Gender-Neutral Toilets: A Qualitative Exploration of Inclusive School Environments for Sexuality and Gender Diverse Youth in Western Australia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Recruitment
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bullying Experiences of SGD Students in Toilets
We’ve got one young man who’s gone from man to woman…when he was going into the boys’ toilets, he was [verbally assaulted]. And then when he first started going into the girls’ toilets as his new identity, he was getting some of them being a bit nasty to him.(School staff #09)
[Toilet provision for trans students is] a big issue…I’m only learning about that now because we’ve only come against it in the last two years.(School staff #09)
There is an increasing number of requests: “we need a toilet, we’ve got a trans child, we need a separate toilet”.(Policy maker #19)
[Trans students] were often bullied at school and they didn’t disclose the bullying because it might lead to a disclosure about their gender identity, which would stigmatise them or make them more of a subject of bullying. So they felt like they had to keep a double secret.(Policy maker #09)
3.2. Support for Gender-Neutral Toilets
I’ve seen that there’s been this development of male toilets, female toilets, and then a unisex toilet. So there’s a choice. If there’s no choice, then you’re stuck with a binary issue which, of course, some kids feel challenged by. And for some transgender [females]… they may well feel quite victimised going into a male toilet because that’s probably a site of bullying.(Policy maker #09)
“Look at me, I have to go to that disabled toilet to go to the toilet, and I’m a boy, but I’m identifying as a girl, and everyone will be going errh?” The way of having the gender-free toilets is that it doesn’t matter which one you go to.(Policy maker #19)
I used to think it was okay to have the disabled toilet, but my principal corrected me the other week and said, “Absolutely not, they should be able to go into the toilet of the gender of which they identify”.(School staff #09)
[Students] can just use it so you don’t have to actually deal with the gender issue… if you can actually have a controlled space and this is your space and you are doing that personal thing, then you feel more comfortable anyway, which takes away that fear. There’s also no opportunity for bullying because it’s a single space for a single person.(Policy maker #01)
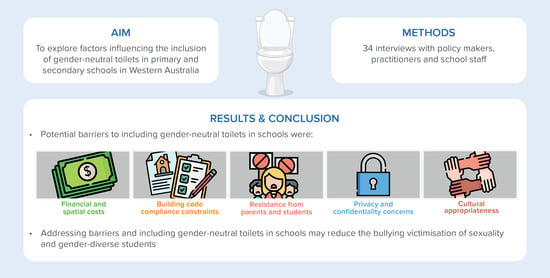
3.3. Barriers to Incorporating Gender-Neutral Toilets into Schools
3.3.1. Financial and Spatial Costs of Gender-Neutral Toilets
The problem with [a gender-neutral self-contained toilet] is it can be [expensive] as well, cost more money and so forth.(Policy maker #01)
Gender-neutral toilets can be done a number of different ways, and the one that is about making a series of completely self-contained cubicles that have hand washing as well, that is the one that immediately takes more space than would currently be briefed, and therefore, would sort of tend not to be the first cab off the rank for an approach.(Policy maker #20)
3.3.2. Building Code Compliance Constraints
There are also some code compliance issues around the gender-neutral toilets because under the National Construction Code there are actually a stipulated number of female, special or male toilets that have to be provided and it doesn’t accommodate things like non-gender.(Policy maker #11)
Anyone who…builds a school…has to follow the codes for that particular type of building… It requires extra consultants to come and design something specifically and tick it off. And that consultant takes responsibility for their design and so it’s not that easy. It’s not cheap and it’s not ideal. We would love to see the NCC changed to something where gender-neutral is recognised easily.(Policy maker #12)
We actually require a lot more toilets than is required under the code, so what we have done in the case of this school I am talking about is the ones which are required to be under the National Construction Code are gendered and all the ones we are not required to provide…we are doing those as gender neutral. And I think that is a really good outcome because we meet code-compliance and we give choice… we will see how it works as a little pilot project and see what reaction we get from students and teachers.(Policy maker #11)
3.3.3. Resistance from Parents and Students
I can’t see us putting in gender-neutral toilets into a primary school. I don’t know how that would work. It would be great but also with challenges. Parents wouldn’t allow it.(Policy maker #12)
At the moment we’re still going with male/female toilets, but then having a number of toilets that are gender-neutral that can be used… obviously, you get two lots of parents’ thinking; [some] want [contained gender-neutral] toilets, and then other parents don’t want their students going to that special toilet… I think it’s just fear of the unknown. …we have parents that don’t even like the students having to use the AATs [Ambulant & Accessible Toilets], which are the student accessible toilets, because it fingers their child as being different… People are worried about their children and what other kids will say about them.(Policy maker #21)
3.3.4. Privacy and Confidentiality Concerns
The school was quite concerned—it’s a high school—about the privacy of the student in the cubicle, and particularly worried about mobile phones and someone lifting a phone up over the top and taking a photo of a kid on the toilet, or under the door and just doing those intimidating things…Instead of doing cubicles we did what we call a super loo, which is where it’s like a home. You have a toilet and a hand basin in a room with a door in a frame with a lock, so you go into the room and you are completely private.(Policy maker #02)
3.3.5. Cultural Appropriateness of Mixing Genders
We are also aware that there is a cultural issue if you suddenly start putting non-binary toilets everywhere. There’s some cultures where that mixing of male and female is actually seen to be really very culturally inappropriate…Muslim and Islamic faith and some parts of Indigenous cultures…There’s quite strict cultural rules around that so it’s not a matter of saying we are just going to do everything like this.(Policy maker #11)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kann, L.; McManus, T.; Harris, W.A.; Shanklin, S.L.; Flint, K.H.; Queen, B.; Lowry, R.; Chyen, D.; Whittle, L.; Thornton, J.; et al. Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance–United States, 2017. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2018, 67, 1–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosciw, J.G.; Greytak, E.A.; Zongrone, A.D.; Clark, C.M.; Truong, N.L. The 2017 National School Climate Survey: The Experiences of Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender, and Queer Youth in our Nation’s Schools. Available online: https://www.glsen.org/sites/default/files/2019-10/GLSEN-2017-National-School-Climate-Survey-NSCS-Full-Report.pdf (accessed on 8 November 2021).
- Henderson, E.R.; Sang, J.M.; Louth-Marquez, W.; Egan, J.E.; Espelage, D.; Friedman, M.; Coulter, R.W.S. “Words aren’t supposed to hurt, but they do”: Sexual and gender minority youth’s bullying experiences. J. Interpers Violence 2020, 37, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birkett, M.; Espelage, D.L.; Koenig, B. LGB and questioning students in schools: The moderating effects of homophobic bullying and school climate on negative outcomes. J. Youth Adolesc. 2009, 38, 989–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-C.; Lin, H.-C.; Chen, M.-H.; Ko, N.-Y.; Chang, Y.-P.; Lin, I.M.; Yen, C.-F. Effects of traditional and cyber homophobic bullying in childhood on depression, anxiety, and physical pain in emerging adulthood and the moderating effects of social support among gay and bisexual men in Taiwan. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2018, 14, 1309–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S.E.; Herman, J.L.; Rankin, S.; Keisling, M.; Mottet, L.; Anafi, M. The Report of the 2015 U.S. Transgender Survey. Available online: https://transequality.org/sites/default/files/docs/usts/USTS-Full-Report-Dec17.pdf (accessed on 29 March 2022).
- Murchison, G.R.; Agénor, M.; Reisner, S.L.; Watson, R.J. School restroom and locker room restrictions and sexual assault risk among transgender youth. Pediatrics 2019, 143, e20182902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, R.-S.; Neary, A.; Gray, B.; Lacey, V. The Post-Primary School Experiences of Transgender and Gender Diverse Youth in Ireland. Available online: https://ulir.ul.ie/handle/10344/9133 (accessed on 14 July 2022).
- Carman, M.; Farrugia, C.; Bourne, A.; Power, J.; Rosenberg, S. Research Matters: How Many People are LGBTIQ? Available online: https://www.rainbowhealthvic.org.au/media/pages/research-resources/research-matters-how-many-people-are-lgbtiq/4170611962-1612761890/researchmatters-numbers-lgbtiq.pdf (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- Fisher, C.M.; Waling, A.; Kerr, L.; Ballamy, R.; Ezer, P.; Mikolajzak, G.; Brown, G.; Carman, M.; Lucke, J. 6th National Survey of Australian Secondary School Student and Sexual Health. Available online: https://www.latrobe.edu.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0004/1031899/National-Survey-of-Secondary-Students-and-Sexual-Health-2018.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2022).
- Hill, A.O.; Lyons, A.; Jones, J.; McGowan, I.; Carman, M.; Parson, M.; Power, J.; Bourne, A. Writing Themselves in 4: The Health and Wellbeing of LGBTQA+ Young People in Australia. National Report, Mongraph Series Number 124. Available online: https://www.latrobe.edu.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0010/1198945/Writing-Themselves-In-4-National-report.pdf (accessed on 11 April 2022).
- Hardacker, C.T.; Baccellieri, A.; Mueller, E.R.; Brubaker, L.; Hutchins, G.; Zhang, J.L.Y.; Hebert-Beirne, J. Bladder health experiences, perceptions and knowledge of sexual and gender minorities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, J.L. Gendered restrooms and minority stress: The public regulation of gender and its impact on transgender people’s lives. J. Public Manag. Soc. Policy 2013, 19, 65. [Google Scholar]
- McBride, R.-S. A literature review of the secondary school experiences of trans youth. J. LGBT Youth 2021, 18, 103–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price-Feeney, M.; Green, A.E.; Dorison, S.H. Impact of bathroom discrimination on mental health among transgender and nonbinary youth. J. Adolesc. Health 2021, 68, 1142–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, C.M.; Gower, A.L.; Mehus, C.J.; Yu, X.; Saewyc, E.M.; Eisenberg, M.E. “Kicked out”: LGBTQ youths’ bathroom experiences and preferences. J. Adolesc. 2017, 56, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Loughlin, C. Gender Neutral Toilets Now an Option for New Schools. Available online: https://www.independent.ie/irish-news/education/gender-neutral-toilets-now-an-option-for-new-schools-40342981.html (accessed on 8 April 2022).
- Wernick, L.J.; Kulick, A.; Chin, M. Gender identity disparities in bathroom safety and wellbeing among high school students. J. Youth Adolesc. 2017, 46, 917–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, K.O. Queering student perspectives: Gender, sexuality and activism in school. Sex Educ. 2016, 16, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, A.E.; Beemyn, G.; Smith, J.Z. What is needed, what is valued: Trans students’ perspectives on trans-inclusive policies and practices in higher education. J. Educ. Psychol. Consult 2019, 29, 27–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colliver, B.; Duffus, M. Queer space: Toilet provision, access and inclusion in the West Midlands. Sex Res. Soc. Policy 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, B.S.; Nesbit, A.E.; Sorrentino, R.M. The transgender bathroom debate at the intersection of politics, law, ethics, and science. J. Am. Acad. Psychiatry Law 2018, 46, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pasha-Robinson, L. Unisex Toilets at London Primary School Spark Outrage among Parents. Available online: www.independent.co.uk/news/uk/home-news/unisex-school-toilets-gender-neutral-london-inclusive-bathrooms-lgbt-samesex-a7441841.html (accessed on 6 April 2022).
- Peng, Y.-W.; Wu, W.-N. Who would (not) use all-gender toilets... and why? A study on university students in Taiwan. Gend. Place Cult. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greed, C. Join the queue: Including women’s toilet needs in public space. Sociol Rev. 2019, 67, 908–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokols, D. Translating social ecological theory into guidelines for community health promotion. Am. J. Health Promot. 1996, 10, 282–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, C.; Mays, N. Reaching the parts other methods cannot reach: An introduction to qualitative methods in health and health services research. BMJ 1995, 311, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acara. Guide to Understanding the Index of Community Socio-educational Advantage (ICSEA). Available online: https://www.myschool.edu.au/media/1820/guide-to-understanding-icsea-values.pdf (accessed on 11 April 2022).
- Olweus, D. Bullying at School: What We Know and What We Can Do; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Hennink, M.M.; Kaiser, B.N.; Marconi, V.C. Code saturation versus meaning saturation: How many interviews are enough? Qual. Health Res. 2017, 27, 591–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebele-Mpofu, F.Y. Saturation controversy in qualitative research: Complexities and underlying assumptions. A literature review. Cogen Soc. Sci 2020, 6, 1838706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, V.; Clarke, V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual. Res. Pscyhol. 2006, 3, 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryman, A. Social Research Methods, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, A.; Sainsbury, P.; Craig, J. Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): A 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. Int. J. Qual. Health Care 2007, 19, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ABCB. National Construction Code. Available online: https://ncc.abcb.gov.au/ (accessed on 8 November 2021).
- Greytak, E.; Kosciw, J.; Diaz, R. Harsh Realities: The Experiences of Transgender Youth in Our Nation’s Schools. Available online: https://www.glsen.org/research/harsh-realities-experiences-trans-youth-schools (accessed on 7 April 2022).
- AlMatrouk, L. The relationship between gender segregation in schools, self-esteem, spiritual values/religion, and peer relations in Kuwait. Near Mid. East J. Res. Educ. 2016, 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department for Education South Australia. Gender Diverse and Intersex Children and Young People Support Procedure. Available online: https://www.education.sa.gov.au/parents-and-families/safety-and-wellbeing/gender-diverse-intersex-and-sexually-diverse-children-and-young-people (accessed on 6 April 2022).
- Colliver, B.; Coyle, A. ‘Risk of sexual violence against women and girls’ in the construction of ‘gender-neutral toilets’: A discourse analysis of comments on YouTube videos. J. Gender. Based Viol. 2020, 4, 359–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, L. Transgender Student Wins as US Supreme Court Rebuffs Bathroom Appeal. Available online: https://www.reuters.com/world/us/us-supreme-court-declines-hear-transgender-school-bathroom-case-2021-06-28/ (accessed on 11 April 2022).
- Hasenbush, A.; Flores, A.R.; Herman, J.L. Gender identity nondiscrimination laws in public accommodations: A review of evidence regarding safety and privacy in public restrooms, locker rooms, and changing rooms. Sex Res. Social Policy 2018, 16, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothblatt, M. The Apartheid of Sex: A Manifesto on the Freedom of Gender; River Oram Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, B. Am I safe here? LGBTQ teens and bullying in schools: By Donn Short, Vancouver: UBC Press, 2017. ISBN: 978-0774890212. J LGBT Youth 2020, 17, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M. How organisational culture influences teachers’ support of openly gay, lesbian and bisexual students. Sex Educ. 2015, 15, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mearns, G.W.; Bonner-Thompson, C.; Hopkins, P. Trans experiences of a university campus in northern England. Area 2020, 52, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.; Jones, R.; Ward, R.; Dixon, J.; Mitchell, A.; Hillier, L. From Blues to Rainbows: The Mental Health and Well-Being of Gender Diverse and Transgender Young People in Australia. Available online: https://www.latrobe.edu.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0007/598804/from-blues-to-rainbows-report-sep2014.pdf (accessed on 8 April 2022).
| Characteristic | Policy Makers (n = 22) | School Staff (n = 12) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | |
| Age (years) | ||||
| 31–40 | 2 | 9.1 | 6 | 50.0 |
| 41–50 | 8 | 36.4 | 9 | 75.0 |
| 51–60 | 6 | 27.3 | 3 | 25.0 |
| 61–70 | 6 | 27.3 | - | - |
| Mean (SD) | 53.3 (8.7) | 47.2 (7.7) | ||
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 10 | 45.5 | 5 | 41.7 |
| Female | 12 | 54.6 | 7 | 58.3 |
| Born in Australia | ||||
| Yes | 15 | 68.2 | 9 | 75.0 |
| No | 7 | 31.8 | 3 | 25.0 |
| Years in role | ||||
| 1–10 | 2 | 9.1 | 3 | 25.0 |
| 11–20 | 8 | 36.4 | 5 | 41.7 |
| 21–30 | 9 | 40.9 | 3 | 25.0 |
| 31–40 | 2 | 9.1 | 1 | 8.4 |
| 41–50 | 1 | 4.5 | - | - |
| Mean (SD) | 23.6 (18.1) | 9.0 (9.1) | ||
| Theme | Category | Code |
|---|---|---|
| Gender-neutral toilets | Need for gender-neutral toilets | Bullying experiences of SGD students in toilets |
| Support for gender-neutral toilets | ||
| Barriers to including gender-neutral toilets in schools | Financial costs | |
| Lack of space | ||
| Building code compliance constraints | ||
| Resistance from parents | ||
| Resistance from students | ||
| Privacy and confidentiality concerns | ||
| Cultural appropriateness |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Francis, J.; Sachan, P.; Waters, Z.; Trapp, G.; Pearce, N.; Burns, S.; Lin, A.; Cross, D. Gender-Neutral Toilets: A Qualitative Exploration of Inclusive School Environments for Sexuality and Gender Diverse Youth in Western Australia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10089. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191610089
Francis J, Sachan P, Waters Z, Trapp G, Pearce N, Burns S, Lin A, Cross D. Gender-Neutral Toilets: A Qualitative Exploration of Inclusive School Environments for Sexuality and Gender Diverse Youth in Western Australia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(16):10089. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191610089
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrancis, Jacinta, Pratishtha Sachan, Zoe Waters, Gina Trapp, Natasha Pearce, Sharyn Burns, Ashleigh Lin, and Donna Cross. 2022. "Gender-Neutral Toilets: A Qualitative Exploration of Inclusive School Environments for Sexuality and Gender Diverse Youth in Western Australia" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 16: 10089. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191610089
APA StyleFrancis, J., Sachan, P., Waters, Z., Trapp, G., Pearce, N., Burns, S., Lin, A., & Cross, D. (2022). Gender-Neutral Toilets: A Qualitative Exploration of Inclusive School Environments for Sexuality and Gender Diverse Youth in Western Australia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(16), 10089. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191610089