Muscular Adaptations to Concurrent Resistance Training and High-Intensity Interval Training in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Pilot Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Exercise Training
2.3. Assessment of Cardiovascular Risk Factors, Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Physical Activity Level
2.4. Muscle Mass and Quality
2.5. Muscle Performance
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Baseline Measurements
4.2. Follow-Up Measurements
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, Regional and Country-Level Diabetes Prevalence Estimates for 2021 and Projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, E.W.; Sattar, N.; Ali, M.K. The Changing Face of Diabetes Complications. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016, 4, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlando, G.; Balducci, S.; Bazzucchi, I.; Pugliese, G.; Sacchetti, M. Neuromuscular Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes: Underlying Mechanisms and Effect of Resistance Training. Diabetes. Metab. Res. Rev. 2016, 32, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lazzarini, P.A.; McPhail, S.M.; van Netten, J.J.; Armstrong, D.G.; Pacella, R.E. Global Disability Burdens of Diabetes-Related Lower-Extremity Complications in 1990 and 2016. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, G.; Sacchetti, M.; D’Errico, V.; Haxhi, J.; Rapisarda, G.; Pugliese, G.; Balducci, S. Muscle Fatigability in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Relation with Long-Term Complications. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2020, 36, e3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyani, R.R.; Tra, Y.; Yeh, H.-C.; Egan, J.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Brancati, F.L. Quadriceps Strength, Quadriceps Power, and Gait Speed in Older U.S. Adults with Diabetes Mellitus: Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999–2002. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2013, 61, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpato, S.; Bianchi, L.; Lauretani, F.; Lauretani, F.; Bandinelli, S.; Guralnik, J.M.; Zuliani, G.; Ferrucci, L. Role of Muscle Mass and Muscle Quality in the Association between Diabetes and Gait Speed. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 1672–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magkos, F.; Hjorth, M.F.; Astrup, A. Diet and Exercise in the Prevention and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codella, R.; Ialacqua, M.; Terruzzi, I.; Luzi, L. May the Force Be with You: Why Resistance Training Is Essential for Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus without Complications. Endocrine 2018, 62, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaley, J.A.; Colberg, S.R.; Corcoran, M.H.; Malin, S.K.; Rodriguez, N.R.; Crespo, C.J.; Kirwan, J.P.; Zierath, J.R. Exercise/Physical Activity in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes: A Consensus Statement from the American College of Sports Medicine. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2022, 54, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colberg, S.R.; Sigal, R.J.; Yardley, J.E.; Riddell, M.C.; Dunstan, D.W.; Dempsey, P.C.; Horton, E.S.; Castorino, K.; Tate, D.F. Physical Activity/Exercise and Diabetes: A Position Statement of the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 2065–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yardley, J.E.; Kenny, G.P.; Perkins, B.A.; Riddell, M.C.; Malcolm, J.; Boulay, P.; Khandwala, F.; Sigal, R.J. Effects of Performing Resistance Exercise before versus after Aerobic Exercise on Glycemia in Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larose, J.; Sigal, R.J.; Khandwala, F.; Kenny, G.P. Comparison of Strength Development with Resistance Training and Combined Exercise Training in Type 2 Diabetes. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2012, 22, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larose, J.; Sigal, R.J.; Boulé, N.G.; Wells, G.A.; Prud’Homme, D.; Fortier, M.S.; Reid, R.D.; Tulloch, H.; Coyle, D.; Phillips, P.; et al. Effect of Exercise Training on Physical Fitness in Type II Diabetes Mellitus. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2010, 42, 1439–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkiakangas, E.E.; Alahuhta, M.A.; Laitinen, J.H. Barriers to Regular Exercise among Adults at High Risk or Diagnosed with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review. Health Promot. Int. 2009, 24, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.X.; Zhu, L.; Li, P.J.; Li, N.; Xu, Y.B. Effectiveness of High-Intensity Interval Training on Glycemic Control and Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 31, 575–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo-Gallego, R.; Madinaveitia-Nisarre, L.; Giné-Gonzalez, J.; Bea, A.M.; Guerra-Torrecilla, L.; Baila-Rueda, L.; Perez-Calahorra, S.; Civeira, F.; Lamiquiz-Moneo, I. The Effects of High-Intensity Interval Training on Glucose Metabolism, Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Weight Control in Subjects with Diabetes: Systematic Review a Meta-Analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 190, 109979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R.; Berentzen, T.; Bradshaw, A.J.; Janssen, I.; Kahn, H.S.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Kuk, J.L.; Seidell, J.C.; Snijder, M.B.; Sørensen, T.I.A.; et al. Does the Relationship between Waist Circumference, Morbidity and Mortality Depend on Measurement Protocol for Waist Circumference? Obes. Rev. 2008, 9, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robergs, R.A. JEP Online Journal of Exercise Physiology Online The “Ugly And Creaking Edifices” Of The Vo 2 Max Concept. Society 2001, 4, 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Trost, S.G.; Mciver, K.L.; Pate, R.R. Conducting Accelerometer-Based Activity Assessments in Field-Based Research. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2005, 37, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troiano, R.P.; Berrigan, D.; Dodd, K.W.; Mâsse, L.C.; Tilert, T.; Mcdowell, M. Physical Activity in the United States Measured by Accelerometer. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2008, 40, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maden-Wilkinson, T.M.; McPhee, J.S.; Jones, D.A.; Degens, H. Age-Related Loss of Muscle Mass, Strength, and Power and Their Association with Mobility in Recreationally-Active Older Adults in the United Kingdom. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2015, 23, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, N.; Layne, J.E.; Gordon, P.L.; Roubenoff, R.; Nelson, M.E.; Castaneda-Sceppa, C. Strength Training Improves Muscle Quality and Insulin Sensitivity in Hispanic Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2007, 4, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugh, J.K.; Faulkner, S.H.; Turner, M.C.; Nimmo, M.A. Satellite Cell Response to Concurrent Resistance Exercise and High-Intensity Interval Training in Sedentary, Overweight/Obese, Middle-Aged Individuals. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2018, 118, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, S.N.; Kohl, H.W.; Barlow, C.E.; Gibbons, L.W.; Paffenbarger, R.S.; Macera, C.A. Changes in Physical Fitness and All-Cause Mortality: A Prospective Study of Healthy and Unhealthy Men. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1995, 273, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabag, A.; Najafi, A.; Michael, S.; Esgin, T.; Halaki, M.; Hackett, D. The Compatibility of Concurrent High Intensity Interval Training and Resistance Training for Muscular Strength and Hypertrophy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Sports Sci. 2018, 36, 2472–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauza, E.; Strehblow, C.; Metz-Schimmerl, S.; Strasser, B.; Hanusch-Enserer, U.; Kostner, K.; Dunstan, D.; Fasching, P.; Haber, P. Effects of Progressive Strength Training on Muscle Mass in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients Determined by Computed Tomography. Wien. Med. Wochenschr. 2009, 159, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaneda, C.; Layne, J.E.; Munoz-Orians, L.; Gordon, P.L.; Walsmith, J.; Foldvari, M.; Roubenoff, R.; Tucker, K.L.; Nelson, M.E. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Resistance Exercise Training to Improve Glycemic Control in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 2335–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | RT | RT + HIIT | p Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of cases | 7 | 5 | - |
| Age (years) | 55.9 ± 1.3 | 54.2 ± 1.6 | 0.438 |
| Diabetes duration (years) | 4 (2; 12) | 2(1.7; 11) | 0.623 |
| Body mass (kg) | 108 (86.2; 115.3) | 89.5 (85; 113) | 0.122 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 33.8 ± 3.6 | 31.8 ± 3.5 | 0.183 |
| Fat mass (kg) | 35 ± 8.7 | 26 ± 8.9 | 0.048 |
| Fat-free mass (kg) | 68.4 ± 8 | 71.2 ± 5.9 | 0.537 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 113.7 ± 11.9 | 110.1 ± 14.2 | 0.646 |
| HbA1c (%) | 6.6 ± 1 | 6.4 ± 1.5 | 0.837 |
| FPG (mg/dl) | 92.7 ± 29.8 | 114 ± 42.4 | 0.327 |
| VO2max (mL/kg/min) | 22 ± 0.9 | 29.7 ± 0.4 | <0.001 |
| Leg step-up (Kg) | 20.7 ± 5.7 | 16.5 ± 6.8 | 0.279 |
| Leg extension (Kg) | 19.8 ± 8.1 | 40.8 ± 31.5 | 0.022 |
| Lat pulldown | 58.7 ± 18.3 | 63.8 ± 7.4 | 0.358 |
| Chest press (kg) | 37.7 ± 15.7 | 42.4 ± 10.6 | 0.383 |
| Muscle power (W) | 328.4 ± 88.1 | 354.2 ± 40.3 | 0.559 |
| Quadriceps volume (cm3) | 1.615 ± 328 | 1.691 ± 317.9 | 0.707 |
| Leg extension muscle quality (kg/cm3) | 0.012 ± 0.003 | 0.026 ± 0.023 | 0.033 |
| Leg step-up muscle quality (kg/cm3) | 0.011 ± 0.003 | 0.010 ± 0.004 | 0.298 |
| Physical activity (min.d) | 0.670 | ||
| Sedentary | 531 ± 33 | 501 ± 42 | 0.535 |
| LPA | 293 ± 35 | 378 ± 49 | 0.129 |
| MVPA | 23 ± 6 | 25 ± 3 | 0.459 |
| RT | RT + HIIT | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Pre | Post | p Values | Pre | Post | p Values |
| Isometric torque (Nm) | 143.2 ± 23.8 | 180.3 ± 54.8 | 0.060 | 209 ± 40.9 | 248.7 ± 39.3 | 0.204 |
| Muscle power (W) | 328.4 ± 88.1 | 387.3 ± 94.2 | 0.021 | 354.2 ± 40.3 | 383.9 ± 26.7 | 0.037 |
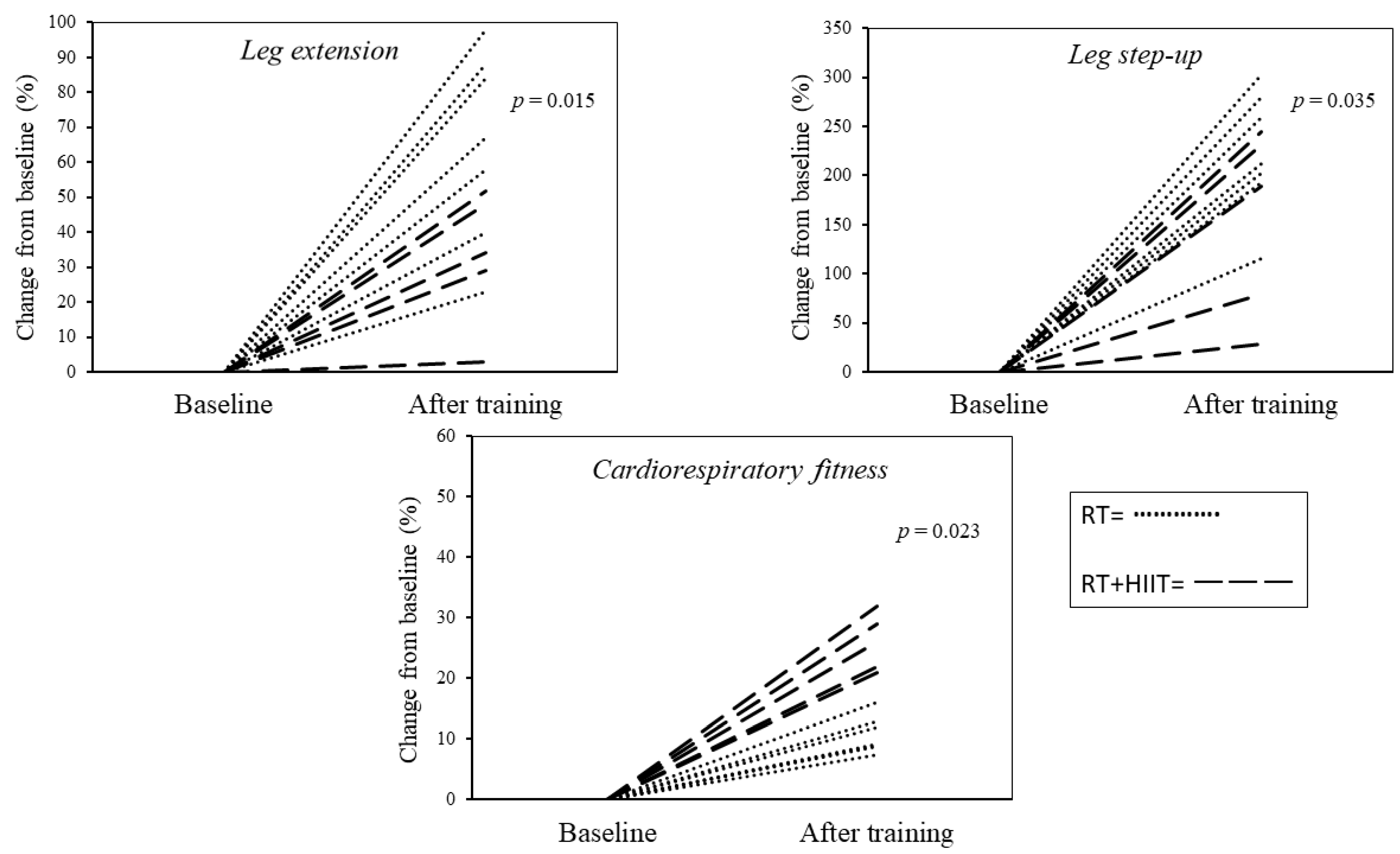
| Leg step-up (kg) | 20.7 ± 5.7 | 72.7 ± 6.7 | <0.001 | 16.5 ± 6.8 | 54.5 ± 32.9 | 0.083 |
| Leg extension (kg) | 19.8 ± 8.1 | 32.1 ± 18.7 | 0.018 | 40.8 ± 31.5 | 50.4 ± 26.1 | 0.068 |
| Lat pulldown (kg) | 58.7 ± 18.3 | 88 ± 23.9 | 0.005 | 63.8 ± 7.4 | 93.4 ± 11.5 | 0.003 |
| Chest press (kg) | 37.7 ± 15.7 | 58 ± 29.2 | 0.041 | 42.4 ± 10.6 | 60.4 ± 25.2 | 0.103 |
| Quadriceps volume (cm3) | 1.615 ± 328 | 1.701 ± 304 | 0.035 | 1.691 ± 317.9 | 1.778 ± 337.2 | 0.004 |
| Leg extension muscle quality (kg/cm3) | 0.012 ± 0.003 | 0.019 ± 0.009 | 0.026 | 0.026 ± 0.023 | 0.030 ± 0.019 | 0.080 |
| Leg step-up muscle quality (kg/cm3) | 0.011 ± 0.003 | 0.039 ± 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.010 ± 0.004 | 0.030 ± 0.009 | 0.072 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orlando, G.; Pugh, J.; Faulkner, S.; Balducci, S.; Sacchetti, M.; Pugliese, G.; Bazzucchi, I.; Haxhi, J.; Martinez-Valdes, E.; Falla, D.; et al. Muscular Adaptations to Concurrent Resistance Training and High-Intensity Interval Training in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 6746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20186746
Orlando G, Pugh J, Faulkner S, Balducci S, Sacchetti M, Pugliese G, Bazzucchi I, Haxhi J, Martinez-Valdes E, Falla D, et al. Muscular Adaptations to Concurrent Resistance Training and High-Intensity Interval Training in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Pilot Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(18):6746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20186746
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrlando, Giorgio, Jamie Pugh, Steve Faulkner, Stefano Balducci, Massimo Sacchetti, Giuseppe Pugliese, Ilenia Bazzucchi, Jonida Haxhi, Eduardo Martinez-Valdes, Deborah Falla, and et al. 2023. "Muscular Adaptations to Concurrent Resistance Training and High-Intensity Interval Training in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Pilot Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 18: 6746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20186746
APA StyleOrlando, G., Pugh, J., Faulkner, S., Balducci, S., Sacchetti, M., Pugliese, G., Bazzucchi, I., Haxhi, J., Martinez-Valdes, E., Falla, D., Manolopoulos, K., & Nimmo, M. A. (2023). Muscular Adaptations to Concurrent Resistance Training and High-Intensity Interval Training in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Pilot Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(18), 6746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20186746









