Comprehensive Assessment of Eutrophication in Xiamen Bay and Its Implications for Management Strategy in Southeast China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Collections
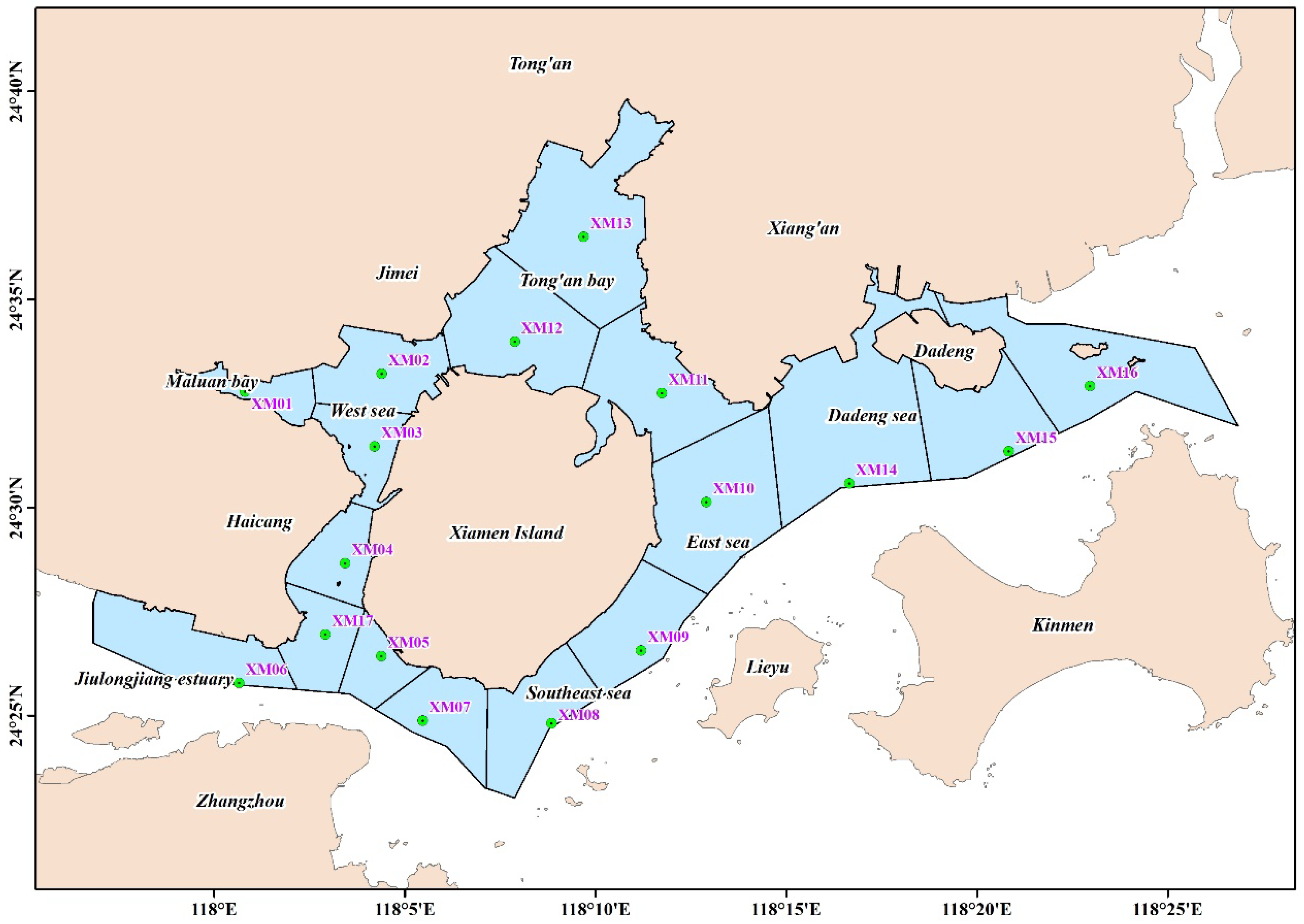
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
3. Methodology Description
3.1. Selection of Assessment Indicators
3.2. Grading and Scoring of Indicators
3.3. Criteria for Grading Indicators
3.3.1. Pressure Indicator
3.3.2. State Indicator
3.3.3. Response Indicator
3.4. Division of Assessment Units and Determination of Indicator Characteristic Values
3.5. Comprehensive Assessment and Final Grading of Eutrophication
4. Results and Discussion
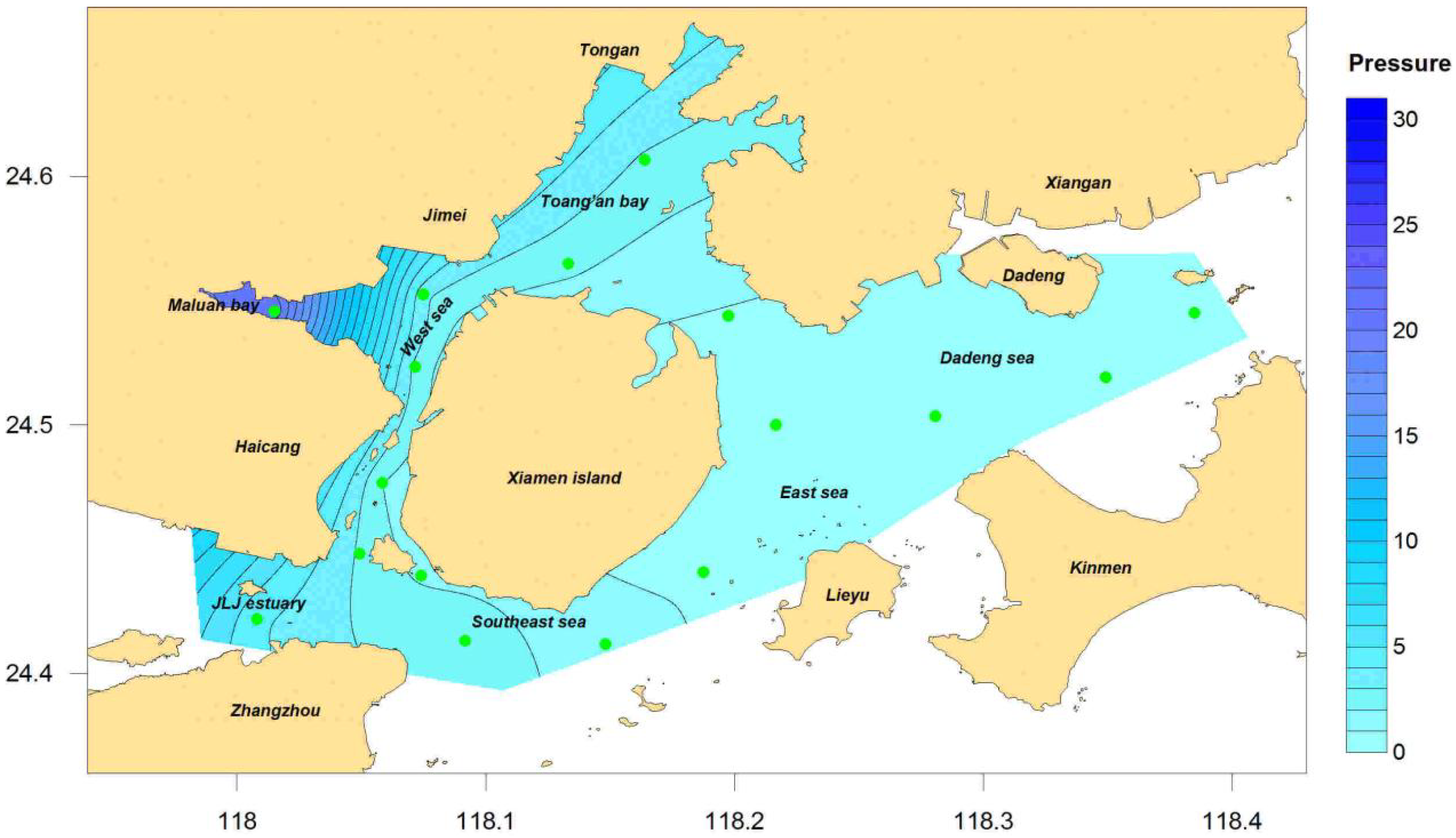
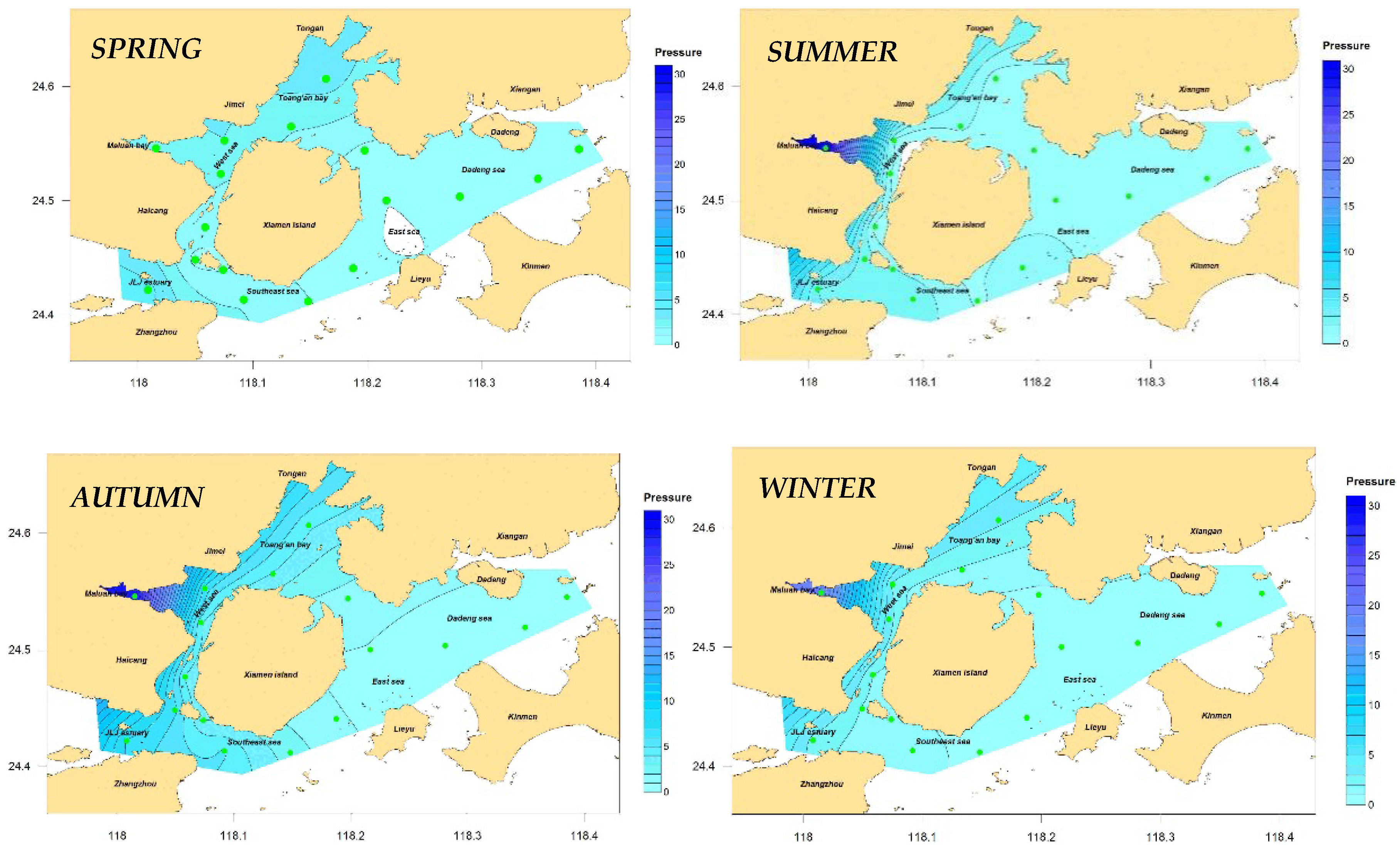
4.1. Pressure Assessment of Eutrophication
4.2. State Assessment of Eutrophication
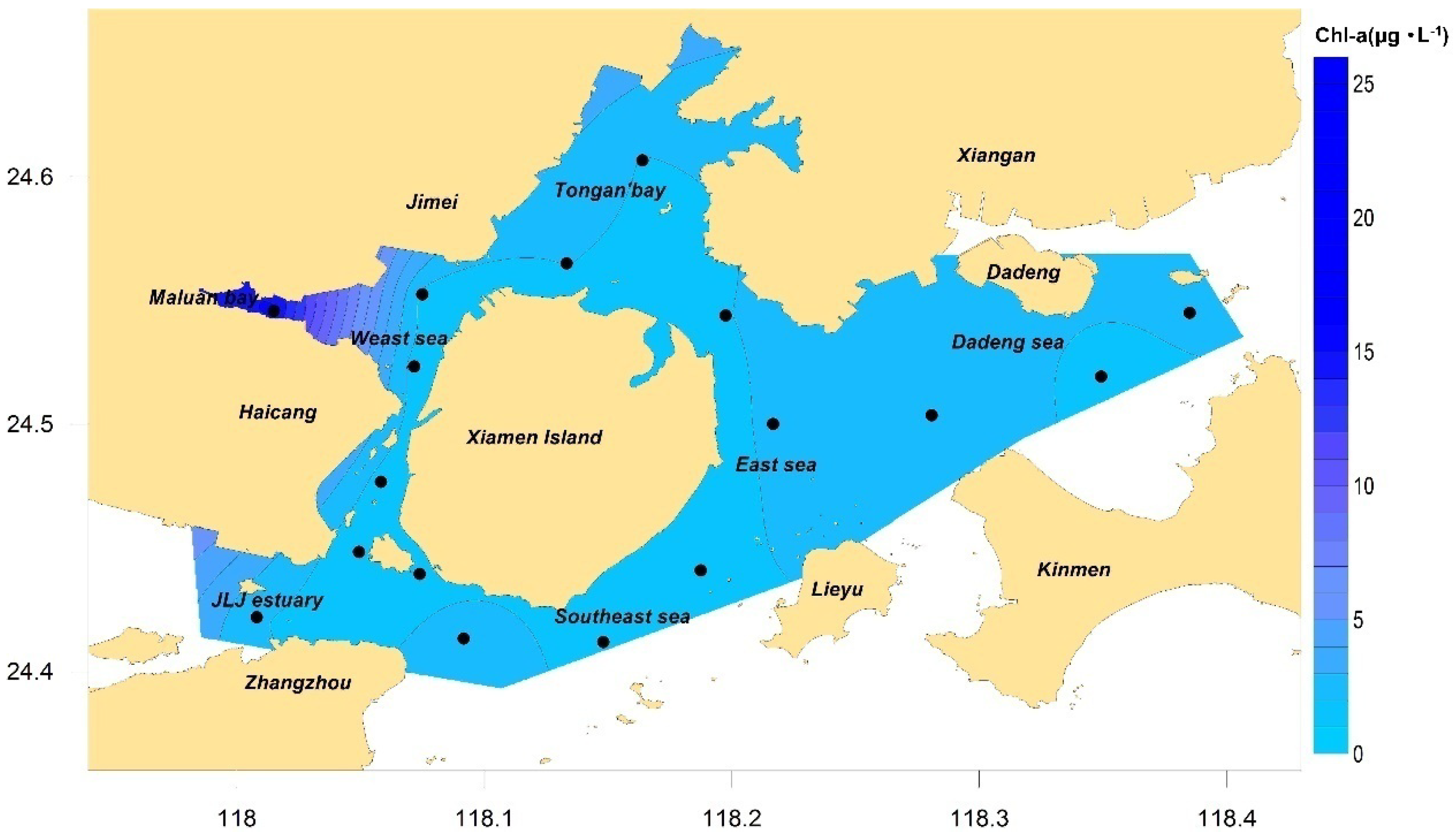
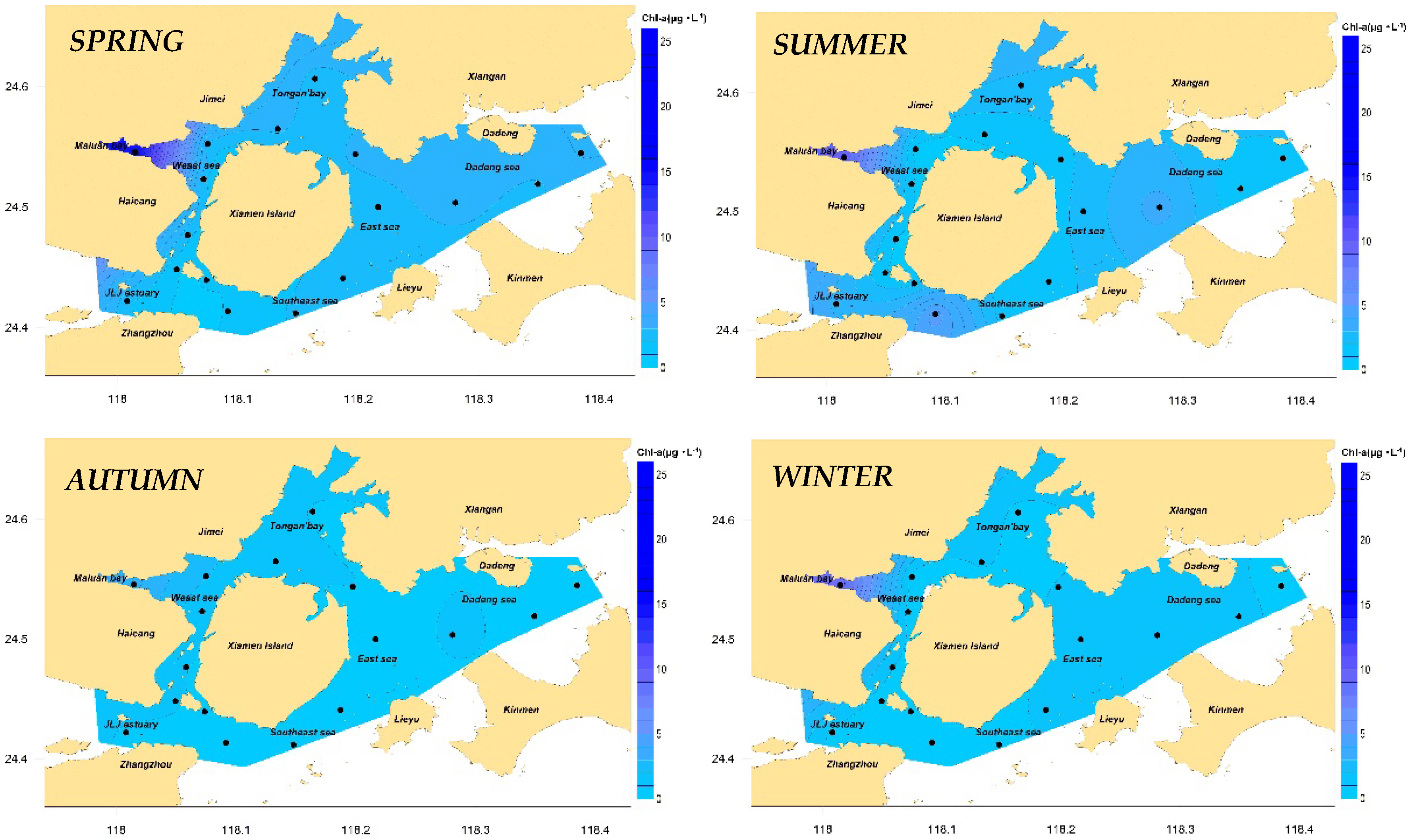
4.2.1. Primary Symptom Assessment
4.2.2. Secondary Symptom Assessment
4.2.3. Results of State Assessment
4.3. Response Assessment of Eutrophication
4.4. Results of Comprehensive Assessment
4.5. Implications for Management Strategies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garmendia, M.; Bricker, S.; Revilla, M.; Borja, Á.; Franco, J.; Bald, J.; Valencia, V. Eutrophication Assessment in Basque Estuaries: Comparing a North American and a European Method. Estuaries Coasts 2012, 35, 991–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidou, A.; Simboura, N.; Rousselaki, E.; Tsapakis, M.; Pagou, K.; Drakopoulou, P.; Assimakopoulou, G.; Kontoyiannis, H.; Panayotidis, P. Methods of eutrophication assessment in the context of the water framework directive: Examples from the Eastern Mediterranean coastal areas. Cont. Shelf Res. 2015, 108, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoicescu, S.-T.; Lips, U.; Liblik, T. Assessment of Eutrophication Status Based on Sub-Surface Oxygen Conditions in the Gulf of Finland (Baltic Sea). Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Q.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y. Research on modern marine environmental governance in China: Subject identification, structural characteristics, and operational mechanisms. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuya, K.; Iwataki, M.; Lim, P.T.; Lu, S.; Leaw, C.-P.; Azanza, R.V.; Kim, H.-G.; Fukuyo, Y. Overview of Harmful Algal Blooms in Asia. In Global Ecology and Oceanography of Harmful Algal Blooms; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 289–308. [Google Scholar]
- Glibert, P.M.; Al-Azri, A.; Allen, J.I.; Bouwman, A.F.; Beusen, A.H.W.; Burford, M.A.; Harrison, P.J.; Zhou, M. Key Questions and Recent Research Advances on Harmful Algal Blooms in Relation to Nutrients and Eutrophication. In Global Ecology and Oceanography of Harmful Algal Blooms; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 229–259. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, S.; Corburn, J.; Ribeiro, H. Challenges regarding water quality of eutrophic reservoirs in urban landscapes: A mapping literature review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, R.-C.; Lü, S.-H.; Liang, Y.-B. Harmful Algal Blooms in the Coastal Waters of China. In Global Ecology and Oceanography of Harmful Algal Blooms; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 309–316. [Google Scholar]
- Nowicka-Krawczyk, P.; Żelazna-Wieczorek, J.; Skrobek, I.; Ziułkiewicz, M.; Adamski, M.; Kaminski, A.; Żmudzki, P. Persistent Cyanobacteria Blooms in Artificial Water Bodies—An Effect of Environmental Conditions or the Result of Anthropogenic Change. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zheng, B.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Liu, F.; Shao, J.; Hu, X. Classification of estuaries in China based on eutrophication susceptibility to nutrient load. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2015, 58, 949–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Jiang, F.; Ke, K.; Xu, M.; Lei, F.; Chen, B. Nutrients distribution and trophic status assessment in the northern Beibu Gulf, China. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2014, 32, 1128–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; He, J.; Wu, J.; Hu, X.; Ye, G.; Christakos, G. Assessing the severe eutrophication status and spatial trend in the coastal waters of Zhejiang province (China). Limnol. Oceanogr. 2019, 64, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Sun, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, C.; Du, Z.; Liu, R. Ecosystem health assessment in coastal waters by considering spatio-temporal variations with intense anthropogenic disturbance. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 96, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, K.; Chen, K.; Liu, C.; Ma, Y.; Wang, X. Size-based bioavailability of land-based DON and its impact on eutrophication of Jiaozhou bay. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 152, 110898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Atique, U.; Mamun, M.; An, K.G. Long-term interannual and seasonal links between the nutrient regime, sestonic chlorophyll and dominant bluegreen algae under the varying intensity of monsoon precipitation in a drinking water reservoir. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, W.; Liu, J.; Ran, X.; Zhang, A.; Zang, J. Variations in the marine seawater environment and the dominant factors in the Lianyungang coastal area. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2022, 52, 102276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricker, S.B.; Ferreira, J.G.; Simas, T. An integrated methodology for assessment of estuarine trophic status. Ecol. Model. 2003, 169, 39–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.; Li, H.; Yang, X.; Xu, Z.; Tong, Y.; Yu, X. Comprehensive Investigation and Assessment of Nutrient and Heavy Metal Contamination in the Surface Water of Coastal Bohai Sea in China. J. Ocean Univ. China 2020, 19, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primpas, I.; Karydis, M. Scaling the trophic index (TRIX) in oligotrophic marine environments. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 178, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borja, A.; Prins, T.C.; Simboura, N.; Andersen, J.H.; Berg, T.; Marques, J.-C.; Neto, J.M.; Papadopoulou, N.; Reker, J.; Teixeira, H.; et al. Tales from a thousand and one ways to integrate marine ecosystem components when assessing the environmental status. Front. Mar. Sci. 2014, 1, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, G.; Li, K.; Liang, S.; Li, Y.; Su, Y.; Wang, X. Compound eutrophication index: An integrated approach for assessing ecological risk and identifying the critical element controlling harmful algal blooms in coastal seas. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, R.W.; Moran, P.W.; Frankforter, J.D. Response of algal metrics to nutrients and physical factors and identification of nutrient thresholds in agricultural streams. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 175, 397–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garmendia, M.; Borja, A.; Franco, J.; Revilla, M. Phytoplankton composition indicators for the assessment of eutrophication in marine waters: Present state and challenges within the European directives. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 66, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, M.T.P.; Brito, A.C.; Pereira, P.; Gonçalves, A.S.; Moita, M.T. A phytoplankton tool for water quality assessment in semi-enclosed coastal lagoons: Open vs. closed regimes. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 110, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloern, J.E. Our evolving conceptual model of the coastal eutrophication problem. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Series 2001, 210, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borja, A.; Bricker, S.B.; Dauer, D.M.; Demetriades, N.T.; Ferreira, J.G.; Forbes, A.T.; Hutchings, P.; Jia, X.; Kenchington, R.; Marques, J.C.; et al. Overview of integrative tools and methods in assessing ecological integrity in estuarine and coastal systems worldwide. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 1519–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricker, S.B.; Longstaff, B.; Dennison, W.; Jones, A.; Boicourt, K.; Wicks, C.; Woerner, J. Effects of nutrient enrichment in the nation’s estuaries: A decade of change. Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CEC (Council of European Communities). Council Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for community action in the field of water policy. Off. J. Eur. Commun. 2000, 327, 1–73. [Google Scholar]
- OSPAR Commission. OSPAR Integrated Report 2003 on the Eutrophication Status of the OSPAR Maritime Area Based Upon the First Application of the Comprehensive Procedure; OSPAR publication no. 189; OSPAR Commission: London, UK, 2003; ISBN 1-904426-25-5. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, G.; Xu, X.; Wang, P.; Liang, S.; Li, Y.; Su, Y.; Li, K.; Wang, X. Methodology for forecast and control of coastal harmful algal blooms by embedding a compound eutrophication index into the ecological risk index. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yu, Z.; Song, X.; Yuan, Y.; Cao, X.; Liang, Y. Application of an integrated methodology for eutrophication assessment: A case study in the Bohai Sea. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2013, 31, 1064–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, J. Reducing eutrophication risk of a reservoir by water replacement: A case study of the Qingcaosha reservoir in the Changjiang Estuary. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2018, 37, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Shen, Z.; Yu, R. Responses of a coastal phytoplankton community to increased nutrient input from the Changjiang (Yangtze) River. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 1483–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Huang, X.; Yang, B.; Dan, S.F.; Kang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Lao, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Wu, H. Composition and Distributions of Nitrogen and Phosphorus and Assessment of Eutrophication Status in the Maowei Sea. J. Ocean Univ. China 2021, 20, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.L.; Wang, Y.S.; Wang, Y.T.; Sun, F.L.; Sun, C.C.; Cheng, H.; Dong, J.-D. Seasonal and spatial variations of water quality and trophic status in Daya Bay, South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 112, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.G.; He, Q.; Kuang, W.M.; Ji, W.D. Assessment of eutrophication status in Xiamen coastal water. Oceans Limnol. 2014, 45, 710–718. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.K.; Chen, P.; Chen, H.Y. Comprehensive assessment of coastal eutrophication in Taiwan and its implications for management strategy. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 97, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.H.; Kang, W.; Xu, D.; Hui, L. Long-term changes in red tide outbreaks in Xiamen Bay in China from 1986 to 2017. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 249, 107095. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, K.; Xu, S.; Zhu, X.; Huang, W.; Liu, S. Estimation of spatial extreme sea levels in Xiamen seas by the quadrature JPM-OS method. Nat. Hazards 2021, 106, 327–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Standard GB 3097-1997; National Seawater Quality Standard, China. State Environmental Protection Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1998.
- Nunes, J.P.; Ferreira, J.G.; Bricker, S.B.; O’Loan, B.; Dabrowski, T.; Dallaghan, B.; Hawkins, A.J.S.; O’Connor, B.; O’Carroll, T. Towards an ecosystem approach to aquaculture: Assessment of sustainable shellfish cultivation at different scales of space, time and complexity. Aquaculture 2011, 315, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simboura, N.; Pavlidou, A.; Bald, J.; Tsapakis, M.; Pagou, K.; Zeri, C.; Androni, A.; Panayotidis, P. Response of ecological indices to nutrient and chemical contaminant stress factors in Eastern Mediterranean coastal waters. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 70, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scavia, D.; Bricker, S.B. Coastal eutrophication assessment in the United States. Biogeochemistry 2006, 79, 187–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.; Yu, Z.; Song, X.; Cao, X. Evaluation of fuzzy synthesis to assess the seawater eutrophication in the Changjiang estuary. Mar. Sci. 2007, 31, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, F.-L.; Yuan, Y.L.; Zhu, M.Y.; Zhao, W.; Ji, R.B.; Pan, Z.D.; Chen, S.; Wan, Z.W. Study on HAB dynamical model and HAB limitation factors for the sea area adjacent to Changjiang river estuary. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2000, 31, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Gao, S.; Zhang, T.; Liu, G. Researching Progress and Application Status of Eutrophication Evaluation Method of Seawater. Adv. Earth Sci. 2018, 33, 373–384. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Wu, H.; Chen, K.; Chen, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J. An integrated assessment method of ecological quality status in coastal waters: Taking Tong’an Bay as a case. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao 2011, 22, 1841–1848. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.X. Chlorophyll characteristics during red tides in Tong’an Bay of Xiamen. J. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2008, 4, 331–334. [Google Scholar]
- Rongkun, T.; Qing, H.; Weidong, J. Characteristics of temporal and spatial variations in chlorophyll contents of waters around Xiamen Island in 2005–2007. J. Oceanogr. Taiwan Strait 2010, 29, 342–351. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, R. Overview of hypoxia around the world. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batiuk, R.A.; Breitburg, D.L.; Diaz, R.J.; Cronin, T.M.; Secor, D.H.; Thursby, G. Derivation of habitat-specific dissolved oxygen criteria for Chesapeake Bay and its tidal tributaries. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2009, 381, S204–S215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Sun, X.; Wei, Q.; Xie, L. A new method for assessment of eutrophication status in estuarine and coastal waters off China and its application. Haiyang Xuebao 2012, 34, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Xiamen Municipal Bureau of Oceans and Fisheries, 2017. 2016 Bulletin of Xiamen Marine Environmental Status [R]. Available online: http://hyj.xm.gov.cn/lszt/hyhjxx/201710/t20171028_1819076.htm (accessed on 12 May 2017).
- Xiamen Municipal Bureau of Oceans and Fisheries, 2018. 2017 Bulletin of Xiamen Marine Eco-Environmental Status [R]. Available online: http://hyj.xm.gov.cn/lszt/hyhjxx/201806/t20180621_1887410.htm (accessed on 6 April 2018).


| Sites | Longitude | Latitude | Frequency | Layer | Areas/km2 | Ratio/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XM01 | 118.0150 | 24.5458 | Seasonal | Surface, bottom | 6.84 | 1.90 |
| XM02 | 118.0750 | 24.5525 | Seasonal | Surface | 16.28 | 4.60 |
| XM03 | 118.0717 | 24.5233 | Monthly | Surface | 10.07 | 2.80 |
| XM04 | 118.0583 | 24.4767 | Seasonal | Surface, bottom | 10.76 | 3.00 |
| XM05 | 118.0739 | 24.4394 | Seasonal | Surface, bottom | 7.80 | 2.20 |
| XM06 | 118.0081 | 24.4219 | Monthly | Surface | 20.15 | 5.70 |
| XM07 | 118.0917 | 24.4133 | Monthly | Surface | 13.15 | 3.70 |
| XM08 | 118.1481 | 24.4119 | Monthly | Surface | 16.56 | 4.70 |
| XM09 | 118.1875 | 24.4408 | Seasonal | Surface, bottom | 17.53 | 4.90 |
| XM10 | 118.2167 | 24.5000 | Seasonal | Surface, bottom | 31.91 | 9.00 |
| XM11 | 118.1975 | 24.5439 | Monthly | Surface | 25.59 | 7.20 |
| XM12 | 118.1333 | 24.5650 | Monthly | Surface | 26.93 | 7.60 |
| XM13 | 118.1639 | 24.6067 | Seasonal | Surface, bottom | 44.38 | 12.50 |
| XM14 | 118.2808 | 24.5036 | Monthly | Surface | 43.44 | 12.20 |
| XM15 | 118.3492 | 24.5192 | Seasonal | Surface, bottom | 20.59 | 5.80 |
| XM16 | 118.3850 | 24.5450 | Monthly | Surface | 31.62 | 8.90 |
| XM17 | 118.0494 | 24.4483 | Seasonal | Surface, bottom | 11.40 | 3.20 |
| Summary | 355.00 | 100.00 | ||||
| Indicators | Grading Standards and Values | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Median–Low | Median | Median–High | High | |||
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | |||
| Pressure | COD | P | ≤0.25 | >0.25, ≤0.50 | >0.50, ≤0.75 | >0.75, ≤1.00 | >1.00 |
| DIN | |||||||
| DIP | |||||||
| State | Chl-a (μg/L) | ≤5.00 | >5.00, ≤10.00 | >10.00, ≤15.00 | >15.00, ≤20.00 | >20.00 | |
| Bottom DO (mg/L) | >5.00 | >4.00, ≤5.00 | >3.00, ≤4.00 | >2.00, ≤3.00 | ≤2.00 | ||
| Red tide duration | <3 days, cumulatively and aperiodically | ≥3 days, cumulatively and aperiodically | ≥7 days, cumulatively and aperiodically or ≥3 days, continuously and periodically | ≥30 days, cumulatively and aperiodically or ≥7 days, continuously and periodically | ≥30 days, cumulatively or ≥14 days, continuously and periodically | ||
| Response | Changing rate of nutrients in future | −10.00% | <−10.00% | 0.00 | <+10.00% | +10.00% | |
| Indicators | Matrix | Status |
|---|---|---|
| P S R | Excellent | |
| P S R | Good | |
| P S R | Median | |
| P S R | Poor | |
| P S R | Worst |
| Sites | Contribution weight | Sum | Values | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indicators | XM1 | XM2 | XM3 | XM4 | XM5 | XM6 | XM7 | XM8 | XM9 | XM10 | XM11 | XM12 | XM13 | XM14 | XM15 | XM16 | XM17 | |||
| Pressure | 0.40 | 0.15 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.24 | 0.11 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.18 | 0.36 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 1.99 | 1.00 | |
| State | Chl-a | 0.29 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.19 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.24 | 0.33 | 0.10 | 0.19 | 0.04 | 2.27 | 5.00 |
| Bottom DO | 0.08 | 0.31 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.37 | 0.26 | 0.33 | 0.35 | 0.66 | 0.49 | 0.51 | 0.87 | 0.91 | 0.42 | 0.65 | 0.22 | 6.97 | 5.00 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Y.; Liu, J.-W.; Wu, J.-W.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, J.-W.; Gao, C.; Lin, Z.-Y. Comprehensive Assessment of Eutrophication in Xiamen Bay and Its Implications for Management Strategy in Southeast China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13055. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192013055
Luo Y, Liu J-W, Wu J-W, Yuan Z, Zhang J-W, Gao C, Lin Z-Y. Comprehensive Assessment of Eutrophication in Xiamen Bay and Its Implications for Management Strategy in Southeast China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(20):13055. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192013055
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Yang, Jin-Wen Liu, Jian-Wei Wu, Zheng Yuan, Ji-Wei Zhang, Chao Gao, and Zhi-Yu Lin. 2022. "Comprehensive Assessment of Eutrophication in Xiamen Bay and Its Implications for Management Strategy in Southeast China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 20: 13055. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192013055
APA StyleLuo, Y., Liu, J.-W., Wu, J.-W., Yuan, Z., Zhang, J.-W., Gao, C., & Lin, Z.-Y. (2022). Comprehensive Assessment of Eutrophication in Xiamen Bay and Its Implications for Management Strategy in Southeast China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(20), 13055. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192013055






