The Effects of Yoga Exercise on Blood Pressure and Hand Grip Strength in Chronic Stroke Patients: A Pilot Controlled Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
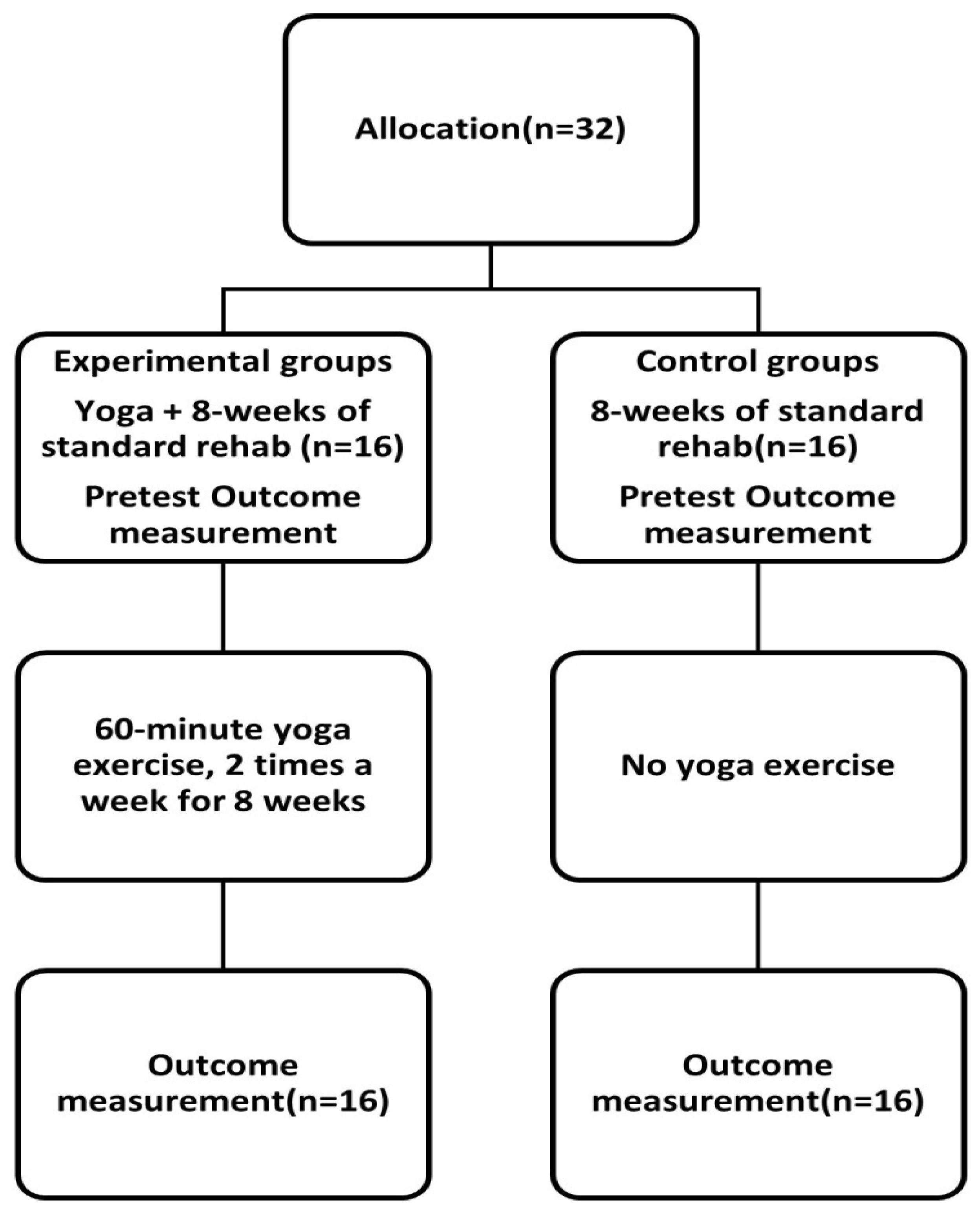
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethic Statement
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Protocol
2.4. Assessment of Outcome
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hsieh, F.I.; Chiou, H.Y. Stroke: Morbidity, risk factors, and care in Taiwan. J. Stroke 2014, 16, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannel, W.B.; Dawber, T.R.; Sorlie, P.; Wolf, P.A. Components of blood pressure and risk of atherothrombotic brain infarction: The Framingham study. Stroke 1976, 7, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turin, T.C.; Okamura, T.; Afzal, A.R.; Rumana, N.; Watanabe, M.; Higashiyama, A.; Nakao, Y.; Nakai, M.; Takegami, M.; Nishimura, K.; et al. Hypertension and lifetime risk of stroke. J. Hypertens. 2016, 34, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipolla, M.J.; Liebeskind, D.S.; Chan, S.L. The importance of comorbidities in ischemic stroke: Impact of hypertension on the cerebral circulation. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2018, 38, 2129–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saptharishi, L.; Soudarssanane, M.; Thiruselvakumar, D.; Navasakthi, D.; Mathanraj, S.; Karthigeyan, M.; Sahai, A. Community-based Randomized Controlled Trial of Non-pharmacological Interventions in Prevention and Control of Hypertension among Young Adults. Indian J. Community Med. 2009, 34, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.; Budzynska, K.; Almasri, N.; Islam, S.; Alyas, F.; Carolan, R.L.; Abraham, B.E.; Castro-Camero, P.A.; Shreve, M.E.; Rees, D.A.; et al. Tight versus standard blood pressure control on the incidence of myocardial infarction and stroke: An observational retrospective cohort study in the general ambulatory setting. BMC Fam. Pract. 2020, 21, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Niiranen, T.J.; Rader, F.; Henglin, M.; Kim, A.; Ebinger, J.E.; Claggett, B.; Merz, C.N.B.; Cheng, S. Sex Differences in Blood Pressure Associations With Cardiovascular Outcomes. Circulation 2021, 143, 761–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellekjaer, H.; Holmen, J.; Ellekjaer, E.; Vatten, L. Physical activity and stroke mortality in women. Ten-year follow-up of the Nord-Trondelag health survey, 1984–1986. Stroke 2000, 31, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Xue, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Geng, Q. Association between hand grip strength and stroke in China: A prospective cohort study. Aging 2021, 13, 8204–8213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burn, J.; Dennis, M.; Bamford, J.; Sandercock, P.; Wade, D.; Warlow, C. Long-term risk of recurrent stroke after a first-ever stroke. The Oxfordshire Community Stroke Project. Stroke 1994, 25, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagins, M.; States, R.; Selfe, T.; Innes, K. Effectiveness of yoga for hypertension: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 649836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, N.; Rastogi, S.; Chia, Y.C.; Siddique, S.; Turana, Y.; Cheng, H.M.; Sogunuru, G.P.; Tay, J.C.; Teo, B.W.; Wang, T.D.; et al. Non-pharmacological management of hypertension. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2021, 23, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, M.; Telles, S. Improvement in hand grip strength in normal volunteers and rheumatoid arthritis patients following yoga training. Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2001, 45, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mazor, M.; Lee, J.Q.; Peled, A.; Zerzan, S.; Irwin, C.; Chesney, M.A.; Serrurier, K.; Sbitany, H.; Dhruva, A.; Sacks, D.; et al. The Effect of Yoga on Arm Volume, Strength, and Range of Motion in Women at Risk for Breast Cancer-Related Lymphedema. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2018, 24, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azami, M.; Hafezi Ahmadi, M.R.; YektaKooshali, M.H.; Qavam, S. Effect of Yoga on Lipid Profile and C-reactive Protein in Women. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2019, 10, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauche, R.; Hunter, D.J.; Adams, J.; Cramer, H. Yoga for Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2019, 21, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, L.; Stebbings, S.; Athens, J.; Cherkin, D.; David Baxter, G. Yoga for the management of pain and sleep in rheumatoid arthritis: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Musculoskelet. Care 2018, 16, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, H.S.; Nakayama, H.; Raaschou, H.O.; Vive-Larsen, J.; Støier, M.; Olsen, T.S. Outcome and time course of recovery in stroke. Part II: Time course of recovery. The Copenhagen Stroke Study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1995, 76, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangavel, D.; Gaur, G.S.; Sharma, V.K.; Bhavanani, A.B.; Rajajeyakumar, M.; Syam, S.A. Effect of slow and fast pranayama training on handgrip strength and endurance in healthy volunteers. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8, Bc01–Bc03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, H. The Efficacy and Safety of Yoga in Managing Hypertension. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2016, 124, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Murikinati, S.R.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X.; Duan, W.M.; Zhao, L.R. Reestablishing neuronal networks in the aged brain by stem cell factor and granulocyte-colony stimulating factor in a mouse model of chronic stroke. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, K.; Wood-Dauphinee, S.; Williams, J.I. The Balance Scale: Reliability assessment with elderly residents and patients with an acute stroke. Scand. J. Rehabil. Med. 1995, 27, 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, Y.-T.; Lin, C.-H.; Hsieh, C.C.; Yang, J.-C.; Tsou, H.-H.; Lin, C.-C.; Li, S.-Y.; Chan, H.-L.; Liu, W.-S. Combining Yoga Exercise with Rehabilitation Improves Balance and Depression in Patients with Chronic Stroke: A Controlled Trial. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owolabi, M.O.; Thrift, A.G.; Mahal, A.; Ishida, M.; Martins, S.; Johnson, W.D.; Pandian, J.; Abd-Allah, F.; Yaria, J.; Phan, H.T.; et al. Primary stroke prevention worldwide: Translating evidence into action. Lancet Public Health 2022, 7, e74–e85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Control hypertension to prevent cardiovascular complications. 24/7 blood pressure control helps reduce stroke risk, especially during the early morning hours, when the incidence is greatest. Heart Advis. 2007, 10, 4–5.
- Park, S.H.; Han, K.S. Blood Pressure Response to Meditation and Yoga: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2017, 23, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.H.; Kang, S.H.; Seo, K.M.; Kim, D.K.; Shin, H.I.; Shin, H.E. Relationship Between Grip and Pinch Strength and Activities of Daily Living in Stroke Patients. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2015, 39, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.H.; Chang, C.Y.; Wu, D.M.; Lu, C.H.; Kuo, C.C.; Chu, N.F. Relationship of Multimorbidity, Obesity Status, and Grip Strength among Older Adults in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, L.; Meng, G.; Wu, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; et al. Grip strength and depressive symptoms in a large-scale adult population: The TCLSIH cohort study. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 279, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieber, M.; Görgülü, E.; Schmidt, D.; Zabel, K.; Etyemez, S.; Friedrichs, B.; Prvulovic, D.; Reif, A.; Oertel, V. Effects of body-oriented yoga: A RCT study for patients with major depressive disorder. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2021, 271, 1217–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Valle, E.; Palermi, S.; Aloe, I.; Marcantonio, R.; Spera, R.; Montagnani, S.; Sirico, F. Effectiveness of Workplace Yoga Interventions to Reduce Perceived Stress in Employees: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2020, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, H.R.S.; Subramanya, P.; Rao, R.M.; Vadiraj, H.S.; Udupa, V. Effects of an Integrated Yoga Program on Quality of Life, Spinal Flexibility, and Strength in Older Adults: A Randomized Control Trial. Adv. Mind Body Med. 2022, 36, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Spartano, N.L.; Lyass, A.; Larson, M.G.; Lewis, G.D.; Vasan, R.S. Submaximal Exercise Systolic Blood Pressure and Heart Rate at 20 Years of Follow-up: Correlates in the Framingham Heart Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e002821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyk, D.; Gorges, W.; Ridder, D.; Wunderlich, M.; Rüther, T.; Sievert, A.; Essfeld, D. Hand-grip strength of young men, women and highly trained female athletes. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 99, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Jin, C.; Li, S.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Cui, L.; Gao, X. Aging, Arterial Stiffness, and Blood Pressure Association in Chinese Adults. Hypertension 2019, 73, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iconaru, E.I.; Ciucurel, M.M.; Georgescu, L.; Ciucurel, C. Hand grip strength as a physical biomarker of aging from the perspective of a Fibonacci mathematical modeling. BMC Geriatr. 2018, 18, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheval, B.; Sieber, S.; Maltagliati, S.; Millet, G.P.; Formánek, T.; Chalabaev, A.; Cullati, S.; Boisgontier, M.P. Muscle strength is associated with COVID-19 hospitalization in adults 50 years of age or older. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2021, 12, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inder, J.D.; Carlson, D.J.; Dieberg, G.; McFarlane, J.R.; Hess, N.C.; Smart, N.A. Isometric exercise training for blood pressure management: A systematic review and meta-analysis to optimize benefit. Hypertens. Res. 2016, 39, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzen, A.M.; Thøgersen, F.D.; Qadri, K.A.N.; Krag, T.; Sveen, M.L.; Vissing, J.; Jeppesen, T.D. Preserved Capacity for Adaptations in Strength and Muscle Regulatory Factors in Elderly in Response to Resistance Exercise Training and Deconditioning. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M.; Celestino Junior, F.T.; Matozinho, H.H.; Govan, L.; Booth, J.; Beecher, J. Yoga for stroke rehabilitation. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 12, Cd011483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, J.Y.Y.; Kwan, J.C.Y.; Auyeung, M.; Mok, V.C.T.; Lau, C.K.Y.; Choi, K.C.; Chan, H.Y.L. Effects of Mindfulness Yoga vs Stretching and Resistance Training Exercises on Anxiety and Depression for People With Parkinson Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooventhan, A.; Nivethitha, L. Evidence based effects of yoga in neurological disorders. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 43, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberti, V.; Palermi, S.; Franceschin, A.; Scapol, G.; Lamberti, V.; Lamberti, C.; Vecchiato, M.; Spera, R.; Sirico, F.; Della Valle, E. The Effectiveness of Adapted Personalized Motor Activity (AMPA) to Improve Health in Individuals with Mental Disorders and Physical Comorbidities: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Sports 2022, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberti, V., Jr.; Nardini, S.; Romano, P.; Menegon, T.; Lamberti, V.S. A new frontier in sports therapy: AMPA system (personalized and adapted motor activity). Med. Dello Sport 2015, 68, 135–162. [Google Scholar]
| Chi-Square | Yoga+ (n = 16) | Control (n = 16) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (M:F) | 10:6 | 8:8 | 0.404 | |
| Age (≤60:>60) | 11:5 | 8:8 | 0.267 | |
| Mean ± SD | All | Yoga+ (n = 16) | Control (n = 16) | p |
| Age (years) | 59.02 ± 10.09 | 57.12 ± 9.12 | 61.19 ±10.74 | 0.241 |
| T-onset (days) | 382 (172–757) | 360 (177.75–763.25) | 418 (142–757) | 0.447 |
| T-rehab (minutes) | 207.42 ± 76.09 | 221.25 ± 84.05 | 195.79 ± 68.82 | 0.331 |
| BP (mmHg) | ||||
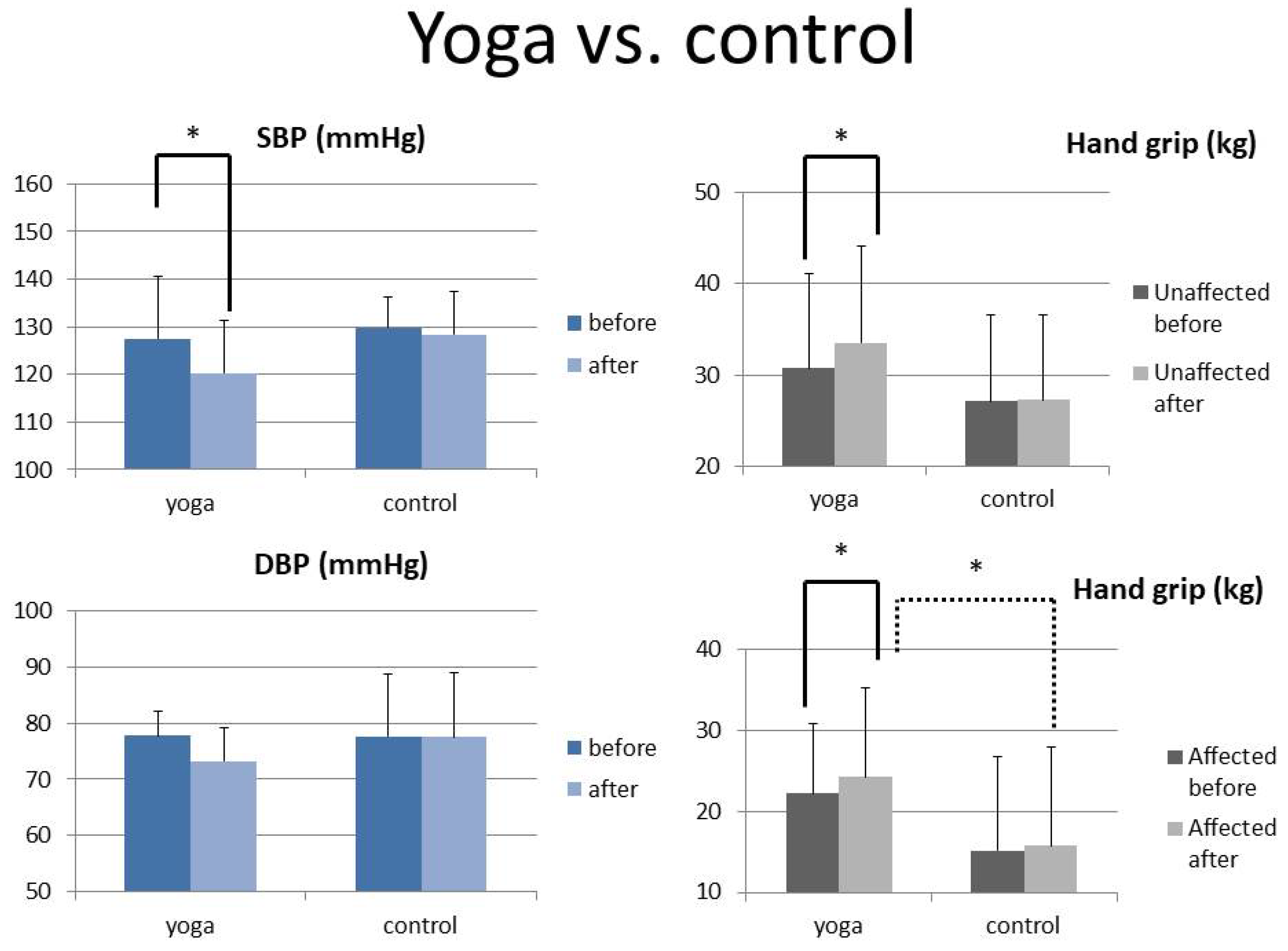
| Systolic BP-before | 128.77 ± 9.73 | 127.53 ± 13.06 | 129.76 ± 6.61 | 0.642 |
| Systolic BP-after | 124.79 ± 10.50 | 120.27 ± 11.10 | 128.41 ± 8.93 | 0.103 |
| Paired t | 0.064 | 0.014 * | 0.661 | |
| Diastolic BP-before | 77.67 ± 8.49 | 77.77 ± 4.42 | 77.58 ± 11.00 | 0.965 |
| Diastolic BP-after | 75.58 ± 9.44 | 73.18 ± 6.07 | 77.51 ± 11.41 | 0.349 |
| Paired t | 0.200 | 0.113 | 0.968 | |
| Hand grip strength (kgs) | ||||
| Unaffected-before | 28.91 ± 9.91 | 30.73 ± 10.34 | 27.11 ± 9.46 | 0.309 |
| Unaffected-after | 30.37 ± 10.24 | 33.49 ± 10.54 | 27.27 ± 9.23 | 0.086 |
| Paired t | 0.010 * | <0.001 * | 0.837 | |
| Affected-before | 18.68 ± 10.67 | 22.21 ± 8.66 | 15.16 ± 11.59 | 0.061 |
| Affected-after | 20.00 ± 12.18 | 24.25 ± 11.03 | 15.76 ± 12.12 | 0.047 * |
| Paired t | 0.012 * | 0.027 * | 0.249 |
| Male (n = 18) | Female (n = 14) | Age ≤ 60 (n = 19) | Age > 60 (n = 13) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | p | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | p | |
| BP (mmHg) | ||||||
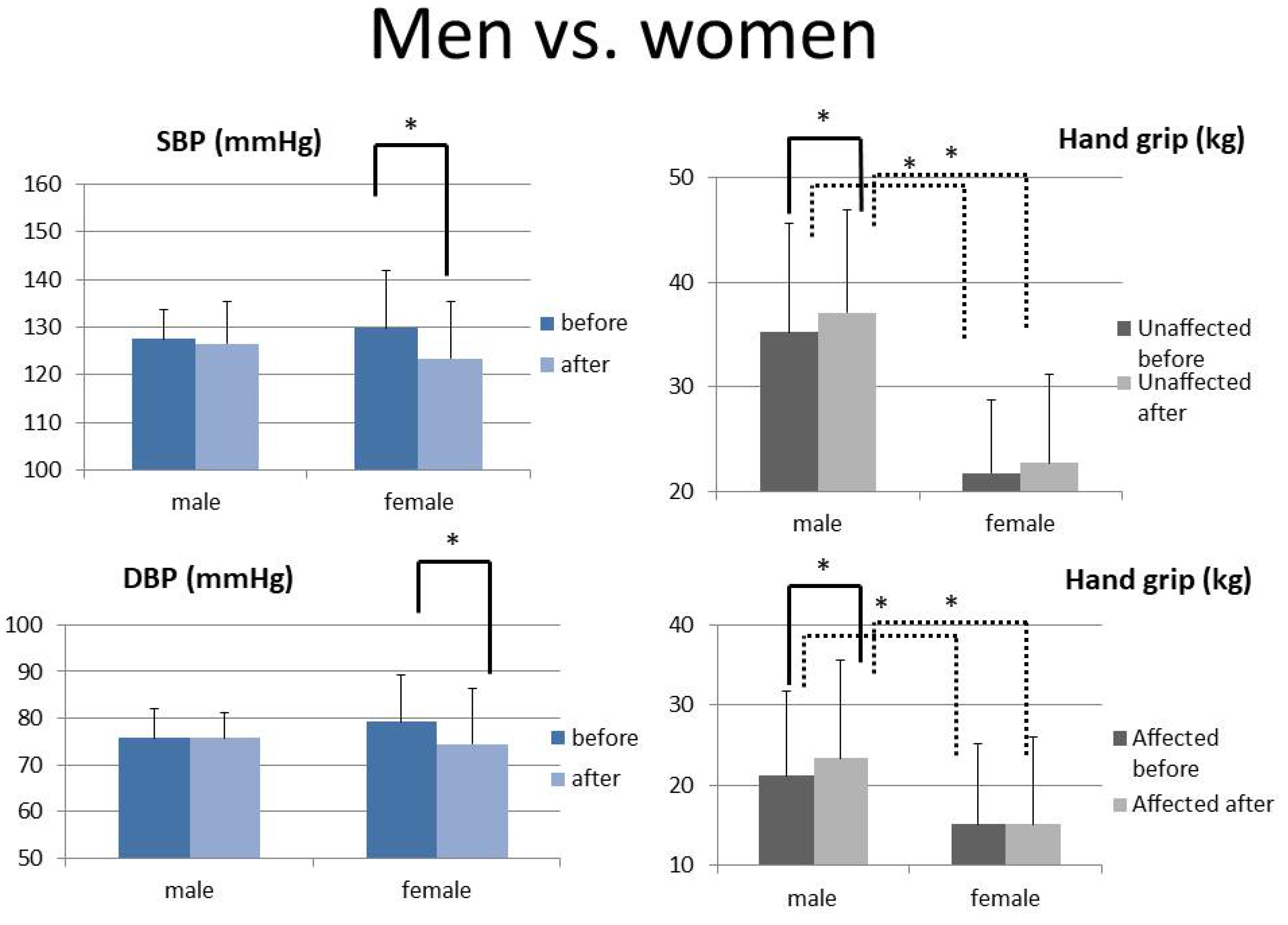
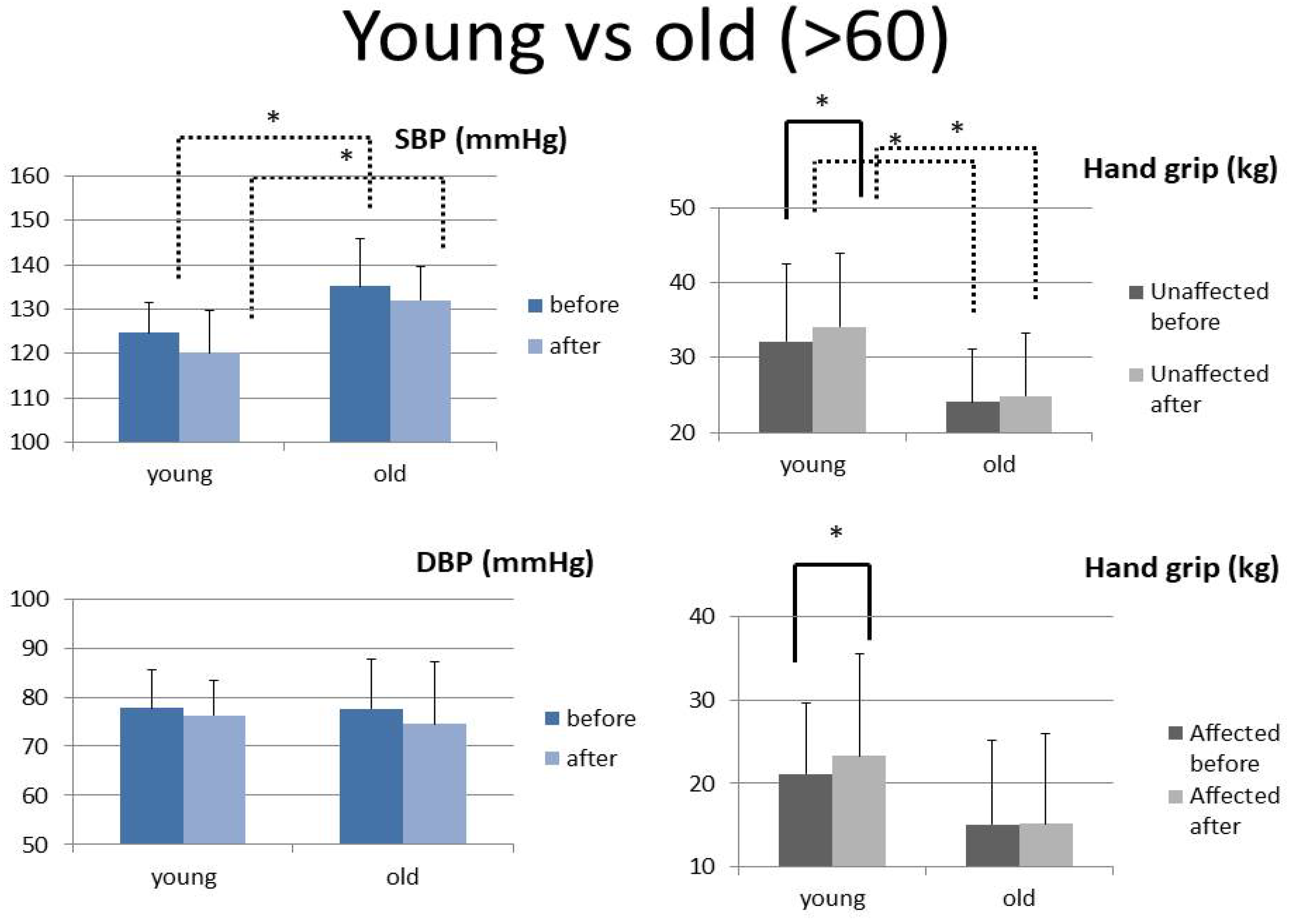
| Systolic BP-before | 127.54 ± 6.06 | 129.75 ± 12.15 | 0.647 | 124.66 ± 6.75 | 135.22 ± 10.62 | 0.020 * |
| Systolic BP-after | 126.52 ± 8.73 | 123.41 ± 12.01 | 0.549 | 120.15 ± 9.59 | 132.08 ± 7.60 | 0.014 * |
| Paired t | 0.716 | 0.049 * | 0.104 | 0.409 | ||
| Diastolic BP-before | 75.77 ± 6.14 | 79.18 ± 10.06 | 0.413 | 77.71 ± 7.75 | 77.60 ± 10.22 | 0.979 |
| Diastolic BP-after | 77.05 ± 5.44 | 74.42 ± 11.91 | 0.573 | 76.29 ± 7.20 | 74.48 ± 12.79 | 0.705 |
| Paired t | 0.539 | 0.042 * | 0.459 | 0.327 | ||
| Hand grip strength (kgs) | ||||||
| Unaffected-before | 35.24 ± 9.69 | 21.74 ± 2.59 | <0.001 * | 32.19 ± 10.40 | 24.13 ± 7.06 | 0.021 * |
| Unaffected-after | 37.13 ± 9.33 | 22.72 ± 3.81 | <0.001 * | 34.15 ± 9.77 | 24.85 ± 8.48 | 0.009 * |
| Paired t | 0.020 * | 0.229 | 0.013 * | 0.364 | ||
| Affected hand-before | 22.94 ± 11.37 | 13.86 ± 7.60 | 0.012 * | 21.13 ± 10.65 | 15.10 ± 10.06 | 0.119 |
| Affected hand-after | 25.45 ± 12.89 | 13.82 ± 7.87 | 0.004 * | 23.33 ± 12.20 | 15.13 ± 10.81 | 0.061 |
| Paired t | 0.003 * | 0.943 | 0.004 * | 0.959 |
| Linear Regression R (p) | All | Yoga+ (n = 16) | Control (n = 16) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Delta Systolic BP vs. Delta Diastolic BP (mmHg) | R = 0.777 p < 0.001 * | R = 0.757 p = 0.011 * | R = 0.815 p = 0.014 * |
| Delta grip of the affected hand vs. Delta grip of the unaffected hand (kgs) | R = 0.587 p < 0.001 * | R = 0.539 p = 0.031 * | R = 0.638 p = 0.009 * |
| Delta BP (mmHg) vs. Delta hand grip strength (kgs) | R = 0.199 p = 0.429 | R = 0.494 p = 0.146 | R = 0.698 p = 0.054 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, Y.-T.; Huang, H.-L.; Hsieh, C.C.; Lin, C.-H.; Yang, J.-C.; Tsou, H.-H.; Lin, C.-C.; Li, S.-Y.; Chan, H.-L.; Liu, W.-S. The Effects of Yoga Exercise on Blood Pressure and Hand Grip Strength in Chronic Stroke Patients: A Pilot Controlled Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1108. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021108
Lai Y-T, Huang H-L, Hsieh CC, Lin C-H, Yang J-C, Tsou H-H, Lin C-C, Li S-Y, Chan H-L, Liu W-S. The Effects of Yoga Exercise on Blood Pressure and Hand Grip Strength in Chronic Stroke Patients: A Pilot Controlled Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(2):1108. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021108
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Yen-Ting, Hsiao-Ling Huang, City C. Hsieh, Chien-Hung Lin, Jung-Cheng Yang, Han-Hsing Tsou, Chih-Ching Lin, Szu-Yuan Li, Hsiang-Lin Chan, and Wen-Sheng Liu. 2023. "The Effects of Yoga Exercise on Blood Pressure and Hand Grip Strength in Chronic Stroke Patients: A Pilot Controlled Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 2: 1108. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021108
APA StyleLai, Y.-T., Huang, H.-L., Hsieh, C. C., Lin, C.-H., Yang, J.-C., Tsou, H.-H., Lin, C.-C., Li, S.-Y., Chan, H.-L., & Liu, W.-S. (2023). The Effects of Yoga Exercise on Blood Pressure and Hand Grip Strength in Chronic Stroke Patients: A Pilot Controlled Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(2), 1108. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021108










