Identification and Genetic Characterization of MERS-Related Coronavirus Isolated from Nathusius’ Pipistrelle (Pipistrellus nathusii) near Zvenigorod (Moscow Region, Russia)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription
2.3. PCR and NGS Screening of Faecal Samples for CoV RNA
2.4. Library Preparation and High-Throughput Viral Genome Sequencing
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.6. Structural Modeling and Molecular Docking
3. Results
3.1. General Description
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
3.3. Docking
4. Discussion
4.1. Abundance of Coronaviruses in Central European Russia
4.2. Taxonomic Position of the MOW-BatCoV: Whether It Is a New Species
4.3. Distribution of MERS-Related Viruses around Europe
4.4. Hedgehogs as Potential Intermediate Hosts between Bats and Other Animals
4.5. MOW-BatCoV/15-22 Possibility to Infect Other Mammalian Species
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Team. Weekly Epidemiological Update on COVID-19—11 May 2022; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Temmam, S.; Vongphayloth, K.; Baquero, E.; Munier, S.; Bonomi, M.; Regnault, B.; Douangboubpha, B.; Karami, Y.; Chrétien, D.; Sanamxay, D.; et al. Bat Coronaviruses Related to SARS-CoV-2 and Infectious for Human Cells. Nature 2022, 604, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaune, D.; Hul, V.; Karlsson, E.A.; Hassanin, A.; Ou, T.P.; Baidaliuk, A.; Gámbaro, F.; Prot, M.; Tu, V.T.; Chea, S.; et al. A Novel SARS-CoV-2 Related Coronavirus in Bats from Cambodia. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Ji, J.; Chen, X.; Bi, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Hu, T.; Song, H.; Zhao, R.; Chen, Y.; et al. Identification of Novel Bat Coronaviruses Sheds Light on the Evolutionary Origins of SARS-CoV-2 and Related Viruses. Cell 2021, 184, 4380–4391.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wacharapluesadee, S.; Tan, C.W.; Maneeorn, P.; Duengkae, P.; Zhu, F.; Joyjinda, Y.; Kaewpom, T.; Chia, W.N.; Ampoot, W.; Lim, B.L.; et al. Evidence for SARS-CoV-2 Related Coronaviruses Circulating in Bats and Pangolins in Southeast Asia. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, S.; Kitamura, T.; Suzuki, J.; Sato, R.; Aoi, T.; Fujii, M.; Matsugo, H.; Kamiki, H.; Ishida, H.; Takenaka-Uema, A.; et al. Detection and Characterization of Bat Sarbecovirus Phylogenetically Related to SARS-CoV-2, Japan. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 3025–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindell, B.G.; Allardice, M.; McBride, J.A.M.; Dennehy, B.; Kindrachuk, J. SARS-CoV-2 and the Missing Link of Intermediate Hosts in Viral Emergence—What We Can Learn From Other Betacoronaviruses. Front. Virol. 2022, 2, 875213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, V.C.C.; Lau, S.K.P.; Woo, P.C.Y.; Yuen, K.Y. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus as an Agent of Emerging and Reemerging Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 660–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lam, W.; Zhong, N.; Tan, W. Overview on SARS in Asia and the World. Respirology 2003, 8, S2–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, D.S.C.; Zumla, A. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 33, 869–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Wit, E.; van Doremalen, N.; Falzarano, D.; Munster, V.J. SARS and MERS: Recent Insights into Emerging Coronaviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, A.M.; van Boheemen, S.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E.; Fouchier, R.A.M. Isolation of a Novel Coronavirus from a Man with Pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1814–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dighe, A.; Jombart, T.; van Kerkhove, M.D.; Ferguson, N. A Systematic Review of MERS-CoV Seroprevalence and RNA Prevalence in Dromedary Camels: Implications for Animal Vaccination. Epidemics 2019, 29, 100350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Team. WHO MERS-CoV Global Summary and Assessment of Risk (WHO/MERS/RA/August18). Available online: www.who.int/publications/i/item/who-mers-cov-global-summary-and-risk-assessment---august-2018 (accessed on 17 May 2022).
- Ramadan, N.; Shaib, H. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV): A Review. Germs 2019, 9, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljasim, T.A.; Almasoud, A.; Aljami, H.A.; Alenazi, M.W.; Alsagaby, S.A.; Alsaleh, A.N.; Alharbi, N.K. High Rate of Circulating MERS-CoV in Dromedary Camels at Slaughterhouses in Riyadh, 2019. Viruses 2020, 12, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, I.; Wang, L.-F. Bats and Their Virome: An Important Source of Emerging Viruses Capable of Infecting Humans. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2013, 3, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z. Emerging Infectious Diseases Associated with Bat Viruses. Sci. China Life Sci. 2013, 56, 678–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, B.; Ge, X.; Wang, L.-F.; Shi, Z. Bat Origin of Human Coronaviruses. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Woo, P.C.Y.; Lau, S.K.P.; Lam, C.S.F.; Lau, C.C.Y.; Tsang, A.K.L.; Lau, J.H.N.; Bai, R.; Teng, J.L.L.; Tsang, C.C.C.; Wang, M.; et al. Discovery of Seven Novel Mammalian and Avian Coronaviruses in the Genus Deltacoronavirus Supports Bat Coronaviruses as the Gene Source of Alphacoronavirus and Betacoronavirus and Avian Coronaviruses as the Gene Source of Gammacoronavirus and Deltacoronavirus. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3995–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calisher, C.H.; Childs, J.E.; Field, H.E.; Holmes, K.V.; Schountz, T. Bats: Important Reservoir Hosts of Emerging Viruses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Groot, R.J.; Cowley, J.A.; Enjuanes, L.; Faaberg, K.S.; Perlman, S.; Rottier, P.J.M.; Snijder, E.J.; Ziebuhr, J.; Gorbalenya, A.E. Virus Taxonomy Classification and Nomenclature of Viruses, 1st ed.; King, A.M.Q., Adams, M.J., Carstens, E.B., Lefkowitz, E.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lelli, D.; Papetti, A.; Sabelli, C.; Rosti, E.; Moreno, A.; Boniotti, M. Detection of Coronaviruses in Bats of Various Species in Italy. Viruses 2013, 5, 2679–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, A.; Li, X.; Lau, S.; Woo, P. Global Epidemiology of Bat Coronaviruses. Viruses 2019, 11, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lau, S.K.P.; Luk, H.K.H.; Wong, A.C.P.; Fan, R.Y.Y.; Lam, C.S.F.; Li, K.S.M.; Ahmed, S.S.; Chow, F.W.N.; Cai, J.-P.; Zhu, X.; et al. Identification of a Novel Betacoronavirus (Merbecovirus) in Amur Hedgehogs from China. Viruses 2019, 11, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moreno, A.; Lelli, D.; de Sabato, L.; Zaccaria, G.; Boni, A.; Sozzi, E.; Prosperi, A.; Lavazza, A.; Cella, E.; Castrucci, M.R.; et al. Detection and Full Genome Characterization of Two Beta CoV Viruses Related to Middle East Respiratory Syndrome from Bats in Italy. Virol. J. 2017, 14, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, P.C.Y.; Lau, S.K.P.; Li, K.S.M.; Poon, R.W.S.; Wong, B.H.L.; Tsoi, H.; Yip, B.C.K.; Huang, Y.; Chan, K.; Yuen, K. Molecular Diversity of Coronaviruses in Bats. Virology 2006, 351, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Li, K.S.; Tsang, A.K.; Yuen, K.-Y. Genetic Relatedness of the Novel Human Group C Betacoronavirus to Tylonycteris Bat Coronavirus HKU4 and Pipistrellus Bat Coronavirus HKU5. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2012, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lau, S.K.P.; Li, K.S.M.; Tsang, A.K.L.; Lam, C.S.F.; Ahmed, S.; Chen, H.; Chan, K.-H.; Woo, P.C.Y.; Yuen, K.-Y. Genetic Characterization of Betacoronavirus Lineage C Viruses in Bats Reveals Marked Sequence Divergence in the Spike Protein of Pipistrellus Bat Coronavirus HKU5 in Japanese Pipistrelle: Implications for the Origin of the Novel Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 8638–8650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alkhovsky, S.; Lenshin, S.; Romashin, A.; Vishnevskaya, T.; Vyshemirsky, O.; Bulycheva, Y.; Lvov, D.; Gitelman, A. SARS-like Coronaviruses in Horseshoe Bats (Rhinolophus Spp.) in Russia, 2020. Viruses 2022, 14, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dedkov, V.G.; Lukashev, A.N.; Deviatkin, A.A.; Kuleshov, K.V.; Safonova, M.V.; Poleshchuk, E.M.; Drexler, J.F.; Shipulin, G.A. Retrospective Diagnosis of Two Rabies Cases in Humans by High Throughput Sequencing. J. Clin. Virol. 2016, 78, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prjibelski, A.; Antipov, D.; Meleshko, D.; Lapidus, A.; Korobeynikov, A. Using SPAdes De Novo Assembler. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2020, 70, e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast Gapped-Read Alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast Model Selection for Accurate Phylogenetic Estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A Fast and Effective Stochastic Algorithm for Estimating Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh, B.Q.; Nguyen, M.A.T.; von Haeseler, A. Ultrafast Approximation for Phylogenetic Bootstrap. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (ITOL) v5: An Online Tool for Phylogenetic Tree Display and Annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwede, T.; Kopp, J.; Guex, N.; Peitsch, M.C. SWISS-MODEL: An Automated Protein Homology-Modeling Server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3381–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, P.; Li, B.; Huang, S.Y. HDOCK: A Web Server for Protein-Protein and Protein-DNA/RNA Docking Based on a Hybrid Strategy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W365–W373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 2.0; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2015.
- Gloza-Rausch, F.; Ipsen, A.; Seebens, A.; Göttsche, M.; Panning, M.; Drexler, J.F.; Petersen, N.; Annan, A.; Grywna, K.; Müller, M.; et al. Detection and Prevalence Patterns of Group I Coronaviruses in Bats, Northern Germany. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annan, A.; Baldwin, H.J.; Corman, V.M.; Klose, S.M.; Owusu, M.; Nkrumah, E.E.; Badu, E.K.; Anti, P.; Agbenyega, O.; Meyer, B.; et al. Human Betacoronavirus 2c EMC/2012-Related Viruses in Bats, Ghana and Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eurobats.Org. Available online: https://www.Eurobats.Org/About_eurobats/Protected_bat_species/Pipistrellus_nathusii (accessed on 22 May 2022).
- Eol.Org. Available online: https://Eol.Org/Pages/289882 (accessed on 31 May 2022).
- Van Boheemen, S.; de Graaf, M.; Lauber, C.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Raj, V.S.; Zaki, A.M.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E.; Haagmans, B.L.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Snijder, E.J.; et al. Genomic Characterization of a Newly Discovered Coronavirus Associated with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Humans. mBio 2012, 3, e00473-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruiz-Aravena, M.; McKee, C.; Gamble, A.; Lunn, T.; Morris, A.; Snedden, C.E.; Yinda, C.K.; Port, J.R.; Buchholz, D.W.; Yeo, Y.Y.; et al. Ecology, Evolution and Spillover of Coronaviruses from Bats. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronaviridae, ICTV 9th Report (2011)—Virus Taxonomy: 2021 Release, EC 53. 2022. Available online: https://ictv.global/report_9th (accessed on 31 May 2022).
- Geldenhuys, M.; Mortlock, M.; Weyer, J.; Bezuidt, O.; Seamark, E.C.J.; Kearney, T.; Gleasner, C.; Erkkila, T.H.; Cui, H.; Markotter, W. A Metagenomic Viral Discovery Approach Identifies Potential Zoonotic and Novel Mammalian Viruses in Neoromicia Bats within South Africa. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersons, G. Seasonal Migrations of North-Eastern Populations of Nathusius’ Bat Pipistrellus Nathusii (Chiroptera). Myotis 2004, 41–42, 29–56. [Google Scholar]
- Alcalde, J.T.; Jiménez, M.; Brila, I.; Vintulis, V.; Voigt, C.C.; Pētersons, G. Transcontinental 2200 Km Migration of a Nathusius’ Pipistrelle (Pipistrellus Nathusii) across Europe. Mammalia 2021, 85, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasenkov, D.; Desmet, J.F.; Popov, I.; Sidorchuk, N. Bats Can Migrate Farther than It Was Previously Known: A New Longest Migration Record by Nathusius’ Pipistrelle Pipistrellus Nathusii (Chiroptera: Vespertilionidae). Mammalia 2022, 86, 524–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corman, V.M.; Kallies, R.; Philipps, H.; Göpner, G.; Müller, M.A.; Eckerle, I.; Brünink, S.; Drosten, C.; Drexler, J.F. Characterization of a Novel Betacoronavirus Related to Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus in European Hedgehogs. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monchatre-Leroy, E.; Boué, F.; Boucher, J.M.; Renault, C.; Moutou, F.; Gouilh, M.A.; Umhang, G. Identification of Alpha and Beta Coronavirus in Wildlife Species in France: Bats, Rodents, Rabbits, and Hedgehogs. Viruses 2017, 9, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pomorska-Mól, M.; Ruszkowski, J.J.; Gogulski, M.; Domanska-Blicharz, K. First Detection of Hedgehog Coronavirus 1 in Poland. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, S.J.; Gilardi, K.; Menachery, V.D.; Goldstein, T.; Ssebide, B.; Mbabazi, R.; Navarrete-Macias, I.; Liang, E.; Wells, H.; Hicks, A.; et al. Further Evidence for Bats as the Evolutionary Source of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus. mBio 2017, 8, e00373-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corman, V.M.; Ithete, N.L.; Richards, L.R.; Schoeman, M.C.; Preiser, W.; Drosten, C.; Drexler, J.F. Rooting the Phylogenetic Tree of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus by Characterization of a Conspecific Virus from an African Bat. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 11297–11303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Qi, J.; Yuan, Y.; Xuan, Y.; Han, P.; Wan, Y.; Ji, W.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Bat Origins of MERS-CoV Supported by Bat Coronavirus HKU4 Usage of Human Receptor CD26. Cell Host. Microbe 2014, 16, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, N.; Shi, X.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, D.; Tong, P.; Guo, D.; Fu, L.; Cui, Y.; Liu, X.; et al. Structure of MERS-CoV Spike Receptor-Binding Domain Complexed with Human Receptor DPP4. Cell Res. 2013, 23, 986–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Letko, M.; Miazgowicz, K.; McMinn, R.; Seifert, S.N.; Sola, I.; Enjuanes, L.; Carmody, A.; van Doremalen, N.; Munster, V. Adaptive Evolution of MERS-CoV to Species Variation in DPP4. Cell Rep. 2018, 24, 1730–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lau, S.K.P.; Zhang, L.; Luk, H.K.H.; Xiong, L.; Peng, X.; Li, K.S.M.; He, X.; Zhao, P.S.H.; Fan, R.Y.Y.; Wong, A.C.P.; et al. Receptor Usage of a Novel Bat Lineage C Betacoronavirus Reveals Evolution of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome-Related Coronavirus Spike Proteins for Human Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Binding. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, H.; Wang, X.; Xiong, Q.; Cao, L.; Ma, C.; Liu, C.; Si, J.; Liu, P.; Gu, M.; Wang, C.; et al. Close Relatives of MERS-CoV in Bats Use ACE2 as Their Functional Receptors. Nature 2022, 612, 748–757. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, C.; Du, L.; Jiang, S.; Shi, Z.; Baric, R.S.; Li, F. Two Mutations Were Critical for Bat-to-Human Transmission of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 9119–9123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Speranskaya, A.S.; Artyushin, I.V.; Samoilov, A.E.; Korneenko, E.V.; Khabudaev, K.; Ilina, E.N.; Yusefovich, A.P.; Safonova, M.V.; Dolgova, A.S.; Gladkikh, A.S.; et al. Identification and Genetic Characterization of MERS-Related Coronavirus Isolated from Nathusius’ Pipistrelle (Pipistrellus Nathusii) near Zvenigorod (Moscow Region, Russia). 2022. Available online: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.06.09.495421v1 (accessed on 10 June 2022).
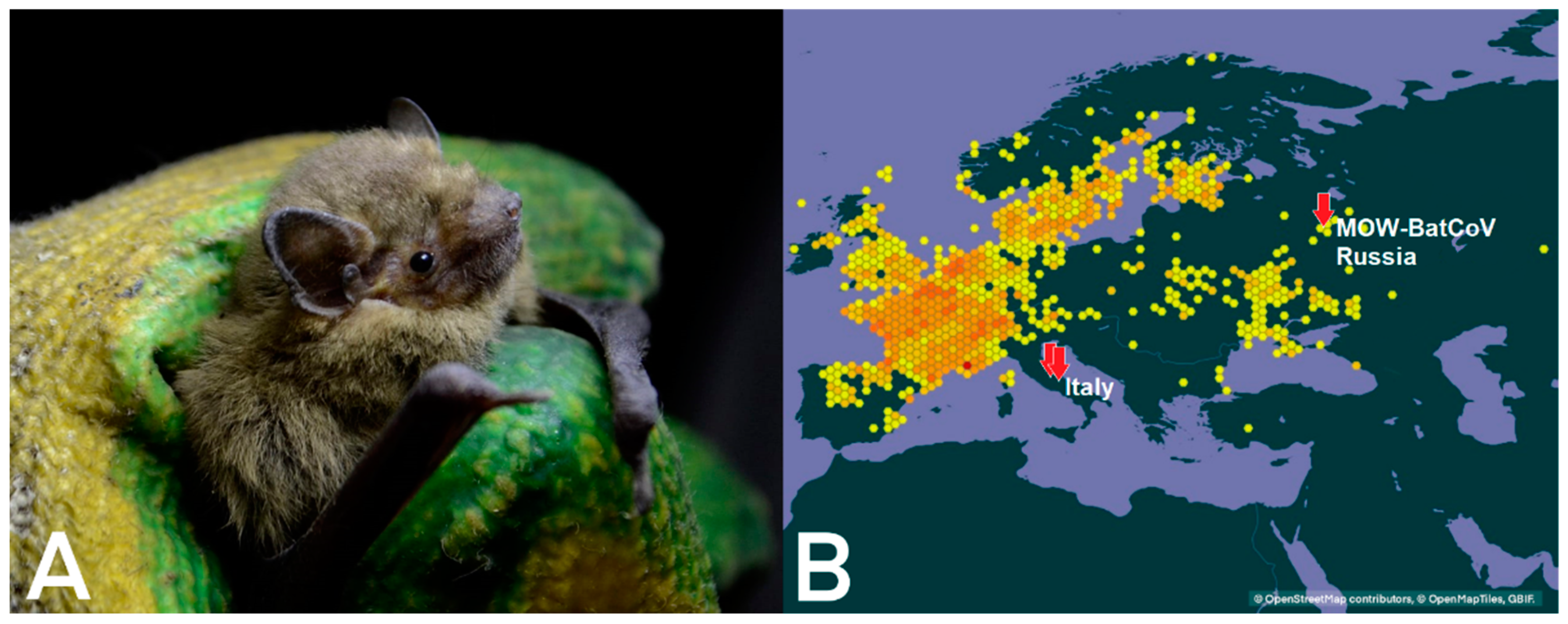
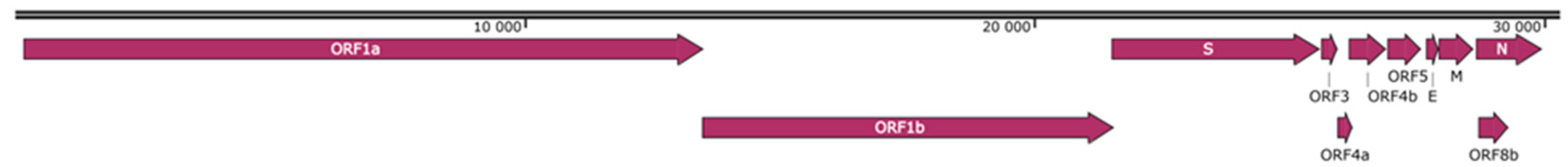
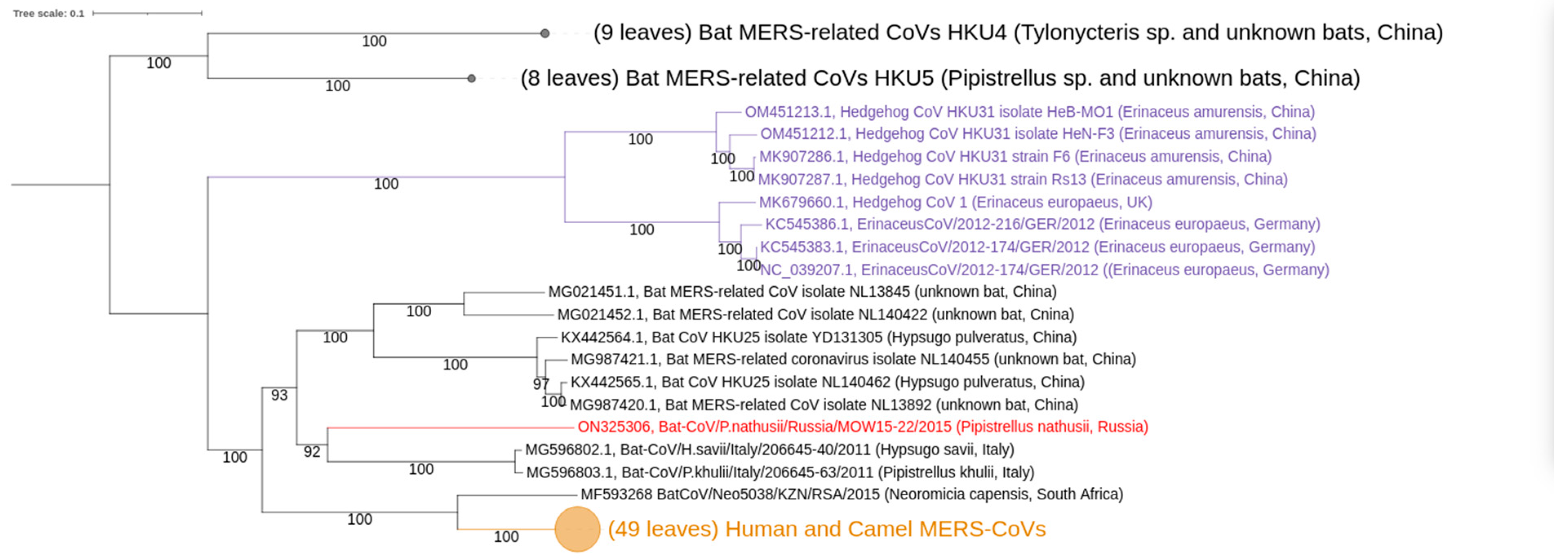
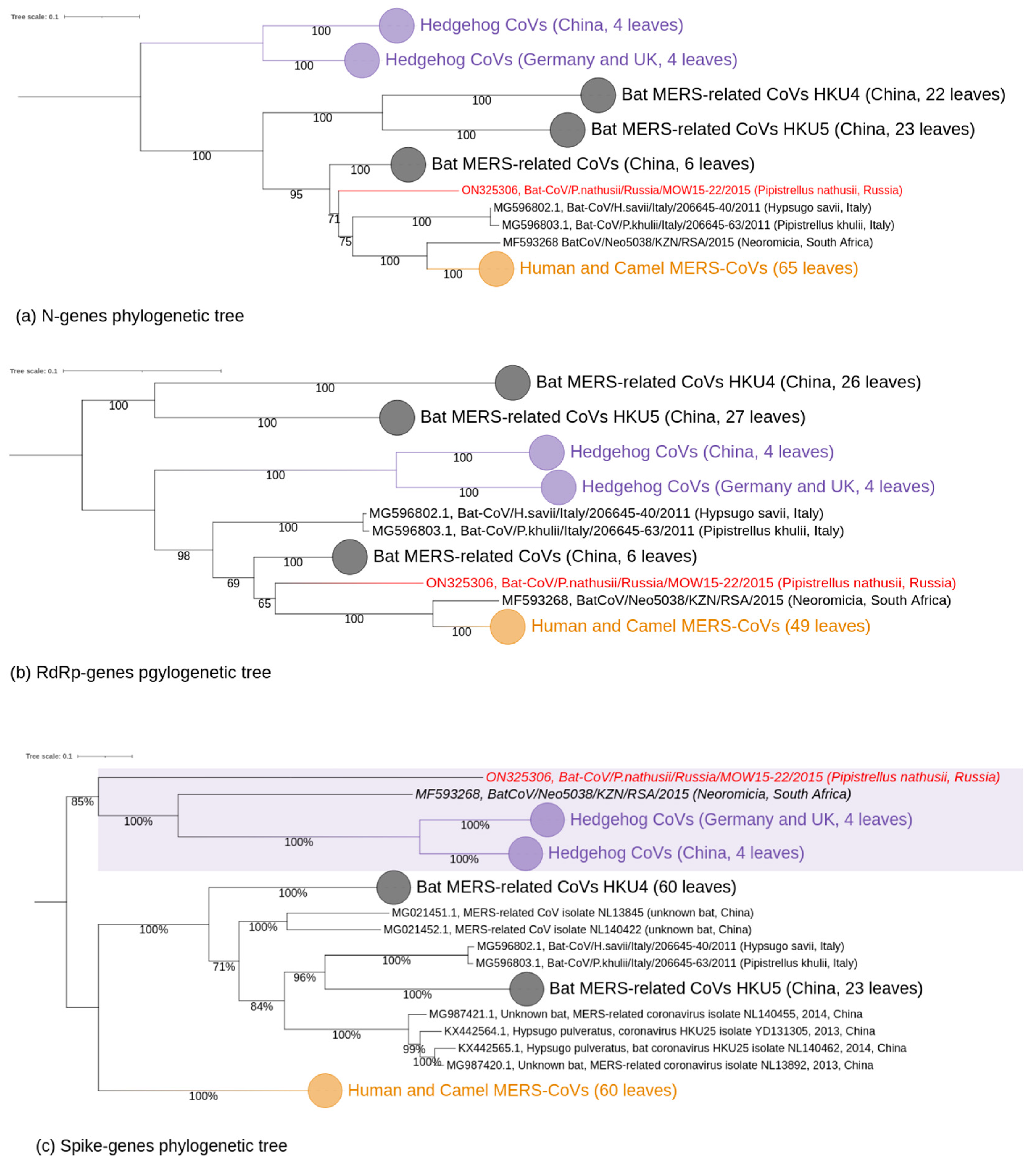
| Sample ID | Gender | Age | Ectoparasites | PCR Product | Fragment Length, bp | GenBank ID, Nearest | Identity, % | Genus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bat№16 | F | Semi-adult | Mites | + | 418 | KC243390.1 | 98.35 | Beta |
| 420 | EU375869.1 | 99.51 | Alpha | |||||
| Bat№21 | F | Semi-adult | Mites | + | 420 | EU375864.1 | 98.77 | Alpha |
| Bat№22 | M | Semi-adult | Mites | + | 418 | KC243390.1 | 98.51 | Beta |
| Bat№23 | M | Adult | Mites | + | 420 | EU375869.1 | 99.51 | Alpha |
| Bat№25 | F | Adult | Many Mites | - | - | - | - | - |
| Bat№33 | M | Semi-adult | Many Mites | + | 420 | EU375864.1 | 98.77 | Alpha |
| 418 | KC243390.1 | 98.35 | Beta |
| ORF | Nt Position (Start-End) | No. of Amino Acids | Putative Leader TRS-L and TRS-B |
|---|---|---|---|
| ORF1a | 175–13,524 | 4449 | TRS-L |
| ORF1ab | 175–21,587 | 7137 | TRS-L |
| S prot | 21,529–25,629 | 1367 | TRS-B |
| ORF3 | 25,645–25,959 | 105 | TRS-B |
| ORF4a | 25,968–26,252 | 95 | TRS-B |
| ORF4b | 26,173–26,925 | 251 | No |
| ORF 5 | 26,935–27,612 | 226 | TRS-B |
| E prot | 27,691–27,939 | 83 | TRS-B |
| M prot | 27,954–28,619 | 222 | TRS-B |
| Nprot | 28,675–29,982 | 436 | TRS-B |
| ORF 8b | 28,721–29,314 | 198 | No |
| NSP | Position of Putative Cleavage Sites | Protein Size (Number of Amino Acids) | Putative Functional Domain(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NSP1 | Met1-Gly195 | 195 | |
| NSP2 | Asp196-Gly858 | 663 | |
| NSP3 | Ala859-Gly2798 | 1940 | ADRP, PL2pro |
| NSP4 | Ala2799-Gln3305 | 507 | |
| NSP5 | Ser3306-Gln3611 | 306 | 3CLpro |
| NSP6 | Ser3612-Gln3903 | 292 | |
| NSP7 | Ser3904-Gln3986 | 83 | |
| NSP8 | Ala3987-Gln4185 | 199 | Primase |
| NSP9 | Asn4186-Gln4295 | 110 | |
| NSP10 | Ala4296-Gln4435 | 140 | |
| NSP11 | Ser4436-Ile4449 | 14 | Short peptide at the end of ORF1a |
| NSP12 | Val4450-Gln5369 | 920 | RdRp |
| NSP13 | Ala5370-Gln5967 | 598 | HEL, NTPase |
| NSP14 | Ser5968-Gln6491 | 524 | ExoN, NMT |
| NSP15 | Gly6492-Gln6834 | 343 | NendoU |
| NSP16 | Ala6835-Cys7137 | 303 | OMT |
| Myotis brandtii | Erinaceus europaeus | |
|---|---|---|
| binding sites | 36, 163, 165, 166, 188, 189, 191, 230, 232, 233, 370, 389, 417, 419, 485, 486, 487, 488, 489, 490, 585, 611, 613, 617, 618, 619, 620, 637, 696, 697, 698, 701, 703, 704, 705, 707, 716, 718, 719, 720, 722, 724, 734 | 36, 38, 39, 154, 156, 157, 158, 159, 163, 165, 166, 188, 189, 190, 191, 197, 230, 232, 233, 370, 389, 416, 417, 419, 485, 486, 487, 488, 489, 490, 585, 613, 617, 618, 619, 620, 697, 698, 699, 703, 704, 718 |
| overlapping binding sites | 36, 163, 165, 166, 188, 189, 191, 230, 232, 233, 370, 389, 417, 419, 485, 486, 487, 488, 489, 490, 585, 613, 617, 618, 619, 620, 697, 698, 703, 704, 718 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Speranskaya, A.S.; Artiushin, I.V.; Samoilov, A.E.; Korneenko, E.V.; Khabudaev, K.V.; Ilina, E.N.; Yusefovich, A.P.; Safonova, M.V.; Dolgova, A.S.; Gladkikh, A.S.; et al. Identification and Genetic Characterization of MERS-Related Coronavirus Isolated from Nathusius’ Pipistrelle (Pipistrellus nathusii) near Zvenigorod (Moscow Region, Russia). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3702. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043702
Speranskaya AS, Artiushin IV, Samoilov AE, Korneenko EV, Khabudaev KV, Ilina EN, Yusefovich AP, Safonova MV, Dolgova AS, Gladkikh AS, et al. Identification and Genetic Characterization of MERS-Related Coronavirus Isolated from Nathusius’ Pipistrelle (Pipistrellus nathusii) near Zvenigorod (Moscow Region, Russia). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(4):3702. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043702
Chicago/Turabian StyleSperanskaya, Anna S., Ilia V. Artiushin, Andrei E. Samoilov, Elena V. Korneenko, Kirill V. Khabudaev, Elena N. Ilina, Alexander P. Yusefovich, Marina V. Safonova, Anna S. Dolgova, Anna S. Gladkikh, and et al. 2023. "Identification and Genetic Characterization of MERS-Related Coronavirus Isolated from Nathusius’ Pipistrelle (Pipistrellus nathusii) near Zvenigorod (Moscow Region, Russia)" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 4: 3702. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043702
APA StyleSperanskaya, A. S., Artiushin, I. V., Samoilov, A. E., Korneenko, E. V., Khabudaev, K. V., Ilina, E. N., Yusefovich, A. P., Safonova, M. V., Dolgova, A. S., Gladkikh, A. S., Dedkov, V. G., & Daszak, P. (2023). Identification and Genetic Characterization of MERS-Related Coronavirus Isolated from Nathusius’ Pipistrelle (Pipistrellus nathusii) near Zvenigorod (Moscow Region, Russia). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(4), 3702. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043702








