Evaluating the Hydraulic Effects of the Flow through and over the Submerged Biofilter Installed in Polluted Streams
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Dupuit formula for flow through horizontal filters
- Fadhil formula for flow through gravel gabion dams
- Fadhil (modified) formula for flow through gravel gabion dams
2. Materials and Methods
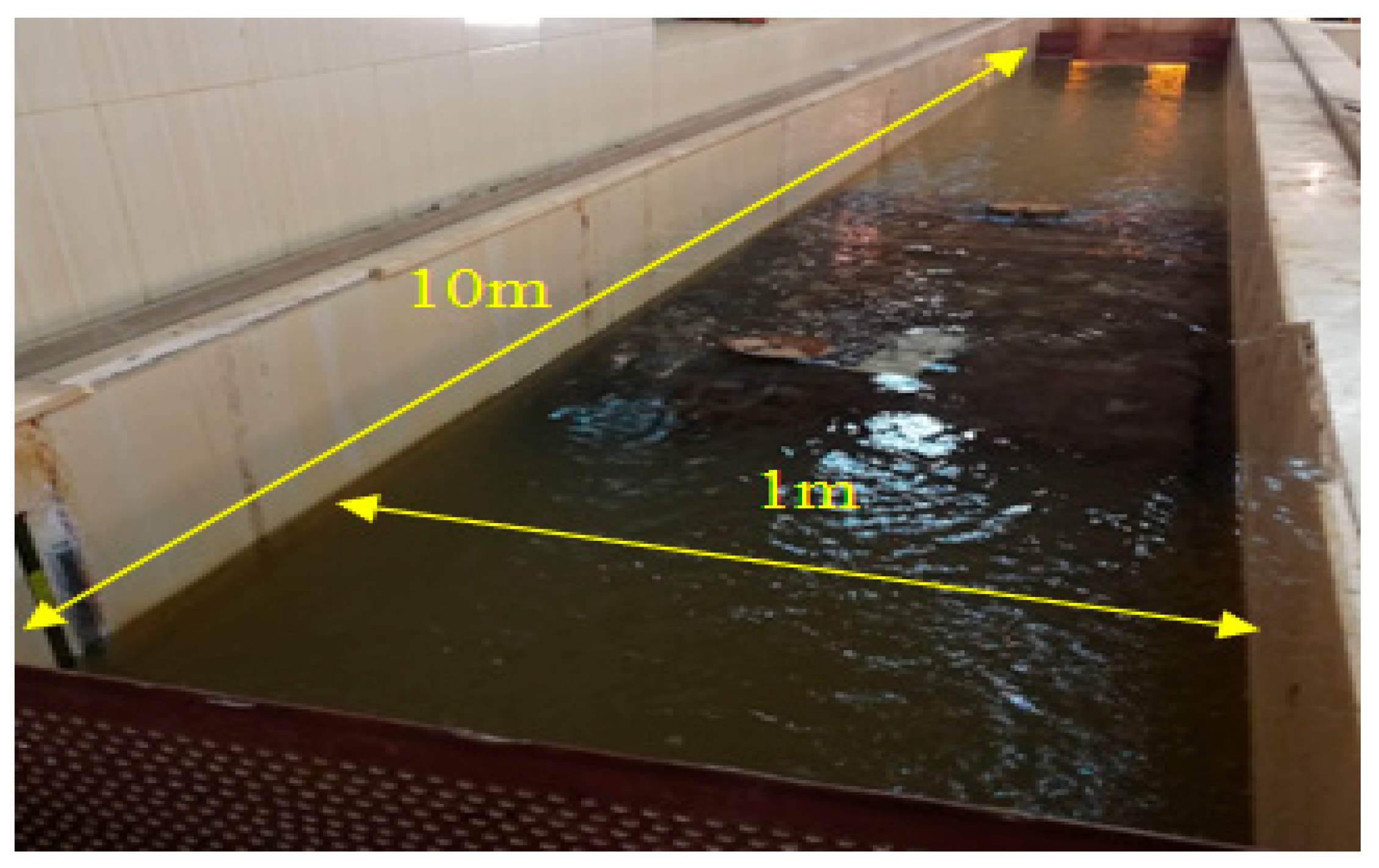
2.1. Experimental Work Description
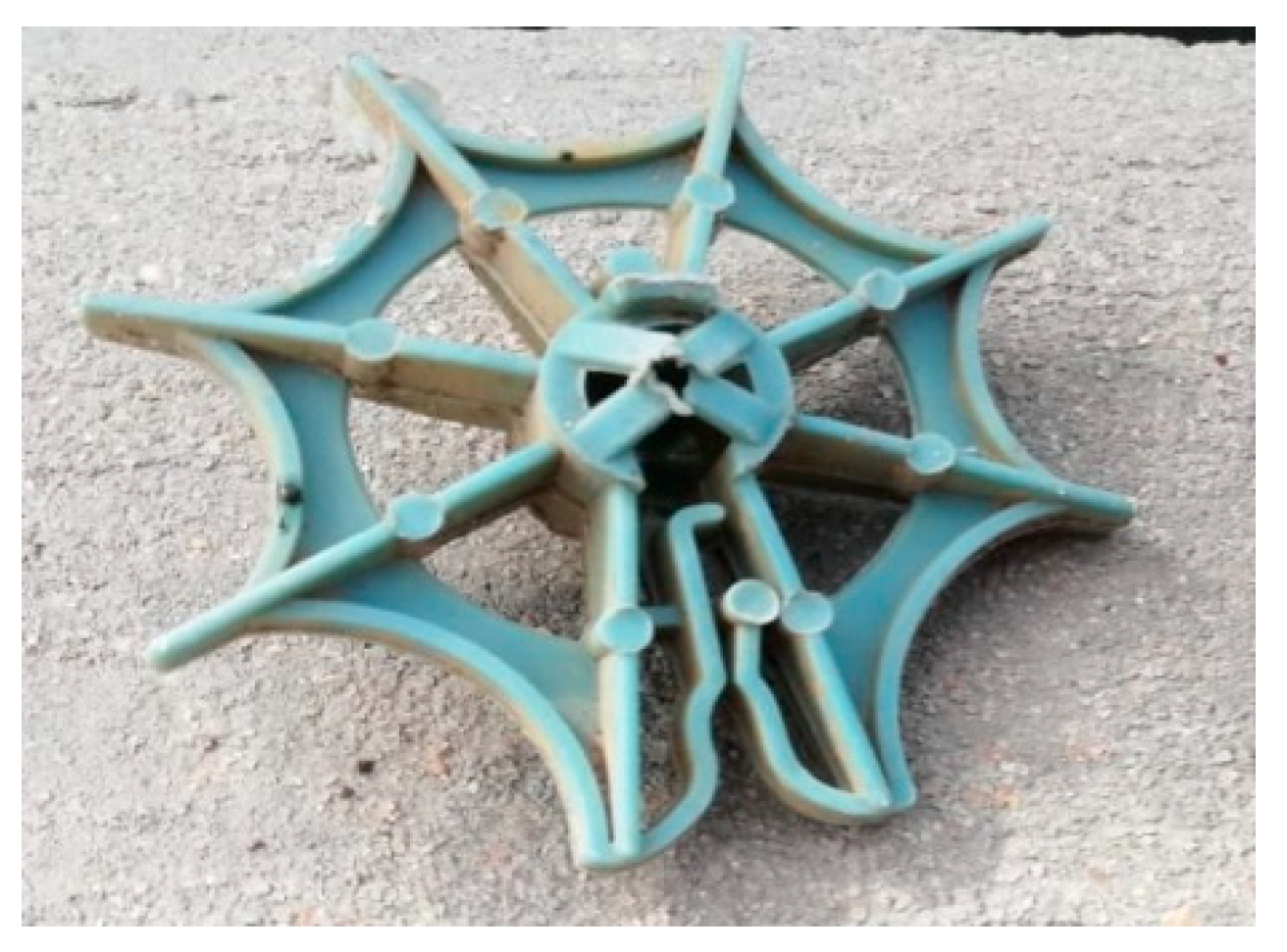
2.2. Biofilter Characteristics
2.3. Experimental Program
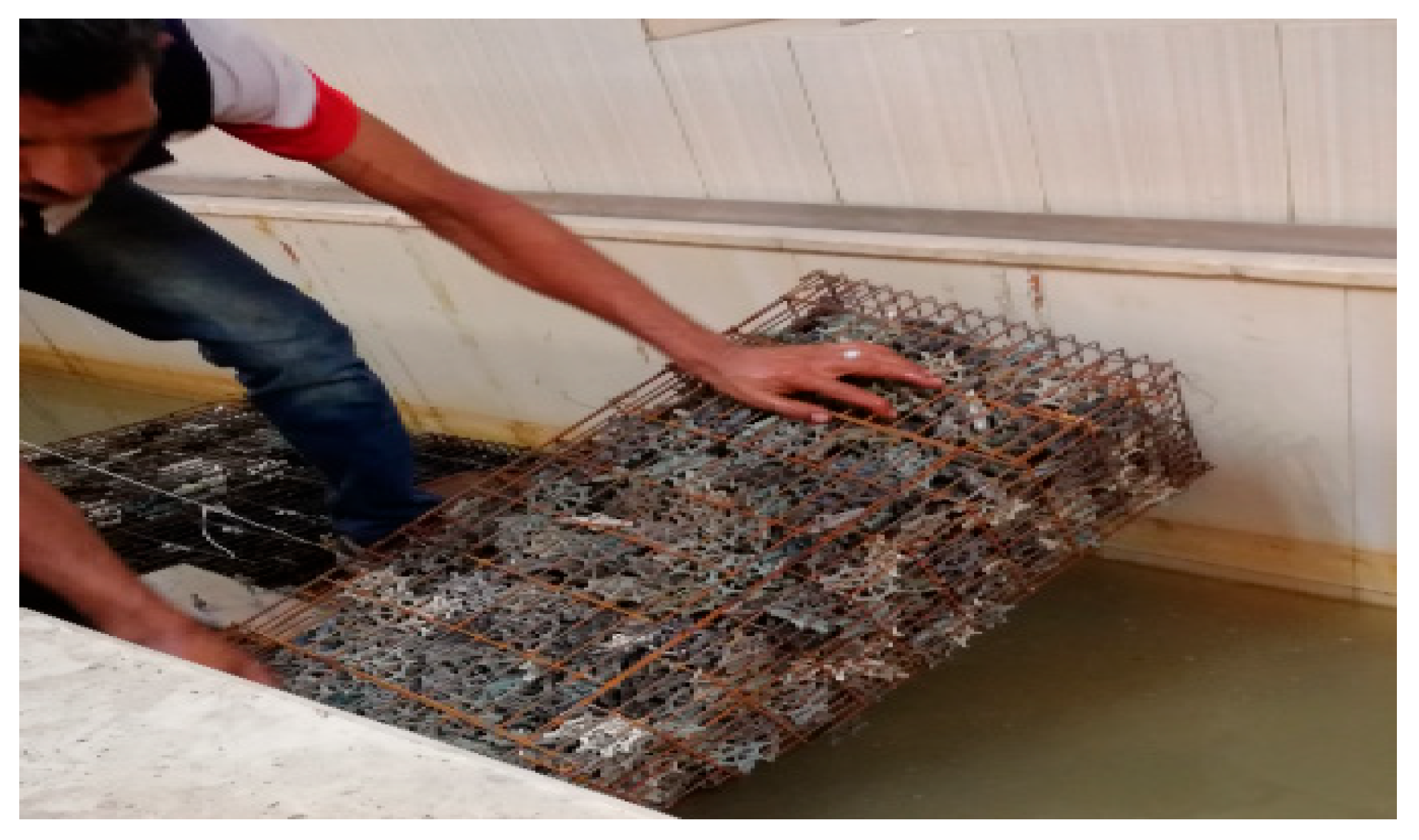
- The cages containing the plastic media were installed inside the channel crosswise (where the length of the cage is 1.0 m equal to the width of the channel) to achieve a height of 0.78 m in the case of flow through the biofilter and 0.52 during flow over the biofilter (as shown in Figure 5a,b);
- Establishing a flow rate by adjusting a control valve in the flume supply line;
- Waiting 10 min so the upstream water depth equilibrium is reached;
- Recording the discharge and water depth upstream and downstream the filter;
- Changing the value of the discharge as in step 2 and repeating steps 3 and 4;
- Repeating steps 2 to 5 for other biofilter length (0.8 m and 1.2 m) 10 times for each length as shown in Figure 5a,b for through flow and overflow regimes.
2.4. Measured Upstream and Downstream Water Levels
3. Dimensional Analysis and Multi-Linear Regression Analysis
4. Result and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramzi, A.I.; El-Nahry, A. Population growth and impacts of nile water deficiency on Egypt using GIS and other techniques. In Proceedings of the ACRS 2015—36th Asian Conference on Remote Sensing: Fostering Resilient Growth in Asia, Manila, Philippines, 19–23 October 2015; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- El-Nashar, W.Y.; Elyamany, A.H. Managing risks of the Grand Ethiopian renaissance dam on Egypt. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2018, 9, 2383–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, M.N.; Allam, G.I. Water resources in Egypt: Future challeges and opportunities. Water Int. 2007, 32, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD (Ed.). OECD Environmental Outlook to 2050. In OECD Environmental Outlook; OECD: Paris, France, 2012; ISBN 9789264122161. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. The State of the World’s Land and Water Resources for Food and Agriculture (SOLAW)—Managing Systems at Risk; The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and Earthscan: Rome, Italy; London, UK, 2011; ISBN 9781849713269. [Google Scholar]
- Ofori, S.; Puškáčová, A.; Růžičková, I.; Wanner, J. Treated wastewater reuse for irrigation: Pros and cons. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 144026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Water & Solar Technologies, Inc. Top 10 Countries with the Worst Water Crisis. 2019. Available online: https://www.worldwatersolar.com/top-10-countries-with-the-worst-water-crisis/ (accessed on 21 July 2022).
- Abd El-Hameed, A.K.M. Towards an Egyptian Benchmark for Water Efficiency During the Core Manufacturing Processes of Building Materials. Am. J. Civ. Environ. Eng. 2018, 3, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, Y. Project Information Document (Appraisal Stage)—EG-Enhanced Water Resources Management—P118090; Banco Mundial: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Onyutha, C. Variability of Rainfall and River Flow in the Nile Basin. 2017. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/320146885_Variability_of_Rainfall_and_River_Flow_in_the_Nile_Basin (accessed on 30 September 2017).
- Abdel-Shafy, H.I.; Aly, R.O. Water issue in Egypt: Resources, pollution and protection endeavors. Cent. Eur. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2002, 8, 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Panagoulia, D.; Vlahogianni, E.I. Nonlinear dynamics and recurrence analysis of extreme precipitation for observed and general circulation model generated-climates. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 2281–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, A.; Sultan, M.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Save, H. Assessment of Extreme Precipitation Events over the Nile Basin and their Impact on Downstream Countries. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstract, Chicago, IL, USA, 12–16 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, A.I.R. Impact of Ethiopian Renaissance Dam and population on future Egypt water needs. Am. J. Eng. Res. 2017, 6, 160–171. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelhafez, A.A.; Metwalley, S.M.; Abbas, H.H. Irrigation: Water resources, types and common problems in Egypt. Technol. Mod. Irrig. Environ. Egypt 2020, 15–34. [Google Scholar]
- Abdalla, F.; Shamrukh, M. Riverbank filtration as an alternative treatment technology: Abu Tieg Case Study, Egypt. In Riverbank Filtration for Water Security in Desert Countries; NATO Science for Peace and Security Series C: Environmental Security; Ray, C., Shamrukh, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 255–268. [Google Scholar]
- El-Rawy, M.; Abdalla, F.; El Alfy, M. Water resources in Egypt. In The Geology of Egypt; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 687–711. [Google Scholar]
- Goel, P.K. Water Pollution: Causes, Effects and Control; New Age International: New Delhi, India, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cairncross, S. Water supply and sanitation: An agenda for research. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1989, 92, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El Gamal, F.; Mostafa, H.; Shalby, A. Reuse of low quality water in Egypt. In Non-Conventional Water Use: WASAMED Project; Hamdy, A., El Gamal, F., Lamaddalena, N., Bogliotti, C., Guelloubi, R., Eds.; CIHEAM/EU DG Research: Bari, Italy, 2005; pp. 93–103. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Rahman, W.H. Discharge of Domestic Wastewater into Rivers. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Engineering, Helwan University, Cairo, Egypt, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Tchobanoglous, G.; Burton, F.L. Wastewater Engineering: Treatment, Disposal and Reuse, 4th ed.; Mcgraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez-Baca, N.; Saucedo-Terán, R.; Manzanares-Papayanopoulos, L.I.; Carrazco-Palafox, J.; Nevárez-Moorillón, G.V. Treatment for small, polluted rivers: Design and performance of an experimental structure. Water 2005, 31, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Monayeri, D.S.; Atta, N.N.; El Mokadem, S.; Abou El-fotoh, A.M. Biological Treatment of Drain’s Water Using Submerged Bioreactors. In Proceedings of the Second Ain Shams University International Conference on Environmental Engineering, Cairo, Egypt, 10–12 April 2007. [Google Scholar]
- ElMonayeri, D.S.; El-Karamany, H.; El-Gohary, E.H. Case study for Bilbeas and El-Qalyoubia Drains; Technical Report; March 2003. [Google Scholar]
- El Monayeri, D.S.; Atta, N.N.; El Mokadem, S.; EL-Gohary, E.H. Enhancement of Bilbeas Drain Water Quailty Using Submerged Biofilters (SBs). In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Water Technology Conference (IWTC11), Sharm El-Sheikh, Egypt, 3–7 June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- El-Gohary, E.H. Enhancement of Streams Water Quality Using In-Situ Filters. Master’s Thesis, Zagazig University, Ash Sharqiyah, Egypt, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; Li, J.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Yang, H. Nitrobacteria community structure during the startup in a submerged biofilters for in-situ remediation of contaminated stream. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2011, 20, 2111–2118. [Google Scholar]
- Salem, R. Monitoring of Pollutants in Waste Water in Some Egypt Drains. J. Plant Prot. Path. Mansoura Univ. 2016, 7, 851–854. [Google Scholar]
- Pachaiappan, R.; Cornejo-Ponce, L.; Rajendran, R.; Manavalan, K.; Femilaa Rajan, V.; Awad, F. A review on biofiltration techniques: Recent advancements in the removal of volatile organic compounds and heavy metals in the treatment of polluted water. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 8432–8477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darcy, H. Les Fontaines Publiques de la Ville de Dijon; Victor Dalmont: Paris, France, 1856. [Google Scholar]
- Bowles, J.E. Physical and Geotechnical Prosperities of Soils; Mcgraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Holtz, R.D.; Kovacs, W.D. AnIintroduction to Geotechnical Engineering; Prentice-Hall: Enlewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Fadhil, M.; Al-Mohammed, M.; Mohammed, S.H. Flow through and over gravel gabion weirs. J. Kerbala Univ. 2015, 11, 193–205. [Google Scholar]
- El-Saiad, A.A.; Abd-Elhamid, H.F.; Salama, Z.I.; Zeleňáková, M.; Weiss, E.; El-Gohary, E.H. Improving the Hydraulic Effects Resulting from the Use of a Submerged Biofiter to Enhance Water Quality in Polluted Streams. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



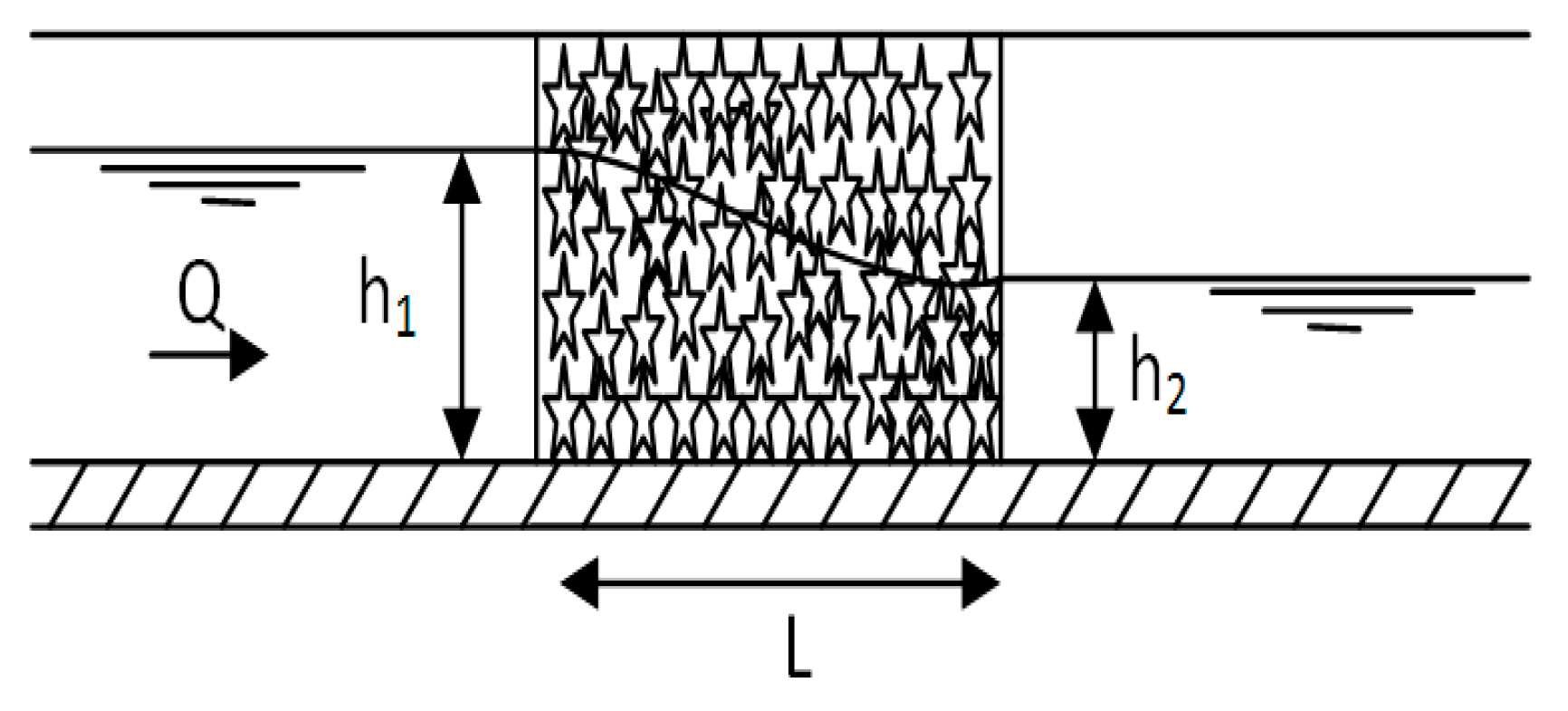


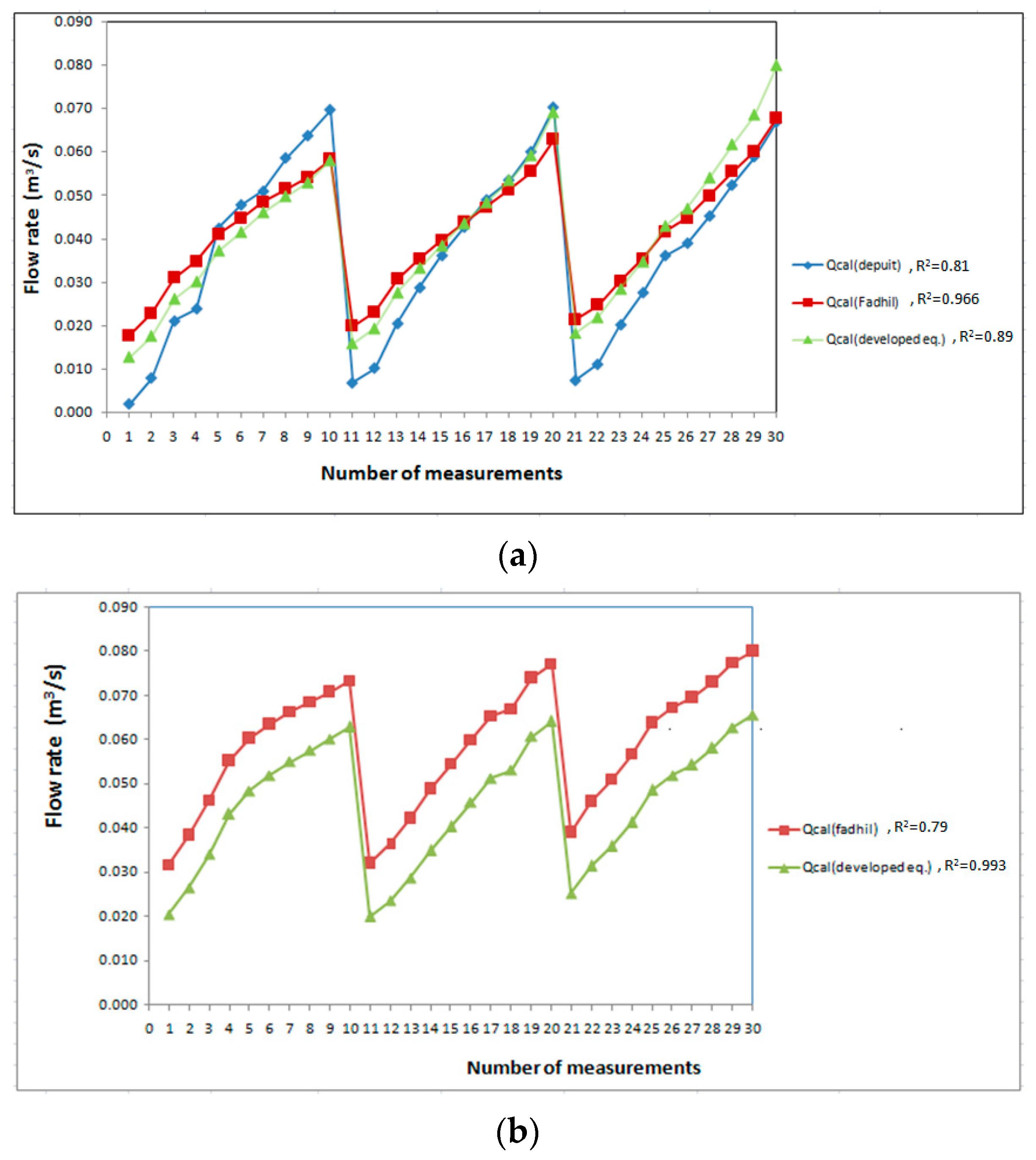


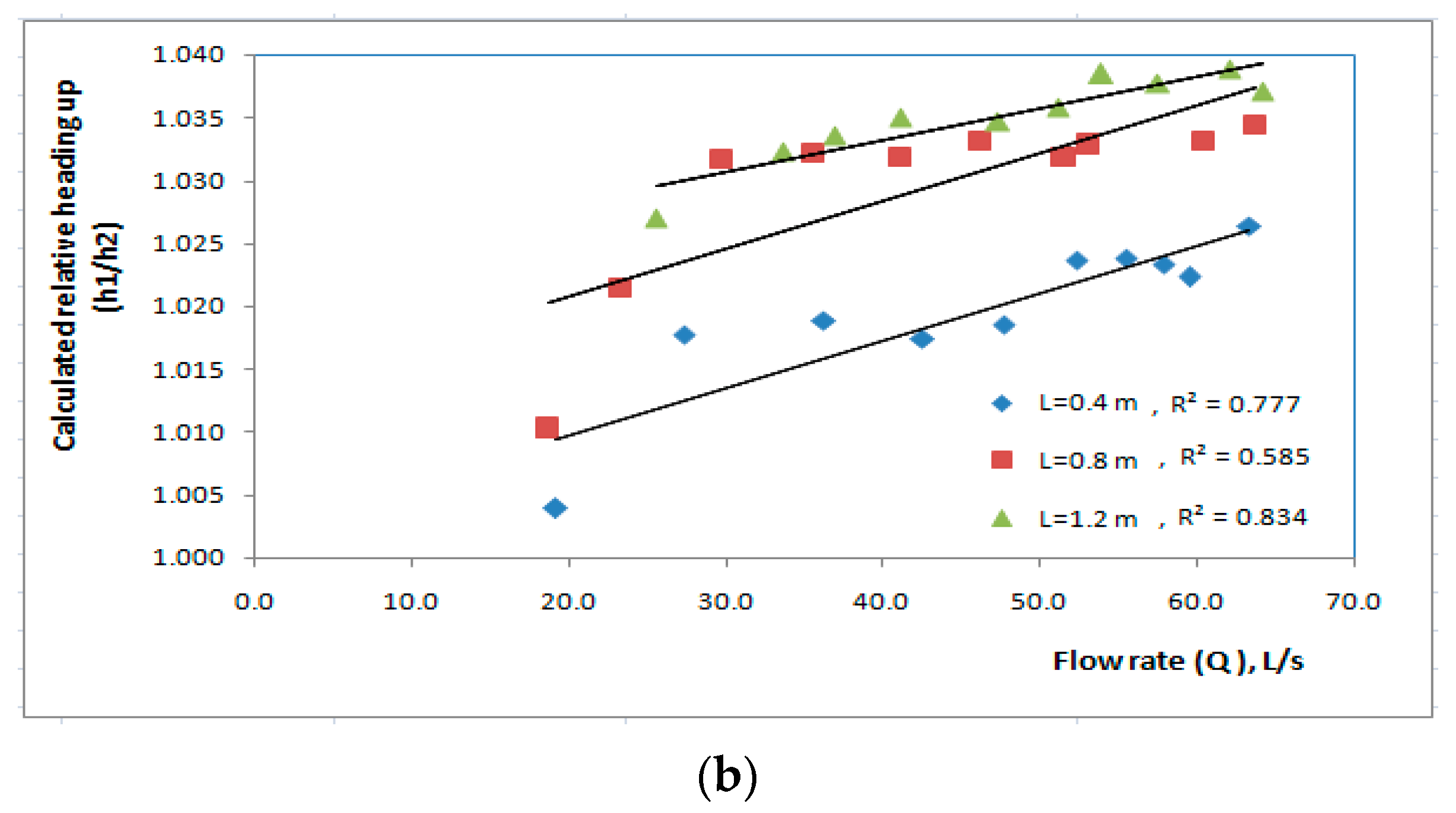

| Runs | Case of Flow | Length (m) | Flow Rate (L/S) | Measured Parameters | Calculated Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Flow through the biofilter | 0.4 | 7.2 to 60.4 | h1, h2 | Relative heading-up (h1/h2) |
| 2 | 0.8 | 14.1 to 62.1 | |||
| 3 | 1.2 | 20.6 to 64.6 | |||
| 1 | Flow over the biofilter | 0.4 | 19.2 to 63.3 | ||
| 2 | 0.8 | 18.7 to 63.7 | |||
| 3 | 1.2 | 18.5 to 64.2 |
| No | L (m) | Measured Flow Rate (m3/s) | Upstream Water Depth (h1) m | Downstream Water Depth (h2) m | Relative Heading-Up (h1/h2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.4 | 0.007 | 0.481 | 0.480 | 1.002 |
| 2 | 0.016 | 0.509 | 0.505 | 1.008 | |
| 3 | 0.029 | 0.545 | 0.535 | 1.019 | |
| 4 | 0.035 | 0.559 | 0.548 | 1.020 | |
| 5 | 0.041 | 0.580 | 0.561 | 1.034 | |
| 6 | 0.045 | 0.591 | 0.570 | 1.037 | |
| 7 | 0.048 | 0.602 | 0.580 | 1.038 | |
| 8 | 0.052 | 0.610 | 0.585 | 1.043 | |
| 9 | 0.056 | 0.617 | 0.590 | 1.046 | |
| 10 | 0.060 | 0.627 | 0.598 | 1.048 | |
| 11 | 0.8 | 0.014 | 0.508 | 0.501 | 1.014 |
| 12 | 0.020 | 0.526 | 0.516 | 1.019 | |
| 13 | 0.032 | 0.560 | 0.541 | 1.035 | |
| 14 | 0.038 | 0.578 | 0.552 | 1.047 | |
| 15 | 0.041 | 0.593 | 0.561 | 1.057 | |
| 16 | 0.046 | 0.606 | 0.569 | 1.065 | |
| 17 | 0.047 | 0.617 | 0.575 | 1.073 | |
| 18 | 0.052 | 0.628 | 0.583 | 1.077 | |
| 19 | 0.055 | 0.639 | 0.589 | 1.085 | |
| 20 | 0.062 | 0.657 | 0.600 | 1.095 | |
| 21 | 1.2 | 0.021 | 0.526 | 0.515 | 1.021 |
| 22 | 0.027 | 0.543 | 0.527 | 1.030 | |
| 23 | 0.032 | 0.568 | 0.540 | 1.052 | |
| 24 | 0.040 | 0.588 | 0.551 | 1.067 | |
| 25 | 0.045 | 0.610 | 0.563 | 1.083 | |
| 26 | 0.047 | 0.620 | 0.570 | 1.088 | |
| 27 | 0.048 | 0.635 | 0.578 | 1.099 | |
| 28 | 0.054 | 0.650 | 0.585 | 1.111 | |
| 29 | 0.058 | 0.662 | 0.590 | 1.122 | |
| 30 | 0.065 | 0.680 | 0.600 | 1.133 |
| No | L (m) | Measured Flow Rate (m3/s) | Upstream Water Depth (h1) m | Downstream Water Depth (h2) m | Relative Heading Up (h1/h2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.4 | 0.019 | 0.52 | 0.513 | 1.014 |
| 2 | 0.027 | 0.54 | 0.533 | 1.013 | |
| 3 | 0.036 | 0.56 | 0.555 | 1.009 | |
| 4 | 0.043 | 0.58 | 0.569 | 1.019 | |
| 5 | 0.048 | 0.59 | 0.578 | 1.021 | |
| 6 | 0.052 | 0.596 | 0.583 | 1.022 | |
| 7 | 0.055 | 0.601 | 0.588 | 1.022 | |
| 8 | 0.058 | 0.605 | 0.592 | 1.022 | |
| 9 | 0.060 | 0.609 | 0.595 | 1.024 | |
| 10 | 0.063 | 0.613 | 0.598 | 1.025 | |
| 11 | 0.8 | 0.019 | 0.522 | 0.512 | 1.020 |
| 12 | 0.023 | 0.535 | 0.523 | 1.023 | |
| 13 | 0.030 | 0.551 | 0.537 | 1.026 | |
| 14 | 0.036 | 0.567 | 0.551 | 1.029 | |
| 15 | 0.041 | 0.579 | 0.563 | 1.028 | |
| 16 | 0.046 | 0.59 | 0.572 | 1.031 | |
| 17 | 0.052 | 0.60 | 0.582 | 1.031 | |
| 18 | 0.053 | 0.603 | 0.584 | 1.033 | |
| 19 | 0.060 | 0.615 | 0.595 | 1.034 | |
| 20 | 0.064 | 0.62 | 0.599 | 1.035 | |
| 21 | 1.2 | 0.026 | 0.543 | 0.530 | 1.025 |
| 22 | 0.034 | 0.561 | 0.549 | 1.022 | |
| 23 | 0.037 | 0.572 | 0.556 | 1.029 | |
| 24 | 0.041 | 0.584 | 0.564 | 1.035 | |
| 25 | 0.047 | 0.598 | 0.576 | 1.038 | |
| 26 | 0.051 | 0.604 | 0.582 | 1.038 | |
| 27 | 0.054 | 0.608 | 0.585 | 1.039 | |
| 28 | 0.058 | 0.614 | 0.591 | 1.039 | |
| 29 | 0.062 | 0.621 | 0.597 | 1.040 | |
| 30 | 0.064 | 0.625 | 0.601 | 1.040 |
| No. | L (m) | Measured Flow Rate (m3/s) | Calculated Flow Rate Q(m3/s) | Calculated Upstream Water Level (h1) m (Developed eq.) | Calculated Relative Heading-Up (h1/h2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dupuit | Fadhil | Developed Equation | |||||
| 1 | 0.4 | 0.007 | 0.002 | 0.018 | 0.013 | 0.436 | 0.908 |
| 2 | 0.016 | 0.008 | 0.023 | 0.018 | 0.503 | 0.996 | |
| 3 | 0.029 | 0.021 | 0.031 | 0.026 | 0.554 | 1.035 | |
| 4 | 0.035 | 0.024 | 0.035 | 0.030 | 0.573 | 1.045 | |
| 5 | 0.041 | 0.043 | 0.041 | 0.037 | 0.590 | 1.052 | |
| 6 | 0.045 | 0.048 | 0.045 | 0.041 | 0.601 | 1.054 | |
| 7 | 0.048 | 0.051 | 0.049 | 0.046 | 0.607 | 1.047 | |
| 8 | 0.052 | 0.059 | 0.052 | 0.050 | 0.616 | 1.052 | |
| 9 | 0.056 | 0.064 | 0.054 | 0.053 | 0.623 | 1.057 | |
| 10 | 0.060 | 0.070 | 0.058 | 0.058 | 0.631 | 1.055 | |
| 11 | 0.8 | 0.014 | 0.007 | 0.020 | 0.016 | 0.498 | 0.993 |
| 12 | 0.020 | 0.010 | 0.023 | 0.019 | 0.529 | 1.025 | |
| 13 | 0.032 | 0.021 | 0.031 | 0.028 | 0.573 | 1.060 | |
| 14 | 0.038 | 0.029 | 0.035 | 0.033 | 0.591 | 1.070 | |
| 15 | 0.041 | 0.036 | 0.040 | 0.039 | 0.601 | 1.071 | |
| 16 | 0.046 | 0.043 | 0.044 | 0.044 | 0.612 | 1.076 | |
| 17 | 0.047 | 0.049 | 0.047 | 0.048 | 0.614 | 1.068 | |
| 18 | 0.052 | 0.053 | 0.051 | 0.054 | 0.624 | 1.070 | |
| 19 | 0.055 | 0.060 | 0.056 | 0.059 | 0.632 | 1.073 | |
| 20 | 0.062 | 0.070 | 0.063 | 0.069 | 0.644 | 1.074 | |
| 21 | 1.2 | 0.021 | 0.007 | 0.021 | 0.018 | 0.537 | 1.042 |
| 22 | 0.027 | 0.011 | 0.025 | 0.022 | 0.562 | 1.066 | |
| 23 | 0.032 | 0.020 | 0.030 | 0.029 | 0.579 | 1.072 | |
| 24 | 0.040 | 0.028 | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.602 | 1.092 | |
| 25 | 0.045 | 0.036 | 0.042 | 0.043 | 0.615 | 1.093 | |
| 26 | 0.047 | 0.039 | 0.045 | 0.047 | 0.619 | 1.086 | |
| 27 | 0.048 | 0.045 | 0.050 | 0.054 | 0.623 | 1.078 | |
| 28 | 0.054 | 0.053 | 0.055 | 0.062 | 0.636 | 1.087 | |
| 29 | 0.058 | 0.059 | 0.060 | 0.069 | 0.643 | 1.090 | |
| 30 | 0.065 | 0.067 | 0.068 | 0.080 | 0.655 | 1.092 | |
| No. | L (m) | Measured Flow Rate (m3/s) | Calculated Flow Rate Q(m3/s) | Calculated Upstream Water Level (h1) m | Calculated Relative Heading-Up (h1/h2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fadhil | Developed Equation | |||||
| 1 | 0.4 | 0.019 | 0.032 | 0.021 | 0.515 | 1.004 |
| 2 | 0.027 | 0.038 | 0.027 | 0.542 | 1.018 | |
| 3 | 0.036 | 0.046 | 0.034 | 0.565 | 1.019 | |
| 4 | 0.043 | 0.055 | 0.043 | 0.579 | 1.017 | |
| 5 | 0.048 | 0.060 | 0.049 | 0.589 | 1.019 | |
| 6 | 0.052 | 0.064 | 0.052 | 0.597 | 1.024 | |
| 7 | 0.055 | 0.066 | 0.055 | 0.602 | 1.024 | |
| 8 | 0.058 | 0.069 | 0.058 | 0.606 | 1.023 | |
| 9 | 0.060 | 0.071 | 0.060 | 0.608 | 1.022 | |
| 10 | 0.063 | 0.073 | 0.063 | 0.614 | 1.026 | |
| 11 | 0.8 | 0.019 | 0.032 | 0.020 | 0.517 | 1.010 |
| 12 | 0.023 | 0.036 | 0.024 | 0.534 | 1.021 | |
| 13 | 0.030 | 0.042 | 0.029 | 0.554 | 1.032 | |
| 14 | 0.036 | 0.049 | 0.035 | 0.569 | 1.032 | |
| 15 | 0.041 | 0.054 | 0.040 | 0.581 | 1.032 | |
| 16 | 0.046 | 0.060 | 0.046 | 0.591 | 1.033 | |
| 17 | 0.052 | 0.065 | 0.051 | 0.601 | 1.032 | |
| 18 | 0.053 | 0.067 | 0.053 | 0.603 | 1.033 | |
| 19 | 0.060 | 0.074 | 0.061 | 0.615 | 1.033 | |
| 20 | 0.064 | 0.077 | 0.064 | 0.620 | 1.034 | |
| 21 | 1.2 | 0.026 | 0.039 | 0.025 | 0.544 | 1.027 |
| 22 | 0.034 | 0.046 | 0.031 | 0.567 | 1.032 | |
| 23 | 0.037 | 0.051 | 0.036 | 0.575 | 1.034 | |
| 24 | 0.041 | 0.057 | 0.041 | 0.584 | 1.035 | |
| 25 | 0.047 | 0.064 | 0.049 | 0.596 | 1.035 | |
| 26 | 0.051 | 0.067 | 0.052 | 0.603 | 1.036 | |
| 27 | 0.054 | 0.070 | 0.054 | 0.608 | 1.038 | |
| 28 | 0.058 | 0.073 | 0.058 | 0.613 | 1.038 | |
| 29 | 0.062 | 0.077 | 0.063 | 0.620 | 1.039 | |
| 30 | 0.064 | 0.080 | 0.066 | 0.623 | 1.037 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abd-Elhamid, H.F.; El-Saiad, A.A.; Salama, Z.I.; Zeleňáková, M.; El-Gohary, E.H. Evaluating the Hydraulic Effects of the Flow through and over the Submerged Biofilter Installed in Polluted Streams. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10324. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191610324
Abd-Elhamid HF, El-Saiad AA, Salama ZI, Zeleňáková M, El-Gohary EH. Evaluating the Hydraulic Effects of the Flow through and over the Submerged Biofilter Installed in Polluted Streams. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(16):10324. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191610324
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbd-Elhamid, Hany F., Atef A. El-Saiad, Zeinab I. Salama, Martina Zeleňáková, and Emad H. El-Gohary. 2022. "Evaluating the Hydraulic Effects of the Flow through and over the Submerged Biofilter Installed in Polluted Streams" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 16: 10324. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191610324
APA StyleAbd-Elhamid, H. F., El-Saiad, A. A., Salama, Z. I., Zeleňáková, M., & El-Gohary, E. H. (2022). Evaluating the Hydraulic Effects of the Flow through and over the Submerged Biofilter Installed in Polluted Streams. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(16), 10324. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191610324








