Nano-Hydroxyapatite (nHAp) in the Remineralization of Early Dental Caries: A Scoping Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Question
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Search Strategy
2.4. Data Charting and Items
2.5. Synthesis of Result
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Included In Vitro Studies
| Author/Year | Type of Study | Conclusion | Reason for Exclusion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sari et al. [34] 2021 | In vitro | Remineralization of teeth and antibacterial/antibiofilm activity with nHAp and Curcuma aeruginosa toothpastes | nHAp was combined with Curcuma aeruginosa (C. aeruginosa) |
| Amaechi et al. [35] 2021 | In situ | Remineralization and demineralization inhibition efficacies of nHAp dental lotion applied immediately after brushing teeth with nHAp toothpaste | 5% nHAp dental lotion was used with 5% nHAp toothpaste |
| Ionescu et al. [36] 2020 | In vitro | Decreased microbial colonization of RBC surfaces | Details of nHAp not clear |
| Kumar et al. [37] 2020 | In vitro | Herbal dentifrice incorporated with nHAp had higher demineralizing potential as compared with a fluoride dentifrice | 50% nHAp crystals were combined with herbal extract |
| Bologa et al. [38] 2020 | In vitro | Dentinal tubules occluded and mineral deposition increased on the dentin surface with nHAp containing toothpastes | Details of nHAp not clear |
| Suryani et al. [39] 2020 | Ex vivo | BAG and CCP-ACPF paste showed better remineralizing potential | Details of nHAp not clear |
| Wierichs et al. [40] 2020 | In situ | Both fluoride-free dentifrices, one containing nHAp, did not hamper demineralization | Details of nHAp not clear |
| Alencar et al. [41] 2020 | RCT | nHAP + PBM are effective in the control of dentin hypersensitivity | Details of nHAp not clear |
| Rajendran et al. [42] 2020 | In vitro | Superior remineralization properties of Sr nHAp paste, found nontoxic | 25 mol% Srn nHAp was used |
| Pei et al. [43] 2019 | In vitro | nHAp-containing desensitizing toothpastes could occlude dentinal tubules. Application of nHAp desensitizers decreased bond strengths of the resin-dentin bonding. | Details of nHAp not clear |
| Alhamed et al. [44] 2019 | Clinical study | nHAp was most effective in the treatment of initial carious lesion | Details of nHAp not clear |
| Reis et al. [45] 2018 | In vitro | nHAp-containing dentifrice promoted less superficial roughness after 14 days | Details of nHAp not clear |
| Nozari et al. [46] 2017 | In vitro | nHAp serum had remineralizing (initial caries) potential similar to NSF and NaF varnish | Details of nHAp not clear |
| Esteves-Oliveira et al. [47] 2017 | In vitro | nHAp did not inhibit caries demineralization | 20% Zinc-carbonate nHAp was used |
| Ebadifar et al. [48] 2017 | In vitro | nHAp-containing toothpaste was more effective in remineralization | 7% nHAp was combined with fluoride |
| Kamath et al. [49] 2017 | In vitro | nHAp showed remineralization potential similar to others | Details of nHAp not clear |
| Ajami et al. [50] 2016 | In vitro | Enamel surfaces and tooth color were not restored with nHAp serum | Details of nHAp not clear |
| Low et al. [51] 2015 | Clinical study | Daily application of toothpaste containing potassium nitrate, sodium monoflurophosphate, and nHAp significantly reduced tooth pain due to dentin hypersensitivity | Details of nHAp not clear |
| Souza et al. [52] 2015 | In situ | 10% nHAp helps in remineralization | 10% nHAp was combined with fluoride |
| Mielczarek and Michalik [53] 2014 | In vitro | Reduction in surface roughness with nHAp but no significant improvement in SMH | 1% nHAp was combined with 1450 ppm fluoride |
3.2. Characteristics of the Included Clinical Studies
3.3. Outcome of the Search Related to the Role of nHAp in Caries Preventive Applications
4. Discussion
4.1. Role of nHAp in Enamel Remineralization
4.2. Role of nHAp in Enamel Demineralization
4.3. Role of nHAp in Reducing Dentinal Sensitivity
4.4. The Optimal Concentration of nHAp
4.5. Limitations
4.6. Future Direction
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kassebaum, N.J.; Bernabé, E.; Dahiya, M.; Bhandari, B.; Murray, C.J.; Marcenes, W. Global burden of untreated caries: A systematic review and metaregression. J. Dent. Res. 2015, 94, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, S.; Rejula, F.; Sam, J.V.G.; Christaline, R.; Nair, M.G.; Dinakaran, S. Comparative evaluation of effect of nano-hydroxyapatite and 8% arginine containing toothpastes in managing dentin hypersensitivity: Double blind randomized clinical trial. Acta Med. (Hradec Kral.) 2017, 60, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastenbom, L.; Falsen, A.; Larsson, P.; Sunnegårdh-Grönberg, K.; Davidson, T. Costs and health-related quality of life in relation to caries. BMC Oral Health 2019, 19, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abou Neel, E.A.; Aljabo, A.; Strange, A.; Ibrahim, S.; Coathup, M.; Young, A.M.; Bozec, L.; Mudera, V. Demineralization-remineralization dynamics in teeth and bone. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 4743–4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P.; Muthuswamy Pandian, S. Bionic effects of nano hydroxyapatite dentifrice on demineralised surface of enamel post orthodontic debonding: In-vivo split mouth study. Prog. Orthod. 2021, 22, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.A.; Mang, T.; Tabbaa, S.; Al-Jewair, T. Analysis of enamel surface roughness after different adhesive removal techniques for orthodontic bracket debonding. Lasers Dent. Sci. 2018, 2, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosin-Grget, K.; Peros, K.; Sutej, I.; Basic, K. The cariostatic mechanisms of fluoride. Acta Med. Acad. 2013, 42, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, M.C.; Clarkson, J.; Glenny, A.M.; Lo, E.C.; Marinho, V.C.; Tsang, B.W.; Walsh, T.; Worthington, H.V. Cochrane reviews on the benefits/risks of fluoride toothpastes. J. Dent. Res. 2011, 90, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roveri, N.; Battistella, E.; Bianchi, C.L.; Foltran, I.; Foresti, E.; Iafisco, M.; Lelli, M.; Naldoni, A.; Palazzo, B.; Rimondini, L. Surface enamel remineralization: Biomimetic apatite nanocrystals and fluoride ions different effects. J. Nanomater. 2009, 2009, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talwar, M.; Borzabadi-Farahani, A.; Lynch, E.; Borsboom, P.; Ruben, J. Remineralization of demineralized enamel and dentine using 3 dentifrices-an invitro study. Dent. J. 2019, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kasemkhun, P.; Rirattanapong, P. The efficacy of non-fluoridated toothpastes on artificial enamel caries in primary teeth: An in vitro study. J. Int Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2021, 11, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pepla, E.; Besharat, L.K.; Palaia, G.; Tenore, G.; Migliau, G. Nano-hydroxyapatite and its applications in preventive, restorative and regenerative dentistry: A review of literature. Ann. Stomatol. 2014, 5, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Gao, S.; Cheng, L.; Yu, H. Remineralization potential of nano-hydroxyapatite on initial enamel lesions: An in vitro study. Caries Res. 2011, 45, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juntavee, A.; Juntavee, N.; Hirunmoon, P. Remineralization potential of nanohydroxyapatite toothpaste compared with tricalcium phosphate and fluoride toothpaste on artificial carious lesions. Int J. Dent. 2021, 2021, 5588832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vano, M.; Derchi, G.; Barone, A.; Pinna, R.; Usai, P.; Covani, U. Reducing dentine hypersensitivity with nano-hydroxyapatite toothpaste: A double-blind randomized controlled trial. Clin. Oral Investig. 2018, 22, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grocholewicz, K.; Matkowska-Cichocka, G.; Makowiecki, P.; Drozdzik, A.; Ey-Chmielewska, H.; Dziewulska, A.; Tomasik, M.; Trybek, G.; Janiszewska-Olszowska, J. Effect of nano-hydroxyapatite and ozone on approximal initial caries: A randomized clinical trial. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaechi, B.T.; Lemke, K.C.; Saha, S.; Luong, M.N.; Gelfond, J. Clinical efficacy of nanohydroxyapatite-containing toothpaste at relieving dentin hypersensitivity: An 8 weeks randomized control trial. BDJ Open 2021, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.H.; Kwon, H.K.; Kim, B.I. The addition of nano-sized hydroxyapatite to a sports drink to inhibit dental erosion: In vitro study using bovine enamel. J. Dent. 2011, 39, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. Prisma extension for scoping reviews (prisma-scr): Checklist and explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colquhoun, H.L.; Levac, D.; O’Brien, K.K.; Straus, S.; Tricco, A.C.; Perrier, L.; Kastner, M.; Moher, D. Scoping reviews: Time for clarity in definition, methods, and reporting. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2014, 67, 1291–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.D.; Godfrey, C.M.; Khalil, H.; McInerney, P.; Parker, D.; Soares, C.B. Guidance for conducting systematic scoping reviews. Int J. Evid. Based Healthc. 2015, 13, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Talioti, E.; Hill, R.; Gillam, D.G. The efficacy of selected desensitizing otc products: A systematic review. ISRN Dent. 2014, 2014, 865761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.L.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, Y.D.; Yan, X.; Li, X.C.; Lin, H. Effect of desensitizing toothpastes on dentine hypersensitivity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Dent. 2018, 75, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghgoo, R.; Ahmadvand, M.; Moshaverinia, S. Remineralizing effect of topical novamin and nano-hydroxyapatite on caries-like lesions in primary teeth. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract 2016, 17, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, N.; Sharma, N.; Kaur, N. Surface remineralization potential of nano-hydroxyapatite, sodium monofluorophosphate, and amine fluoride containing dentifrices on primary and permanent enamel surfaces: An in vitro study. J. Indian Soc. Pedod. Prev. Dent. 2018, 36, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geeta, R.D.; Vallabhaneni, S.; Fatima, K. Comparative evaluation of remineralization potential of nanohydroxyapatite crystals, bioactive glass, casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate, and fluoride on initial enamel lesion (scanning electron microscope analysis)—An in vitro study. J. Conserv. Dent. 2020, 23, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyavhare, S.; Sharma, D.S.; Kulkarni, V.K. Effect of three different pastes on remineralization of initial enamel lesion: An in vitro study. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2015, 39, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, C.; Gohil, U.; Parekh, V.; Joshi, S. Comparative evaluation of the remineralizing potential of commercially available agents on artificially demineralized human enamel: An in vitro study. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2019, 10, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comar, L.P.; Souza, B.M.; Gracindo, L.F.; Buzalaf, M.A.; Magalhaes, A.C. Impact of experimental nano-hap pastes on bovine enamel and dentin submitted to a ph cycling model. Braz. Dent. J. 2013, 24, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leal, A.M.C.; Beserra Dos Santos, M.V.; da Silva Filho, E.C.; Menezes de Carvalho, A.L.; Tabchoury, C.P.M.; Vale, G.C. Development of an experimental dentifrice with hydroxyapatite nanoparticles and high fluoride concentration to manage root dentin demineralization. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 7469–7479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, S.M.; El-Wassefy, N.A.; Alsayed, M.A. Evaluation of color changes of white spot lesions treated with three different treatment approaches: An in-vitro study. Dent. Press J. Orthod. 2020, 25, 26–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hwang, J.-M.; Kang, J.-O.; Park, Y.-d.; Choi, Y.-s. Research About Bovine Teeth Brightness with Using Dentifrice Slurry Including Nano-Hydroxyapatite. In Proceedings of the 2010 3rd International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Informatics, Yantai, China, 16–18 October 2010; pp. 1958–1960. [Google Scholar]
- Manchery, N.; John, J.; Nagappan, N.; Subbiah, G.K.; Premnath, P. Remineralization potential of dentifrice containing nanohydroxyapatite on artificial carious lesions of enamel: A comparative in vitro study. Dent. Res. J. (Isfahan) 2019, 16, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, Y.W.; Nuzulia, N.A.; Wahyuni, W.T.; Bahtiar, A.; Saputra, A.; Subroto, M.H.A.; Ariesanti, Y.; Syafitri, U.; Bachtiar, I. Remineralization and antibacterial/antibiofilm effects of toothpaste containing nanohydroxyapatite and curcuma aeruginosa extract. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaechi, B.T.; Alshareif, D.O.; Azees, P.A.A.; Shehata, M.A.; Lima, P.P.; Abdollahi, A.; Kalkhorani, P.S.; Evans, V.; Bagheri, A.; Okoye, L.O. Anti-caries evaluation of a nano-hydroxyapatite dental lotion for use after toothbrushing: An in situ study. J. Dent. 2021, 115, 103863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ionescu, A.C.; Cazzaniga, G.; Ottobelli, M.; Garcia-Godoy, F.; Brambilla, E. Substituted nano-hydroxyapatite toothpastes reduce biofilm formation on enamel and resin-based composite surfaces. J. Funct. Biomater. 2020, 11, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.P.; Arumugham, I.M.; Anusha, D.; Sakthi, S.; Kengadaran, S. Effect of nano-hydroxyapatite crystal incorporated herbal dentifrice on remineralization of incipient caries lesion- a pilot study. J. Pharm. Res. Int. 2020, 32, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Bologa, E.; Stoleriu, S.; Iovan, G.; Ghiorghe, C.A.; Nica, I.; Andrian, S.; Amza, O.E. Effects of dentifrices containing nanohydroxyapatite on dentinal tubule occlusion—A scanning electron microscopy and edx study. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryani, H.; Gehlot, P.M.; Manjunath, M.K. Evaluation of the remineralisation potential of bioactive glass, nanohydroxyapatite and casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate fluoride-based toothpastes on enamel erosion lesion -an ex vivo study. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2020, 31, 670–677. [Google Scholar]
- Wierichs, R.J.; Musiol, J.; Erdwey, D.; Esteves-Oliveira, M.; Apel, C.; Meyer-Lueckel, H. Re- and demineralization characteristics of dentin depending on fluoride application and baseline characteristics in situ. J. Dent. 2020, 94, 103305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alencar, C.D.; Ortiz, M.I.; Silva, F.A.; Alves, E.B.; Araujo, J.L.; Silva, C.M. Effect of nanohydroxyapatite associated with photobiomodulation in the control of dentin hypersensitivity: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Am. J. Dent. 2020, 33, 138–144. [Google Scholar]
- Rajendran, R.; Nair, K.R.; Sandhya, R.; Ashik, P.M.; Veedu, R.P.; Saleem, S. Evaluation of remineralization potential and cytotoxicity of a novel strontium-doped nanohydroxyapatite paste: An in vitro study. J. Conserv. Dent. 2020, 23, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, D.; Meng, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Lu, Y. Influence of nano-hydroxyapatite containing desensitizing toothpastes on the sealing ability of dentinal tubules and bonding performance of self-etch adhesives. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 91, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhamed, M.; Almalki, F.; Alselami, A.; Alotaibi, T.; Elkwatehy, W. Effect of different remineralizing agents on the initial carious lesions—A comparative study. Saudi Dent. J. 2020, 32, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, P.Q.; da Silva, E.M.; Calazans, F.S.; Lopes, L.S.; Poubel, L.A.; Alves, W.V.; Barceleiro, M.O. Effect of a dentifrice containing nanohydroxyapatite on the roughness, color, lightness, and brightness of dental enamel subjected to a demineralization challenge. Gen. Dent. 2018, 66, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nozari, A.; Ajami, S.; Rafiei, A.; Niazi, E. Impact of nano hydroxyapatite, nano silver fluoride and sodium fluoride varnish on primary teeth enamel remineralization: An in vitro study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, ZC97–ZC100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Esteves-Oliveira, M.; Santos, N.M.; Meyer-Lueckel, H.; Wierichs, R.J.; Rodrigues, J.A. Caries-preventive effect of anti-erosive and nano-hydroxyapatite-containing toothpastes in vitro. Clin. Oral Investig. 2017, 21, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebadifar, A.; Nomani, M.; Fatemi, S.A. Effect of nano-hydroxyapatite toothpaste on microhardness ofartificial carious lesions created on extracted teeth. J. Dent. Res. Dent. Clin. Dent. Prospect. 2017, 11, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamath, P.; Nayak, R.; Kamath, S.U.; Pai, D. A comparative evaluation of the remineralization potential of three commercially available remineralizing agents on white spot lesions in primary teeth: An in vitro study. J. Indian Soc. Pedod. Prev. Dent. 2017, 35, 229–237. [Google Scholar]
- Ajami, S.; Pakshir, H.R.; Babanouri, N. Impact of nanohydroxyapatite on enamel surface roughness and color change after orthodontic debonding. Prog. Orthod. 2016, 17, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Low, S.B.; Allen, E.P.; Kontogiorgos, E.D. Reduction in dental hypersensitivity with nano-hydroxyapatite, potassium nitrate, sodium monoflurophosphate and antioxidants. Open Dent. J. 2015, 9, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souza, B.M.; Comar, L.P.; Vertuan, M.; Fernandes Neto, C.; Buzalaf, M.A.; Magalhaes, A.C. Effect of an experimental paste with hydroxyapatite nanoparticles and fluoride on dental demineralisation and remineralisation in situ. Caries Res. 2015, 49, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielczarek, A.; Michalik, J. The effect of nano-hydroxyapatite toothpaste on enamel surface remineralization. An in vitro study. Am. J. Dent. 2014, 27, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jena, A.; Kala, S.; Shashirekha, G. Comparing the effectiveness of four desensitizing toothpastes on dentinal tubule occlusion: A scanning electron microscope analysis. J. Conserv. Dent. 2017, 20, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulal, R.; Jayanti, I.; Sambashivaiah, S.; Bilchodmath, S. An in-vitro comparison of nano hydroxyapatite, novamin and proargin desensitizing toothpastes—A sem study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, ZC51–ZC54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschoppe, P.; Zandim, D.L.; Martus, P.; Kielbassa, A.M. Enamel and dentine remineralization by nano-hydroxyapatite toothpastes. J. Dent. 2011, 39, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Magalhaes, A.C.; Francisconi-Dos-Rios, L.F.; Calabria, M.P.; Araujo, D.; Buzalaf, M.; Lauris, J.; Pereira, J.C. Treatment of dentin hypersensitivity using nano-hydroxyapatite pastes: A randomized three-month clinical trial. Oper Dent. 2016, 41, E93–E101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vano, M.; Derchi, G.; Barone, A.; Covani, U. Effectiveness of nano-hydroxyapatite toothpaste in reducing dentin hypersensitivity: A double-blind randomized controlled trial. Quintessence Int. 2014, 45, 703–711. [Google Scholar]
- Gopinath, N.M.; John, J.; Nagappan, N.; Prabhu, S.; Kumar, E.S. Evaluation of dentifrice containing nano-hydroxyapatite for dentinal hypersensitivity: A randomized controlled trial. J. Int. Oral Health 2015, 7, 118–122. [Google Scholar]
- Amaechi, B.T.; Mathews, S.M.; Ramalingam, K.; Mensinkai, P.K. Evaluation of nanohydroxyapatite-containing toothpaste for occluding dentin tubules. Am. J. Dent. 2015, 28, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Najibfard, K.; Ramalingam, K.; Chedjieu, I.; Amaechi, B.T. Remineralization of early caries by a nano-hydroxyapatite dentifrice. J. Clin. Dent. 2011, 22, 139–143. [Google Scholar]
- Badiee, M.; Jafari, N.; Fatemi, S.; Ameli, N.; Kasraei, S.; Ebadifar, A. Comparison of the effects of toothpastes containing nanohydroxyapatite and fluoride on white spot lesions in orthodontic patients: A randomized clinical trial. Dent. Res. J. (Isfahan) 2020, 17, 354–359. [Google Scholar]
- Amaechi, B.T.; Lemke, K.C.; Saha, S.; Gelfond, J. Clinical efficacy in relieving dentin hypersensitivity of nanohydroxyapatite-containing cream: A randomized controlled trial. Open Dent. J. 2018, 12, 572–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margolis, H.C.; Moreno, E.C. Kinetics of hydroxyapatite dissolution in acetic, lactic, and phosphoric acid solutions. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1992, 50, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Featherstone, J.D. Remineralization, the natural caries repair process--the need for new approaches. Adv. Dent. Res. 2009, 21, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Gao, S.; Cheng, L.; Yu, H. Combined effects of nano-hydroxyapatite and galla chinensis on remineralisation of initial enamel lesion in vitro. J. Dent. 2010, 38, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, F.; Beasley, T.; Abraham, P. In vivo delivery of fluoride and calcium from toothpaste containing 2% hydroxyapatite. Int. Dent. J. 2009, 59, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, M.; Poornima, P.; Praveen, S.; Nagaveni, N.B.; Roopa, K.B.; Neena, I.E.; Bharath, K.P. Comparison of cpp-acp, tri-calcium phosphate and hydroxyapatite on reminerallization of artificial caries like lesions on primary enamel—An in vitro study. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2016, 40, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.B.; Gao, S.S.; Yu, H.Y. Effect of nano-hydroxyapatite concentration on remineralization of initial enamel lesion in vitro. Biomed. Mater. 2009, 4, 34104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.; Kwon, H.; Choi, C.H.; Kim, B. Combined effects of nano-hydroxyapatite and naf on remineralization of early caries lesion. In Key Engineering Materials; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Freienbach, Switzerland, 2007; pp. 1347–1350. [Google Scholar]
- Ten Cate, J.M.; Featherstone, J.D. Mechanistic aspects of the interactions between fluoride and dental enamel. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 1991, 2, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
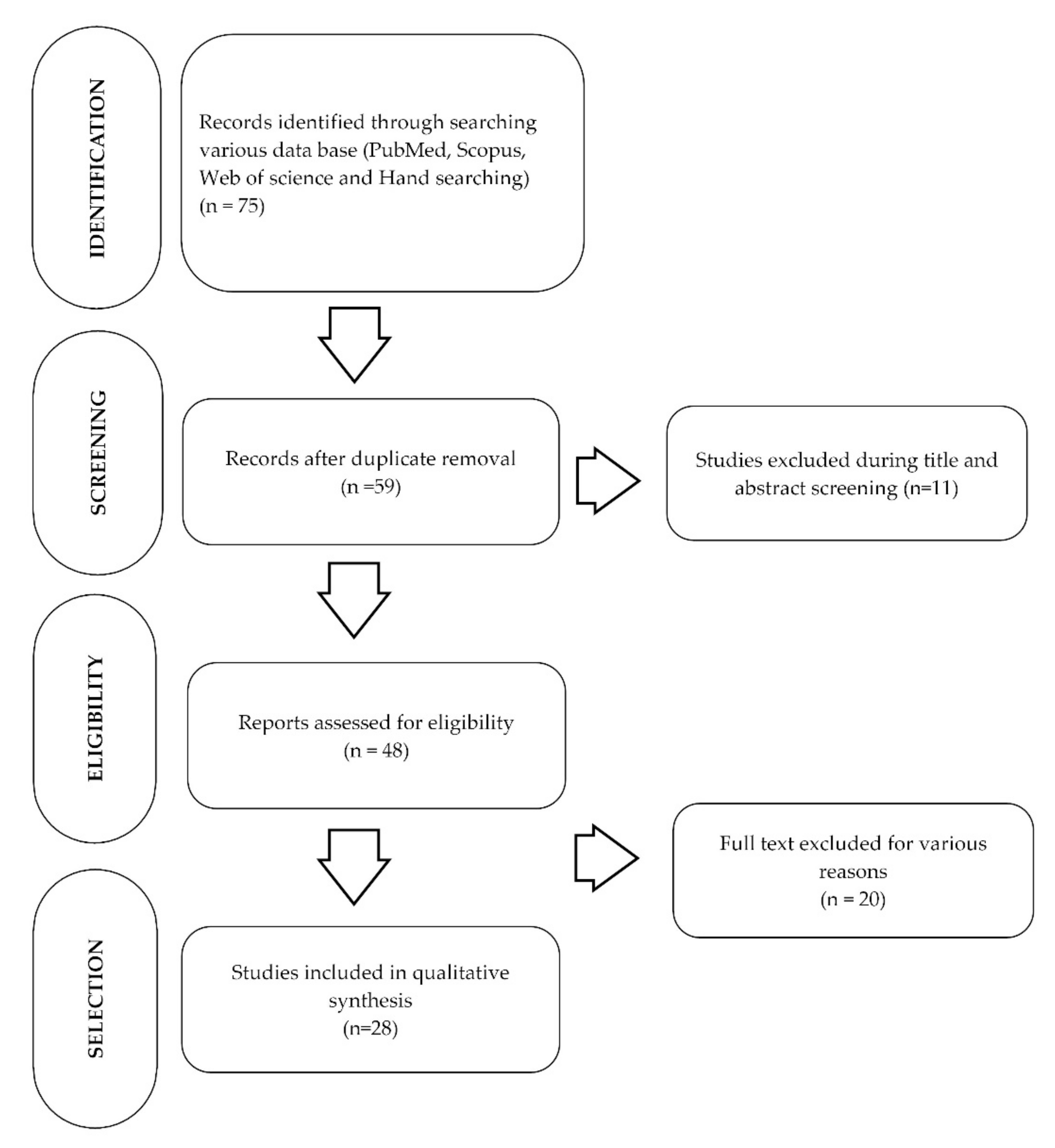
| Search Strategy | MeSH/Keywords | Result |
|---|---|---|
| #1 | ((“nano” [Journal] OR “nano” [All Fields]) AND (“durapatite” [MeSH Terms] OR “durapatite” [All Fields] OR “hydroxyapatite” [All Fields] OR “hydroxyapatites” [MeSH Terms] OR “hydroxyapatites” [All Fields])) AND (2000:2022 [pdat]) | 2423 |
| #2 | (“dentifrices” [Pharmacological Action] OR “dentifrices” [MeSH Terms] OR “dentifrices” [All Fields] OR “dentifrice” [All Fields]) AND (2000:2021 [pdat]) | 7839 |
| #3 | “toothpastes” [All Fields] OR “toothpastes” [MeSH Terms] OR “toothpastes” [All Fields] OR “toothpaste” [All Fields] | 6022 |
| #4 | #2 OR #3 | 9751 |
| #5 | #1 AND #4 | 59 |
| Title and abstract screening | 48 | |
| Full text with inclusion and exclusion criteria | 28 | |
| Excluded studies | 20 |
| Author/ Year | Aim | Samples Assessed | Percentage of nHAp | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Verma and Pandian [5] 2021 | Effects of nHAp dentifrice on demineralized surface of enamel post orthodontic debonding | Maxillary premolars, therapeutic extraction | 10% nHAp | Superior remineralizing effect of nHAp dentifrice on enamel after post- orthodontic debonding |
| Juntavee et al. [14] 2021 | Remineralization effect of various non-fluoridated and fluoridated toothpaste | Extracted human premolars | 10% nHAp | nHAP improved remineralization for treating initial carious lesions |
| Kasemkhun and Rirattanapong, [11] 2021 | Remineralizing effect of various non-fluoridated toothpastes on artificial caries in primary teeth | Intact primary incisor teeth | 10% nHAp | Better remineralizing of primary teeth with nHAp than 1000 ppm fluoridated toothpaste |
| Geeta et al. [26] 2020 | Remineralizing effect of four agents on initial enamel lesion | Human maxillary central incisors | 1% nHAp | nHAp-containing dentifrice has highest remineralizing potential |
| Hammad et al. [31] 2020 | Color changes and stability of the resin infiltrant on WSLs with nHAp | Enamel surfaces with artificially created WSLs | 10% nHAp | Better color change of WSLs with resin infiltrant than nHAp toothpaste |
| Leal et al. [30] 2020 | Effectiveness of high fluoride and nHAp-containing dentifrice on root dentin demineralization. | Dentin specimens were obtained from bovine incisors | 20% nHAp | nHAp reduced dentin demineralization |
| Manchery et al. [33] 2019 | Remineralization ability of nHAp, NovaMin, and amine fluoride dentifrice on artificial enamel caries | Extracted sound premolars | 10% nHAp | nHAp can remineralize artificial carious lesions |
| Joshi et al. [28] 2019 | Estimate initial stage of demineralization through remineralization potential of four commercially available agents | Permanent intact premolar | 1% nHAp | nHAp improved remineralization and SMH |
| Grewal et al. [25] 2018 | Remineralizing efficacy of the three dentifrices on both primary and permanent enamel surfaces | Enamel sections from primary and permanent molars | 10% nHAp | nHAp exhibited highest remineralization (mineral gain) |
| Jena et al. [54] 2017 | SEM study of dentinal tubule occlusion using four different desensitizing dentifrices | Dentin blocks from human molars | 15% nHAp | Reduction in dentinal hypersensitivity with 15% nHAp |
| Haghgoo et al. [24] 2016 | Remineralizing of primary tooth caries-like lesions with NovaMin and nHAp | Sound human primary anterior teeth | 10% nHAp | Equal effect of nHAp and NovaMin in caries like lesions of primary teeth remineralization |
| Kulal et al. [55] 2016 | Dentinal permeability and tubule occlusion with 15% nHAp | Dentin specimen premolars | 15% nHAp | nHAp exerts desensitizing effect |
| Vyavhare et al. [27] 2015 | Effect of nHAp on remineralization of early carious lesions | Initial artificial caries in maxillary incisors | 10% nHAp | nHAp can remineralize initial enamel lesions |
| Comar et al. [29] 2013 | Preventive potential of experimental nHAp pastes with or without fluoride | Bovine enamel | 10% and 20% nHAp | No effect of nHAp in reducing dental demineralization in vitro. |
| Tschoppe et al. [56] 2011 | Effects of nHAp toothpastes on remineralization | Bovine enamel and dentin subsurface lesions | 7 wt.% pure nHAp | Toothpastes containing nHAp showed better remineralization than amine fluoride toothpastes |
| Huang et al. [13] 2011 | Artificial enamel caries remineralization effect of nHAp | Demineralized bovine enamel | 10% nHAp | Good remineralizing potential of nHAp in initial enamel caries |
| Hwang et al. [32] 2010 | Effect of nHAp on remineralization | Bovine tooth | 15% nHAp | Dentifrices with nHAp increased in brightness, enamel remineralization, decrease in caries susceptibility |
| Author/Year | Aim | Study Design/Population | Duration of Application | Percentage of nHAp | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amaechi et al. [17] 2021 | DH reduction using nHAp and CSPS | RCT/18–80-year-old subjects with DH, permanent teeth | 2 min twice a day for 8 weeks | 10% and 15% nHAp | Toothpaste containing nHAp (10 or 15%) DH symptoms |
| Grocholewicz et al. [16] 2020 | Remineralization of initial approximal caries using three methods | RCT/92 patients between 20–30 years of age | 6 Months daily use | 10% of nHAp | Improved remineralization when nHAp gel and ozone therapy were combined |
| Badiee et al. [62] 2019 | Remineralization of early enamel lesions in nHAp dentifrice users | RCT/50 patients on fixed orthodontic treatment | Twice daily for 6 months | 6.7% nHAp | Better remineralization and reduction in extent of lesion with nHAp toothpaste |
| Vano et al. [15] 2018 | Efficacy of nHAp toothpaste compared to fluoride in reducing DH | RCT/105 subjects | Twice daily for 4 weeks | 25% nHAp | nHAp fluoride free toothpaste is effective, reduces DH |
| Amaechi et al. [63] 2018 | Reduction in DH with nHAP dental cream and pure silica | RCT/51 subjects aged 18 to 80 years | 5-min application once daily | 20% nHAp | Both showed similar relief for DH, but silica reduced dental pain score better than nHAp |
| Anand et al. [2] 2017 | nHAp toothpaste in the management of DH | RCT/30 patients in each group (2 groups) | 1-min application/brushing 2 min twice | 1% nHAp | DH decreased with nHAp |
| Wang et al. [57] 2016 | Desensitizing effect of nHAp | RCT/28 subjects with 137 teeth | Twice a day 4 min with cotton swab | 10% and 20% nHAp | nHAp was effective in reducing dentin hypersensitivity |
| Amaechi et al. [60] 2015 | Comparison of dentin tubule occlusion by different toothpaste | In situ/80 participants | 1 min twice a day for 2 weeks | 10% and 15% nHAp | nHAP more effectiveness in occluding dentin tubules |
| Gopinath et al. [59] 2015 | Effectiveness of nHAp in reducing DH | RCT/36 patients | 2 min twice a day for 4 weeks | 1% nHAp | nHAp reduced DH |
| Vano et al. [58] 2014 | Efficacy in reducing DH with nHAp | RCT/105 subjects | 2 min twice a day for 2 weeks/4 weeks | 15% nHAp | nHAp toothpaste effective as a desensitizing agent |
| Najibfard et al. [61] 2011 | Efficacy of nHAp dentifrices on caries remineralization and demineralization inhibition | In situ/30 adults in four-phase study lasting 28 days | 28 Days constantly | 5% and 10% nHAp 10% nHAp | Remineralization and inhibition of caries occurred with nHAp dentifrice |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anil, A.; Ibraheem, W.I.; Meshni, A.A.; Preethanath, R.S.; Anil, S. Nano-Hydroxyapatite (nHAp) in the Remineralization of Early Dental Caries: A Scoping Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5629. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19095629
Anil A, Ibraheem WI, Meshni AA, Preethanath RS, Anil S. Nano-Hydroxyapatite (nHAp) in the Remineralization of Early Dental Caries: A Scoping Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(9):5629. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19095629
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnil, Aiswarya, Wael I. Ibraheem, Abdullah A. Meshni, Reghunathan S. Preethanath, and Sukumaran Anil. 2022. "Nano-Hydroxyapatite (nHAp) in the Remineralization of Early Dental Caries: A Scoping Review" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 9: 5629. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19095629
APA StyleAnil, A., Ibraheem, W. I., Meshni, A. A., Preethanath, R. S., & Anil, S. (2022). Nano-Hydroxyapatite (nHAp) in the Remineralization of Early Dental Caries: A Scoping Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(9), 5629. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19095629







