpapers, stickers, children’s toys and food packages [3,4]. Most phthalates are semi-volatile organic compounds (SVOCs) that exist in multiple phases indoors. Gaseous phthalates can be easily absorbed in airborne particles, settled dust and surfaces due to their low vapor pressure [2]. Humans are exposed to phthalates via inhalation, oral ingestion and dermal pathways [5,6,7,8,9]. Phthalates are rapidly metabolized after entering the human body and most phthalate metabolites are excreted in the urine [10,11,12,13]. This is of great concern owing to the associated toxicologic risks, such as endocrine disruption [14,15,16], reproductive system dysfunction [17,18,19], childhood asthma [20,21,22], neurodevelopmental disorders [23,24] and cancer [25].
The European Union and the US has been issuing regulations to restrict the usage of plasticizers in artificial products since the end of the last century [26,27,28]. However, the usage of plasticizers in China keeps growing due to rapid urbanization and modernization in the past few decades. In 2013, the production and consumption of plasticizers reached 4.3 and 2.45 million tons, respectively, accounting for 52% and 45% of global production and consumption [29]. Numerous phthalate-containing materials have been identified in the Chinese market, such as PVC floorings, wallpapers, window stickers and floor mats; the mass fractions of phthalates in those products could reach 10% or even greater [30,31]. Phthalates can be continuously released from those source materials, leading to the deterioration of indoor air quality. Previous studies have indicated that indoor phthalate concentrations in typical cities in China are at higher levels compared with those measured in other countries [32,33].
Children are more likely to be exposed to phthalates due to their exploratory behaviors [34], and their absorbed doses are usually higher than adults because they breathe or eat more per unit of body weight [35]. Bu et al. found that preschool children’s exposure to phthalates in Chinese indoor environments was roughly 80% higher than that for adults [32]. Previous studies have primarily focused on phthalate pollution in the Chinese home environment since it is the most important site for children’s indoor exposure [36,37,38]. Meanwhile, preschool children also spend many of their waking hours in daycare centers or kindergartens (e.g., 8–10 h per day, 5 days per week) [39]. However, research regarding phthalate pollution in daycare centers or kindergartens is limited in China. Recently, Wang et al. reported a median dust-phase level (the sum of 15 phthalates) in kindergarten buildings of 760 μg/g, which was higher than that measured in the home environment (i.e., 488 μg/g) in Beijing [40]. Another study found that the mean airborne concentrations of di(isobutyl) phthalate (DiBP), di-n-butyl phthalate (DnBP) and di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP) in kindergarten classrooms in Beijing were 1.13, 0.93 and 0.22 μg/m3, respectively [41]. These reported values were comparable to or even higher than those measured in Chinese residences [33,36,42]. Given that a lot of synthetic decoration materials (e.g., PVC flooring, soft polymers, wall papers) and plastic toys can be found in kindergarten classrooms, the identification of phthalates from these artificial products is important to understand phthalate transfer and estimate children’s exposure in kindergartens.
Therefore, the objectives of the current study were to: (1) identify phthalates in twenty-six artificial products commonly found in Chinese kindergarten classrooms and investigate the emission characteristics of the phthalates in these materials; (2) estimate phthalate concentrations and try to explore major sources in kindergarten classrooms based on their emission characteristics and a mass transfer model; and (3) estimate preschool children’s exposure to phthalates in kindergarten classrooms based on modeled concentrations and investigate their potential contribution to total indoor exposures in China.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Chemicals
Six common phthalates were selected as the target compounds, i.e., dimethyl phthalate (DMP), diethyl phthalate (DEP), DnBP, butyl benzyl phthalate (BBzP), DEHP, and di-n-octyl phthalate (DOP). A standard mixture of these chemicals (2000 mg/L of each phthalate in hexane) was purchased from the Organic Standard Solutions International Co., LLC, Columbia, SC, USA. Dichloromethane (DCM, TEDIA Co. Inc., Fairfield, OH, USA, HPLC grade) was used as the solvent for extraction.
2.2. Test Materials
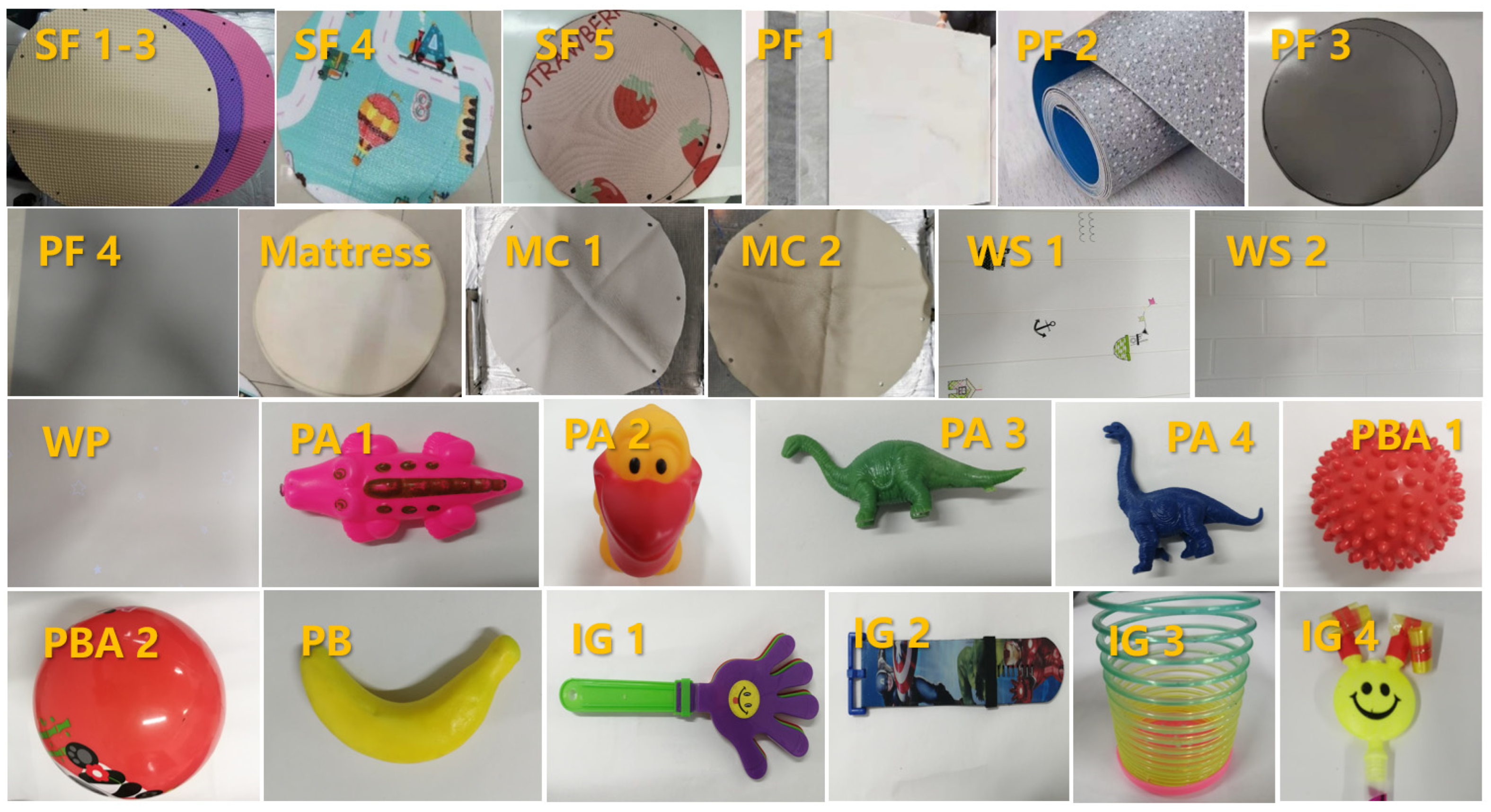
In this study, fifteen flat materials and eleven toys commonly found in kindergarten classrooms were selected as the test materials (shown in Figure 1). All the materials were purchased from a Chinese online shopping website. The flat materials included five soft floor mats (SF 1–5), four PVC flooring materials (PF 1–4), two mattress covers (MC 1 and 2), one mattress, two wall stickers (WS 1 and 2) and one wallpaper (WP). The toys were four plastic animals (PA 1–4), two plastic balls (PBA 1 and 2), one plastic banana (PB) and four other irregular shaped plastic toys (IG 1–4).

Figure 1.
Photos of test materials in this study.
2.3. Identification of Phthalates from Test Materials
Three samples (approximately 0.3–0.8 g of each) were cut from random locations on each material. The samples were extracted separately with 60 mL of dichloromethane (DCM) at 70 °C for 6 h using a Soxhlet extractor. The extracts were concentrated into approximately 20 mL using a rotary evaporator, filtered through a 0.45 μm polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) microporous membrane, and then transferred into a Kuderna–Danish (K–D) tube. Thereafter, the clean extracts were further concentrated to 1 mL under a purified nitrogen stream. Finally, 200 μL of the concentrated extracts were transferred from the K–D tubes into 2 mL sample vials (Agilent Technologies, Part No. 5182-0553) equipped with 250 μL microvolume inserts. Final samples were stored at 4 °C in a laboratory refrigerator until analysis by a gas chromatograph–mass spectrometer (GC–MS) system (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA, GC-7890N, MS-5975C). Detailed information on the chemical analysis by GC–MS is in Section S1 of the Supplementary Information (SI).
2.4. Measurement of Emission Characteristics of Phthalates from the Materials
Existing studies have concluded that phthalate emissions from solid materials can be characterized with a critical parameter: the gas-phase concentration immediately adjacent to the material surface (designated as y0, μg/m3) [43,44]. In this study, a solid-phase microextractor (SPME)-based sealed chamber method developed by Cao et al. [45] was applied to measure the y0 value of the flat materials at typical room temperature (25 °C), due to its short experimental time, the ease of the sampling procedure, and the simplicity of the experimental system. The y0 measurements were only conducted for DEHP because we found that DEHP was the most predominant phthalate in the material extraction experiments (see the results below). Details on the experimental procedure and method principle for determining y0 are provided in SI Section S2.
2.5. Estimation of Phthalate Concentrations in Kindergarten Classrooms
In our previous study, the transport of indoor SVOCs was described by a proposed mechanistic model [46]. Assuming that the transport of phthalates in the classroom has reached a steady state, the mass balance of gas- and particle-phase phthalates and suspended particles can be described as follows:
where Ae (m2) is the surface area of the phthalate sources (the subscript “i” refers to the ith source material); hm (m/s) is the mass transfer coefficient above the source surface; Cg (μg/m3) is the concentration of the gas-phase phthalate in the kindergarten classroom; V (m3) is the volume of the bedroom; αn (s−1) is the natural air exchange rate; Csp (μg/m3) is the concentration of the gas-phase phthalate in the classroom; vd (s−1) is the particle deposition rate constant; Asp (m−1) is the ratio between the surface area and the volume of a single particle; Cp (μg/m3) is the mass concentration of suspended particles in the classroom; hmp (m/s) is the phthalate mass transfer coefficient between a single particle and air; ρp (μg/m3) is the density of suspended particles; Kp (m3/μg) is the partitioning coefficient between the particle- and gas-phase phthalate; P (-) is the particle penetration coefficient; and Cp_out (μg/m3) is the mass concentration of suspended particles outdoors. As atmospheric phthalate concentrations were much lower than the indoor concentrations, the influence of atmospheric phthalates was not taken into account in the model. Phthalates also exist in indoor settled dust. The corresponding dust-phase concentration (Xdust, μg/μg) can be estimated simply from the gas-phase by a linear equilibrium equation [47]:
where Kdust (m3/μg) is the dust-air partitioning coefficient of a given phthalate. Combining Equations (1)–(4), the Cg, Csp, Cp and Xdust in kindergarten classrooms at a steady state can be predicted.
The values of y0 in the flat source materials were based on our measurements as described in Section 2.4. For plastic toys, the corresponding y0 values were determined from the mass contents of given phthalates based on the method detailed by Cao et al. [45]. PM10 was considered to represent the outdoor suspended particles. One should be mindful that some particle-related parameters (Asp, hmp, vd and P) are related to particle size. For these parameters, we used integrated values (based on size-dependent values) to calculate airborne phthalate concentrations at a steady state. The outdoor PM10 was divided into 11 size bins according to Kawanaka et al.’s study [48]. The value for each size bin was first determined and then the integrated value was obtained by weighing the size-dependent concentrations by their mass fractions in the room air [30,31]. The size-dependent penetration coefficients of the outdoor particles were extracted from Liu et al.’s study [49]. The determination of the key parameters used in our calculations is further detailed in SI Section S3.
Indoor phthalate concentrations are related to some key environmental factors, such as the outdoor particle concentration (Cp_out), air exchange rate (an) and room temperature (T). Therefore, a sensitivity analysis was conducted to illustrate the variations in Cp_out, an and T on the modeled concentrations. Based on the annual concentration of outdoor PM10 in typical Chinese cities over the last five years, a baseline value of 80 μg/m3 was applied in the present study [46]. The lower and upper limits of Cp_out were set to be 50 and 120 μg/m3, respectively, to represent an acceptable and heavily polluted level for the ambient air. The natural air exchange rate in the kindergarten classroom was set to be 1 h−1 under baseline conditions. The lower limit of an was set to be 0.5 h−1 to reflect a poorly ventilated scenario and the upper limit was set to be 4 h−1 based on the average value recommended by the Chinese trade standard JGJ 39-2016, Code for the design of nursey and kindergarten buildings [50]. The range for the room temperature was set to be 16–28 °C according to the recommendations for conditioned spaces in the Chinese indoor air quality standard (GB/T 18883-2002) [51].
2.6. Children’s Exposure Assessments in Kindergarten Classrooms
In the present study, preschool children aged 1–5 years old were chosen as the target population. Inhalation, oral and dermal pathways were the typical exposure pathways during children’s indoor activities in kindergartens. For oral intake, only dust ingestion was considered since dietary ingestion was not included in the current study. For dermal pathways, only dermal absorption from the gas phase was considered. Children’s daily intakes via inhalation (IE, μg/kg/day), oral ingestion (OE, μg/kg/day) and dermal absorption (DE, μg/kg/day) were estimated based on the corresponding airborne concentrations at a steady state:
where IRinh (m3/day) is the inhalation rate; EF (h/day) is the children’s exposure frequency in kindergartens, i.e., 5.7 h/day for a week-long exposure (assuming 8 h/day on weekdays and zero on weekends); BW (kg) is the body weight; IRdust (g/day) is the dust ingestion rate; kp_g (m/day) is the transdermal permeability coefficient between air and dermal capillaries; SA (m2) is the total skin area; and fs (-) is the fraction of total skin exposed to room air. Detailed exposure factors for Chinese preschool children are listed in SI Table S1.
3. Results
3.1. Mass Fractions and Emissions of Phthalates in Test Materials
The mean values of the mass fractions in the test materials are listed in Table 1. Six target phthalates were detected in most of the artificial products except for DEP and BBzP. DEHP was the most abundant phthalate in both the flat materials and plastic toys, with a detection frequency of 100%. The results were in consistent with the fact that DEHP is currently the most frequently used plasticizer in China. Generally, the mass fractions of the target phthalates were not high (<1%) for all the materials. DEHP content was slightly higher in the flat materials than that in the plastic toys. For the flat materials, mass fractions in SF 5, MC 2 and PF 3 and 4 were at higher levels (0.37–0.74%). For plastic toys, phthalate contents were lower, except for DnBP in PBA 2 and DEHP in IG 2.

Table 1.
Mass fractions of target phthalates in test materials a.
The y0 values of the five flat materials with the highest mass factions of DEHP (SF 5, PF 3 and 4, MC 3 and WP) were measured. The y0 values for the other flat materials could not be quantitively determined based on the SPME method due to their low DEHP content. As shown in Table 2, the mean y0 values of DEHP for the target flat materials were in the range of 0.14–0.30 μg/m3 at room temperature.

Table 2.
Measured y0 values of DEHP emitted from target flat materials.
3.2. Modeled DEHP Concentratiosn in Kindergarten Classrooms
As shown in Table 3, the modeled gas- and particle-phase DEHP concentrations at a steady state under baseline conditions were 0.014 μg/m3 and 0.098 μg/m3, respectively. The corresponding dust-phase concentration was 840 μg/g. The variations in the air exchange rate and room temperature had a stronger impact on airborne DEHP concentrations than outdoor particle concentrations. The airborne DEHP concentration changed by 40–68% from its baseline value when the air exchange rate varied from 0.5 h−1 to 4 h−1 and the airborne concentration changed by 50–63% when the room temperature varied from 16 °C to 28 °C. Changes in the dust-phase DEHP levels were more sensitive to the outdoor particle concentrations and room temperature than the air exchange rate. The dust-phase DEHP concentration changed by 30–46% and 57–74%, respectively, when Cp_out and T varied within their ranges.

Table 3.
Modeled DEHP concentrations in kindergarten classrooms and sensitivity analysis.
3.3. Children’s Exposure to DEHP in Kindergarten Classrooms
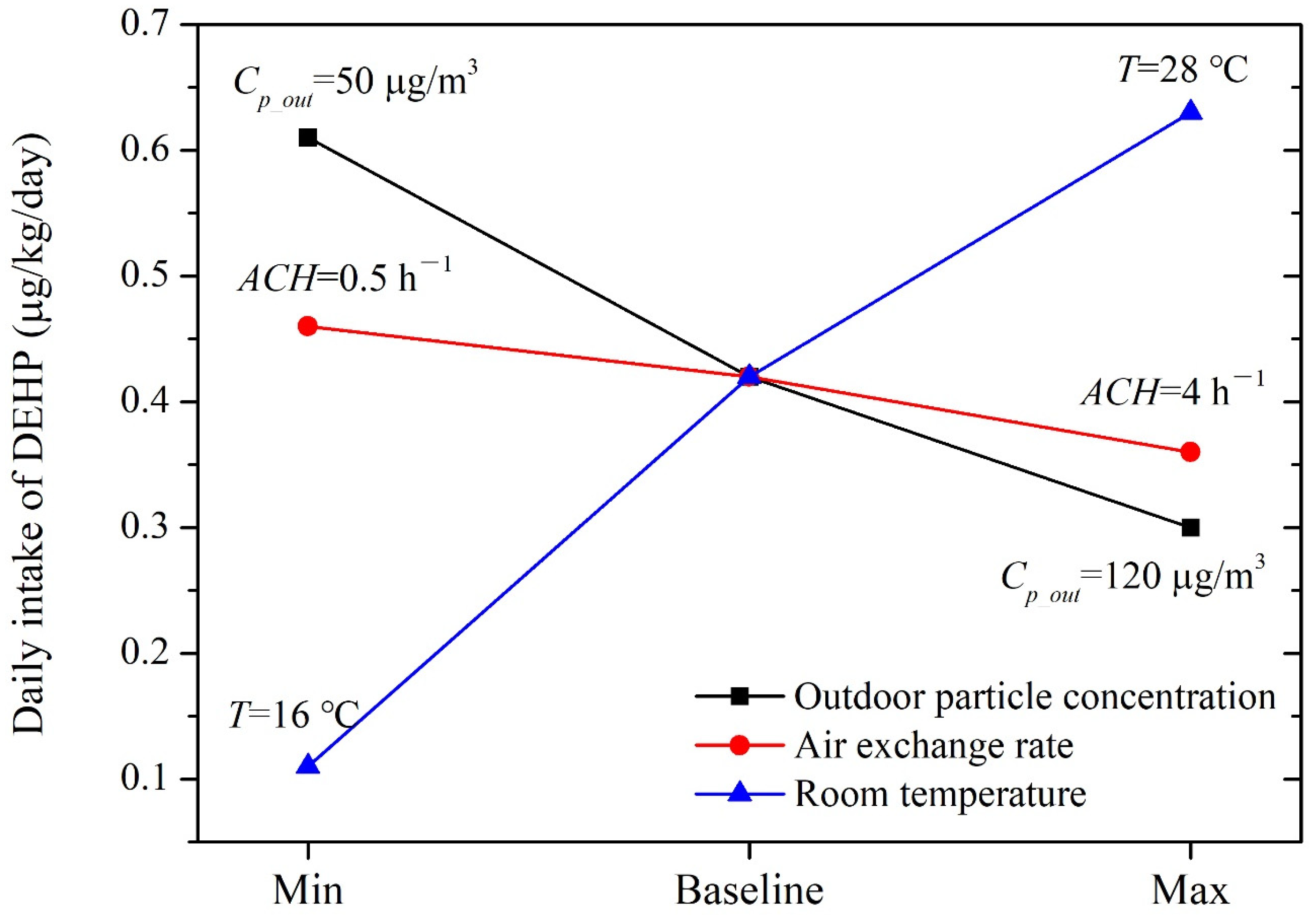
Under baseline conditions, children’s exposure to DEHP via three typical pathways was 0.42 μg/kg/day during daily activities in kindergarten classrooms. Exposure via dust ingestion contributed over 95% of the total intake. As shown in Figure 2, the estimated exposures were more sensitive to outdoor particle concentrations and room temperature than the air exchange rate. Children’s total daily intakes of DEHP varied within the ranges of 0.30–0.61 μg/kg/day and 0.11–0.63 μg/kg/day, respectively, when Cp_out and T changed from the minimum to the maximum values. Children’s intakes changed from 0.46 μg/kg/day to 0.36 μg/kg/day when an varied from 0.5 h−1 to 4 h−1 as the dust-phase concentration slightly changed with respect to variations in an.
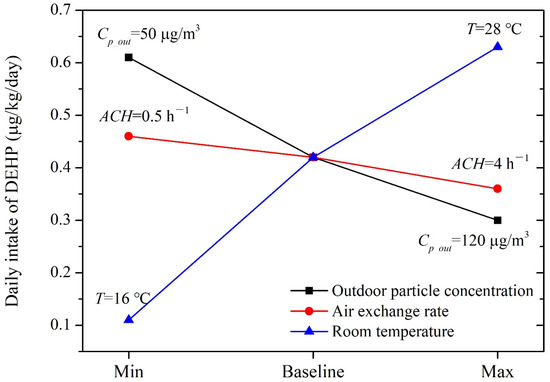
Figure 2.
Sensitivity of the modeled DEHP exposure to key input parameters.
We compared these exposure estimates with children’s total daily intake in typical indoor environments to illustrate the potential contribution of exposure in kindergarten classrooms in China. Bu et al. reported a total daily intake of DEHP of 2.28 μg/kg/day (via inhalation, dust-ingestion and dermal absorption from the gas-phase) for children aged 1–5 years old [32]. Based on this value, it could be found that the exposure in kindergarten classrooms contributed roughly 18% under baseline conditions (with a range of 5–30%) to total indoor exposure to DEHP for preschool children in China.
4. Discussion
Previous studies have investigated the mass contents of phthalates in artificial products in Chinese indoor environments. For example, Shi et al. measured the mass contents of phthalates in 23 decoration materials in Chinese residences [31]. They found that DEHP was the predominant compound and that the highest mass fraction could reach 17%. Bu et al. reported phthalate levels in nine decoration materials in Chinese vehicle cabins and also found that the highest mass fractions were for DEHP (3–23%) [30]. These reported values were significantly higher than those observed for decoration materials or plastic toys in kindergarten classrooms in the present study. Currently, there are only two national standards (Limit of Harmful Substances of Coatings for Toys (GB 24613-2009) [52] and Toys Safety (GB 6675-2014) [53]) that provide guidelines for phthalate usage in children’s daily used products in China: i.e., the summed mass fraction of DnBP, BBzP and DEHP in a given toy or coating for toys should not exceed 0.1%. Based on this requirement, the phthalate contents (summed mass fraction of DnBP, BBzP and DEHP) in seven flat materials (SF 5, MC 3, WP and PF 1–4) and two toys (PBA 1 and IG 2; with a range of 0.14–0.95%) were higher than the threshold. Taken together, although the mass contents of the phthalates were relatively lower in the studied materials, more than one third of these artificial products used in kindergarten classrooms (at least in our measurements) did not meet the requirements specified in our national standards.
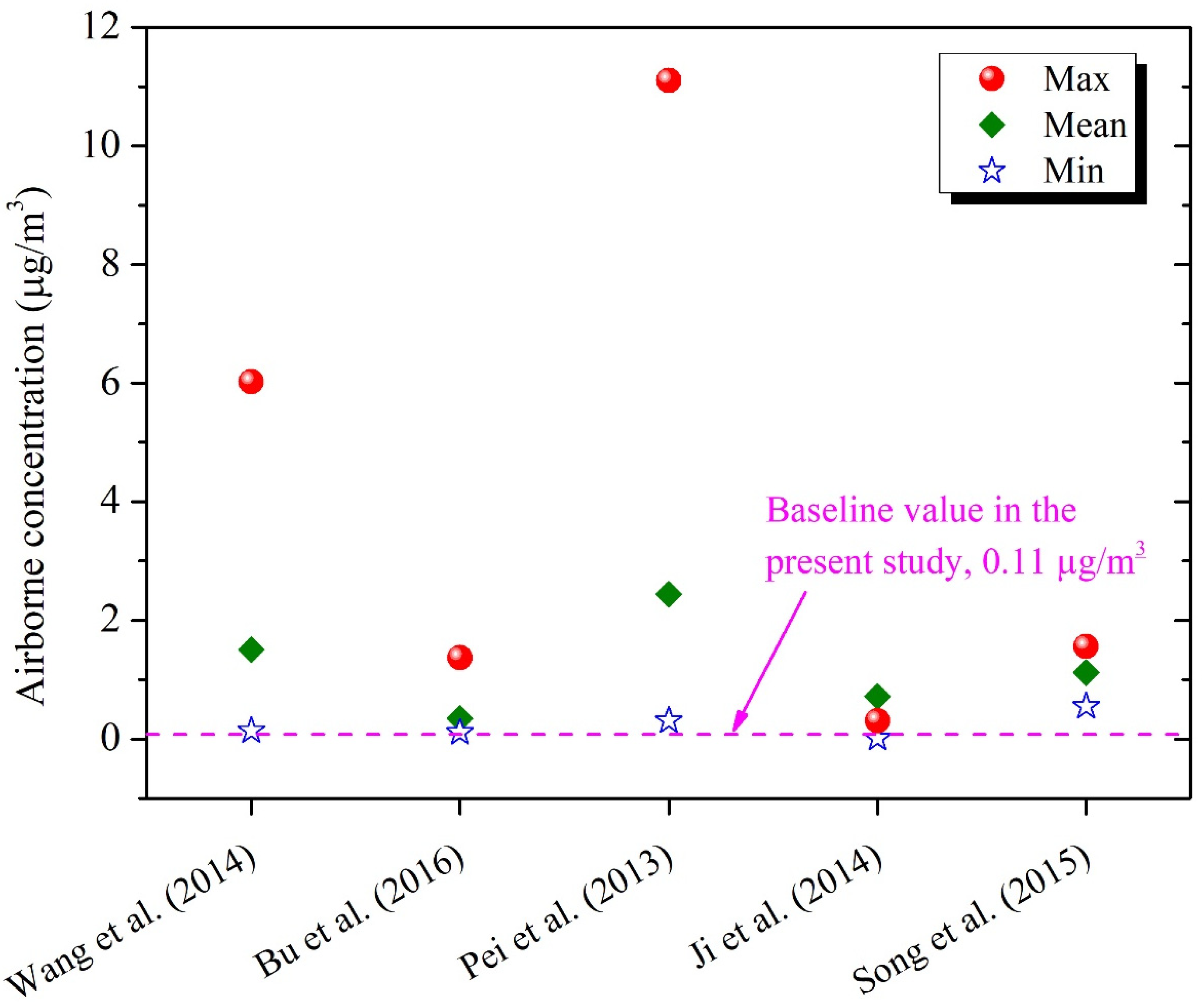
We compared our predicted DEHP concentrations with those measured in kindergartens in China. Wang et al. reported airborne-phase and dust-phase DEHP concentrations for six kindergartens in three districts of Beijing, with ranges of 0.09–0.48 μg/m3 and 16.7–2240 μg/g, respectively (means: 0.22 μg/m3 and 330 μg/g) [41]. It was found that our estimates were generally comparable with those measured, indicating that these artificial products might be the major sources of DEHP in kindergarten classrooms in China. Wang et al. also reported considerable airborne concentrations of DMP and DnBP, i.e., 0.07–2.09 and 0.02–1.59 μg/m3, respectively [41]. However, the contents of these two phthalates were quite low in target materials based on our extraction experiments, indicating that there might be other potential sources of DMP and DnBP in Chinese kindergarten classrooms. Further research is required to identify the major sources of these lower molecular weight phthalates since they may also be used as solvents or carriers in consumer products, such as personal care products, varnishes or coatings [3,4]. Given that the parameters used in our model can hardly be consistent with those in the real environment, we acknowledged that the obtained data might not be enough to make a convincing comparison. We further compared our estimates with those measured for Chinese residences or office buildings (shown in Figure 3). The results indicated that airborne DEHP concentrations in kindergartens were lower than those in residential or office buildings [33,36,42,54,55], suggesting that DEHP pollution might be a more serious problem in residences or offices in China.
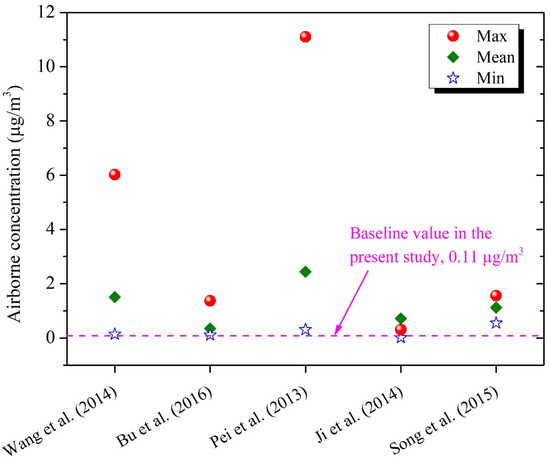
Figure 3.
Comparison between our modeled DEHP concentrations and those measured in Chinese residences/offices. Only gas-phase concentrations were reported by Bu et al. [36], while airborne concentrations were reported for other studies [33,42,54,55].
In the present study, a simplified model (with steady-state assumptions) was applied to describe the fate of phthalates in the classrooms. Moreover, when calculating inhaled doses, the desorption of particle-phase phthalates in the respiratory tract [56] was not considered. These simplified particle–gas interactions could lead to considerable uncertainties for inhalation exposure estimates [49,57,58]. For phthalates accumulated in settled dust, a linear partitioning behavior between the dust- and the gas-phase was considered. Recent studies have illustrated that a considerable percentage of phthalates could transfer from the source to dust if the dust is directly settled on the source surfaces [59,60,61], e.g., the PVC flooring and floor mats in our measurements. Given that oral ingestion contributed a large portion of children’s DEHP exposure indoors, the ignorance of direct transfer from source to dust could lead to considerable underestimation of exposure estimates. On the other hand, phthalate transfer from both source and sink surfaces to hands via children’s surface touch behaviors was not considered. This would consequently result in underestimation of daily intakes via both hand-to-mouth contact [62,63,64] and dermal absorption [65,66,67]. In addition, the impact of clothing on children’s dermal absorption [68,69] was not taken into account. Previous studies have indicated that dermal uptakes of phthalates could significantly increase when occupants wear phthalate-containing clothes [70,71,72]. Taken together, the modeled exposures in the present study might be a conservative estimation, indicating that Chinese children might be facing serious exposure to DEHP in kindergarten classrooms. In addition to refined phthalate transfer mechanisms and detailed exposure pathways (including surface touches), an internal exposure assessment approach (e.g., detection of metabolites in urine samples) could be helpful to improve the estimation of children’s exposure to phthalates in Chinese kindergartens.
5. Conclusions
Phthalates from twenty-six artificial products in Chinese kindergarten classrooms were identified. DEHP was the most predominant compound in all the materials. The gas-phase DEHP concentration immediately adjacent to the flat material surface was measured using an SPME-based method. Multi-phase DEHP concentrations in kindergarten classrooms were predicted based on the emission characteristics and a mechanistic model. The predicted DEHP concentrations were comparable with those measured in Chinese kindergartens, suggesting that these materials might be the major DEHP sources in kindergarten classrooms. The exposure estimates showed that preschool children’s exposure in kindergarten classrooms contributed 5–30% to the total DEHP exposure in typical indoor environments in China. The results indicate that the kindergarten classroom could be an important environment for preschool children’s indoor exposure to DEHP in China.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijerph19138011/s1. Section S1, Detailed information on the chemical analysis by the GC–MS system; Section S2, Detailed information for measuring the y0 values of DEHP; Section S3, Parameters for estimating DEHP concentrations in kindergarten classrooms; Table S1, Exposure factors for preschool children (1–5 years old) in urban China; Figure S1, Size distribution of outdoor particles. References [73,74,75,76,77,78,79] are cited in the Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.W., C.D. and Z.B.; methodology, J.W., Z.X., C.D. and Z.B.; data curation, J.W., Z.X., J.Y., M.H. and Y.S.; formal analysis, J.W., Z.X. and J.Y.; investigation, J.W., M.H. and Y.S.; supervision, C.D. and Z.B; funding acquisition, C.D. and Z.B. writing—original draft, J.W., Z.X. and J.Y.; writing—review and editing, C.D. and Z.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (Grant No. LY22E080006) and the Science and Technology Planning Project of Ningbo Municipality (Grant No. 2019B10045).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the Supplementary Material of this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
References
- Weschler, C.J. Changes in indoor pollutants since the 1950s. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weschler, C.J.; Nazaroff, W.W. Semivolatile organic compounds in indoor environments. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 9018–9040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wormuth, M.; Scheringer, M.; Vollenweider, M.; Hungerbuhler, K. What are the sources of exposure to eight frequently used phthalic acid esters in Europeans? Risk Anal. 2006, 26, 803–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wypych, G. Handbook of Plasticizers; ChemTec Publishing: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sioen, I.; Fierens, T.; Van Holderbeke, M.; Geerts, L.; Bellemans, M.; De Maeyer, M.; Servaes, K.; Vanermen, G.; Boon, P.; De Henauw, S. Phthalates dietary exposure and food sources for Belgian preschool children and adults. Environ. Int. 2012, 48, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromme, H.; Lahrz, T.; Piloty, M.; Gebhart, H.; Oddoy, A.; Ruden, H. Occurrence of phthalates and musk fragrances in indoor air and dust from apartments and kindergartens in Berlin (Germany). Indoor Air 2004, 14, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Hu, M.; Yuan, F.; Ye, H.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, G.; Dong, C.; Mmereki, D.; Xu, Y.; et al. Exposure to phthalates in the sleeping microenvironment of university dormitories: A preliminary estimate based on skin wipe and dust sampling. Build. Environ. 2022, 218, 109135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevao, B.; Al-Ghadban, A.N.; Bahloul, M.; Uddin, S.; Zafar, J. Phthalates in indoor dust in Kuwait: Implications for non-dietary human exposure. Indoor Air 2013, 23, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salthammer, T.; Zhang, Y.; Mo, J.; Koch, H.M.; Weschler, C.J. Assessing Human Exposure to Organic Pollutants in the Indoor Environment. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2018, 57, 12228–12263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callesen, M.; Beko, G.; Weschler, C.J.; Langer, S.; Brive, L.; Clausen, G.; Toftum, J.; Sigsgaard, T.; Host, A.; Jensen, T.K. Phthalate metabolites in urine and asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis and atopic dermatitis in preschool children. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2014, 217, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Weschler, C.J.; Liu, L.; Shen, H.; Huang, L.; Sundell, J.; Zhang, Y. Phthalate metabolites in urine samples from Beijing children and correlations with phthalate levels in their handwipes. Indoor Air 2015, 25, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, S.; Beko, G.; Weschler, C.J.; Brive, L.M.; Toftum, J.; Callesen, M.; Clausen, G. Phthalate metabolites in urine samples from Danish children and correlations with phthalates in dust samples from their homes and daycare centers. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2014, 217, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Chen, J.; Tang, C.; Mao, I. The internal exposure of Taiwanese to phthalate--an evidence of intensive use of plastic materials. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araki, A.; Mitsui, T.; Goudarzi, H.; Nakajima, T.; Miyashita, C.; Itoh, S.; Sasaki, S.; Cho, K.; Moriya, K.; Shinohara, N.; et al. Prenatal di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate exposure and disruption of adrenal androgens and glucocorticoids levels in cord blood: The Hokkaido Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581–582, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arbuckle, T.E.; Agarwal, A.; MacPherson, S.H.; Fraser, W.D.; Sathyanarayana, S.; Ramsay, T.; Dodds, L.; Muckle, G.; Fisher, M.; Foster, W.; et al. Prenatal exposure to phthalates and phenols and infant endocrine-sensitive outcomes: The MIREC study. Environ. Int. 2018, 120, 572–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Han, Y.; Shen, R.; Huang, K.; Xu, Y.Y.; Wang, Q.N.; Zhou, S.S.; Xu, D.X.; Tao, F.B. Gestational di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate exposure causes fetal intrauterine growth restriction through disturbing placental thyroid hormone receptor signaling. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 294, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, H.B.; Jukic, A.M.; Wilcox, A.J.; Weinberg, C.R.; Ferguson, K.K.; Calafat, A.M.; McConnaughey, D.R.; Baird, D.D. Association of urinary concentrations of phthalate metabolites and bisphenol A with early pregnancy endpoints. Environ. Res. 2018, 168, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radke, E.G.; Braun, J.M.; Meeker, J.D.; Cooper, G.S. Phthalate exposure and male reproductive outcomes: A systematic review of the human epidemiological evidence. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 764–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smarr, M.M.; Kannan, K.; Sun, L.; Honda, M.; Wang, W.; Karthikraj, R.; Chen, Z.; Weck, J.; Buck Louis, G.M. Preconception seminal plasma concentrations of endocrine disrupting chemicals in relation to semen quality parameters among male partners planning for pregnancy. Environ. Res. 2018, 167, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornehag, C.-G.; Sundell, J.; Weschler, C.J.; Sigsgaard, T.; Lundgren, B.; Hasselgren, M.; Hägerhed-Engman, L. The association between asthma and allergic symptoms in children and phthalates in house dust: A nested case-control study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 1393–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.C.; Chen, C.H.; Guo, Y.L. Phthalate esters and childhood asthma: A systematic review and congener-specific meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Lin, Z.; Liao, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Cai, J.; Zou, Z.; Wang, H.; Norback, D.; et al. Urinary phthalate metabolites in relation to childhood asthmatic and allergic symptoms in Shanghai. Environ. Int. 2018, 121 Pt 1, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, J.M. Early-life exposure to EDCs: Role in childhood obesity and neurodevelopment. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.W.; Kim, M.S.; Lim, Y.H.; Lee, N.; Hong, Y.C. Prenatal and postnatal exposure to di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate and neurodevelopmental outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Res. 2018, 167, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. EPA. Di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (DEHP) (CASRN 117-81-7). Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/iris/iris_documents/documents/subst/0014_summary.pdf (accessed on 30 March 2022).
- U.S. EPA. Phthalates Action Plan. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-09/documents/phthalates_actionplan_revised_2012-03-14.pdf (accessed on 30 March 2022).
- EU. Commission Decision of 7 December 1999 adopting measures prohibiting the placing on the market of toys and childcare articles intended to be placed in the mouth by children under three years of age made of soft PVC containing one or more of the substances di-iso-nonyl phthalate (DINP), di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP), dibutyl phthalate (DBP), di-iso-decyl phthalate (DIDP), di-n-octyl phthalate (DNOP), and butylbenzyl phthalate (BBP). Off. J. Eur. Communities 1999, L315, 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- EU. Commission Directive 2007/19/EC of 30 March 2007 amending Directive 2002/72/EC relating to plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food and Council Direvtive 85/572/EEC laying down the list of simulants to be used for testing migration of constituents of plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2007, L91, 17–36. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.H. Development background and trend of plasticizer industry in China. Econ. Anal. China Pet. Chem. Ind. 2014, 11, 53–57. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bu, Z.; Hu, M.; Yuan, F.; Xu, Y.; Dong, C.; Zhang, N.; Mmereki, D.; Cao, J.; Zheng, Y. Phthalates in Chinese vehicular environments: Source emissions, concentrations, and human exposure. Indoor Air 2021, 31, 2118–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, B. Emissions of Phthalates from Indoor Flat Materials in Chinese Residences. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 13166–13173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Z.; Mmereki, D.; Wang, J.; Dong, C. Exposure to commonly-used phthalates and the associated health risks in indoor environment of urban China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tao, W.; Xu, Y.; Feng, J.; Wang, F. Indoor phthalate concentration and exposure in residential and office buildings in Xi’an, China. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 87, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen Hubal, E.A.; Sheldon, L.S.; Burke, J.M.; McCurdy, T.R.; Berry, M.R.; Rigas, M.L.; Zartarian, V.G.; Freeman, N.C. Children’s exposure assessment: A review of factors influencing children’s exposure, and the data available to characterize and assess that exposure. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Selevan, S.G.; Kimmel, C.A.; Mendola, P. Identifying critical windows of exposure for children’s health. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108 (Suppl. 3), 451–455. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Mmereki, D.; Yu, W.; Li, B. Indoor phthalate concentration in residential apartments in Chongqing, China: Implications for preschool children’s exposure and risk assessment. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 127, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Xie, J.; Yoshino, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Li, N.; Liu, J.; Lv, Y.; Zhu, S.; Yanagi, U.; et al. Common SVOCs in house dust from urban dwellings with schoolchildren in six typical cities of China and associated non-dietary exposure and health risk assessment. Environ. Int. 2018, 120, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lu, X.M.; Zhang, X.L.; Sun, Y.G.; Zhu, D.M.; Wang, B.L.; Zhao, R.Z.; Zhang, Z.D. Levels of phthalate esters in settled house dust from urban dwellings with young children in Nanjing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 69, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulve, N.S.; Jones, P.A.; Nishioka, M.G.; Fortmann, R.C.; Croghan, C.W.; Zhou, J.Y.; Fraser, A.; Cavel, C.; Friedman, W. Pesticide measurements from the First National Environmental Health Survey of Child Care Centers using a multi-residue GC/MS analysis method. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 6269–6274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gong, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Phthalates in dust collected from various indoor environments in Beijing, China and resulting non-dietary human exposure. Build. Environ. 2017, 124, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, Z.; Gong, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Non-dietary exposure to phthalates for pre-school children in kindergarten in Beijing, China. Build. Environ. 2020, 167, 106438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; Shan, C.; Bai, Z.; Sun, Z.; Liu, L.; Shen, B. A comprehensive assessment of human exposure to phthalates from environmental media and food in Tianjin, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 279, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, P.A.; Liu, Z.; Kofoed-Sorensen, V.; Little, J.C.; Wolkoff, P. Infuence of temperature on the emission of di-(2-ethylhexyl)-phthalate (DEHP) from PVC fooring in the emission cell FLEC. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Little, J.C. Predicting emissioins of SVOCs from polymeric materials and their interaction with airborne particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Zhang, X.; Little, J.C.; Zhang, Y. A SPME-based method for rapidly and accurately measuring the characteristic parameter for DEHP emitted from PVC floorings. Indoor Air 2017, 27, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, Z.; Dong, C.; Mmereki, D.; Ye, Y.; Cheng, Z. Modeled exposure to phthalates via inhalation and dermal pathway in children’s sleeping environment: A preliminary study and its implications. Build. Simulation. 2021, 14, 1785–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weschler, C.J.; Nazaroff, W.W. SVOC partitioning between the gas phase and settled dust indoors. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 3609–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawanaka, Y.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Yun, S.; Sakamoto, K. Size distributions of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the atmosphere and estimation of the contribution of ultrafine particles to their lung deposition. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6851–6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, Y. The influence of aerosol dynamics on indoor exposure to airborne DEHP. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1952–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JGJ39-2016; Code for Design of Nursey and Kindergarten Buildings. China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2016. (In Chinese)
- GB/T18883-2002; Indoor Air Quality Standard. National Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2002. (In Chinese)
- GB24613-2009; Limit of Harmful Substances of Coatings for Toys. National Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2009. (In Chinese)
- GB6675-2014; Toys Safety. National Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2014. (In Chinese)
- Pei, X.; Song, M.; Guo, M.; Mo, F.; Shen, X. Concentration and risk assessment of phthalates present in indoor air from newly decorated apartments. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 68, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Chi, C.; Guo, M.; Wang, X.; Cheng, L.; Shen, X. Pollution levels and characteristics of phthalate esters in indoor air of offices. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 28, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Weschler, C.J. Exposure to SVOCs from Inhaled Particles: Impact of Desorption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6220–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Shi, S.; Weschler, C.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, Y. Analysis of the Dynamic Interaction Between SVOCs and Airborne Particles. Aerosol Sci. Tech. 2013, 47, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Mo, J.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Y. Indoor particle age, a new concept for improving the accuracy of estimating indoor airborne SVOC concentrations, and applications. Build. Environ. 2018, 136, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, C.Y.; Wang, X.K.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Xu, Y. Direct transfer of phthalate and alternative plasticizers from indoor source products to dust: Laboratory measurements and predictive modeling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukiene, V.; von Goetz, N.; Gerecke, A.C.; Bakker, M.I.; Delmaar, C.J.; Hungerbuhler, K. Direct and Air-Mediated Transfer of Labeled SVOCs from Indoor Sources to Dust. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3269–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.; Kim, K.; Choi, K. Migration of DEHP and DINP into dust from PVC flooring products at different surface temperature. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 547, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Arnot, J.A.; Wania, F. Revisiting the Contributions of Far- and Near-Field Routes to Aggregate Human Exposure to Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 6974–6984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hughes, L.; Arnot, J.A. Addressing uncertainty in mouthing-mediated ingestion of chemicals on indoor surfaces, objects, and dust. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Harris, S.A.; Jantunen, L.M.; Kvasnicka, J.; Nguyen, L.V.; Diamond, M.L. Phthalates: Relationships between Air, Dust, Electronic Devices, and Hands with Implications for Exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 8186–8197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Z.; Wang, J.; Yu, W.; Li, B. Dermal exposure to phthalates in home environment: Handwipes, influencing factors and implications. Build. Environ. 2018, 133, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Zhang, Y.; Weschler, C.J. Measurement of phthalates in skin wipes: Estimating exposure from dermal absorption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7428–7435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weschler, C.J.; Nazaroff, W.W. SVOC exposure indoors: Fresh look at dermal pathways. Indoor Air 2012, 22, 356–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Liu, N.; Zhang, Y. SPME-Based Ca-History Method for Measuring SVOC Diffusion Coefficients in Clothing Material. Environ Sci Technol. 2017, 51, 9137–9145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licina, D.; Morrison, G.C.; Beko, G.; Weschler, C.J.; Nazaroff, W.W. Clothing-Mediated Exposures to Chemicals and Particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 5559–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licina, D.; Bekö, G.; Cao, J. Role of Clothing in Exposure to Indoor Pollutants. In Handbook of Indoor Air Quality; Zhang, Y., Hopke, P.K., Mandin, C., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Cao, J.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y. Role of Clothing in Skin Exposure to Di(n-butyl) Phthalate and Tris(1-chloro-2-propyl) Phosphate: Experimental Observations via Skin Wipes. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y. Predicting Dermal Exposure to Gas-Phase Semivolatile Organic Compounds (SVOCs): A Further Study of SVOC Mass Transfer between Clothing and Skin Surface Lipids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 4676–4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, G.; Pawliszyn, J. A critical review in calibration methods for solid-phase microextraction. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2008, 627, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugg, G.A. Diffusion coefficients of some organic and other vapors in air. Anal. Chem. 1968, 40, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Mandin, C.; Blanchard, O.; Mercier, F.; Pelletier, M.; Le Bot, B.; Glorennec, P.; Ramalho, O. Distributions of the particle/gas and dust/gas partition coefficients for seventy-two semi-volatile organic compounds in indoor environment. Chemosphere 2016, 153, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axley, J.W. Adsorption modelling for building contaminant dispersal analysis. Indoor Air. 1991, 2, 147–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Zhao, B. Estimating indoor semi-volatile organic compounds (SVOCs) associated with settled dust by an integrated kinetic model accounting for aerosol dynamics. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 107, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Benning, J.L.; Little, J.C. The effect of ventilation on indoor exposure to semivolatile organic compounds. Indoor Air 2015, 25, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Weschler, C.J. The impact of mass transfer limitations on size distributions of particle associated SVOCs in outdoor and indoor environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 497–498, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).