Properties of Particulate Matter in the Air of the Wieliczka Salt Mine and Related Health Benefits for Tourists
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Site
2.2. Sampling Method
2.3. Result Analysis
- Di is the average dose of inhaled aerosol during the stay at the i-th measurement point (tourist route/passage to the health resort/health resort) [µg],
- DFi is the deposition factor at the i-th measuring point,
- Ci is the average concentration of respirable fraction PM (PM4) at the i-th measurement point [µg/m3],
- ti is the average time of stay at the i-th measurement point [day],
- InhR is inhalation rate (m3/day).
3. Results
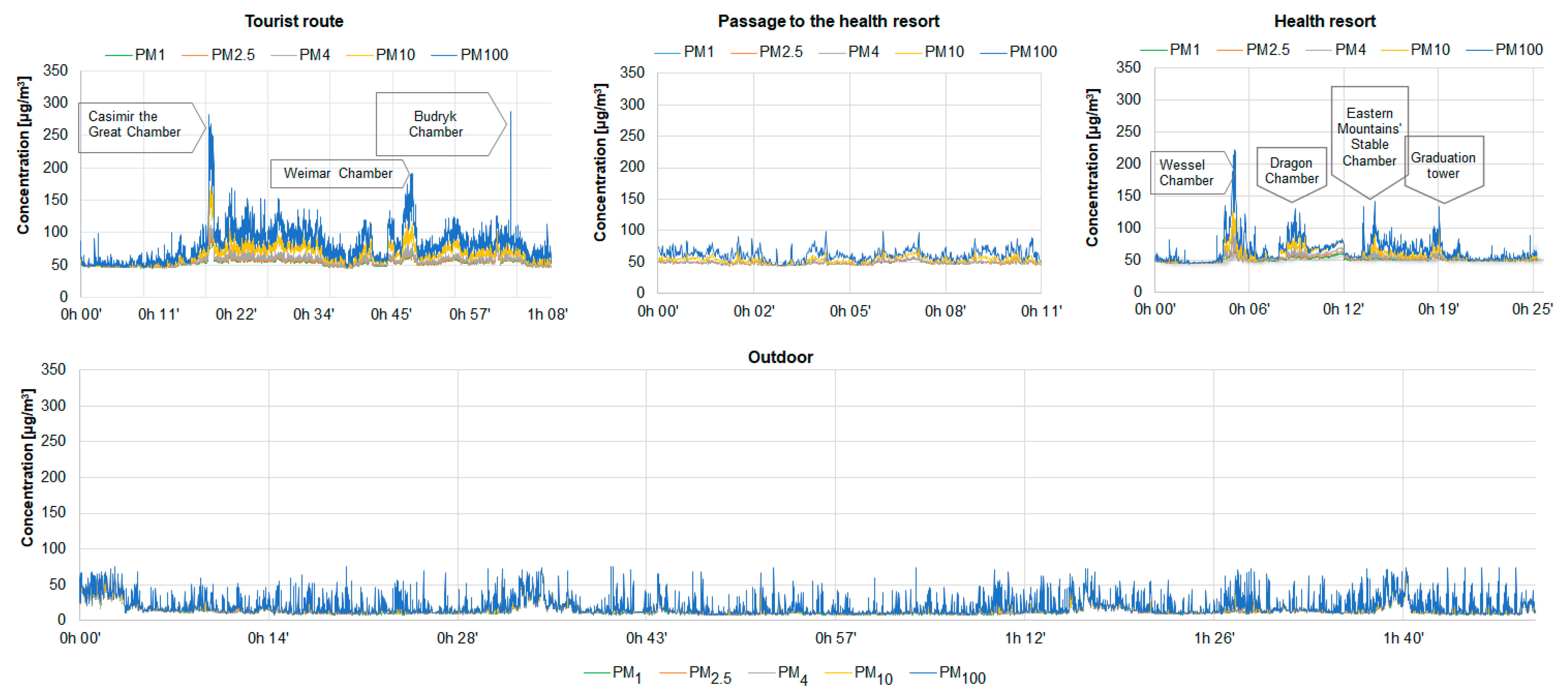
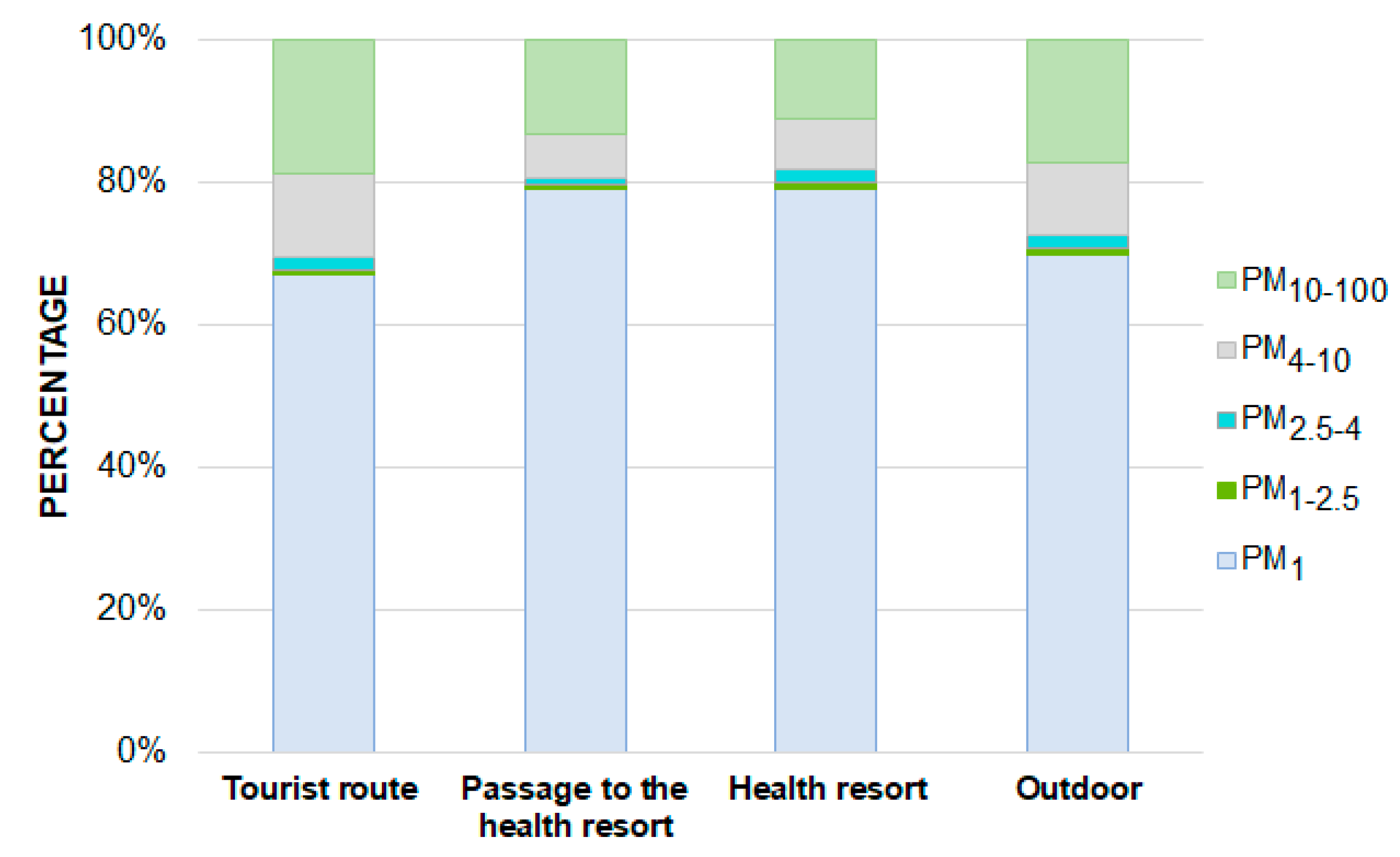
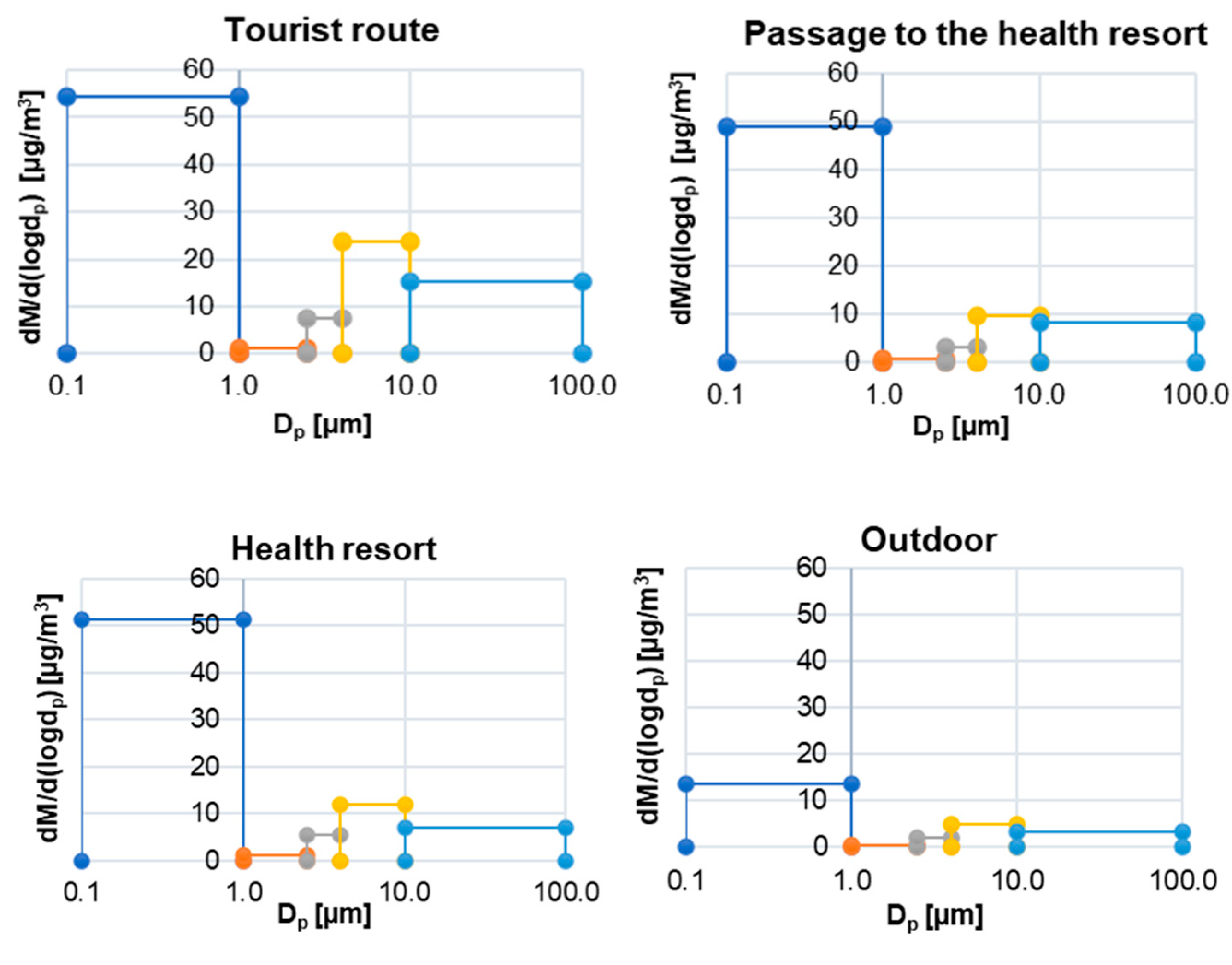
3.1. Distribution of Particulate Matter Concentrations in the Mine
3.2. Particulate Matter Deposition and Dose of Dry Salt Aerosol Inhaled during the Stay in the Mine
4. Conclusions
- In general, the highest concentrations of PM were recorded on the tourist route (54.5–81.2 µg/m3), while the lowest in the passage to the health resort (48.9–61.7 µg/m3).
- At all measuring points, the vast majority of the PM mass (more than 60%) was accumulated in fine particles with aerodynamic diameters smaller than 2.5 µm.
- The highest concentrations of PM were recorded in places where tourists were passed and in chambers characterised by large cubature, as well as in places with large rock walls.
- Tourist traffic undoubtedly affects the concentration of coarse PM in the underground chambers, however, the microclimate of the mine and ventilation solutions cause a quick and effective reduction of the concentration of this PM fraction.
- High air humidity in underground chambers prevents PM resuspension.
- Probably due to the relatively short time of measurements, PM concentrations outside the mine were at a relatively constant level. The comparison of the distribution of PM concentrations inside and outside the mine allows us to exclude an influence of atmospheric air and anthropogenic sources on PM concentrations inside the mine.
- In this manuscript, the concentrations of the dry aerosol with particles smaller than 100 µm were examined. The wet aerosol concentrations in the mine are certainly higher.
- Due to the high air humidity in the underground chambers of the mine, in the future, when measuring PM concentrations in real-time with the use of optical meters, it is worth using solutions allowing for air drying.
- Due to the high proportion of fine particles in the total PM mass, the PM deposition factors in the respiratory tracts of patients and mine visitors are relatively high (0.58–0.70).
- High PM deposition factors at all measurement points and prevalence of respirable particles in PM composition guarantees the efficiency of action and penetration of all sections of the respiratory tract right up to the deepest, which at the same time indicates the high therapeutic effectiveness of the stay in the mine, even while visiting the mine.
- In children, most of the PM is deposited in the deeper parts of the respiratory system (trachea and bronchi and alveoli), while in adults the largest mass of dry NaCl is deposited in the upper respiratory tract.
- During a single visit to the mine’s tourist route, going to the health resort and treatment in the health resort, an average adult inhales approximately 84 µg of dry salt aerosol.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beamon, S.; Falkenbach, A.; Fainburg, G.; Linde, K. Speleotherapy for asthma. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2001, 2, CD001741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostrzon, M.; Sliwka, A.; Wloch, T.; Szpunar, M.; Ankowska, D.; Nowobilski, R. Subterranean pulmonary rehabilitation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1176, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frączek, K.; Górny, R.L.; Ropek, D. Bioaerosols of subterraneotherapy chambers at salt mine health resort. Aerobiologia 2013, 29, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Obtułowicz, K. Mechanism of therapeutic effects of subterraneotherapy in the chambers of the Salt Mine Wieliczka. Alergol. Immunol. 2013, 10, 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Obtułowicz, K.; Myszkowska, D.; Dyga, W.; Mazur, M.; Czarnobilska, E. Hypoallergic subterraneotherapy in salt chambers of Wieliczka Mine of the therapy of airways and skin allergy. The role of bioaerosol. Alergol. Immunol. 2013, 10, 2–3. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Mętel, S.; Kostrzon, M.; Adamiak, J.; Gattner, H.; Kościelecka, D.; Sosulska, A.; Szczygieł, E.; Golec, J. The influence of speleotherapy combined with pulmonary rehabilitation on functional fitness in older adults—Preliminary report. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2020, 14, 1753466620926952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skulimowski, M. Treatment of bronchial asthma patients in the chambers of the rock salt mine in Wieliczka. Arch. Phys. Ther. 1965, 17, 417–421. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Czajka, K.; Sziwa, D.; Drobnik, M.; Latour, T. Comparison of properties of microclimate and aerosols in mine excavations and above-ground salt caves. Balneol. Pol. 2006, 3, 176–181. [Google Scholar]
- Pop, N.; Bican-Brisan, N.; Beldean-Galea, M.S.; Mera, O.; Dumitrascu, I. Changes of the Turda Salt Mine underground microclimate induced by its rehabilitation and touristic exploitation. ProEnvironment 2010, 3, 385–394. [Google Scholar]
- Rogula-Kozłowska, W.; Kostrzon, M.; Rogula-Kopiec, P.; Badyda, A.J. Particulate matter in the air of the underground chamber complex of the Wieliczka Salt Mine Health Resort. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 955, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wiszniewski, A. Environment of air-ions in healing chambers in the Wieliczka Salt Mine. Acta Phys. Pol. 2015, 127, 1661–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostrzon, M.; Czarnobilski, K.; Badyda, A.J. Climate characteristics of salt chambers used for therapeutic purposes in the ‘Wieliczka’ Salt Mine. Acta Balneol. 2015, 57, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Myszkowska, D.; Kostrzon, M.; Dyga, W.; Kędzierska, J.; Namysł, M.; Stanisz, A.; Zagórska, M.; Ziemianin, M.; Obtułowicz, K.; Czarnobilska, E. Bioaerosol of salt chambers in the ‘Wieliczka’ Salt Mine, Poland. Aerobiologia 2019, 35, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pośpiech, S.; Barucha, P.; Damijan, Z.; Błaszczyk, J.; Czapkowicz-Pośpiech, R. Evaluation of the influence of the underground Salt Chambers Microclimate of King Spa in Wieliczka Salt Mine on the body weight, fatty tissue content and lipid balance—Preliminary study. Acta Bio-Opt. Inform. Med. 2014, 20, 204–216. [Google Scholar]
- Puławska, A.; Manecki, M.; Flasza, M.; Styszko, K. Origin, distribution, and perspective health benefits of particulate matter in the air of underground salt mine: A case study from Bochnia, Poland. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 3533–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flory, R.; Ametepe, J.; Bowers, B. A randomized, placebo–controlled trial of bright light and high–density negative air ions for treatment of Seasonal Affective Disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2010, 177, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, C.A., III; Burnett, R.T.; Thurston, G.D.; Thun, M.J.; Calle, E.E.; Krewski, D.; Godleski, J.J. Cardiovascular mortality and long-term exposure to particulate air pollution epidemiological evidence of general pathophysiological pathways of disease. Circulation 2004, 6, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kappos, A.D.; Bruckmann, P.; Eikmann, T.; Englert, N.; Heinrich, U.; Höppe, P.; Koch, E.; Krause, G.H.; Kreyling, W.G.; Rauchfuss, K.; et al. Health effects of particles in ambient air. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2004, 207, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abelsohn, A.; Stieb, D.M. Health effects of outdoor air pollution. Approach to counseling patients using the Air Quality Health Index. Can. Fam. Physician 2011, 57, 881–887. [Google Scholar]
- Badyda, A.J.; Grellier, J.; Dąbrowiecki, P. Ambient PM2.5 Exposure and Mortality Due to Lung Cancer and Cardiopulmonary Diseases in Polish Cities. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 944, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Hoek, G. Long-term exposure to PM and all-cause and cause-specific mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Int. 2020, 143, 105974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajczak, A.; Badyda, A.; Czechowski, P.O.; Czarnecki, A.; Dubrawski, M.; Feleszko, W. Air pollution increases the incidence of upper respiratory tract symptoms among polish children. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morawska, L.; Salthammer, T. Indoor Environment: Airborne Particles and Settled Dust; Wiley-VCH GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2006; pp. 387–406. [Google Scholar]
- Kampa, M.; Castanas, E. Human health effects of air pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 151, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogula-Kozłowska, W. Size-segregated urban particulate matter: Mass closure, chemical composition, and primary and secondary matter content. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2016, 9, 533–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frijlink, H.W.; De Boer, A.H. Dry powder inhalers for pulmonary drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2004, 1, 67–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zając, J.; Bojar, I.; Helbin, J.; Kolarzyk, E.; Owoc, A. Salt caves as simulation of natural environment and significance of halotherapy. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2014, 21, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bokwa, A. Environmental impacts of long-term air pollution Changes in Kraków, Poland. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2008, 17, 673–686. [Google Scholar]
- Ćwiek, K.; Majewski, G. The influence of meteorological factors on the development of air pollutants concentration—Cracow case study. Sci. Rev. Eng. Environ. Sci. 2015, 24, 54–66. [Google Scholar]
- Saramak, A. Comparative analysis of indoor and outdoor concentration of PM10 particulate matter on example of Cracow City Center. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 6609–6616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The Main Inspectorate of Environmental Protection. Annual Assessment of Air Quality in the Małopolska Region. Voivodship Report for 2018 and 2019; GIOŚ: Warsaw, Poland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mirek, J. Analysis of the tourist traffic carried out in the Wieliczka Salt Mine health resort as part of health tourism. EPT 2016, 3, 223–236. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Wieliczka Salt Mine. Available online: https://www.wieliczka-saltmine.com/individual-tourist/tourist-route (accessed on 29 November 2021).
- Kingham, S.; Durand, M.; Aberkane, T.; Harrison, J.; Wilson, G.; Epton, M. Winter comparison of TEOM, MiniVol and DustTrak PM10 monitors in a woodsmoke environment. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Smith, T.J.; Davis, M.E.; Levy, J.I.; Herrick, R.; Jiang, H. Comparing gravimetric and real-time sampling of PM2.5 concentrations inside truck cabins. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2011, 8, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rivas, I.; Mazaheri, M.; Viana, M.; Moreno, T.; Clifford, S.; He, C.; Bischof, O.F.; Martins, V.; Reche, C.; Alastuey, A.; et al. Identification of technical problems affecting performance of DustTrak DRX aerosol monitors. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 15, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roguski, M.; Badyda, A. Investigation of Low-Cost and Optical Particulate Matter Sensors for Ambient Monitoring. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EC Working Group. Guide to the Demonstration of Equivalence of Ambient Air Monitoring Methods; EC Working Group on Guidance for the Demonstration of Equivalence; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Ispra, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hinds, W.C. Aerosol Technology. Properties, Behavior, and Measurement of Airborne Particles, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Nag, S.; Gupta, A.K.; Mukhopadhay, U.K. Size distribution of atmospheric aerosols in Kolkata, India and the assessment of pulmonary deposition of particle mass. Indoor Built. Environ. 2005, 14, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezemer, G. Particle Deposition Clearance from Respiratory Tract; Institute for Risk Assessment Sciences: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- US EPA. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund Volume I: Human Health Evaluation Manual. (Part F, Supplemental Guidance for Inhalation Risk Assessment); U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- Widziewicz, K.; Rogula-Kozłowska, W. Urban environment as a factor modulating metals deposition in the respiratory track and associated cancer risk. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2018, 9, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Lyu, Y.; Xu, T.; Yao, B.; Song, W.; Li, M.; Yang, X.; Cheng, T.; Li, X. Particle size distribution and respiratory deposition estimates of airborne perfluoroalkyl acids during the haze period in the megacity of Shanghai. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bralewska, K.; Rogula-Kozłowska, W. Health exposure of users of indoor sports centers related to the physico-chemical properties of particulate matter. Build. Environ. 2020, 180, 106935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, K.; Castanha, E.; Fow, A.; Feigley, C.; Salzberg, D. Human K10 epithelial keratin is the most abundant protein in airborne dust of both occupied and unoccupied school rooms. J. Environ. Monit. 2008, 10, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labiris, N.R.; Dolovich, M.B. Pulmonary drug delivery. Part II: The role of inhalant delivery devices and drug formulations in therapeutic effectiveness of aerosolized medications. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2003, 56, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wieliczka Salt Mine. Available online: https://www.wieliczka-saltmine.com/health-resort/prices/underground-treatment-prices?_ga=2.233041559.808985942.1637664119-615630245.1637664118 (accessed on 29 November 2021).
- Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Ren, T.; Wu, J.; Lin, H.; Shuang, H. Respirable dust pollution characteristics within an underground heading face driven with continuous miner–A CFD modelling approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 217, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieliczka Salt Mine. Available online: https://www.kopalnia.pl/uzdrowisko/informacje-praktyczne/wazne-informacje/pobyty-1-3-dni (accessed on 29 November 2021).
- Thatcher, T.L.; Layton, D. Deposition, Resuspension, and Penetration of Particles within a Residence. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 1487–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colbeck, I.; Lazaridi, M. Aerosols and environmental pollution. Naturwissenschaften 2010, 97, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmon, L.G.; Cass, G.R.; Kozłowski, R.; Hejda, A.; Spiker, E.C.; Bates, A.L. Air Pollutant Intrusion into the Wieliczka Salt Mine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, A.; Chang, D.P.; Kleeman, M.J.; Perry, K.D.; Cahill, T.A.; Dutcher, D.; McDougall, E.M.; Stroud, K. Comparison of real-time instruments used to monitor airborne particulate matter. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2001, 51, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gębicki, J.; Szymańska, K. Comparison of Tests for Equivalence of Methods for Measuring PM10 Dust in Ambient Air. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2011, 20, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Calderón, L.; Patton, A.P.; Sorensen Allacci, M.; Senick, J.; Wener, R.; Andrews, C.J.; Mainelis, G. Comparison of Real-Time Instruments and Gravimetric Method When Measuring Particulate Matter in a Residential Building. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2016, 66, 1109–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intra, P.; Yawootti, A.; Siri-achawawath, T. Field comparison between electrostatic charge and light scattering monitors for continuous monitoring of airborne PM1.0, PM2.5, and PM10 mass concentrations. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2018, 40, 339–346. [Google Scholar]
- Rogula-Kozłowska, W.; Klejnowski, K.; Rogula-Kopiec, P.; Ośródka, L.; Krajny, E.; Błaszczak, B.; Mathews, B. Spatial and seasonal variability of the mass concentration and chemical composition, of PM2.5 in Poland. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2014, 7, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rogula-Kozłowska, W.; Majewski, G.; Błaszczak, B.; Klejnowski, K.; Rogula-Kopiec, P. Origin-oriented elemental profile of fine ambient particulate matter in central European suburban conditions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majewski, G.; Rogula-Kozłowska, W.; Czechowski, P.O.; Badyda, A.; Brandyk, A. The impact of selected parameters on visibility: First results from a long-term campaign in Warsaw, Poland. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1154–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majewski, G.; Rogula-Kozłowska, W.; Rozbicka, K.; Rogula-Kopiec, P.; Mathews, B.; Brandyk, A. Concentration, chemical composition and origin of PM1: Results from the first long-term measurement campaign in Warsaw (Poland). Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 636–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raizer, M.; Juda-Rezler, K. Explaining the high PM10 concentrations observed in Polish urban areas. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2016, 9, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sówka, I.; Chlebowska-Styś, A.; Pachurka, Ł.; Rogula-Kozłowska, W.; Mathews, B. Analysis of Particulate Matter Concentration Variability and Origin in Selected Urban Areas in Poland. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newman, S.P. Aerosol Deposition Considerations in Inhalation Therapy. Chest 1985, 88, 152S–160S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.M.; Chang, K.H.; Moon, S.H.; Park, B.J.; Yoo, S.K.; Nam, K.C. In vitro delivery efficiencies of nebulizers for different breathing patterns. Biomed. Eng. OnLine 2021, 20, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuskowska, K.; Rogula-Kozłowska, W.; Widziewicz, K. Preliminary study of the concentrations and mass size distributions of particulate matter in indoor sports facilities before and during athlete training. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2019, 45, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sracic, M.K. Modeled regional airway deposition of inhaled particles in athletes at exertion. J. Aerosol Sci. 2016, 99, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, S.H.; Rony, A.; Karim, F.I.; Mridha, M.F.; Abdul Hamid, M. Evaluate and predict concentration of particulate matter (PM2.5) using machine learninga. In International Conference on Innovative Computing and Communications. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Gupta, D., Khanna, A., Bhattacharyya, S., Hassanien, A.E., Anand, S., Jaiswal, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; Volume 1166. [Google Scholar]
- Neto, P.S.D.M.; Firmino, P.R.A.; Siqueira, H.; Tadano, Y.D.S.; Alves, T.A.; De Oliveira, J.F.L.; Marinho, M.H.D.N.; Madeiro, F. Neural-based ensembles for particulate matter forecasting. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 14470–14490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbal, Y.; Unlu, K.D. A deep learning approach to model daily particular matter of Ankara: Key features and forecasting. Int. J. Enron. Sci. Technol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Age | Respiration Frequency [Breath/min] | Breathing Volume [mL] | Lung Volume [mL] | Upper Airway Volume [mL] | InhR [m3/day] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Children 8+ years | 17 | 278.20 | 740.42 | 21.03 | 7.63 |
| Adults 21+ years | 14 | 477.20 | 2792.50 | 42.30 | 15.20 |
| Measurement Point | PM Fraction | Statistical Parameter | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean [µg/m3] | Median [µg/m3] | Minimum [µg/m3] | Maximum [µg/m3] | Standard Deviation | ||
| Tourist route | PM1 | 54.5 | 53.9 | 44.2 | 155.0 | 7.6 |
| PM2.5 | 55.0 | 54.5 | 44.3 | 156.0 | 7.9 | |
| PM4 | 56.5 | 56.1 | 44.4 | 158.0 | 8.9 | |
| PM10 | 66.0 | 65.0 | 44.8 | 177.0 | 16.1 | |
| PM100 | 81.2 | 78.1 | 45.5 | 288.0 | 28.5 | |
| Passage to the health resort | PM1 | 48.9 | 48.3 | 44.0 | 73.5 | 3.5 |
| PM2.5 | 49.1 | 48.5 | 44.1 | 74.5 | 3.6 | |
| PM4 | 49.7 | 49.1 | 44.2 | 76.0 | 3.9 | |
| PM10 | 53.5 | 52.9 | 44.3 | 85.9 | 5.2 | |
| PM100 | 61.7 | 60.9 | 44.3 | 101.0 | 9.5 | |
| Health resort | PM1 | 51.4 | 50.2 | 43.9 | 117.0 | 5.7 |
| PM2.5 | 51.9 | 50.7 | 44.0 | 118.0 | 6 | |
| PM4 | 53.0 | 51.6 | 44.0 | 121.0 | 6.8 | |
| PM10 | 57.7 | 54.4 | 44.3 | 152.0 | 11.1 | |
| PM100 | 64.8 | 59.4 | 44.3 | 222.0 | 19.9 | |
| Outdoor | PM1 | 13.7 | 11.0 | 7.0 | 73.0 | 8.3 |
| PM2.5 | 13.9 | 11.0 | 7.0 | 73.0 | 8.3 | |
| PM4 | 14.3 | 11.0 | 8.0 | 73.0 | 8.3 | |
| PM10 | 16.3 | 13.0 | 8.0 | 73.0 | 9.2 | |
| PM100 | 19.6 | 15.0 | 8.0 | 75.0 | 12.8 | |
| Place of Measurement | MMAD [µm] | GSD [µm] |
|---|---|---|
| Tourist route | 2.49 | 10.38 |
| Passage to the health resort | 1.48 | 9.44 |
| Health resort | 1.46 | 8.75 |
| Outdoor | 2.19 | 9.98 |
| Sampling Site | DF | Total DF | t [h] | Dose [µg] | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adults | Children | Adults | Children | Adults | Children | ||||||
| H | TB | P | H | TB | P | ||||||
| Tourist route | 0.43 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.33 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.59 | 0.67 | 2.00 | 37.16 | 21.18 |
| Passage to the health resort | 0.34 | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0.31 | 0.58 | 0.70 | 0.25 | 4.02 | 2.43 |
| Health resort | 0.33 | 0.05 | 0.2 | 0.26 | 0.08 | 0.31 | 0.58 | 0.65 | 2.50 | 42.83 | 24.09 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bralewska, K.; Rogula-Kozłowska, W.; Mucha, D.; Badyda, A.J.; Kostrzon, M.; Bralewski, A.; Biedugnis, S. Properties of Particulate Matter in the Air of the Wieliczka Salt Mine and Related Health Benefits for Tourists. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 826. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19020826
Bralewska K, Rogula-Kozłowska W, Mucha D, Badyda AJ, Kostrzon M, Bralewski A, Biedugnis S. Properties of Particulate Matter in the Air of the Wieliczka Salt Mine and Related Health Benefits for Tourists. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(2):826. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19020826
Chicago/Turabian StyleBralewska, Karolina, Wioletta Rogula-Kozłowska, Dominika Mucha, Artur Jerzy Badyda, Magdalena Kostrzon, Adrian Bralewski, and Stanisław Biedugnis. 2022. "Properties of Particulate Matter in the Air of the Wieliczka Salt Mine and Related Health Benefits for Tourists" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 2: 826. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19020826







