Spatial-Temporal Variations in of Soil Conservation Service and Its Influencing Factors under the Background of Ecological Engineering in the Taihang Mountain Area, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Pretreatment
2.3. InVEST Model
2.3.1. Rainfall Erosivity Factor
2.3.2. Soil Erodibility Factor
2.4. Quantification of the Intensity of Ecological Engineering
2.5. Geographical Detector Model
3. Results
3.1. Model Validation
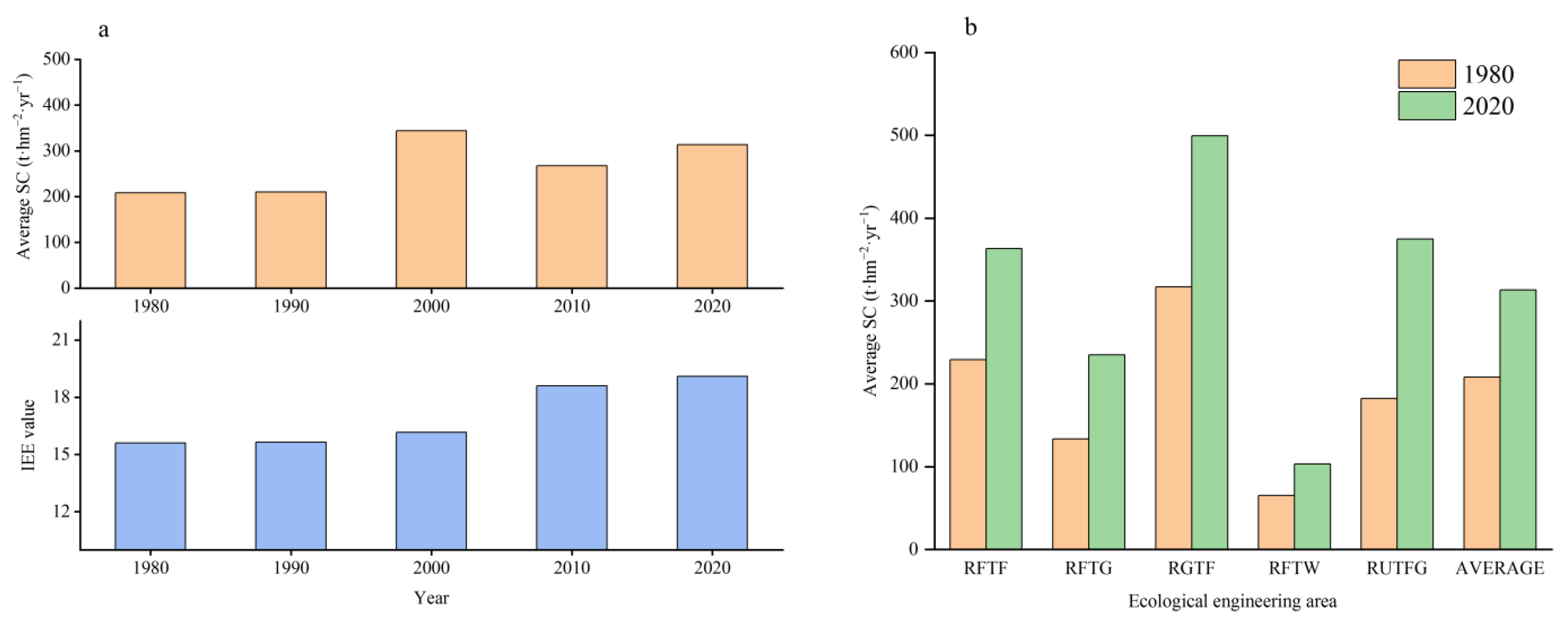
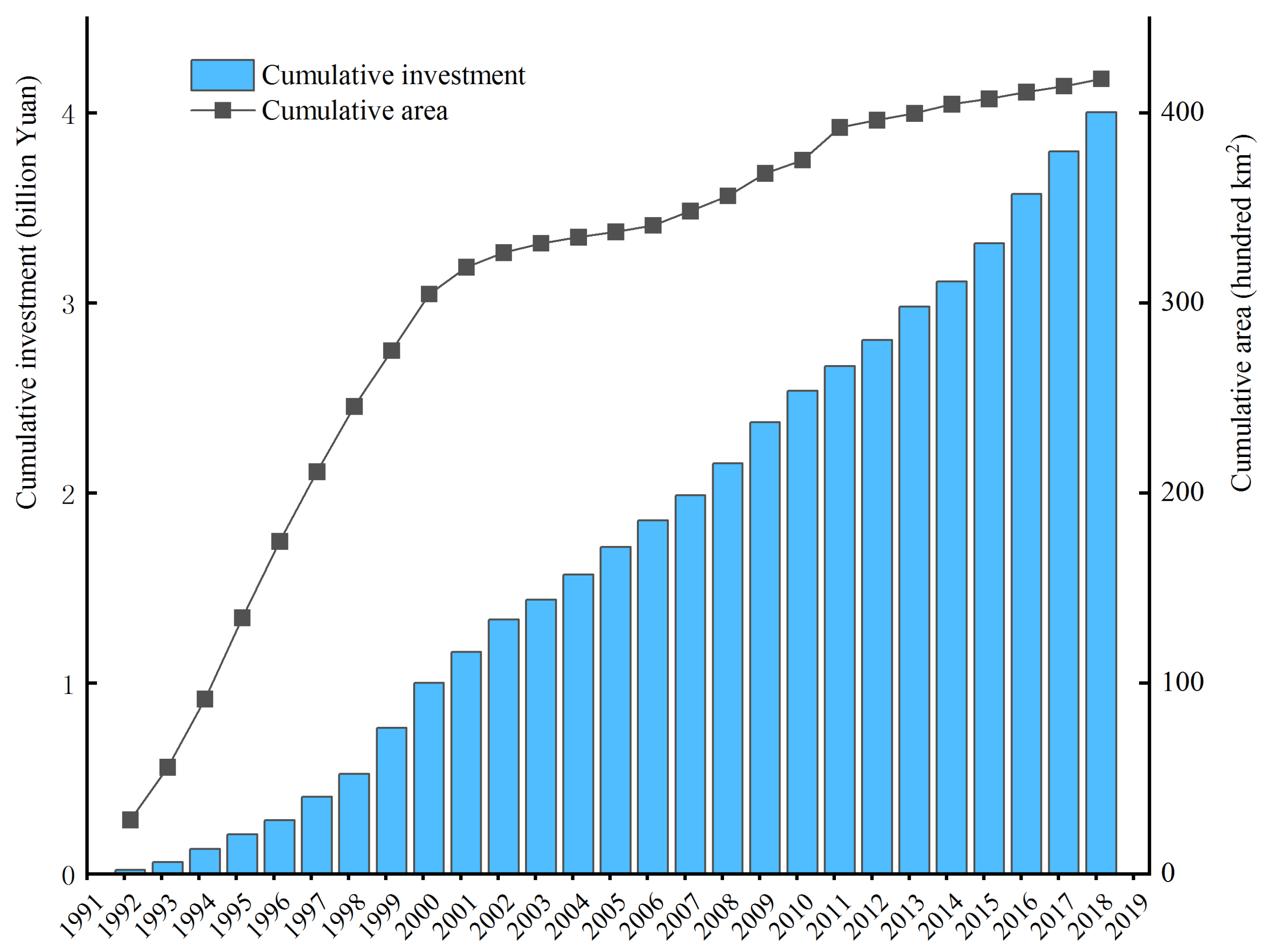
3.2. Temporal Changes in Ecological Engineering and Soil Conservation
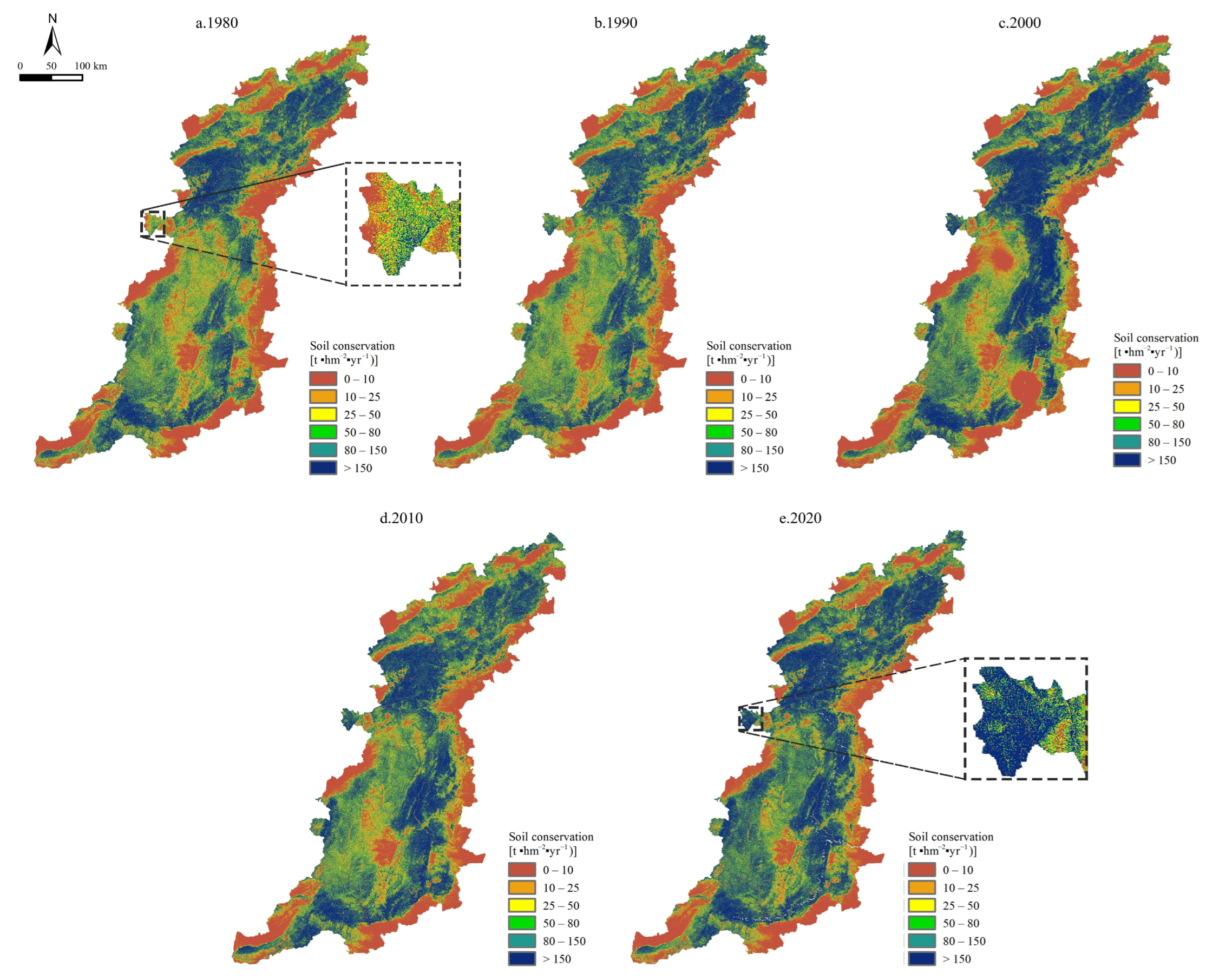
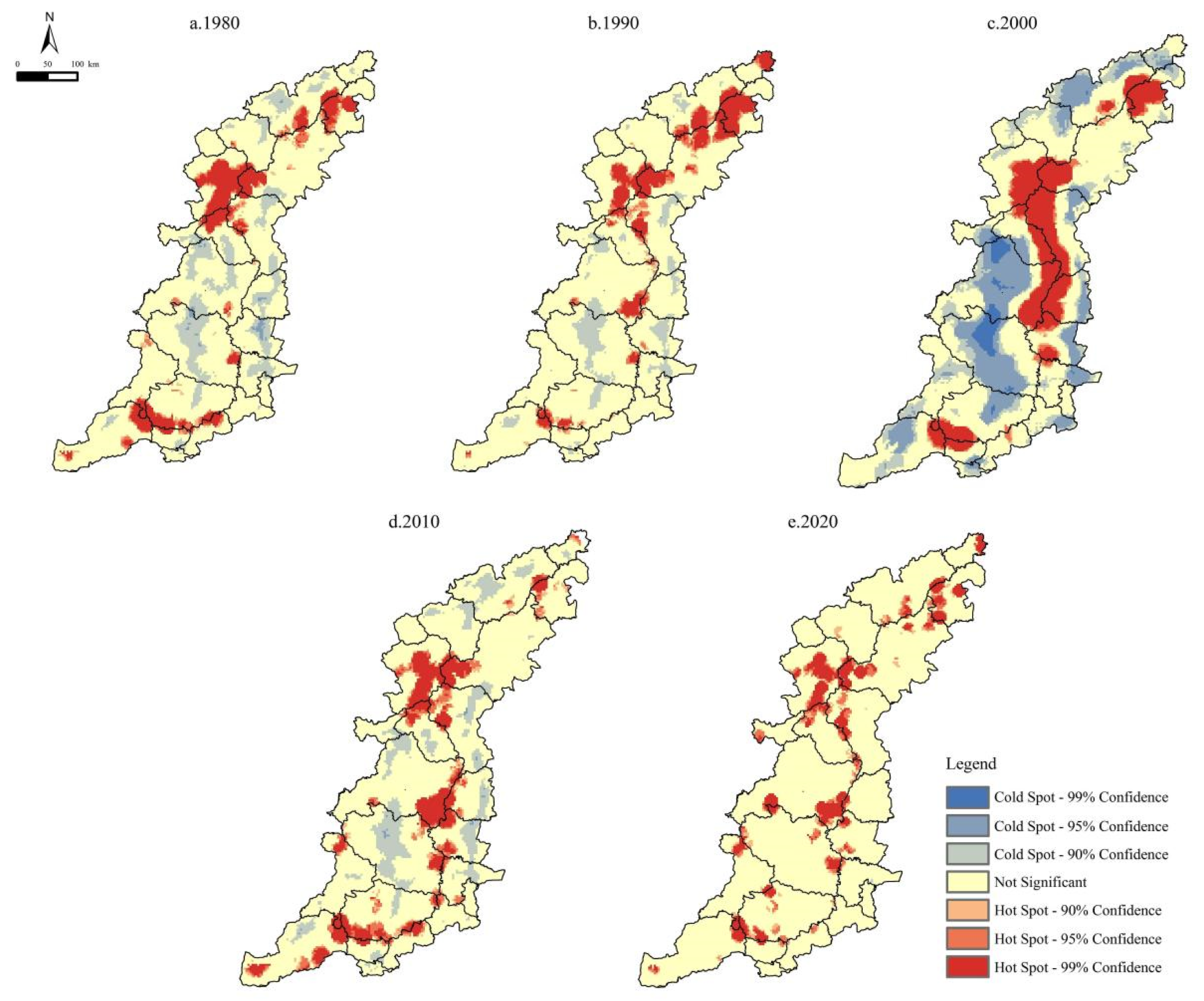
3.3. Spatial Distribution of Soil Conservation Services
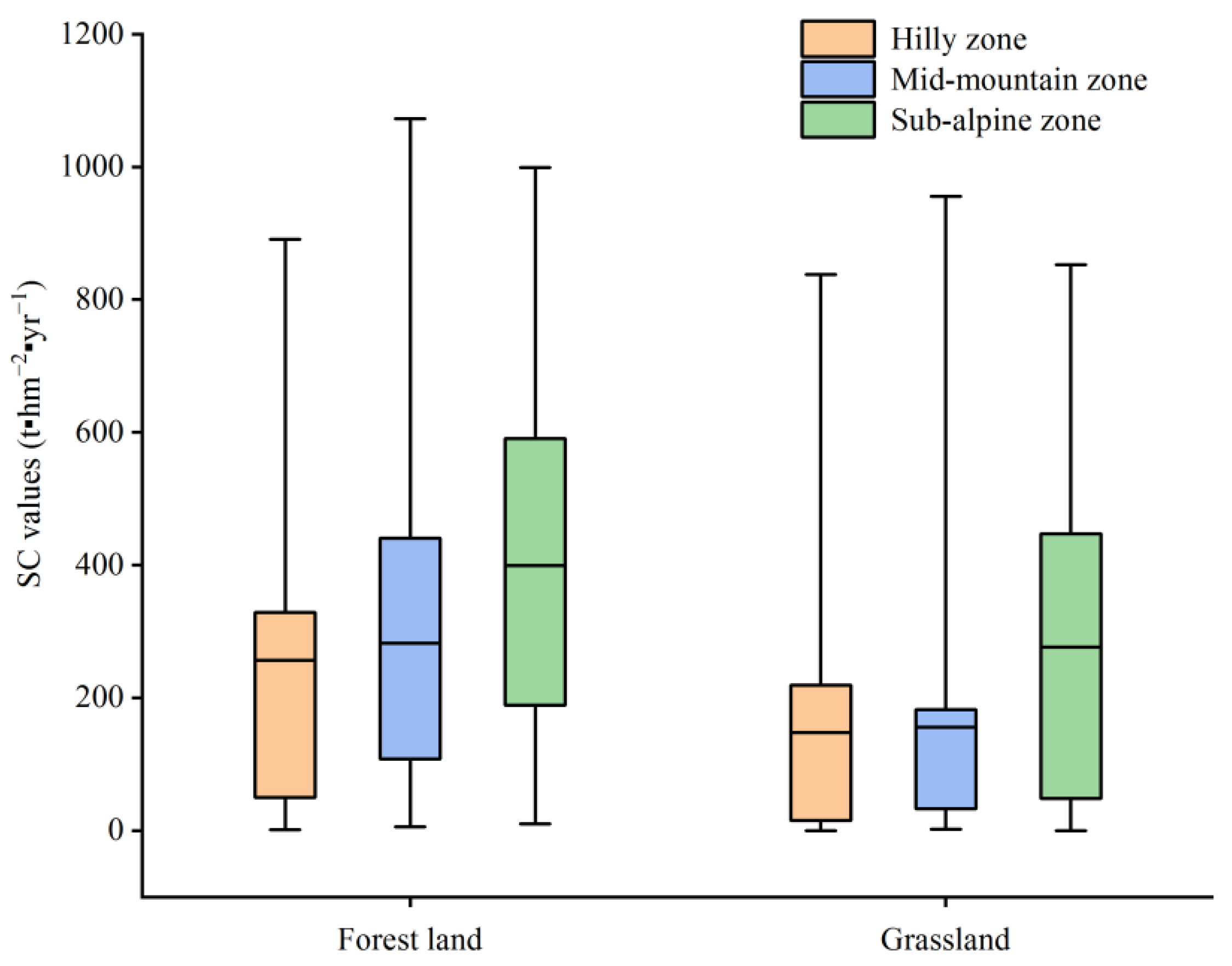
3.4. Quantitative Identification of the Relationships between the Soil Conservation and Variables in the Different Altitude Zones
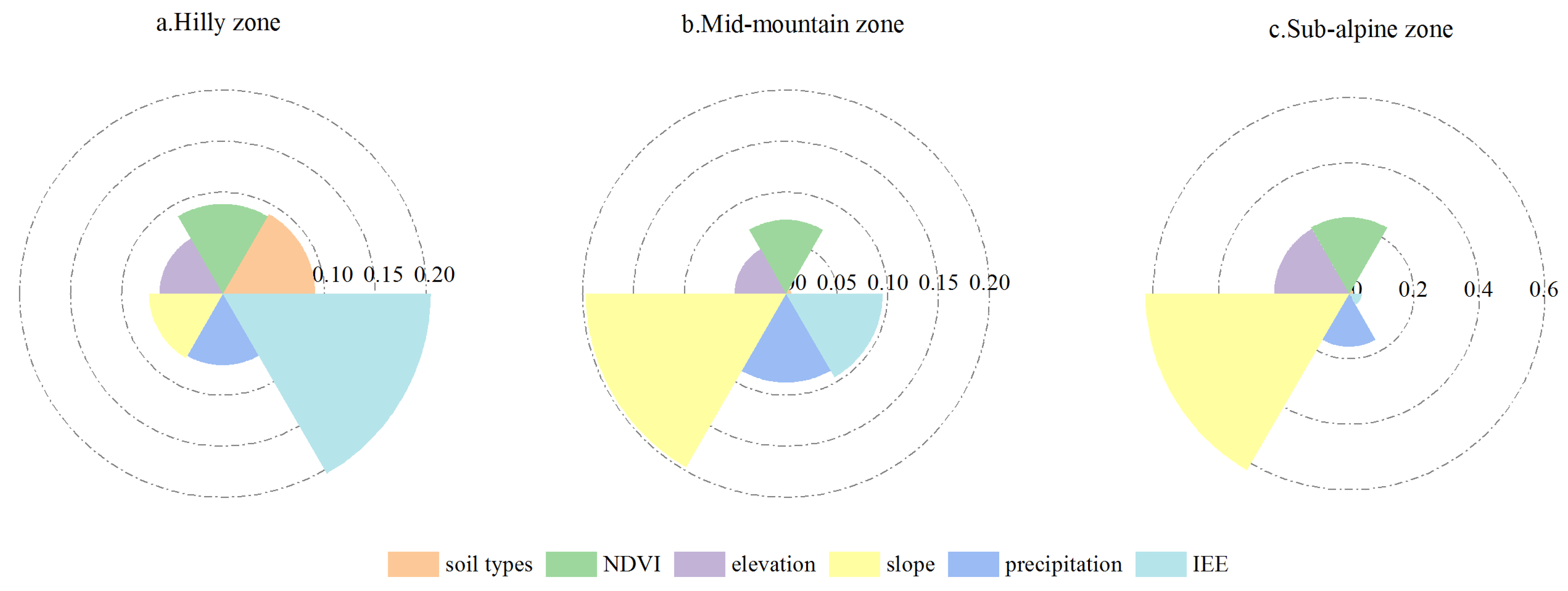
3.4.1. Attribution Analysis of Single Dominant Factors
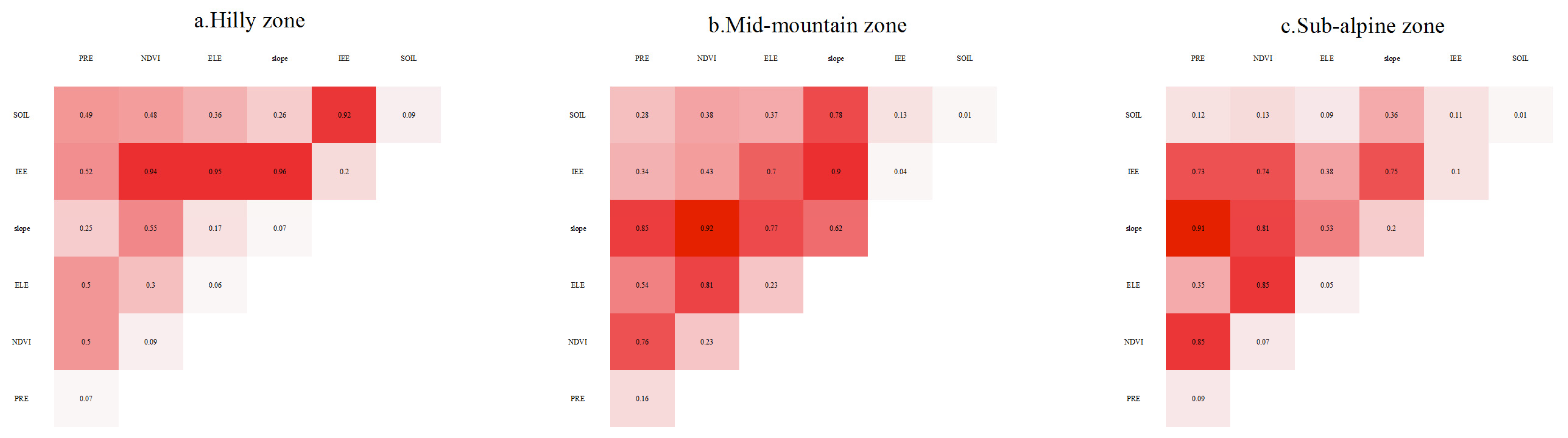
3.4.2. Quantitative Attribution of Interaction Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Ecological Engineering and Its Impact on Land Use Change
4.2. Spatial and Temporal Variations in the Soil Conservation Services in Mountainous Regions
4.3. Influencing Factors of Soil Conservation Services
4.4. Limitations of This Study and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McDonough, S.; Gallardo, W.; Berg, H.; Trai, N.V.; Yen, N.Q. Wetland ecosystem service values and shrimp aquaculture relationships in Can Gio, Vietnam. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 46, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Wang, F.J.; Chen, F.; Malemela, M.P.; Zhang, H.L. Comparison of three tillage systems in the wheat-maize system on carbon sequestration in the North China Plain. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 54, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faverial, J.; Sierra, J. Home composting of household biodegradable wastes under the tropical conditions of Guadeloupe (French Antilles). J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 83, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.; Scholes, R.; Ash, N. (Eds.) Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Current State and Trends: Synthesis; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; pp. 829–838. [Google Scholar]
- Bryan, B.A.; Gao, L.; Ye, Y.; Sun, X.; Connor, J.D.; Crossman, N.D.; Stafford-Smith, M.; Wu, J.; He, C.; Yu, D.; et al. China’s response to a national land-system sustainability emergency. Nature 2018, 559, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, J.; Velicogna, I.; Liang, C.; Li, Z. Ecological restoration impact on total terrestrial water storage. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 4, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsch, W.J. What is ecological engineering? Ecol. Eng. 2012, 45, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H. Spatial and Temporal Changes of Soil Erosion and its Driving Factors before and after the “Grain for Green” Project in the Loess Plateau; Northwest A&F University: Xianyang, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, K.; Liu, H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Yue, Y.; Qi, X. How ecological restoration alters ecosystem services: An analysis of vegetation carbon sequestration in the karst area of northwest Guangxi, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 5307–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Lu, K.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, B. Vegetation restoration projects and their influence on runoff and sediment in China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 95, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, L.; Lu, X.; Xu, J. Effects of Vegetation Restoration on Soil Conservation and Sediment Loads in China: A Critical Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 43, 1384–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Liu, J.; Jiang, G.; Gao, H.; Qi, F.; Wang, F. Influences of pedodiversity on ecosystem services in a mountainous area. Catena 2022, 217, 106505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y. The Evaluation on Ecological Effects of the Project of Returning Farmland to Forest in Liaoning Province, Based on Remote Sensing and In VEST Model; Jilin University: Jilin, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Cao, W.; Xin, X.; Jiang, F.; Jun, W. The Ecological Effects of Ecological Security Barrier Protection and Construction Project in Tibet Plateau. J. Nat. Resour. 2018, 33, 398–411. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, D.; Luo, F.; Bai, J.; Fu, Y. Impact of vegetation restoration on ecosystem services in the Loess plateau, a case study in the Jinghe Watershed, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Jiang, Y.; Anker, Y. Contribution analysis on spatial tradeoff/synergy of Karst soil conservation and water retention for various geomorphological types: Geographical detector application. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhu, J.H.; Li, Q.; Feng, Y.; Li, C.; Xiao, W. Spatial and temporal distribution of soil conservation and its driving forces in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Chin. J. Ecol. 2020, 39, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B.J.; Yu, D.D. Trade-off analyses and synthetic integrated method of multiple ecosystem services. Resour. Sci. 2016, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, F.M.; Lu, Q.; Li, Y.P.; Weng, S.H.; Han, D.C. Effects of Ecological Construction Projects on Primary Ecosystem Services in Horqin Sandy Land. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 41, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.T.; Shi, P.; Li, Z.B.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, S.H. Effect of Grain for Green Project on Ecosystem Service in Dali River Basin. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 25, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Lei, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yu, S.; Wang, L. Research on ecosystem services of water conservation and soil retention: A bibliometric analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 2995–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, T.; Zhao, W.; Pereira, P. Opinionated Views on Grassland Restoration Programs on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 861200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FaFang, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, W.; Sun, J.; Cao, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, L. Identifying the impacts of natural and human factors on ecosystem service in the Yangtze and Yellow River Basins. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 127995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-F.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Z.-H.; López-Vicente, M.; Wu, G.-L. Effectiveness of re-vegetated forest and grassland on soil erosion control in the semi-arid Loess Plateau. CATENA 2020, 11, 104787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Fu, B.; Piao, S.; Wang, S.; Ciais, P.; Zeng, Z.; Lü, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X.; et al. Revegetation in China’s Loess Plateau is approaching sustainable water resource limits. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, Y.; Polasky, S.; Liu, J.; Xu, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Rao, E. Improvements in ecosystem services from investments in natural capital. Science 2016, 352, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokkoris, I.P.; Drakou, E.G.; Maes, J.; Dimopoulos, P. Ecosystem services supply in protected mountains of Greece: Setting the baseline for conservation management. Int. J. Biodivers. Sci. Ecosyst. Serv. Manag. 2018, 14, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Briner, S.; Huber, R.; Bebi, P.; Elkin, C.; Schmatz, D.R.; Grêt-Regamey, A. Trade-Offs between Ecosystem Services in a Mountain Region. Ecol. Soc. 2013, 18, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.T.; Shen, J.S.; Qin, D.H.; Li, S.C. Original Articles Trade-off analyses of multiple mountain ecosystem services along elevation, vegetation cover and precipitation gradients: A case study in the Taihang Mountains. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 103, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, J.J. The Function of Soil Conservation on Taihang Mountain Qihe River Basin Based on InVEST Model. J. Henan Univ. 2018, 48, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Xi, Y.; Li, J. The relationships between environment and plant communities in the middle part of Taihang Mountain Range, North China. Community Ecol. 2006, 7, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, B.; Zhang, C.; Ji, Q.; Feng, L.; Zhao, Q.K. A primary study on scheme of soil and water conservation regionalization in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2013, 03, 307–317. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, E.; Wang, Y.; Ma, L.; Li, S.C.; Zhang, H.Q.; Xin, L.J.; Xu, E.Q.; Gao, J.B.; Zhu, L.Q.; Wang, Y.K. Land use change and its ecological effects in typical mountainous areas in China. Chin. J. Nat. 2018, 40, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, W.; Weiming, C.; Shenglin, Q.; Chenghu, Z.; Wenjie, Z.; Chiming, T. Sensitive evaluation and spatial analysis of soil and water loss based on USLE and GIS: Taking Taihang Mountain area of Hebei Province as an example. Geogr. Res. 2014, 33, 614–624. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Liu, J.T.; Fu, T.G.; Gao, H.; Qi, F. Spatio-temporal variations in soil erosion and its influence factors in Taihang Mountain area based on RUSLE modeling. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2022, 30, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J. Research on Water Movement and High-Efficient Utilization on Slope Characterized by a Soil-Rock Binary Medium in Mountain Area of Taihang Mountain; Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Science: Beijing, China, 2011. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fu, T.; Han, L.; Gao, H.; Liang, H.; Liu, J. Geostatistical analysis of pedodiversity in Taihang Mountain region in North China. Geoderma 2018, 328, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Han, L.; Gao, H.; Liang, H.; Li, X.; Liu, J. Pedodiversity and its controlling factors in mountain regions — A case study of Taihang Mountain, China. Geoderma 2018, 310, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, R.; Tallis, H.; Ricketts, T.; Guerry, A.; Wood, S.; Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Nelson, E.; Ennaanay, D.; Wolny, S.; Olwero, N. InVEST+ VERSION+ User’s Guide. The Natural Capital Project; Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA; University of Minnesota, The Nature Conservancy and World Wildlife Fund: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; McCool, D.; Yoder, D.C. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE). Agricultural Handbook; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Hamel, P.; Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Sim, S.; Mueller, C. A new approach to modeling the sediment retention service (InVEST 3.0): Case study of the Cape Fear catchment, North Carolina, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 524–525, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning. In United States Department of Agriculture Handbook; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1978; No. 537. [Google Scholar]
- Zhizun, M. A method for determining factors of USLE by using satellite photos. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1989, 3, 26–29+65. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.H.; Li, L.T.; McVicar, T.R.; Van Niel, T.G.; Yang, Q.K.; Li, R. Introduction of the Professional Interpolation Software for Meteorology Data: ANUSPLI.N. Meteorol. Mon. 2008, 32, 92–100. [Google Scholar]
- Qiuxia, W. Characteristics of Hydraulic Erosion in Each Soil Layers of Collapsing Wall in Granite Collapse Region; Huazhong Agricultural University: Huazhong, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.; Jones, C.; Dyke, P. A modeling approach to determining the relationship between erosion and productivity. Trans. ASAE 1984, 27, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keli, Z.; Wenying, P.; Hongli, Y. Soil Erodibility and Its Estimation For Agricultural Soil In China. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2007, 44, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, X.; Tang, Q. Human activity intensity of land surface: Concept, methods and application in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 1349–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K. Response of hydrological systems to the intensity of ecological engineering. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 296, 113173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivhare, N.; Dikshit, P.K.S.; Dwivedi, S.B. A comparison of SWAT model calibration techniques for hydrological modeling in the ganga river watershed. Engineering 2018, 4, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Yan, S.; Liang, Z.; Jiao, K.; Li, D.; Wei, F.; Li, S. Strength of association between vegetation greenness and its drivers across China between 1982 and 2015: Regional differences and temporal variations. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 128, 107470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Zuo, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Sun, F.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Y. Impact of land use change on water conservation: A case study of Zhangjiakou in yongding river. Sustainability 2020, 13, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, Y.; Lü, D.; Feng, X.; Fu, B. Multi-scale analyses on the ecosystem services in the Chinese Loess Plateau and implications for dryland sustainability. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2021, 48, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Hai, X.; Shanguan, Z.; Deng, L. Driving factors of ecosystem services and their spatiotemporal change assessment based on land use types in the Loess Plateau. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 311, 114835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.J.; Peng, X.W.; Liu, Y.L.; Liu, J.T. Soil Erosion and Conservation in Taihang Mountain Areas Based on InVEST Model. J. Hebei Norm. Univ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 35, 58–66. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, X.; Deng, X.; Zhang, F. Scale effects of vegetation restoration on soil and water conservation in a semi-arid region in China: Resources conservation and sustainable management. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 151, 104474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Jiang, X.; Lei, Y.; Cai, W.; Zhang, J. Temporal and Spatial Variation and Driving Forces of Soil Erosion on the Loess Plateau before and after the Implementation of the Grain-for-Green Project: A Case Study in the Yanhe River Basin, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L. Research on the Soil and Water Conservation Ecological Effects at Slope and Small Watershed Scales in the Rocky Mountain Areas of Northern China; Beijing Forestry University: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.S. A study on the recovery process of the vegetation and it’s effects on water and soil conservation. Sci. Silvae Sin. 1989, 1, 40–50. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhou, Z.X.; Liu, T.; Bai, J.Z. Vegetation restoration and ecosystem soil conservation service value increment in Yanhe Watershed, Loess Plateau. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 2557–2570. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Fan, J.; Liu, J.; Xu, F.; Zhang, X. Evaluating the Dominant Controls of Water Erosion in Three Dry Valley Types Using the RUSLE and Geodetector Method. Land 2021, 10, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhao, W. Soil conservation efficiency assessment based on land use scenarios in the Nile River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 119, 106864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; He, W.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, Y.; Tan, S.; He, H. Spatial and temporal characteristics of soil conservation service in the area of the upper and middle of the Yellow River, China. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prasannakumar, V.; Shiny, R.; Geetha, N.; Vijith, H. Spatial prediction of soil erosion risk by remote sensing, GIS and RUSLE approach: A case study of Siruvani river watershed in Attapady valley, Kerala, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Jiao, J.Y.; Bai, L.C.; Zhang, Y.F.; Chen, Y.X.; Tang, B.Z.; Liang, Y.; Zhao, C.J.; Wang, H.L. Magnitude of soil erosion in small catchments with different land use patterns under an extreme rainstorm event over the Northern Loess Plateau, China. CATENA 2020, 195, 104780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degife, A.; Worku, H.; Gizaw, S. Environmental implications of soil erosion and sediment yield in Lake Hawassa watershed, south-central Ethiopia. Environ. Syst. Res. 2021, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Yu, D. Water-soil conservation services dynamic and its implication for landscape management in a fragile semiarid landscape. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, G.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z. Processes and driving forces for changing vegetation ecosystem services: Insights from the Shaanxi Province of China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 106105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M. Analysis on the Spatio-Temporal Changes and Driving Factors of the Ecosystem in Jing-Jin-Ji Region; Guilin University of Technology: Guilin, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
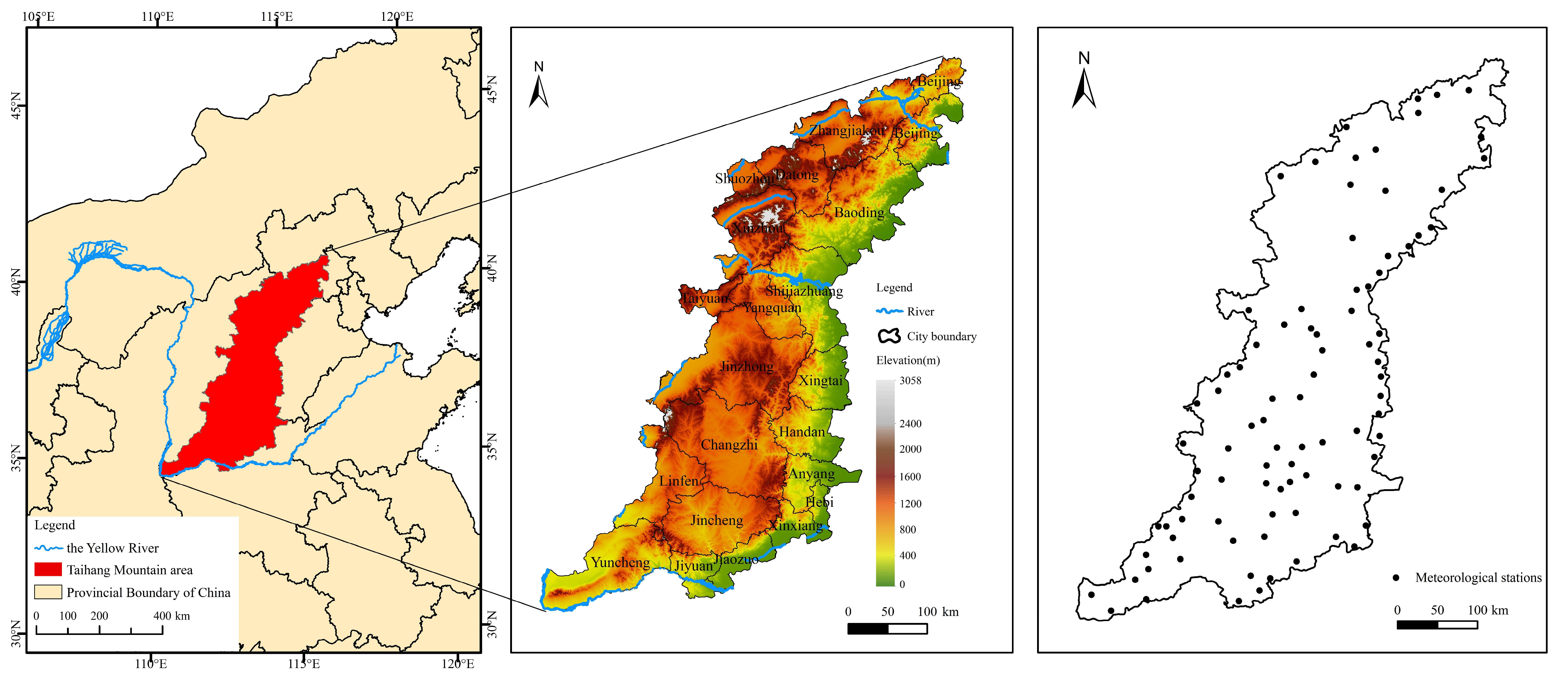
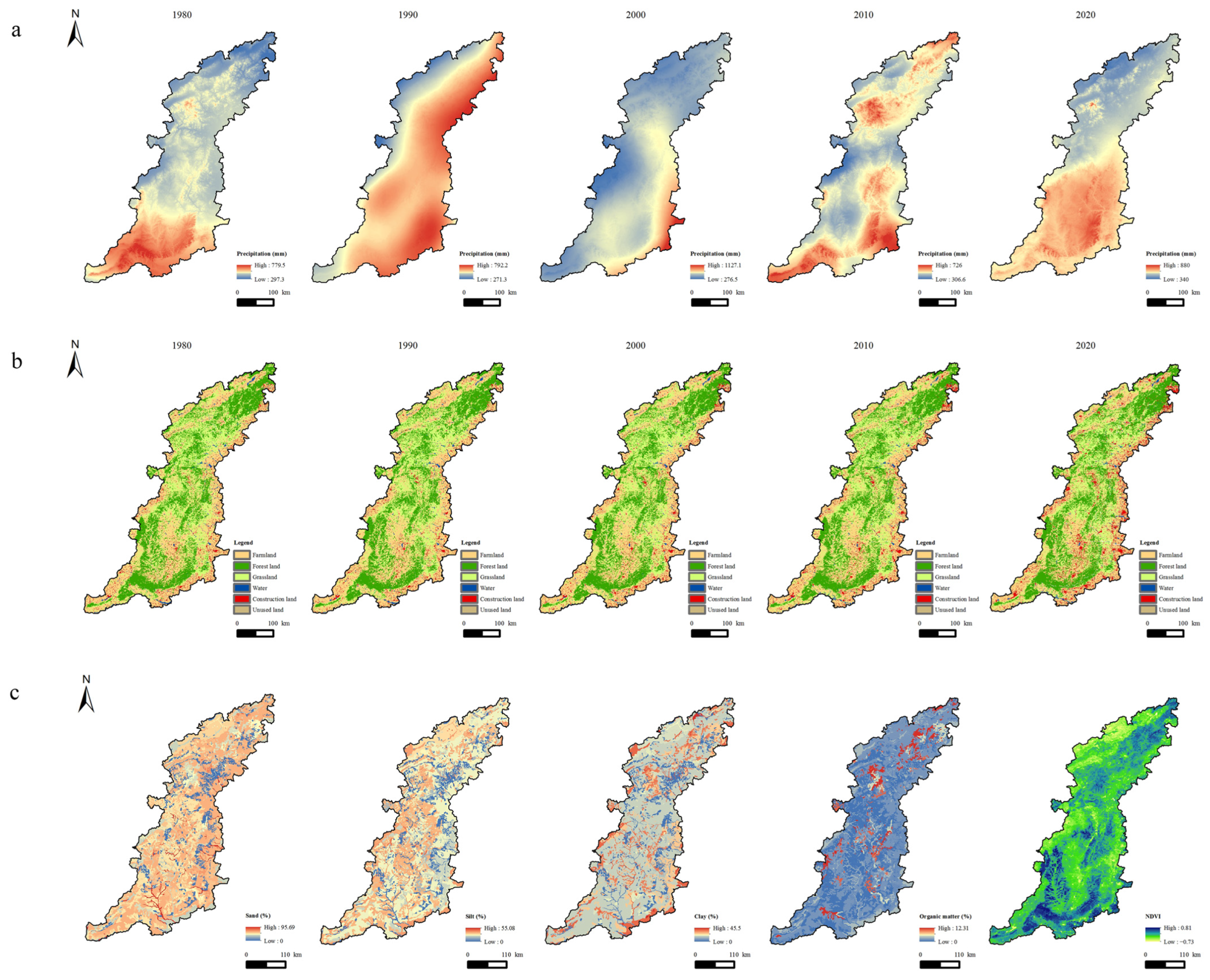
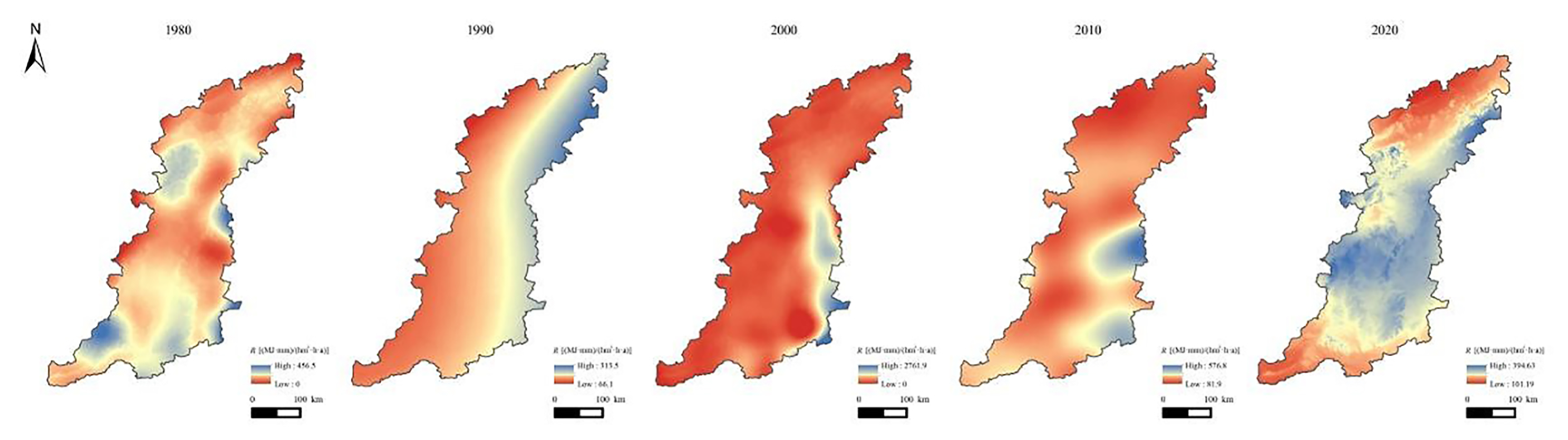
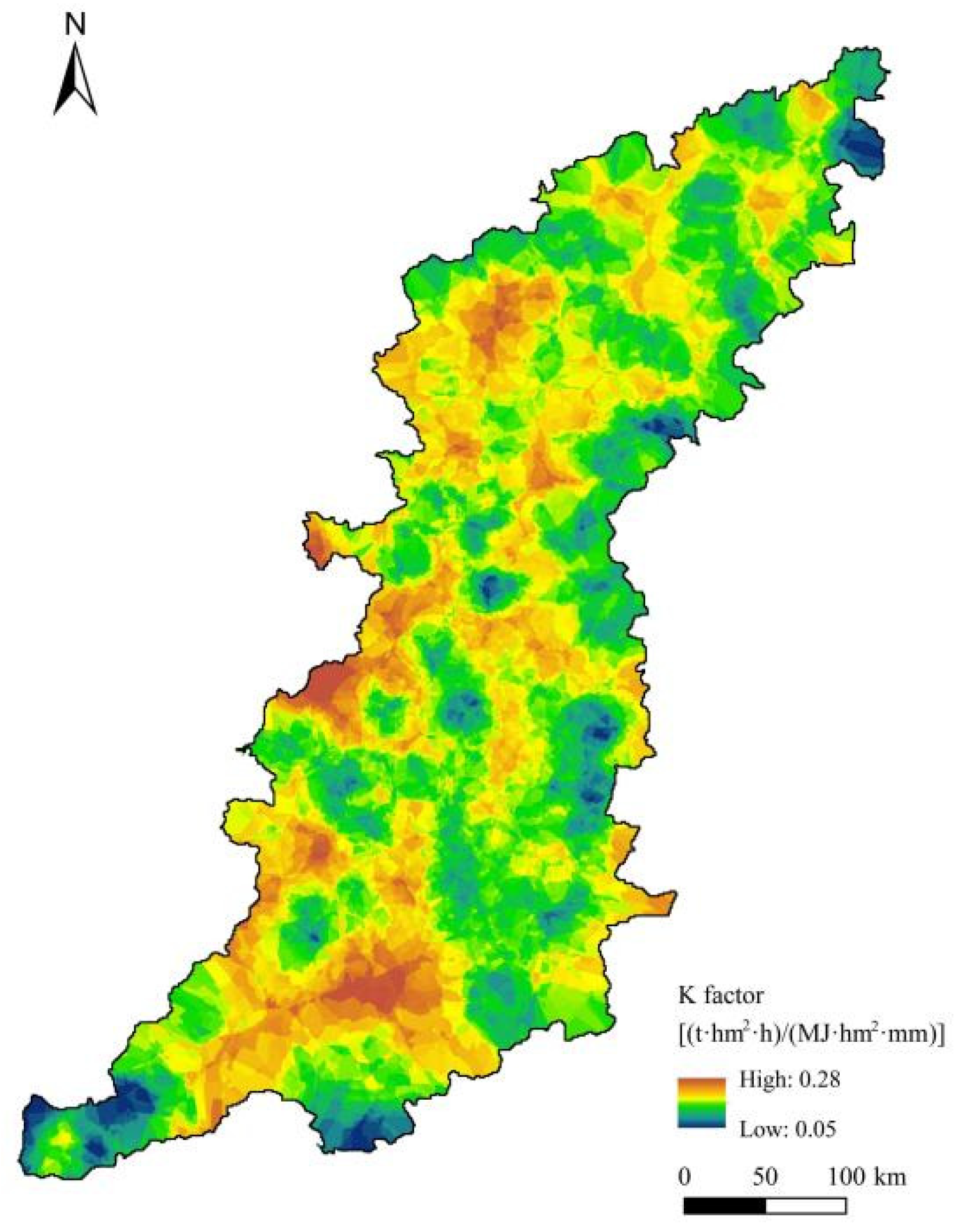

| Data Types | Contents | Resolution or Spatial Distribution | Data Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topographic data | DEM | 30 m | http://www.gscloud.cn/ (accessed on 13 October 2020). |
| Meteorological data | Monthly precipitation data | 88 points | Meteorological administrations in the study area |
| Soil data | Percentage composition of sand, silt, clay, and organic matter | 1:1,000,000 | China’s second national soil survey |
| Vegetation data | Monthly NDVI data for 2020 | 1000 m | https://search.earthdata.nasa.gov (accessed on 9 September 2021). |
| LULC | Farmland, forest land, grassland, construction land, water, unused land | 1000 m | https://www.resdc.cn/ (accessed on 21 May 2021). |
| Types | 1980 (%) | 1990 (%) | 2000 (%) | 2010 (%) | 2020 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cold spots | 12.54 | 7.42 | 31.94 | 10.76 | 0.03 |
| Not significant | 72.71 | 77.70 | 49.57 | 72.56 | 86.20 |
| Hot spots | 14.75 | 14.88 | 18.49 | 16.68 | 13.77 |
| Altitude Interval | Forest Land (%) | Grassland (%) | Average SC (t hm−2 yr−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hilly zone | 9.13 | 20.41 | 149.71 |
| Mid-mountain zone | 33.54 | 27.48 | 359.56 |
| Sub-alpine zone | 57.59 | 34.19 | 456.96 |
| Land Use Types | Categories | Hilly Zone | Mid-Mountain Zone | Sub-Alpine Zone |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farmland | Variation (km2) | −2918 | −1810 | 6 |
| Rate (%) | −13.96 | −5.84 | 0.73 | |
| Forest land | Variation (km2) | 291 | −31 | −135 |
| Rate (%) | 9.85 | −0.1 | −1.92 | |
| Grassland | Variation (km2) | −368 | −1006 | −50 |
| Rate (%) | −4.83 | −3.97 | −1.2 | |
| Water | Variation (km2) | −87 | −61 | 5 |
| Rate (%) | −6.97 | −7.88 | 40.7 | |
| Construction land | Variation (km2) | 2897 | 2657 | 114 |
| Rate (%) | 100.1 | 140.76 | 765.35 | |
| Unused land | Variation (km2) | 44 | −69 | −2 |
| Rate (%) | 81.07 | −54.63 | −27.72 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, F.; Liu, J.; Fu, T.; Gao, H.; Qi, F. Spatial-Temporal Variations in of Soil Conservation Service and Its Influencing Factors under the Background of Ecological Engineering in the Taihang Mountain Area, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043427
Wang F, Liu J, Fu T, Gao H, Qi F. Spatial-Temporal Variations in of Soil Conservation Service and Its Influencing Factors under the Background of Ecological Engineering in the Taihang Mountain Area, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(4):3427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043427
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Feng, Jintong Liu, Tonggang Fu, Hui Gao, and Fei Qi. 2023. "Spatial-Temporal Variations in of Soil Conservation Service and Its Influencing Factors under the Background of Ecological Engineering in the Taihang Mountain Area, China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 4: 3427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043427
APA StyleWang, F., Liu, J., Fu, T., Gao, H., & Qi, F. (2023). Spatial-Temporal Variations in of Soil Conservation Service and Its Influencing Factors under the Background of Ecological Engineering in the Taihang Mountain Area, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(4), 3427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043427






