Glycyrrhizic Acid Attenuates Pulmonary Fibrosis of Silicosis by Inhibiting the Interaction between HMGB1 and BRG1 through PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Model
2.2. Cell Lines, Small Interference RNA and Transfection
2.3. Histologic Analysis
2.4. Immunohistochemical Analysis
2.5. Protein Extraction and Western Blot Analysis
2.6. RNA Extraction and Quantitative real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Assays
2.7. Cell Scratch Assay
2.8. Co-Immunoprecipitation
2.9. String Database
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
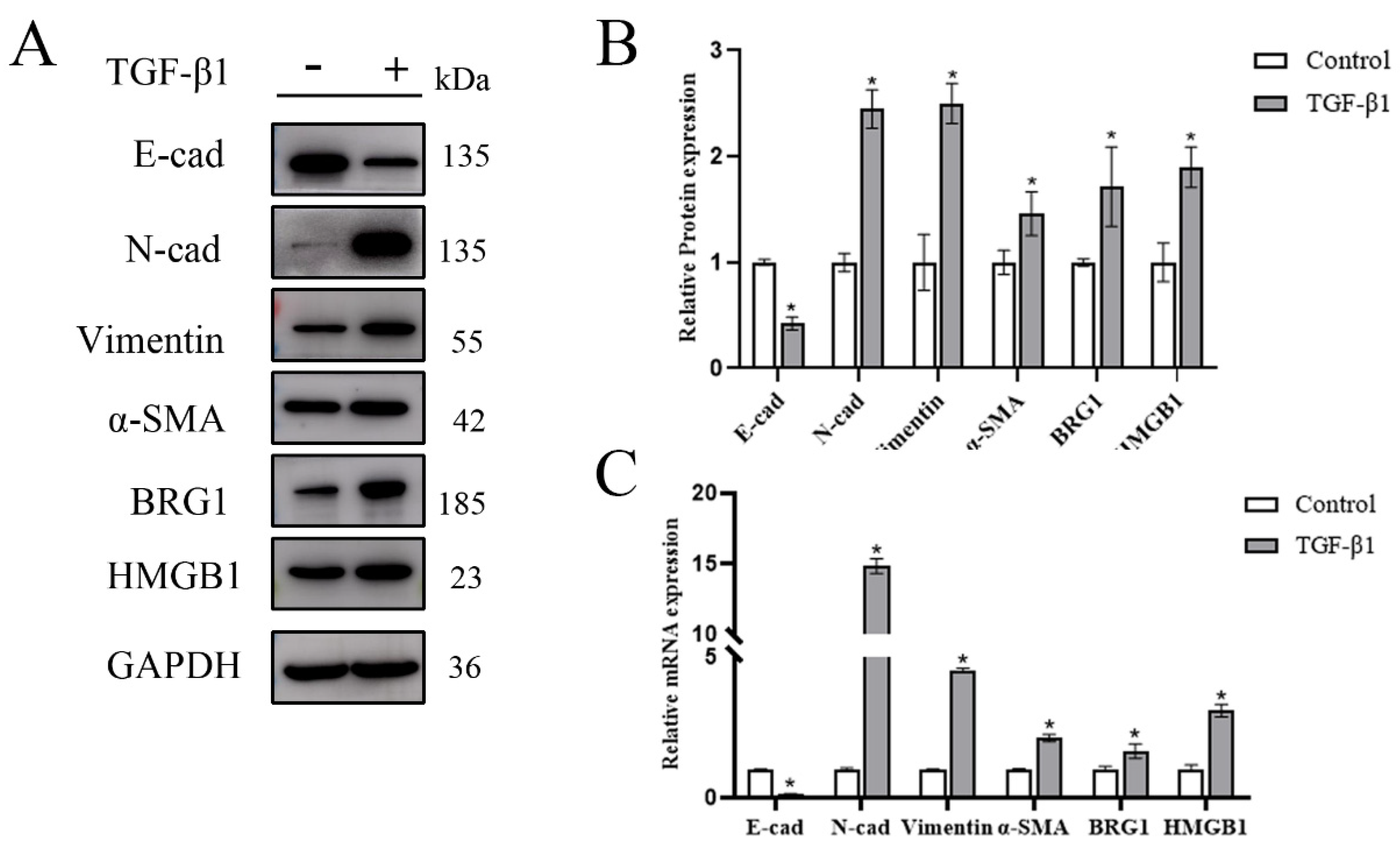
3.1. Both HMGB1 and BRG1 Are Elevated in TGF-β1-Induced EMT
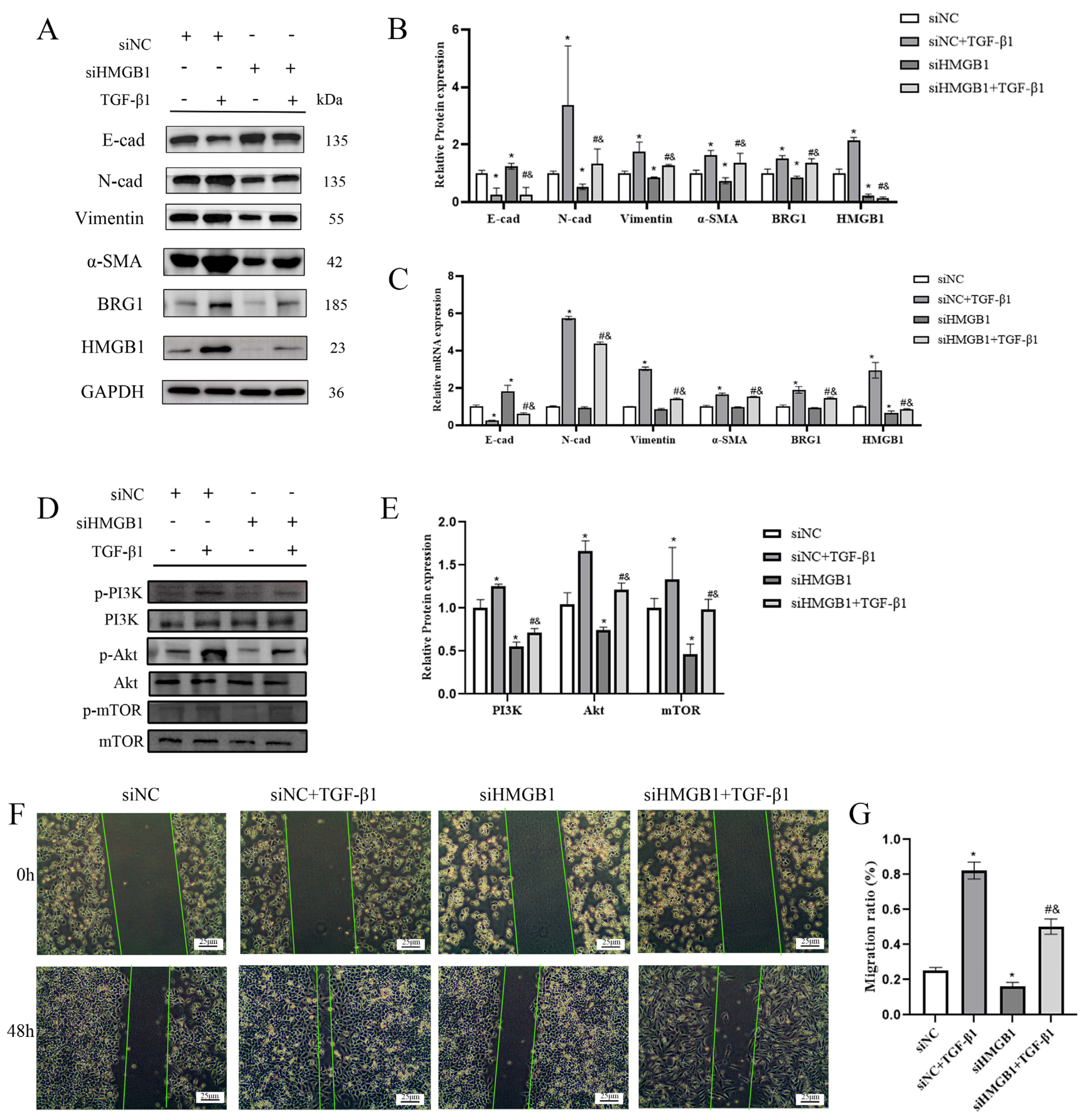
3.2. Silencing the Expression of HMGB1 Can Inhibit the EMT Process of A549 Cells
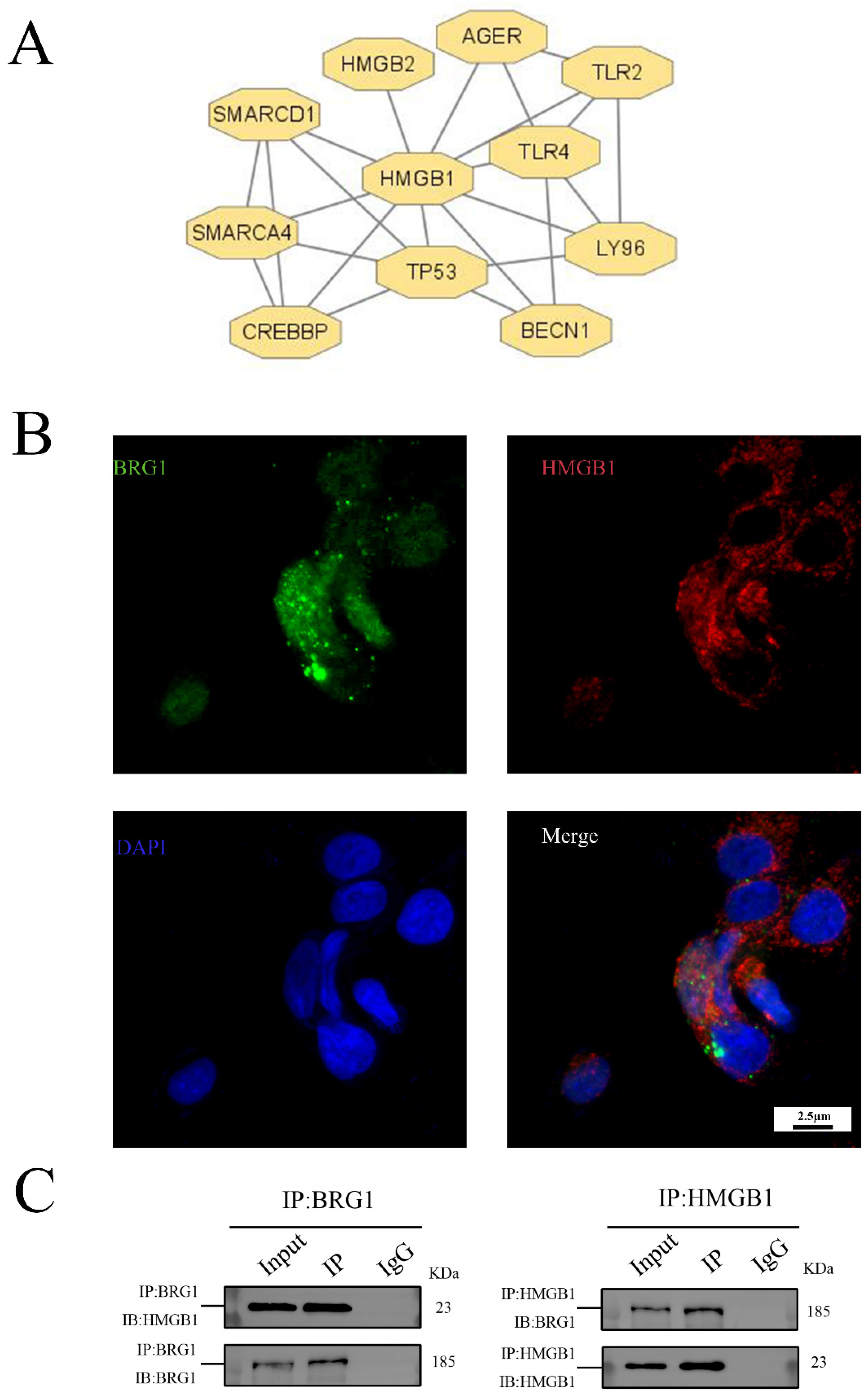
3.3. HMGB1 Can Interact with BRG1 in A549 Cells
3.4. Silencing BRG1 Can Inhibit EMT Process, While up-Regulation of HMGB1 Can Reverse This Inhibition
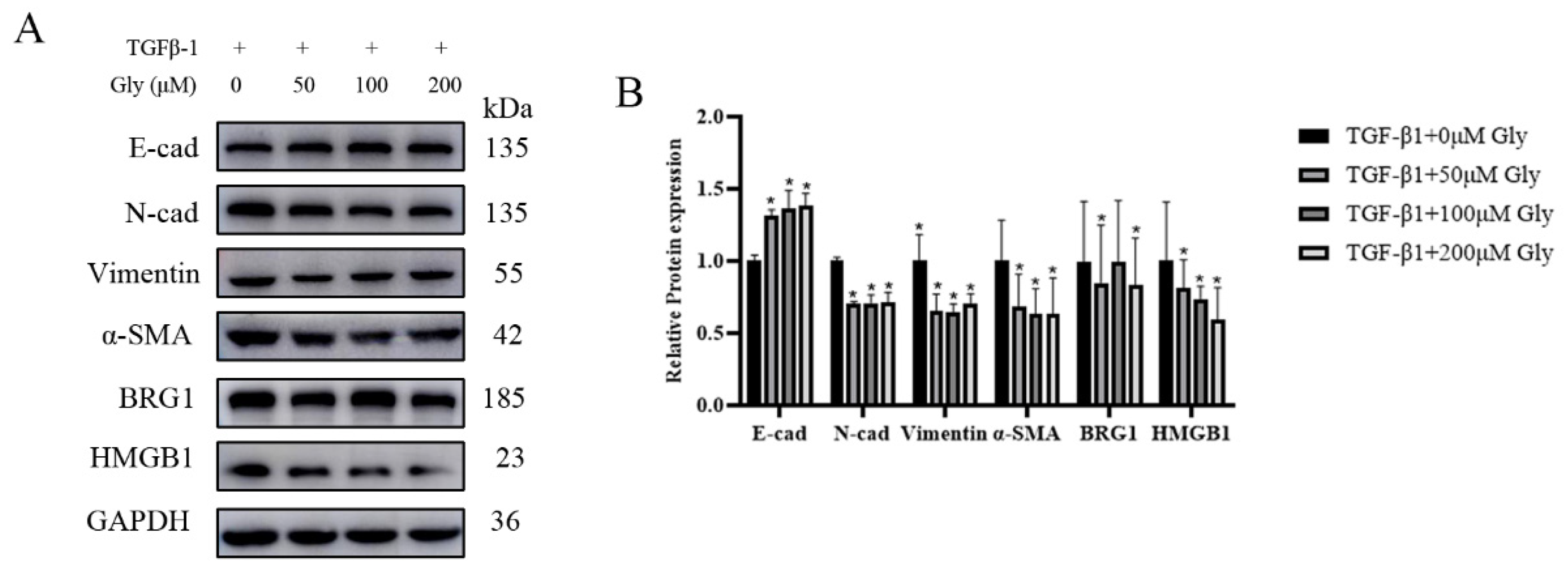
3.5. Different Concentrations of Glycyrrhizic Acid Could Inhibit the EMT-Like Changes Caused by TGF-β1
3.6. Protective Effect of Glycyrrhizic Acid on Silica-Induced Silicosis in Mice
3.7. Glycyrrhizic Acid Can Alleviate the EMT Process in Mice Silicosis
3.8. Glycyrrhizic Acid Inhibits the Interaction between HMGB1 and BRG1 through PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kolahian, S.; Fernandez, I.E.; Eickelberg, O.; Hartl, D. Immune Mechanisms in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. 2016, 55, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richeldi, L.; Collard, H.R.; Jones, M.G. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet 2017, 389, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bi, Z.; Liu, S.; Gao, S.; Cui, Y.; Huang, K.; Huang, M.; Mao, J.; Li, L.; Gao, J.; et al. Antifibrotic Mechanism of Cinobufagin in Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.J.; Li, Q.; Weng, C.M.; Duan, Z.X.; Zhang, D.D.; Chen, Z.Q.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.M. Bleomycin-enhanced alternative splicing of fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 induces epithelial to mesenchymal transition in lung fibrosis. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20180445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galan-Cobo, A.; Arellano-Orden, E.; Sanchez Silva, R.; Lopez-Campos, J.L.; Gutierrez Rivera, C.; Gomez Izquierdo, L.; Suarez-Luna, N.; Molina-Molina, M.; Rodriguez Portal, J.A.; Echevarria, M. The Expression of AQP1 IS Modified in Lung of Patients With Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Addressing a Possible New Target. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2018, 5, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, T.; You, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Z.Z. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT): A biological process in the development, stem cell differentiation, and tumorigenesis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 3261–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stros, M. HMGB proteins: Interactions with DNA and chromatin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1799, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czura, C.J.; Wang, H.C.; Tracey, K.J. Dual roles for HMGB1: DNA binding and cytokine. J. Endotoxin Res. 2001, 7, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ugrinova, I.; Pasheva, E. HMGB1 Protein: A Therapeutic Target Inside and Outside the Cell. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2017, 107, 37–76. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, F.J.; Wang, S.; Yan, Y.J.; Wang, C.Y.; Guan, Z.Y.; Zhang, J. Recombined humanized endostatin-induced suppression of HMGB1 expression inhibits proliferation of NSCLC cancer cells. Thorac. Cancer 2019, 10, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumari, T.; Kumar, B. High-mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1) gene polymorphisms and cancer susceptibility: A comprehensive meta-analysis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 483, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Tillo, E.; Lazaro, A.; Torrent, R.; Cuatrecasas, M.; Vaquero, E.C.; Castells, A.; Engel, P.; Postigo, A. ZEB1 represses E-cadherin and induces an EMT by recruiting the SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling protein BRG1. Oncogene 2010, 29, 3490–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, D.J.; Song, X.L.; Huang, B.; Yu, Y.Z.; Shu, F.P.; Wang, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.B.; Zhao, S.C. HMGB1 Promotes Prostate Cancer Development and Metastasis by Interacting with Brahma-Related Gene 1 and Activating the Akt Signaling Pathway. Theranostics 2019, 9, 5166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musumeci, D.; Roviello, G.N.; Montesarchio, D. An overview on HMGB1 inhibitors as potential therapeutic agents in HMGB1-related pathologies. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 141, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.H.; Li, X.; He, L.F.; Cai, H.F.; Ye, B.; Wu, Z.M. Glycyrrhizic acid, as an inhibitor of HMGB1, alleviates bleomycin-induced pulmonary toxicity in mice through the MAPK and Smad3 pathways. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2021, 43, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, Y.; Sun, J.; You, W.; Wei, Y.; Tian, H.; Jiang, S. Glycyrrhizin suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition by inhibiting high-mobility group box1 via the TGF-beta1/Smad2/3 pathway in lung epithelial cells. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, R.X.; Hao, C.F.; Wang, D.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Li, C.; Wang, C.; Yao, W. SPP1 derived from silica-exposed macrophage exosomes triggers fibroblast transdifferentiation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2021, 422, 115559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynn, T.A. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of fibrosis. J. Pathol. 2008, 214, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolters, P.J.; Collard, H.R.; Jones, K.D. Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2014, 9, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Chen, M.; Liu, F.; Wu, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, M.; Li, X. N-acetylcysteine tiherapeutically protects against pulmonary fibrosis in a mouse model of silicosis. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20190681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.W.; Yang, Z.F.; Jia, Q.; Bo, C.X.; Shao, H.; Zhang, Z.L. Pirfenidone inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and pulmonary fibrosis in the rat silicosis model. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 300, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Z.H.; Yang, G.X.; An, G.L.; Li, X.L.; Niu, P.Y.; Chen, L.; Tian, L. BMP-7 attenuated silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis through modulation of the balance between TGF-beta/Smad and BMP-7/Smad signaling pathway. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 243, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.H.; Ma, N.J.; Luo, H.; Chen, S.Z.; Yu, F.X. Downregulated long non-coding RNA LINC01093 in liver fibrosis promotes hepatocyte apoptosis via increasing ubiquitination of SIRT1. J. Biochem. 2020, 167, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Gauthier, A.; Daley, L.; Dial, K.; Wu, J.; Woo, J.; Lin, M.; Ashby, C.; Mantell, L.L. The Role of HMGB1, a Nuclear Damage-Associated Molecular Pattern Molecule, in the Pathogenesis of Lung Diseases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2019, 31, 954–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, H.; Sakamoto, S.; Isshiki, T.; Furuya, K.; Kurosaki, A.; Homma, S. Association of serum high-mobility group box protein 1 level with outcomes of acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and fibrosing nonspecific interstitial pneumonia. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dacwag, C.S.; Ohkawa, Y.; Pal, S.; Sif, S.; Imbalzano, A.N. The protein arginine methyltransferase Prmt5 is required for myogenesis because it facilitates ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kidder, B.L.; Palmer, S.; Knott, J.G. SWI/SNF-Brg1 Regulates Self-Renewal and Occupies Core Pluripotency-Related Genes in Embryonic Stem Cells. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.J.; Lan, J.Q.; Han, C.S.; Guo, K.X.; Wang, G.H.; Hu, J.B.; Gong, J.P.; Luo, X.L.; Cao, Z.X. Brg1 promotes liver fibrosis via activation of hepatic stellate cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 364, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zou, W.; Niu, C.; Ding, F.; Wang, Y.; Cai, S.; Zhu, H.; Tian, D.; Dai, J.; Liu, E.; et al. Brg1 inhibits E-cadherin expression in lung epithelial cells and disrupts epithelial integrity. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 95, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sansam, C.G.; Thom, C.S.; Metzger, D.; Evans, J.A.; Nguyen, P.T.L.; Roberts, C.W.M. Oncogenesis Caused by Loss of the SNF5 Tumor Suppressor Is Dependent on Activity of BRG1, the ATPase of the SWI/SNF Chromatin Remodeling Complex. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 8094–8101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, A.; Tawfik, O.; Gayed, B.; Thrasher, J.B.; Hoestje, S.; Li, C.Y.; Li, B. Aberrant expression of SWI/SNF catalytic subunits BRGI/BRM is associated with tumor development and increased invasiveness in prostate cancers. Prostate 2007, 67, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.C.; Gao, J.; Li, J. Emerging role of HMGB1 in fibrotic diseases. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2014, 18, 2331–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Men, M.; Xie, B.; Shan, J.G.; Wang, C.X.; Liu, J.D.; Zheng, H.; Yang, W.G.; Xue, S.; Guo, C.F. Inhibition of PKR protects against H2O2-induced injury on neonatal cardiac myocytes by attenuating apoptosis and inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rieg, A.D.; Suleiman, S.; Anker, C.; Verjans, E.; Rossaint, R.; Uhlig, S.; Martin, C. PDGF-BB regulates the pulmonary vascular tone: Impact of prostaglandins, calcium, MAPK- and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling and actin polymerisation in pulmonary veins of guinea pigs. Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.Y.; Gai, R.H.; Chen, Z.B.; Wang, Y.J.; Liao, S.D.; Dong, R.; Zhu, H.; Gu, Y.C.; He, Q.J.; Yang, B. The dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 prevents epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by hypoxia and TGF-beta 1. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 729, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, E.; Fruciano, M.; Fagone, E.; Gili, E.; Caraci, F.; Iemmolo, M.; Crimi, N.; Vancheri, C. Inhibition of PI3K Prevents the Proliferation and Differentiation of Human Lung Fibroblasts into Myofibroblasts: The Role of Class I P110 Isoforms. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nie, Y.J.; Sun, L.; Wu, Y.X.; Yang, Y.Y.; Wang, J.; He, H.Q.; Hu, Y.D.; Chang, Y.H.; Liang, Q.; Zhu, J.W.; et al. AKT2 Regulates Pulmonary Inflammation and Fibrosis via Modulating Macrophage Activation. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 4470–4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kida, T.; Seno, T.; Nagahara, H.; Inoue, T.; Nakabayashi, A.; Kukida, Y.; Fujioka, K.; Fujii, W.; Wada, M.; Kohno, M.; et al. Roles of high-mobility group box 1 and thrombin in murine pulmonary fibrosis and the therapeutic potential of thrombomodulin. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2018, 314, L473–L483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.P.; Tong, X.; Ren, S.; Wang, X.L.; Chen, J.M.; Mu, Y.P.; Sun, M.Y.; Chen, G.F.; Zhang, H.; Liu, P. Synergistic anti-liver fibrosis actions of total astragalus saponins and glycyrrhizic acid via TGF-beta 1/Smads signaling pathway modulation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 190, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lin, Y.J.; Zhen, Y.Z.; Hu, G.; Meng, X.; Li, X.X.; Men, X.L. Therapeutic Effect of Glycyrrhizin Arginine Salt on Rat Cholestatic Cirrhosis and its Mechanism. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2018, 46, 1111–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Qu, L.H.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.; He, W.; Shen, L.; Zhang, R. Glycyrrhizic Acid Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Regulating Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-2 (ACE2) and Caveolin-1 Signaling Pathway. Inflammation 2022, 45, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.C.; Gao, J.M.; Shen, J.Y.; Zhu, X.Q.; Wang, H.; Feng, S.Y.; Huang, C.; Shen, H.T.; Liu, H.L. Glycyrrhizic Acid Improves Cognitive Levels of Aging Mice by Regulating T/B Cell Proliferation. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 570116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.L.; Gao, S.J.; Sun, X.F. Glycyrrhizic acid ammonium salt alleviates Concanavalin A-induced immunological liver injury in mice through the regulation of the balance of immune cells and the inhibition of hepatocyte apoptosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 120, 109481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.C.; Li, D.L.; Xu, L.; Mo, X.T.; Cui, W.H.; Zhao, P.; Zhou, W.C.; Gao, J.; Li, J. High-Mobility Group Box 1 Mediates Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Pulmonary Fibrosis Involving Transforming Growth Factor-beta1/Smad2/3 Signaling. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2015, 354, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niu, Z.; Lin, J.; Hao, C.; Xu, X.; Wang, C.; Dai, K.; Deng, X.; Deng, M.; Guo, Y.; Yao, W. Glycyrrhizic Acid Attenuates Pulmonary Fibrosis of Silicosis by Inhibiting the Interaction between HMGB1 and BRG1 through PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8743. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19148743
Niu Z, Lin J, Hao C, Xu X, Wang C, Dai K, Deng X, Deng M, Guo Y, Yao W. Glycyrrhizic Acid Attenuates Pulmonary Fibrosis of Silicosis by Inhibiting the Interaction between HMGB1 and BRG1 through PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(14):8743. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19148743
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Zhuoya, Jisong Lin, Changfu Hao, Xiao Xu, Chen Wang, Kai Dai, Xuedan Deng, Meng Deng, Yonghua Guo, and Wu Yao. 2022. "Glycyrrhizic Acid Attenuates Pulmonary Fibrosis of Silicosis by Inhibiting the Interaction between HMGB1 and BRG1 through PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 14: 8743. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19148743
APA StyleNiu, Z., Lin, J., Hao, C., Xu, X., Wang, C., Dai, K., Deng, X., Deng, M., Guo, Y., & Yao, W. (2022). Glycyrrhizic Acid Attenuates Pulmonary Fibrosis of Silicosis by Inhibiting the Interaction between HMGB1 and BRG1 through PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(14), 8743. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19148743






