“Digital Dividend” or “Digital Divide”: What Role Does the Internet Play in the Health Inequalities among Chinese Residents?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Research Hypothesis
2.1. Literature Review
2.2. Research Hypothesis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Source and Sample Selection
3.2. Variables Selection
3.2.1. Explained Variable
3.2.2. Explanatory Variable
3.2.3. Mediating Variables
3.2.4. Control Variable
3.3. Research Methods
3.3.1. Basic Model
3.3.2. Mediating Effect Model
3.3.3. Treatment Effect Model
3.3.4. Quantile Regression
4. Results
4.1. Descriptive Statistics
4.2. Benchmark Regression Results
4.3. Robustness Test
4.3.1. Change the Variables
4.3.2. Endogenous Test
4.3.3. Selection Error Test
4.3.4. Propensity Score Matching
4.4. Test of Mediating Effect
4.5. Heterogeneity Analysis
4.5.1. Heterogeneity Analysis of Different Groups
4.5.2. Quantile Regression
4.5.3. Internet Access Opportunities Differences
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, C.; Zhan, Y.; Du, G. Can Value-Added Tax Incentives of New Energy Industry Increase Firm’s Profitability? Evidence from Financial Data of China’s Listed Companies. Energy Econ. 2020, 86, 104654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deaton, A. Health, Inequality, and Economic Development. J. Econ. Lit. 2003, 41, 113–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yu, Y. Increasing Health Inequality in China: An Empirical Study with Ordinal Data. J. Econ. Inequal. 2016, 14, 41–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yan, F.; Hoekstra, E.J.; Zhuo, J. One Country, Two Worlds—The Health Disparity in China. Glob. Public Health 2012, 7, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Fu, H. China’s Health Care System Reform: Progress and Prospects. Int. J. Health Plann. Manag. 2017, 32, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Liu, C.P. Research on theIntegration of Medical Insurance for Urban and Rural Residents, Health and Health Inequality for the Rural Elderly. Soc. Secur. Stud. 2022, 3, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.J.; Yang, J. The Impact of the Implementation of Hierarchical Medical Policy on Health Inequality among the Chinese Elderly. Soc. Secur. Stud. 2022, 1, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, P.; Sun, B. Can the Internet Narrow Regional Economic Disparities? Reg. Stud. 2022, 56, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Luo, P. Does the Internet Promote China’s Total Factor Productivity. Manag. World 2016, 10, 34–49. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhong, K. Digital Economy Development, Industrial Structure Upgrading and Green Total Factor Productivity: Empirical Evidence from China’s Cities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurseth, P.B. The Effect of the Internet on Economic Growth: Counter-Evidence from Cross-Country Panel Data. Econ. Lett. 2018, 172, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Aaron Gulliver, T.; Le, K.N. BP Neural Network-Based ABEP Performance Prediction for Mobile Internet of Things Communication Systems. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 16025–16041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celbis, M.G.; de Crombrugghe, D. Internet Infrastructure and Regional Convergence: Evidence from Turkey. Pap. Reg. Sci. 2018, 97, 387–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J. Regional Inequalities in the Impact of Broadband on Productivity: Evidence from Brazil. Recer. Dipòs. Recer. Catalunya 2015, 56177. [Google Scholar]
- Pickett, K.E.; Wilkinson, R.G. Income Inequality and Health: A Causal Review. Soc. Sci. Med. 2015, 128, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakwani, N.; Wagstaff, A.; van Doorslaer, E. Socioeconomic Inequalities in Health: Measurement, Computation, and Statistical Inference. J. Econom. 1997, 77, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Doorslaer, E.; Jones, A.M. Inequalities in Self-Reported Health: Validation of a New Approach to Measurement. J. Health Econ. 2003, 22, 61–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, M.; Wren-Lewis, L. Accounting for Changes in Income Inequality: Decomposition Analyses for the UK, 1978–2008. Oxf. Bull. Econ. Stat. 2016, 78, 289–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erreygers, G. Correcting the Concentration Index. J. Health Econ. 2009, 28, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobus, M.; Miłoś, P. Inequality Decomposition by Population Subgroups for Ordinal Data. J. Health Econ. 2012, 31, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakwani, N. The Relative Deprivation Curve and Its Applications. J. Bus. Econ. Stat. 2012, 2, 384–394. [Google Scholar]
- Nawaz, S. Energy Poverty, Climate Shocks, and Health Deprivations. Energy Econ. 2021, 100, 105338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi, V.; Olulana, O.; Avula, V.; Chaudhary, D.; Khan, A.; Shahjouei, S.; Li, J.; Zand, R. Racial, Economic, and Health Inequality and COVID-19 Infection in the United States. J. Racial Ethn. Health Disparities 2021, 8, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, S. Income Inequality and Individual Health Status: Evidence from India. J. Quant. Econ. 2021, 19, 269–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M. Social Determinants of Health and Related Inequalities: Confusion and Implications. Front. Public Health 2019, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.L. Influence of Poverty on Older Adults’ Mental Health and the Differences between Urban and Rural Areas: Based on the Dataset from CLASS. Lanzhou Acad. J. 2020, 7, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbulut-Yuksel, M. War during Childhood: The Long Run Effects of Warfare on Health. J. Health Econ. 2017, 53, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelsen, S.; Stratmann, T. Effects of Prenatal and Early Life Malnutrition: Evidence from the Greek Famine. J. Health Econ. 2011, 30, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almond, D. Is the 1918 Influenza Pandemic over? Long-Term Effects of in Utero Influenza Exposure in the Post-1940 US Population. J. Polit. Econ. 2006, 114, 672–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Ebi, K. Preventing and Mitigating Health Risks of Climate Change. Environ. Res. 2019, 174, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Wel, K.A.; Saltkjel, T.; Chen, W.-H.; Dahl, E.; Halvorsen, K. European Health Inequality through the ‘Great Recession’: Social Policy Matters. Sociol. Health Illn. 2018, 40, 750–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.L.; Wu, Z.M. The Long-Term Consequences of Early Life Misfortune on Health Inequality. Sociol. Stud. 2018, 33, 166–194. [Google Scholar]
- Silbersdorff, A.; Lynch, J.; Klasen, S.; Kneib, T. Reconsidering the Income-Health Relationship Using Distributional Regression. Health Econ. 2018, 27, 1074–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamadi, E.; Olyaee Manesh, A.; Takian, A.; Majdzadeh, R.; Hosseinzadeh Lotfi, F.; Sharafi, H.; Jowett, M.; Kiani, M.M.; Hosseini Qavam Abadi, L.; Fazaeli, A.a.; et al. Technical Efficiency in Health Production: A Comparison between Iran and Other Upper Middle-Income Countries. Health Policy Technol. 2020, 9, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q. Analysis of the Relevant Factors Influencing Teenagers’ Physical Exercise Habits. Front. Educ. Res. 2019, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Xindong, Z. How Does Education Affect the Health Level of the Elderly in China? J. Financ. Econ. 2020, 46, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranchor, A.V.; Bouma, J.; Sanderman, R. Vulnerability and Social Class: Differential Patterns of Personality and Social Support over the Social Classes. Personal. Individ. Differ. 1996, 20, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Geng, L. An Integrated Analysis of Social, Economic, and Environmental Indicators’ Effects on Public Health and Health Inequality Globally: From the Perspective of Vulnerability. Soc. Indic. Res. 2022, 162, 1261–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davillas, A.; Jones, A.M.; Benzeval, M. The Income-Health Gradient: Evidence from Self-Reported Health and Biomarkers in Understanding Society. In Panel Data Econometrics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 709–741. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Y.; Liu, J.; Lu, Z.-N.; Shi, R.; Wu, H. Impact of Income Inequality and Fiscal Decentralization on Public Health: Evidence from China. Econ. Model. 2021, 94, 934–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Lee, J. Decomposing Income-Related Inequalities in Self-Reported Depression and Self-Rated Health among Married Immigrants in South Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2019, 16, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Lyu, S.; Li, C.; Coyte, P.C. The Contribution of Urban and Rural Resident Basic Medical Insurance to Income-Related Inequality in Depression among Middle-Aged and Older Adults: Evidence from China. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 293, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwosu, C.O.; Oyenubi, A. Income-Related Health Inequalities Associated with the Coronavirus Pandemic in South Africa: A Decomposition Analysis. Int. J. Equity Health 2021, 20, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stormacq, C.; Van den Broucke, S.; Wosinski, J. Does Health Literacy Mediate the Relationship between Socioeconomic Status and Health Disparities? Integrative Review. Health Promot. Int. 2019, 34, e1–e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, J.M.; Sleeman, K.E.; Leniz, J.; Wilson, R.; Higginson, I.J.; Verne, J.; Maddocks, M.; Murtagh, F.E. Socioeconomic Position and Use of Healthcare in the Last Year of Life: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS Med. 2019, 16, e1002782. [Google Scholar]
- Dieker, A.C.; IJzelenberg, W.; Proper, K.I.; Burdorf, A.; Ket, J.C.; van der Beek, A.J.; Hulsegge, G. The Contribution of Work and Lifestyle Factors to Socioeconomic Inequalities in Self-Rated Health–a Systematic Review. Scand. J. Work. Environ. Health 2019, 45, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, G.; Heckman, J.; Urzua, S. The Education-Health Gradient. Am. Econ. Rev. 2010, 100, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.D.; Fang, X.M. Community Sports Infrastructure, Health Status and Inequality among the Middle-aged and Elderly: Evidence from China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study. Stud. Lab Econ. 2018, 6, 119–144. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Liu, W. Does Air Pollution Affect Public Health and Health Inequality? Empirical Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 203, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Qin, L. Healthy Migrant and Salmon Bias Hypotheses: A Study of Health and Internal Migration in China. Soc. Sci. Med. 2014, 102, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.A.; Zhou, Z.; Fang, Y.; Shi, L. The Digital Divide and Health Disparities in China: Evidence from a National Survey and Policy Implications. J. Med. Internet Res. 2017, 19, e7786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naslund, J.A.; Bondre, A.; Torous, J.; Aschbrenner, K.A. Social Media and Mental Health: Benefits, Risks, and Opportunities for Research and Practice. J. Technol. Behav. Sci. 2020, 5, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, R.; Wu, W.; Shang, X.; Liu, M. Relationship between Internet Health Information and Patient Compliance Based on Trust: Empirical Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2018, 20, e9364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, W.; Amuta, A.O.; Jeon, K.C. Health Information Seeking in the Digital Age: An Analysis of Health Information Seeking Behavior among US Adults. Cogent Soc. Sci. 2017, 3, 1302785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rains, S.A. Health at High Speed: Broadband Internet Access, Health Communication, and the Digital Divide. Commun. Res. 2008, 35, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brod, C. Technostress: The Human Cost of the Computer Revolution; Addison-Wesley: Reading, MA, USA, 1984; pp. 201–226. [Google Scholar]
- Allcott, H.; Braghieri, L.; Eichmeyer, S.; Gentzkow, M. The Welfare Effects of Social Media. Am. Econ. Rev. 2020, 110, 629–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, L.R.; Brett, J.M. Mediators, Moderators, and Tests for Mediation. J. Appl. Psychol. 1984, 69, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, C.M.; Kenny, D.A. Process Analysis: Estimating Mediation in Treatment Evaluations. Eval. Rev. 1981, 5, 602–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, J.L. Estimation of Monotonic Regression Models under Quantile Restrictions. Nonparametr. Semiparametr. Methods Econom. 1991, 357–384. [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy, S.; Koenker, R. The Gaussian Hare and the Laplacian Tortoise: Computability of Squared-Error versus Absolute-Error Estimators. Stat. Sci. 1997, 12, 279–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, L.H.; Gant, L.M. In Defense of the Internet: The Relationship between Internet Communication and Depression, Loneliness, Self-Esteem, and Perceived Social Support. Rev. Psicol. Trab. Las Organ. 2004, 37, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

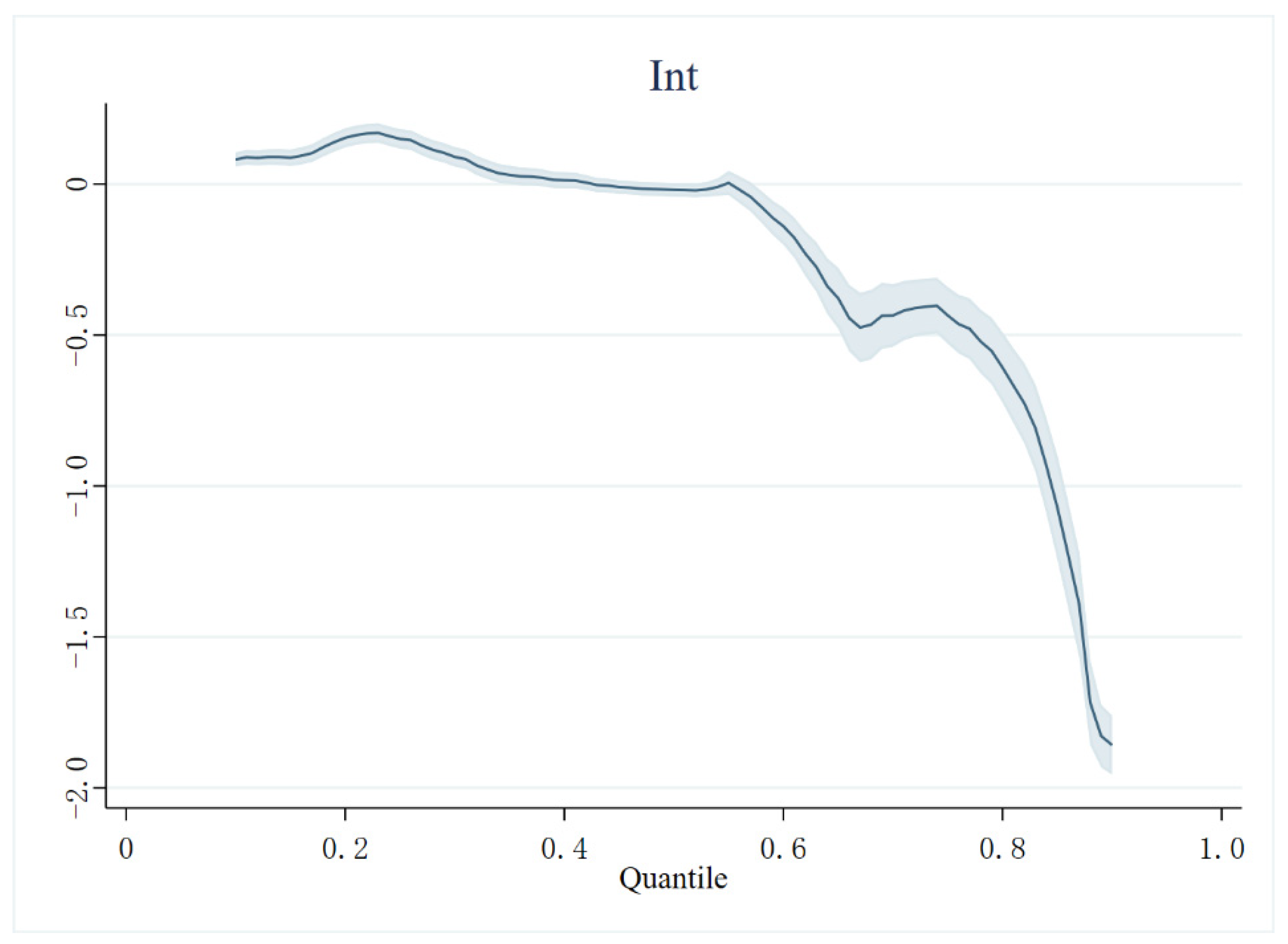
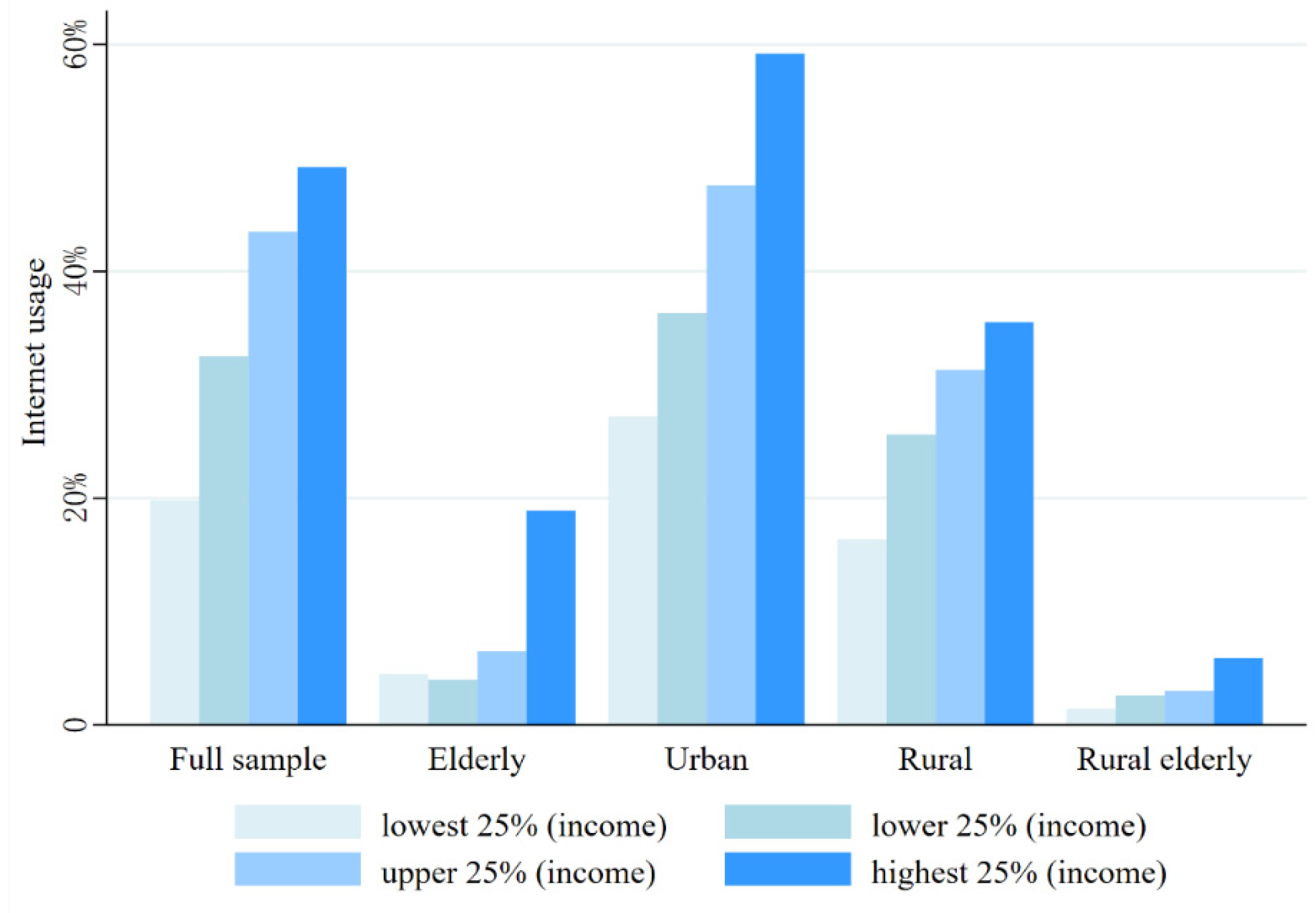
| Variables Type | Variable | Variable Description | Full Sample | Internet (Yes) | Internet (No) | Diff | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Sd | Mean | Mean | Mean | |||
| Explained variable | HI | Calculated according to Formula (2) | 2.217 | 2.052 | 1.620 | 2.540 | −0.920 *** |
| Explanatory variable | Int | 1 = yes, 0 = no | 0.351 | 0.477 | |||
| Mediating variables | Ini | Income inequality level | 0.394 | 0.105 | 0.383 | 0.401 | −0.018 *** |
| Dep | CES-D scale score | 3.902 | 3.432 | 3.564 | 4.084 | −0.520 *** | |
| Exe | Number of physical exercises per week | 2.310 | 3.197 | 2.421 | 2.251 | 0.170 *** | |
| Control variables | Age | Resident age | 49.058 | 15.230 | 37.581 | 55.256 | −17.675 *** |
| Urb | 1 = yes, 0 = no | 0.472 | 0.499 | 0.619 | 0.393 | 0.225 *** | |
| Gen | 1 = male, 0 = female | 0.483 | 0.500 | 0.507 | 0.470 | 0.037 *** | |
| Mar | 1 = married, 0 = unmarried | 0.843 | 0.363 | 0.765 | 0.886 | −0.120 *** | |
| Reg | 1 = agricultural household registration, 0 = else | 0.719 | 0.450 | 0.587 | 0.790 | −0.203 *** | |
| Pin | The logarithm of per capita household net income | 8.865 | 1.734 | 9.325 | 8.616 | 0.708 *** | |
| Fam | Number of family members | 4.212 | 1.963 | 4.242 | 4.195 | 0.046 ** | |
| GDP | Logarithm of GDP per capita | 10.732 | 0.418 | 10.802 | 10.694 | 0.108 *** | |
| Urr | Urban population ratio | 0.575 | 0.123 | 0.596 | 0.565 | 0.031 *** | |
| Gov | Financial revenue/GDP | 0.109 | 0.030 | 0.111 | 0.109 | 0.002 *** | |
| Fin | Logarithm of fiscal expenditure | 8.607 | 0.411 | 8.646 | 8.586 | 0.060 *** | |
| Med | Number of medical institutions/Permanent population | 7.627 | 2.606 | 7.385 | 7.758 | −0.372 *** | |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Int | −0.920 *** | −0.193 *** | −0.185 *** | −0.142 *** | −0.187 *** |
| (−49.646) | (−8.499) | (−8.095) | (−6.092) | (−7.803) | |
| Age | 0.038 *** | 0.037 *** | 0.038 *** | 0.037 *** | |
| (54.993) | (51.789) | (52.424) | (49.785) | ||
| Urb | −0.078 *** | −0.076 *** | −0.079 *** | −0.074 *** | |
| (−3.949) | (−3.807) | (−3.943) | (−3.631) | ||
| Gen | −0.448 *** | −0.448 *** | −0.454 *** | −0.457 *** | |
| (−26.059) | (−26.129) | (−26.489) | (−26.772) | ||
| Mar | −0.037 | −0.006 | −0.001 | 0.020 | |
| (−1.522) | (−0.264) | (−0.034) | (0.816) | ||
| Reg | 0.098 *** | 0.085 *** | 0.101 *** | 0.084 *** | |
| (4.398) | (3.761) | (4.384) | (3.566) | ||
| Pin | −0.042 *** | −0.043 *** | −0.037 *** | ||
| (−8.243) | (−8.400) | (−7.210) | |||
| Fam | −0.025 *** | −0.027 *** | −0.037 *** | ||
| (−5.493) | (−5.793) | (−7.736) | |||
| GDP | −0.057 | −0.434 | |||
| (−0.888) | (−1.454) | ||||
| Urr | −0.731 *** | 0.010 | |||
| (−3.550) | (0.011) | ||||
| Gov | 0.183 | 1.436 | |||
| (0.391) | (0.707) | ||||
| Fin | −0.145 *** | 0.141 | |||
| (−4.264) | (0.420) | ||||
| Med | −0.058 *** | −0.008 | |||
| (−11.518) | (−0.148) | ||||
| Provincial-fixed effect | YES | ||||
| Year-fixed effect | YES | ||||
| Constant | 2.540 *** | 0.619 *** | 1.143 *** | 3.781 *** | 4.477 |
| (231.393) | (12.136) | (15.371) | (7.269) | (1.542) | |
| Observations | 51,375 | 51,375 | 51,375 | 51,375 | 51,375 |
| R-squared | 0.046 | 0.108 | 0.110 | 0.112 | 0.120 |
| Variables | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Change Variable | IV | TEM | PSM | |
| Internet time | −0.002 ** | |||
| (−2.408) | ||||
| Int | −0.975 *** | −0.922 *** | −0.920 *** | |
| (−4.690) | (−9.131) | (−49.646) | ||
| Control variables | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Constant | 3.899 | 7.559 ** | 5.025 * | |
| (1.286) | (2.391) | (1.734) | ||
| Observations | 51,375 | 51,375 | 51,375 | 51,375 |
| R-squared | 0.119 | 0.101 |
| Variables | (10) | (11) | (12) | (13) | (14) | (15) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ini | HI | Dep | HI | Exe | HI | |
| Int | −0.020 *** | −0.173 *** | −0.078 ** | −0.173 *** | 0.599 *** | −0.170 *** |
| (−16.839) | (−7.210) | (−2.080) | (−7.565) | (16.233) | (−7.087) | |
| Ini | 0.698 *** | |||||
| (7.770) | ||||||
| Dep | 0.168 *** | |||||
| (66.732) | ||||||
| Exe | −0.028 *** | |||||
| (−10.136) | ||||||
| Control variables | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Provincial-fixed effect | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Year-fixed effect | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Constant | 2.363 *** | 2.827 | 13.352 ** | 2.233 | 16.497 *** | 4.942 * |
| (16.577) | (0.971) | (2.513) | (0.802) | (3.549) | (1.703) | |
| Observations | 51,375 | 51,375 | 51,375 | 51,375 | 51,375 | 51,375 |
| R-squared | 0.508 | 0.121 | 0.110 | 0.190 | 0.089 | 0.122 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, D.; Zhang, G.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P. “Digital Dividend” or “Digital Divide”: What Role Does the Internet Play in the Health Inequalities among Chinese Residents? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215162
Zhang D, Zhang G, Jiao Y, Wang Y, Wang P. “Digital Dividend” or “Digital Divide”: What Role Does the Internet Play in the Health Inequalities among Chinese Residents? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(22):15162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215162
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Dongling, Guoqing Zhang, Yuxin Jiao, Yanyan Wang, and Pengnian Wang. 2022. "“Digital Dividend” or “Digital Divide”: What Role Does the Internet Play in the Health Inequalities among Chinese Residents?" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 22: 15162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215162
APA StyleZhang, D., Zhang, G., Jiao, Y., Wang, Y., & Wang, P. (2022). “Digital Dividend” or “Digital Divide”: What Role Does the Internet Play in the Health Inequalities among Chinese Residents? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(22), 15162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215162







