Evaluating the Performance of Ball-Milled Silk Fibroin Films for Simultaneous Adsorption of Eight Pharmaceuticals from Water
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Preparation of Silk Adsorbents
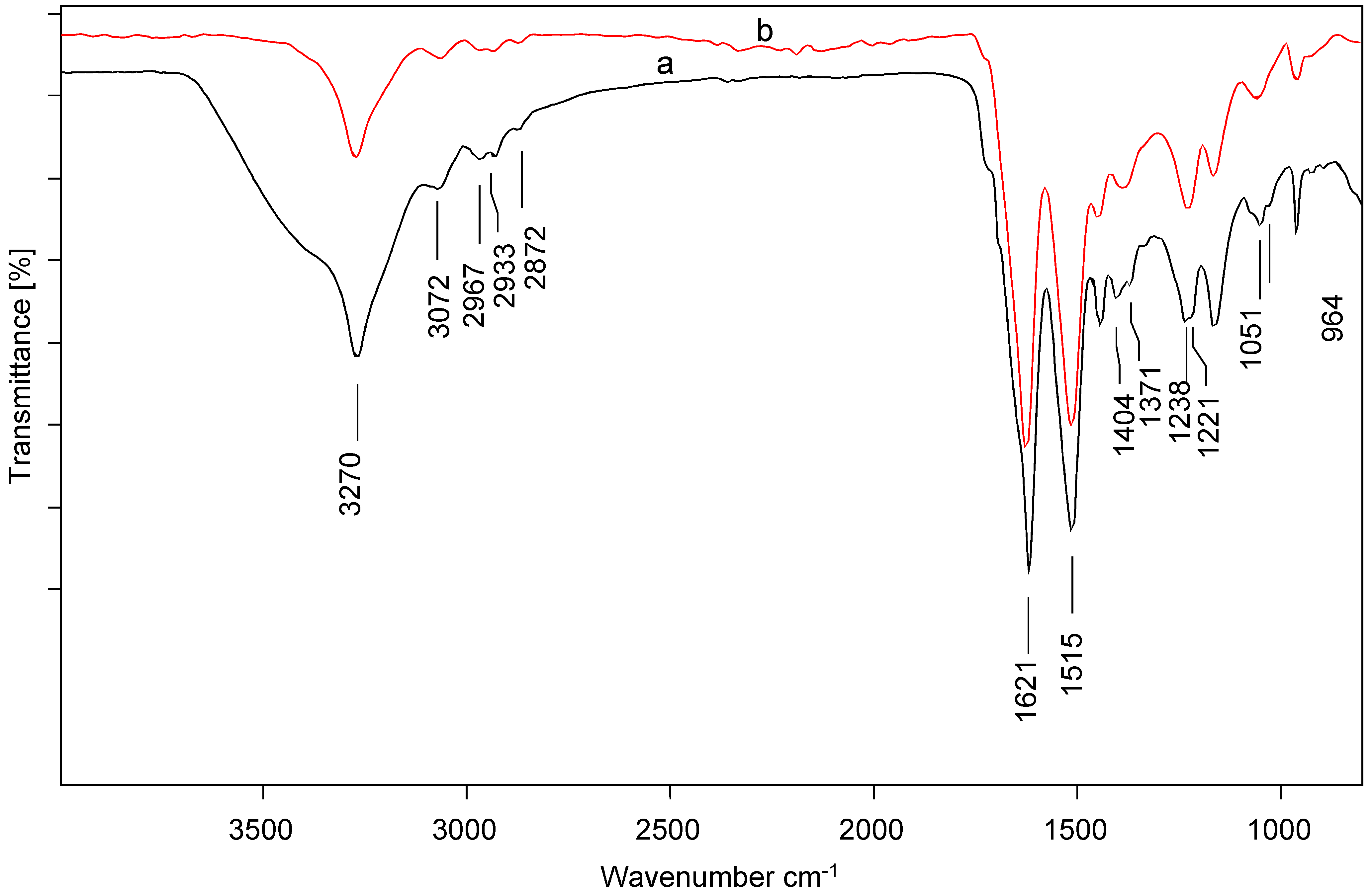
2.3. Characterization Techniques
2.4. Sampling and Sample Preparation
2.5. Batch Adsorption Experiments
2.6. Application to Real Water Samples
3. Results
3.1. Structure and Morphology of Silk Adsorbents
3.2. Effect of pH
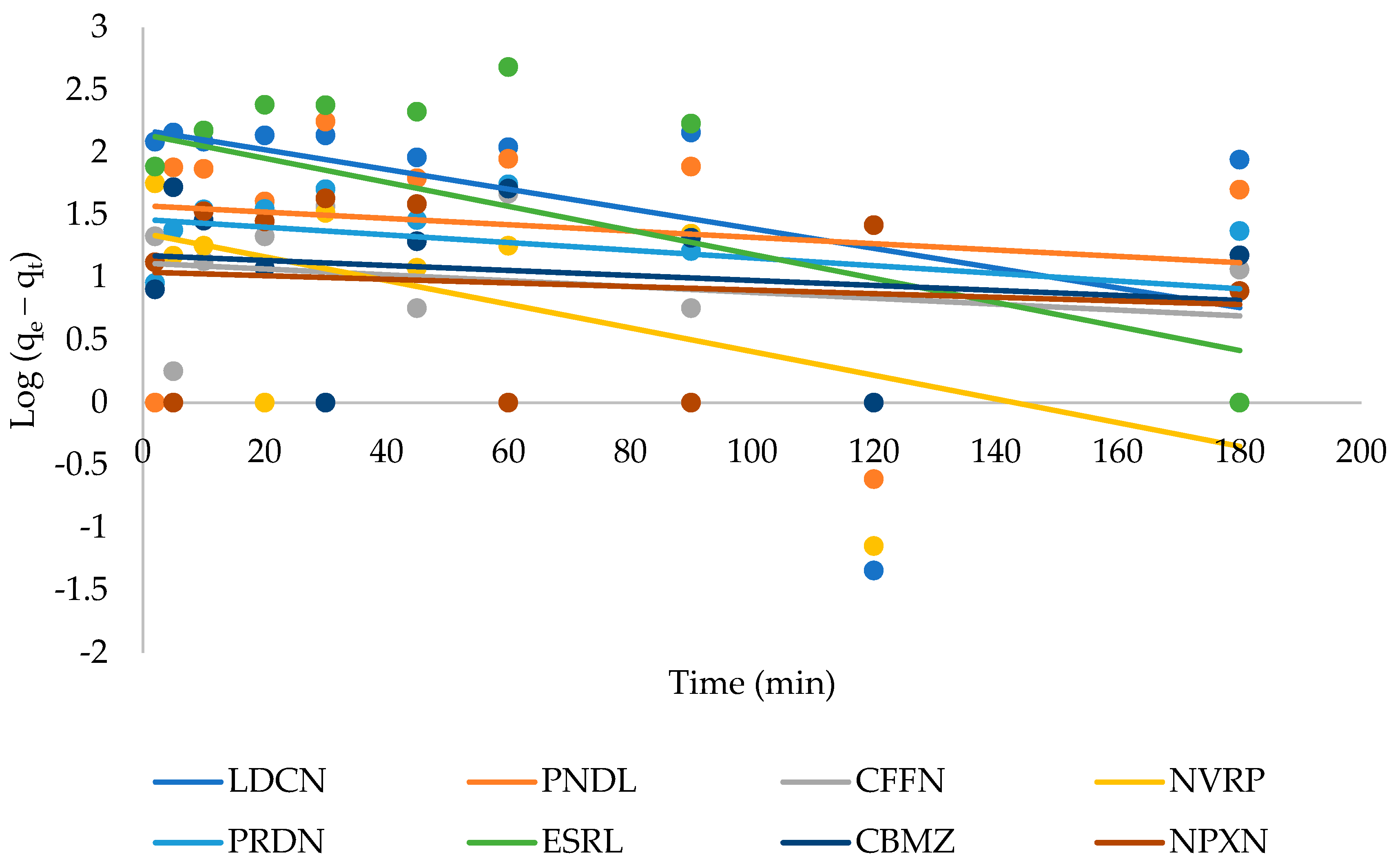
3.3. Adsorption Kinetics
3.4. Adsorption Isotherms
3.5. Thermodynamic Studies
3.6. Adsorption Mechanisms
3.7. Performance of Silk Adsorbent in Environmental Water Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shore, L.S.; Gurevitz, M.; Shemesh, M. Estrogen as an Environmental Pollutant. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1993, 51, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heberer, T.; Schmidt, K.; Stan, H.-J. Occurrence and Distribution of Organic Contaminants in the Aquatic System in Berlin. Part I: Drug Residues and Other Polar Contaminants in Berlin Surface and Groundwater. Acta Hydrochim. Et Hydrobiol. 1998, 26, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ternes, T.A. Occurrence of Drugs in German Sewage Treatment Plants and Rivers. Water Res. 1998, 32, 3245–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhuka, V.; Dube, S.; Nindi, M.M. Occurrence of Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products (PPCPs) in Wastewater and Receiving Waters in South Africa Using LC-OrbitrapTM MS. Emerg. Contam. 2020, 6, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halling-Sorensen, B.; Nielsen, S.N.; Lanzky, P.F.; Ingerslev, F.; Liitzhofl, H.C.H.; Jorgensen, S.E. Occurrence, Fate and Effects of Pharmaceutical Substances in the Environment-A Review. Chemosphere 1998, 36, 357–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K’oreje, K.O.; Vergeynst, L.; Ombaka, D.; de Wispelaere, P.; Okoth, M.; van Langenhove, H.; Demeestere, K. Occurrence Patterns of Pharmaceutical Residues in Wastewater, Surface Water and Groundwater of Nairobi and Kisumu City, Kenya. Chemosphere 2016, 149, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waleng, N.J.; Nomngongo, P.N. Occurrence of Pharmaceuticals in the Environmental Waters: African and Asian Perspectives. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2022, 4, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrie, B.; Barden, R.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. A Review on Emerging Contaminats in Wastewater and the Environment: Current Knowledge, Understudied Areas and Recommendations for Future Monitorig. Water Res. 2015, 72, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Kumar, R.; Kishor, K.; Mlsna, T.; Pittman, C.U.; Mohan, D. Pharmaceuticals of Emerging Concern in Aquatic Systems: Chemistry, Occurrence, Effects, and Removal Methods. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 3510–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Sánchez-Polo, M.; Ferro-García, M.Á.; Prados-Joya, G.; Ocampo-Pérez, R. Pharmaceuticals as Emerging Contaminants and Their Removal from Water. A Review. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 1268–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyayula, V.K.K.; Deng, S.; Mitchell, M.C.; Smith, G.B. Application of Carbon Nanotube Technology for Removal of Contaminants in Drinking Water: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 408, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, M.; Kaykioglu, G.; Belgiorno, V.; Lofrano, G. Removal of Emerging Contaminants from Water and Wastewater by Adsorption Process. In Ermerging Compounds Removal from Wastewater; Lofrano, G., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 15–37. ISBN 9789400739161. [Google Scholar]
- Gore, P.M.; Naebe, M.; Wang, X.; Kandasubramanian, B. Progress in Silk Materials for Integrated Water Treatments: Fabrication, Modification and Applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 374, 437–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Maleh, H.; Ayati, A.; Davoodi, R.; Tanhaei, B.; Karimi, F.; Malekmohammadi, S.; Orooji, Y.; Fu, L.; Sillanpää, M. Recent Advances in Using of Chitosan-Based Adsorbents for Removal of Pharmaceutical Contaminants: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 291, 125880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, T.G.; Seroto, M.B.; Chokwe, R.C.; Dube, S.; Nindi, M.M. Adsorption of Antiretroviral (ARVs) and Related Drugs from Environmental Wastewaters Using Nanofibers. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, T.G.; Dube, S.; Nindi, M.M. Removal of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) and Carbamazepine from Wastewater Using Water-Soluble Protein Extracted from Moringa Stenopetala Seeds. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3095–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Wang, Z.; Ma, H.; Yang, H.; Xu, W. Effective Removal of Dyes from Aqueous Solution Using Ultrafine Silk Fibroin Powder. Adv. Powder Technol. 2014, 25, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Zhang, D.Y.; Yao, X.H.; Feng, F.; Wu, G.H. Preparation of a Regenerated Silk Fibroin Film and its Adsorbability to Azo Dyes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campagnolo, L.; Morselli, D.; Magrì, D.; Scarpellini, A.; Demirci, C.; Colombo, M.; Athanassiou, A.; Fragouli, D. Silk Fibroin/Orange Peel Foam: An Efficient Biocomposite for Water Remediation. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2018, 3, 1800097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verma, V.K.; Subbiah, S. Sericin-coated Polymeric Microfiltration Membrane for Removal of Drug-based Micropollutants. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 94, 3625–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.K.; Subbiah, S. Prospects of Silk Sericin as an Adsorbent for Removal of Ibuprofen from Aqueous Solution. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 10142–10154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhuka, V.; Dube, S.; Nindi, M.M.; Torto, N. Fabrication and Structural Characterization of Electrospun Nanofibres from Gonometa Postica and Gonometa Rufobrunnae Regenerated Silk Fibroin. Macromol. Res. 2013, 21, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kgomo, H.; Ncube, S.; Mhuka, V.; Kebede, T.G.; Dube, S.; Nindi, M.M. A Comparative Study on the Dissolution of Argema Mimosae Silk Fibroin and Fabrication of Films and Nanofibers. Polymers 2021, 13, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teshome, A.; Raina, S.K.; Vollrath, F. Structure and Properties of Silk from the African Wild Silkmoth Gonometa Postica Reared Indoors. J. Insect Sci. 2014, 14, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aktar, J. Batch Adsorption Process in Water Treatment. In Intelligent Environmental Data Monitoring for Pollution Management; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 1–24. ISBN 9780128196717. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.L.; Zhang, Y.Q. Greener Degumming Production of Layered Sericin Peptides from a Silkworm Cocoon and Their Physicochemical Characteristics and Bioactivities in Vitro. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 121080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, D.; Sarma, N.S.; Talukdar, B.; Chetri, P.; Baruah, K.C.; Dass, N.N. Study of the Structure of Degummed Antheraea Assamensis (Muga) Silk Fibre. J. Text. Inst. 2011, 102, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkhowa, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, X. Ultra-Fine Silk Powder Preparation through Rotary and Ball Milling. Powder Technol. 2008, 185, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkhowa, R.; Wang, L.; Kanwar, J.; Wang, X. Fabrication of Ultrafine Powder from Eri Silk through Attritor and Jet Milling. Powder Technol. 2009, 191, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khulu, S.; Ncube, S.; Kgame, T.; Mavhunga, E.; Chimuka, L. Synthesis, Characterization and Application of a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer as an Adsorbent for Solid-Phase Extraction of Selected Pharmaceuticals from Water Samples. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 1287–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, T.G.; Dube, S.; Nindi, M.M. Biopolymer Electrospun Nanofibres for the Adsorption of Pharmaceuticals from Water Systems. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limousin, G.; Gaudet, J.; Charlet, L.; Szenknect, S.; Barthes, V.; Krimissa, M. Sorption Isotherms: A Review on Physical Bases, Modeling and Measurement. Appl. Geochem. 2007, 22, 249–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk Sekulic, M.; Boskovic, N.; Milanovic, M.; Grujic Letic, N.; Gligoric, E.; Pap, S. An Insight into the Adsorption of Three Emerging Pharmaceutical Contaminants on Multifunctional Carbonous Adsorbent: Mechanisms, Modelling and Metal Coadsorption. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 284, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, F.; Akbar, J.; Iqbal, S.; Noreen, S.; Bukhari, S.N.A. Study of Isothermal, Kinetic, and Thermodynamic Parameters for Adsorption of Cadmium: An Overview of Linear and Nonlinear Approach and Error Analysis. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2018, 2018, 3463724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazetta, A.L.; Martins, A.C.; Pezoti, O.; Bedin, K.C.; Beltrame, K.K.; Asefa, T.; Almeida, V.C. Synthesis and Application of N-S-Doped Mesoporous Carbon Obtained from Nanocasting Method Using Bone Char as Heteroatom Precursor and Template. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 300, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynel-Avila, H.E.; Mendoza-Castillo, D.I.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Silvestre-Albero, J. Assessment of Naproxen Adsorption on Bone Char in Aqueous Solutions Using Batch and Fixed-Bed Processes. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 209, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuerda-Correa, E.M.; Domínguez-Vargas, J.R.; Olivares-Marín, F.J.; de Heredia, J.B. On the Use of Carbon Blacks as Potential Low-Cost Adsorbents for the Removal of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs from River Water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, Z.; Jeon, J.; Jhung, S.H. Adsorptive Removal of Naproxen and Clofibric Acid from Water Using Metal-Organic Frameworks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 209–210, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.S.; Strock, T.J.; Sarmah, A.K.; Rao, P.S.C. Sorption and Dissipation of Testosterone, Estrogens, and Their Primary Transformation Products in Soils and Sediment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4098–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamato, H.; Liljestrand, H.M.; Shimizu, Y.; Morita, M. Effects of Physical—Chemical Characteristics on Sorption of Selected Endocrine Disruptors by Dissolved Organic Matter Surrogates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 2646–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeola, A.O.; de Lange, J.; Forbes, P.B.C. Adsorption of Antiretroviral Drugs, Efavirenz and Nevirapine from Aqueous Solution by Graphene Wool: Kinetic, Equilibrium, Thermodynamic and Computational Studies. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2021, 6, 100157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazri, H.; Ghorbel-Abid, I.; Kalfat, R.; Trabelsi-Ayadi, M. Removal of Ibuprofen, Naproxen and Carbamazepine in Aqueous Solution onto Natural Clay: Equilibrium, Kinetics, and Thermodynamic Study. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 3031–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailler, R.; Gasperi, J.; Coquet, Y.; Derome, C.; Buleté, A.; Vulliet, E.; Bressy, A.; Varrault, G.; Chebbo, G.; Rocher, V. Removal of emerging micropollutants from wastewater by activated carbon adsorption: Experimental study of different activated carbons and factors influencing the adsorption of micropollutants in wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1102–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Compound | Acronym | Class | CAS | Molecular Weight (g mol−1) | Log Kow | pKa | Structures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pindolol | PNDL | β-blocker | 13523-86-9 | 248.3 | 1.75 | 9.25 |  |
| Lidocaine | LDCN | Anesthetic | 137-58-6 | 234.3 | 2.26 | 7.86 |  |
| Caffeine | CFN | Stimulant | 58-08-2 | 194.2 | −0.07 | 10.4 |  |
| Nevirapine | NVRP | Antiviral | 129618-40-2 | 266.3 | 3.89 | 2.8 | 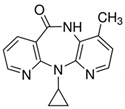 |
| Prednisolone | PRDN | Steroid | 50-24-8 | 360.4 | 1.62 | 2.912.59 | 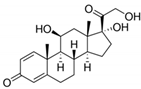 |
| Estriol | ESTR | Steroid | 50-27-1 | 288.4 | 2.45 | 10.4 |  |
| Carbamazepine | CARB | Anti-epileptic | 298-46-4 | 236.3 | 2.45 | 13.95 |  |
| Naproxen | NPXN | NSAID | 22204-53-1 | 230.2 | 3.18 | 4.15 |  |
| Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceuticals | μg g−1 | μg g−1 | min−1 | R2 | μg g−1 | min−1 | min | μg g−1 min−1 | R2 |
| Lidocaine | 508 | 151 | 1.8 × 10−2 | 0.179 | 435 | 8.4 × 10−4 | 2.7 | 158 | 0.979 |
| Pindolol | 331 | 38 | 5.8 × 10−3 | 0.024 | 294 | 5.7 × 10−4 | 6.0 | 49 | 0.965 |
| Caffeine | 76 | 13 | 5.4 × 103 | 0.062 | 68 | 1.4 × 10−3 | 10.4 | 7 | 0.832 |
| Nevirapine | 164 | 23 | 2.2 × 10−2 | 0.367 | 135 | 1.7 × 10−3 | 4.4 | 31 | 0.985 |
| Prednisolone | 355 | 29 | 7.1 × 10−3 | 0.123 | 333 | 2.3 × 10−3 | 1.3 | 250 | 0.996 |
| Estriol | 750 | 140 | 2.2 × 10−2 | 0.246 | 769 | 1.3 × 10−4 | 10.4 | 74 | 0.962 |
| Carbamazepine | 281 | 15 | 4.6 × 10−3 | 0.036 | 270 | 3.7 × 10−3 | 1.1 | 238 | 0.996 |
| Naproxen | 375 | 11 | 3.3 × 10−3 | 0.014 | 370 | 2.7 × 10−3 | 1.0 | 370 | 0.998 |
| Langmuir | Freundlich | Temkin | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical | μg g−1 | L μg−1 | R2 | R2 | J mol−1 | L μg−1 | R2 | ||
| Lidocaine | 400 | 2.3 × 10−3 | 0.503 | 2.0 | 1.2 × 10−4 | 0.985 | 8.0 | 2.1 × 10−3 | 0.958 |
| Pindolol | 556 | 4.5 × 10−4 | 0.992 | 0.73 | 1.6 | 0.998 | 20.4 | 4.5 × 10−3 | 0.965 |
| Caffeine | 40 | 4.2 × 10−3 | 0.934 | 0.43 | 2.9 × 10−3 | 0.908 | 16.9 | 154 | 0.934 |
| Nevirapine | 769 | 8.9 × 10−4 | 0.991 | 0.71 | 1.2 | 0.989 | 17.8 | 51 | 0.937 |
| Prednisolone | 500 | 3.9 × 10−2 | 0.751 | 1.3 | 1.0 | 0.976 | 3.4 | 1.6 × 10−2 | 0.883 |
| Estriol | 5000 | 1.2 × 10−3 | 0.994 | 0.89 | 8.9 | 0.998 | 2.2 | 1.4 × 10−2 | 0.996 |
| Carbamazepine | 5000 | 4.0 × 10−4 | 0.983 | 0.99 | 2.4 | 0.988 | 5.3 | 1.3 × 10−2 | 0.922 |
| Naproxen | 1429 | 2.0 × 10−3 | 0.880 | 1.54 | 5.0 | 0.908 | 2.4 | 2.5 × 10−1 | 0.955 |
| Phamaceuticals | R2 | (KJ mol−1) | (KJ mol−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 288 K | 298 K | 318 K | ||||
| Lidocaine | 0.926 | −3.5 | −1.1 | 0.8 | −42.9 | −0.1 |
| Pindolol | 0.914 | −4.1 | −3.9 | 2.2 | −68.9 | −0.2 |
| Caffeine | 0.991 | 2.1 | 3.8 | 6.3 | −37.4 | −0.1 |
| Nevirapine | 0.995 | 0.48 | 2.4 | 7.5 | −68.0 | −0.2 |
| Prednisolone | 0.995 | −4.4 | −4.3 | −4.1 | −7.4 | −0.01 |
| Estriol | 0.957 | −3.9 | −3.4 | −3.0 | −12.3 | −0.03 |
| Carbamazepine | 0.938 | −3.2 | −1.2 | −1.1 | −24.6 | −0.07 |
| Naproxen | 0.933 | −3.2 | −1.3 | −1.1 | 97.2 | 0.3 |
| Pharmaceuticals | Adsorbent | Water Type | Adsorbent Dose | Removal Efficiency/Adsorption Capacity | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbamazepine | MIP | Dam water | 10 mg L−1 | 418 ng mg−1 | [30] |
| Moringa protein /PVA nanofibersseed | Ultrapure water | 10 mg | 0.0353 mg g−1 | [31] | |
| Clay | Ultrapure water | 25 mg | 32 mg g−1 | [42] | |
| PAC (wood) | Wastewater | 10 mg/L | 63% | [43] | |
| PAC (Coal) | Wastewater | 44% | |||
| PAC (Peat) | Wastewater | 48% | |||
| PAC (Coconut) | Wastewater | 16% | |||
| Silk film powder | River water | 10 mg | 48% | Current study | |
| Wastewater inf | 50% | ||||
| Wastewater eff | 53% | ||||
| Nevirapine | MIP | Dam water | 10 mg | 299 ng mg−1 | [30] |
| Mondia whitei/PVA nanofibers | Wastewater Inf | 40 mg | 174 mg g−1 | [15] | |
| Wastewater eff | 189 mg g−1 | ||||
| Deionized water | 201 mg g−1 | ||||
| Naproxen | Clay | Ultrapure water | 25 mg | 37 mg g−1 | [42] |
| Lidocaine | Mondia whitei/PVA nanofibers | Wastewater Inf | 40 mg | 61 mg g−1 | [15] |
| Wastewater eff | 5 mg g−1 | ||||
| Deionized water | 73 mg g−1 | ||||
| Prednisolone | Mondia whitei/PVA nanofibers | Wastewater Inf | 40 mg | 113 mg g−1 | [15] |
| Wastewater eff | 154 mg g−1 | ||||
| Deionized water | 174 mg g−1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kgomo, H.; Dube, S.; Nindi, M.M. Evaluating the Performance of Ball-Milled Silk Fibroin Films for Simultaneous Adsorption of Eight Pharmaceuticals from Water. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192214922
Kgomo H, Dube S, Nindi MM. Evaluating the Performance of Ball-Milled Silk Fibroin Films for Simultaneous Adsorption of Eight Pharmaceuticals from Water. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(22):14922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192214922
Chicago/Turabian StyleKgomo, Hlobsile, Simiso Dube, and Mathew Muzi Nindi. 2022. "Evaluating the Performance of Ball-Milled Silk Fibroin Films for Simultaneous Adsorption of Eight Pharmaceuticals from Water" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 22: 14922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192214922
APA StyleKgomo, H., Dube, S., & Nindi, M. M. (2022). Evaluating the Performance of Ball-Milled Silk Fibroin Films for Simultaneous Adsorption of Eight Pharmaceuticals from Water. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(22), 14922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192214922








