Air Pollution in Kosovo: Short Term Effects on Hospital Visits of Children Due to Respiratory Health Diagnoses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Air Pollution Data
2.2. Health Data
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Air Pollution Data
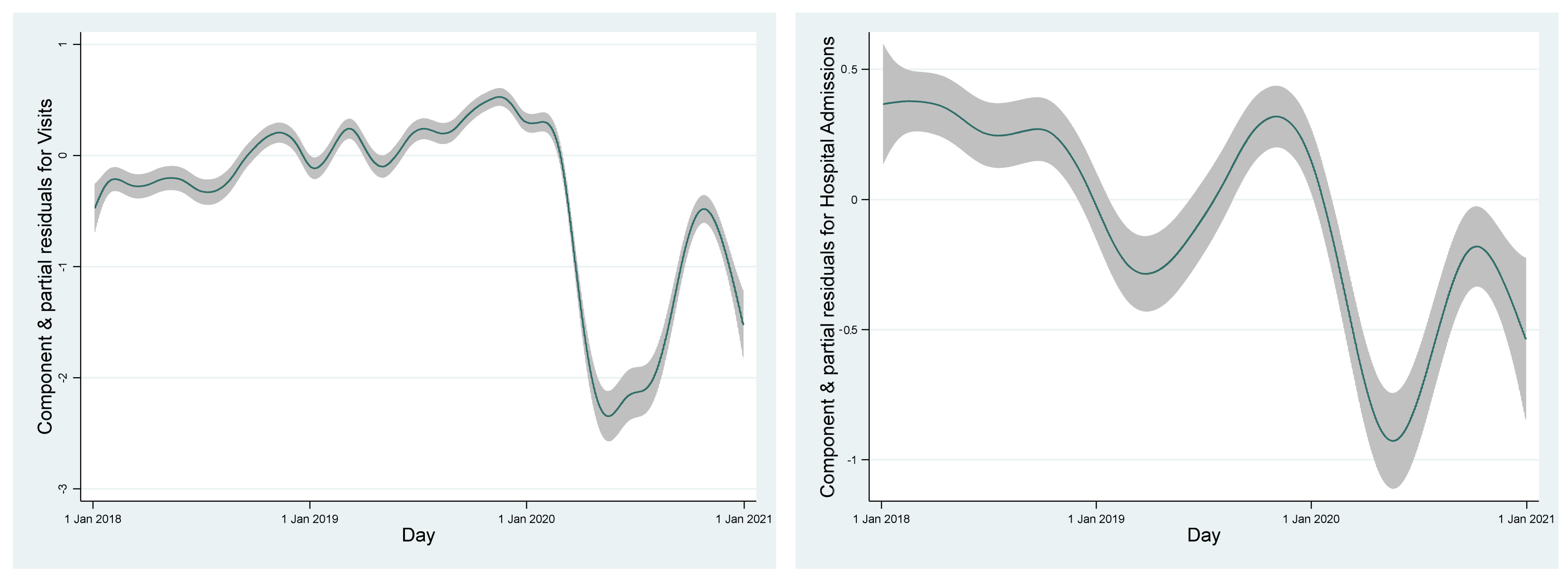
3.2. Time Course of Ambulatory Visits and Hospital Admissions
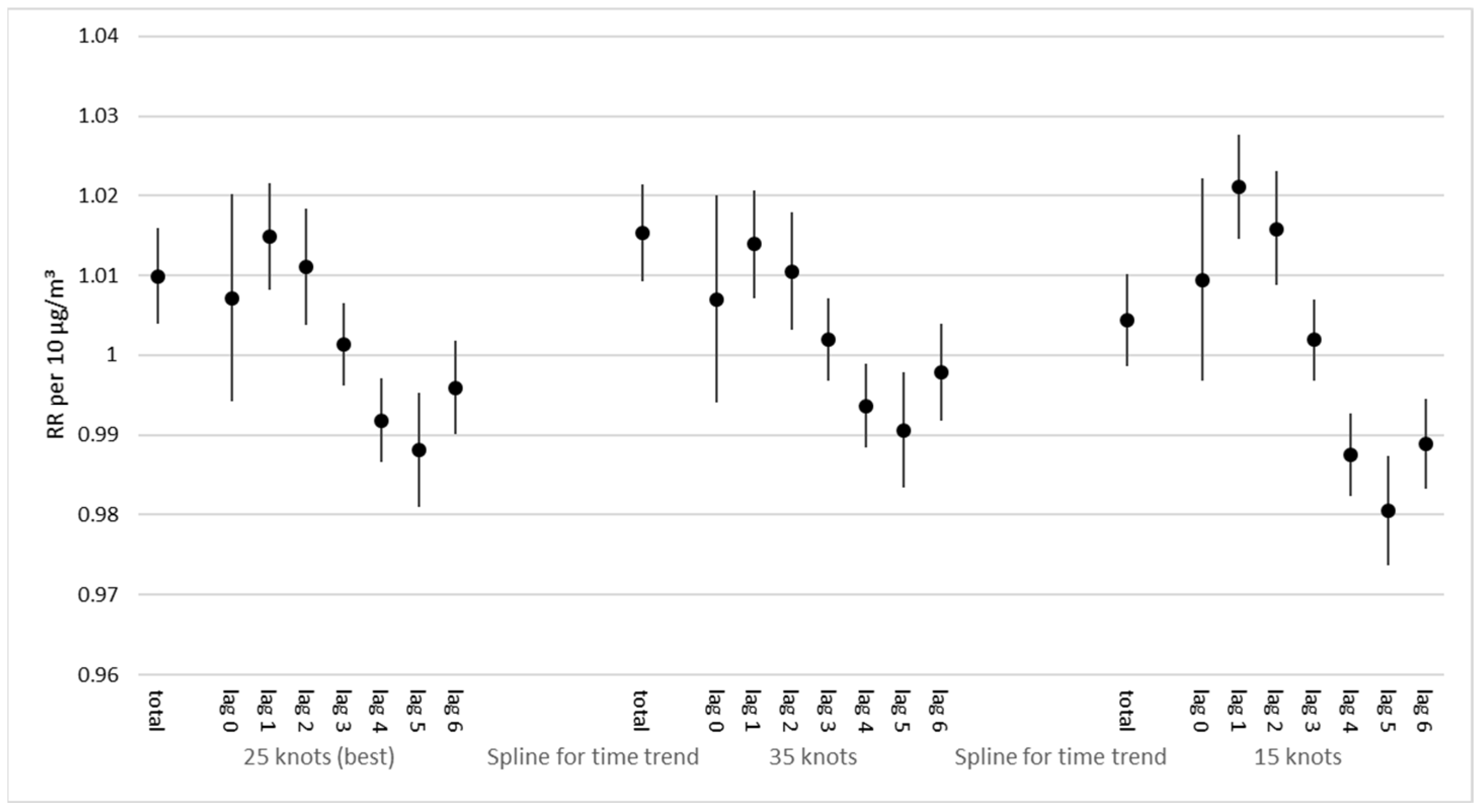
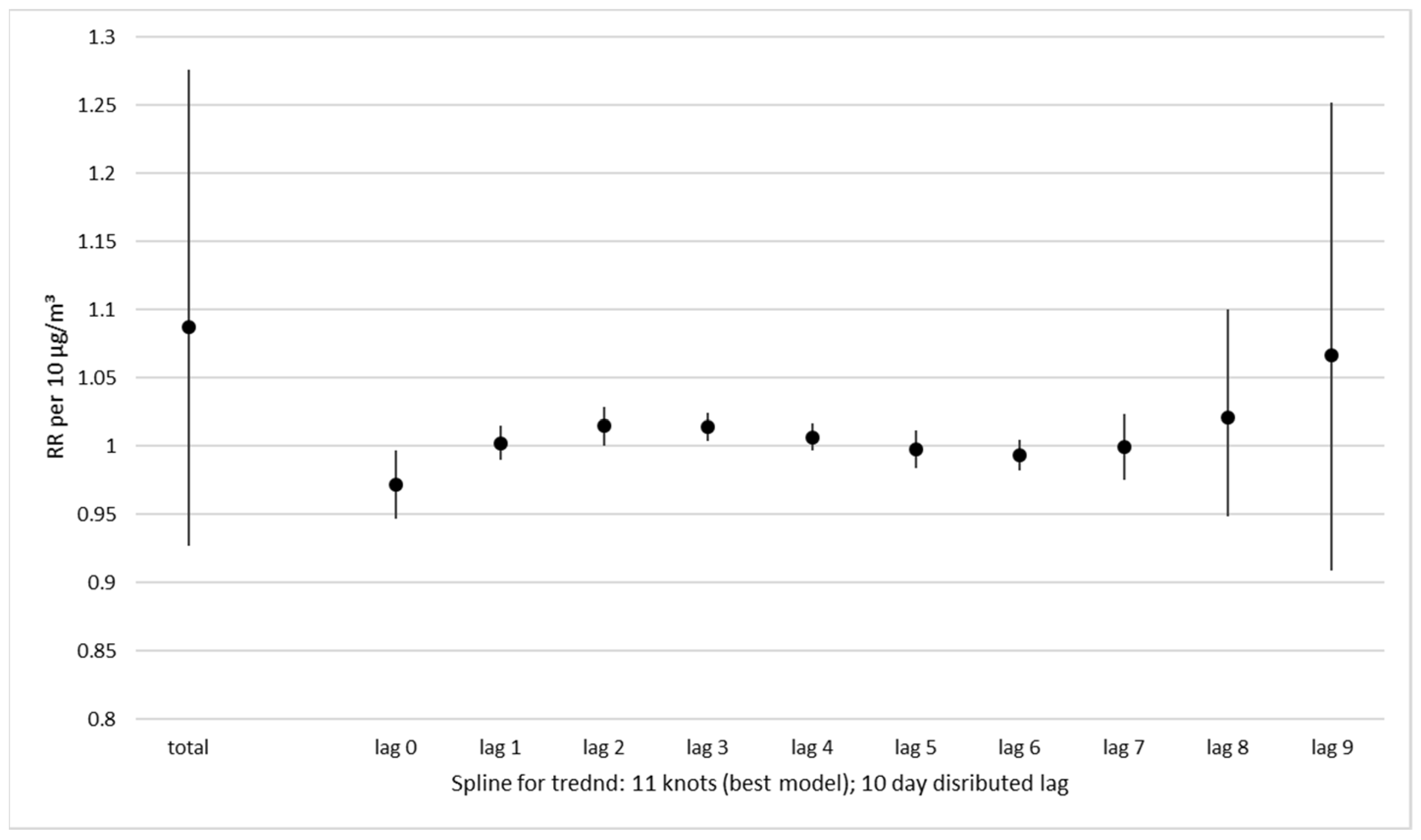
3.3. Short-Term Effect of Particulate Air Pollution (PM2.5)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | em | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1 | |||||||||||
| B | 0.9248 | 1 | ||||||||||
| C | 0.9056 | 0.8576 | 1 | |||||||||
| D | 0.8714 | 0.8662 | 0.8665 | 1 | ||||||||
| E | 0.8549 | 0.8433 | 0.8443 | 0.8621 | 1 | |||||||
| F | 0.765 | 0.7249 | 0.7796 | 0.7543 | 0.8745 | 1 | ||||||
| G | 0.8288 | 0.8212 | 0.7769 | 0.8574 | 0.8386 | 0.6882 | 1 | |||||
| H | 0.8254 | 0.8068 | 0.7497 | 0.7685 | 0.8342 | 0.7298 | 0.7541 | 1 | ||||
| I | 0.9172 | 0.8441 | 0.9023 | 0.8579 | 0.8622 | 0.7333 | 0.8122 | 0.7422 | 1 | |||
| J | 0.9208 | 0.8673 | 0.9242 | 0.8777 | 0.8787 | 0.7871 | 0.8342 | 0.8277 | 0.9467 | 1 | ||
| K | 0.9056 | 0.8396 | 0.9192 | 0.8456 | 0.845 | 0.7492 | 0.7933 | 0.8077 | 0.9584 | 0.9618 | 1 | |
| em | 0.9002 | 0.916 | 0.8714 | 0.8452 | 0.8587 | 0.7768 | 0.7918 | 0.8358 | 0.9158 | 0.9219 | 0.9155 | 1 |
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | em | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1 | |||||||||||
| B | 0.9511 | 1 | ||||||||||
| C | 0.9267 | 0.8643 | 1 | |||||||||
| D | 0.8771 | 0.8384 | 0.8626 | 1 | ||||||||
| E | 0.8387 | 0.8549 | 0.7422 | 0.6888 | 1 | |||||||
| F | 0.7869 | 0.683 | 0.8024 | 0.7594 | 0.7937 | 1 | ||||||
| G | 0.7521 | 0.7655 | 0.7521 | 0.7544 | 0.5857 | 0.4586 | 1 | |||||
| H | 0.793 | 0.8483 | 0.7557 | 0.7042 | 0.7869 | 0.5689 | 0.6805 | 1 | ||||
| I | 0.9167 | 0.8106 | 0.9342 | 0.9204 | 0.9028 | 0.8951 | 0.8641 | 0.6844 | 1 | |||
| J | 0.9218 | 0.8431 | 0.9132 | 0.8979 | 0.9099 | 0.8836 | 0.8336 | 0.7979 | 0.9561 | 1 | ||
| K | 0.9227 | 0.824 | 0.9436 | 0.9012 | 0.9083 | 0.904 | 0.8282 | 0.7347 | 0.9818 | 0.964 | 1 | |
| em | 0.9026 | 0.8561 | 0.8127 | 0.7742 | 0.8268 | 0.8285 | 0.5952 | 0.6564 | 0.9291 | 0.9165 | 0.9314 | 1 |
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | em | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1 | |||||||||||
| B | 0.8988 | 1 | ||||||||||
| C | 0.8767 | 0.8135 | 1 | |||||||||
| D | 0.828 | 0.8131 | 0.8258 | 1 | ||||||||
| E | 0.7997 | 0.7679 | 0.7942 | 0.8056 | 1 | |||||||
| F | 0.6802 | 0.6126 | 0.7039 | 0.6414 | 0.8118 | 1 | ||||||
| G | 0.7915 | 0.7556 | 0.7156 | 0.8135 | 0.7712 | 0.5755 | 1 | |||||
| H | 0.7707 | 0.7201 | 0.6731 | 0.6759 | 0.7464 | 0.6219 | 0.6564 | 1 | ||||
| I | 0.9279 | 0.8559 | 0.9057 | 0.8491 | 0.8185 | 0.6878 | 0.781 | 0.7641 | 1 | |||
| J | 0.9084 | 0.8304 | 0.9026 | 0.83 | 0.8248 | 0.7083 | 0.7648 | 0.7965 | 0.9496 | 1 | ||
| K | 0.8892 | 0.8064 | 0.8981 | 0.7967 | 0.7791 | 0.6694 | 0.7191 | 0.7948 | 0.9534 | 0.9515 | 1 | |
| em | 0.8858 | 0.8959 | 0.8397 | 0.797 | 0.8029 | 0.6927 | 0.7578 | 0.7977 | 0.9242 | 0.9114 | 0.9032 | 1 |
| Abbreviation | Location | Type | Operative Since |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | AQMS Prishtine–IHMK | suburban background | March 2018 |
| B | AQMS Prishtine, Rilindje | urban background | April 2018 |
| C | Drenas-Municipality | urban background | April 2018 |
| D | Mitrovice | urban background | May 2018 |
| E | AQMS Peje | urban background | May 2018 |
| F | AQMS Prizren | urban background | April 2018 |
| G | AQMS Hani i Elezit | suburban background | November 2019 |
| H | AQMS Gjilan | urban background | April 2018 |
| I | AQMS Palaj, Obiliq | suburban background | October 2019 |
| J | AQMS Obiliq, Obiliq | urban background | Sept 2019 |
| K | AQMS Dardhishte, Obiliq | suburban background | October 2019 |
| em | US embassy | at least 2017 |


References
- Dimovska, M.; Gjorgjev, D. Assessing Health Impact of Air Pollution in Macedonian Cities. Biomed. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2018, 10, 7522–7531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.R.; Bruce, N.; Balakrishnan, K.; Adair-Rohani, H.; Balmes, J.; Chafe, Z.; Dherani, M.; Hosgood, H.D.; Mehta, S.; Pope, D.; et al. HAP CRA Risk Expert Group. Millions dead: How do we know and what does it mean? Methods used in the comparative risk assessment of household air pollution. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2014, 35, 185–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Torné, A.; Vidal, M.; Trzaska, D.K.; Passante, L.; Crisafulli, A.; Laang, H.; van de Loo, J.W.; Berkouk, K.; Draghia-Akli, R. Chronic respiratory diseases and lung cancer research: A perspective from the European Union. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 1270–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taj, T.; Malmqvist, E.; Stroh, E.; Oudin Åström, D.; Jakobsson, K.; Oudin, A. Short-Term Associations between Air Pollution Concentrations and Respiratory Health-Comparing Primary Health Care Visits, Hospital Admissions, and Emergency Department Visits in a Multi-Municipality Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Global Status Report on Noncommunicable Diseases 2010. 2015. Available online: http://www.who.int/nmh/publications/ncd_report2010/en/ (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- D’Antoni, D.; Smith, L.; Auyeung, V.; Weinman, J. Psychosocial and demographic predictors of adherence and non-adherence to health advice accompanying air quality warning systems: A systematic review. Environ. Health 2017, 16, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukëhaxhaj, A.; Gjorgjev, D.; Ramadani, M.; Krasniqi, S.; Gjergji, T.; Zogaj, D. Air pollution in Pristina, influence on cardiovascular hospital morbidity. Med. Arch. 2013, 67, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshammer, H.; Neuberger, M. The active surface of suspended particles as a predictor of lung function and pulmonary symptoms in Austrian school children. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 1737–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuberger, M.; Moshammer, H.; Kundi, M. Declining ambient air pollution and lung function improvement in Austrian children. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 1733–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linden, B. Air pollution: Outdoor air quality and health. Br. J. Card. Nurs. 2019, 14, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COMEAP. Review of the UK Air Quality Index. A Report by the Committee on the Medical Effects of Air Pollutants. 2011. Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/304633/COMEAP_review_of_the_uk_air_quality_index.pdf (accessed on 9 February 2021).
- Jakubiak-Lasocka, J.; Lasocki, J.; Badyda, A.J. The influence of particulate matter on respiratory morbidity and mortality in children and infants. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 849, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, R.W.; Butland, B.K.; Dimitroulopoulou, C.; Heal, M.R.; Stedman, J.R.; Carslaw, N.; Jarvis, D.; Heaviside, C.; Vardoulakis, S.; Walton, H.; et al. Long-term exposure to ambient ozone and mortality: A quantitative systematic review and meta-analysis of evidence from cohort studies. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e009493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloemsma, L.D.; Hoek, G.; Smit, L.A.M. Panel studies of air pollution in patients with COPD: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Res. 2016, 151, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.F.; Xu, Y.H.; Shi, M.H.; Lian, Y.X. The impact of PM2.5 on the human respiratory system. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, E69–E74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshammer, H.; Poteser, M.; Kundi, M.; Lemmerer, K.; Weitensfelder, L.; Wallner, P.; Hutter, H.-P. Nitrogen-dioxide remains a valid air quality indicator. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshammer, H.; Hutter, H.-P.; Kundi, M. Which metric of ambient ozone to predict daily mortality? Atmos. Environ. 2013, 65, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, T.; Zhou, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Cui, Y. Ambient Air Pollution and Daily Hospital Admissions for Respiratory Disease in Children in Guiyang, China. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, E.J.; Lee, W.S.; Jo, H.Y.; Kim, C.H.; Eom, J.S.; Mok, J.H.; Kim, M.H.; Lee, K.; Kim, K.U.; Lee, M.K.; et al. Effects of particulate matter on respiratory disease and the impact of meteorological factors in Busan, Korea. Respir. Med. 2017, 124, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuurbier, M.; Lundqvist, C.; Salines, G.; Stansfeld, S.; Hanke, W.; Babisch, W.; Bistrup, M.L.; Van Den Hazel, P.; Moshammer, H. The Environmental Health of Children: Priorities in Europe. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2007, 20, 291–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukëhaxhaj, A.; Ramadani, N.; Gjorgjev, D.; Krasniqi, S.; Maloku, T.; Zogaj, D.; Gashi, S.; Loxha, A. Association of particulate air pollution with hospital admissions in pediatric clinics in Pristine, Kosovo. Albanian Med. J. 2013, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki, S.; Shima, M.; Yoda, Y.; Oka, K.; Kurosaka, F.; Shimizu, S.; Takahashi, H.; Nakatani, Y.; Nishikawa, J.; Fujiwara, K.; et al. Exposure to air pollution and meteorological factors associated with children’s primary care visits at night due to asthma attack: Case-crossover design for 3-year pooled patients. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e005736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ségala, C.; Poizeau, D.; Mesbah, M.; Willems, S.; Maidenberg, M. Winter air pollution and infant bronchiolitis in Paris. Environ. Res. 2008, 106, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Rahman, S.; Ismail, S.N.S.; Sahani, M.; Firuz, R.; Latif, M. A case crossover analysis of primary air pollutants association on acute respiratory infection (ARI) among children in urban region of Klang valley, Malaysia. Ann. Trop. Med. Public Health 2017, 10, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, S.Y.; Lau, S.Y.F.; Kwok, K.L.; Mohammad, K.N.; Chan, P.K.S.; Chong, K.C. Short-term association among meteorological variation, outdoor air pollution and acute bronchiolitis in children in a subtropical setting. Thorax 2021, 76, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUR-Lex. Directive 2008/50/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 May 2008 on Ambient Air Quality and Cleaner Air for Europe. 2008. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/en/ALL/?uri=CELEX:32008L0050 (accessed on 11 August 2022).
- World Health Organization. WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines: Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide. 2021. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/345329 (accessed on 13 July 2022).
- World Bank. Document of the World Bank. Report No: AUS0001229. Western Balkans Regional AQM—Western Balkans Report—AQM in Kosovo. 2019. Available online: https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/214511576520047805/pdf/Air-Pollution-Management-in-Kosovo.pdf (accessed on 30 June 2022).
- JFE Techno-Research Corporation. Republic of Kosovo, Ministry of Environment and Spatial Planning, Republic of Kosovo Expert for Air Pollution Control. Final Report. Available online: https://openjicareport.jica.go.jp/pdf/12260998.pdf (accessed on 30 June 2022).
- UNFPA Kosovo. The UNFPA Kosovo (UNSCR 1244)* Programme Evaluation Report. (Period Covered by the Evaluation: 2013–2018). Available online: https://web2.unfpa.org/public/about/oversight/evaluations/downloadapprsp.unfpa;jsessionid=02A48B3CA4798E5E1B2D64E06B36D52D?docId=136&annex (accessed on 30 June 2022).
- Republic of Kosova. Vjetari Statistikor i Republikës së Kosovës 2021. 2021. Available online: https://ask.rks-gov.net/media/6800/vjetari-statistikor-2021f.pdf (accessed on 30 June 2022).
- Osmani, A.A.; Marušic, D.; Halimi, R.; Muharremi, R.; Rupel, V.P. Health care reform in Kosovo. Eurohealth 2017, 23, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- European Environment Agency. Air Quality e-Reporting (AQ e-Reporting) EEA. 2021. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/data/aqereporting-9 (accessed on 30 June 2022).
- KHMI. Data from Monitoring Stations. 2022. Available online: https://airqualitykosova.rks-gov.net/en/reports-for-the-monitoring-stations/ (accessed on 30 June 2022).
- AirNow. Available online: https://www.airnow.gov/international/us-embassies-and-consulates/#Kosovo$Pristina (accessed on 30 June 2022).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 30 June 2022).
- Neuberger, M.; Rabczenko, D.; Moshammer, H. Extended effects of air pollution on cardiopulmonary mortality in Vienna. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 8549–8556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuberger, M.; Moshammer, H.; Rabczenko, D. Acute and subacute effects of urban air pollution on cardiopulmonary emergencies and mortality: Time series studies in Austrian cities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 4728–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Generalized Additive Models, 1st ed.; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, J. Harvesting and long term exposure effects in the relation between air pollution and mortality. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2000, 151, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominici, F.; McDermott, A.; Zeger, S.L.; Samet, J.M. On the use of generalized additive models in time-series studies of air pollution and health. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2002, 156, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominici, F.; Dermott, A.; Hastie, T. Improved Semiparametric Time Series Models of Air Pollution and Mortality. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2004, 99, 938–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsouyanni, K.; Touloumi, G.; Samoli, E.; Gryparis, A.; Le Tertre, A.; Monopolis, Y.; Rossi, G.; Zmirou, D.; Ballester, F.; Boumghar, A.; et al. Confounding and effect modification in the short-term effects of ambient particles on total mortality: Results from 29 European cities within the APHEA2 project. Epidemiology 2001, 12, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, H. Information theory as an extension of the maximum likelihood principle. In Proceedings of the Second International Symposium on Information Theory, Tsahkadsor, Armenia, 2–8 September 1971; Petrov, B.N., Csaksi, F., Eds.; Akademiai Kiado: Budapest, Hungary, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Maintaining Essential Health Services in Kosovo. Available online: https://hlh.who.int/learning-briefs/action-brief-kosovo---deep-dive (accessed on 29 June 2022).
- Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Tao, N.; Song, W.; Cui, L.; Li, H. Association between ambient PM2.5 and children’s hospital admissions for respiratory diseases in Jinan, China. Environ. Sci Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 24112–24120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Zhou, T.; Fang, S.; Zhou, X.; Bai, Y. Association of air pollutants and hospital admissions for respiratory diseases in Lanzhou, China, 2014–2019. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 6, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, T.; Chen, D.; Jiao, K.; Wang, X.; Suo, J.; Yang, H.; Liao, J.; Ma, L. Effect of ambient fine particulates (PM2.5) on hospital admissions for respiratory and cardiovascular diseases in Wuhan, China. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albahar, S.; Li, J.; Al-Zoughool, M.; Al-Hemoud, A.; Gasana, J.; Aldashti, H.; Alahmad, B. Air Pollution and Respiratory Hospital Admissions in Kuwait: The Epidemiological Applicability of Predicted PM2.5 in Arid Regions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.C. Statistical Methods in Environmental Epidemiology; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; p. 165f. ISBN 10 0199232903. [Google Scholar]
- Rabl, A. Air pollution mortality: Harvesting and loss of life expectancy. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2005, 68, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J. The Distributed Lag between Air Pollution and Daily Deaths. Epidemiology 2000, 11, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeger, S.L.; Dominici, F.; Samet, J. Harvesting-resistant estimates of air pollution effects on mortality. Epidemiology 1999, 10, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, K.; Krewski, D.; Burnett, R.; Dominici, F. Testing the harvesting hypothesis by time-domain regression analysis. I: Baseline analysis. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2005, 68, 1137–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimmel, H.; Murawski, T.J. The relation of air pollution to mortality. J. Occup. Med. 1976, 18, 316–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuberger, M.; Schimek, M.G.; Horak, F.; Moshammer, H.; Kundi, M.; Frischer, T.; Gomiscek, B.; Puxbaum, H.; Hauck, H. Acute effects of particulate matter on respiratory diseases, symptoms and functions: Epidemiological results of the Austrian Project on Health Effects of Particulate Matter (AUPHEP). Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 3971–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shabani Isenaj, Z.; Berisha, M.; Gjorgjev, D.; Dimovska, M.; Moshammer, H.; Ukëhaxhaj, A. Air Pollution in Kosovo: Short Term Effects on Hospital Visits of Children Due to Respiratory Health Diagnoses. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191610141
Shabani Isenaj Z, Berisha M, Gjorgjev D, Dimovska M, Moshammer H, Ukëhaxhaj A. Air Pollution in Kosovo: Short Term Effects on Hospital Visits of Children Due to Respiratory Health Diagnoses. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(16):10141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191610141
Chicago/Turabian StyleShabani Isenaj, Zana, Merita Berisha, Dragan Gjorgjev, Mirjana Dimovska, Hanns Moshammer, and Antigona Ukëhaxhaj. 2022. "Air Pollution in Kosovo: Short Term Effects on Hospital Visits of Children Due to Respiratory Health Diagnoses" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 16: 10141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191610141
APA StyleShabani Isenaj, Z., Berisha, M., Gjorgjev, D., Dimovska, M., Moshammer, H., & Ukëhaxhaj, A. (2022). Air Pollution in Kosovo: Short Term Effects on Hospital Visits of Children Due to Respiratory Health Diagnoses. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(16), 10141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191610141







