Pathogen Profile of Children Hospitalised with Severe Acute Respiratory Infections during COVID-19 Pandemic in the Free State Province, South Africa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Definition of the COVID-19 Waves
2.3. Patient Enrolment
2.4. Specimen Collection
2.5. Pathogen Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. General Information, Demographics, and Clinical Presentations
3.2. Detected Pathogens and Co-Infections
3.3. Evaluation of Clinical Symptoms with Viral Co-Infection
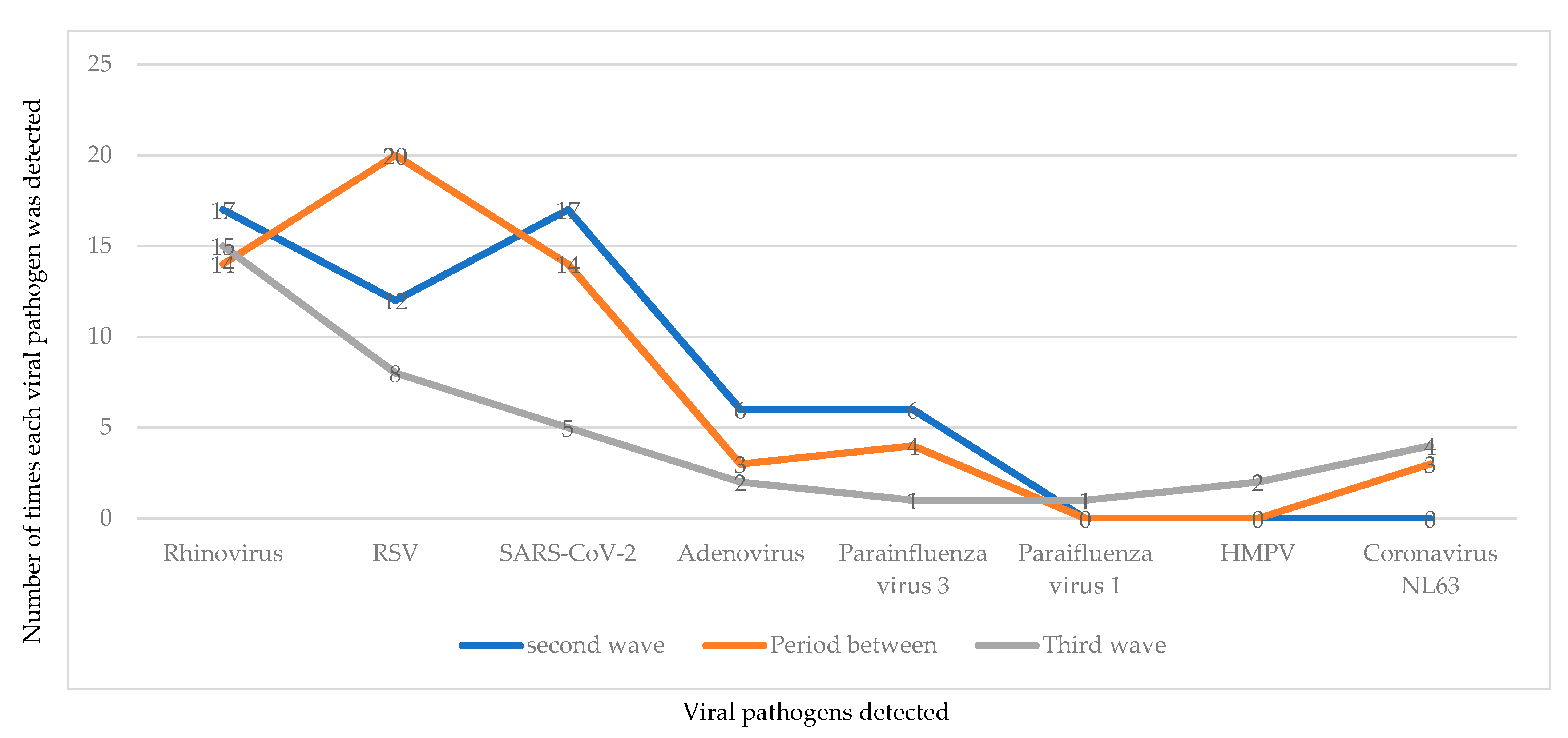
3.4. Profile of Pathogens Detected during Each Wave of the COVID-19 Infection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fitzner, J.; Qasmieh, S.; Mounts, A.W.; Alexander, B.; Besselaar, T.; Briand, S.; Brown, C.; Clark, S.; Dueger, E.; Gross, D.; et al. Revision of clinical case definitions: Influenza-like illness and severe acute respiratory infection. Bull. World Health Organ. 2018, 96, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, S.; McCracken, J.P.; Contreras, C.L.; Lopez, M.R.; Bernart, C.; Moir, J.C.; Escobar, K.; Reyes, L.; Arvelo, W.; Lindblade, K.; et al. Factors associated with fatal cases of acute respiratory infection (ARI) among hospitalized patients in Guatemala. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.-J.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Ren, L.-L.; Lu, Q.-B.; Ren, X.; Zhang, C.-H.; Wang, Y.-F.; Lin, S.-H.; Zhang, X.-A.; Li, J.; et al. Etiological and epidemiological features of acute respiratory infections in China. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathmawati, F.; Rauf, S.; Indraswari, B.W. Factors related with the incidence of acute respiratory infections in toddlers in Sleman, Yogyakarta, Indonesia: Evidence from the Sleman Health and Demographic Surveillance System. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perin, J.; Mulick, A.; Yeung, D.; Villavicencio, F.; Lopez, G.; Strong, K.L.; Prieto-Merino, D.; Cousens, S.; E Black, R.; Liu, L. Global, regional, and national causes of under-5 mortality in 2000–19: An updated systematic analysis with implications for the Sustainable Development Goals. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2022, 6, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, Q.; Enarson, P.; Kissoon, N.; Klassen, T.P.; Johnson, D.W. Rapid viral diagnosis for acute febrile respiratory illness in children in the Emergency Department. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 9, CD006452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebey-López, M.; Herberg, J.; Pardo-Seco, J.; Gómez-Carballa, A.; Martinón-Torres, N.; Salas, A.; Martinón-Sánchez, J.M.; Gormley, S.; Sumner, E.; Fink, C.; et al. Viral Co-Infections in Pediatric Patients Hospitalized with Lower Tract Acute Respiratory Infections. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Hu, P.; Zhou, T.; Zheng, T.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, C.; Pei, X. Epidemiology and clinical characteristics of acute respiratory tract infections among hospitalized infants and young children in Chengdu, West China, 2009–2014. BMC Pediatr. 2018, 18, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Samudio, V.; Landires, I. Epidemiology of viral respiratory infections in a pediatric reference hospital in Central Panama. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurskaya, O.; Ryabichenko, T.; Leonova, N.; Shi, W.; Bi, H.; Sharshov, K.; Kazachkova, E.; Sobolev, I.; Prokopyeva, E.; Kartseva, T.; et al. Viral etiology of acute respiratory infections in hospitalized children in Novosibirsk City, Russia (2013–2017). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirley, M. FebriDx®: A Rapid Diagnostic Test for Differentiating Bacterial and Viral Aetiologies in Acute Respiratory Infections. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2019, 23, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, L.; Liu, W.; Zhang, X.-A.; Liu, E.-M.; Wo, Y.; Cowling, B.J.; Cao, W.-C. Detection of Viral and Bacterial Pathogens in Hospitalized Children With Acute Respiratory Illnesses, Chongqing, 2009–2013. Medicine 2015, 94, e742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juliana, A.E.; Tang, M.-J.; Kemps, L.; Noort, A.C.; Hermelijn, S.; Plötz, F.B.; Zonneveld, R.; Wilschut, J.C. Viral causes of severe acute respiratory infection in hospitalized children and association with outcomes: A two-year prospective surveillance study in Suriname. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, K.C.; Dueger, E.L.; Kandeel, A.; Abdallat, M.; El Kholy, A.; Al-Awaidy, S.; Kohlani, A.H.; Amer, H.; El-Khal, A.L.; Said, M.; et al. Viral etiology, seasonality and severity of hospitalized patients with severe acute respiratory infections in the Eastern Mediterranean Region, 2007–2014. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swamy, M.A.; Malhotra, B.; Reddy, P.J.; Tiwari, J. Profile of Respiratory Pathogens Causing Acute Respiratory Infections in Hospitalised Children at Rajasthan a 4 Year’s Study. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 36, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, B.; Swamy, M.A.; Reddy, P.V.J.; Gupta, M.L. Viruses causing severe acute respiratory infections (SARI) in children ≤5 years of age at a tertiary care hospital in Rajasthan, India. Indian J. Med. Res. 2016, 144, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, S. Pathogenic viruses of the respiratory tract—A review. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2017, 7, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, E.H.; Simmon, K.E.; Tardif, K.D.; Hymas, W.; Flygare, S.; Eilbeck, K.; Yandell, M.; Schlaberg, R. Unbiased Detection of Respiratory Viruses by Use of RNA Sequencing-Based Metagenomics: A Systematic Comparison to a Commercial PCR Panel. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, M.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J. Metagenomic next-generation sequencing for accurate diagnosis and management of lower respiratory tract infections. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 122, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, X.; Orrico, M.; Morillo, T.; Manzano, A.; Jimbo, R.; Armijos, L. Reducing unnecessary antibiotic prescription through implementation of a clinical guideline on self-limiting respiratory tract infections. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Houten, C.B.; Cohen, A.; Engelhard, D.; Hays, J.P.; Karlsson, R.; Moore, E.; Fernández, D.; Kreisberg, R.; Collins, L.V.; de Waal, W.; et al. Antibiotic misuse in respiratory tract infections in children and adults—A prospective, multicentre study (TAILORED Treatment). Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 38, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bruning, A.H.L.; Leeflang, M.M.G.; Vos, J.M.B.W.; Spijker, R.; De Jong, M.D.; Wolthers, K.C.; Pajkrt, D. Rapid Tests for Influenza, Respiratory Syncytial Virus, and Other Respiratory Viruses: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, M.S.; Choi, E.H.; Chang, S.H.; Jin, B.-L.; Lee, E.J.; Kim, B.N.; Kim, M.K.; Doo, K.; Seo, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-J.; et al. Clinical Characteristics and Viral RNA Detection in Children With Coronavirus Disease 2019 in the Republic of Korea. JAMA Pediatr. 2021, 175, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tönshoff, B.; Müller, B.; Elling, R.; Renk, H.; Meissner, P.; Hengel, H.; Garbade, S.F.; Kieser, M.; Jeltsch, K.; Grulich-Henn, J.; et al. Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Children and Their Parents in Southwest Germany. JAMA Pediatr. 2021, 175, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.J.; Snelling, T.; Moore, H.; Blyth, C.C. Advances in Vaccines to Prevent Viral Respiratory Illnesses in Children. Pediatr. Drugs 2017, 19, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, S.; Argentiero, A.; Camilloni, B.; Silvestri, E.; Alunno, A.; Esposito, S. Vaccination against Paediatric Respiratory Pathogens. Vaccines 2019, 7, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, B.; Qian, R.; Wu, F.; He, X.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, J.; Ni, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Epidemiological and virological characteristics of respiratory tract infections in children during COVID-19 outbreak. BMC Pediatr. 2021, 21, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Xu, M.; Cao, L.; Su, L.; Lu, L.; Dong, N.; Jia, R.; Zhu, X.; Xu, J. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on the prevalence of respiratory viruses in children with lower respiratory tract infections in China. Virol. J. 2021, 18, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-X.; Lian, H.-B.; Lin, G.-Y.; Zhang, D.-G.; Cai, X.-Y.; Cai, Z.-W.; Wen, F.-Q. Pathogen spectrum changes of respiratory tract infections in children in Chaoshan area under the influence of COVID-19. Epidemiol. Infect. 2021, 149, E170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.S.; Wood, T.; Jelley, L.; Jennings, T.; Jefferies, S.; Daniells, K.; Nesdale, A.; Dowell, T.; Turner, N.; Campbell-Stokes, P.; et al. Impact of the COVID-19 nonpharmaceutical interventions on influenza and other respiratory viral infections in New Zealand. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittucci, A.C.; Piccioni, L.; Coltella, L.; Ciarlitto, C.; Antilici, L.; Bozzola, E.; Midulla, F.; Palma, P.; Perno, C.F.; Villani, A. The Disappearance of Respiratory Viruses in Children during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leber, A.L.; Lisby, J.G.; Hansen, G.; Relich, R.F.; Vest Schneider, U.; Granato, P.; Young, S.; Pareja, J.; Hannet, I. Multicenter Evaluation of the QIAstat-Dx Respiratory Panel for Detection of Viruses and Bacteria in Nasopharyngeal Swab Specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e00155-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parčina, M.; Vest Schneider, U.; Visseaux, B.; Jozić, R.; Hannet, I.; Lisby, J.G. Multicenter evaluation of the QIAstat Respiratory Panel—A new rapid highly multiplexed PCR based assay for diagnosis of acute respiratory tract infections. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visseaux, B.; Le Hingrat, Q.; Collin, G.; Bouzid, D.; Lebourgeois, S.; Le Pluart, D.; Deconinck, L.; Lescure, F.-X.; Lucet, J.-C.; Bouadma, L.; et al. Evaluation of the QIAstat-Dx Respiratory SARS-CoV-2 Panel, the First Rapid Multiplex PCR Commercial Assay for SARS-CoV-2 Detection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e00630-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute for Communicable Diseases. Proposed definition of COVID-19 wave in South Africa. Commun. Dis. Commun. 2021, 20, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Boers, S.A.; Melchers, W.J.G.; Peters, C.J.A.; Toonen, M.; McHugh, M.P.; Templeton, K.E.; Claas, E.C.J. Multicenter Evaluation of QIAstat-Dx Respiratory Panel V2 for Detection of Viral and Bacterial Respiratory Pathogens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e01793-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breiman, R.F.; Cosmas, L.; Njenga, M.K.; Williamson, J.; A Mott, J.; A Katz, M.; Erdman, D.D.; Schneider, E.; Oberste, M.S.; Neatherlin, J.C.; et al. Severe acute respiratory infection in children in a densely populated urban slum in Kenya, 2007–2011. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wansaula, Z.; Olsen, S.J.; Casal, M.G.; Golenko, C.; Erhart, L.M.; E Kammerer, P.; Whitfield, N.; McCotter, O.Z. Surveillance for severe acute respiratory infections in S outhern A rizona, 2010–2014. Influ. Other Respir. Viruses 2016, 10, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatem, A.; Mohamed, S.; Abu Elhassan, U.E.; Ismael, E.A.M.; Rizk, M.S.; El-Kholy, A.; El-Harras, M. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with severe acute respiratory infections (SARI): Results from the Egyptian surveillance study 2010–2014. Multidiscip. Respir. Med. 2019, 14, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wishaupt, J.O.; Van Der Ploeg, T.; De Groot, R.; Versteegh, F.G.A.; Hartwig, N.G. Single- and multiple viral respiratory infections in children: Disease and management cannot be related to a specific pathogen. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, C.; Yang, L.; Lou, C.T.; Yang, F.; SiTou, K.I.; Hu, H.; Io, K.; Cheok, K.T.; Pan, B.; Ung, C.O.L. Viral etiology and epidemiology of pediatric patients hospitalized for acute respiratory tract infections in Macao: A retrospective study from 2014 to 2017. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, M.K.; Loens, K.; Sigfrid, L.; Iosifidis, E.; Epalza, C.; Donà, D.; Matheeussen, V.; Papachristou, S.; Roilides, E.; Gijon, M.; et al. Aetiology of acute respiratory infection in preschool children requiring hospitalisation in Europe—results from the PED-MERMAIDS multicentre case–control study. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2021, 8, e000887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebourgeois, S.; Storto, A.; Gout, B.; Le Hingrat, Q.; Tjader, G.A.; Cerdan, M.D.C.; English, A.; Pareja, J.; Love, J.; Houhou-Fidouh, N.; et al. Performance evaluation of the QIAstat-Dx® Respiratory SARS-CoV-2 Panel. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 107, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.-Y.; Wu, W.-T.; Chang, C.-Y.; Wong, Y.-C.; Lai, C.-C.; Chan, Y.-J.; Wu, K.-G.; Hung, M.-C. Viral etiologies of acute respiratory tract infections among hospitalized children–A comparison between single and multiple viral infections. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2019, 52, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Tiwari, S.; Deb, M.K.; Marty, J.L. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2): A global pandemic and treatment strategies. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 56, 106054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunno, J.; Supawattanabodee, B.; Sumanasrethakul, C.; Wiriyasivaj, B.; Kuratong, S.; Kaewchandee, C. Comparison of Different Waves during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Retrospective Descriptive Study in Thailand. Adv. Prev. Med. 2021, 8, 5807056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhibber-Goel, J.; Malhotra, S.; Krishnan, N.A.; Sharma, A. The profiles of first and second SARS-CoV-2 waves in the top ten COVID-19 affected countries. J. Glob. Health Rep. 2021, 5, e2021082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, H.; Jun, H.; Gu, J.; Yun, J.; Jin, H. Comparison of the second and third waves of the COVID-19 pandemic in South Korea: Importance of early public health intervention. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 104, 742–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahase, E. Omicron: South Africa says fourth wave peak has passed as it lifts curfew. BMJ 2022, 376, o7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turabian, J.L. Acute respiratory infections in children during Coronavirus Disease 2019: Without reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction test and with risk of over-prescription of antibiotics, the perfect storm. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. 2020, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempia, S.; Walaza, S.; Bhiman, J.N.; McMorrow, M.L.; Moyes, J.; Mkhencele, T.; Meiring, S.; Quan, V.; Bishop, K.; McAnerney, J.M.; et al. Decline of influenza and respiratory syncytial virus detection in facility-based surveillance during the COVID-19 pandemic, South Africa, January to October 2020. Eurosurveillance 2021, 26, 2001600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takashita, E.; Kawakami, C.; Momoki, T.; Saikusa, M.; Shimizu, K.; Ozawa, H.; Kumazaki, M.; Usuku, S.; Tanaka, N.; Okubo, I.; et al. Increased risk of rhinovirus infection in children during the coronavirus disease-19 pandemic. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2021, 15, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.M.; Lee, E.J.; Lee, N.; Woo, S.H.; Kim, J.; Rhee, J.E.; Kim, E. Impact of coronavirus disease 2019 on respiratory surveillance and explanation of high detection rate of human rhinovirus during the pandemic in the Republic of Korea. Influ. Other Respir. Viruses 2021, 15, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuitunen, I.; Artama, M.; Bm, M.H.; Renko, M. Rhinovirus spread in children during the COVID-19 pandemic despite social restrictions—A nationwide register study in Finland. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 6063–6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savolainen-Kopra, C.; Korpela, T.; Simonen-Tikka, M.-L.; Amiryousefi, A.; Ziegler, T.; Roivainen, M.; Hovi, T. Single treatment with ethanol hand rub is ineffective against human rhinovirus-hand washing with soap and water removes the virus efficiently. J. Med. Virol. 2012, 84, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winther, B.; McCue, K.; Ashe, K.; Rubino, J.R.; Hendley, J.O. Environmental contamination with rhinovirus and transfer to fingers of healthy individuals by daily life activity. J. Med. Virol. 2007, 79, 1606–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoh, D.K.; Foley, D.A.; Minney-Smith, C.A.; Martin, A.C.; Mace, A.O.; Sikazwe, C.T.; Le, H.; Levy, A.; Blyth, C.C.; Moore, H.C. Impact of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Public Health Measures on Detections of Influenza and Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Children During the 2020 Australian Winter. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, 2199–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.J.; Azziz-Baumgartner, E.; Budd, A.P.; Brammer, L.; Sullivan, S.; Pineda, R.F.; Cohen, C.; Fry, A.M. Decreased Influenza Activity During the COVID-19 Pandemic–United States, Australia, Chile, and South Africa, 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 1305–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, H.; Ishikane, M.; Ueda, P. Seasonal Influenza Activity During the SARS-CoV-2 Outbreak in Japan. JAMA-J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020, 323, 1969–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ippolito, G.; La Vecchia, A.; Umbrello, G.; Di Pietro, G.; Bono, P.; Scalia, S.; Pinzani, R.; Tagliabue, C.; Bosis, S.; Agostoni, C.; et al. Disappearance of Seasonal Respiratory Viruses in Children Under Two Years Old During COVID-19 Pandemic: A Monocentric Retrospective Study in Milan, Italy. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggerstaff, M.; Cauchemez, S.; Reed, C.; Gambhir, M.; Finelli, L. Estimates of the reproduction number for seasonal, pandemic, and zoonotic influenza: A systematic review of the literature. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weber, A.; Weber, M.; Milligan, P. Modeling epidemics caused by respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Math. Biosci. 2001, 172, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickbakhsh, S.; Mair, C.; Matthews, L.; Reeve, R.; Johnson, P.C.D.; Thorburn, F.; von Wissmann, B.; Reynolds, A.; McMenamin, J.; Gunson, R.N.; et al. Virus–virus interactions impact the population dynamics of influenza and the common cold. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 27142–27150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, A.; Mihaylova, V.T.; Landry, M.L.; Foxman, E.F. Interference between rhinovirus and influenza A virus: A clinical data analysis and experimental infection study. Lancet Microbe 2020, 1, e254–e262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teherani, M.F.; Kao, C.; Camacho-Gonzalez, A.; Banskota, S.; Shane, A.L.; Linam, W.M.; Jaggi, P. Burden of illness in households with SARS-CoV-2 infected children. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2020, 9, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, W.; Dozier, M.; He, Y.; Kirolos, A.; Theodoratou, E. The role of children in transmission of SARS-CoV-2: A rapid review. J. Glob. Health 2020, 10, 011101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kholy, A.A.; Mostafa, N.A.; Ali, A.A.; Soliman, M.M.S.; El-Sherbini, S.A.; Ismail, R.I.; El Basha, N.; Magdy, R.I.; El Rifai, N.; Hamed, D.H. The use of multiplex PCR for the diagnosis of viral severe acute respiratory infection in children: A high rate of co-detection during the winter season. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 1607–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visseaux, B.; Collin, G.; Ichou, H.; Charpentier, C.; Bendhafer, S.; Dumitrescu, M.; Allal, L.; Cojocaru, B.; Desfrère, L.; Descamps, D.; et al. Usefulness of multiplex PCR methods and respiratory viruses’ distribution in children below 15 years old according to age, seasons and clinical units in France: A 3 years retrospective study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Roig, A.; Salvadó, M.; Caballero-Rabasco, M.; Sánchez-Buenavida, A.; López-Segura, N.; Bonet-Alcaina, M. Viral Coinfection in Childhood Respiratory Tract Infections. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2015, 51, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asner, S.A.; Science, M.E.; Tran, D.; Smieja, M.; Merglen, A.; Mertz, D. Clinical Disease Severity of Respiratory Viral Co-Infection versus Single Viral Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franz, A.; Adams, O.; Willems, R.; Bonzel, L.; Neuhausen, N.; Schweizer-Krantz, S.; Ruggeberg, J.U.; Willers, R.; Henrich, B.; Schroten, H.; et al. Correlation of viral load of respiratory pathogens and co-infections with disease severity in children hospitalized for lower respiratory tract infection. J. Clin. Virol. 2010, 48, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, E.T.; Kuypers, J.; Wald, A.; Englund, J.A. Multiple versus single virus respiratory infections: Viral load and clinical disease severity in hospitalized children. Influ. Other Respir. Viruses 2012, 6, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goka, E.A.; Vallely, P.J.; Mutton, K.J.; Klapper, P.E. Single, dual and multiple respiratory virus infections and risk of hospitalization and mortality. Epidemiol. Infect. 2015, 143, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goka, E.A.; Vallely, P.J.; Mutton, K.J.; Klapper, P.E. Single and multiple respiratory virus infections and severity of respiratory disease: A systematic review. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2014, 15, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scotta, M.C.; Chakr, V.C.B.G.; de Moura, A.; Becker, R.G.; de Souza, A.P.; Jones, M.H.; Pinto, L.A.; Sarria, E.E.; Pitrez, P.M.; Stein, R.T.; et al. Respiratory viral coinfection and disease severity in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Virol. 2016, 80, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, F.J.; De Klerk, N.; Blyth, C.C.; Fathima, P.; Moore, H.C. Systematic review and meta-analysis of respiratory viral coinfections in children. Respirology 2016, 21, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ayeni, O.A.; Walaza, S.; Tempia, S.; Groome, M.; Kahn, K.; Madhi, S.A.; Cohen, A.L.; Moyes, J.; Venter, M.; Pretorius, M.; et al. Mortality in children aged <5 years with severe acute respiratory illness in a high HIV-prevalence urban and rural areas of South Africa, 2009–2013. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhi, S.A.; Schoub, B.; Simmank, K.; Blackburn, N.; Klugman, K.P. Increased burden of respiratory viral associated severe lower respiratory tract infections in children infected with human immunodeficiency virus type-1. J. Pediatr. 2000, 137, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazinya, A.A.; Halle-Ekane, G.E.; Mbuagbaw, L.T.; Abanda, M.; Atashili, J.; Obama, M.T. Risk factors for acute respiratory infections in children under five years attending the Bamenda Regional Hospital in Cameroon. BMC Pulm. Med. 2018, 18, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rabie, H.; Goussard, P. Tuberculosis and pneumonia in HIV-infected children: An overview. Pneumonia 2016, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moyes, J.; Cohen, C.; Pretorius, M.; Groome, M.; von Gottberg, A.; Wolter, N.; Walaza, S.; Haffejee, S.; Chhagan, M.; Naby, F.; et al. Epidemiology of Respiratory Syncytial Virus-Associated Acute Lower Respiratory Tract Infection Hospitalizations Among HIV-Infected and HIV-Uninfected South African Children, 2010–2011. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 208, S217–S226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Famoroti, T.; Sibanda, W.; Ndung, T. Prevalence and seasonality of common viral respiratory pathogens, including Cytomegalovirus in children, between 0–5 years of age in KwaZulu-Natal, an HIV endemic province in South Africa. BMC Pediatr. 2018, 18, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, C.; Walaza, S.; Moyes, J.; Groome, M.; Tempia, S.; Pretorius, M.; Hellferscee, O.; Dawood, H.; Chhagan, M.; Naby, F.; et al. Epidemiology of Viral-associated Acute Lower Respiratory Tract Infection among Children <5 Years of Age in a High HIV Prevalence Setting, South Africa, 2009–2012. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2015, 34, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majozi, N.P.; Nkwanyana, N.; Thula, S.; Coutsoudis, A. Association between HIV and proven viral lower respiratory tract infection in paediatric intensive care unit patients at Inkosi Albert Luthuli Central Hospital, Durban, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Child Health 2017, 11, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, P.P.; Rath, B.A.; Fragkou, P.C.; Antalis, E.; Tsiodras, S.; Skevaki, C. Current and future point-of-care tests for emerging and new respiratory viruses and future perspectives. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenberg, O.; Martiny, D.; Rochas, O.; van Belkum, A.; Kozlakidis, Z. Considerations for diagnostic COVID-19 tests. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Waves | Second Wave | Period between | Third Wave |
|---|---|---|---|
| Timeline | December 2020–February 2021 | February–April 2021 | June 2021–August 2021 |
| Definition | Period with greater than 30 cases per 100,000 persons | Period between second and third waves with fewer than 30 cases per 100,000 persons | Period with greater than 30 cases per 100,000 persons |
| Viral Pathogens Detected | No. of Times Pathogens Was/Were Detected | Average Ct Values a | Standard Deviation b |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single viral infections RSV HRV HMPV SARS-CoV-2 Adv | 8 5 1 5 1 | 24.1 27.9 34.3 35.3 31.1 | 4.84 1.95 n/a 0.9 n/a |
| Double viral co-infections RSV + SARS-CoV-2 HRV/EVs + SARS-CoV-2 HRV/EVs + RSV RSV + Adv SARS-CoV-2 + Adv SARS-CoV-2 + PIV 3 PIV 3 + HRV/EVs RSV + Coronavirus NL63 Coronavirus NL63 + HRV/EVs HMPV + HRV/EVs HRV/EVs + Adv PIV 1 + RSV | 4 7 9 1 1 1 1 3 1 1 1 1 | 25.6 & 33.4 29.0 & 33.6 30.9 & 28.5 30.6 & 34.1 32.5 & 33.4 37.9 & 33.3 26.3 & 33.4 28.7 & 32.3 34.8 & 32.5 31.1 & 30.3 27.6 & 32.3 33.1 & 25.6 | 5.0 & 3.3 2.62 & 1.52 2.4 & 4.40 n/a n/a n/a n/a 1.67 & 1.37 n/a n/a n/a n/a |
| Triple viral co-infections SARS-CoV-2 + PIV 3 + RSV PIV 3 + HRV/EVs + SARS-CoV-2 HRV + Adv + SARS-CoV-2 PIV 3 + HRV/EVs + Adv SARS-CoV-2 + RSV + HRV/EVs RSV + HRV/EVs + PIV 3 SARS-CoV-2 + RSV + Adv Coronavirus NL63 + PIV 3 + HRV/EVs Coronavirus NL63 + RSV + HRV/EVs Coronavirus NL63 + HRV/EVs + Adv | 1 3 2 1 7 1 1 1 1 1 | 32.5 & 28.9 & 21.1 31.0 & 30.7 & 33.8 33.3 & 31 & 34.1 31.3 & 27.6 & 33.7 34.7 & 26.5 & 32 26.5 & 32.0 & 31.0 35.1 & 30.6 & 35.7 36.2 & 32.0 & 33.7 34.2 & 28.6 & 34.4 29.1 & 30.6 & 35.7 | n/a 1.38 & 1.8 & 0.75 1.9 & 4.7 & 1.1 n/a 0.9 & 3.1 & 1.76 n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a |
| Quadruple viral co-infections SARS-CoV-2 + RSV + HRV/EVs + PIV 3 SARS-CoV-2 + RSV + Adv + HRV/EVs SARS-CoV-2 + Adv + HRV/EVs + PIV3 | 2 1 1 | 34.9 & 30.3 & 30.4 & 29.3 35.3 & 26.5 & 35.1 & 31.4 34.5 & 35.7 & 32.2 & 27.8 | 1.3 & 3.45 & 1.1 & 3.2 n/a n/a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ogunbayo, A.E.; Mogotsi, M.T.; Sondlane, H.; Nkwadipo, K.R.; Sabiu, S.; Nyaga, M.M. Pathogen Profile of Children Hospitalised with Severe Acute Respiratory Infections during COVID-19 Pandemic in the Free State Province, South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10418. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191610418
Ogunbayo AE, Mogotsi MT, Sondlane H, Nkwadipo KR, Sabiu S, Nyaga MM. Pathogen Profile of Children Hospitalised with Severe Acute Respiratory Infections during COVID-19 Pandemic in the Free State Province, South Africa. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(16):10418. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191610418
Chicago/Turabian StyleOgunbayo, Ayodeji E., Milton T. Mogotsi, Hlengiwe Sondlane, Kelebogile R. Nkwadipo, Saheed Sabiu, and Martin M. Nyaga. 2022. "Pathogen Profile of Children Hospitalised with Severe Acute Respiratory Infections during COVID-19 Pandemic in the Free State Province, South Africa" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 16: 10418. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191610418
APA StyleOgunbayo, A. E., Mogotsi, M. T., Sondlane, H., Nkwadipo, K. R., Sabiu, S., & Nyaga, M. M. (2022). Pathogen Profile of Children Hospitalised with Severe Acute Respiratory Infections during COVID-19 Pandemic in the Free State Province, South Africa. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(16), 10418. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191610418








