Association between Serum Uric Acid Levels and Bone Mineral Density in Taiwanese Elderly Population
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
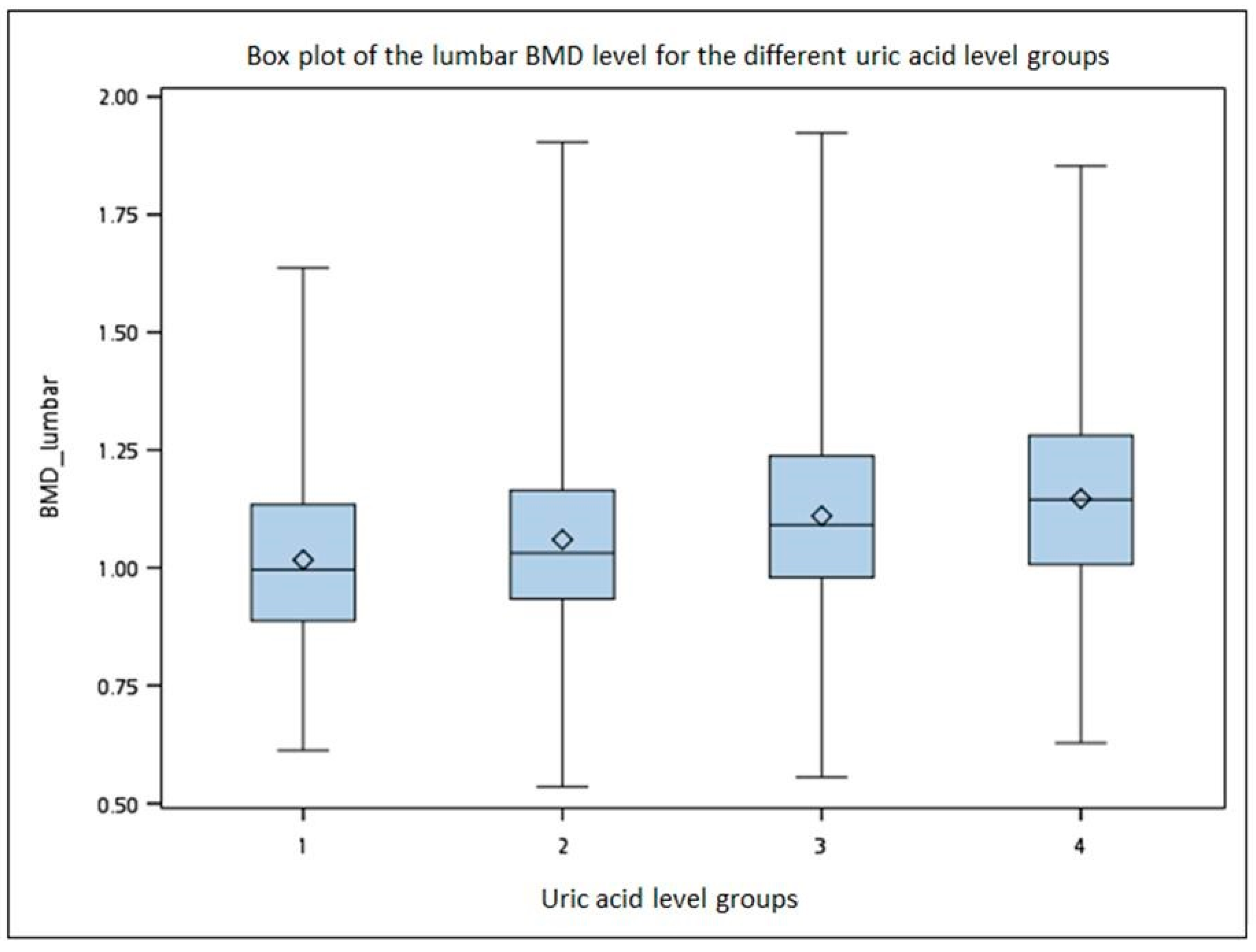
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sözen, T.; Özışık, L.; Başaran, N.Ç. An overview and management of osteoporosis. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 4, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.; Yang, F.; Yang, I.; Yin, Y.; Luo, J.J.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.F. Uric acid, hyperuricemia and vascular diseases. Front. Biosci. Landmark Ed. 2012, 17, 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Bobulescu, I.A.; Maalouf, N.M.; Adams-Huet, B.; Poindexter, J.; Park, S.; Wei, F.; Chen, C.; Moe, O.W.; Sakhaee, K. Relationship between serum uric acid and bone mineral density in the general population and in rats with experimental hyperuricemia. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2015, 30, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Kwon, D.; Lee, J.; Chung, Y.J.; Kim, M.R.; Namkung, J.; Jeung, I.C. Association between serum uric acid levels and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women: A cross-sectional and longitudinal study. Healthcare 2021, 9, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Kwon, B.C.; Choi, H.G. Analyses of the relationship between hyperuricemia and osteoporosis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Lee, J.I.; Lu, C.C.; Su, Y.D.; Chiu, C.T.; Chen, S.C.; Geng, J.H.; Chen, C.H. Hyperuricemia and its association with osteoporosis in a large Asian cohort. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; Chen, L.; Xu, H.; Zhu, Z. The association between serum uric acid and bone mineral density in older adults. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 2020, 3082318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makovey, J.; Macara, M.; Chen, J.S.; Hayward, C.S.; March, L.; Seibel, M.J.; Sambrook, P.N. Serum uric acid plays a protective role for bone loss in peri- and postmenopausal women: A longitudinal study. Bone 2013, 52, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.M.; Lu, C.L.; Hung, K.C.; Wu, P.C.; Pan, C.F.; Wu, C.J.; Syu, R.S.; Chen, J.S.; Hsiao, P.J.; Lu, K.C. The paradoxical role of uric acid in osteoporosis. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalbeth, N.; Horne, A.; Mihov, B.; Stewart, A.; Gamble, G.D.; Merriman, T.R.; Stamp, L.K.; Reid, I.R. Elevated urate levels do not alter bone turnover markers: Randomized controlled trial of inosine supplementation in postmenopausal women. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 1758–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lin, Z.; Zhao, C.; Xu, S.; Lin, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Chu, Y. Prevalence and risk factors for bone loss in rheumatoid arthritis patients from South China: Modeled by three methods. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FitzGerald, J.D.; Dalbeth, N.; Mikuls, T.; Brignardello-Petersen, R.; Guyatt, G.; Abeles, A.M.; Gelber, A.C.; Harrold, L.R.; Khanna, D.; King, C.; et al. American College of Rheumatology guideline for the management of gout. Arthritis Care Res. 2020, 72, 744–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glantzounis, G.K.; Tsimoyiannis, E.C.; Kappas, A.M.; Galaris, D.A. Uric acid and oxidative stress. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005, 11, 4145–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ames, B.N.; Cathcart, R.; Schwiers, E.; Hochstein, P. Uric acid provides an antioxidant defense in humans against oxidant- and radical-caused aging and cancer: A hypothesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 6858–6862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, N.E.; Parimi, N.; Lui, L.Y.; Wise, B.L.; Yao, W.; Lay, Y.A.; Cawthon, P.M.; Orwoll, E. Osteoporotic Fractures in Men Study Group Association of serum uric acid and incident nonspine fractures in elderly men: The Osteoporotic Fractures in Men (MrOS) study. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2014, 29, 1701–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Ramos, M.; Vargas, L.A.; Fortoul Van der Goes, T.I.; Cervantes-Sandoval, A.; Mendoza-Nunez, V.M. Supplementation of ascorbic acid and alpha-tocopherol is useful to preventing bone loss linked to oxidative stress in elderly. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2010, 14, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, T.; Bůžková, P.; Sarnak, M.J.; Chonchol, M.; Cauley, J.A.; Wallace, E.; Fink, H.A.; Robbins, J.; Jalal, D. Serum urate levels and the risk of hip fractures: Data from the cardiovascular Health Study. Metabolism 2015, 64, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paik, J.M.; Kim, S.C.; Feskanich, D.; Choi, H.K.; Solomon, D.H.; Curhan, G.C. Gout and risk of fracture in women: A prospective cohort study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | All Participants | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | p | |
| Uric Acid (mg/dL) | <4.7 | 4.7–5.6 | 5.7–6.5 | ≥6.6 | |
| Age (years, %) | |||||
| 60–69 | 401 (77.7) | 465 (77.6) | 435 (77.7) | 425 (73.9) | <0.05 |
| 70–79 | 107 (20.7) | 127 (21.2) | 106 (18.9) | 127 (22.1) | <0.05 |
| ≥80 | 8 (1.6) | 7 (1.2) | 19 (3.4) | 23 (4) | <0.05 |
| Sex (n, %) | |||||
| Men | 138 (26.7) | 266 (44.4) | 339 (60.5) | 420 (73.0) | <0.001 |
| Women | 378 (73.3) | 333 (55.6) | 221 (39.5) | 155 (27.0) | <0.001 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2, %) | |||||
| <24 | 353 (68.4) | 343 (57.3) | 249 (44.5) | 211 (36.8) | <0.001 |
| 24–26.9 | 115 (22.3) | 166 (27.7) | 200 (35.7) | 211 (36.8) | <0.001 |
| ≥27 | 48 (9.3) | 90 (15) | 111 (19.8) | 152 (26.5) | <0.001 |
| Comorbidities (n, %) | |||||
| Hypertension | 145 (28.2) | 210 (35.3) | 195 (34.8) | 219 (38.2) | <0.05 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 81 (24.5) | 92 (24.5) | 105 (29.7) | 105 (28.5) | 0.26 |
| Hyperlipidaemia | 317 (61.7) | 416 (70) | 372 (66.7) | 427 (75) | <0.001 |
| Thyroid disease | 74 (14.5) | 72 (12.1) | 57 (10.3) | 79 (13.9) | 0.14 |
| Chronic Kidney disease | 11 (2.1) | 24 (4) | 31 (5.5) | 102 (17.7) | <0.001 |
| Bone Mineral Density (gm/cm2, SD) | |||||
| Lumbar | 1.02 (0.18) | 1.06 (0.2) | 1.11 (0.2) | 1.15 (0.2) | |
| Left hip | 0.79 (0.13) | 0.81 (0.13) | 0.83 (0.14) | 0.86 (0.16) | |
| T score (SD) | |||||
| Lumbar | −0.78 (1.47) | −0.45 (1.58) | −0.12 (1.61) | 0.2 (1.63) | |
| Left hip | −1.18 (0.9) | −1.04 (0.99) | −1 (1.04) | −0.75 (1.16) | |
| Osteoporosis (n, %) | 74 (14.5) | 72 (12.1) | 57 (10.3) | 79 (13.9) | 0.15 |
| Osteopenia (n, %) | 310 (71.1) | 323 (64.3) | 273 (58.3) | 232 (42.2) | <0.001 |
| Serum Uric Acid Categories (mg/dL) | Q1 <4.7 | Q2 4.7–5.6 | Q3 5.7–6.5 | Q4 ≥6.6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude OR (95% CI), p value | 1 | 0.73 (0.56–0.97), <0.05 | 0.57 (0.43–0.75), <0.001 | 0.38 (0.29–0.50), <0.001 |
| Model 1 OR (95% CI), p value | 1 | 0.84 (0.63–1.12), 0.23 | 0.76 (0.57–1.02), 0.06 | 0.54 (0.41–0.73), <0.001 |
| Model 2 OR (95% CI), p value | 1 | 0.91 (0.68–1.22), 0.54 | 0.89 (0.66–1.20), 0.44 | 0.68 (0.50–0.92), <0.05 |
| β | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Serum uric acid (mg/dL) | ||
| Lumbar BMD (g/cm2) | 0.011 | <0.05 |
| Hip BMD (g/cm2) | 0.005 | <0.05 |
| Serum Uric Acid Categories (mg/dL) | <6.6 | 6.6–7.5 | 7.6–8.5 | ≥8.6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude odds ratios (95% CI) p value | 1 | 0.55 (0.43–0.70) <0.001 | 0.46 (0.30–0.69) <0.001 | 0.44 (0.26–0.74) <0.001 |
| Model 1 odds ratios (95% CI) p value | 1 | 0.69 (0.54–0.89), <0.05 | 0.55 (0.36–0.84), <0.05 | 0.56 (0.32–0.96), <0.05 |
| Model 2 odds ratios (95% CI) p value | 1 | 0.78 (0.60–1.01), 0.06 | 0.62 (0.40–0.97), <0.05 | 0.67 (0.38–1.17), 0.16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chung, P.-T.; Ma, H.-C.; Huang, S.-Y.; Lien, H.-N.; Ho, K.-H.; Hsu, H.-Y.; Hwang, L.-C.; Tsou, M.-T.; Lin, H.-H.; Chan, H.-L. Association between Serum Uric Acid Levels and Bone Mineral Density in Taiwanese Elderly Population. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043448
Chung P-T, Ma H-C, Huang S-Y, Lien H-N, Ho K-H, Hsu H-Y, Hwang L-C, Tsou M-T, Lin H-H, Chan H-L. Association between Serum Uric Acid Levels and Bone Mineral Density in Taiwanese Elderly Population. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(4):3448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043448
Chicago/Turabian StyleChung, Pei-Ting, Hsiao-Chi Ma, Sin-Yi Huang, Hsin-Ning Lien, Kuan-Hsun Ho, Hsin-Yin Hsu, Lee-Ching Hwang, Meng-Ting Tsou, Hsin-Hui Lin, and Hsin-Lung Chan. 2023. "Association between Serum Uric Acid Levels and Bone Mineral Density in Taiwanese Elderly Population" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 4: 3448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043448
APA StyleChung, P.-T., Ma, H.-C., Huang, S.-Y., Lien, H.-N., Ho, K.-H., Hsu, H.-Y., Hwang, L.-C., Tsou, M.-T., Lin, H.-H., & Chan, H.-L. (2023). Association between Serum Uric Acid Levels and Bone Mineral Density in Taiwanese Elderly Population. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(4), 3448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043448





