Etanercept Prevents Endothelial Dysfunction in Cafeteria Diet-Fed Rats
Abstract: Background
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Preparation and Experimental Design
2.2. Organ Bath Studies
2.3. Agonist-Induced Contractions
2.4. Agonist-Induced Relaxations
2.5. Solutions and Drugs
2.6. Immunohistochemical Analyses
2.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.8. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
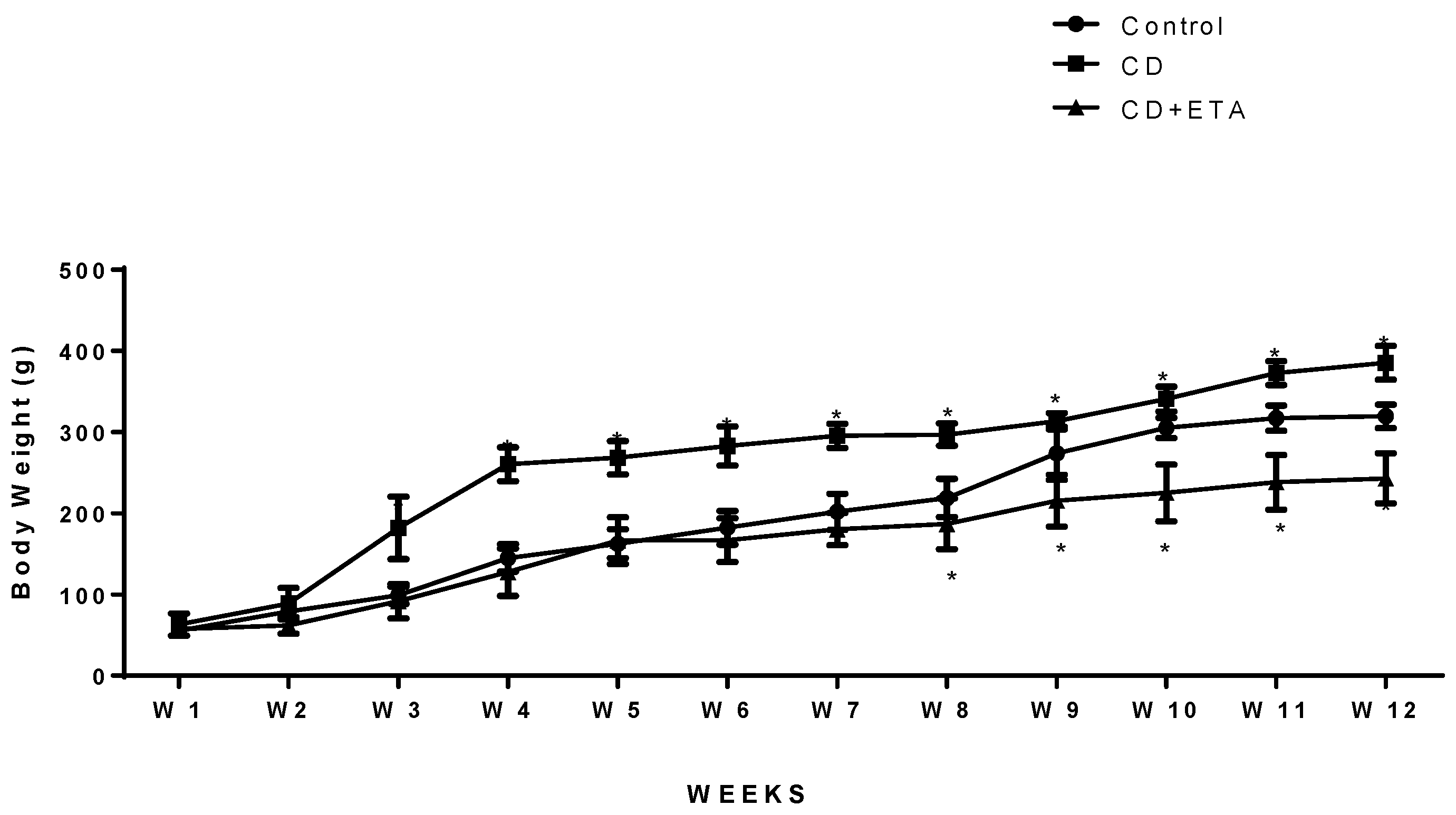
3.1. Etanercept Treatment Reduced Body Weight
3.2. Etanercept Treatment Improved Vascular Contractility and Vasorelaxation
3.3. Etanercept Treatment Corrected Alterations of Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase (eNOS) Immunoreactivity
3.4. Etanercept Improved Alterations of Serum and Aortic Inflammatory Markers and Aortic eNOS Expressions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calabrò, P.; Golia, E.; Maddaloni, V.; Malvezzi, M.; Casillo, B.; Marotta, C.; Calabrò, R.; Golino, P. Adipose tissue-mediated inflammation: The missing link between obesity and cardiovascular disease? Intern. Emerg. Med. 2008, 4, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Suwaidi, J.; Higano, S.T.; Holmes, D.R.; Lennon, R.; Lerman, A. Obesity is independently associated with coronary endothelial dysfunction in patients with normal or mildly diseased coronary arteries. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2001, 37, 1523–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perticone, F.; Ceravolo, R.; Candigliota, M.; Ventura, G.; Iacopino, S.; Sinopoli, F.; Mattioli, P.L. Obesity and body fat distribution induce endothelial dysfunction by oxidative stress: Protective effect of vitamin C. Diabetes 2001, 50, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grassi, G.; Seravalle, G.; Scopelliti, F.; Dell’Oro, R.; Fattori, L.; Quarti-Trevano, F.; Brambilla, G.; Schiffrin, E.; Mancia, G. Structural and Functional Alterations of Subcutaneous Small Resistance Arteries in Severe Human Obesity. Obesity 2010, 18, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Yu, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, B. Exendin-4 directly improves endothelial dysfunction in isolated aortas from obese rats through the cAMP or AMPK-eNOS pathways. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2012, 97, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrendt, D.; Ganz, P. Endothelial function: From vascular biology to clinical applications. Am. J. Cardiol. 2002, 90, L40–L48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, I.; Wheatcroft, S.; Shah, A.; Kearney, M. Obesity, atherosclerosis and the vascular endothelium: Mechanisms of reduced nitric oxide bioavailability in obese humans. Int. J. Obes. 2002, 26, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Park, Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, X.P.; Lee, S.; Yang, J.; Dellsperger, K.C.; Zhang, C. Role of TNF-α in vascular dysfunction. Clin. Sci. 2009, 116, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berk, B.C.; Abe, J.-I.; Min, W.; Surapisitchat, J.; Yan, C. Endothelial Atheroprotective and Anti-inflammatory Mechanisms. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 947, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, R. Tumor necrosis factor in CHF: A double facet cytokine. Cardiovasc. Res. 1998, 37, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Tsai, B.M.; Reiger, K.M.; Brown, J.W.; Meldrum, D.R. Human myocardial tissue TNFalpha expression following acute global ischemia in vivo. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 1998, 30, 1683–1689. [Google Scholar]
- Chia, S.; Qadan, M.; Newton, R.; Ludlam, C.A.; Fox, K.; Newby, D.E. Intra-Arterial Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Impairs Endothelium-Dependent Vasodilatation and Stimulates Local Tissue Plasminogen Activator Release in Humans. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoshizumi, M.; Perrella, M.A.; Burnett, J.C., Jr.; Lee, M.E. Tumor necrosis factor down regulates an endothelial nitric oxide synthase mRNA by shortening its half-life. Circ. Res. 1993, 73, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neumann, P.; Gertzberg, N.; Johnson, A. TNF-α induces a decrease in eNOS promoter activity. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2004, 286, L452–L459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, I.P.; Marti, A.; Milagro, F.I.; Zulet, M.D.L.A.; Moreno-Aliaga, M.J.; Martinez, J.A.; De Miguel, C. DNA Microarray Analysis of Genes Differentially Expressed in Diet-Induced (Cafeteria) Obese Rats. Obes. Res. 2003, 11, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dandona, P.; Weinstock, R.; Thusu, K.; Abdel-Rahman, E.; Aljada, A.; Wadden, T. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α in Sera of Obese Patients: Fall with Weight Loss. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83, 2907–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Justo, M.L.; Candiracci, M.; Dantas, A.P.; de Sotomayor, M.A.; Parrado, J.; Vila, E.; Herrera, M.D.; Rodriguez-Rodriguez, R. Rice bran enzymatic extract restores endothelial function and vascular contractility in obese rats by reducing vascular inflammation and oxidative stress. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virdis, A.; Santini, F.; Colucci, R.; Duranti, E.; Salvetti, G.; Rugani, I.; Segnani, C.; Anselmino, M.; Bernardini, N.; Blandizzi, C.; et al. Vascular Generation of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Reduces Nitric Oxide Availability in Small Arteries from Visceral Fat of Obese Patients. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkan, T.; Yazir, Y.; Karson, A.; Bayramgurler, D. Etanercept Improves Cognitive Performance and Increases eNOS and BDNF Expression During Experimental Vascular Dementia in Streptozotocin- induced Diabetes. Curr. Neurovascular Res. 2015, 12, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Diaz, D.F.; Campion, J.; Milagro, F.I.; Paternain, L.; Solomon, A.; Martinez, J.A. Ascorbic acid oral treatment modifies lipolytic response and behavioural activity but not glucocorticoid metabolism in cafeteria diet-fed rats. Acta Physiol. 2009, 195, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Díaz, D.; Campión, J.; Milagro, F.I.; Martínez, J.A. Adiposity dependent apelin gene expression: Relationships with oxidative and inflammation markers. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2007, 305, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, I.; Milagro, F.; Martí, A.; Moreno-Aliaga, M.; Martínez, J.; De Miguel, C. Gene expression changes in rat white adipose tissue after a high-fat diet determined by differential display. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 318, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furchgott, R.F. Role of endothelium in responses of vascular smooth muscle. Circ. Res. 1983, 53, 557–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moncada, S.; Palmer, R.M.; Higgs, E.A. Nitric oxide: Physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 1991, 43, 109–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kobayasi, R.; Akamine, E.H.; Davel, A.P.; Rodrigues, M.A.; Carvalho, C.R.; Rossoni, L.V. Oxidative stress and inflammatory mediators contribute to endothelial dysfunction in high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice. J. Hypertens. 2010, 28, 2111–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Canales, J.S.; Cuenca, J.L.; López-Canales, O.A.; Aguilar-Carrasco, J.C.; Aranda-Zepeda, L.; López-Sánchez, P.; Castillo-Henkel, E.F.; López-Mayorga, R.M.; Valencia-Hernández, I. Pharmacological characterization of mechanisms involved in the vasorelaxation produced by rosuvastatin in aortic rings from rats with a cafeteria-style diet. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2015, 42, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Virdis, A.; Duranti, E.; Rossi, C.; Dell’Agnello, U.; Santini, E.; Anselmino, M.; Chiarugi, M.; Taddei, S.; Solini, A. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha participates on the endothelin-1/nitric oxide imbalance in small arteries from obese patients: Role of perivascular adipose tissue. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nyström, T.; Nygren, A.; Sjöholm, Å. Increased levels of tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in patients with Type II diabetes mellitus after myocardial infarction are related to endothelial dysfunction. Clin. Sci. 2006, 110, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Belmadani, S.; Picchi, A.; Xu, X.; Potter, B.J.; Tewari-Singh, N.; Capobianco, S.; Chilian, W.M.; Zhang, C. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Induces Endothelial Dysfunction in Lepr db Mice. Circulation 2007, 115, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, X.; Potter, B.J.; Wang, W.; Kuo, L.; Michael, L.; Bagby, G.J.; Chilian, W.M. TNF-a contributes to endothelial dysfunction in ischemia/reperfusion injury. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Rizzo, V. TNF-α potentiates protein-tyrosine nitration through activation of NADPH oxidase and eNOS localized in membrane rafts and caveolae of bovine aortic endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2007, 292, H954–H962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, S.; Xie, J.; Wang, Y.; Cai, B.; Kolls, J.; Nelson, S.; Hyman, A.; Summer, W.R.; Lippton, H. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibits endothelium-dependent relaxation. J. Appl. Physiol. 1993, 74, 2394–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, B.L.; Pendleton, L.C.; Levy, M.M.; Solomonson, L.P.; Eichler, D.C. Tumor necrosis factor-α reduces argininosuccinate synthase expression and nitric oxide production in aortic endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2007, 293, H1115–H1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, H.; Rahmutula, D.; Gardner, D.G. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Inhibits Endothelial Nitric-oxide Synthase Gene Promoter Activity in Bovine Aortic Endothelial Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nishimatsu, H.; Suzuki, E.; Takeda, R.; Takahashi, M.; Oba, S.; Kimura, K.; Nagano, T.; Hirata, Y. Blockade of Endogenous Proinflammatory Cytokines Ameliorates Endothelial Dysfunction in Obese Zucker Rats. Hypertens. Res. 2008, 31, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, J.; Kim, S.; Jeung, M.; Eun, S.; Woo, C.; Yoon, S.-Y.; Lee, K.-H. Serum Adiponectin, C-Reactive Protein and TNF-α Levels in Obese Korean Children. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 21, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picchi, A.; Gao, X.; Belmadani, S.; Potter, B.J.; Focardi, M.; Chilian, W.M.; Zhang, C. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Induces Endothelial Dysfunction in the Prediabetic Metabolic Syndrome. Circ. Res. 2006, 99, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardillo, C.; Schinzari, F.; Mores, N.; Mettimano, M.; Melina, D.; Zoli, A.; Ferraccioli, G. Intravascular tumor necrosis factor? blockade reverses endothelial dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 80, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, A.D.; Jayne, D.R.W.; Kharbanda, R.K.; McEniery, C.M.; Mackenzie, I.S.; Brown, J.; Wilkinson, I.B. Infliximab improves endothelial dysfunction in systemic vasculitis: A model of vascular inflammation. Circulation 2004, 109, 1718–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schinzari, F.; Armuzzi, A.; De Pascalis, B.; Mores, N.; Tesauro, M.; Melina, D.; Cardillo, C. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonism improves endothelial dysfunction in patients with Crohn’s disease. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 83, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilsborough, W.; Keen, H.; Taylor, A.; O’driscoll, G.J.; Arnolda, L.; Green, D.J. Anti-tumour necrosis factor-alpha therapy over conventional therapy improves endothelial function in adults with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2006, 26, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fichtlscherer, S.; Rössig, L.; Breuer, S.; Vasa, M.; Dimmeler, S.; Zeiher, A.M. Tumor Necrosis Factor Antagonism with Etanercept Improves Systemic Endothelial Vasoreactivity in Patients with Advanced Heart Failure. Circulation 2001, 104, 3023–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bayramgurler, D.; Karson, A.; Yazir, Y.; Celikyurt, I.K.; Kurnaz, S.; Utkan, T. The effect of etanercept on aortic nitric oxide-dependent vasorelaxation in an unpredictable chronic, mild stress model of depression in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 710, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirtaş, T.; Utkan, T.; Karson, A.; Yazır, Y.; Bayramgürler, D.; Gacar, N.; Yazir, Y. The Link Between Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress Model for Depression and Vascular Inflammation? Inflammation 2014, 37, 1432–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesauro, M.; Schinzari, F.; Rovella, V.; Melina, D.; Mores, N.; Barini, A.; Mettimano, M.; Lauro, D.; Iantorno, M.; Quon, M.J.; et al. Tumor Necrosis Factor- Antagonism Improves Vasodilation During Hyperinsulinemia in Metabolic Syndrome. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 1439–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dominguez, H.; Storgaard, H.; Rask-Madsen, C.; Hermann, T.S.; Ihlemann, N.; Nielsen, D.B.; Spohr, C.; Kober, L.; Vaag, A.A.; Torp-Pedersen, C. Metabolic and Vascular Effects of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Blockade with Etanercept in Obese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Vasc. Res. 2005, 42, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.A.; Farrah, T.; Goodwin, R.G. The TNF receptor superfamily of cellular and viral proteins: Activation, costimulation, and death. Cell 1994, 76, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Yin, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, J.; Jiang, X.; Yuan, L.; Wang, C.-Y.; Li, Z. Blockade of Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) Receptor Type 1-Mediated TNF-α Signaling Protected Wistar Rats from Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 2943–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romanatto, T.; Roman, E.A.; Arruda, A.P.; Denis, R.; Solon, C.; Milanski, M.; Moraes, J.C.; Bonfleur, M.L.; Degasperi, G.; Picardi, P.K.; et al. Deletion of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Receptor 1 (TNFR1) Protects against Diet-induced Obesity by Means of Increased Thermogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 36213–36222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamato, M.; Shiba, T.; Ide, T.; Seri, N.; Kudo, W.; Ando, M.; Yamada, K.-I.; Kinugawa, S.; Tsutsui, H. High-fat diet–induced obesity and insulin resistance were ameliorated via enhanced fecal bile acid excretion in tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptor knockout mice. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 359, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.A.; O’flanagan, C.H.; Bowers, L.W.; Allott, E.H.; Hursting, S.D. Translating Mechanism-Based Strategies to Break the Obesity−Cancer Link: A Narrative Review. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 118, 652–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reynolds, J.V.; Donohoe, C.L.; Doyle, S.L. Diet, obesity and cancer. Ir. J. Med Sci. 2010, 180, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Control (n = 10) | CD (n = 10) | CD + ETA (n = 10) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial body weight (g) | 55.1 ± 4.65 | 61.10 ± 9.23 | 58.99 ± 10.46 |
| Final body weight (g) | 265.5 ± 10.11 | 334.9 ± 7.87 * | 293.9 ± 18.68 * |
| Body weight gain at 12 weeks (g) | 210.4 ± 7.55 | 273.5 ± 4.33 * | 234.9 ± 10.65 * |
| kcal intake/day (kcal) | 35.17 ± 1.33 | 131.7 ± 9.01 * | 134.1 ± 11.34 * |
| Control (n = 10) | CD (n = 10) | CD + ETA (n = 10) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbachol Emax pD2 | 93.50 ± 1.67 6.95 ± 0.06 | 80.38 ± 3.25 * 6.66 ± 0.13 * | 93.60 ± 1.90 6.92 ± 0.28 |
| SNP Emax pD2 | 100.00 ± 0.00 7.34 ± 0.25 | 100.00 ± 0.00 7.26 ± 0.51 | 99.50 ± 1.58 7.36 ± 0.41 |
| KCl Emax | 904.38 ± 250.87 | 999.80 ± 260.92 | 926.75 ± 243.16 |
| Papaverine Emax | 100 ± 0.00 | 100 ± 0.00 | 100 ± 0.00 |
| Animal | Control | CD | CD + ETA |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 2 | 2+ 3+ 2+ 2+ 3+ 2+ 2+ 2+ 2+ 1+ | 1+ 2+ 1+ 1+ 2+ 1+ 1+ 1+ 2+ 1+ | 2+ 2+ 3+ 2+ 2+ 1+ 2+ 2+ 3+ 3+ |
| 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Răzvan-Valentin, S.; Güler, S.A.; Utkan, T.; Şahin, T.D.; Gacar, G.; Yazir, Y.; Rencber, S.F.; Mircea, L.; Cristian, B.; Bogdan, P.; et al. Etanercept Prevents Endothelial Dysfunction in Cafeteria Diet-Fed Rats. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2138. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19042138
Răzvan-Valentin S, Güler SA, Utkan T, Şahin TD, Gacar G, Yazir Y, Rencber SF, Mircea L, Cristian B, Bogdan P, et al. Etanercept Prevents Endothelial Dysfunction in Cafeteria Diet-Fed Rats. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(4):2138. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19042138
Chicago/Turabian StyleRăzvan-Valentin, Scăunaşu, Sertaç Ata Güler, Tijen Utkan, Tuğçe Demirtaş Şahin, Gulcin Gacar, Yusufhan Yazir, Selenay Furat Rencber, Lupușoru Mircea, Bălălău Cristian, Popescu Bogdan, and et al. 2022. "Etanercept Prevents Endothelial Dysfunction in Cafeteria Diet-Fed Rats" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 4: 2138. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19042138
APA StyleRăzvan-Valentin, S., Güler, S. A., Utkan, T., Şahin, T. D., Gacar, G., Yazir, Y., Rencber, S. F., Mircea, L., Cristian, B., Bogdan, P., & Utkan, N. Z. (2022). Etanercept Prevents Endothelial Dysfunction in Cafeteria Diet-Fed Rats. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(4), 2138. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19042138







