Hair Sample Analysis as a Method of Monitoring Exposure to Bisphenol A in Dogs
Abstract
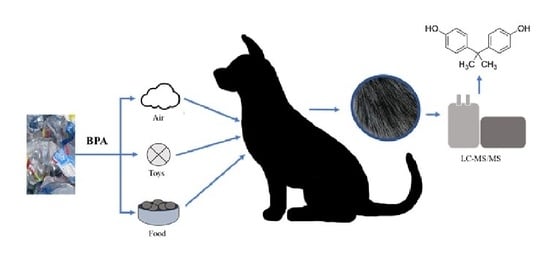
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Reagents
2.2. Hair Sample Collection
2.3. BPA Extraction and Analysis of Its Levels
2.4. Background and Quality Control
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ide, Y.; Kagawa, N.; Itakura, M.; Imae, I.; Sadakane, M.; Sano, T. Effective and selective bisphenol A synthesis on a layered silicate with spatially arranged sulfonic acid. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 2186–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michałowicz, J. Bisphenol A—Sources, toxicity and biotransformation. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 37, 738–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Hauser, R.; Marcus, M.; Olea, N.; Welshons, W.V. Human exposure to bisphenol A (BPA). Reprod. Toxicol. 2007, 24, 139–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konieczna, A.; Rutkowska, A.; Rachoń, D. Health risk of exposure to Bisphenol A (BPA). Rocz. Panstw. Zakl. Hig. 2015, 66, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gonsioroski, A.; Mourikes, V.E.; Flaws, J.A. Endocrine disruptors in water and their effects on the reproductive system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maragou, N.C.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Theodoridis, G.A.; Lampi, E.N.; Koupparis, M.A. Determination of bisphenol A in canned food by microwave assisted extraction, molecularly imprinted polymer-solid phase extraction and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life. Sci. 2020, 1137, 121938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaborowska, M.; Wyszkowska, J.; Borowik, A.; Kucharski, J. Bisphenol A—A dangerous pollutant distorting the biological properties of soil. Int. J. Mol Sci. 2021, 22, 12753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emnet, P.; Gaw, S.; Northcott, G.; Storey, B.; Graham, L. Personal care products and steroid hormones in the Antarctic coastal environment associated with two Antarctic research stations, McMurdo Station and Scott Base. Environ. Res. 2015, 136, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biedermann, S.; Tschudin, P.; Grob, K. Transfer of bisphenol A from thermal printer paper to the skin. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teeguarden, J.G.; Twaddle, N.C.; Churchwell, M.I.; Yang, X.; Fisher, J.W.; Seryak, L.M.; Doerge, D.R. 24-hour human urine and serum profiles of bisphenol A following ingestion in soup: Individual pharmacokinetic data and emographics. Data Brief 2015, 4, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Martin, J.W. Comparison of bisphenol A and bisphenol S percutaneous absorption and biotransformation. Environ. Health Perspect. 2019, 127, 67008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, J.; Yang, C.; Liu, T.; Tan, H.J.J.; Sheng, Y.; Wei, L.; Tang, P.; Huang, H.; Zeng, X.; Liu, S.; et al. Prenatal exposure to bisphenols and risk of preterm birth: Findings from Guangxi Zhuang birth cohort in China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 228, 112960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Shao, C.; Huang, X.; Qi, J.; Ge, R.; Guan, H.; Lin, Z. Extraction and detection of bisphenol A in human serum and urine by aptamer-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 1885–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodziach, K.; Staniszewska, M.; Falkowska, L.; Nehring, I.; Ożarowska, A.; Zaniewicz, G.; Meissner, W. Gastrointestinal and respiratory exposure of water birds to endocrine disrupting phenolic compounds. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovaříková, S.; Maršálek, P.; Habánová, M.; Konvalinová, J. Serum concentration of bisphenol A in elderly cats and its association with clinicopathological findings. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2021, 23, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iribarne-Durán, L.M.; Peinado, F.M.; Freire, C.; Castillero-Rosales, I.; Artacho-Cordón, F.; Olea, N. Concentrations of bisphenols, parabens, and benzophenones in human breast milk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochester, J.R. Bisphenol A and human health: A review of the literature. Reprod. Toxicol. 2013, 42, 132–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priego, A.R.; Parra, E.G.; Mas, S.; Morgado-Pascual, J.L.; Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Rayego-Mateos, S. Bisphenol A modulates autophagy and exacerbates chronic kidney damage in mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhao, Z.; Ji, W. Bisphenol A induces apoptosis, oxidative stress and inflammatory response in colon and liver of mice in a mitochondria-dependent manner. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 109182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoene, M.; Godlewski, J.; Rytel, L.; Dzika, E.; Bejer-Olenska, E.; Wojtkiewicz, J. Alterations in porcine intrahepatic sympathetic nerves after bisphenol A administration. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2018, 1, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Song, N.; Ren, J.; Li, W.; Xu, B.; Li, H.; Shen, G. Metabonomics reveals bisphenol A affects fatty acid and glucose metabolism through activation of LXR in the liver of male mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federico, A.; Dallio, M.; Gravina, A.G.; Diano, N.; Errico, S.; Masarone, M.; Romeo, M.; Tuccillo, C.; Stiuso, P.; Morisco, F.; et al. The Bisphenol A Induced Oxidative Stress in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Male Patients: A Clinical Strategy to Antagonize the Progression of the Disease. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, S.J.; Yang, E.J.; Oh, S.; Park, K.J.; Kim, T.; Hong, Y.P.; Yang, Y.J. The association between urinary bisphenol A levels and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Korean adults: Korean National Environmental Health Survey (KoNEHS) 2015–2017. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2021, 26, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukjamnong, S.; Thongkorn, S.; Kanlayaprasit, S.; Saeliw, T.; Hussem, K.; Warayanon, W.; Hu, V.W.; Tencomnao, T.; Sarachana, T. Prenatal exposure to bisphenol A alters the transcriptome-interactome profiles of genes associated with Alzheimer’s disease in the offspring hippocampus. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Bermejo, M.; Mas-Pérez, I.; Murillo-Llorente, M.T. The role of the bisphenol A in diabetes and obesity. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makowska, K.; Martín, J.; Rychlik, A.; Aparicio, I.; Santos, J.L.; Alonso, E.; Gonkowski, S. Assessment of exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in dogs by fur analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 286, 117435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makowska, K.; Martín, J.; Rychlik, A.; Aparicio, I.; Santos, J.L.; Alonso, E.; Gonkowski, S. Biomonitoring parabens in dogs using fur sample analysis—Preliminary studies. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikraj, R.; Lee, S.; Kannan, K. Biomonitoring of exposure to bisphenols, benzophenones, triclosan, and triclocarban in pet dogs and cats. Environ. Res. 2020, 180, 108821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koestel, Z.L.; Backus, R.C.; Tsuruta, K.; Spollen, W.G.; Johnson, S.A.; Javurek, A.B.; Ellersieck, M.R.; Wiedmeyer, C.E.; Kannan, K.; Xue, J.; et al. Bisphenol A (BPA) in the serum of pet dogs following short-term consumption of canned dog food and potential health consequences of exposure to BPA. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1804–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.H.; Kondo, F. Determination of bisphenol A in canned pet foods. Res. Vet. Sci. 2002, 73, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Hu, F.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, Y. Bisphenol A exposure perturbs visual function of adult cats by remodeling the neuronal activity in the primary visual pathway. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.; Liu, J.; Xu, G.; Wang, H.; Shen, J.; Zhou, Y. Bisphenol A exposure inhibits contrast sensitivity in cats involving increased response noise and inhibitory synaptic transmission. Brain. Res. Bull. 2020, 157, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabakci, R.; Macun, H.C.; Polat, I.M.; Yildirim, E. Inhibitory effect of Bisphenol A on in vitro feline uterine contractions. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2019, 205, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.C.; Huang, J.K.; Chou, C.T.; Cheng, J.S.; Tsai, J.Y.; Fang, Y.C.; Hsu, S.S.; Liao, W.C.; Chang, H.T.; Ho, C.M.; et al. Effect of bisphenol A on Ca(2+) fluxes and viability in Madin-Darby canine renal tubular cells. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 34, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, J.; Santos, J.L.; Aparicio, I.; Alonso, E. Exposure assessment to parabens, bisphenol A and perfluoroalkyl compounds in children, women and men by hair analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 695, 133864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsikantami, I.; Tzatzarakis, M.N.; Karzi, V.; Stavroulaki, A.; Xezonaki, P.; Vakonaki, E.; Alegakis, A.K.; Sifakis, S.; Rizos, A.K.; Tsatsakis, A.M. Biomonitoring of bisphenols A and S and phthalate metabolites in hair from pregnant women in Crete. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 712, 135651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzatzarakis, M.N.; Vakonaki, E.; Kavvalakis, M.P.; Barmpas, M.; Kokkinakis, E.N.; Xenos, K.; Tsatsakis, A.M. Biomonitoring of bisphenol A in hair of Greek population. Chemosphere 2015, 118, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, J.; Santos, J.L.; Aparicio, I.; Alonso, E. Analytical method for biomonitoring of endocrine-disrupting compounds (bisphenol A, parabens, perfluoroalkyl compounds and a brominated flame retardant) in human hair by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 945, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karzi, V.; Tzatzarakis, M.N.; Vakonaki, E.; Alegakis, T.; Katsikantami, I.; Sifakis, S.; Rizos, A.; Tsatsakis, A.M. Biomonitoring of bisphenol A, triclosan and perfluorooctanoic acid in hair samples of children and adults. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2018, 38, 1144–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.; Jacobs, G.; Vanermen, G.; Covaci, A.; Voorspoels, S. New approach for assessing human perfluoroalkyl exposure via hair. Talanta 2015, 144, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.L.; Bang, H.T.; Ji, S.Y.; Jeong, J.Y.; Kim, M.; Kim, B.; Lee, S.D.; Lee, Y.K.; Reddy, K.E.; Kim, K.H. A simple method to evaluate body condition score to maintain the optimal body weight in dogs. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2019, 61, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santonicola, S.; Ferrante, M.C.; Murru, N.; Gallo, P.; Mercogliano, R. Hot topic: Bisphenol A in cow milk and dietary exposure at the farm level. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siddique, M.A.B.; Harrison, S.M.; Monahan, F.J.; Cummins, E.; Brunton, N.P. Bisphenol A and metabolites in meat and meat products: Occurrence, toxicity, and recent development in analytical methods. Foods 2021, 10, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geens, T.; Roosens, L.; Neels, H.; Covaci, A. Assessment of human exposure to Bisphenol-A, Triclosan and Tetrabromobisphenol-A through indoor dust intake in Belgium. Chemosphere 2009, 76, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, S.N.; Kannan, K. Occurrence of bisphenol A in indoor dust from two locations in the eastern United States and implications for human exposures. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 61, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Abualnaja, K.O.; Asimakopoulos, A.G.; Covaci, A.; Gevao, B.; Johnson-Restrepo, B.; Kumosani, T.A.; Malarvannan, G.; Minh, T.B.; Moon, H.B.; et al. A comparative assessment of human exposure to tetrabromobisphenol A and eight bisphenols including bisphenol A via indoor dust ingestion in twelve countries. Environ. Int. 2015, 83, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasiljevic, T.; Harner, T. Bisphenol A and its analogues in outdoor and indoor air: Properties, sources and global levels. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 148013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooten, K.J.; Smith, P.N. Canine toys and training devices as sources of exposure to phthalates and bisphenol A: Quantitation of chemicals in leachate and in vitro screening for endocrine activity. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2245–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guignard, D.; Gauderat, G.; Gayrard, V.; Lacroix, M.Z.; Picard-Hagen, N.; Puel, S.; Toutain, P.L.; Viguié, C. Characterization of the contribution of buccal absorption to internal exposure to bisphenol A through the diet. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 93, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björnsdotter, M.K.; de Boer, J.; Ballesteros-Gómez, A. Bisphenol A and replacements in thermal paper: A review. Chemosphere 2017, 182, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becher, R.; Wellendorf, H.; Sakhi, A.K.; Samuelsen, J.T.; Thomsen, C.; Bølling, A.K.; Kopperud, H.M. Presence and leaching of bisphenol a (BPA) from dental materials. Acta Biomater. Odontol. Scand. 2018, 4, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehring, I.; Staniszewska, M.; Falkowska, L. Human hair, Baltic grey seal (Halichoerus grypus) fur and herring gull (Larus argentatus) feathers as accumulators of bisphenol A and alkylphenols. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 72, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Legeay, S.; Faure, S. Is bisphenol A an environmental obesogen? Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 31, 594–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rubin, B.S.; Schaeberle, C.M.; Soto, A.M. The case for BPA as an obesogen: Contributors to the controversy. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ronn, M.; Lind, L.; Orberg, J.; Kullberg, J.; Söderberg, S.; Larsson, A.; Johansson, L.; Ahlström, H.; Lind, P.M. Bisphenol A is related to circulating levels of adiponectin, leptin and ghrelin, but not to fat mass or fat distribution in humans. Chemosphere 2014, 112, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menale, C.; Grandone, A.; Nicolucci, C.; Cirillo, G.; Crispi, S.; Di Sessa, A.; Marzuillo, P.; Rossi, S.; Mita, D.G.; Perrone, L.; et al. Bisphenol A is associated with insulin resistance and modulates adiponectin and resistin gene expression in obese children. Pediatr. Obes. 2017, 12, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calafat, A.M.; Ye, X.Y.; Wong, L.Y.; Reidy, J.A.; Needham, L.L. Exposure of the US population to bisphenol A and 4-tertiary-octylphenol: 2003–2004. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeuchi, T.; Tsutsumi, O. Serum bisphenol a concentrations showed gender differences, possibly linked to androgen levels. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 291, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalingaiah, S.; Meeker, J.D.; Pearson, K.R.; Calafat, A.M.; Ye, X.; Petrozza, J.; Hauser, R. Temporal variability and predictors of urinary bisphenol A concentrations in men and women. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kim, C.S.; Park, S.; Han, S.Y.; Pyo, M.Y.; Yang, M. Gender differences in the levels of bisphenol A metabolites in urine. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 312, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claessens, J.; Pirard, C.; Charlier, C. Determination of contamination levels for multiple endocrine disruptors in hair from a non-occupationally exposed population living in Liege (Belgium). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 815, 152734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Kim, C.H.; Kim, S.; Cho, S.-H. Simultaneous determination of bisphenol A and estrogens in hair samples by liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1058, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Gómez, R.; Martín, J.; Zafra-Gómez, A.; Alonso, E.; Vílchez, J.L.; Navalón, A. Biomonitoring of 21 endocrine disrupting chemicals in human hair samples using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Hair Sample Number | Concentration Levels of BPA (ng/g) | |
|---|---|---|
| Geometric Mean (n = 3) | Standard Deviation (n = 3) | |
| 1 | 307 | 9.56 |
| 2 | 114 | 7.49 |
| 3 | 27.2 | 0.90 |
| 4 | 436 | 7.16 |
| 5 | 52.4 | 2.30 |
| 6 | 178 | 7.40 |
| 7 | 58.6 | 3.91 |
| 8 | 50.2 | 1.42 |
| 9 | <MDL | - |
| 10 | 13.5 | 1.23 |
| 11 | 289 | 60.4 |
| 12 | 80.7 | 5.76 |
| 13 | 126 | 1.65 |
| 14 | 14.4 | 1.28 |
| 15 | 24.3 | 1.30 |
| 16 | 99.0 | 14.0 |
| 17 | 31.1 | 2.98 |
| 18 | 47.6 | 1.57 |
| 19 | 25.5 | 1.09 |
| 20 | 10.6 | 1.62 |
| 21 | 7.85 | 0.60 |
| 21 | 47.1 | 1.57 |
| 23 | <MDL | - |
| 24 | 7.75 | 0.65 |
| 25 | 7.05 | 0.51 |
| 26 | 25.5 | 2.13 |
| 27 | 74.0 | 1.17 |
| 28 | 40.1 | 2.19 |
| 29 | 9.68 | 0.89 |
| 30 | 72.4 | 1.32 |
| Cumulative data | ||
| Range (ng/g) | <MDL–436 | |
| Arithmetic mean (ng/g) | 81.30 | |
| Geometric mean (ng/g) | 43.32 | |
| Median (ng/g) | 47.35 | |
| Frequency of detection (%) | 93.33 | |
| Species | Group of Animals | Mean BPA Levels (ng/mL) | Matrix | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cats | All cats included in the study | 1.06 ± 0.908 | serum | [15] |
| Indoor cats | 1.27 ± 0.992 | |||
| Cats with outdoor access | 06.60 ± 0.529 | |||
| Mature cats (7–10 years old) | 1.28 ± 0.994 | |||
| Geriatric cats (over 15 years old | 0 420 ± 0.240 | |||
| Cats fed with canned food | 1.23 ± 0.935 | |||
| Cats not fed with canned food | 0.774 ± 0.795 | |||
| Males | 1.14 ± 1.15 | |||
| Females | 0.992 ± 0.728 | |||
| All cats included in the study | 22.3 ± 155 | urine | [28] | |
| Dogs | All dogs included in the study | 1.3 ± 4.6 | ||
| Dogs before feeding with the canned food containing BPA | 0.7 ± 0.15 | serum | [29] | |
| Dogs after 14 days of feeding with canned foods containing BPS | 2.2 ± 0.15 |
| Species | Country | Number of Samples | BPA Concentration Levels (ng/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human | Belgium | 114 | <LOQ–587.1 | [61] |
| Greece | 69 | 13.1–192.8 | [37] | |
| Greece | 122 | 2.6–205 | [39] | |
| Greece | 100 | 9.6–650.3 | [36] | |
| Korea | 10 | 17–22.9 | [62] | |
| Spain | 6 | 24–158 | [38] | |
| Spain | 6 | 9.2–45 | [63] | |
| Spain | 42 | 24.4–1427 | [35] | |
| Poland | 42 | 26.1–1498.6 | [52] | |
| Grey seal | Poland | 17 | <LOQ–137.2 | [52] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Makowska, K.; Martín, J.; Rychlik, A.; Aparicio, I.; Santos, J.L.; Alonso, E.; Gonkowski, S. Hair Sample Analysis as a Method of Monitoring Exposure to Bisphenol A in Dogs. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19084600
Makowska K, Martín J, Rychlik A, Aparicio I, Santos JL, Alonso E, Gonkowski S. Hair Sample Analysis as a Method of Monitoring Exposure to Bisphenol A in Dogs. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(8):4600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19084600
Chicago/Turabian StyleMakowska, Krystyna, Julia Martín, Andrzej Rychlik, Irene Aparicio, Juan Luis Santos, Esteban Alonso, and Sławomir Gonkowski. 2022. "Hair Sample Analysis as a Method of Monitoring Exposure to Bisphenol A in Dogs" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 8: 4600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19084600
APA StyleMakowska, K., Martín, J., Rychlik, A., Aparicio, I., Santos, J. L., Alonso, E., & Gonkowski, S. (2022). Hair Sample Analysis as a Method of Monitoring Exposure to Bisphenol A in Dogs. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(8), 4600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19084600