Application Effect of MF-OP on Collection of Trivalent Holmium from Rare Earth Mining Wastewater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
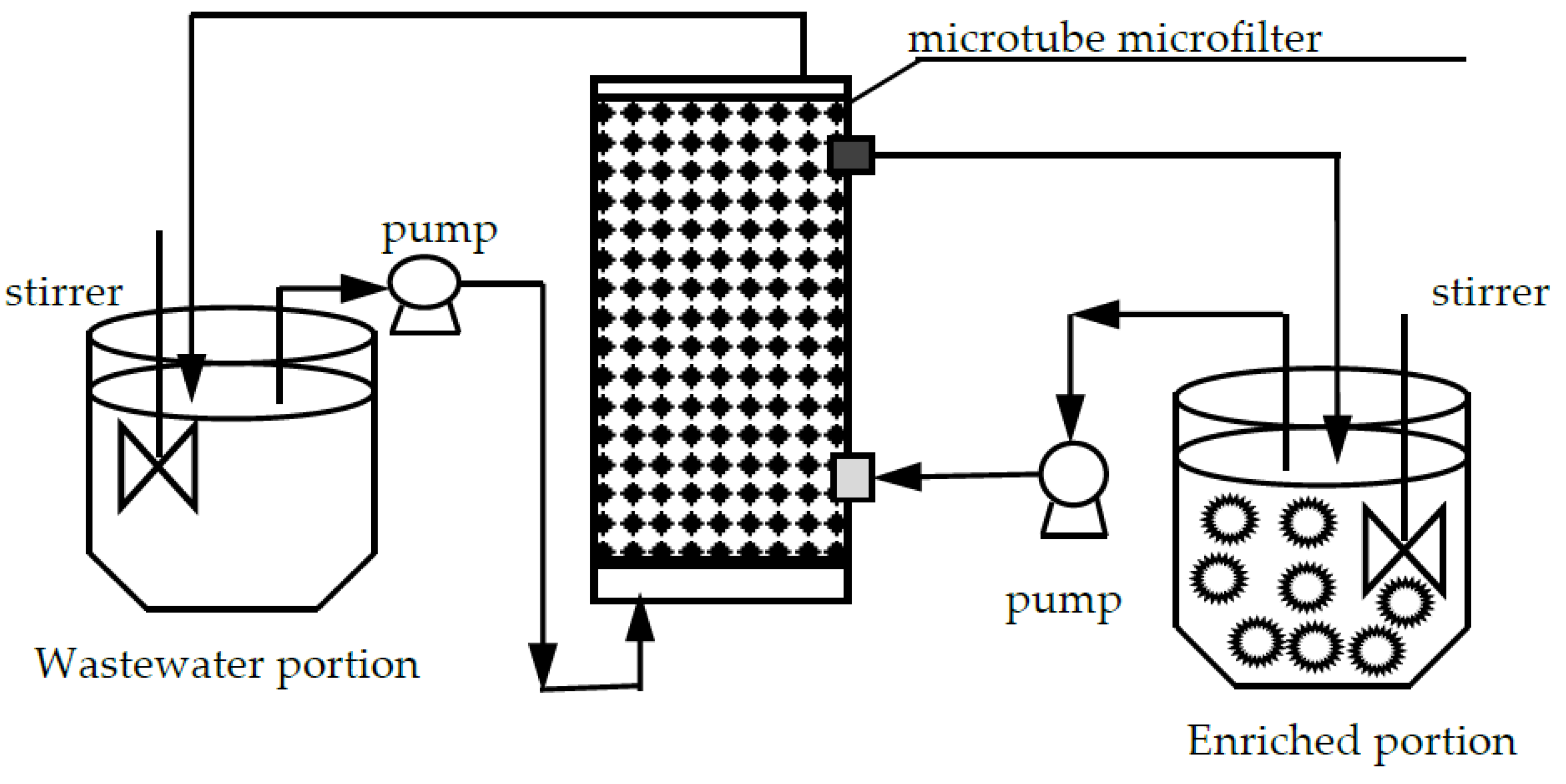
2.1. MF-OP Collection Procedure
2.2. Rereagent
2.3. Preparation of Fluid
2.4. Test Equipment and Related Measuring Instruments
2.5. Experimental Condition Data
3. Results and Discussion
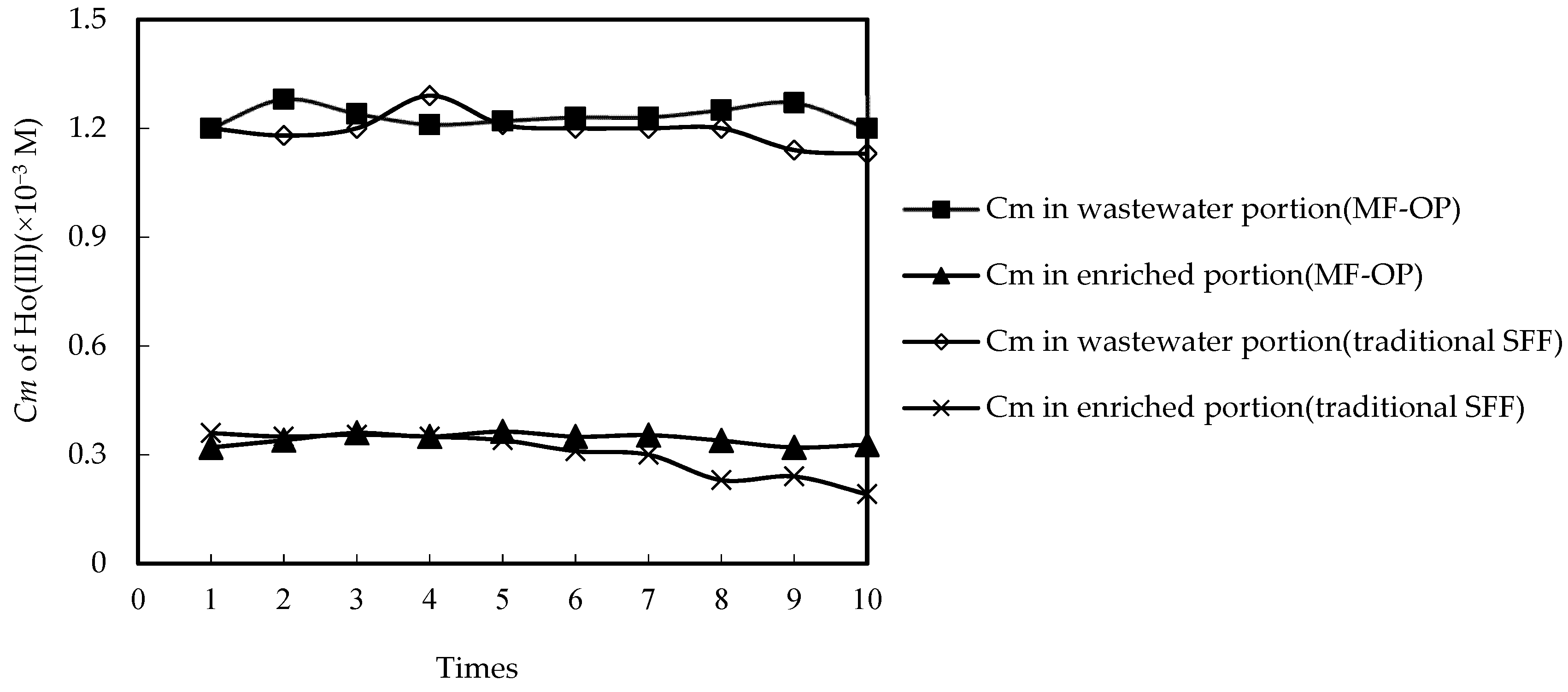
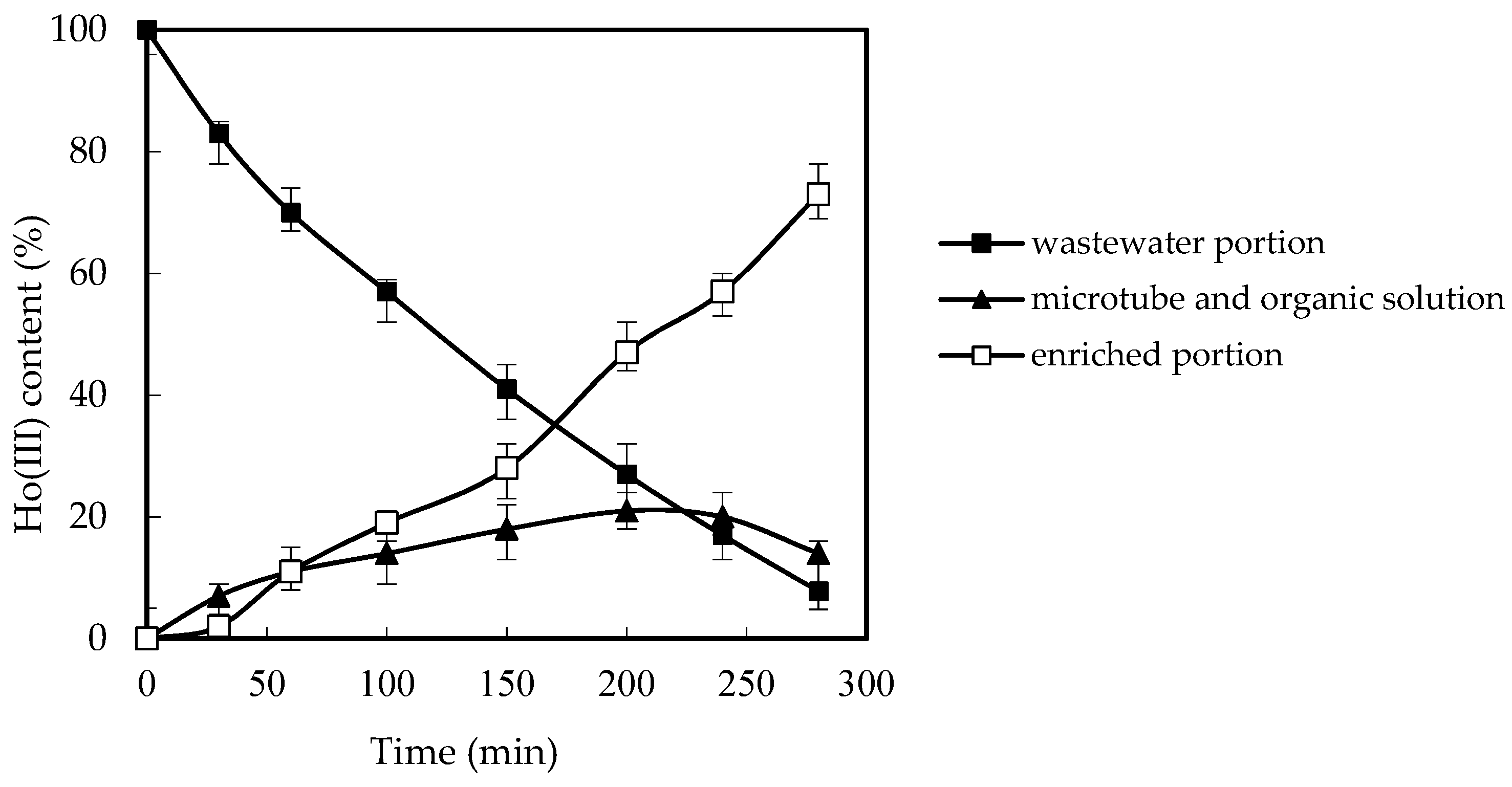
3.1. Constancy of MF-OP
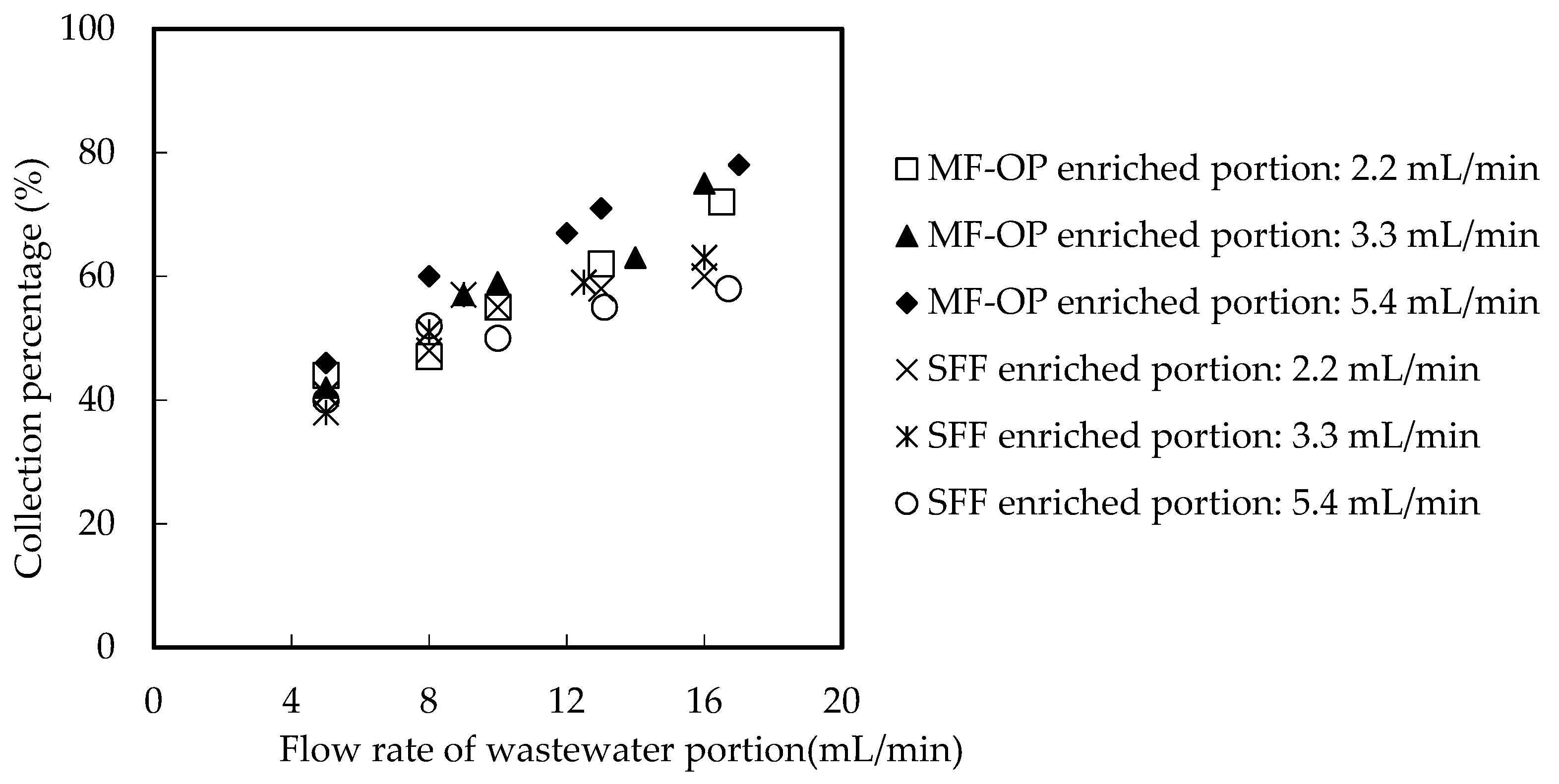
3.2. Influence of Current Speed of Wastewater Portion and Enriched Portion
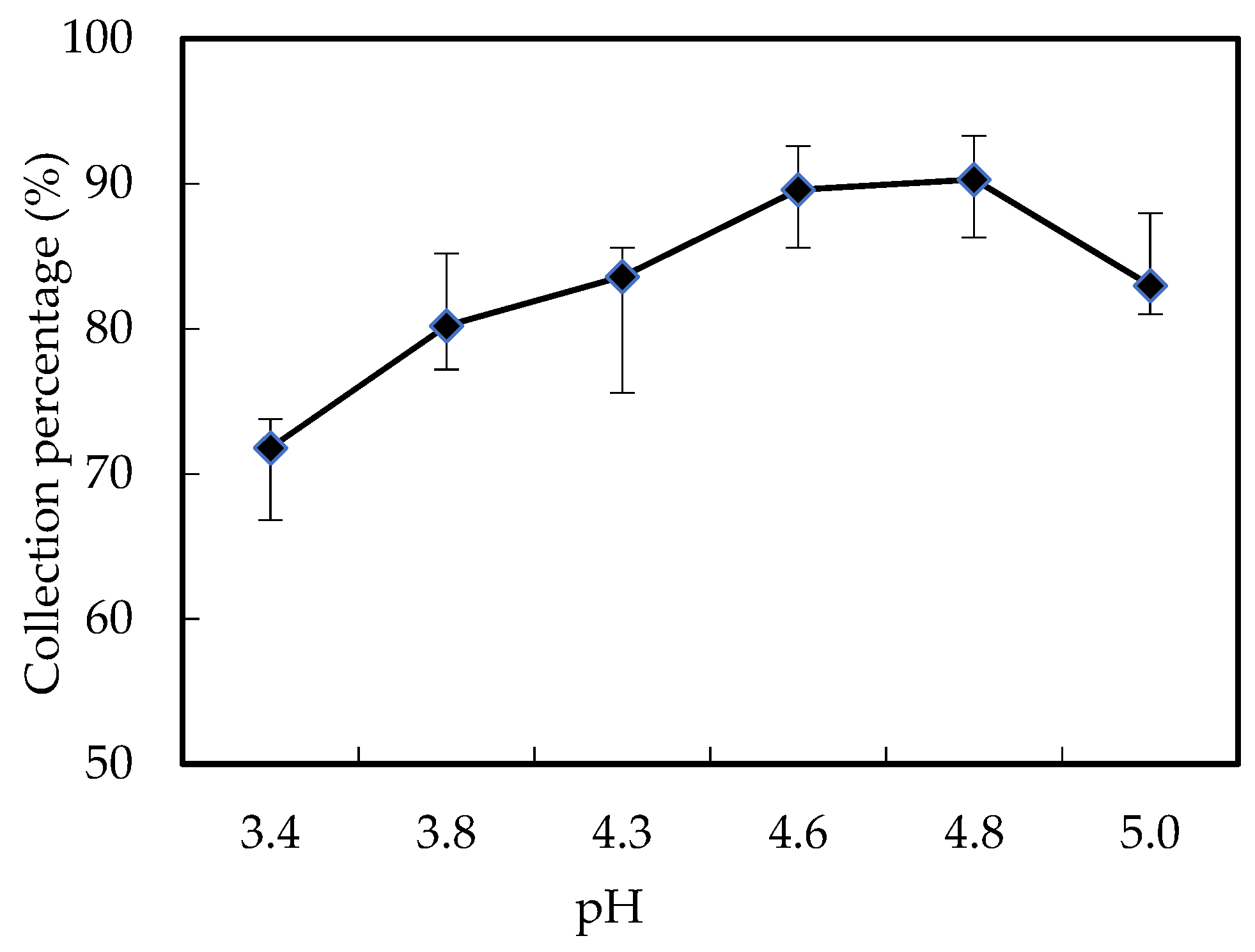
3.3. Influence of Wastewater pH
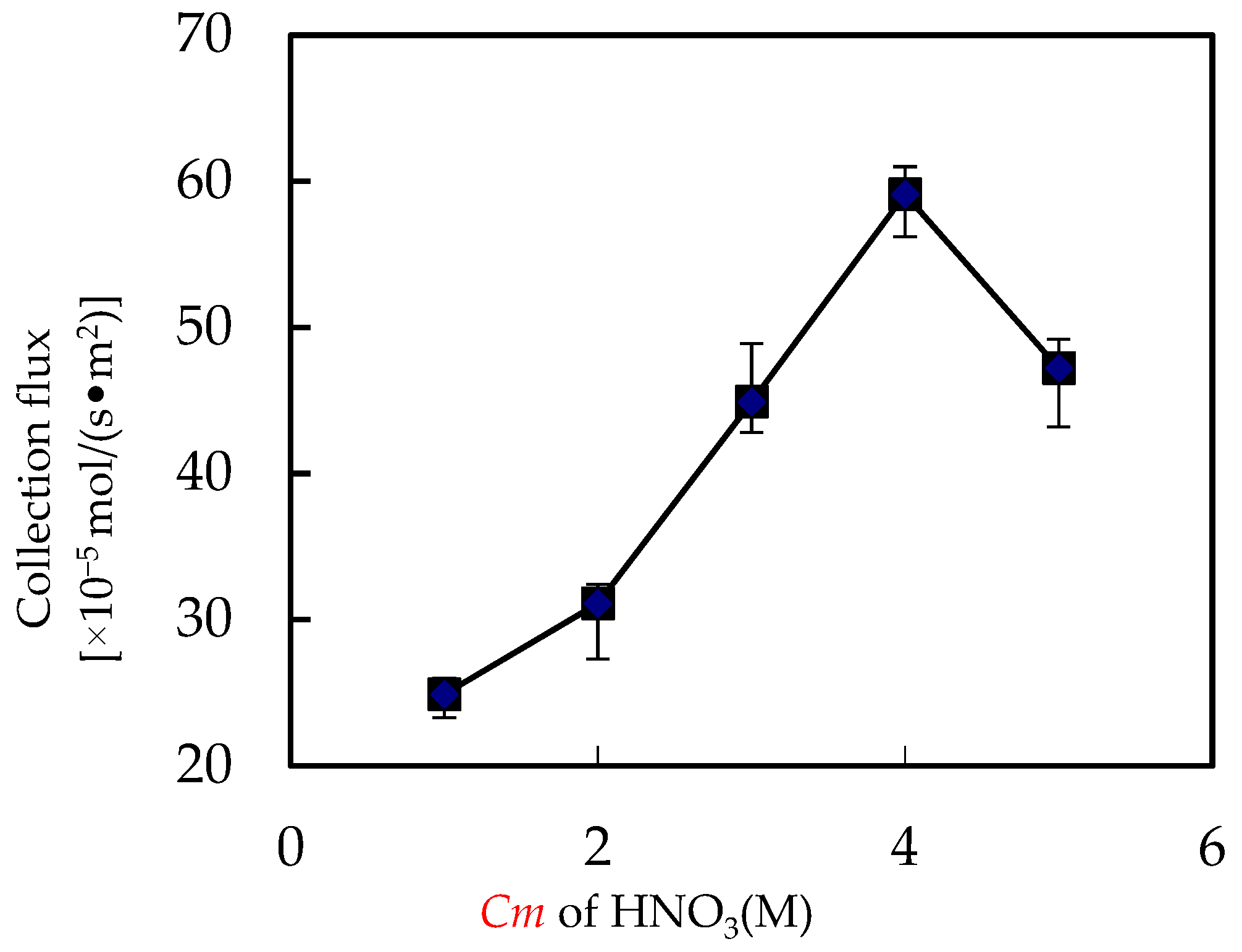
3.4. Influence of Acid Cm in Enriched Portion
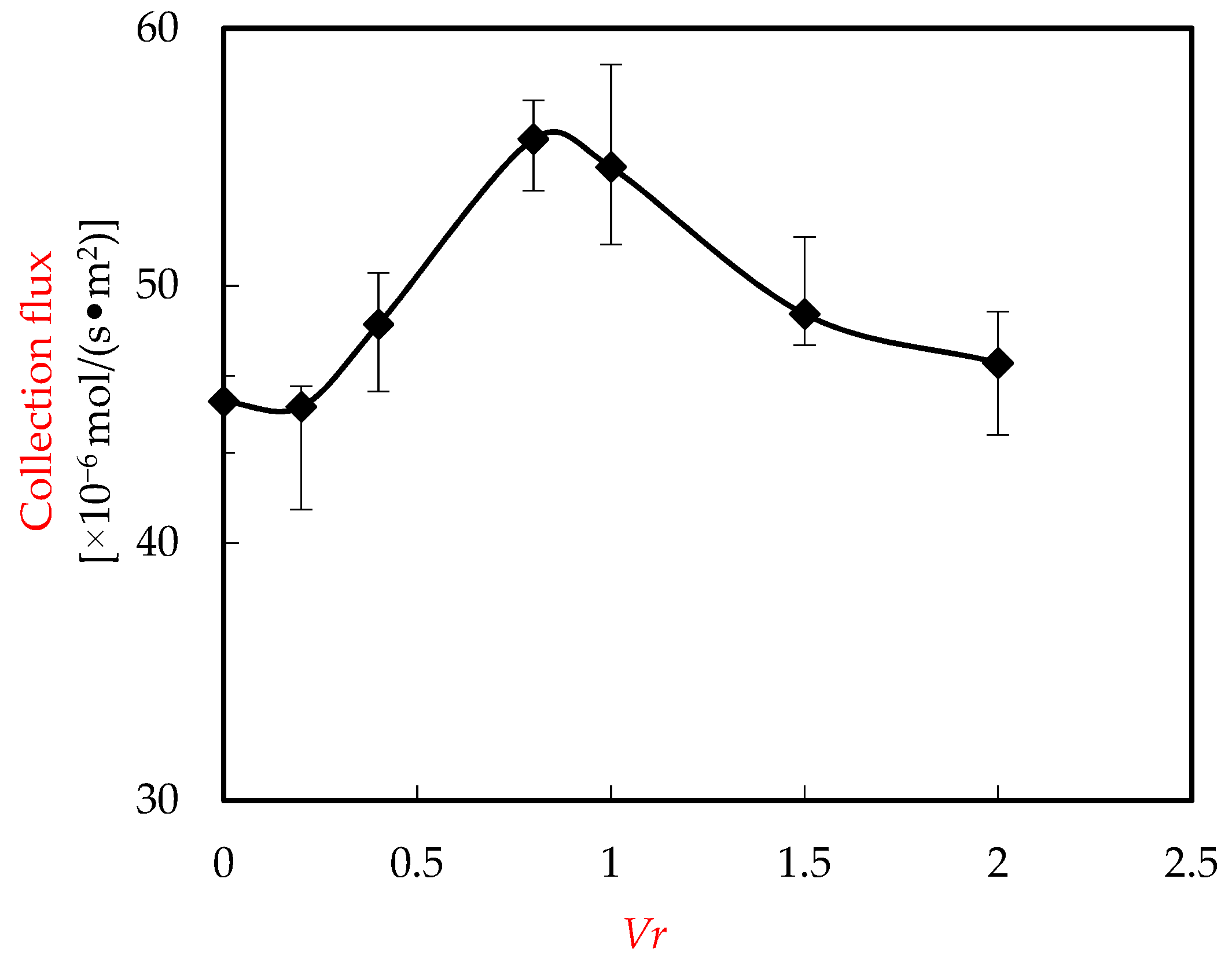
3.5. Influence of Voluminal Proportion of Enriched Portion (Vr)
3.6. Influence of Ho(III) Co in Wastewater Portion
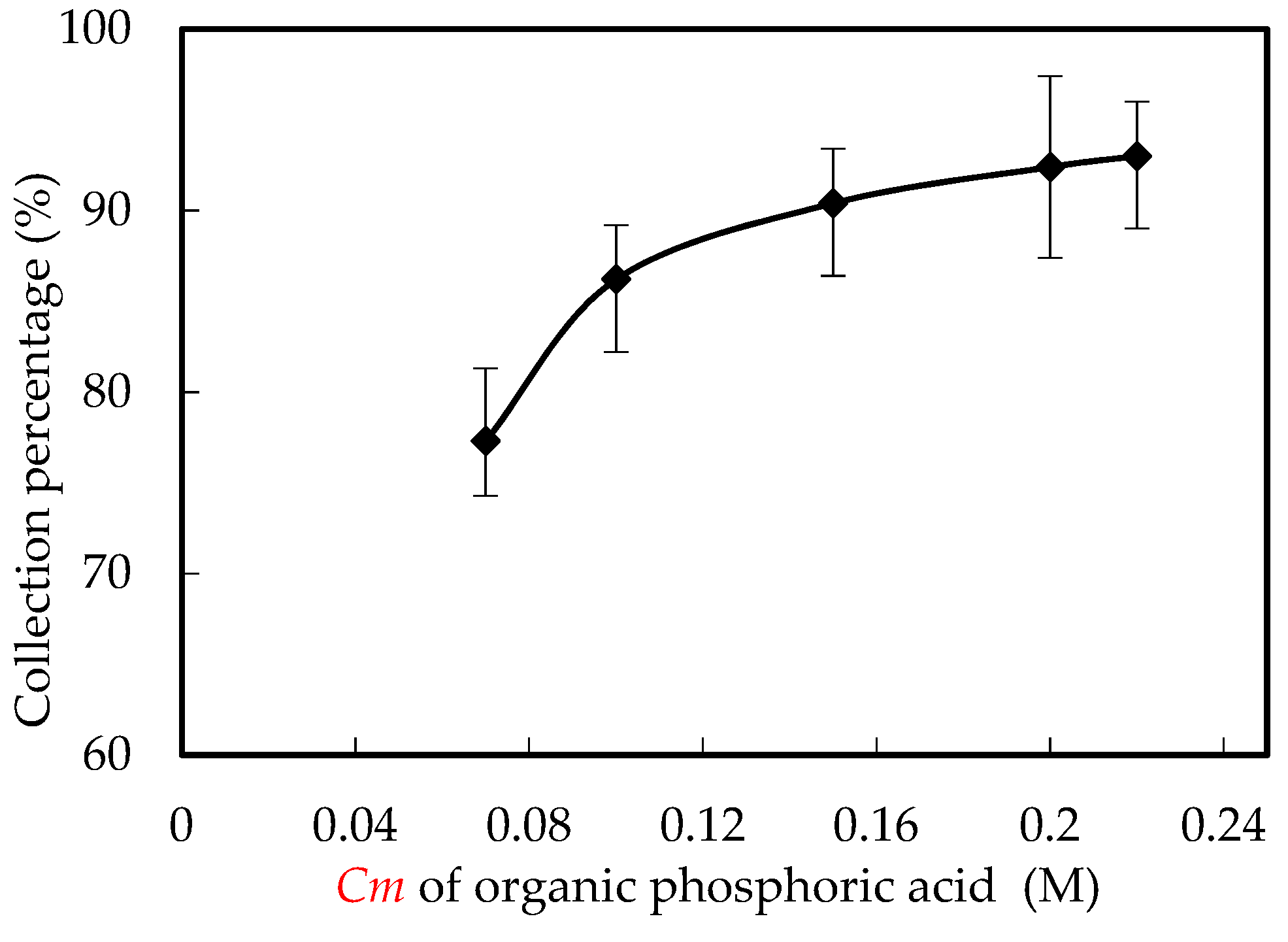
3.7. Influence of Organic Phosphoric Cm
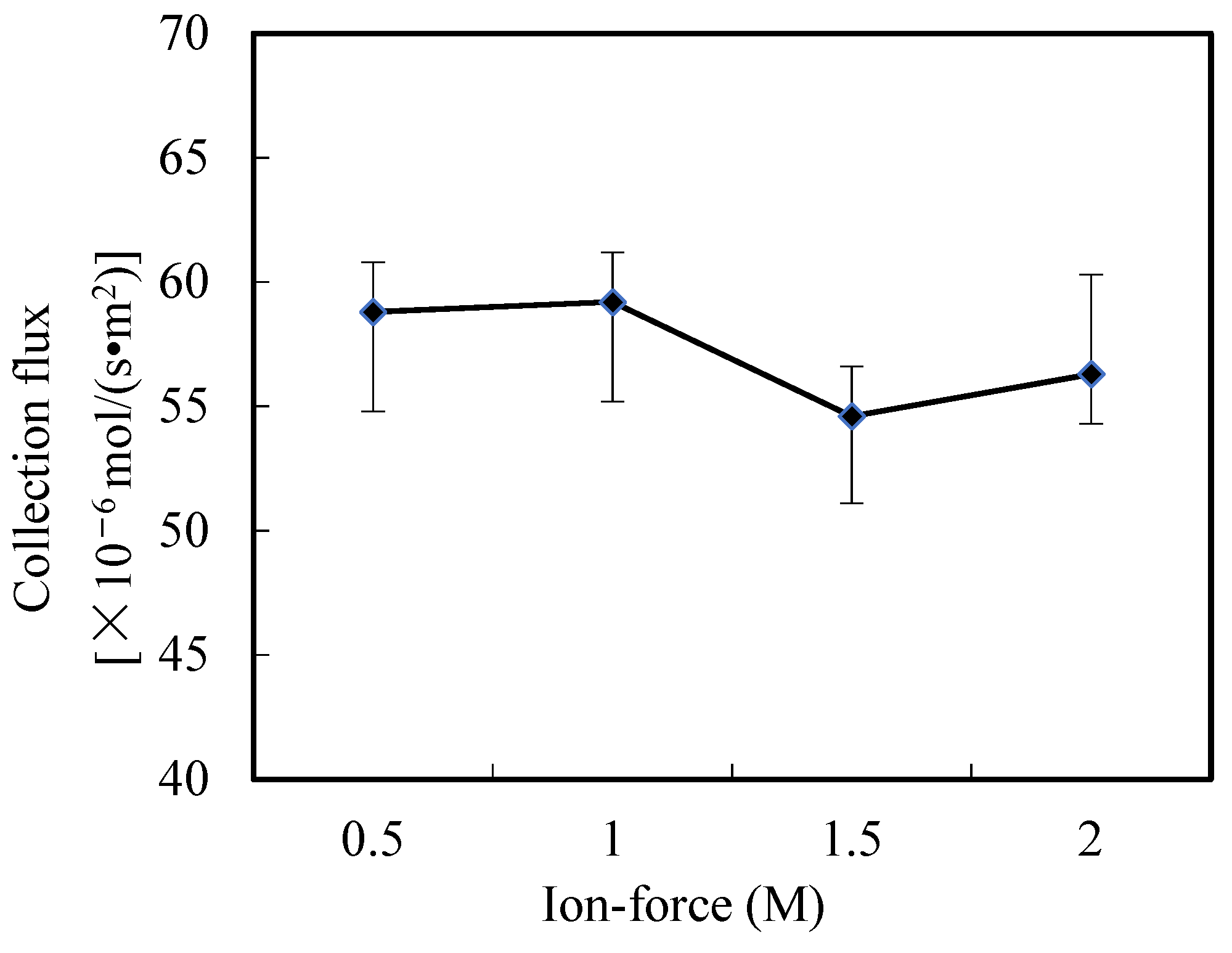
3.8. Influence of Ion-Force in Wastewater
3.9. Retention in Microfilter and Resolving Influences
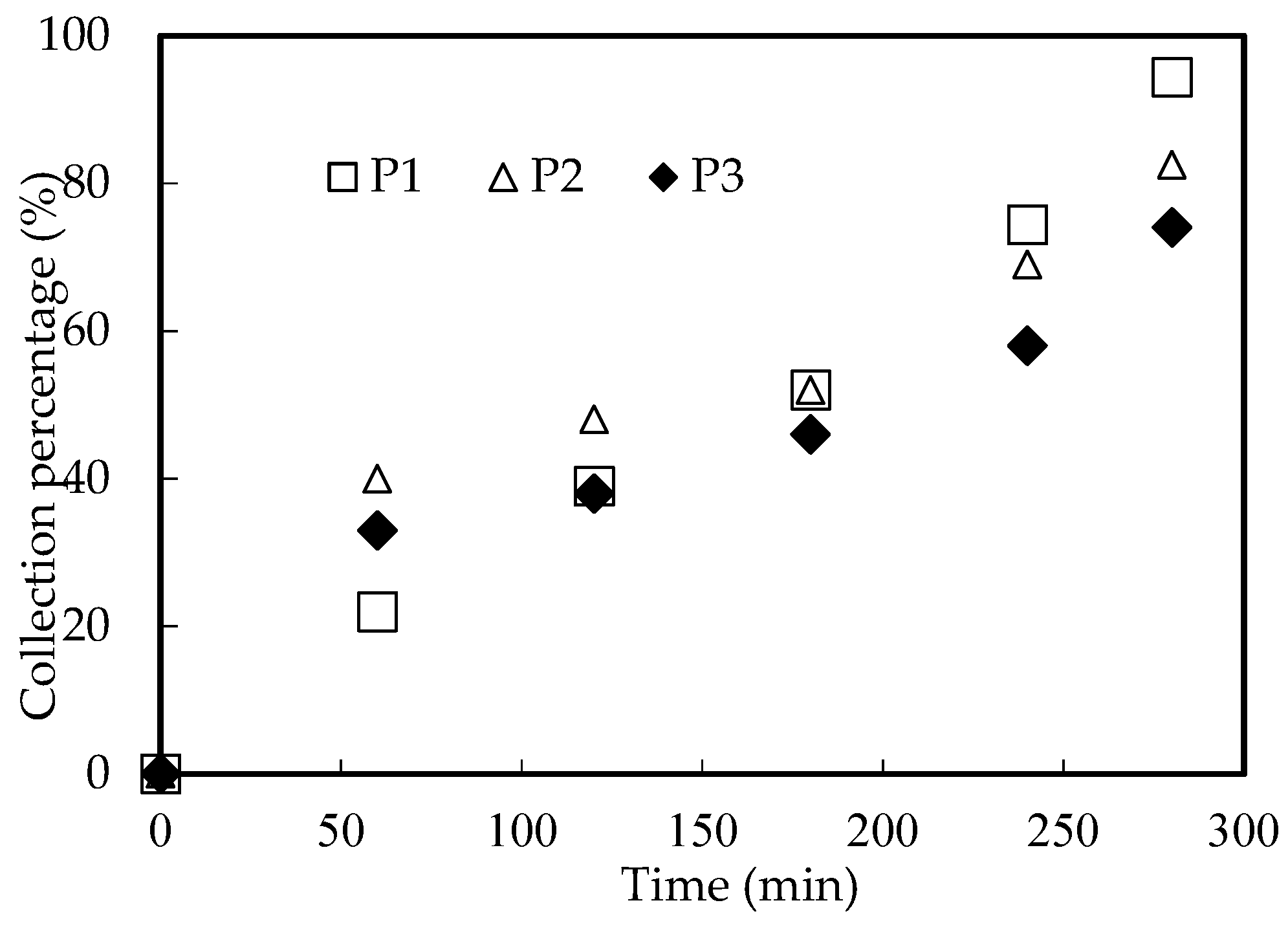
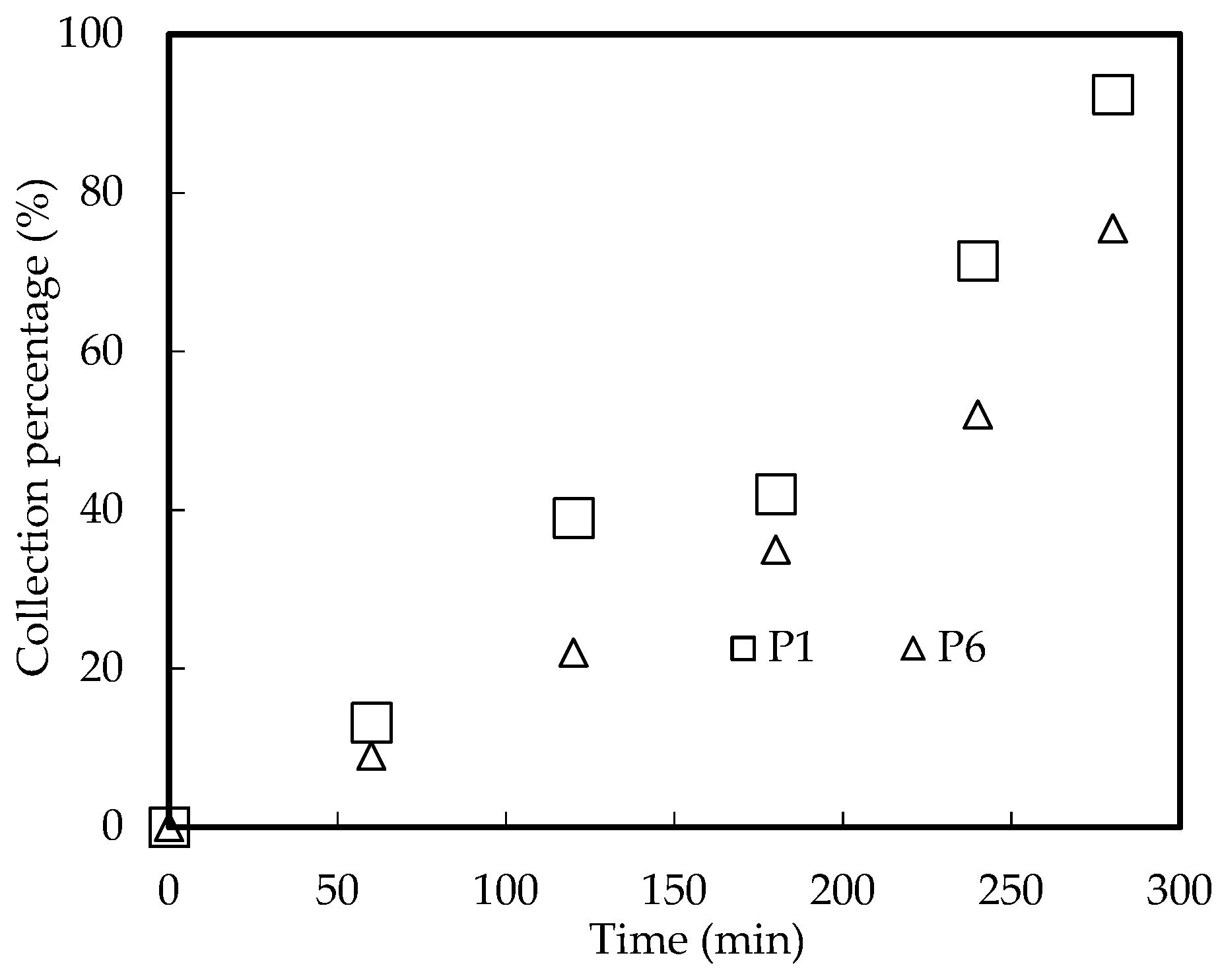
3.10. Influence of Parameters of Microfilter Microtubes
3.10.1. Influence of Tube–Shell Thickness
3.10.2. Influence of Tube Holes Proportion
3.10.3. Influence of Tube Inradius
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Islam, M.N.; Jung, H.Y.; Park, J.H. Subcritical water treatment of explosive and heavy metallic-ion co-contaminated soil: Removal of the explosive, and immobilization and risk assessment of heavy metallic-ion. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 163, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oron, G.; Armon, R.; Mandelbaum, R.; Manor, Y.; Campos, C.; Gillerman, L.; Saigot, M.; Gerba, C.; Klein, I.; Enriquez, C. Secondary wastewater disposal for crop irrigation with minimal risks. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 43, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadayonnejad, M.; Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Dashtaki, S.G. Changing soil hydraulic properties and water repellency in a pomegranate orchard irrigated with saline water by applying polyacrylamide. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 188, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badruzzaman, J.A.M.; Oppenheimer, J.; Jacangelo, G. Impact of environmental conditions on the suitability of microconstituents as markers for determining nutrient loading from reclaimed water. Water Res. 2013, 46, 6198–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Aguilar, V.; Godínez-Alvarez, H.; Moreno-Torres, R.; Rodríguez-Zaragoza, S. Soil physico-chemical properties affecting the distribution of biological soil crusts along an environmental transect at Zapotitlán drylands, Mexico. J. Arid. Environ. 2009, 63, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Piero, R.G. Identification of phase II pharmaceutical metabolites in reclaimed water using high refluid benchtop Orbitrap mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 2014, 106, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, F.; Cabrera, F.; Fernández-Bo, E. Irrigation with saline water in the reclaimed marsh soils of south-west Spain: Impact on soil properties and cotton and sugar beet crops. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 48, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichihara, M.; Yamamoto, A.; Takakura, K.-i.; Kakutani, N.; Sudo, M. Distribution and pollutant load of hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) in wastewater treatment plants and water from Japanese Rivers. Chemosphere 2014, 110, 68–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Kuisi, M.; Aljazzar, T.; Rüde, T.; Margane, A. Impact of the use of reclaimed water on the quality of groundwater resources in the Jordan Valley, Jordan. Clean-Soil Air Water 2008, 36, 1001–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchongkawarin, C.; Gomez-Mont, C.; Stuckey, D.C.; Chachuat, B. Optimization-based methodology for the development of wastewater facilities for energy and nutrient collection. Chemosphere 2015, 140, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, L.; Xiao, J.A.; Sun, L.Y. The effects of reclaimed water irrigation on the soil characteristics and microbial populations of plant rhizosphere. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 29, 17570–17579. [Google Scholar]
- Mutamim, N.S.A.; Noor, Z.Z.; Hassan, M.A.A.; Olsson, G. Application of film bioreactor technology in treating high strength industrial wastewater: A performance review. Desalination 2012, 305, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.Z.; Salih, K.A.M.; Hamza, M.F.; Castellon, E.R.; Guibal, E. Novel phosphonate-functionalized composite sorbent for the recovery of lanthanum(III) and terbium(III) from synthetic solutions and ore leachate. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 424, 130500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.; Fonseka, C.; Naidu, G.; Loganathan, P.; Moon, H.; Kandasamy, J.; Vigneswaran, S. Recovery of rare earth elements (Lu, Y) by adsorption using functionalized SBA-15 and MIL-101 (Cr). Chemosphere 2021, 291, 130896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnyk, I.V.; Goncharyk, V.P.; Stolyarchuk, N.V.; Kozhara, L.I.; Lunochkina, A.S.; Alonso, B.; Zub, Y.L. Dy(III) sorption from water solutions by mesoporous silicas functionalized with phosphonic acid groups. J. Porous Mterilas 2012, 19, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolti, A.; Green, S.J.; Ben Mordechay, E.; Hadar, Y.; Minz, D. Root microbiome response to treated wastewater irrigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 655, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.S.; Li, Y.; Zou, Y.N.; He, X.H. Arbuscular mycorrhiza mediates glomalin-related soil protein production and soil enzyme activities in the rhizosphere of trifoliate orange grown under different p levels. Mycorrhiza 2015, 25, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, L.; Wang, L.M.; Guo, W.; Nan, Z. Resolving dispersion hollow fiber liquid membrane containing PC-88A as carrier and HCl for transport behavior of trivalent dysprosium. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 378, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, L.; Wang, L. Migration of Trivalent Ho from Tombarthite Sewage by Microtubule Ultrafiltration Reactor with Organophosphorus in Fuel Oil. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koupaie, E.H.; Eskicioglu, C. Health risk assessment of heavy metallic-ion through the consumption of food crops fertilized by biosolids: A probabilistic-based analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 300, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.J.; Feng, Q.; Li, C.S. Spatial Variations of Soil Microbial Activities in Saline Groundwater-Irrigated Soil Ecosystem. Environ. Manag. 2016, 57, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Q.; Wang, L.; Pan, B.; Guan, W.; Sun, X.; Cai, A. Distribution features and controls of heavy metallic-ion in surface sediments from the riverbed of the Ningxia-Inner Mongolian reaches, Yellow River, China. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Hoffen, L.P.; Säumel, I. Orchards for edible cities: Cadmium and lead content in nuts, berries, pome and stone fruits harvested within the inner city neighbourhoods in Berlin, Germany. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 101, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Min, Q.L. A passive and active microwave-vector radiative transfer (PAM-VRT) model. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2015, 165, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero-Huguet, M.; Marshall, W.D. Scaling up a treatment to simultaneously remove persistent organic pollutants and heavy metallic-ion from contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantz, A.; Pottier, M.-A.; Karimi, B.; Corbel, H. Contrasting levels of heavy metallic-ion in the feathers of urban pigeons from close habitats suggest limited movements at a restricted scale. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 168, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, M.J.; Rodriguez, J.H.; Nieto, G.L.; Pignata, M.L. influences of heavy metal concentrtions (Cd, Zn and Pb) in agricultural soils near different emission sources on quality, accumulation and food safety in soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merrill]. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 233–234, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhid, P.; Davis, T.W.; Bunn, S.E.; Burford, M.A. Influences Of Inorganic Nutrients In Recycled Water On Freshwater Phytoplankton Biomass And Composition. Water Res. 2013, 46, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosabal, A.; Morillo, E.; Undabeytia, T.; Maqueda, C.; Justo, A.; Herencia, J.F. Long-term impacts of wastewater irrigation on Cuban soils. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2007, 71, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gołdyn, B.; Chudzińska, M.; Barałkiewicz, D.; Celewicz-Gołdyn, S. Heavy metal contents in the sediments of astatic ponds: Influence of geomorphology, hydroperiod, water chemistry and vegetation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 118, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziubanek, G.; Piekut, A.; Rusin, M.; Baranowska, R.; Hajok, I. Contamination of food crops grown on soils with elevated heavy metallic-ion content. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 118, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierens, T.; Cornelis, C.; Standaert, A.; Sioen, I.; De Henauw, S.; Van Holderbeke, M. Modelling the environmental transfer of phthalates and polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans intoagricultural products: The EN-forc model. Environ. Res. 2014, 133, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Tang, X.Y.; Jaeshin, K.; Korshin, V.G. Formation of aldehydes and carboxylic acids in ozonated surface water and wastewater: A clear relationship with fluorescence changes. Chemosphere 2015, 125, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.F.; Jiang, Y.; Shu, Y.; Hu Xing Liu, L.M.; Luo, F. influences of mining wastewater discharges on heavy metal pollution and soil enzyme activity of the paddy fields. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 146, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clidia, E.M.; Pinto, D.; Farias, F. Food safety assessment of an antifungal protein from Moringa oleifera seeds in an agricultural biotechnology perspective. Food Chem. Toxiology 2015, 83, 1–9. [Google Scholar]




| Time (Min) | Collection Proportion (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.00 × 10−4 M | 1.07 × 10−3 M | 1.35 × 10−3 M | 1.80 × 10−3 M | 2.00 × 10−3 M | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 60 | 40.70 | 39.70 | 27.20 | 22.70 | 14.30 |
| 120 | 81.20 | 54.60 | 42.90 | 36.70 | 21.40 |
| 180 | 92.10 | 73.20 | 69.50 | 60.90 | 48.70 |
| 240 | - | 87.30 | 80.10 | 77.90 | 61.20 |
| 280 | - | - | 89.30 | 90.10 | 71.40 |
| No | Parameters of Microtube Construction | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length of Tube, L/(m) | Proportion of Holes | Number of Tubes | Inradius of Tube, di/(mm) | Thickness of Tube–Shell, dm/(mm) | |
| P1 | 0.30 | 63% | 28 | 2.93 | 0.31 |
| P2 | 0.30 | 63% | 34 | 2.93 | 0.54 |
| P3 | 0.30 | 63% | 28 | 2.93 | 0.62 |
| P4 | 0.30 | 63% | 34 | 2.22 | 0.53 |
| P5 | 0.30 | 63% | 28 | 1.71 | 0.44 |
| P6 | 0.30 | 22% | 36 | 2.93 | 0.31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pei, L.; Sun, L. Application Effect of MF-OP on Collection of Trivalent Holmium from Rare Earth Mining Wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021498
Pei L, Sun L. Application Effect of MF-OP on Collection of Trivalent Holmium from Rare Earth Mining Wastewater. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(2):1498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021498
Chicago/Turabian StylePei, Liang, and Liying Sun. 2023. "Application Effect of MF-OP on Collection of Trivalent Holmium from Rare Earth Mining Wastewater" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 2: 1498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021498
APA StylePei, L., & Sun, L. (2023). Application Effect of MF-OP on Collection of Trivalent Holmium from Rare Earth Mining Wastewater. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(2), 1498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021498









