Abstract
Our aim was to assess the impact of combined orthodontic–surgical treatment on patients’ oral health-related quality of life (OHRQoL) according to type of dentofacial deformities, by synthesizing the available evidence. Methods: Search was conducted in the PubMed, Embase/MEDLINE, Scopus, and Cochrane databases. The eligibility criteria were studies that measured OHRQoL before–after orthognathic surgery, with results disaggregated by Class II and III. Two researchers independently performed the selection process, data extraction, and methodological quality assessment. Meta-analysis of the standard mean differences (SMD) was performed using random effect models. Results: The search identified 1047 references. Thirteen studies met the inclusion criteria, and four were included in the meta-analysis. The SMD of OHRQL global score showed large improvement 4–7 months after surgery in Class II and III patients (2.09, 95% CI 0.68 to 3.49 and 1.96, 95% CI 1.22 to 2.70, respectively). The sensitivity analyses, excluding studies with weak methodological quality, showed that Class III patients’ improvement in functional limitation was significantly higher than in Class II patients (SMD 0.57, 95% CI 0.12–1.02). Conclusions: There is not enough evidence to support differences between Class II and III patients in the OHRQoL impact after orthognathic surgery, but findings suggest lower improvement of some domains in Class II patients.
1. Introduction
Dentofacial deformities refer to significant deviations from normal proportions of the maxillo-mandibular complex, being one of the oral health problems most perceived by the population. This condition affects the quality of social relationships, self-esteem [1,2], and oral health-related quality of life (OHRQoL) [2,3], which has been defined as a “multidimensional construct that includes a subjective evaluation of the individual’s oral health, functional well-being, emotional well-being, expectations and satisfaction with care, and sense of self” [3].
The combination of orthodontic and orthognathic surgery is the most established treatment to correct Class II and Class III dentofacial deformities [4,5,6,7]. The main objective of orthognathic surgery is to correct the facial skeleton, to facilitate malocclusion orthodontic therapy. Interest from traditional clinical outcomes of orthognathic surgery (aesthetic, functional, planning, surgical technique, and complications) [8,9,10,11] has moved to OHRQoL since the beginning of the 21st century to incorporate the patients’ perspective [12,13,14]. Achieving a better quality of life in patients with dentofacial deformities is one of the objectives of the treatment, based mainly on the need to improve aspects related to aesthetic, functional, and psychosocial factors [13,15,16].
The first systematic review [17] about quality of life assessment in patients with dentofacial deformities undergoing orthognathic surgery, published in 2013, described the different motivations and perceptions of patients towards surgical treatment, the methods and instruments used to measure quality of life and psychosocial aspects, but not the changes between before and after surgery. Subsequently, five systematic reviews, two with narrative synthesis [18,19], and the other three with quantitative synthesis through meta-analysis [20,21,22], have focused on this outcome, showing OHRQoL improvement. None of these systematic reviews stratified by type of dentofacial deformity, despite consistently reported differences between Class II and Class III patients [15,23,24,25].
The aim of this study was to assess the impact of combined orthodontic–surgical treatment on OHRQoL in patients with dentofacial deformities of Class II and Class III by synthesizing the available evidence through a systematic review with meta-analysis.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
A systematic review was conducted in accordance with the Cochrane Handbook for the Systematic Review of Interventions [26] and reported according to the guidelines of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA 2020 statement) [27] (Supplementary Table S2). The study was registered at the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) from the National Institute for Health Research database (www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero) (accessed on 17 September 2021) with registration number CRD42019116092.
Following the PICO (patient, intervention, comparison, outcome) framework, our research question was: In patients with dentofacial deformities of Class II and Class III (P), does the combined orthodontic–surgical treatment (I) have an impact (C) on their oral health-related quality of life (O)? Impact here refers to the comparison between before and after treatment, with or without control group.
2.2. Elegibility Criteria
Inclusion criteria: randomized and nonrandomized clinical trials with or without control group, in patients with dentofacial deformities submitted to combined orthodontic–surgical treatment, that measured OHRQoL before and after surgery; including patients over 15 years old; using validated OHRQoL instruments; and presenting results disaggregated by dentofacial deformity of Class II and Class III. Exclusion criteria: patients undergoing a surgery-first approach or sleep apnea surgical treatment; studies related to patients with congenital abnormalities, such as craniofacial syndrome or cleft lip and palate, and sequels due to maxillofacial trauma; using only generic instruments to assess HRQoL, such as SF36 or EQ5D, not those specific for oral health; assessing psychometric properties; case reports or cases series or studies that were not primary; and not published in English, Spanish, German, or Portuguese.
2.3. Information Sources and Search Strategy
Searches for eligible articles were undertaken in four databases—PubMed, Embase/MEDLINE, Scopus, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL)—from their inception to October 2021. The following terms were used in the search: “dentofacial deformities”, “orthognathic surgery”, and “quality of life”. No limits of date or languages were added to the searches since the first orthognathic surgery was described in 1849. The details of the search strategy used in each database are listed in the supplementary data (Supplementary Table S1). Gray literature was explored by reviewing reference lists of selected primary studies and other published systematic reviews to identify studies.
2.4. Selections Process
The systematic review followed three stages using COVIDENCE online software (Veritas Health Innovation, Melbourne, Australia) (www.covidence.org) (accessed on 21 November 2021): (1) title- and abstract-screening; (2) full-text review with data extraction; and (3) review of references listed in articles. Title- and abstract-screening were performed independently by two reviewers of the study team (V.D. and M.D.), based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria previously established; disagreement was resolved by consensus or by a third reviewer (C.Z.), who acted as an arbitrator. Subsequently, all the selected articles were independently full-text reviewed by two reviewers (V.D. and M.A.).
2.5. Data Collection Process
Data extraction of the studies was conducted independently by two investigators (V.D. and M.A.) using a standardized, predefined collection form that was piloted prior to its use. In order to obtain data which were not provided in the articles of interest, the authors of these studies were contacted.
2.6. Data Items
The information extracted from the included studies was publication data, study design, country in which the study was conducted, sample size, patient characteristics, type of dentofacial deformity, OHRQoL instrument used, follow-up data collection times, and results obtained from each group evaluated (mean and standard deviation of global and domain scores). We did not consider missing data as a reason to exclude any of the trials from the review. We did not carry out data imputation, as we assumed all missing data to be at random.
2.7. Study of Methodological Quality
The methodological quality was assessed with the Effective Public Health Practice Project (EPHPP) quality assessment tool [28,29] for quantitative studies, which has six components: (a) selection bias, (b) study design, (c) confounders, (d) blinding, (e) data collection methods, and (f) withdrawals/dropouts. Each component was classified as “strong”, “moderate”, or “weak”, and a global rating was obtained according to the number of components rated as weak (0, 1, or >1) [28]. Studies with weak methodological quality had a higher risk of bias. Two researchers (J.S. and M.D.) performed the risk of bias assessment independently; any disagreements were resolved by a third researcher (C.Z.).
2.8. Effect Measures and Synthesis Methods
A narrative description was carried out using the characteristics and main results of all studies that fulfilled inclusion criteria. Since most studies assessed OHRQoL immediately prior to surgery (with presurgical orthodontic treatment) and 4–7 months after surgery, change between these time assessments was selected as the main outcome of interest for quantitative synthesis. When mean and SD of change were not reported, mean and SD at each evaluation were collected to calculate the standardized mean difference (SMD) between both evaluations, and SD was estimated with the formula [26]:
The magnitude of SMD was considered small for 0.2, moderate for 0.5, and large for 0.8 [30].
Forest plots were constructed showing the summary and 95% CI estimated in the meta-analyses, together with results from individual studies. We used a random effect model (the DerSimonian–Laird method), as we expected variation in effects due to differences in study populations, questionnaires, and methods. First, we estimated the SMD of global scores separately for Class II and Class III patients and performed subgroup analysis according to the OHRQoL instrument, as a potential source of heterogeneity. Second, we estimated the SMD of dimension scores, performing subgroup analysis according to Class II and Class III patients, to examine differences between them. Third, we also estimated the difference between SMD in Class II and Class III. Finally, sensitivity analyses were carried out by excluding studies with weak methodological quality. Heterogeneity among studies was evaluated using the I2 statistic, categorized as follows: <30% not important; 30–50% moderate; 50–75% substantial; and 75–100% considerable [26]. Funnel plots were planned to explore possible publication bias.
The software used was Review Manager 5.4 (Cochrane IMS, Copenhagen, Denmark).
2.9. Certainty Assessment
The Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) system was used to assess the overall quality of evidence per comparison and outcome [31]. We constructed a “Summary of Findings” table using GRADEpro GDT software (http://gdt.guidelinedevelopment.org) (accessed on 18 November 2021). The GRADE approach appraises the quality of a body of evidence based on the extent to which one can be confident that an estimate of effect or association reflects the outcome being assessed. We assessed the quality of the body of evidence with reference to the overall risk of bias of the included studies, directness of the evidence, inconsistency of the results, precision of the estimates, risk of publication bias, and magnitude of the effect. The quality of the evidence can be downgraded by one or two levels for each of these factors, reducing the confidence in the estimate of the effect. There are three factors that can increase the quality of evidence: large magnitude of an effect, dose–response gradient, and effect of plausible residual confounding. We categorized the quality of the body of evidence for each of the primary outcomes as high, moderate, low, or very low.
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
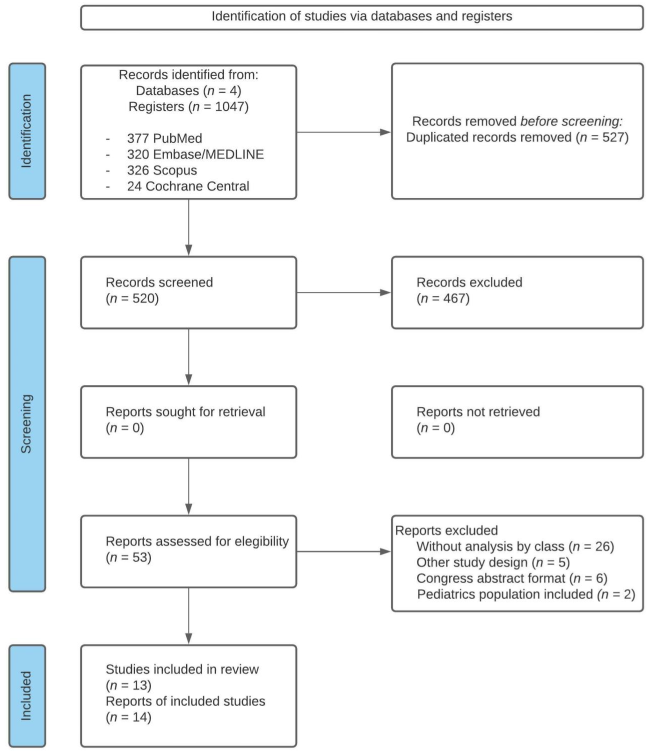
The search identified 1047 references (Figure 1); after the removal of duplicates, 520 were screened for title and abstract, and the 53 articles selected according to the eligibility criteria were fully read.
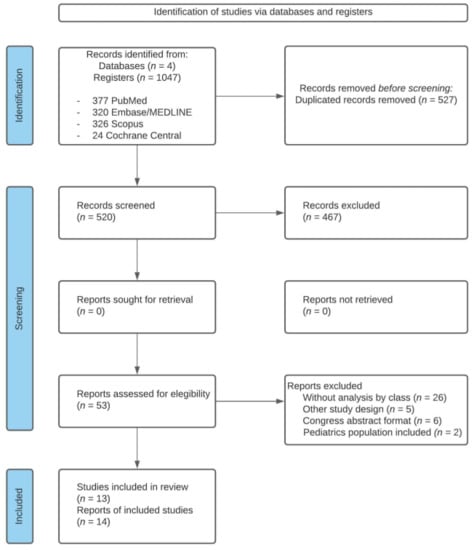
Figure 1.
Flow chart of systematic literature review.
Among the 53 full-text articles reviewed, 39 were excluded for the following reasons: 26 studies had no analysis by type of deformity, 5 were not before–after studies, 6 were congress abstracts, and 2 included a pediatric population (participants under 15 years of age). Finally, 13 studies (14 articles) were included in our qualitative synthesis, and 4 in our quantitative synthesis (meta-analysis).
3.2. Study Characteristics
Details of the included studies are summarized in Table 1. Among the 13 prospective before–after studies included, only 3 had a control group composed of: female students at the university who had a normal occlusion (n = 14) [32], volunteers aged 19–20 years old attending a nonmedical, specialty university and with no jaw deformities (n = 96) [24]; and healthy individuals, mainly patients’ relatives, classmates, or colleagues (n = 24) [33]. The final sample size of patients with dentofacial deformities ranged from 14 to 85 subjects, and the mean of age ranged from 21.3 to 31 years. Seven studies used the Oral Health Impact Profile (OHIP-14) [13,15,25,34,35,36,37] to measure OHRQoL, one used the modified Japanese version of OHIP-49 (OHIPJ54) [32], two used the Orthognathic Quality of Life Questionnaire (OQLQ) [23,38], and three studies used both OHIP-14 and OQLQ [24,33,39]. Pre-surgical OHRQoL assessment was carried out during the orthodontic treatment and the last follow-up, around 6 months after surgery in most studies.

Table 1.
Characteristics of included studies and main results.
The reasons why certain studies could not be included in the meta-analysis were: pre-surgery assessment carried out prior to orthodontic appliance installation [13,34], or after setting orthodontic appliances but at an undetermined time or far from surgery [33,38]; no assessment at 4–7 months after surgery [39]; mean, SD or number of participants by class not reported [32,35,36]; and results provided only at item level [37].
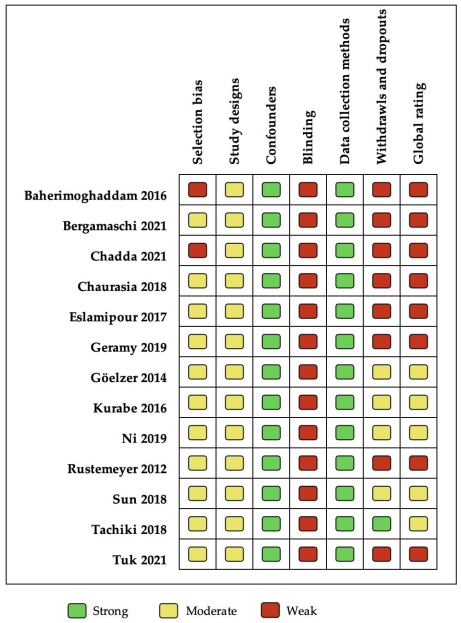
3.3. Risk of Bias within Studies
Figure 2 shows that five studies were rated as having a moderate methodological quality [24,25,32,33,38], and eight were qualified as being of weak quality, according to the global rating [13,15,23,34,35,36,37,39]. “Data collection methods” was the best evaluated domain, with all studies showing strong quality because they had used a validated OHRQoL instrument. All the studies included were qualified moderate in “study design” because they were before–after studies. “Blinding” was qualified as weak, due to most studies reporting that study participants were not blinded to the research questions. The “Confounders” component was qualified as strong since before–after studies are characterized by the fact that each individual compares with themself, that is, they are their own control. The “selection bias” was moderate because of the limited representativity of the sample. Finally, “withdrawals/dropouts” was the most variable item, with five studies classified as weak mainly because the data was not reported. No study was qualified as having strong methodological quality in the “global rating”, mainly due to nonblinding and the withdrawals/dropouts reported.
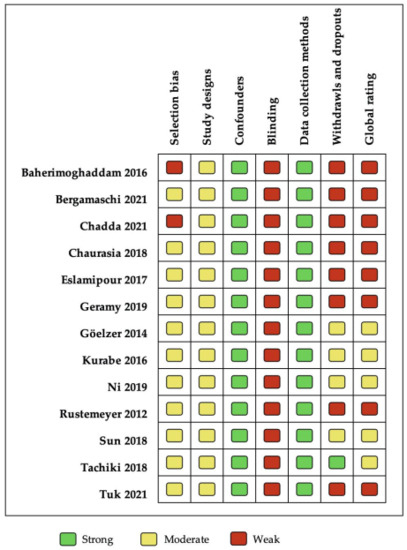
Figure 2.
Methodological quality assessed by EPHPP.
3.4. Results of Individual Studies
All the included studies showed an improvement in the OHRQoL, regardless of the questionnaire used. The single study providing information on the OQLQ domains [23] reported a significant improvement in all of them (social aspects, dentofacial aesthetics, oral function, and awareness of dentofacial deformity). The facial aesthetics domains of the OQLQ [23,24,39] and the psychological domains of the OHIP-14 presented the greatest improvement at 6 months after surgery [15,24,25,34].
Two studies reported no difference between Class II and III patients [23,35], while another study [32] reported significant differences in the global score and all OHIP-14 domains except functional limitation. No statistically significative change in Class II patients was observed in some studies for functional limitation [25,32,36] and physical disability domains [36], and Sun et al. [24] reported no significant improvement in any domain. Findings from two studies with Class III patients (Tachiki et al. [38] and Ni et al. [33]) showed significant improvement in global and all domain scores, except for awareness [33,38] and social aspects [33].
Baherimoghaddam et al. [15] reported a significative worsening during the pre-surgical stage in OHIP-14 overall score and functional limitation, physical disability, and psychological disability domains in Class II patients. A significant worsening in the domain of functional limitation and physical disability was also observed in Class III patients. However, the global score and all domains in both classes showed a significant improvement in the OHRQoL from before the installation of pre-surgical orthodontic appliances to 6 months after surgery.
3.5. Synthesis of Results
Of the four studies that provided data before surgery and 4–7 months after surgery to be included in the meta-analysis, two used the OHIP-14 [15,25], one the OQLQ [23], and one study used both instruments [24].
3.5.1. OHRQL Changes in Class II and Class III Patients Measured with Global Scores of OQLQ and OHIP-14
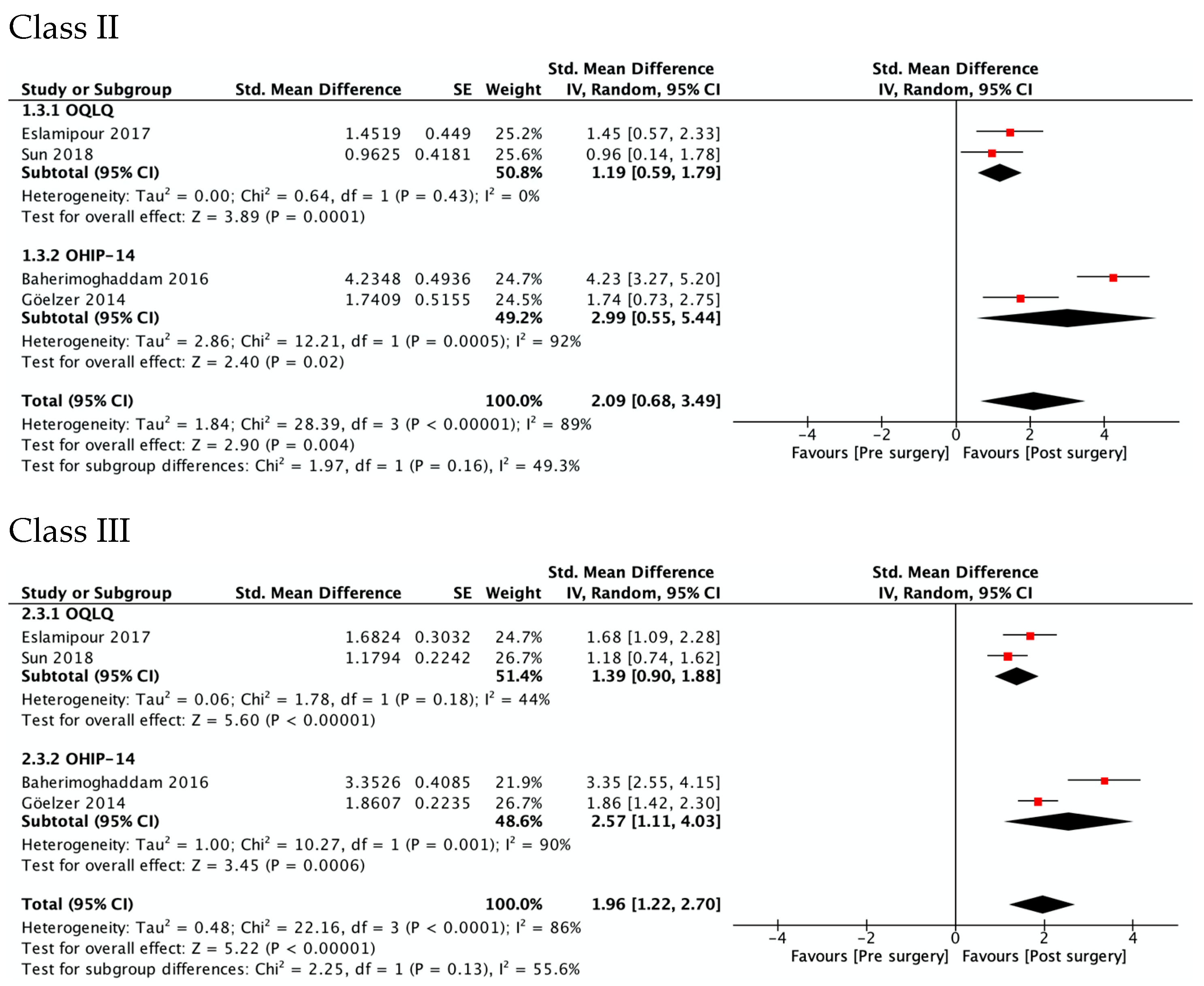
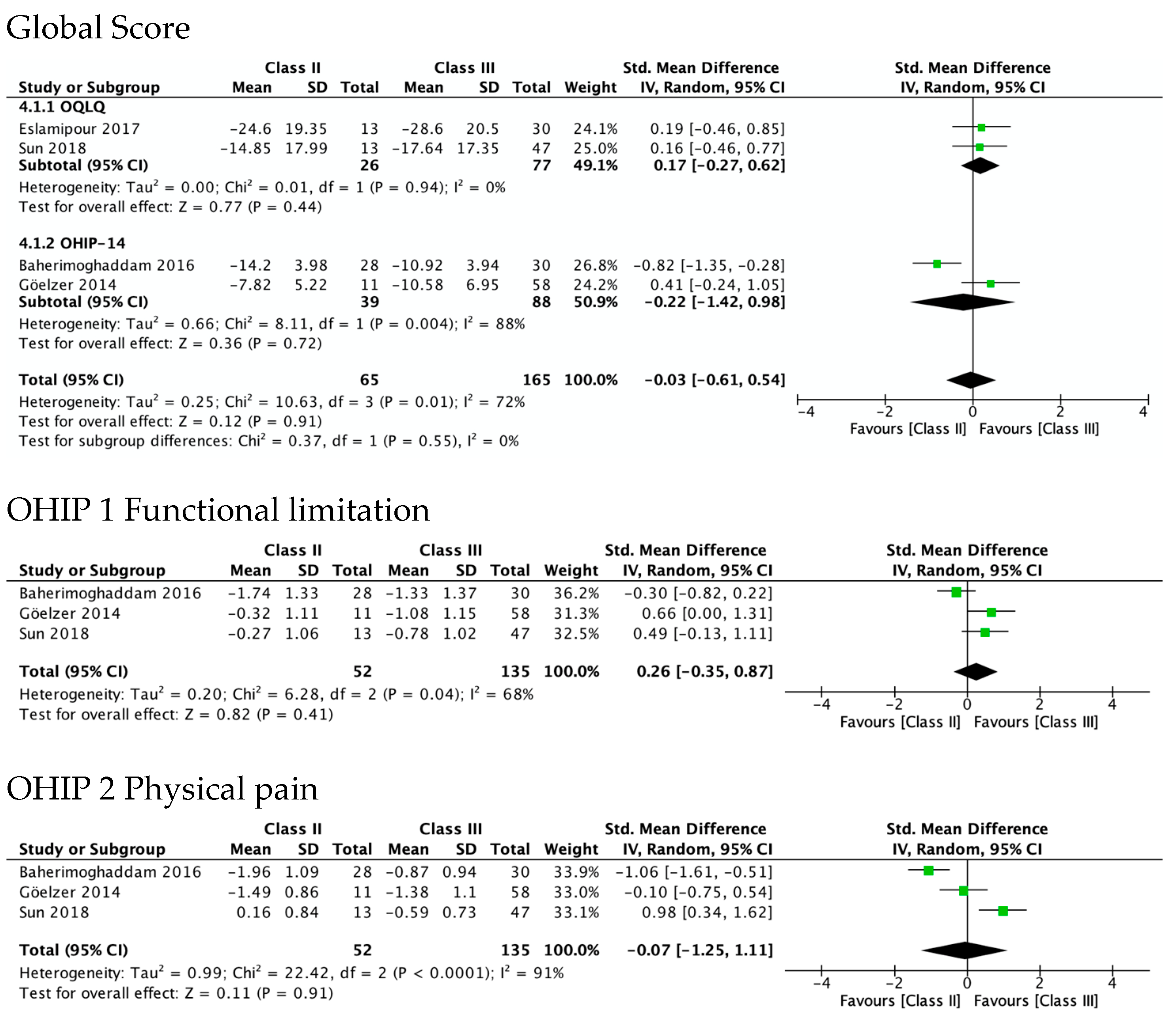
Figure 3 shows OHRQoL improvement at 4–7 months after surgery in Class II (SMD 2.09, 95% CI 0.68 to 3.49; I2 = 89%; very low quality of evidence) and Class III patients (SMD 1.96, 95% CI 1.22 to 2.70; I2 = 86%, low quality of evidence). No differences were observed between the estimators from the two questionnaires, OQLQ and OHIP-14 (p value 0.16 in Class II and 0.13 in Class III patients). Regarding the study of Sun et al., OQLQ data was selected for these forest plots because it was designed specifically to measure the impact of orthognathic surgery, while the OHIP-14 is an OHRQL generic instrument.
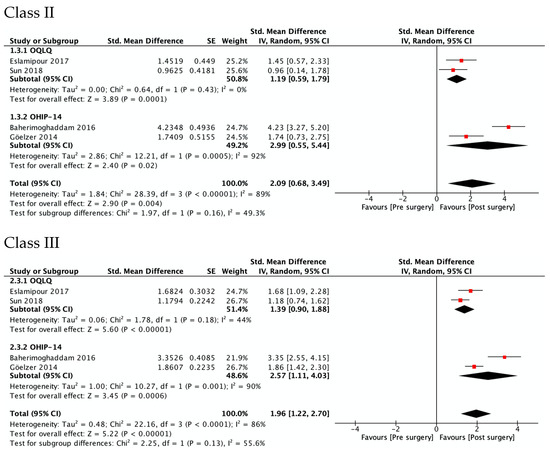
Figure 3.
Meta-analysis of the change from pre-surgery to 4–7 months after surgery on the OHRQoL global scores by type of dentofacial deformity.
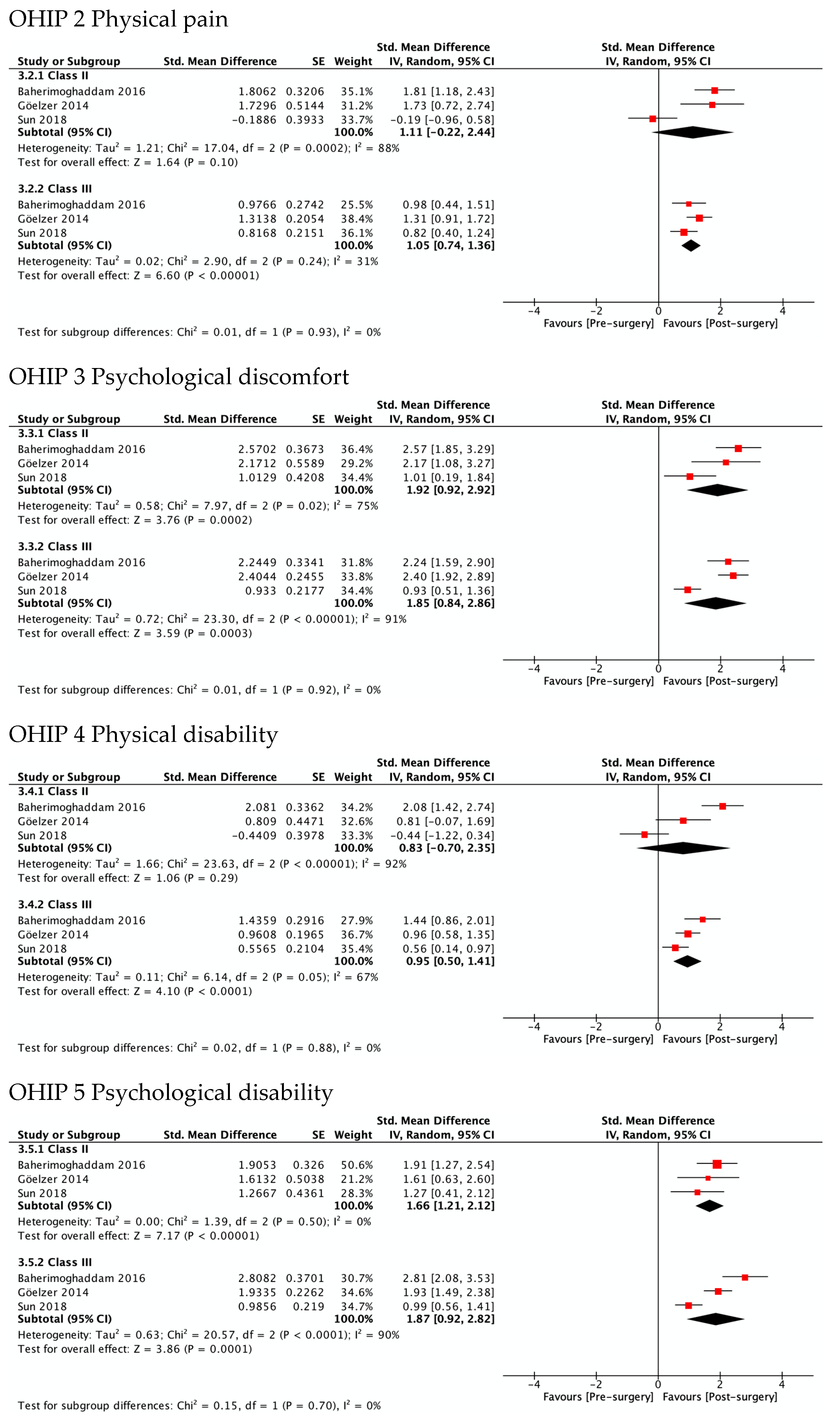
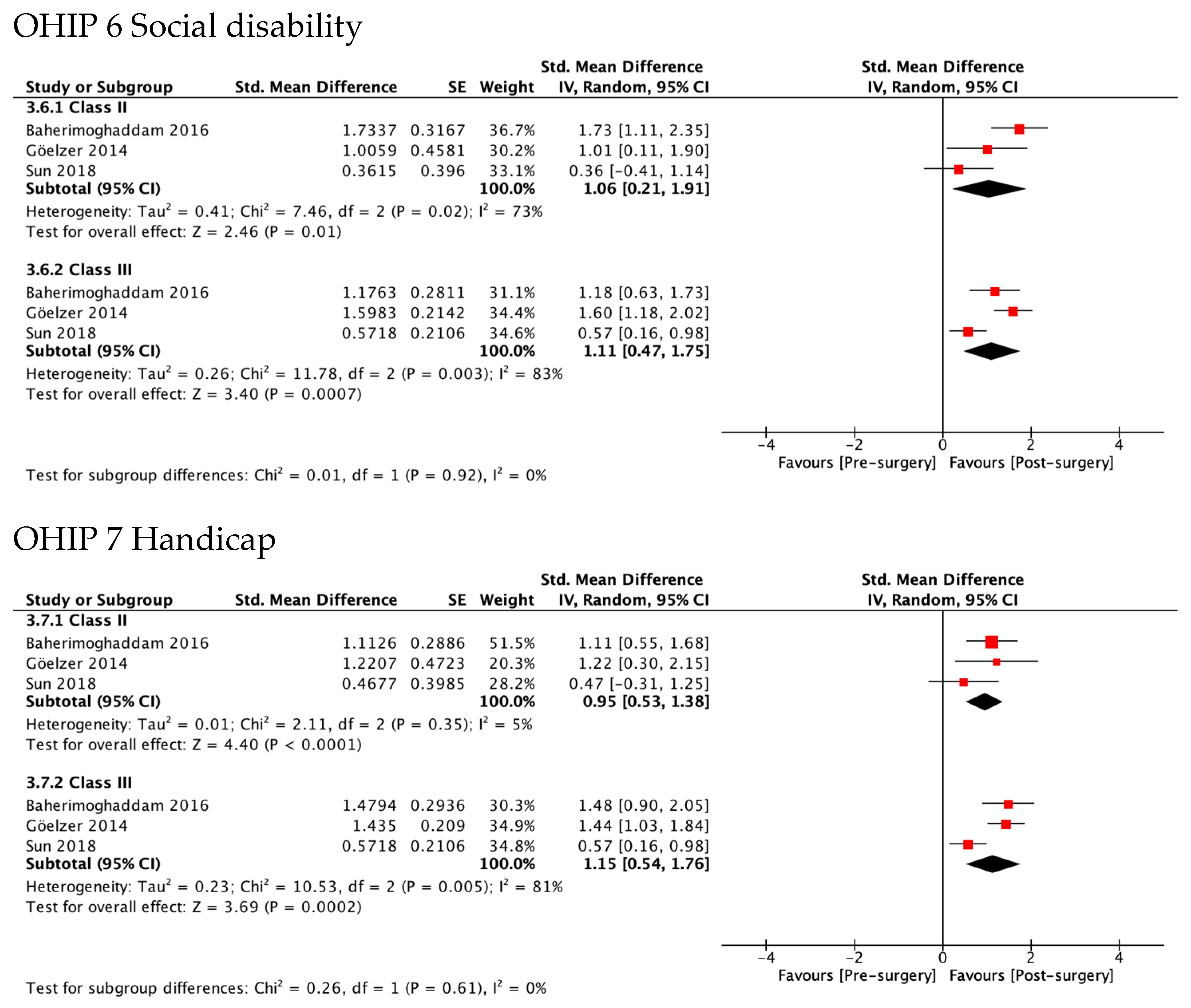
3.5.2. OHRQL Changes in Class II and Class III Patients in OHIP-14 Domains
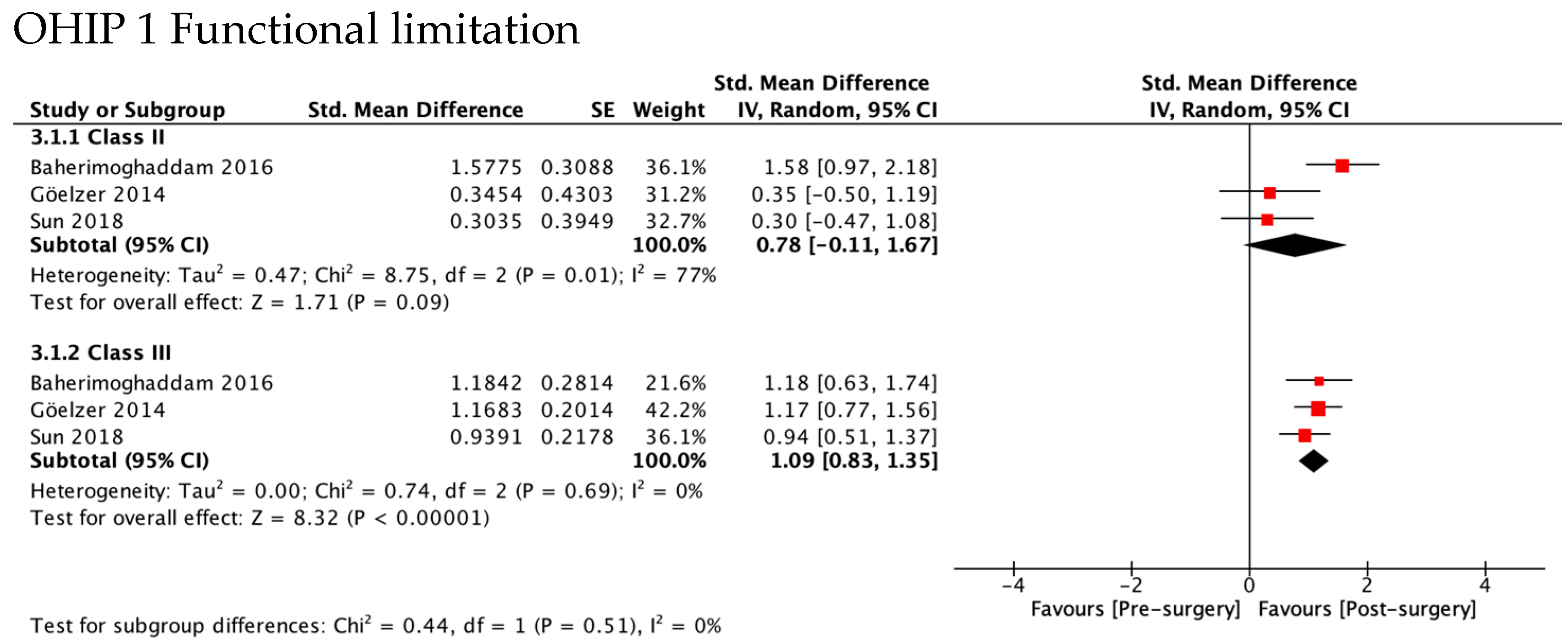
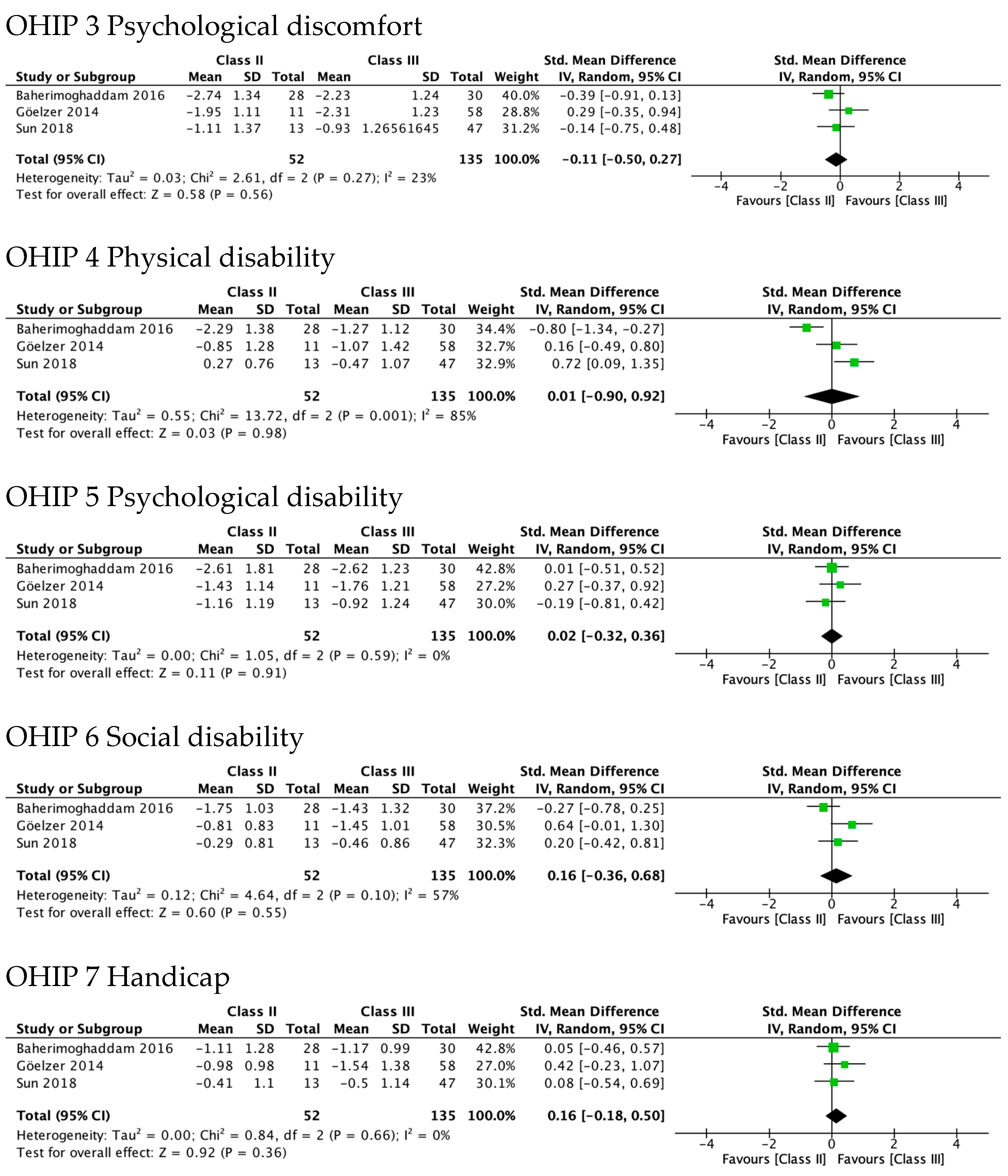
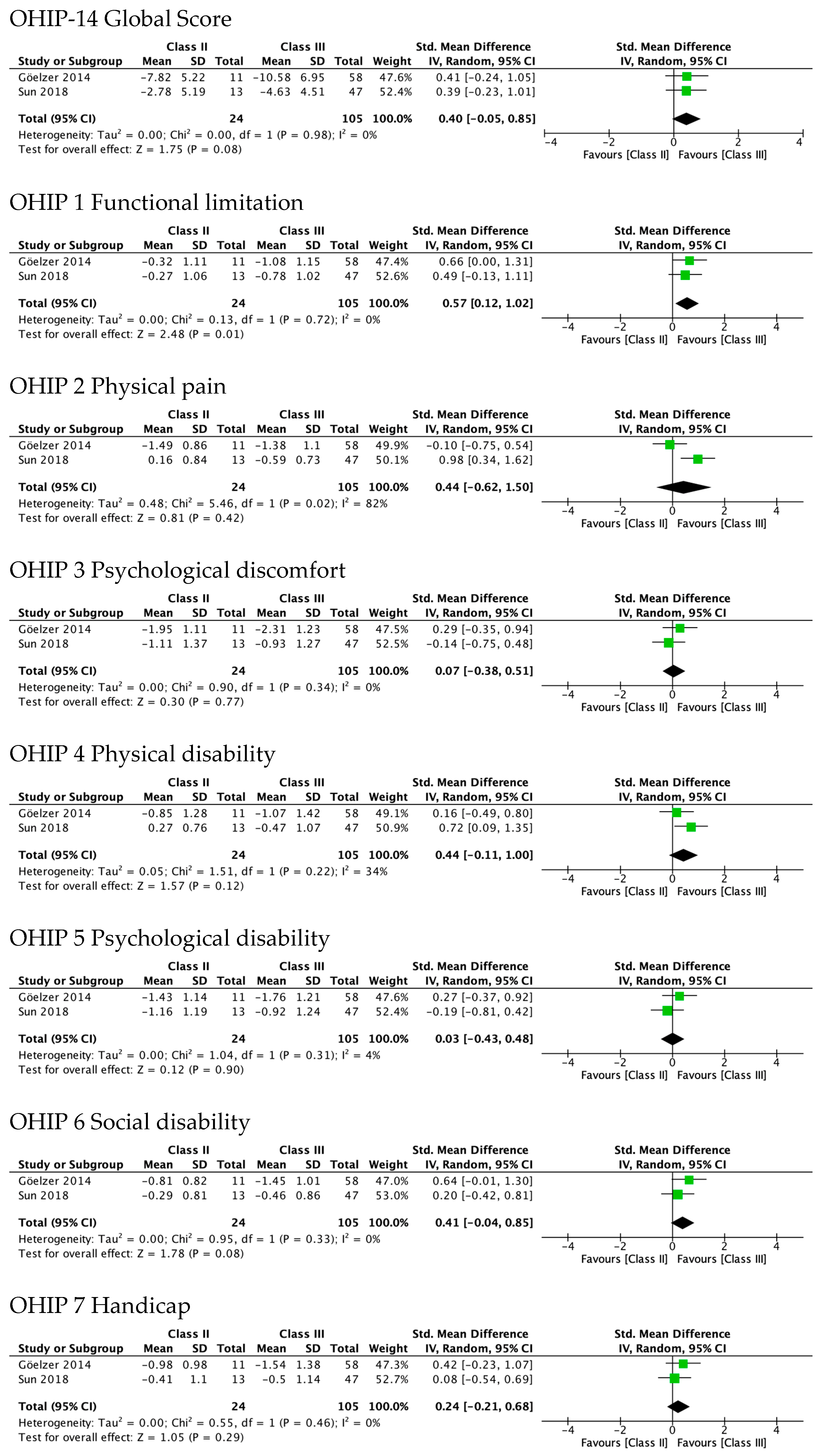
Figure 4 shows the greatest improvement for both Class II and Class III in psychological discomfort (SMD 1.92 and 1.85) and psychological disability (SMD 1.66 and 1.87), both significantly higher than zero. The lowest was observed for functional limitation in Class II patients (SMD 0.78, 95% CI—0.11 to 1.67) and for physical disability in Class III (SMD 0.95, 95% CI 0.50 to 1.41). No test for subgroups was statistically significant, indicating that there were no differences between Class II and Class III. These results are consistent with meta-analyses of the differences between SMD in Class II and Class III (Figure 5), which also showed statistically insignificant differences of small magnitude: SMD of OHIP-14 scores ranged from 0.26 (95% CI—0.35 to 0.87; I2 = 68%) in functional limitation to 0.01 (95% CI −0.90 to 0.92; I2 = 85%) in physical disability. The SMD between Class II and Class III patients on the OQLQ and OHIP-14 total score was −0.03 (95% CI—0.61 to 0.54).
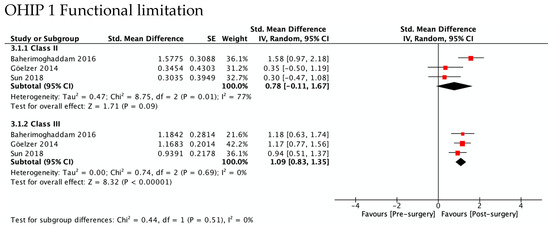
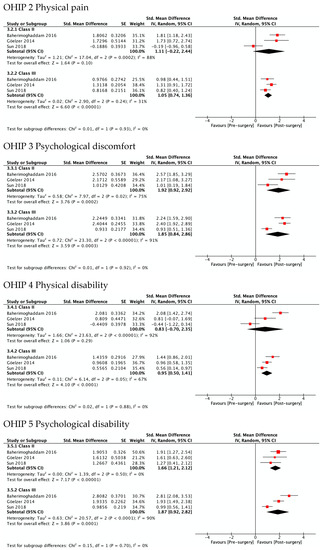
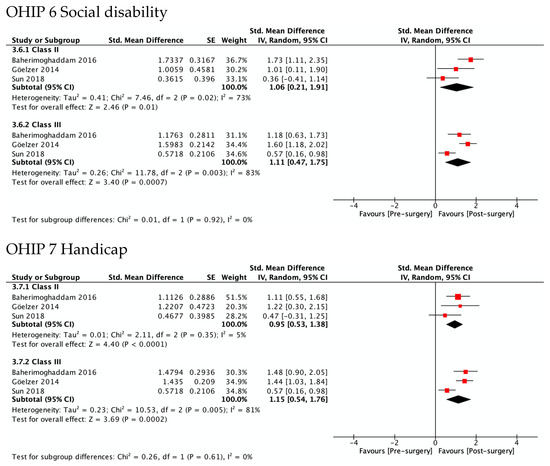
Figure 4.
Meta-analysis of the standard mean differences of the OHIP-14 domains’ scores pre-surgery and post-surgery 4–7 months follow-up by type of deformity Class II and III.
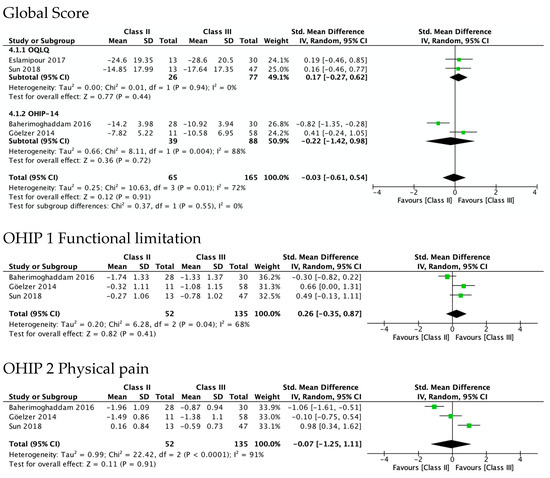
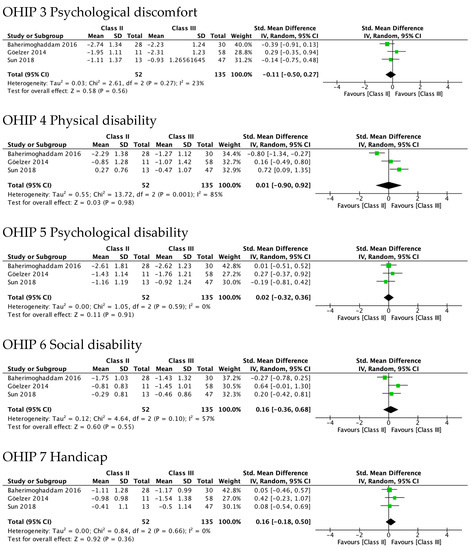
Figure 5.
Meta-analysis of the differences between Class II and Class III standard mean differences (from pre-surgery to 4–7 months after surgery) in OHRQoL global scores and OHIP-14 domains’ scores.
3.6. Sensivity Analysis
Figure 6 shows sensitivity analyses performed after excluding the two studies rated as weak in their methodological quality [15,23]. The results from meta-analysis of the differences between Class II and Class III showed that it was only statistically significant in functional limitation (SMD 0.57, 95% CI 0.12–1.02). The difference in the domain of physical disability was of almost-moderate magnitude, but not statistically significant (SMD 0.44, 95% CI −0.11 to 1.00).
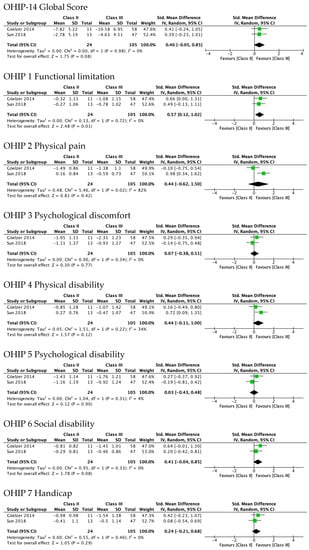
Figure 6.
Results of sensitivity analysis after excluding studies with weak methodological quality. Meta-analysis of the differences between Class II and Class III standard mean differences (from pre-surgery to 4–7 months after surgery) in OHRQoL global scores and OHIP-14 domains’ scores.
Consistently, the Supplementary Figure S1 shows that the test for subgroups between Class II and Class III was statistically significant in the domain of functional limitation (p = 0.02). In fact, Class II patients did not improve significantly (0.32, 95% CI—0.25 to 0.89; I2 = 0%), while those in Class III did (1.06, 95% CI 0.77 to 1.35; I2 = 0%). This pattern was also observed in the domain of physical disability (SMD 0.17 and 0.77) although the test for subgroups was not statistically significant.
3.7. Reporting Bias
Funnel plots to explore possible publication biases were not constructed, as we did not have more than 10 studies to pool in any meta-analysis.
3.8. Certainty of Evidence
All studies included were of observational design; therefore, the quality of evidence starts out low (Table 2). In addition, the quality of evidence was downgraded, mainly due to methodological limitations, inconsistency, and imprecision. Risk of bias was serious.

Table 2.
Summary of findings for the main results.
Due to concerns regarding blinding and withdrawals/dropouts, serious inconsistency downgraded certainty one level due to considerable heterogeneity and imprecision in one outcome. Indirectness of results was considered not serious since the studies included appropriately answer the question in terms of population, intervention, comparison, and results studied. Publication bias was also rated as not serious.
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Findings
The OHRQoL of patients with dentofacial deformities of Class II and III improved after orthognathic surgery. Improvement was of large magnitude in the global scores of both OHRQoL instruments applied in the studies, OQLQ and OHIP-14, and also in all OHIP-14 domains. No statistically significant differences by type of dentofacial deformity were found, but the sensitivity analyses (after excluding studies with weak methodological quality) showed that Class III patients’ improvement in the functional limitation domain was significantly higher than that of Class II patients. However, there was uncertainty in determining whether the type of dentofacial deformity affects the impact of orthognathic surgery on OHRQoL.
Findings obtained through the meta-analysis show improvement of large magnitude in all domains for both types of dentofacial deformities, but in Class II patients, only psychological domains (discomfort and disability), social disability, and handicap were statistically significant (not functional limitation, physical pain, and disability). Few studies incorporating Patient-Reported Outcomes (PROs) to measure the impact of orthognathic surgery on OHRQoL provided data for each type of dentofacial deformity, and sample sizes of Class II patients are smaller than those of Class III. Therefore, confidence intervals of the summary estimators obtained in our meta-analysis are very wide, especially for Class II patients.
On the other hand, the studies included in our meta-analysis used mostly the OHIP-14 [15,24,25], which was not specifically designed to measure the impact of orthognathic surgery. The OQLQ, specifically designed for this purpose, could have a higher sensitivity and show a greater improvement and a more precise estimator [40]. Therefore, studies using condition-specific instruments such as the OQLQ can allow one to distinguish the gradual impact of the treatment through the severity of the dentofacial deformity.
Previous systematic reviews consistently showed a positive impact of orthognathic surgery on OHRQoL in general [17,18,19,20,21,22], but none of them considered the type of dentofacial deformity. A meta-analysis of results focused on the OQLQ, specifically designed to measure the impact of the orthognathic surgery [20], showed improvement in the overall score and in the domains of social aspects and facial aesthetics. We also found improvement in the OQLQ global score, but we could not construct a meta-analysis by OQLQ domain since only one study [24] stratified according to type of dentofacial deformity reported data by domains. Statistically significative improvement for all domains of the OQLQ and OHIP-14 was estimated by two other systematic reviews with meta-analyses [21,22], which was consistent with our results in Class III patients. However, we found no statistically significant improvement in physical pain or physical disability of OHIP-14 in Class II patients.
In accordance with previous research [21], our findings showed a very low level of quality of evidence due to methodological limitations. Most studies included in our systematic review had an uncontrolled before–after design, which limited capacity to control for all relevant potential confounders due to lack of randomization and, therefore, they are more vulnerable to bias.
The sensitivity analysis performed to take into account the methodological quality of primary studies is especially relevant in this context. After excluding the methodologically weak quality studies, improvement differences between Class III and Class II patients were greater in the functional limitations, physical pain, and physical disability domains of OHIP-14. In these domains, improvement was of large magnitude and statistically significant in Class III patients, but small or moderate and not statistically significant in Class II patients. These findings support the need for further research to clarify the impact of orthognathic surgery considering the type of dentofacial deformities.
There is high variability among the studies regarding the time assessment, especially before surgery. Some studies considered the baseline as the stage prior to any intervention (before the installation of pre-surgical orthodontic appliances), other studies just before surgery, and a few in at undetermined timepoint of the pre-surgical period. Between the evaluation before pre-surgical orthodontic treatment and the preoperative phase, just before surgery, studies reported a significant worsening in OHRQoL [20,39,41] due to pre-surgical orthodontic decompensation.
Although the real impact of orthodontic–surgical treatment should be obtained by comparing the baseline measurement before the installation of pre-surgical orthodontic appliances with the end of the treatment, when the postsurgical orthodontics have been removed, only one study had this design [15]. This study showed statistically significant improvement (from before the installation of pre-surgical orthodontic appliances to after removal of the postsurgical orthodontics) in the OHIP-14 global score and all its domains in Class II and Class III patients [15]. This improvement was of a large magnitude except in functional limitation, physical pain, and physical disability in Class III patients. The other studies with OHRQoL assessment before the installation of pre-surgical orthodontic appliances [13,33,34,38] did not clarify whether the last follow-up occurred after removal of the postsurgical orthodontics.
The time point when the follow-up assessment was performed in the studies included in our meta-analysis ranges from 4 to 7 months after surgery. Changes in functional and facial aesthetics resulting from orthognathic surgery are dependent on the stability of surgical procedures [42]. The authors agree that the profile has attained its definitive configuration after 6 months [43] since edema and muscular readaptation are expected to resolve between 6 and 12 months [44,45]. Although there is a lack of consensus on the suitable times to assess the impact of orthognathic surgery, studies extending follow-up beyond 6 months are necessary to estimate the real impact of the orthognathic surgery.
4.2. Strengths and Limitations
The present study was strictly conducted in accordance within the guidelines of the Cochrane Handbook for the Systematic Review of Interventions [26]. Even though the impact of orthognathic surgery on OHRQoL is a subject of great interest and assessed in numerous studies, only a few of them analyze the differences according to the type of dentofacial deformities.
The variability among studies on the assessment times before and after surgery limited their inclusion in the meta-analysis. In addition, clinical diversity due to variability in the participants according to age, gender, or degree of severity of dentofacial deformity introduced considerable heterogeneity. However, in order to minimize this, we used a random-effects model in the analysis.
Finally, our findings should be interpreted with caution due to the very low certainty of the evidence, which translates into a significant uncertainty of the real magnitude of the impact of dentofacial deformities on the OHRQoL.
4.3. Implications for Practice and Research
The quantitative synthesis of results obtained in studies with moderate methodological quality suggests differences according to types of dentofacial deformities in the magnitude of the OHRQoL improvement experienced by patients.
Future research comparing types of dentofacial deformities, measuring OHRQoL with condition-specific instruments such as the OQLQ, and with robust methods are needed to clarify this issue. It is relevant to incorporate PROs as a measure of the patient’s perspective, and not only to evaluate the results of the treatment from the aesthetic and functional points of view. Sociocultural conditions and severity of the dentofacial deformity could influence the motivation for treatment and its impact on the OHRQoL.
5. Conclusions
There is not enough evidence to support differences between Class II and III patients in the OHRQoL impact at 4–7 months follow-up after orthognathic surgery. However, sensitive analyses excluding those studies with weak methodological quality suggest differences according to these types of dentofacial deformities in the domains of functional limitation, physical pain, and physical disability.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijerph19041940/s1: Figure S1. Results of sensitivity analysis after excluding studies with weak methodological quality. Meta-analysis of the change from pre-surgery to 4–7 months after surgery in the OHIP-14 domain scores by type of dentofacial deformity; Table S1. Search strategy for each data base; Table S2. Checklist PRISMA 2020.
Author Contributions
V.D., C.Z., J.V. and M.F. conceived the study. V.D., C.Z., M.F., J.V., M.D. and J.S. contributed to the design of this study and interpreted the results. V.D., M.A., M.D., J.S. and C.Z. did the selection of the studies, quality assessment, and data extraction V.D., C.Z., M.F. and À.P. performed the data analysis. V.D., C.Z. and M.F. drafted the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data and materials supporting the conclusions of this manuscript are included in the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Aurea Martin for her support in English editing, proofreading, and preparing this manuscript for submission.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest with any financial organization regarding the material discussed in the manuscript.
Differences between the Protocol and the Review Conducted
The original title of the protocol was “Quality of life in patients with dentofacial deformities treated with orthognathic surgery. A systematic review”; it was changed to “Oral Health-related quality of life changes in patients with dentofacial deformities Class II and III after orthognathic surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis” since we modified the main outcome. We also adjusted the age range of the included patients to those over 15 years old treated with conventional ortho-surgical technique.
References
- Hunt, O.T.; Johnston, C.D.; Hepper, P.G.; Burden, D.J. The Psychosocial Impact of Orthognathic Surgery: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2001, 120, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, F.S.; Barnard, M.; Cunningham, S.J. Impact of Dentofacial Deformity and Motivation for Treatment: A Qualitative Study. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2012, 141, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sischo, L.; Broder, H.L. Oral Health-Related Quality of Life: What, Why, How, and Future Implications. J. Dent Res. 2011, 90, 1264–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miloro, M.; Ghali, G.E.; Larsen, P.E.; Waite, P. Peterson’s Principles of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 2nd ed.; B C Decker: Hamilton, ON, Canada; London, UK, 2004; ISBN 978-1-55009-234-9. [Google Scholar]
- Joh, B.; Bayome, M.; Park, J.H.; Park, J.U.; Kim, Y.; Kook, Y.-A. Evaluation of Minimal Versus Conventional Presurgical Orthodontics in Skeletal Class III Patients Treated with Two-Jaw Surgery. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 71, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzatto, S.M.D.; Macedo de Menezes, L.; da Cunha Filho, J.J.; Allgayer, S. Conventional Surgical-Orthodontic Approach with Double-Jaw Surgery for a Patient with a Skeletal Class III Malocclusion: Stability of Results 10 Years Posttreatment. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2018, 154, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngan, P.; Moon, W. Evolution of Class III Treatment in Orthodontics. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2015, 148, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, P.; King, T.; Lee, M.; Erasmus, J. Retrospective Study of Eligibility for Orthognathic Surgery Using the Index of Orthognathic Functional Treatment Need (IOFTN). Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 56, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parappallil, C.J.; Parameswaran, R.; Vijayalakshmi, D.; Mavelil, B.G.T. A Comparative Evaluation of Changes in Soft Tissues After Single-Jaw Surgery and Bimaxillary Surgery in Skeletal Class III Patients. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2018, 17, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friscia, M.; Sbordone, C.; Petrocelli, M.; Vaira, L.A.; Attanasi, F.; Cassandro, F.M.; Paternoster, M.; Iaconetta, G.; Califano, L. Complications after Orthognathic Surgery: Our Experience on 423 Cases. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 21, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soydan, S.S.; Uckan, S.; Ustdal, A.; Bayram, B.; Bayrak, B. The Influence of Bilateral Sagittal Split Ramus Osteotomy on Submental-Cervical Aesthetics. J. Oral. Rehabil. 2014, 41, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, J.A.M.; Palomares, N.B.; Feu, D. Life-Quality of Orthognathic Surgery Patients: The Search for an Integral Diagnosis. Dent. Press J. Orthod. 2014, 19, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rustemeyer, J.; Gregersen, J. Quality of Life in Orthognathic Surgery Patients: Post-Surgical Improvements in Aesthetics and Self-Confidence. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 40, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hugo, B.; Becker, S.; Witt, E. Assessment of the combined orthodontic- surgical treatment from the patients’ point of view: A longitudinal study. J. Orofac. Orthop./Kieferorthop. 1996, 57, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baherimoghaddam, T.; Tabrizi, R.; Naseri, N.; Pouzesh, A.; Oshagh, M.; Torkan, S. Assessment of the Changes in Quality of Life of Patients with Class II and III Deformities during and after Orthodontic–Surgical Treatment. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, C.; Kearns, G.; Sleeman, D.; Cronin, M.; Allen, P.F. The Clinical Relevance of Orthognathic Surgery on Quality of Life. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 40, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soh, C.L.; Narayanan, V. Quality of Life Assessment in Patients with Dentofacial Deformity Undergoing Orthognathic Surgery—A Systematic Review. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 42, 974–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.N.; Yates, J.M. Patient Related Outcomes and Improvements in Quality of Life Following Orthognathic Surgery. Oral. Surg. 2020, 13, 67–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamboni, R.; de Moura, F.R.R.; Brew, M.C.; Rivaldo, E.G.; Braz, M.A.; Grossmann, E.; Bavaresco, C.S. Impacts of Orthognathic Surgery on Patient Satisfaction, Overall Quality of Life, and Oral Health-Related Quality of Life: A Systematic Literature Review. Int. J. Dent. 2019, 2019, 2864216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Lu, W.; Xiao, J.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Z. Effect of Conventional Combined Orthodontic-Surgical Treatment on Oral Health-Related Quality of Life: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2019, 156, 29–43.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araujo, C.M.; Schroder, A.G.D.; de Araujo, B.M.d.M.; Cavalcante-Leão, B.L.; Stechman-Neto, J.; Zeigelboim, B.S.; Santos, R.S.; Guariza-Filho, O. Impact of Orthodontic-Surgical Treatment on Quality of Life: A Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Orthod. 2020, 42, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meger, M.N.; Fatturi, A.L.; Gerber, J.T.; Weiss, S.G.; Rocha, J.S.; Scariot, R.; Wambier, L.M. Impact of Orthognathic Surgery on Quality of Life of Patients with Dentofacial Deformity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 59, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslamipour, F.; Najimi, A.; Tadayonfard, A.; Azamian, Z. Impact of Orthognathic Surgery on Quality of Life in Patients with Dentofacial Deformities. Int. J. Dent. 2017, 2017, 4103905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Shang, H.; He, L.; Ding, M.; Su, Z.; Shi, Y. Assessing the Quality of Life in Patients With Dentofacial Deformities Before and After Orthognathic Surgery. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 76, 2192–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Göelzer, J.G.; Becker, O.E.; Haas Junior, O.L.; Scolari, N.; Santos Melo, M.F.; Heitz, C.; de Oliveira, R.B. Assessing Change in Quality of Life Using the Oral Health Impact Profile (OHIP) in Patients with Different Dentofacial Deformities Undergoing Orthognathic Surgery: A before and after Comparison. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 43, 1352–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. (Eds.) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, 1st ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-1-119-53662-8. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.H.; Ciliska, D.; Dobbins, M.; Micucci, S. A Process for Systematically Reviewing the Literature: Providing the Research Evidence for Public Health Nursing Interventions. Worldviews Evid.-Based Nurs. 2004, 1, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armijo-Olivo, S.; Stiles, C.R.; Hagen, N.A.; Biondo, P.D.; Cummings, G.G. Assessment of Study Quality for Systematic Reviews: A Comparison of the Cochrane Collaboration Risk of Bias Tool and the Effective Public Health Practice Project Quality Assessment Tool: Methodological Research: Quality Assessment for Systematic Reviews. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2012, 18, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middel, B.; van Sonderen, E. Statistical Significant Change versus Relevant or Important Change in (Quasi) Experimental Design: Some Conceptual and Methodological Problems in Estimating Magnitude of Intervention-Related Change in Health Services Research. Int. J. Integr. Care 2002, 2, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, D.; Eccles, M.; Flottorp, S.; Guyatt, G.H.; Henry, D.; Hill, S.; Liberati, A.; O’Connell, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Phillips, B.; et al. Systems for Grading the Quality of Evidence and the Strength of Recommendations I: Critical Appraisal of Existing Approaches The GRADE Working Group. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2004, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurabe, K.; Kojima, T.; Kato, Y.; Saito, I.; Kobayashi, T. Impact of Orthognathic Surgery on Oral Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Jaw Deformities. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 1513–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Song, S.; Zhou, N. Impact of Surgical Orthodontic Treatment on Quality of Life in Chinese Young Adults with Class III Malocclusion: A Longitudinal Study. BMC Oral. Health 2019, 19, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geramy, A.; Mazaheri Nazarifar, A.; Saffar Shahroudi, A.; Sheikhzadeh, S. Oral Health-Related Quality of Life Following Orthognathic Surgery for Class III Correction Its Relationship with Cephalometric Changes. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 48, 1434–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuk, J.G.; Lindeboom, J.A.; Tan, M.L.; de Lange, J. Impact of Orthognathic Surgery on Quality of Life in Patients with Different Dentofacial Deformities: Longitudinal Study of the Oral Health Impact Profile (OHIP-14) with at Least 1 Year of Follow-Up. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergamaschi, I.P.; Cavalcante, R.C.; Fanderuff, M.; Gerber, J.T.; Petinati, M.F.P.; Sebastiani, A.M.; da Costa, D.J.; Scariot, R. Orthognathic Surgery in Class II Patients: A Longitudinal Study on Quality of Life, TMD, and Psychological Aspects. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2021, 25, 3801–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadda, D.; Majumdar, S.K.; Shome, A.; Das, R.K. Evaluation of Cephalometric Changes and Its Relation to Changes in Patients’ Quality of Life After Mandibular Setback Surgery. J. Maxillofac. Oral. Surg. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachiki, C.; Nishii, Y.; Takaki, T.; Sueishi, K. Condition-Specific Quality of Life Assessment at Each Stage of Class III Surgical Orthodontic Treatment—A Prospective Study. Bull. Tokyo Dent. Coll. 2018, 59, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaurasia, N.; Upadhyaya, C.; Srivastava, S.; Dulal, S. Assessment of Changes in Quality of Life in Patients with Dentofacial Deformities after Orthognathic Surgery—A Study in Nepalese Population. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Med. Pathol. 2018, 30, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manterola, D.C.; Urrutia, S.; Otzen, H.T. Calidad de Vida Relacionada Con Salud: Una Variable Resultado a Considerar En Investigación Clínica. Int. J. Morphol. 2013, 31, 1517–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cunningham, S.J.; Garratt, A.M.; Hunt, N.P. Development of a Condition-Specific Quality of Life Measure for Patients with Dentofacial Deformity: II. Validity and Responsiveness Testing. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 2002, 30, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lir, A.L.S.; de Moura, W.L.; Oliveira Ruellas, A.C.; Gomes Souza, M.M.; Nojima, L.I. Long-Term Skeletal and Profile Stability after Surgical-Orthodontic Treatment of Class II and Class III Malocclusion. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 41, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mommaerts, M.Y.; Lippens, F.; Abeloos, J.V.S.; Neyt, L.F. Nasal Profile Changes after Maxillary Impaction and Advancement Surgery. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2000, 58, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, L.J.; Dover, A.J.; Proffit, W.R. Long-Term Soft Tissue Changes after Orthodontic and Surgical Corrections of Skeletal Class III Malocclusions. Angle Orthod. 2007, 77, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, M.; Ross, R.B. Soft Tissue Response to Mandibular Advancement and Genioplasty. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1992, 101, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).