Health Implications of Virtual Architecture: An Interdisciplinary Exploration of the Transferability of Findings from Neuroarchitecture
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Use of Virtual Technologies by Children, Adolescents or Young Adults
3. The Uses of Virtual Architecture
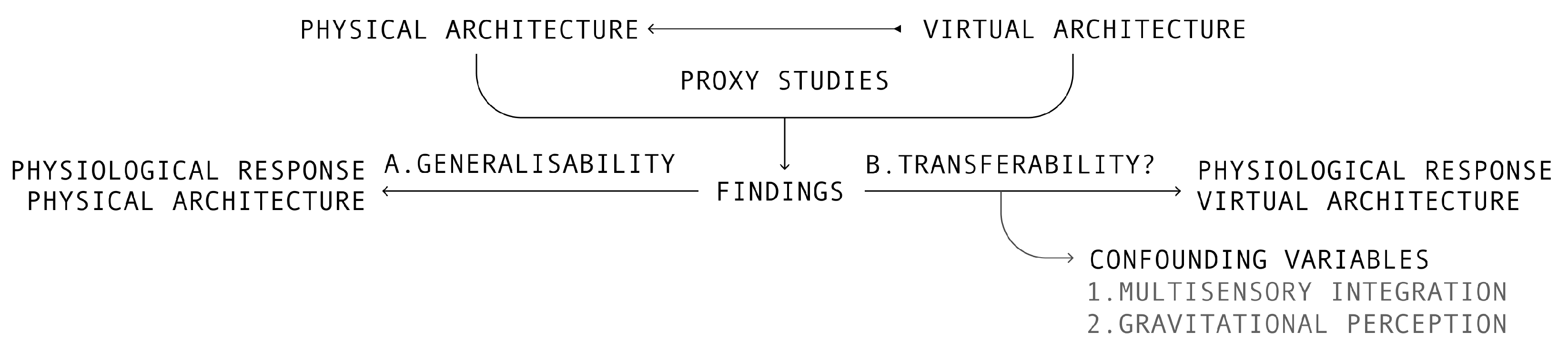
4. Virtual Architecture as a Proxy for Measuring the Health Impacts of Physical Architecture
5. The Generalisability of Proxy Studies
6. Confounding Variables in Virtual Architecture
6.1. Multisensory Integration and the Unisensory Nature of Virtual Architecture
6.2. Gravitational Perception in Virtual Architecture
7. Summary of Issues
8. Future Research
9. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VA | Virtual Architecture |
| PA | Physical Architecture |
| VR | Virtual Reality |
| 3D | Three Dimensional |
References
- Keil, J.; Edler, D.; Schmitt, T.; Dickmann, F. Creating Immersive Virtual Environments Based on Open Geospatial Data and Game Engines. KN J. Cartogr. Geogr. Inf. 2021, 71, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, M. The Metaverse: What It Is, Where to Find it, and Who Will Build It. 2021. Available online: https://www.matthewball.vc/all/themetaverse (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Moneta, A. Architecture, heritage and metaverse: New approaches and methods for the digital built environment. Tradit. Dwell. Settl. Rev. 2020, 32, 37–49. [Google Scholar]
- Isaac, M. Meta spent $10 billion on the metaverse in 2021, dragging down profit. The New York Times, 3 February 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Finney, A. Zaha Hadid Architects Designs Virtual Liberland Metaverse City. 2022. Available online: https://www.dezeen.com/2022/03/11/liberland-metaverse-city-zaha-hadid-architects/ (accessed on 9 December 2021).
- Architecture, W. BIG Designs Virtual Office Building in the Metaverse for Vice Media Group. 2021. Available online: https://www.dezeen.com/2022/03/02/big-viceverse-metaverse-virtual-office-vice-media/ (accessed on 9 December 2021).
- Lima, C.B.D.; Walton, S.; Owen, T. A critical outlook at augmented reality and its adoption in education. Comput. Educ. Open 2022, 3, 100103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoie, R.; Main, K.; King, C.; King, D. Virtual experience, real consequences: The potential negative emotional consequences of virtual reality gameplay. Virtual Real. 2021, 25, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérard, P.F. A Virtual Architecture Framework for Immersive Learning Environments. Ph.D. Thesis, University of London, London, UK, 2020; p. 265. [Google Scholar]
- West, G.L.; Konishi, K.; Diarra, M.; Benady-Chorney, J.; Drisdelle, B.L.; Dahmani, L.; Sodums, D.J.; Lepore, F.; Jolicoeur, P.; Bohbot, V.D. Impact of video games on plasticity of the hippocampus. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 23, 1566–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionisio, J.D.N.; Burns, W.G., III; Gilbert, R. 3D Virtual worlds and the metaverse: Current status and future possibilities. ACM Comput. Surv. 2013, 45, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogarty, J.; McCormick, J.; El-Tawil, S. Improving Student Understanding of Complex Spatial Arrangements with Virtual Reality. J. Prof. Issues Eng. Educ. Pract. 2018, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yi, W.; Chi, H.L.; Wang, X.; Chan, A.P.C. A critical review of virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR) applications in construction safety. Autom. Constr. 2018, 86, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanzadeh, S.; Polys, N.F.; de la Garza, J.M. Presence, Mixed Reality, and Risk-Taking Behavior: A Study in Safety Interventions. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2020, 26, 2115–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Du, J.; Ahn, C.R.; Ragan, E. Impact assessment of reinforced learning methods on construction workers’ fall risk behavior using virtual reality. Autom. Constr. 2019, 104, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagavathula, R.; Williams, B.; Owens, J.; Gibbons, R. The Reality of Virtual Reality: A Comparison of Pedestrian Behavior in Real and Virtual Environments. Proc. Hum. Factors Ergon. Soc. Annu. Meet. 2018, 62, 2056–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, S.H.M.; Qiu, L.; Esposito, G.; Mai, K.P.; Tam, K.P.; Cui, J. Nature in virtual reality improves mood and reduces stress: Evidence from young adults and senior citizens. Virtual Real. 2021, 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heydarian, A.; Carneiro, J.P.; Gerber, D.; Becerik-Gerber, B.; Hayes, T.; Wood, W. Immersive virtual environments versus physical built environments: A benchmarking study for building design and user-built environment explorations. Autom. Constr. 2015, 54, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lach, E.; Benek, I.; Zalewski, K.; Skurowski, P.; Kocur, A.; Kotula, A.; Macura, M.; Pamuła, Z.; Stankiewicz, M.; Wyrobek, T. Immersive Virtual Reality for Assisting in Inclusive Architectural Design. In Proceedings of the Man-Machine Interactions 6; Gruca, A., Czachórski, T., Deorowicz, S., Harężlak, K., Piotrowska, A., Eds.; Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing. Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Kang, S.C.; Al-Hussein, M. Virtual reality applications for the built environment: Research trends and opportunities. Autom. Constr. 2020, 118, 103311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagerhall, C.; Laike, T.; Kuller, M.; Marcheschi, E.; Boydston, C.; Taylor, R. Human Physiological Benefits of Viewing Nature: EEG Responses to Exact and Statistical Fractal Patterns. Nonlinear Dyn. Psychol. Life Sci. 2015, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Yeom, S.; Kim, H.; Hong, T. Psychological and physiological effects of a green wall on occupants: A cross-over study in virtual reality. Build. Environ. 2021, 204, 108134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentine, C. Architectural Neuroimmunology: A Pilot Study Examining the Impact of Biophilic Architectural Design on Neuroinflammation Using Quantitative Electroencephalography. Master’s Thesis, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ergan, S.; Radwan, A.; Zou, Z.; Tseng, H.A.; Han, X. Quantifying Human Experience in Architectural Spaces with Integrated Virtual Reality and Body Sensor Networks. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2019, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawil, N.; Sztuka, I.M.; Pohlmann, K.; Sudimac, S.; Kühn, S. The Living Space: Psychological Well-Being and Mental Health in Response to Interiors Presented in Virtual Reality. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Yuan, J.; Arfaei, N.; Catalano, P.J.; Allen, J.G.; Spengler, J.D. Effects of biophilic indoor environment on stress and anxiety recovery: A between-subjects experiment in virtual reality. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zhu, S.; MacNaughton, P.; Allen, J.G.; Spengler, J.D. Physiological and cognitive performance of exposure to biophilic indoor environment. Build. Environ. 2018, 132, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Garza, J.; Darfler, M.; Rounds, J.; Gao, E.; Kalantari, S. EEG-based Investigation of the Impact of Classroom Design on Cognitive Performance of Students. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.03629. [Google Scholar]
- Shemesh, A.; Leisman, G.; Bar, M.; Grobman, Y.J. A neurocognitive study of the emotional impact of geometrical criteria of architectural space. Archit. Sci. Rev. 2021, 64, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vartanian, O.; Navarrete, G.; Chatterjee, A.; Fich, L.B.; Gonzalez-Mora, J.L.; Leder, H.; Modroño, C.; Nadal, M.; Rostrup, N.; Skov, M. Architectural design and the brain: Effects of ceiling height and perceived enclosure on beauty judgments and approach-avoidance decisions. J. Environ. Psychol. 2015, 41, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IET. Generation VR; IET: Stevenage, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kaimara, P.; Oikonomou, A.; Deliyannis, I. Could virtual reality applications pose real risks to children and adolescents? A systematic review of ethical issues and concerns. Virtual Real. 2022, 26, 697–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaffer, D.W.; Squire, K.R.; Halverson, R.; Gee, J.P. Video Games and the Future of Learning. Phi Delta Kappan 2005, 87, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, J. Learning and Games. In The Ecology of Games: Connecting Youth, Games, and Learning; John, D., Catherine, T., MacArthur Foundation, Salen, K., Eds.; The Series on Digital Media and Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 21–40. [Google Scholar]
- Dalgarno, B.; Lee, M.J.W. What are the learning affordances of 3-D virtual environments? Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2010, 41, 10–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granic, I.; Lobel, A.; Engels, R.C.M.E. The benefits of playing video games. Am. Psychol. 2014, 69, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, C. Virtual reality and learning: Where is the pedagogy? Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2015, 46, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passig, D.; Tzuriel, D.; Eshel-Kedmi, G. Improving children’s cognitive modifiability by dynamic assessment in 3D Immersive Virtual Reality environments. Comput. Educ. 2016, 95, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaus, M.; Marron, E.M.; Viejo-Sobera, R.; Redolar-Ripoll, D. Neural Basis of Video Gaming: A Systematic Review. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Carmona, R.; Pertegal-Felices, M.L.; Jimeno-Morenilla, A.; Mora-Mora, H. Virtual Reality Learning Activities for Multimedia Students to Enhance Spatial Ability. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaimara, P.; Deliyannis, I. Why Should I Play This Game? The Role of Motivation in Smart Pedagogy. In Didactics of Smart Pedagogy; Daniela, L., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 113–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, R.E. Computer Games in Education. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2019, 70, 531–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makransky, G.; Borre-Gude, S.; Mayer, R.E. Motivational and cognitive benefits of training in immersive virtual reality based on multiple assessments. J. Comput. Assist. Learn. 2019, 35, 691–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checa, D.; Bustillo, A. A review of immersive virtual reality serious games to enhance learning and training. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 5501–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaimara, P.; Fokides, E.; Oikonomou, A.; Deliyannis, I. Potential Barriers to the Implementation of Digital Game-Based Learning in the Classroom: Pre-service Teachers’ Views. Technol. Knowl. Learn. 2021, 26, 825–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.C.; Hsu, T.C.; Kuo, W.C.; Jong, M.S.Y. Effects of applying a VR-based two-tier test strategy to promote elementary students’ learning performance in a Geology class. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2020, 51, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallavicini, F.; Pepe, A. Virtual Reality Games and the Role of Body Involvement in Enhancing Positive Emotions and Decreasing Anxiety: Within-Subjects Pilot Study. JMIR Serious Games 2020, 8, e15635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvert, S.L.; Staiano, A.E.; Bond, B.J. Electronic Gaming and the Obesity Crisis. New Dir. Child Adolesc. Dev. 2013, 2013, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, E.B.; Spruijt-Metz, D.; O’Reilly, G.; Jordan-Marsh, M.; Gotsis, M.; Pentz, M.A.; Dunton, G.F. mHealth approaches to child obesity prevention: Successes, unique challenges, and next directions. Transl. Behav. Med. 2013, 3, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turel, O.; Romashkin, A.; Morrison, K.M. Health Outcomes of Information System Use Lifestyles among Adolescents: Videogame Addiction, Sleep Curtailment and Cardio-Metabolic Deficiencies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thierer, A.D.; Camp, J. Permissionless Innovation and Immersive Technology: Public Policy for Virtual and Augmented Reality. SSRN Electron. J. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuller, C.; Lehman, E.; Hicks, S.; Novick, M.B. Bedtime Use of Technology and Associated Sleep Problems in Children. Glob. Pediatr. Health 2017, 4, 2333794X1773697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenney, E.L.; Gortmaker, S.L. United States Adolescents’ Television, Computer, Videogame, Smartphone, and Tablet Use: Associations with Sugary Drinks, Sleep, Physical Activity, and Obesity. J. Pediatr. 2017, 182, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turel, O.; Romashkin, A.; Morrison, K.M. A model linking video gaming, sleep quality, sweet drinks consumption and obesity among children and youth: Video gaming, sleep, sweet drinks and obesity. Clin. Obes. 2017, 7, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behr, K.M.; Nosper, A.; Klimmt, C.; Hartmann, T. Some Practical Considerations of Ethical Issues in VR Research. Presence Teleoperators Virtual Environ. 2005, 14, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K. Understanding Online Gaming Addiction and Treatment Issues for Adolescents. Am. J. Fam. Ther. 2009, 37, 355–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kade, D. Ethics of Virtual Reality Applications in Computer Game Production. Philosophies 2015, 1, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madary, M.; Metzinger, T.K. Recommendations for Good Scientific Practice and the Consumers of VR-Technology. Front. Robot. AI 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenwright, B. Virtual Reality: Ethical Challenges and Dangers [Opinion]. IEEE Technol. Soc. Mag. 2018, 37, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, T.D. Ethics and educational technologies. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2021, 69, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davila Delgado, J.M.; Oyedele, L.; Demian, P.; Beach, T. A research agenda for augmented and virtual reality in architecture, engineering and construction. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2020, 45, 101122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Mojica Cabico, C.D. Development and Evaluation of an Augmented Reality Learning Tool for Construction Engineering Education. In Proceedings of the Construction Research Congress 2018, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–4 April 2018; pp. 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastli, M.; Zhang, J. Interactive Highway Construction Simulation Using Game Engine and Virtual Reality for Education and Training Purpose. In Proceedings of the ASCE International Workshop on Computing in Civil Engineering 2017, Seattle, WA, USA, 25–27 June 2017; pp. 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkan, Y.; Radkowski, R.; Karabulut-Ilgu, A.; Behzadan, A.H.; Chen, A. Mobile augmented reality for teaching structural analysis. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2017, 34, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, H.F.; Gheisari, M. A Review of Virtual and Mixed Reality Applications in Construction Safety Literature. Safety 2019, 5, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.S.; Kim, H.J. A framework for construction safety management and visualization system. Autom. Constr. 2013, 33, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Lin, J.; Li, N. A virtual reality based study of indoor fire evacuation after active or passive spatial exploration. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2019, 90, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhu, R.; Li, N.; Becerik-Gerber, B. Do people follow the crowd in building emergency evacuation? A cross-cultural immersive virtual reality-based study. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2020, 43, 101040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rounds, J.D.; Cruz-Garza, J.G.; Kalantari, S. Using Posterior EEG Theta Band to Assess the Effects of Architectural Designs on Landmark Recognition in an Urban Setting. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stieglitz, T. Why Neurotechnologies? About the Purposes, Opportunities and Limitations of Neurotechnologies in Clinical Applications. Neuroethics 2021, 14, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, T.; Bowen, J.P. Rethinking Museum Exhibitions: Merging Physical and Digital Culture—Past to Present. In Museums and Digital Culture: New Perspectives and Research; Giannini, T., Bowen, J.P., Eds.; Springer Series on Cultural Computing; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 163–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delle Monache, S.; Indovina, I.; Zago, M.; Daprati, E.; Lacquaniti, F.; Bosco, G. Watching the Effects of Gravity. Vestibular Cortex and the Neural Representation of “Visual” Gravity. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 793634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J. Advertising in the Metaverse: Research Agenda. J. Interact. Advert. 2021, 21, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.H.; Braud, T.; Zhou, P.; Wang, L.; Xu, D.; Lin, Z.; Kumar, A.; Bermejo, C.; Hui, P. All One Needs to Know about Metaverse: A Complete Survey on Technological Singularity, Virtual Ecosystem, and Research Agenda. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.05352. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, J. Meta ‘Horizon Worlds’ Sees Monthly User Base of 300,000 Users | 10 Times Increase in Just 3 Months? 2022. Available online: https://www.techtimes.com/articles/272005/20220218/meta-horizon-worlds-sees-monthly-user-base-300-000-users.htm (accessed on 10 December 2021).
- Architecture, W. Krista Kim’s Mars House is ‘first NFT Digital House’ to Be Sold Over $500,000. 2021. Available online: https://worldarchitecture.org/article-links/evzfc/krista-kim-s-mars-house-is-first-nft-digital-house-to-be-sold-over-500-000.html (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Frank, R. Metaverse Real Estate Sales Top $500 Million, and Are Projected to Double This Year. 2022. Available online: https://www.cnbc.com/2022/02/01/metaverse-real-estate-sales-top-500-million-metametric-solutions-says.html (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Robertson, H. The Metaverse Is a $1 Trillion Opportunity, Crypto Giant Grayscale Says as Virtual Land Sales Boom. 2021. Available online: https://markets.businessinsider.com/news/currencies/metaverse-1-trillion-opportunity-grayscale-virual-land-sales-decentraland-2021-11 (accessed on 11 December 2021).
- Reynolds, E. ONE Sotheby’s Is Selling the First Real-World Home through the Metaverse Using NFT Technology. 2022. Available online: https://www.wikibit.com/en/202201109224819286.html (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Aronson, J.K.; Ferner, R.E. Biomarkers—A General Review. Curr. Protoc. Pharmacol. 2017, 76, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantari, S.; Rounds, J.D.; Kan, J.; Tripathi, V.; Cruz-Garza, J.G. Comparing physiological responses during cognitive tests in virtual environments vs. in identical real-world environments. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamilothori, K.; Wienold, J.; Andersen, M. Adequacy of Immersive Virtual Reality for the Perception of Daylit Spaces: Comparison of Real and Virtual Environments. Leukos 2019, 15, 203–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollazadeh, M.; Zhu, Y. Application of Virtual Environments for Biophilic Design: A Critical Review. Buildings 2021, 11, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altomonte, S.; Allen, J.; Bluyssen, P.M.; Brager, G.; Heschong, L.; Loder, A.; Schiavon, S.; Veitch, J.A.; Wang, L.; Wargocki, P. Ten questions concerning well-being in the built environment. Build. Environ. 2020, 180, 106949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, C. Senses of place: Architectural design for the multisensory mind. Cogn. Res. Princ. Implic. 2020, 5, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedeño-Laurent, J.; Williams, A.; MacNaughton, P.; Cao, X.; Eitland, E.; Spengler, J.; Allen, J. Building Evidence for Health: Green Buildings, Current Science, and Future Challenges. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2018, 39, 291–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Prado Bert, P.; Mercader, E.M.H.; Pujol, J.; Sunyer, J.; Mortamais, M. The Effects of Air Pollution on the Brain: A Review of Studies Interfacing Environmental Epidemiology and Neuroimaging. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2018, 5, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holøs, S.B.; Yang, A.; Lind, M.; Thunshelle, K.; Schild, P.; Mysen, M. VOC emission rates in newly built and renovated buildings, and the influence of ventilation—A review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Vent. 2019, 18, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, F.; Whitaker, R.; LeChevallier, M.W.; Liu, W.T. Drinking water microbiome assembly induced by water stagnation. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1520–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoads, W.J.; Pruden, A.; Edwards, M.A. Survey of green building water systems reveals elevated water age and water quality concerns. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2016, 2, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin Robbins, L.J.; Rodgers, K.M.; Walsh, B.; Ain, R.; Dodson, R.E. Pruning chemicals from the green building landscape. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2020, 30, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomas, K.J.; Porritt, S.M. Overheating in buildings: Lessons from research. Build. Res. Inf. 2017, 45, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; de Dear, R.; Hancock, P. Effects of moderate thermal environments on cognitive performance: A multidisciplinary review. Appl. Energy 2019, 236, 760–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fich, L.B.; Jönsson, P.; Kirkegaard, P.H.; Wallergård, M.; Garde, A.H.; Hansen, Å. Can architectural design alter the physiological reaction to psychosocial stress? A virtual TSST experiment. Physiol. Behav. 2014, 135, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dePaiva, A.; Jedon, R. Short- and long-term effects of architecture on the brain: Toward theoretical formalization. Front. Archit. Res. 2019, 8, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, A. The effects of chronic stress on health: New insights into the molecular mechanisms of brain–body communication. Future Sci. OA 2015, 1, FSO23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, B.S. Allostasis and Allostatic Load: Implications for Neuropsychopharmacology. Neuropsychopharmacology 2000, 22, 108–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abd-Alhamid, F.; Kent, M.; Calautit, J.; Wu, Y. Evaluating the impact of viewing location on view perception using a virtual environment. Build. Environ. 2020, 180, 106932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Schröder, T.; Bekkering, J. Biophilic design in architecture and its contributions to health, well-being, and sustainability: A critical review. Front. Archit. Res. 2022, 11, 114–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.P.; Yeo, N.L.; Vassiljev, P.; Lundstedt, R.; Wallergård, M.; Albin, M.; Lõhmus, M. A prescription for “nature”—The potential of using virtual nature in therapeutics. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2018, 14, 3001–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillis, K.; Gatersleben, B. A review of psychological literature on the health and wellbeing benefits of biophilic design. Buildings 2015, 5, 948–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joye, Y. Architectural Lessons From Environmental Psychology: The Case of Biophilic Architecture. Rev. Gen. Psychol. 2007, 11, 305–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söderlund, J.; Newman, P. Biophilic architecture: A review of the rationale and outcomes. AIMS Environ. Sci. 2015, 2, 950–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, M.; ElSharkawy, M.; Mahmoud, A. Analysing user daylight preferences in heritage buildings using virtual reality. Build. Simul. 2022, 15, 1561–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armougum, A.; Orriols, E.; Gaston-Bellegarde, A.; Marle, C.; Piolino, P. Virtual reality: A new method to investigate cognitive load during navigation. J. Environ. Psychol. 2019, 65, 101338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.C.; Chiu, Y.C. Evaluating Stress Relief from Architecture: A Case Study Based on Buildings in Taiwan, China and Japan. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukull, W.A.; Ganguli, M. Generalizability. Neurology 2012, 78, 1886–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barnes, J.; Conrad, K.; Demont-Heinrich, C.; Graziano, M.; Kowalski, D.; Neufeld, J.; Zamora, J.; Palmquist, M. Generalizability and Transferability—The WAC Clearinghouse. 2022. Available online: https://wac.colostate.edu/repository/resources/writing/guides/gentrans/ (accessed on 14 December 2021).
- Heydarian, A.; Becerik-Gerber, B. Use of Immersive Virtual Environments for Occupant Behaviour Monitoring and Data Collection. J. Build. Perform. Simul. 2017, 10, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, M.; Gonçalves, G.; Monteiro, P.; Coelho, H.; Vasconcelos-Raposo, J.; Bessa, M. Do Multisensory Stimuli Benefit the Virtual Reality Experience? A Systematic Review. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2022, 28, 1428–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flavián, C.; Ibáñez-Sánchez, S.; Orús, C. The impact of virtual, augmented and mixed reality technologies on the customer experience. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 100, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassini, S.; Laumann, K.; de Martin Topranin, V.; Thorp, S. Evaluating the effect of multi-sensory stimulations on simulator sickness and sense of presence during HMD-mediated VR experience. Ergonomics 2021, 64, 1532–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.M. Why Presence Occurs: Evolutionary Psychology, Media Equation, and Presence. Presence Teleoperators Virtual Environ. 2004, 13, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchiato, G.; Tieri, G.; Jelic, A.; Matteis, F.D.; Maglione, A.G.; Babiloni, F. Electroencephalographic Correlates of Sensorimotor Integration and Embodiment during the Appreciation of Virtual Architectural Environments. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, P.R.K.; Phillips, J.R. Ocular effects of virtual reality headset wear in young adults. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soret, R.; Montes-Solano, A.M.; Manzini, C.; Peysakhovich, V.; Fabre, E. Pushing open the door to reality: On facilitating the transitions from virtual to real environments. Appl. Ergon. 2021, 97, 103535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Hu, S.; Lu, M.; He, M.; Zhang, X.; Liu, G. Analysis of human electroencephalogram features in different indoor environments. Build. Environ. 2020, 186, 107328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzazy, S.; Ghaffarianhoseini, A.; GhaffarianHoseini, A.; Naismith, N.; Doborjeh, Z. A critical review on the impact of built environment on users’ measured brain activity. Archit. Sci. Rev. 2021, 64, 319–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osibona, O.; Solomon, B.D.; Fecht, D. Lighting in the Home and Health: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flies, E.J.; Mavoa, S.; Zosky, G.R.; Mantzioris, E.; Williams, C.; Eri, R.; Brook, B.W.; Buettel, J.C. Urban-associated diseases: Candidate diseases, environmental risk factors, and a path forward. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halperin, D. Environmental noise and sleep disturbances: A threat to health? Sleep Sci. 2014, 7, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, E.M. Air Pollution, Stress, and Allostatic Load: Linking Systemic and Central Nervous System Impacts. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2019, 69, 597–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, J.M. Critical Analysis of Strategies for Determining Rigor in Qualitative Inquiry. Qual. Health Res. 2015, 25, 1212–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marucci, M.; Di Flumeri, G.; Borghini, G.; Sciaraffa, N.; Scandola, M.; Pavone, E.; Babiloni, F.; Betti, V.; Aricò, P. The impact of multisensory integration and perceptual load in virtual reality settings on performance, workload and presence. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coburn, A.; Vartanian, O.; Chatterjee, A. Buildings, Beauty, and the Brain: A Neuroscience of Architectural Experience. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2017, 29, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, M.O.; Bülthoff, H.H. Merging the senses into a robust percept. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2004, 8, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, B.E.; Stanford, T.R.; Rowland, B.A. Multisensory Integration and the Society for Neuroscience: Then and Now. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valzolgher, C.; Alzhaler, M.; Gessa, E.; Todeschini, M.; Nieto, P.; Verdelet, G.; Salemme, R.; Gaveau, V.; Marx, M.; Truy, E.; et al. The impact of a visual spatial frame on real sound-source localization in virtual reality. Curr. Res. Behav. Sci. 2020, 1, 100003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassini, S.; Laumann, K. Immersive visual technologies and human health. In Proceedings of the 32nd European Conference on Cognitive Ergonomics, Siena, Italy, 26–29 April 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reason, J.T.; Brand, J.J. Motion Sickness; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 1975; Volume II, p. 310. [Google Scholar]
- Lécuyer, A. Playing with Senses in VR: Alternate Perceptions Combining Vision and Touch. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 2017, 37, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordahl, R.; Nilsson, N.C. The Sound of Being There: Presence and Interactive Audio in Immersive Virtual Reality. In The Oxford Handbook of Interactive Audio; Oxford Handbooks; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, P.; Väljamäe, A.; Västfjäll, D.; Tajadura-Jiménez, A.; Kleiner, M. Auditory-Induced Presence in Mixed Reality Environments and Related Technology. In The Engineering of Mixed Reality Systems; Dubois, E., Gray, P., Nigay, L., Eds.; Human-Computer Interaction Series; Springer: London, UK, 2010; pp. 143–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reason, J.T. Motion sickness adaptation: A neural mismatch model. J. R. Soc. Med. 1978, 71, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, M.; Van Zandt, E. A meta-analysis of the virtual reality problem: Unequal effects of virtual reality sickness across individual differences. Virtual Real. 2021, 25, 1221–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshev, V.; de Bougrenet de la Tocnaye, J.L.; Cochener, B.; Nourrit, V. Predicting virtual reality discomfort. Electron. Imaging 2021, 2021, 168-1–168-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pöhlmann, K.; Föcker, J.; Dickinson, P.; Parke, A.; O’Hare, L. The relationship between vection, cybersickness and head movements elicited by illusory motion in virtual reality. Displays 2022, 71, 102111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, T.L. Representational gravity: Empirical findings and theoretical implications. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2020, 27, 36–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, M.; Torok, A.; Klaas, J.; Ferrè, E.R. Gravity prior in human behaviour: A perceptual or semantic phenomenon? Exp. Brain Res. 2020, 238, 1957–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguado, B.; López-Moliner, J. Gravity and Known Size Calibrate Visual Information to Time Parabolic Trajectories. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 642025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano Porras, D.; Zeilig, G.; Doniger, G.M.; Bahat, Y.; Inzelberg, R.; Plotnik, M. Seeing Gravity: Gait Adaptations to Visual and Physical Inclines—A Virtual Reality Study. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.B.; Whang, H.J. A Study on the Effects of ’Defying Gravity’ in Aesthetic Preference of Architectural Forms. J. Archit. Inst. Korea Plan. Des. 2015, 31, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, J. Andrés Reisinger Sells Collection of “Impossible” Virtual Furniture for $450,000. 2021. Available online: https://www.dezeen.com/2021/02/23/andres-reisinger-the-shipping-digital-furniture-auction/ (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Jörges, B.; López-Moliner, J. Gravity as a Strong Prior: Implications for Perception and Action. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, R.A.; Ghose, D.; Fister, J.K.; Sarko, D.K.; Altieri, N.A.; Nidiffer, A.R.; Kurela, L.R.; Siemann, J.K.; James, T.W.; Wallace, M.T. Identifying and Quantifying Multisensory Integration: A Tutorial Review. Brain Topogr. 2014, 27, 707–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakin, C.; Rosenberg, A. Gravity estimation and verticality perception. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 159, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valentine, C. Health Implications of Virtual Architecture: An Interdisciplinary Exploration of the Transferability of Findings from Neuroarchitecture. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2735. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20032735
Valentine C. Health Implications of Virtual Architecture: An Interdisciplinary Exploration of the Transferability of Findings from Neuroarchitecture. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(3):2735. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20032735
Chicago/Turabian StyleValentine, Cleo. 2023. "Health Implications of Virtual Architecture: An Interdisciplinary Exploration of the Transferability of Findings from Neuroarchitecture" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 3: 2735. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20032735
APA StyleValentine, C. (2023). Health Implications of Virtual Architecture: An Interdisciplinary Exploration of the Transferability of Findings from Neuroarchitecture. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(3), 2735. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20032735





