After a Century of Research into Environmental Mutagens and Carcinogens, Where Do We Stand?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. A Brief Historical Overview of Cancer and Pollution
3. A Traditionalist View on Legacy and Emerging Carcinogens
3.1. The Paradigmatic Case of Asbestos
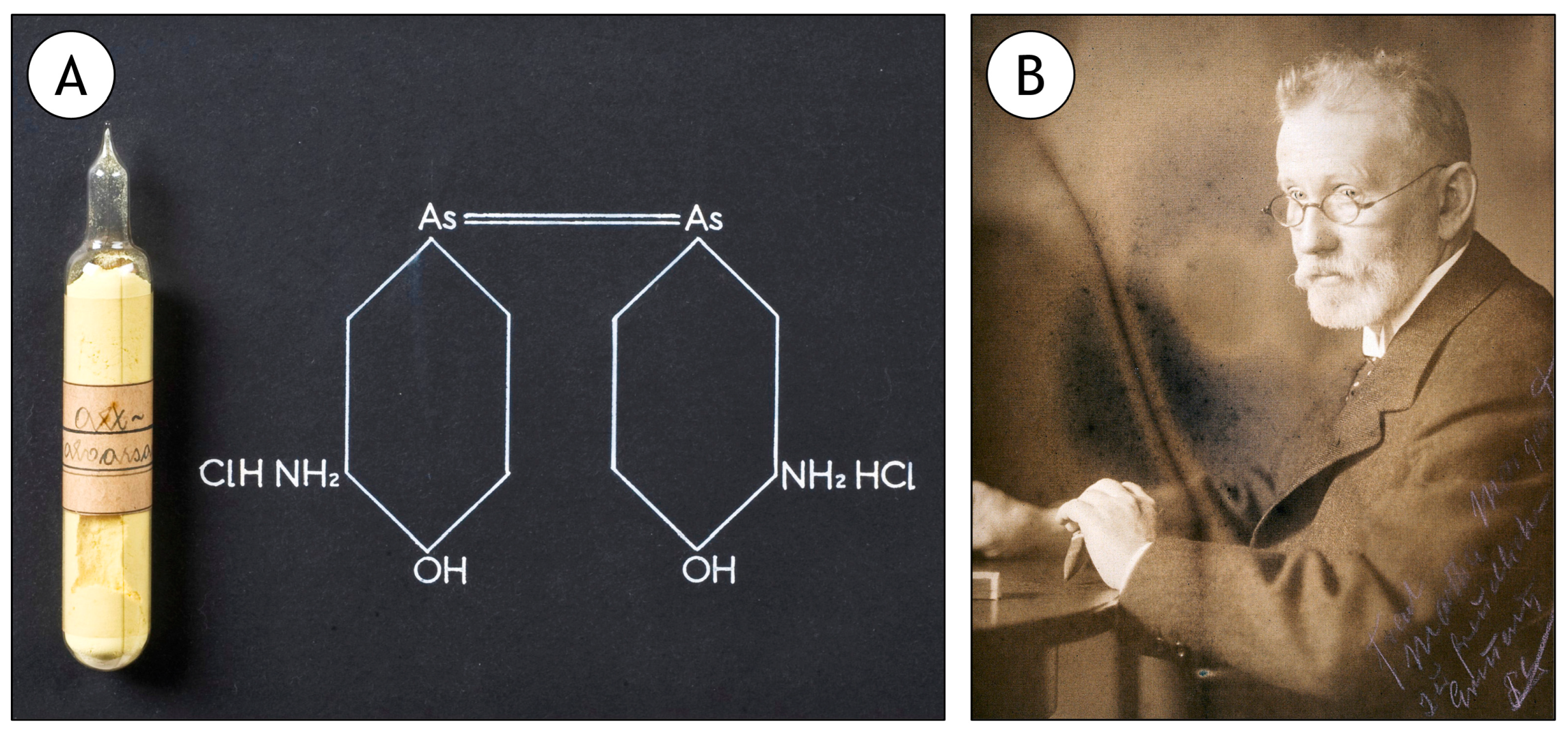
3.2. Arsenic, the Base of the First True Medicine
3.3. Cadmium versus PAHs: A Matter of Mechanism
3.4. Novel and ‘Emerging’ Pollutants
4. Novel Approaches to Mechanism and Causation: Cancer and the Exposome
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ahr | aryl hydrocarbon receptor |
| AO | adverse outcome |
| AOP | adverse outcome pathway |
| B[a]P | Benzo[a]pyrene |
| CYP | cytochrome P450 |
| DDT | dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane |
| IARC | International Agency for Research on Cancer |
| KE | key event |
| KER | key event relationships |
| MIE | molecular initiating event |
| MWCNT | multi-walled carbon nanotube |
| NP | nanoparticle |
| OECD | Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development |
| PAH | polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon |
| WHO | World Health Organisation |
References
- Sullivan, R. The identity and work of the ancient Egyptian surgeon. J. R. Soc. Med. 1996, 89, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faguet, G.B. A brief history of cancer: Age-old milestones underlying our current knowledge database. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 136, 2022–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colditz, G.A.; Wei, E.K. Preventability of cancer: The relative contributions of biologic and social and physical environmental determinants of cancer mortality. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2012, 33, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madia, F.; Worth, A.; Whelan, M.; Corvi, R. Carcinogenicity assessment: Addressing the challenges of cancer and chemicals in the environment. Environ. Int. 2019, 128, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothschild, B.M.; Tanke, D.H.; Helbling, M., II; Martin, L.D. Epidemiologic study of tumors in dinosaurs. Naturwissenschaften 2003, 90, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avery, O.T.; MacLeod, C.M.; McCarty, M. Studies on the chemical nature of the substance inducing transformation of pneumococcal types. Induction of transformation by a desoxyribosenucleic acid fraction isolated from Pneumococcus type III. J. Exp. Med. 1944, 79, 137–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin, R.E.; Gosling, R.G. The structure of sodium thymonucleate fibres. I. The influence of water content. Acta Crystallogr. 1953, 6, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.D.; Crick, F.H.C. Molecular structure of nucleic acids: A structure for deoxyribose nucleic acid. Nature 1953, 171, 737–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.; Weinberg, R.A. Isolation of a transforming sequence from a human bladder carcinoma cell line. Cell 1982, 29, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duesberg, P.H.; Vogt, P.K. Differences between the ribonucleic acids of transforming and nontransforming avian tumor vi-ruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 67, 1673–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, E.P.; Reynolds, R.K.; Santos, E.; Barbacid, M. A point mutation is responsible for the acquisition of transforming properties by the T24 human bladder carcinoma oncogene. Nature 1982, 300, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, P.M. Current aspects of DNA damage and repair in ecotoxicology: A mini-review. Ecotoxicology 2022, 31, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, J.; Nesnow, S. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Correlations between DNA adducts and ras oncogene mutations. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 1999, 424, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moorthy, B.; Chu, C.; Carlin, D.J. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: From metabolism to lung cancer. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 145, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMarini, D.M.; Linak, W.P. Mutagenicity and carcinogenicity of combustion emissions are impacted more by combustor technology than by fuel composition: A brief review. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2022, 63, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.R.; Goldstone, J.V.; Stegeman, J.J. The cytochrome P450 genesis locus: The origin and evolution of animal cytochrome P450s. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20120474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, A.; Satta, Y. Substrate-dependent evolution of cytochrome P450: Rapid turnover of the detoxification-type and conservation of the biosynthesis-type. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankley, G.T.; Bennett, R.S.; Erickson, R.J.; Hoff, D.J.; Hornung, M.W.; Johnson, R.D.; Mount, D.R.; Nichols, J.W.; Russom, C.L.; Schmieder, P.K.; et al. Adverse outcome pathways: A conceptual framework to support ecotoxicology research and risk assessment. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2010, 29, 730–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.; Dreij, K.; Costa, P.M. The state-of-the art of environmental toxicogenomics: Challenges and perspectives of “omics” approaches directed to toxicant mixtures. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.N.; Gilbert, S.G. Historical milestones and discoveries that shaped the toxicology sciences. EXS 2009, 99, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, G. Bernardino Ramazzini’s De Morbis Artificum Diatriba on workers’ health–the birth of a new discipline. J. UOEH 2021, 43, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdu, S.I. A note from history: Landmarks in history of cancer, part 1. Cancer 2011, 117, 1097–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lonardo, A.; Nasi, S.; Pulciani, S. Cancer: We should not forget the past. J. Cancer 2015, 6, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdu, S.I. A note from history: Landmarks in history of cancer, part 2. Cancer 2011, 117, 2811–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdu, S.I. A note from history: Landmarks in history of cancer, part 3. Cancer 2012, 118, 1155–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, R. Mortality from Lung Cancer in Asbestos Workers. Occup. Environ. Med. 1955, 12, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, W. IARC: 20 Years Old. World Health 1986, 1986, 28–29. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, M.S.; Johnson, L.L.; Collier, T.K. Establishing the causal relationship between polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) exposure and hepatic neoplasms and neoplasia-related liver lesions in English sole (Pleuronectes vetulus). Hum. Ecol. Risk Assessment Int. J. 2003, 9, 67–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Benzopyrene. In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; IARC: Lyon, France, 2012; Volume 100F. [Google Scholar]
- Grosse, Y.; Loomis, D.; Guyton, K.Z.; Lauby-Secretan, B.; El Ghissassi, F.; Bouvard, V.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Guha, N.; Scoc-cianti, C.; Mattock, H.; et al. Carcinogenicity of fluoro-edenite, silicon carbide fibres and whiskers, and carbon nanotubes. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1427–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Carbon nanotubes. In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; IARC: Lyon, France, 2014; Volume 111. [Google Scholar]
- Kennaway, E.L. On the cancer-producing factor in tar. Br. Med. J. 1924, 1, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagiwa, K.; Ichikawa, K. Über die künstliche Erzeugung von Papillom. Verh. Jap. Path. 1915, 5, 142–148. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, D.H. Fifty years of benzo(a)pyrene. Nature 1983, 303, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiki, H. Gist of Dr. Katsusaburo Yamagiwa’s papers entitled “Experimental study on the pathogenesis of epithelial tumors” (I to VI reports). Cancer Sci. 2014, 105, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boveri, T. Concerning the Origin of Malignant Tumours by Theodor Boveri. Translated and annotated by Henry Harris. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 1–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognesi, C.; Perrone, E.; Roggieri, P.; Pampanin, D.M.; Sciutto, A. Assessment of micronuclei induction in peripheral eryth-rocytes of fish exposed to xenobiotics under controlled conditions. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 78, S93–S98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.M.; Costa, M.H. Genotoxicity assessment in fish peripheral blood: A method for a more efficient analysis of micronuclei. J. Fish Biol. 2007, 71, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenech, M.; Kirsch-Volders, M.; Natarajan, A.T.; Surralles, J.; Crott, J.W.; Parry, J.; Norppa, H.; Eastmond, D.A.; Tucker, J.D.; Thomas, P. Molecular mechanisms of micronucleus, nucleoplasmic bridge and nuclear bud formation in mammalian and human cells. Mutagenesis 2010, 26, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.P.; Mccoy, M.T.; Tice, R.R.; Scineider, E.L. A simple technique for quantification of low levels of DNA in individual cells. Exp. Cell. Res. 1988, 175, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, H.; Neary, G.; Williamson, F. The relative biological efficiency of single doses of fast neutrons and gamma-rays on Vicia faba roots and the effect of oxygen. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. Relat. Stud. Phys. Chem. Med. 1959, 1, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, H.J. Artificial transmutation of the gene. Science 1927, 66, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunderman, R.B.; Gonda, A.S. Radium girls. Radiology 2015, 274, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, R. Silent Spring; Houghton Mifflin: Boston, MA, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Patterson, C.C. Contaminated and natural lead environments of Man. Arch. Environ. Health Int. J. 1965, 11, 344–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Inorganic and Organic Lead Compounds. In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; IARC: Lyon, France, 2006; Volume 87. [Google Scholar]
- IARC. DDT, Lindane, and 2,4-D. In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; IARC: Lyon, France, 2018; Volume 113. [Google Scholar]
- Iijima, S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogliano, V.J.; Baan, R.; Straif, K.; Grosse, Y.; Lauby-Secretan, B.; El Ghissassi, F.; Bouvard, V.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Guha, N.; Freeman, C.; et al. Preventable exposures associated with human cancers. Gynecol. Oncol. 2011, 103, 1827–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorwald, A.J.; Karr, J.W. Pneumoconiosis and pulmonary carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 1938, 14, 49–58.1. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, M. Biological effects of asbestos: New York Academy of Sciences 1964. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2003, 43, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyokuni, S. Mechanisms of asbestos-induced carcinogenesis. Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 2009, 71, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Arsenic and arsenic compounds. In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; IARC: Lyon, France, 2012; Volume 100C. [Google Scholar]
- Tokar, E.J.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Ward, J.M.; Lunn, R.; Sams, R.L., II; Waalkes, M.P. Cancer in experimental animals exposed to arsenic and arsenic compounds. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2010, 40, 912–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, V.D.; Vucic, E.A.; Becker-Santos, D.D.; Gil, L.; Lam, W.L. Arsenic exposure and the induction of human cancers. J. Toxicol. 2011, 2011, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Cadmium and cadmium compounds. In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; IARC: Lyon, France, 1993; Volume 58. [Google Scholar]
- Nordberg, G.F. Historical perspectives on cadmium toxicology. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 238, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huff, J.; Lunn, R.M.; Waalkes, M.P.; Tomatis, L.; Infante, P.F. Cadmium-induced Cancers in Animals and in Humans. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health 2007, 13, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartwig, A. Mechanisms in cadmium-induced carcinogenicity: Recent insights. BioMetals 2010, 23, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kienzler, A.; Bony, S.; Devaux, A. DNA repair activity in fish and interest in ecotoxicology: A review. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 134–135, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Bi, L.; Jin, L.; Peng, R. Toxic effects of cadmium on fish. Toxics 2022, 10, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent-Hubert, F.; Arini, A.; Gourlay-Francé, C. Early genotoxic effects in gill cells and haemocytes of Dreissena polymorpha exposed to cadmium, B[a]P and a combination of B[a]P and Cd. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2011, 723, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Glyphosate. In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; IARC: Lyon, France, 2016; Volume 112-10. [Google Scholar]
- Ojelade, B.S.; Durowoju, O.S.; Adesoye, P.O.; Gibb, S.W.; Ekosse, G.-I. Review of glyphosate-based herbicide and ami-nomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA): Environmental and health impacts. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Rana, I.; Shaffer, R.M.; Taioli, E.; Sheppard, L. Exposure to glyphosate-based herbicides and risk for non-Hodgkin lymphoma: A meta-analysis and supporting evidence. Mutat. Res. Mutat. Res. 2019, 781, 186–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, U.; Adelodun, B.; Cabreros, C.; Kumar, P.; Suresh, S.; Dey, A.; Ballesteros, F., Jr.; Bontempi, E. Occurrence, transfor-mation, bioaccumulation, risk and analysis of pharmaceutical and personal care products from wastewater: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 3883–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Estrogen-only menopausal therapy. In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; IARC: Lyon, France, 2012; Volume 100A. [Google Scholar]
- Antunes, C.M.; Strolley, P.D.; Rosenshein, N.B.; Davies, J.L.; Tonascia, J.A.; Brown, C.; Burnett, L.; Rutledge, A.; Pokempner, M.; Garcia, R. Endometrial cancer and estrogen use. Report of a large case-control study. N. Engl. J. Med. 1979, 300, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ideker, T.; Galitski, T.; Hood, L. A NEW APPROACH TO DECODING LIFE: Systems Biology. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2001, 2, 343–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ideker, T.; Thorsson, V.; Ranish, J.A.; Christmas, R.; Buhler, J.; Eng, J.K.; Bumgarner, R.; Goodlett, D.R.; Aebersold, R.; Hood, L. Integrated genomic and proteomic analyses of a systematically perturbed metabolic network. Science 2001, 292, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturla, S.J.; Boobis, A.R.; Fitzgerald, R.E.; Hoeng, J.; Kavlock, R.J.; Schirmer, K.; Whelan, M.; Wilks, M.F.; Peitsch, M.C. Systems toxicology: From basic research to risk assessment. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2014, 27, 314–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, P.M.; Fadeel, B. Emerging systems biology approaches in nanotoxicology: Towards a mechanism-based understanding of nanomaterial hazard and risk. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2016, 299, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madeira., C.; Costa, P.M. Proteomics in systems toxicology. Adv. Protein. Chem. Struct. Biol. 2021, 127, 55–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, F.; Lambert, I.B.; Yauk, C.L. Adverse Outcome Pathway on Cyp2E1 Activation Leading to Liver Cancer; OECD Series on Adverse Outcome Pathways; OECD Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2021; p. 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nymark, P.; Karlsson, H.L.; Halappanavar, S.; Vogel, U. Adverse outcome pathway development for assessment of lung carcinogenicity by nanoparticles. Front. Toxicol. 2021, 3, 653386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, L.; Jornod, F.; Zgheib, E.; Tomkiewicz, C.; Koual, M.; Coustillet, T.; Barouki, R.; Audouze, K.; Vinken, M.; Coumoul, X. Adverse outcome pathway from activation of the AhR to breast cancer-related death. Environ. Int. 2022, 165, 107323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, C.P. Complementing the genome with an “exposome”: The outstanding challenge of environmental exposure meas-urement in molecular epidemiology. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2005, 14, 1847–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vitorino, J.D.; Costa, P.M. After a Century of Research into Environmental Mutagens and Carcinogens, Where Do We Stand? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021040
Vitorino JD, Costa PM. After a Century of Research into Environmental Mutagens and Carcinogens, Where Do We Stand? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(2):1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021040
Chicago/Turabian StyleVitorino, João D., and Pedro M. Costa. 2023. "After a Century of Research into Environmental Mutagens and Carcinogens, Where Do We Stand?" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 2: 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021040
APA StyleVitorino, J. D., & Costa, P. M. (2023). After a Century of Research into Environmental Mutagens and Carcinogens, Where Do We Stand? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(2), 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021040




