Clinical Protocols and Treatment Guidelines for the Management of Maternal and Congenital Syphilis in Brazil and Portugal: Analysis and Comparisons: A Narrative Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
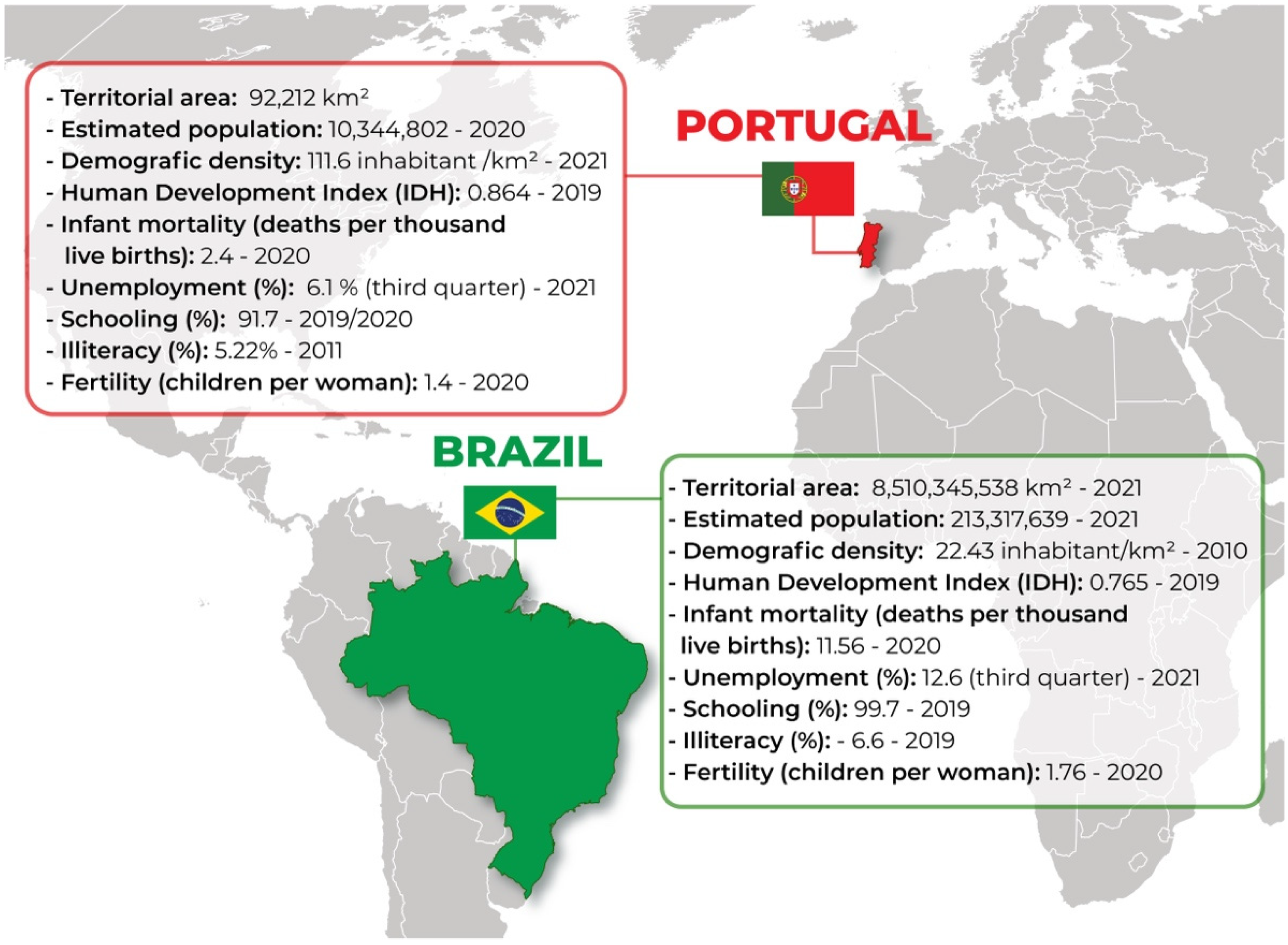
1.1. Sociodemographic Aspects of Brazil and Portugal
1.2. Clinical Protocols and Treatment Guidelines (CPTG)
2. Materials and Methods
Study Design and Search Strategy
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Current Epidemiology
3.2. “Syphilis No!” Project (SNP)
3.3. Guidelines
3.3.1. Portuguese Guidelines
3.3.2. Brazilian Guidelines
3.4. Protocol Gaps
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eickhoff, C.A.; Decker, C.F. Syphilis. Dis. Mon. 2016, 62, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Andrade, I.G.M.; de Medeiros Valentim, R.A.; de Oliveira, C.A.P. The influence of the No Syphilis Project on congenital syphilis admissions between 2018 and 2019. DST J. Bras. Doenças Sex. Transm. 2020, 32, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Tudor, M.E.; Al Aboud, A.M.; Gossman, W.G. Syphilis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534780/ (accessed on 3 August 2021).
- Da Rocha, M.A.; dos Santos, M.M.; Fontes, R.S.; de Melo, A.S.P.; Cunha-Oliveira, A.; Miranda, A.E.; de Oliveira, C.A.P.; Oliveira, H.G.; Gusmão, C.M.G.; Lima, T.G.F.M.S.; et al. The Text Mining Technique Applied to the Analysis of Health Interventions to Combat Congenital Syphilis in Brazil: The Case of the “Syphilis No!” Project. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 855680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentim, R.A.M.; Caldeira-Silva, G.J.P.; da Silva, R.D.; Albuquerque, G.A.; de Andrade, I.G.M.; Sales-Moioli, A.I.L.; Pinto, T.K.D.B.; Miranda, A.E.; Galvão-Lima, L.J.; Cruz, A.S.; et al. Stochastic Petri net model describing the relationship between reported maternal and congenital syphilis cases in Brazil. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2022, 22, 40. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Global Health Sector Strategy on Sexually Transmitted Infections, 2016–2021; The WHO’s Strategy for STI Treatment; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; Available online: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/246296/WHO-RHR-16.09-eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 3 August 2021).
- Kojima, N.; Klausner, J.D. An Update on the Global Epidemiology of Syphilis. Curr. Epidemiol. Rep. 2018, 5, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, I. Syphilis—An update. Med. Mon. Pharm. 2017, 40, 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Spiteri, G.; Unemo, M.; Mårdh, O.; Amato-Gauci, A.J. The resurgence of syphilis in high-income countries in the 2000s: A focus on Europe. Epidemiol. Infect. 2019, 147, e143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arando, M.; Fernandez-Naval, C.; Mota-Foix, M.; Martinez, D.; Armengol, P.; Barberá, M.J.; Esperalba, J.; Vall-Mayans, M. Early syphilis: Risk factors and clinical manifestations focusing on HIV-positive patients. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Syphilis and Congenital Syphilis in Europe—A Review of Epidemiological Trends (2007–2018) and Options for Response; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Grimpel, E.; Sanchez, P.J.; Wendel, G.D.; Burstain, J.M.; McCracken, G.H., Jr.; Radolf, J.D.; Norgard, M.V. Use of polymerase chain reaction and rabbit infectivity testing to detect Treponema pallidum in amniotic fluid, fetal and neonatal sera, and cerebrospinal fluid. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1991, 29, 1711–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nathan, L.; Twickler, D.M.; Peters, M.T.; Sánchez, P.J.; Wendel, G.D., Jr. Fetal syphilis: Correlation of sonographic findings and rabbit infectivity testing of amniotic fluid. J. Ultrasound Med. 1993, 12, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, F.; Jacques, S.M.; Reyes, M.P. Placental histopathology in syphilis. Hum. Pathol. 1993, 24, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Publishes New Estimates on Congenital Syphilis. Global Decrease but Cases Remain High, Causing 200,000 Stillbirths and Newborn Deaths Every Year. 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/26-02-2019-who-publishes-new-estimates-on-congenital-syphilis (accessed on 5 July 2021).
- Singh, A.E.; Romanowski, B. Syphilis: Review with emphasis on clinical, epidemiologic, and some biologic features. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 187–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization Guideline on Syphilis Screening and Treatment for Pregnant Women; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; Available online: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/259003/9789241550093-eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 5 July 2021).
- Teixeira, L.O.; Belarmino, V.; Gonçalves, C.V.; Mendoza-Sassi, R.A. Tendência temporal e distribuição espacial da sífilis congênita no estado do Rio Grande do Sul entre 2001 e 2012. Ciênc. Saúde Colet. 2018, 23, 2587–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keuning, M.W.; Kamp, G.A.; Schonenberg-Meinema, D.; Dorigo-Zetsma, J.W.; van Zuiden, J.M.; Pajkrt, D. Congenital syphilis, the great imitator-case report and review. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, e173–e179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.A.; Vaidya, R. Congenital Syphilis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537087/ (accessed on 3 August 2021).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Antimicrobial Consumption in the EU/EEA—Annual Epidemiological Report 2019; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Nurse-Findlay, S.; Taylor, M.M.; Savage, M.; Mello, M.B.; Saliyou, S.; Lavayen, M.; Pyne-Mercier, L. Shortages of benzathine penicillin for prevention of mother-to-child transmission of syphilis: An evaluation from multi-country surveys and stakeholder interviews. PLoS Med. 2017, 14, e1002473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- 4—Recommendations for Treatment of Syphilis. In WHO Guidelines for the Treatment of Treponema pallidum (Syphilis); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK384905/ (accessed on 3 August 2021).
- Cardoso, A.; Santana, G.; Costa, E.A.; Araújo, P.S.; Lima, Y.O.R. Desabastecimento da Penicilina e Impactos para a Saúde da População; Observatório de Análise Política em Saúde: Salvador, Brazil, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bezerra, M.L.D.M.B.; Fernandes, F.E.C.V.; de Oliveira Nunes, J.P.; de Araújo, S.L.S.M. Congenital syphilis as a measure of maternal and child healthcare, Brazil. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan American Health Organization. Elimination of Mother-To-Child Transmission of HIV and Syphilis in the Americas; Update 2016; PAHO: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; Available online: http://iris.paho.org/xmlui/bitstream/handle/123456789/34072/9789275119556-eng.pdf (accessed on 6 September 2021).
- Comissão da Organização Pan-Americana da Saúde sobre Equidade e Desigualdades em Saúde nas Américas. Sociedades Justas: Equidade em Saúde e Vida Com Dignidade. Relatório da Comissão da Organização Pan-Americana da Saúde Sobre Equidade e Desigualdades em Saúde nas Américas; PAHO: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; Available online: https://iris.paho.org/handle/10665.2/51613 (accessed on 3 August 2022).
- Cançado, T.C.L.; de Souza, R.S.; da Silva Cardoso, C.B. Trabalhando o conceito de Vulnerabilidade Social; Universidate de Brasília: Brasília, Brazil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Buss, P.M.; Hartz, Z.M.D.A.; Pinto, L.F.; Rocha, C.M.F. Promoção da saúde e qualidade de vida: Uma perspectiva histórica ao longo dos últimos 40 anos (1980-2020). Ciênc. Saúde Colet. 2020, 25, 4723–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharbi, N.; Dutheillet, C.; Ioualalen, M. Colored stochastic petri nets for modelling and analysis of multiclass retrial systems. Math. Comput. Model. 2009, 49, 1436–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, R.; Valentim, R.; da Silva, L.F.; de Souza, G.F.; de Moura Santos, T.G.F.; de Oliveira, C.A.P.; Atun, R. Use of interrupted time series analysis in understanding the course of the congenital syphilis epidemic in Brazil. Lancet Reg. Health-Am. 2022, 7, 100163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.B.; Feng, T.J.; Yang, T.B.; Hong, F.C.; Lan, L.N.; Zhang, C.L. Maternal and paternal factors associated with congenital syphilis in Shenzhen, China: A prospective cohort study. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil. Ministério da Saúde, Secretaria de Atenção à Saúde. Boletim Epidemiológico de Sífilis—2016. 2016 [citado em 18 de dezembro de 2017]. Available online: http://www.aids.gov.br/pt-br/pub/2016/boletim-epidemiologico-de-sifilis-2016 (accessed on 4 August 2022).
- Domingues, R.M.S.M.; Saracen, V.; Hartz, Z.M.D.A.; Leal, M.D.C. Congenital syphilis: A sentinel event in antenatal care quality. Rev. Saude Publica 2013, 47, 147–157. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafetá, K.R.; Martelli Júnior, H.; Silveira, M.F.; Paranaíba, L.M. Maternal and congenital syphilis, underreported and difficult to control. Rev. Bras. Epidemiol. 2016, 19, 63–74. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lorenzi, D.R.S.; Fiaminghi, L.C.; Artico, G.R. Transmissão vertical da sífilis: Prevenção, diagnóstico e tratamento. FEMINA 2009, 37, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Brasil Ministério da Saúde. Secretaria de Atenção à Saúde, Departamento de Atenção Básica. Atenção ao Pré-Natal de Baixo Risco [Recurso Eletrônico]/Ministério da Saúde. Secretaria de Atenção à Saúde. Departamento de Atenção Básica; Editora do Ministério da Saúde: Brasília, Brazil, 2013; 318p. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, M.Z.N.D.; Andrade, A.B.D.; Bosi, M.L.M. Acesso e acolhimento no cuidado pré-natal à luz de experiências de gestantes na Atenção Básica. Saúde Debate 2014, 38, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil Conselho Nacional de Secretários de Saúde. A Atenção Primária e as Redes de Atenção à Saúde/Conselho Nacional de Secretários de Saúde; CONASS: Brasília, Brazil, 2015; 127p. [Google Scholar]
- Brasil Ministério da Saúde, Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde. Programa Nacional de DST/AIDS. Diretrizes para controle da sífilis congênita: Manual de bolso/Ministério da Saúde, Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde, Programa Nacional de DST/Aids; Ministério da Saúde: Brasília, Brazil, 2006; 72p. [Google Scholar]
- Brasil Ministério da Saúde, Departamento de Doenças de Condições Crônicas e Infecções Sexualmente Transmissíveis. Available online: http://www.aids.gov.br/pt-br/gestores/vigilancia-epidemiologica (accessed on 4 August 2022).
- Moraes, I.H.S.; Gómez, M.N.G. Informação e in- Formática em Saúde: Caleidoscópio Contemporâneo da Saúde. Ciênc. Saúde Colet. 2007, 12, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, Y.B.; Rezende, L.C.M.; Queiroga, M.M.D.; Santos, S.R. Sistemas de Informação em Saúde: Inconsistências de informações no contexto da atenção primária. J. Health Inf. 2016, 8, 164–170. [Google Scholar]
- Campelo, F. Sistemas de informação da atenção à saúde: Da fragmentação à interoperabilidade. In Ministério da Saúde, Organizador. Sistemas de Informação da Atenção à Saúde: Contextos Históricos, Avanços e Perspectivas No SUS; Editora Cidade Gráfica e Editoria: Brasília, Brazil, 2016; pp. 9–21. [Google Scholar]
- de Morais, C.M.; Teixeira, I.V.; Sadok, S.; Endo, P.T.; Kelner, J. Syphilis Trigram: A domain-specific visualisation to combat syphilis epidemic and improve the quality of maternal and child health in Brazil. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2022, 22, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministério da Saúde. Portaria 204, de 17 de Fevereiro de 2016. Define a Lista Nacional de Notificação Compulsória de Doenças, Agravos e Eventos de Saúde Pública nos Serviços de Saúde Públicos e Privados em Todo o Território Nacional, nos Termos do Anexo, e dá Outras Providências. Brasília: MS. 2016. Available online: http://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/saudelegis/gm/2016/prt0204_17_02_2016.html (accessed on 4 August 2022).
- Garbin, A.J.Í.; Martins, R.J.; Belila, N.D.M.; Exaltação, S.M.; Garbin, C.A.S. Reemerging diseases in Brazil: Sociodemographic and epidemiological characteristics of syphilis and its under-reporting. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2019, 52, e20180226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.M.d.; Rosendo, T.M.S.d.S.; Lopes, A.K.B.; Roncalli, A.G.; Lima, K.C.d. Weaknesses in primary health care favor the growth of acquired syphilis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, 000908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Direção Nacional da Saúde (DGS). SINAVE—Sistema Nacional de Vigilância Epidemiológica—Sífilis e Sífilis Congênita em Portugal; DGS: Lisbon, Portugal, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Instituto Nacional de Estatística. Available online: https://www.ine.pt/xportal/xmain?xpgid=ine_tema&xpid=INE&tema_cod=1115&xlang=pt (accessed on 5 August 2022).
- Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. Available online: https://www.ibge.gov.br/apps/populacao/projecao/index.html (accessed on 5 August 2022).
- Magalhães, M.; Basto, L.; Areia, A.L.; Franco, S.; Malheiro, M.E.; Afonso, M.E.; Moura, P. Syphilis in Pregnancy and Congenital Syphilis: Reality in a Portuguese Central University Hospital. Rev. Bras. Ginecol. Obs. 2017, 39, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Direção Nacional da Saúde (DGS). A Saúde dos Portugueses—Perspectiva 2015; DGS: Lisbon, Portugal, 2015; Available online: https://www.omd.pt/content/uploads/2017/12/dgs-saude-portugueses-2015.pdf (accessed on 5 August 2022).
- Diagnóstico Situacional Sobre a Implementação da Recomendação Opção B+, da Transmissão Vertical do VIH e da Sífilis Congênita, no Âmbito da Comunidade de Países de Língua Portuguesa—CPLP. RELATÓRIO FINAL—CPLP—IMPLEMENTAÇÃO DA OPÇÃO B+—PORTUGAL_2018. Available online: https://saude.cplp.org/media/1928/cplp_portugal_2018.pdf (accessed on 6 August 2022).
- Serviço Nacional da Saúde—Direção Geral de Saúde. Available online: https://www.dgs.pt/servicos-on-line1/sinave-sistema-nacional-de-vigilancia-epidemiologica.aspx (accessed on 6 August 2022).
- Report on 2018–2019 Pre-Validation Assessment of Elimination of Mother-To-Child Transmission of HIV and Syphilis in Ukraine; WHO Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2020.
- Trinh, T.A.; Leal, F.; Mello, M.B.; Taylor, M.M.; Barrow, R.; Wi, T.E.; Kambg, F.L. Syphilis management in pregnancy: A review of guideline recommendations from countries around the world. Sex. Reprod. Health Matters 2019, 27, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez-Cerdeira, C.; Silami-Lopes, V.G. Congenital syphilis in the 21st century. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2012, 103, 679–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, V.; Su, J.; Torrone, E.; Kidd, S.; Weinstock, H. Increase in incidence of congenital syphilis—United States, 2012–2014. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2015, 64, 1241–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoltey, J.; Chew Ng, R.A.; Denny, C.C.; Park, I.; Bauer, H. Identifying missed opportunities for prevention: Congenital syphilis case review, California project area, 2007–2014. Sex. Transm. Dis. 2016, 43, S148. [Google Scholar]
- Slutsker, J.S.; Hennessy, R.R.; Schillinger, J.A. Factors contributing to congenital syphilis cases—New York City, 2010–2016. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2018, 67, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rother, E.T. Systematic literature review X narrative review. Acta Paul. Enferm. 2007, 20, v–vi. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Green, B.N.; Johnson, C.D.; Adams, A. Writing narrative literature reviews for peer-reviewed journals: Secrets of the trade. J. Chiropr. Med. 2006, 5, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ministério da Saúde. Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde. Boletim Epidemiológico 2021. Número Especial|Out. 2021 Ano V: Ministério da Saúde; Brasília. 2021. Available online: http://www.aids.gov.br/pt-br/pub/2021/boletim-epidemiologico-de-sifilis-2021 (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- De Morais Pinto, R.; de Medeiros Valentim, R.A.; Fernandes da Silva, L.; Góis Farias de Moura Santos Lima, T.; Kumar, V.; Pereira de Oliveira, C.A.; Martins Gomes de Gusmão, C.; de Paiva, J.C.; de Andrade, I. Analyzing the reach of public health campaigns based on multidimensional aspects: The case of the syphilis epidemic in Brazil. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Congenital syphilis. In Annual Epidemiological Report for 2016; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Congenital syphilis. In Annual epidemiological Report for 2018; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Brasil, Ministério da Saúde. Portaria 542/1986. Diário Oficial da União, 24 dez 1986, Seção 1, p. 19827. Available online: http://pesquisa.bvsalud.org/ses/resource/pt/crt-3619 (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Tang, S.; Shi, L.; Chen, W.; Zhao, P.; Zheng, H.; Yang, B.; Wang, C.; Ling, L. Spatiotemporal distribution and sociodemographic and socioeconomic factors associated with primary and secondary syphilis in Guangdong, China, 2005–2017. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Direção-Geral da Saúde. Título: Programa Nacional para a Vigilância da Gravidez de Baixo Risco; DGS: Lisbon, Portugal, 2015; Available online: https://www.dgs.pt/em-destaque/programa-nacional-para-a-vigilancia-da-gravidez-de-baixo-risco-pdf11.aspx (accessed on 15 September 2021).
- Direção-Geral da Saúde. Norma DGS n° 037/2011 de 30/09/2011 Atualizada a 20/12/2013; DGS: Lisbon, Portugal, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Comissão Nacional de Incorporação de Tecnologias no sus (Conitec). Available online: http://conitec.gov.br/images/Artigos_Publicacoes/Diretrizes/PCDT_Atencao_Integral_IST_22-10-18.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2021).
- Domingues, C.S.B.; Duarte, G.; Passos, M.R.L.; Sztajnbok, D.C.D.N.; Menezes, M.L.B. Brazilian Protocol for Sexually Transmitted Infections, 2020: Congenital syphilis and child exposed to syphilis. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2021, 54 (Suppl. S1), e2020597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde, Ministério da Saúde. Diretrizes para o Controle da Sífilis Congênita; Ministério da Saúde: Brasília, Brazil, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Araújo, C.L.; Shimizu, H.E.; Souza, A.I.A.; Hamann, E.M. Incidence of congenital syphilis in Brazil and its relationship with the Family Health Strategy. Rev. Saúde Pública 2012, 46, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Korenromp, E.L.; Rowley, J.; Alonso, M.; Mello, M.B.; Wijesooriya, N.S.; Mahiané, S.G.; Ishikawa, N.; Le, L.V.; Newman-Owiredu, M.; Nagelkerke, N.; et al. Global burden of maternal and congenital syphilis and associated adverse birth outcomes-Estimates for 2016 and progress since 2012. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization—WHO. Eliminação Mundial da Sífilis Congênita: Fundamento Lógico e Estratégia Para Ação; OMS: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pan American Health Organization. Plan of Action for the Prevention and Control of HIV and Sexually Transmitted Infections (2016–2021); 55th Directing Council, 68th Session of the Regional Committee of WHO for the Americas, Resolution CD55.R5; PAHO: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; Available online: http://iris.paho.org/xmlui/handle/123456789/31411 (accessed on 15 September 2021).
- Costa, F.; Mendes, M.; Ferreira, M.; Barroso, R. Congenital syphilis: A revision of the cases over the last 18 years in a referral hospital in Lisbon. J. Pediatr. Neonatal Individ. Med. 2019, 8, e080119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, J.; Munguti, K.; Grosskurth, H.; Mngara, J.; Changalucha, J.; Mayaud, P.; Mosha, F.; Gavyole, A.; Mabey, D.; Hayes, R. Risk factors for active syphilis and TPHA seroconversion in a rural African population. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2001, 77, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lubiganon, P.; Piaggio, G.; Villar, J.; Pinol, A.; Bakketeig, L.; Bergsjo, P.; Al-Mazrou, Y.; Ba’Aqeel, H.; Belizán, J.M.; Farnot, U.; et al. The epidemiology of syphilis in pregnancy. Int. J. STD AIDS 2002, 13, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saloojee, H.; Velaphi, S.; Goga, Y.; Afadapa, N.; Steen, R.; Lincetto, O. The prevention and management of congenital syphilis: An overview and recommendations. Bull. World Health Organ. 2004, 82, 424–430. [Google Scholar]
- Direcção-Geral da Saúde. Assunto: PRESTAÇÃO DE CUIDADOS PRÉ-CONCEPCIONAIS Nº: 02/DSMIA DATA: 16/01/2006 Para: Todos os Médicos e Enfermeiros Que Exerçam Actividade na Área da Saúde Reprodutiva; Circular Normativa; DGS: Lisbon, Portugal, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zammarchi, L.; Borchi, B.; Chiappini, E.; Galli, L.; Brogi, M.; Sterrantino, G.; Trotta, M. Syphilis in pregnancy in Tuscany, description of a case series from a global health perspective. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012, 25, 2601–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshed, M.G.; Singh, A.E. Recent trends in the serologic diagnosis of syphilis. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2015, 22, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunseth, C.D.; Ford, B.A.; Krasowski, M.D. Traditional versus reverse syphilis algorithms: A comparison at a large academic medical center. Pract. Lab. Med. 2017, 8, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.E.; Bazan, J.A.; Turner, A.N.; Thung, S.F.; Hanlon, C.; Pettus, T.R.; Sánchez, P.J. Reverse sequence syphilis screening and discordant results in pregnancy. J. Pediatr. 2020, 219, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil Ministério da Saúde (MS). Brasil Reafirma Compromisso Pelo Fim de Epidemias Até 2030; MS: Brasília, Brazil, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cunha-Oliveira, A.; Camarneiro, A.P.; Gómez-Cantarino, S.; Cipriano-Crespo, C.; Queirós, P.J.P.; Cardoso, D.; Santos, D.G.; Ugarte-Gurrutxaga, M.I. The Integration of Gender Perspective into Young People’s Sexuality Education in Spain and Portugal: Legislation and Educational Models. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro, C.B.L.; Veiga, L. O Conceito de Inclusão, Dimensões e Indicadores Belo Horizonte: Secretaria Municipal de Coordenação da Política Social. Tese de Doutorado em Ciências Humanas: Sociologia e Política, da Faculdade de Filosofia e Ciências Humanas da Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, 2005, 334f. Available online: https://www.livrosgratis.com.br/ler-livro-online-63812/programas-de-protecao-social-e-superacao-da-pobreza--concepcoes-e-estrategias-de-intervencao (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- Aragão, J.D.S.; França, I.S.X.D.; Coura, A.S.; Medeiros, C.C.M.; Enders, B.C. Vulnerabilidade associada às infecções sexualmente transmissíveis em pessoas com deficiência física. Ciênc. Saúde Colet. 2016, 21, 3143–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Brito Pinto, T.K.; da Cunha-Oliveira, A.C.G.D.P.; Sales-Moioli, A.I.L.; Dantas, J.F.; da Costa, R.M.M.; Silva Moura, J.P.; Gómez-Cantarino, S.; Valentim, R.A.d.M. Clinical Protocols and Treatment Guidelines for the Management of Maternal and Congenital Syphilis in Brazil and Portugal: Analysis and Comparisons: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191710513
de Brito Pinto TK, da Cunha-Oliveira ACGDP, Sales-Moioli AIL, Dantas JF, da Costa RMM, Silva Moura JP, Gómez-Cantarino S, Valentim RAdM. Clinical Protocols and Treatment Guidelines for the Management of Maternal and Congenital Syphilis in Brazil and Portugal: Analysis and Comparisons: A Narrative Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(17):10513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191710513
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Brito Pinto, Talita Katiane, Aliete Cristina Gomes Dias Pedrosa da Cunha-Oliveira, Ana Isabela Lopes Sales-Moioli, Jane Francinete Dantas, Rosângela Maria Morais da Costa, José Paulo Silva Moura, Sagrario Gómez-Cantarino, and Ricardo Alexsandro de Medeiros Valentim. 2022. "Clinical Protocols and Treatment Guidelines for the Management of Maternal and Congenital Syphilis in Brazil and Portugal: Analysis and Comparisons: A Narrative Review" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 17: 10513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191710513
APA Stylede Brito Pinto, T. K., da Cunha-Oliveira, A. C. G. D. P., Sales-Moioli, A. I. L., Dantas, J. F., da Costa, R. M. M., Silva Moura, J. P., Gómez-Cantarino, S., & Valentim, R. A. d. M. (2022). Clinical Protocols and Treatment Guidelines for the Management of Maternal and Congenital Syphilis in Brazil and Portugal: Analysis and Comparisons: A Narrative Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(17), 10513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191710513









