Environmental Challenges in Southern Brazil: Impacts of Pollution and Extreme Weather Events on Biodiversity and Human Health
Abstract
1. Introduction: A Brief Overview of Eco-Social Aspects of Rio Grande do Sul
2. Objective and Methodological Notes
3. Revisiting the Historical Participation of Rio Grande do Sul in Brazilian Environmentalism
4. Main Pollution-Related Issues in Rio Grande do Sul
5. Recent Extreme Weather Events Observed in Rio Grande do Sul
6. Pollution by Potentially Toxic Elements
6.1. Impacts on Humans
6.2. Impacts on Biodiversity
7. Atmospheric Pollution
7.1. Impacts on Humans
7.2. Impacts on Biodiversity
8. Plastic Pollution
8.1. Impacts on Humans
8.2. Impacts on Biodiversity
9. Pesticide Pollution
9.1. Impacts on Humans
9.2. Impacts on Biodiversity
10. Extreme Weather Events
10.1. Impacts on Humans: Enphasis on Pathogen Pollution
10.2. Impacts on Biodiversity
11. Perspectives
12. Conclusions
- Two biomes occur in Rio Grande do Sul, the Pampa and the Atlantic Forest. The transition between these two biomes, known as an ecotone zone, associated with the characteristic landscape of each biome, creates landscapes with great biodiversity.
- Pollution intensified in Rio Grande do Sul starting from the colonization of the state by Europeans (especially in the 19th century) and subsequent industrialization process in the second half of the 20th century.
- Historically, Rio Grande do Sul has played an important role in Brazilian environmentalism, being a pioneering state in various awareness and environmental policy actions.
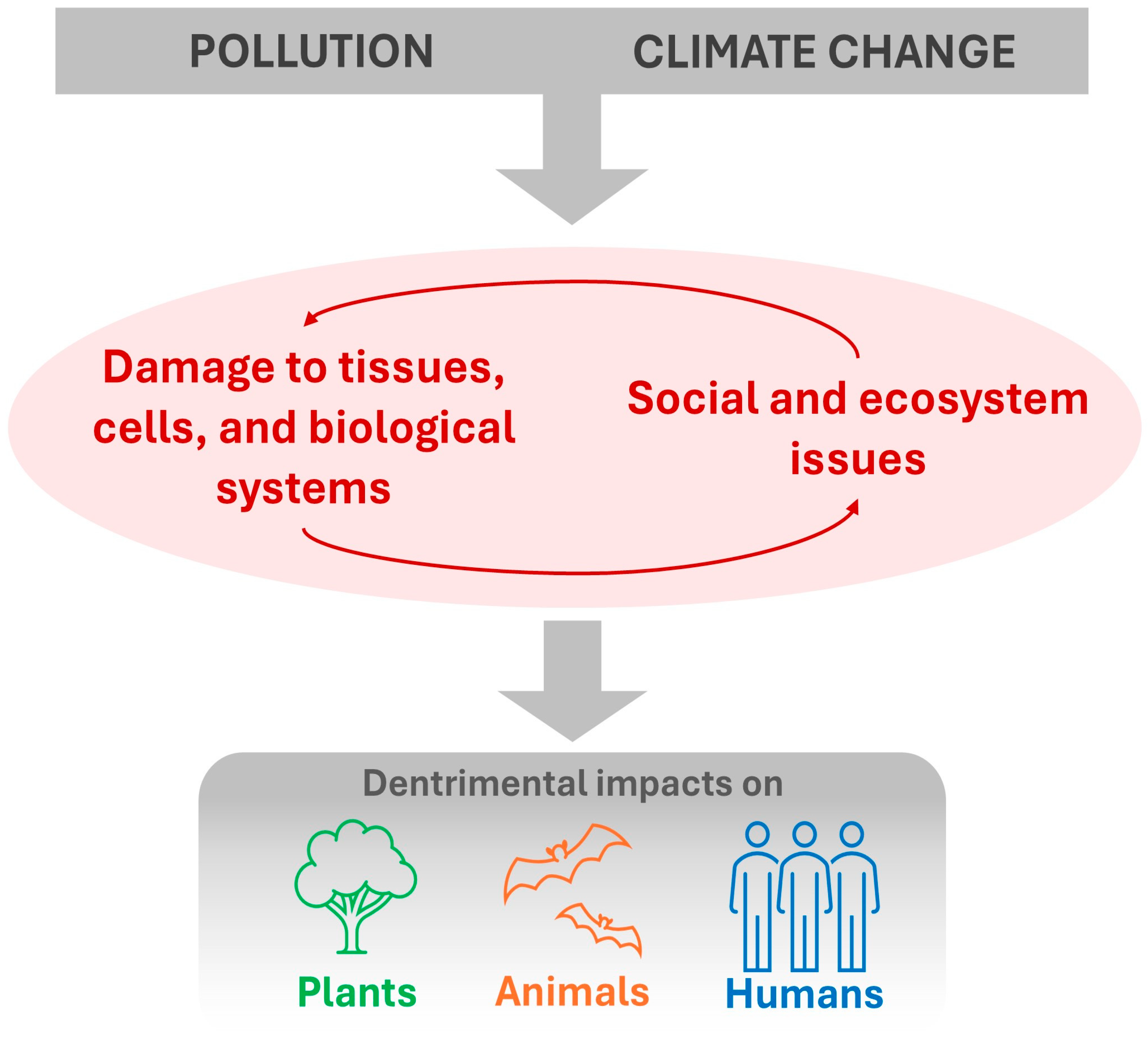
- Currently, activities such as mining, agriculture, industrial tree farming, and unplanned urban expansion in Rio Grande do Sul threaten biodiversity and human health. These threats are exacerbated by climate change and the combined effects of different pollutants.
- Extreme weather events are an increasing threat to Rio Grande do Sul.
- Deficiencies in sanitation systems are observed in different cities of Rio Grande do Sul, including the capital Porto Alegre, facilitating the contamination of the environment with different pathogens and toxic pollutants.
- In 2024, a mega flood hit Rio Grande do Sul, causing immense damage to human health and biodiversity. This flood, associated with pathogenic pollution, caused a major leptospirosis outbreak.
- Agricultural activities in monoculture systems (cash crop plantations such as soybeans, rice, and tobacco) are so intense in Rio Grande do Sul that they place the state among the largest consumers of pesticides in Brazil, contaminating soil, water, and air, and thus harming humans, fauna, and flora.
- Plastic pollution causes visual pollution and threatens the survival of wildlife in Rio Grande do Sul.
- Microplastic pollution is widespread in the different ecosystems of Rio Grande do Sul, posing health risks to different animal species and humans.
- Mining activities in Rio Grande do Sul are important sources of pollution by toxic metals that contaminate soil, air, and water, causing deleterious effects to different cells, organs, and tissues.
- Climate change can exacerbate PTE pollution in the state, as it has the capacity to modify the distribution of these elements in ecosystems, exposing species to new combinations of toxic agents.
- Industrial activities, mining, and the vehicle fleet in Rio Grande do Sul pollute the air with particulate matter that carries different toxic substances, such as metals and organic pollutants.
- Fires in the Pampa and other Brazilian biomes, such as the Amazon Forest and Pantanal, contribute to the atmospheric pollution observed in Rio Grande do Sul.
- Construction activities in Rio Grande do Sul are an important source of solid waste and greenhouse gases that contribute to climate change.
- The plastisphere associated with deficiencies in sanitation systems can facilitate the spread of infectious diseases in Rio Grande do Sul.
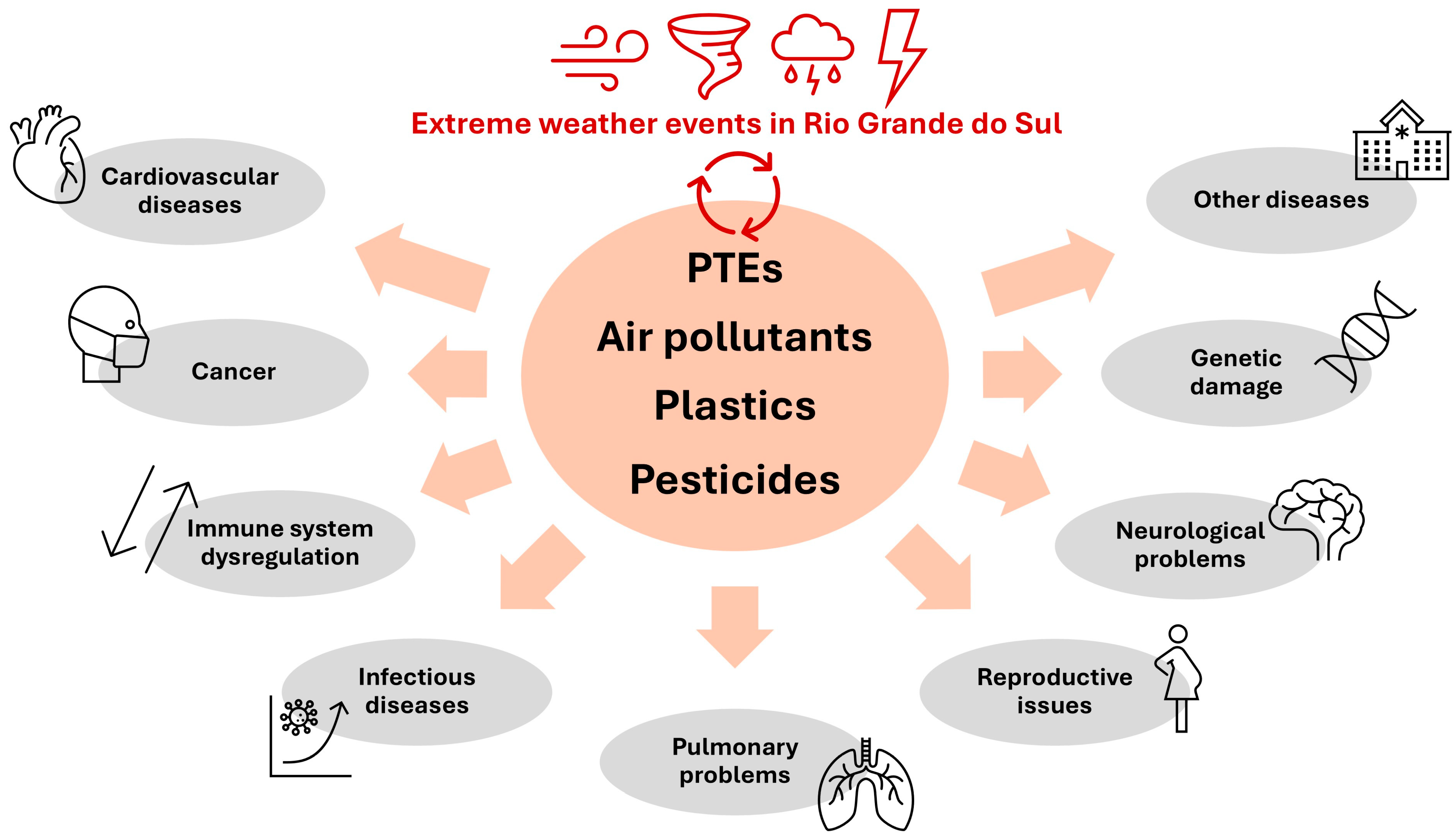
- The different classes of pollutants of greatest importance in Rio Grande do Sul (i.e., atmospheric pollutants, toxic metals, plastics, and pesticides) are associated with genetic damage, neurological, pulmonary, reproductive and cardiovascular problems, dysregulation of the immune system, and cancer, among other diseases in humans. Climate change may exacerbate these health problems (Figure 8).
- Pollution associated with climate change is a major driver of biodiversity loss in southern Brazil.
- Improvements in solid waste management and sanitation systems are essential actions to control pollution in Rio Grande do Sul.
- State and municipal environmental protection agencies need to increase monitoring of industrial, mining, and agricultural activities in the state, punishing irregularities efficiently.
- Mining projects in Rio Grande do Sul must be reduced as they show highly polluting potential.
- Air quality monitoring and control in the state needs to be urgently improved.
- Climate change adaptation plans must be implemented in Rio Grande do Sul, associated with policies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from the state’s agricultural, industrial and livestock activities.
- Environmental agencies, environmental activities, and researchers must intensify the study of the biodiversity of the Pampa biome, in addition to increasing the study of the impacts of pollution and climate change on the rich biodiversity of this often neglected biome.
- Active public participation is crucial to ensuring the effective implementation of environmental protection measures in Rio Grande do Sul, helping to reduce pollution and mitigate climate change.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cordeiro, J.L.; Hasenack, H. Cobertura vegetal atual do Rio Grande do Sul. In Campos Sulinos—Conservação e Uso Sustentável da Biodiversidade; Pillar, V.P., Müller, S.C., Castilhos, Z.M.S., Jacques, A.V.A., Eds.; Ministério do Meio Ambiente: Brasília, Brazil, 2009; pp. 285–299. ISBN 978-85-7738-117-3. [Google Scholar]
- Tomazelli, L.J.; Villwock, J.A. O Cenozóico costeiro do Rio grande do Sul. In Geologia do Rio Grande do Sul; Holz, M., De Ros, L.F., Eds.; Edição CIGO/UFRGS: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2000; pp. 375–406. Available online: https://www.ufrgs.br/estratigrafia/Diversos/Tomazelli%20&%20Villwock%202000.pdf (accessed on 27 September 2024).
- Reginato, P.A.R.; Ahlert, S. Geologia: Formação geológica da planície das lagoas costeiras. In Atlas Socioambiental dos Municípios de Cidreira, Balneário Pinhal, Palmares do Sul; Schäfer, A., Lanzer, R., Scur, L., Eds.; Educs: Caxias do Sul, Brazil, 2013; p. 193. [Google Scholar]
- Echer, R.; da Cruz, J.A.W.; Estrela, C.C.; Moreira, M.; Gravato, F. Usos da terra e ameaças para a conservação da biodiversidade no bioma Pampa, Rio Grande do Sul. Rev. Thema 2015, 12, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Külkamp, J.; Heiden, G.; Iganci, J.R.V. Endemic plants from the Southern Brazilian Highland Grasslands. Rodriguésia 2018, 69, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellwanger, J.H.; Bach, E.; Müller, N.F.D.; Cardoso, J.C.; Seger, G.D.S.; Chies, J.A.B. Diversity of mosquitoes from Porto Alegre region, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil: Ecological and public health perspectives. J. Insect. Conserv. 2022, 26, 873–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Just, J.P.G.; Colvero, R.D.; Zocche, J.J. Bird diversity in a protected area in the Atlantic Forest-Pampas ecotone of coastal Rio Grande do Sul State, southern Brazil. Acta Biológica Catarin. 2022, 9, 75–93. [Google Scholar]
- Ziliotto, M.; Ellwanger, J.H.; Chies, J.A.B. Soil-transmitted helminths detected from environmental samples in a campus of southern Brazil. Sci. One Health 2022, 1, 100016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MapBiomas—Coleção [Versão 2024] da Série Anual de Mapas de Cobertura e Uso da Terra do Brasil. Available online: https://brasil.mapbiomas.org/ (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- Zarth, P.A.; Gerhardt, M. Uma história ambiental do Pampa do Rio Grande do Sul. In Lavouras de Destruição: A (im)posição do Consenso; Teixeira Filho, A., Ed.; UFPEL: Pelotas, Brazil, 2009; pp. 249–295. [Google Scholar]
- Zarth, P.A. Agricultura e impactos ambientais no Planalto do Rio Grande do Sul. In História Ambiental e Migrações; Nodari, E.S., Gerhardt, M., Moretto, S.P., Eds.; Editora da Universidade Federal da Fronteira Sul: São Leopoldo, Brazil, 2012; pp. 54–76. [Google Scholar]
- Governo do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul, Secretaria de Desenvolvimento Rural. Os Povos Indígenas do Rio Grande do Sul: Conheça as ações da SDR. Available online: https://www.sdr.rs.gov.br/os-povos-indigenas-do-rio-grande-do-sul (accessed on 30 October 2024).
- Kulmann-Leal, B.; Ellwanger, J.H.; Chies, J.A.B. CCR5Δ32 in Brazil: Impacts of a European Genetic Variant on a Highly Admixed Population. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 758358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IBGE—Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. Brasil, Rio Grande do Sul. Available online: https://cidades.ibge.gov.br/brasil/rs/panorama (accessed on 31 October 2024).
- Governo do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul, Secretaria de Planejamento, Governança e Gestão. Atlas Socioeconômico do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul. Available online: https://atlassocioeconomico.rs.gov.br/inicial (accessed on 31 October 2024).
- National Institutes of Health, National Library of Medicine, National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Scientific Electronic Library Online—SciELO. SciELO Brasil. Available online: https://www.scielo.br/ (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Google. Google Scholar. Available online: https://scholar.google.com/ (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Duarte, R.H. “Turn to pollute”: Poluição atmosférica e modelo de desenvolvimento no “milagre” brasileiro (1967–1973). Rev. Tempo 2015, 21, 0064–0087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Viola, E.J.; Vieira, P.F. Da preservação da natureza e do controle da poluição ao desenvolvimento sustentável: Um desafio ideológico e organizacional ao movimento ambientalista no Brasil. Rev. Adm. Púb. 1992, 26, 81–104. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, E.M. Da proteção à natureza ao desenvolvimento sustentável: A defesa ambiental no Rio Grande do Sul. Tempos Históricos 2011, 15, 117–153. Available online: https://e-revista.unioeste.br/index.php/temposhistoricos/article/view/7202 (accessed on 31 October 2024).
- Pereira, E.M. A ciência a serviço da saúde humana e ambiental: Entrevista com o químico, geneticista e ambientalista Flávio Lewgoy. História Ciências Saúde-Manguinhos 2017, 24, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.M. Movimentos ambientalistas no Rio Grande do Sul (décadas 1970-80). Oficina Hist. 2018, 11, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prestes, F. Movimentos de Porto Alegre se Inspiram na Tradição Ambiental da Cidade para Barrar Projeto de Mineração. Available online: https://mineracao.sul21.com.br/2019/08/11/movimentos-de-porto-alegre-se-inspiram-na-tradicao-ambiental-da-cidade-para-barrar-projeto-de-mineracao/ (accessed on 31 October 2024).
- Ferreira, M. Brasil de Fato, Produtora da Primeira Feira Ecológica do Brasil Fala Sobre os 33 anos de História da FAE. 2022. Available online: https://www.brasildefators.com.br/2022/10/15/produtora-da-primeira-feira-ecologica-do-brasil-fala-sobre-os-33-anos-de-historia-da-fae (accessed on 27 September 2024).
- Leão, J.; Reinholz, F. Brasil de Fato, Feira Ecológica do Bom Fim Completa 33 Anos Com Celebração da Agroecologia. 2024. Available online: https://www.brasildefators.com.br/2024/09/02/feira-ecologica-do-bonfim-completa-33-anos-com-celebracao-da-agroecologia (accessed on 27 September 2024).
- Prefeitura de Porto Alegre. Feiras Ecológicas. Available online: https://prefeitura.poa.br/carta-de-servicos/feiras-ecologicas (accessed on 14 November 2024).
- Teixeira, E.C.; Feltes, S.; de Santana, E.R.R. Estudo das emissões de fontes móveis na região metropolitana de Porto Alegre, Rio Grande do Sul. Quím Nova. 2008, 31, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, E.C.; Mattiuzi, C.D.P.; Agudelo-Castañeda, D.M.; Garcia, K.O.; Wiegand, F. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons study in atmospheric fine and coarse particles using diagnostic ratios and receptor model in urban/industrial region. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 9587–9602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, E.C.; Agudelo-Castañeda, D.M.; Mattiuzi, C.D.P. Contribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) sources to the urban environment: A comparison of receptor models. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.P.; Oliveira, C.R. A percepção da poluição na cidade do Rio Grande-RS. SINERGIA 2011, 15, 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Fragomeni, L.P.M.; Roisenberg, A. Poluição por mercúrio em aterros urbanos do período colonial no extremo sul do Brasil. Quím. Nova 2010, 33, 1631–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossato, M.V.; de Lima, J.E.; Lírio, V.S. Condições econômicas e nível de qualidade ambiental no Estado do Rio Grande do Sul. Rev. Econ. Sociol Rural 2010, 48, 587–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombardi, L.M. Agrotóxicos e Colonialismo Químico; Elefante: São Paulo, Brazil, 2023; 108p, ISBN 978-6560080225. [Google Scholar]
- Marchesan, E.; Sartori, G.M.S.; de Avila, L.A.; Machado, S.L.O.; Zanella, R.; Primel, E.G.; Macedo, V.R.M.; Marchezan, M.G. Resíduos de agrotóxicos na água de rios da Depressão Central do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul, Brasil. Ciência Rural 2010, 40, 1053–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziliotto, M.; Kulmann-Leal, B.; Roitman, A.; Chies, J.A.B.; Ellwanger, J.H. Pesticide Pollution in the Brazilian Pampa: Detrimental Impacts on Ecosystems and Human Health in a Neglected Biome. Pollutants 2023, 3, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellwanger, J.H.; Ziliotto, M.; Chies, J.A.B. Protect Brazil’s overlooked Pampa biome. Science 2022, 377, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziliotto, M.; Ellwanger, J.H.; Chies, J.A.B. Geo-helmintíases no Rio Grande do Sul: Uma análise a partir da perspectiva de Saúde Única. Bio Diverso 2022, 2, 66–94. [Google Scholar]
- Mirlean, N.; Casartelli, M.R.; Garcia, M.R.D. Propagação da poluição atmosférica por flúor nas águas subterrâneas e solos de regiões próximas às indústrias de fertilizantes (Rio Grande, RS). Quím. Nova 2002, 25, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanz, A.; Mirlean, N.; Baisch, P. Avaliação de poluição do ar por chumbo particulado: Uma abordagem geoquímica. Quím. Nova 2003, 26, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santin, M.F.C.L.; Reis, A. Distribuição espacial da poluição industrial no Estado do Rio Grande do Sul. Rev. CCEI—URCAMP 2007, 11, 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Bonumá, N.B.; Gastaldini, M.C.C.; de Paiva, J.B.D. Análise da carga difusa de poluição gerada por atividades de mineração. RBRH—Rev. Bras. Recur. Hídricos. 2008, 13, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegel, C.G.Z.; Cornélio, P.F.O. Resíduos sólidos urbanos: Depósitos irregulares no munícipio de Passo Fundo, Rio Grande do Sul, Brasil. R. Gest. Sust. Ambient. 2013, 2, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, L.A.; Henkes, J.A. Poluição hídrica: Poluição industrial no Rio dos Sinos-RS. R. Gest. Sust. Ambient. 2013, 2, 186–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centeno, L.N.; Cecconello, S.T.; Guedes, H.A.S.; Leandro, D. Utilização da estatística multivariada como ferramenta para identificação das possíveis fontes de poluição do arroio Lavras do Sul/RS, Brasil. TECNO-LÓGICA 2017, 21, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourinho, P.S.; Ivar do Sul, J.A.; Fillmann, G. Is marine debris ingestion still a problem for the coastal marine biota of southern Brazil? Mar Pollut Bull. 2010, 60, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoldi, C.; Lara, L.Z.; Mizushima, F.A.L.; Martins, F.C.G.; Battisti, M.A.; Hinrichs, R.; Fernandes, A.N. First evidence of microplastic contamination in the freshwater of Lake Guaíba, Porto Alegre, Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoldi, C.; Lara, L.Z.; Fernandes, A.N. Revealing microplastic dynamics: The impact of precipitation and depth in urban river ecosystems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 111231–111243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, I.; Maffessoni, D. Pellets plásticos no sedimento arenoso de praias no litoral médio do estado do Rio Grande do Sul, Brasil. Rev. Gest. Soc. Ambient. 2024, 18, e04447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.B.P.; Ozorio, C.P. Avaliação sobre os banhados do Rio Grande do Sul, Brasil. Rev. Ciências Ambient. 2007, 1, 83–95. Available online: https://revistas.unilasalle.edu.br/index.php/Rbca/article/view/171 (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Andrade, L.C.; Rodrigues, L.R.; Andreazza, R.; Camargo, F.A.O. Lago Guaíba: Uma análise histórico-cultural da poluição hídrica em Porto Alegre, RS, Brasil. Eng. Sanit. Ambient. 2019, 24, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziliotto, M.; Chies, J.A.B.; Ellwanger, J.H. Environmental Sanitation in Porto Alegre City, Brazil: A Basic Step towards Sustainable Development. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, L.; Gomes, L.E.; Astrada, C.; Leal, M.; Ávila, A.; Castro, A.; Romagna, D.; Berwanger, J.; Velleda, L.; Castro, L.; et al. Coletivo Farpa. Donos da Cidade—Sul21. Available online: https://sul21.com.br/donos-da-cidade/# (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Delongui, L.; Pinheiro, R.J.B.; Pereira, D.S.; Specht, L.P.; Cervo, T.C. Panorama dos resíduos da construção civil na região central do Rio Grande do Sul. Teor. E Prática Na Eng. Civ. 2011, 18, 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Santoro, J.F.; Kripka, M. Determinação das emissões de dióxido de carbono das matérias primas do concreto produzido na região norte do Rio Grande do Sul. Ambiente Construído 2016, 16, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hartinger, S.M.; Palmeiro-Silva, Y.K.; Llerena-Cayo, C.; Blanco-Villafuerte, L.; Escobar, L.E.; Diaz, A.; Sarmiento, J.H.; Lescano, A.G.; Melo, O.; Rojas-Rueda, D.; et al. The 2023 Latin America report of the Lancet Countdown on health and climate change: The imperative for health-centred climate-resilient development. Lancet Reg. Health Am. 2024, 33, 100746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, F. Aquecimento global e suas manifestações regionais e locais: Alguns indicadores da região sul do Brasil. Rev. Bras. Climatol. 2006, 2, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambos, S.H.; Mello, R.S.P.; da Silva, A.N.; Binkowski, P. Mudanças climáticas e seus efeitos no Litoral Médio do Rio Grande do Sul. Rev. Elet. Cient. 2017, 3, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Viana, D.R.; Aquino, F.E.; Muñoz, V.A. Avaliação de desastres no Rio Grande do Sul associados a complexos convectivos de mesoescala. Soc. Nat. 2009, 21, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, V.R.; Cunha, A.P.M.A.; Pineda, L.A.C.; Leal, K.R.D.; Costa, L.C.O.; Broedel, E.; França, D.A.; Alvalá, R.C.S.; Seluchi, M.E.; Marengo, J. Secas e os impactos na região sul do Brasil. Rev. Bras. Climatol. 2021, 28, 561–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelinson, D.; Fan, F.M. A seca de 2019/2020 no estado do Rio Grande do Sul a partir de dados sistemáticos e não-sistemáticos. Rev. Gestão Água América Lat. 2023, 20, e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado, T.J.C.; Prochnow, D.; Eltz, F.L.F. Perdas de solo e água em períodos de anomalias climáticas: “El Niño” e “La Niña” no sul do Brasil. R. Bras. Ci Solo. 2002, 26, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, J.; Alcântara, E.; Pampuch, L.A.; Baião, C.F.P.; Park, E.; Custódio, M.S.; Gozzo, L.F.; Bortolozo, C.A. Assessing flood risks in the Taquari-Antas Basin (Southeast Brazil) during the September 2023 extreme rainfall surge. Npj Nat. Hazards 2024, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenharo, M. How to recover when a climate disaster destroys your city. Nature 2024, 634, 1032–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillar, V.D.; Overbeck, G.E. Learning from a climate disaster: The catastrophic floods in southern Brazil. Science 2024, 385, eadr8356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canuto, R. Flooding and climate denialism are harming millions of people in southern Brazil. BMJ 2024, 386, q1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Rocha, P.R.; Reboita, M.S.; Crespo, N.M. Análise do evento extremo de precipitação ocorrido no Rio Grande do Sul entre abril e maio de 2024. J. Health NPEPS 2024, 9, e12603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marengo, J.A.; Dolif, G.; Cuartas, A.; Camarinha, P.; Gonçcalves, D.; Luiz, R.; Silva, L.; Alvara, R.C.S.; Seluchii, M.E.; Moraes, O.L.; et al. O maior desastre climático do Brasil: Chuvas e inundações no estado do Rio Grande do Sul em abril-maio 2024. Estud. Avançados 2024, 38, 203–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, L.F.; Neves, D.M.; Jarenkow, J.A. Habitat-specific impacts of climate change in the Mata Atlântica biodiversity hotspot. Divers Distrib. 2019, 25, 1846–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagundes, H.O.; de Paiva, R.C.D.; Brêda, J.P.L.F.; Fassoni-Andrade, A.C.; Borrelli, P.; Fan, F.M. An assessment of South American sediment fluxes under climate changes. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 879, 163056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moura, F.R.; da Silva Júnior, F.M.R. 2030 Agenda: Discussion on Brazilian priorities facing air pollution and climate change challenges. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 8376–8390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourret, O.; Hursthouse, A. It’s Time to Replace the Term “Heavy Metals” with “Potentially Toxic Elements” When Reporting Environmental Research. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellwanger, J.H.; Franke, S.I.R.; Bordin, D.L.; Prá, D.; Henriques, J.A.P. Biological functions of selenium and its potential influence on Parkinson’s disease. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2016, 88, 1655–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC—US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. About Childhood Lead Poisoning Prevention. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/lead-prevention/about/index.html#:~:text=There%20are%20no%20safe%20levels,exposure%20before%20any%20harm%20occurs (accessed on 24 November 2024).
- WHO—World Health Organization. Lead poisoning. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/lead-poisoning-and-health (accessed on 24 November 2024).
- Ellwanger, J.H.; Chies, J.A.B. Brazil’s heavy metal pollution harms humans and ecosystems. Sci. One Health 2023, 2, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niede, R.; Benbi, D.K. Integrated review of the nexus between toxic elements in the environment and human health. AIMS Public Health 2022, 9, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korchagin, J.; Moterle, D.F.; Esconteguy, P.A.V.; Bortoluzzi, E.C. Distribution of copper and zinc fractions in a Regosol profile under centenary vineyard. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummes, A.P.; Bortoluzzi, E.C.; Tonini, V.; Silva, L.P.; Petry, C. Transfer of Copper and Zinc from Soil to Grapevine-Derived Products in Young and Centenarian Vineyards. Water Air Soil Poll. 2019, 230, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirlean, N.; Roisenberg, A.; Chies, J.O. Copper-Based Fungicide Contamination and Metal Distribution in Brazilian Grape Products. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2005, 75, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ma, T.; Wei, M.; Lan, T.; Bao, S.; Zhao, Q.; Fang, Y.; Sun, X. Copper in grape and wine industry: Source, presence, impacts on production and human health, and removal methods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 1794–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, N.M.; Lucheta, F.; Käffer, M.I.; Martins, S.M.A.; Vargas, V.M.F. Air quality assessment in different urban areas from Rio Grande do Sul state, Brazil, using lichen transplants. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2018, 90, 2233–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzoni, A.C.; Lanzer, R.; Bordin, J.; Schafer, A.; Wasum, R. Mosses as indicators of atmospheric metal deposition in an industrial area of southern Brazil. Acta Bot. Bras. 2012, 26, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casali, C.A.; Moterle, D.F.; Rheinheimer, D.S.; Brunetto, G.; Corcini, A.L.M.; Kaminski, J.; Melo, G.W.B. Copper forms and desorption in soils under grapevine in the Serra Gaúcha of Rio Grande do Sul. Rev. Bras. De Ciência Do Solo 2008, 32, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirlean, N.; Roisenberg, A.; Chies, J.O. Metal contamination of vineyard soils in wet subtropics (southern Brazil). Environ. Pollut. 2007, 149, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirlean, N.; Gripp, M.L.R. Geochemical mapping and environmental indexing of an urban area (Rio Grande, RS). Geochim. Bras. 2018, 32, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niencheski, L.; Windom, H.; Smith, R. Distribution of particulate trace metal in Patos Lagoon estuary (Brazil). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1994, 28, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, W.; Li, C.; Zhu, F.; Luo, X.; Feng, J.; Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, C.; Hartley, W.; Xue, S. Effect of potentially toxic elements on soil multifunctionality at a lead smelting site. J. Hazard Mater. 2023, 454, 131525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garau, M.; Garau, G.; Diquattro, S.; Roggero, P.P.; Castaldi, P. Mobility, bioaccessibility and toxicity of potentially toxic elements in a contaminated soil treated with municipal solid waste compost. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 186, 109766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodrzeieski, P.A.; Andrade, L.C.; Tiecher, T.; Camargo, F.A.O. Physico-chemical variability and heavy metal pollution of surface sediment in a non-channeled section of Dilúvio Stream (Southern Brazil) and the influence of channeled section in sediment pollution. Ambiente Água—Interdiscip. J. Appl. Sci. 2019, 14, E2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, L.C.; Tiecher, T.; Oliveira, J.S.; Andreazza, R.; Inda, A.V.; Camargo, F.A.O. Sediment pollution in margins of the Lake Guaíba, Southern Brazil. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelmann, P.M.; Santos, V.H.J.M.; Moser, L.I.; Bruzza, E.C.; Barbieri, C.B.; Barela, P.S.; Moraes, D.P.; Augustin, A.H.; Goudinho, F.S.; Melo, C.L.; et al. Environmental monitoring of water resources around a municipal landfill of the Rio Grande do Sul state, Brazil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 21398–22141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolarova, N.; Napiórkowski, P. Trace elements in aquatic environment. Origin, distribution, assessment and toxicity effect for the aquatic biota. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2021, 21, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.A.R.; Botero, W.G.; Oliveira, L.C. Natural and anthropogenic sources of potentially toxic elements to aquatic environment: A systematic literature review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 51318–51338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robaina, L.E.; Formoso, M.L.; Pires, C.A.F. Metais pesados nos sedimentos de corrente, como indicadores de risco ambiental—Vale do Rio dos Sinos, RS. Rev. Do Inst. Geológico 2002, 23, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.B.; Reis, D.S.B.F.; Morales, D.C.; Kapusta, S.C.; Nonohay, J.S. Metal analysis and cytogenotoxicity assessment of the Jacuí River Delta water, Rio Grande do Sul. Rev. Thema 2022, 21, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, V.M.; Silva, J.; Silva, F.R.; Heuser, V.D.; Dias, J.F.; Yoneama, M.L.; Freitas, T.R.O. Fish as bioindicators to assess the effects of pollution in two southern Brazilian rivers using the Comet assay and micronucleus test. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2004, 44, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laybauer, L.; Bidone, E.D. Mass balance estimation of natural and anthropogenic heavy metal fluxes in streams near the camaquã copper mines, Rio Grande do sul, Brazil. In Environmental Geochemistry in the Tropics; Lecture Notes in Earth Sciences; Wasserman, J.C., Silva-Filho, E.V., Villas-Boas, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 1998; Volume 72, ISBN-13: 978-3540637301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, E.C.; Ortiz, L.S.; Alves, M.F.C.C.; Sanchez, J.C.D. Distribution of selected heavy metals in fluvial sediments of the coal mining region of Baixo Jacuí, RS, Brazil. Environ. Geol. 2001, 41, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.L.K.; Formoso, M.L.L. Metal Contamination of Stream Waters under the Impact of Tanneries. Pesqui. Em Geociências 2006, 33, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, C.B.; Schwarzbold, A.; Raya Rodriguez, M.T. Environmental Crime Investigation in Arroio do Meio, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil: Tannery and Shoe Factory Waste Landfill Case Study. Environ. Forensics 2007, 8, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.T.G.; Rolim, S.B.A.; Mello-Farias, P.C.; Meneguzzi, A.; Lutckmeier, C. Industrial Pollution of Environmental Compartments in the Sinos River Valley, RS, Brazil: Geochemical–Biogeochemical Characterization and Remote Sensing. Water Air Soil Poll. 2008, 192, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, M.; Andrade, S.; Faugeron, S.; Lagos, N.; Mella, D.; Correa, J. Biodiversity of rocky intertidal benthic communities associated with copper mine tailing discharges in northern Chile. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwinyihija, M. Main Pollutants and Environmental Impacts of the Tanning Industry. In Ecotoxicological Diagnosis in the Tanning Industry; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Pizzol, G.E.; Rosano, V.A.; Rezende, E.; Kilpp, J.C.; Ferretto, M.M.; Mistura, E.; da Silva, A.N.; Bertol, C.D.; Roffrigues, L.B.; Friedrich, M.T.; et al. Pesticide and trace element bioaccumulation in wild owls in Brazil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 37843–37850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masood, F.; Malik, A. Environmental Concerns of the Tanning Industry. In Environmental Deterioration and Human Health; Malik, A., Grohmann, E., Akhtar, R., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capoane, V.; Tiecher, T.; Schaefer, G.L.; Alvarez, J.W.R.; Burrow, R.A.; Santos, D.R. Avaliação da qualidade dos sedimentos de leito em uma bacia hidrográfica do noroeste do Rio Grande do Sul. Bol. Gaúcho Geogr. 2016, 43, 202–223. [Google Scholar]
- Velleda, L. Sul21: Projeto de Mineração de Fosfato em Lavras do Sul Revolta Pecuaristas Familiares da Região. Available online: https://sul21.com.br/noticias/meio-ambiente/2024/11/projeto-de-mineracao-de-fosfato-em-lavras-do-sul-revolta-pecuaristas-familiares-da-regiao/ (accessed on 20 November 2024).
- Amigas da Terra Brasil. Brasil de Fato: Projeto Retiro: Extração de Titânio e Outros Minerais Ameaça Territórios de vida em São José do Norte (RS). Available online: https://www.brasildefators.com.br/2024/04/23/projeto-retiro-extracao-de-titanio-e-outros-minerais-ameaca-territorios-de-vida-em-sao-jose-do-norte-rs (accessed on 20 November 2024).
- dos Santos, C.F.; Ilha, J.G.; Sichelero, G.A. Os desastres ambientais no Rio Grande do Sul e o discurso da energia verde: Apontamentos sobre a energia eólica e o hidrogênio verde. Revista CEDEPEM 2023, 3, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Sha, A.; Xiong, Z.; Luo, Y.; Peng, L.; Zou, L.; Zhao, C.; Li, Q. The Easily Overlooked Effect of Global Warming: Diffusion of Heavy Metals. Toxics 2024, 12, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, C.; Schmidt, M.I.; Cousin, E.; Malta, D.C.; Naghavi, M.; Oliveira, P.P.V.; Ribeiro, A.L.P.; Duncan, B.B. Exposure to and Burden of Major Non-Communicable Disease Risk Factors in Brazil and its States, 1990-2019: The Global Burden of Disease Study. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2022, 55 (Suppl. S1), e0275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agudelo-Castañeda, D.M.; Teixeira, E.C.; Schneider, I.L.; Lara, S.R.; Silva, L.F.O. Exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in atmospheric PM1.0 of urban environments: Carcinogenic and mutagenic respiratory health risk by age groups. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 224, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.R.; Viana, V.P.; Müller, A.M.; Livi, F.P.; Dalcin, P.T.R. Respiratory viral infections and effects of meteorological parameters and air pollution in adults with respiratory symptoms admitted to the emergency room. Influenza Other. Respir. Viruses 2014, 8, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brum, A.N.; de Lima Brum, R.; da Silva Bonifácio, A.; Tavella, R.A.; Penteado, J.O.; Siebel, A.M.; da Silva Júnior, F.M.R.; Zhang, L. Two decades of air pollution: Health impacts in the metropolitan área of Porto Alegre, Brazil. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brucker, N.; do Nascimento, S.N.; Bernardini, L.; Charão, M.F.; Garcia, S.C. Biomarkers of exposure, effect, and susceptibility in occupational exposure to traffic-related air pollution: A review. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2020, 40, 722–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brucker, N.; Moro, A.M.; Charão, M.F.; Durgante, J.; Freitas, F.; Baierle, M.; Nascimento, S.; Gauer, B.; Bulcão, R.P.; Bubols, G.B.; et al. Biomarkers of occupational exposure to air pollution, inflammation and oxidative damage in taxi drivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463–464, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brucker, N.; Charão, M.F.; Moro, A.M.; Ferrari, P.; Bubols, G.; Sauer, E.; Fracasso, R.; Durgante, J.; Thiesen, F.V.; Duarte, M.M.; et al. Atherosclerotic process in taxi drivers occupationally exposed to air pollution and co-morbidities. Environ. Res. 2014, 131, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, A.; Brucker, N.; Moro, A.M.; Nascimento, S.; Goethel, G.; Souto, C.; Fracasso, R.; Sauer, E.; Altknecht, L.; da Costa, B.; et al. Association between inflammation processes, DNA damage, and exposure to environmental pollutants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauer, B.; Brucker, N.; Barth, A.; Arbo, M.D.; Gioda, A.; Thiesen, F.V.; Nardi, J.; Garcia, S.C. Are metals and pyrene levels additional factors playing a pivotal role in air pollution-induced inflammation in taxi drivers? Toxicol. Res. (Camb) 2017, 7, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauer, B.; Sauer, E.; Nascimento, S.; Göethel, G.; Peruzzi, C.; Flesch, I.; Fão, N.; Cestonaro, L.; Sant’Pierre, T.; Gioda, A.; et al. Cellular response to chemicals present in air pollution in occupationally exposed workers and its potential cancer susceptibility. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, V.M.F.; da Silva Júnior, F.M.R.; da Silva Pereira, T.; da Silva, C.S.; Coronas, M.V. A comprehensive overview of genotoxicity and mutagenicity associated with outdoor air pollution exposure in Brazil. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2023, 26, 172–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleck, A.S.; Vieira, M.; Amantéa, S.L.; Rhoden, C.R. A comparison of the human buccal cell assay and the pollen abortion assay in assessing genotoxicity in an urban-rural gradient. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 8825–8838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, C.S.; Rossato, J.M.; Rocha, J.A.V.; Vargas, V.M.F. Characterization of an area of reference for inhalable particulate matter (PM2.5) associated with genetic biomonitoring in children. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2015, 778, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, V.M.F. Mutagenic activity as a parameter to assess ambient air quality for protection of the environment and human health. Mutat. Res. 2003, 544, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, T.S.; Gotor, G.N.; Beltrami, L.S.; Nolla, C.G.; Rocha, J.A.V.; Broto, F.P.; Comellas, L.R.; Vargas, V.M.F. Salmonella mutagenicity assessment of airborne particulate matter collected from urban areas of Rio Grande do Sul State, Brazil, differing in anthropogenic influences and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon levels. Mutat. Res. 2010, 702, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Käffer, M.I.; Lemos, A.T.; Apel, M.A.; Rocha, J.V.; Martins, S.M.A.; Vargas, V.M.F. Use of bioindicators to evaluate air quality and genotoxic compounds in an urban environment in Southern Brazil. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 163, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, M.R.; Garcia, A.L.H.; Dalberto, D.; Martins, G.; Picinini, J.; Souza, G.M.S.; Chytry, P.; Dias, J.F.; Bobermin, L.D.; Quincozes-Santos, A.; et al. Environmental exposure to mineral coal and by-products: Influence on human health and genomic instability. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceglinski, L.V.; Tavella, R.A.; Bonifácio, A.S.; Santos, J.E.K.; da Silva Júnior, F.M.R. Weekend effect on air pollutant levels in southernmost cities of Brazil with different economic activities. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honscha, L.C.; Reis, F.O.; Aikawa, P.; Coronas, M.V.; Muccillo-Baisch, A.L.; Baisch, P.R.M.; da Silva Júnior, F.M.R. Human health risk assessment of air pollutants in the largest coal mining area in Brazil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 59499–59509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigliardi, A.; dos Santos, M.; Fernandes, C.L.F.; Garcia, E.M.; dos Santos, M.E.T.; Jones, M.H.; Soares, M.C.F.; Baisch, A.L.M.; da Silva Júnior, F.M.R. Lung function among residents from the largest coal region in Brazil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 46803–46812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honscha, L.C.; Penteado, J.O.; de Sá Gama, V.; da Silva Bonifácio, A.; Aikawa, P.; dos Santos, M.; Baisch, P.R.M.; Muccillo-Baisch, A.L.; da Silva Júnior, F.M.R. Health impact assessment of air pollution in an area of the largest coal mine in Brazil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 14176–14184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, B.D.; Kautzmann, R.M.; da Silveira, F.R.; da Silva Civeira, M.; de Vargas, F.C.; Taffarel, S.R. Quantitative evaluation of total volatile organic compounds in urban and rural schools of southern Brazil. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nóbrega, M.R.; Krusche, N. Diagnóstico qualitativo da poluição atmosférica em Rio Grande-RS, 2000 a 2002. Geosul 2010, 25, 129–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmedo, A.P.B.F.; de Silva, M.G.C.; Muccillo-Baisch, A.L.; Soares, M.C.F. Avaliação da função pulmonar em escolares expostos à poluição atmosférica em Rio Grande. Vittalle 2012, 24, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Coronas, M.V.; Bavaresco, J.; Rocha, J.A.V.; Geller, A.M.; Caramão, E.B.; Rodrigues, M.L.K.; Vargas, V.M.F. Attic dust assessment near a wood treatment plant: Past air pollution and potential exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 95, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemos, A.T.; Lemos, C.T.; Coronas, M.V.; Rocha, J.R.; Vargas, V.M.F. Integrated study of genotoxicity biomarkers in schoolchildren and inhalable particles in areas under petrochemical influence. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, L.D.; da Costa, G.M.; Gehlen, G.; Droste, A.; Schmitt, J.L. Morphometric differences of Microgramma squamulosa (Kaulf.) de la Sota (Polypodiaceae) leaves in environments with distinct atmospheric air quality. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2014, 86, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, D.D.; Osório, D.M.M.; Rodrigues, M.A.S.; Illi, J.C.; Bianchin, L.; Benvenuti, T. Concentrations of PM2.5–10 and PM2.5 and metallic elements around the Schmidt Stream area, in the Sinos River Basin, southern Brazil. Braz. J. Biol. 2015, 75 (Suppl. 2), 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassanego, M.B.B.; Sasamori, M.H.; Petry, C.T.; Droste, A. Biomonitoring the genotoxic potential of the air on Tradescantia pallida var. purpurea under climatic conditions in the Sinos River basin, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Braz. J. Biol. 2015, 75 (Suppl. 1), 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Illi, J.C.; Vancetta, T.; Alves, D.D.; Osório, D.M.M.; Bianchin, L.; de Quevedo, D.M.; Juchem, F. Integrated assessment of air pollution by metals and source apportionment using ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum Lam.) in southern Brazil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 2790–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dihl, R.R.; da Silva, C.G.A.; do Amaral, V.S.; Reguly, M.L.; de Andrade, H.H.R. Mutagenic and recombinagenic activity of airborne particulates, PM10 and TSP, organic extracts in the Drosophila wing-spot test. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 151, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, D.D.; Backes, E.; Rocha-Uriartt, L.; Riegel, R.P.; de Quevedo, D.M.; Schmitt, J.L.; da Costa, G.M.; Osório, D.M.M. Chemical composition of rainwater in the Sinos River Basin, Southern Brazil: A source apportionment study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 24150–24161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, N.M.; Branquinho, C.; Matos, P.; Pinho, P.; Lucheta, F.; Martins, S.M.A.; Vargas, V.M.F. The application of lichens as ecological surrogates of air pollution in the subtropics: A case study in South Brazil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 20819–20834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, N.M.; Matos, P.; Branquinho, C.; Pinho, P.; Lucheta, F.; Martins, S.M.A.; Vargas, V.M.F. Selecting lichen functional traits as ecological indicators of the effects of urban environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, S.M.A.; Käffer, M.I.; Lemos, A. Liquens como bioindicadores da qualidade do ar numa área de termoelétrica, Rio Grande do Sul, Brasil. Hoehnea 2008, 35, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Käffer, M.I.; Martins, S.M.A.; Alves, C.; Pereira, V.C.; Fachel, J.; Vargas, V.M.F. Corticolous lichens as environmental indicators in urban areas in southern Brazil. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 1319–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Feng, Q.; Wang, J. Mini-review of microplastics in the atmosphere and their risks to humans. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.; Love, D.C.; Rochman, C.M.; Neff, R.A. Microplastics in Seafood and the Implications for Human Health. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2018, 5, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, C.Q.Y.; Valiyaveettil, S.; Tang, B.L. Toxicity of Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Mammalian Systems. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vethaak, A.D.; Legler, J. Microplastics and human health. Science 2021, 371, 672–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Liu, J.; Rillig, M.C.; Bank, M.S.; Fantke, P.; Zhu, D.; Zhu, Y.G.; Jin, L.N. What harmful microbes are lurking in the world’s 7 billion tonnes of plastic waste? Nature 2024, 634, 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziani, K.; Ioniță-Mîndrican, C.B.; Mititelu, M.; Neacșu, S.M.; Negrei, C.; Moroșan, E.; Drăgănescu, D.; Preda, O.T. Microplastics: A Real Global Threat for Environment and Food Safety: A State of the Art Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, J.V.; Torres-Florez, J.P.; Fagundes, L.; Barbosa, L.; Franco-Assis, M.; Ramos, M.A.B.; Fernandes, M.F.; Gil, N. Raio-X dos Resíduos na Costa Brasileira. Available online: https://seashepherd.org.br/files/relatorio_olne.pdf (accessed on 14 November 2024).
- Portz, L.; Manzolli, R.P.; Ivair do Sul, J.A. Marine debris on Rio Grande do Sul north coast, Brazil: Spatial and temporal patterns. J. Integr. Coast. Zone Manag. 2011, 11, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petry, M.V.; Araújo, L.D.; Brum, A.C.; Benemann, V.R.F.; Finger, J.V.G. Plastic ingestion by juvenile green turtles (Chelonia mydas) off the coast of Southern Brazil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 167, 112337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugoni, L.; Krause, L.; Petry, M.V. Marine Debris and Human Impacts on Sea Turtles in Southern Brazil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2001, 42, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petry, M.V.; Petersen, E.S.; Scherer, J.F.M.; Kruger, L.; Sherer, A.L. Notes on the occurrence and diet of Southern Giant Petrels, Macronectes giganteus in Rio Grande do Sul, southern Brazil. Rev. Bras. Ornitol. 2010, 18, 237–239. [Google Scholar]
- Pelegrini, K.; Pereira, T.C.B.; Wertheimer, C.C.S.; Teodoro, L.S.; Basso, N.R.S.; Ligabue, R.A.; Bogo, M.R. Microplastics Beach Pollution: Composition, Quantification and Distribution on the Southern Coast of Brazil. Water Air Soil Poll. 2024, 235, 265–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, M.; Bauer, A.L.; Valiati, V.H.; Schulz, U.H. Microplastic Concentrations in Raw and Drinking Water in the Sinos River, Southern Brazil. Water 2020, 12, 3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Trata Brasil, Ranking do Saneamento 2024. Available online: https://tratabrasil.org.br/ranking-do-saneamento-2024/ (accessed on 14 November 2024).
- Ellwanger, J.H.; Chies, J.A.B. Pathogen Pollution: Viral Diseases Associated with Poor Sanitation in Brazil. Hygiene 2023, 3, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.H.S.; Sousa, F.D.B. Microplastic pollution of Patos Lagoon, south of Brazil. Environ. Chall. 2021, 4, 100076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortoluzzi, E.C.; Rheinheimer, D.S.; Gonçalves, C.S.; Pellegrini, J.B.R.; Maroneze, A.M.; Kurz, M.H.S.; Bacar, N.M.; Zanella, R. Investigation of the occurrence of pesticide residues in rural wells and surface water. Quim. Nova 2007, 30, 1872–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Amaral, A.M.B.; de Moura, L.K.; de Pellegrin, D.; Guerra, L.J.; Cerezer, F.O.; Saibt, N.; Osmar, D.P.; Zanella, R.; Loro, V.L.; Clasen, B. Seasonal factors driving biochemical biomarkers in two fish species from a subtropical reservoir in southern Brazil: An integrated approach. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seben, D.; Toebe, M.; Wastowski, A.D.; Hofstätter, K.; Volpatto, F.; Zanella, R.; Prestes, O.D.; Golombieski, J.I. Water quality variables and emerging environmental contaminant in water for human consumption in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Environ. Chall. 2021, 5, 100266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primel, E.G.; Milani, M.R.; Demoliner, A.; Niencheski, L.F.H.; Escarrone, A.L.V. Development and application of methods using SPE, HPLC-DAD, LC-ESI-MS/MS and GFAAS for the determination of herbicides and metals in surface and drinking water. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2010, 90, 1048–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldas, S.S.; Bolzan, C.M.; Guilherme, J.R.; Silveira, M.A.K.; Escarrone, A.L.V.; Primel, E.G. Determination of pharmaceuticals, personal care products, and pesticides in surface and treated waters: Method development and survey. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 5855–5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riquinho, D.L.; Souto, L.H.D.; Carlotto, F.D.; Pinto, L.; Zini, L.B.; Tavares, J.P. Mortality rate and water contamination by atrazine in Rio Grande do Sul state: An ecological study. Int. J. Dev. Res. 2020, 10, 38235–38240. Available online: https://www.journalijdr.com/mortality-rate-and-water-contamination-atrazine-rio-grande-do-sul-state-ecological-study (accessed on 30 October 2024).
- Pereira, T.S.; Rocha, J.A.V.; Duccatti, A.; Silveira, G.A.; Pastoriza, T.F.; Bringuenti, L.; Vargas, V.M.F. Evaluation of mutagenic activity in supply water at three sites in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2007, 629, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, J.S.; Schwanz, T.G.; Coelho, A.N.; Heck-Marques, M.C.; Mexia, M.M.; Emanuelli, T.; Costabeber, I. Estimated daily intake of organochlorine pesticides from dairy products in Brazil. Food Control 2015, 53, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, M.C.; Sifuentes dos Santos, J.; Bogusz Junior, S.; Costabeber, I.; Emanuelli, T. Estimation of children exposure to organochlorine compounds through milk in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Júnior, A.L.M.; Sattler, A.; Blochtein, B.; Barreto, A.L.H.; Pereira, F.M.; Guarienti, E.M. Analysis of pesticide residues in honey samples of Apis mellifera obtained from canola blooms from municipalities in Rio Grande do Sul state, Brazil. Braz. J. Anim. Environ. Res. 2023, 6, 2006–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, M.; Vareli, C.S.; Janisch, B.; Pizzuti, I.R.; Fortes, J.; Sautter, C.K.; Costabeber, I.H. Contamination of polychlorinated biphenyls in honey from the Brazilian state of Rio Grande do Sul. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2021, 38, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, G.P.; Berlitz, F.; Bender, R.J. Pesticide residues in strawberries cultivated in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Cienc. Rural 2023, 53, e20220153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferronato, G.; Viera, M.S.; Prestes, O.D.; Adaime, M.B.; Zanella, R. Determination of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in breast milk from Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil, using a modified QuEChERS method and gas chromatography-negative chemical ionisation-mass spectrometry. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2018, 98, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viera, M.S.; Ferronato, G.; Abreu, H.D.F.; Prestes, O.D.; Adaime, M.B.; Zanella, R. Simultaneous GC-NCI-MS Determination of Persistent Organic Pollutants and Current-Use Pesticides in Breast Milk Samples. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2022, 33, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sule, R.O.; Condon, L.; Gomes, A.V. A Common Feature of Pesticides: Oxidative Stress—The Role of Oxidative Stress in Pesticide-Induced Toxicity. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 5563759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.S.; Ferasso, D.C.; Prestes, O.D.; Zanella, R.; Grando, R.C.; Treichel, H.; Coelho, G.C.; Mossi, A.J. Quality of Meliponinae honey: Pesticides residues, pollen identity, and microbiological profiles. Environ. Qual. Manag. 2018, 27, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.S.; Xavier, A.A.O.; Ries, E.F.; Costabeber, I.H.; Emanuelli, T. Níveis de organoclorados em queijos produzidos no Estado do Rio Grande do Sul. Cienc. Rural 2006, 36, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasso, E.L.; Cattaneo, R.; Storck, T.R.; Mayer, M.S.; Sant’Anna, V.; Clasen, B. Occupational exposure of rural workers to pesticides in a vegetable-producing region in Brazil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 25758–25769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, C.M.; Calsing, A.K.; da Silva, L.B. Assessment of DNA damage in floriculturists in southern Brazil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 8182–8189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, A.; Medeiros, A.R.; Souza, A.C.; Wink, M.; Siqueira, I.R.; Ferreira, M.B.C.; Fernandes, L.; Hidalgo, M.P.L.; Torres, I.L.S. Evaluation of the impact of exposure to pesticides on the health of the rural population: Vale do Taquari, State of Rio Grande do Sul (Brazil). Cienc. Saúde Coletiva 2011, 16, 3519–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahl, V.F.S.; Simon, D.; Salvador, M.; Branco, C.S.; Dias, J.F.; da Silva, F.R.; de Souza, C.T.; da Silva, J. Telomere measurement in individuals occupationally exposed to pesticide mixtures in tobacco fields. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2016, 57, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Castro Lima, J.A.M.; Labanowski, J.; Bastos, M.C.; Zanella, R.; Prestes, O.D.; de Vargas, J.P.R.; Mondamert, L.; Granado, E.; Tiecher, T.; Zafar, M.; et al. “Modern agriculture” transfers many pesticides to watercourses: A case study of a representative rural catchment of southern Brazil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 10581–10598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grützmacher, D.D.; Grützmacher, A.D.; Agostinetto, D.; Loeck, A.E.; Roman, R.; Peixoto, S.C.; Zanella, R. Monitoring of pesticides in two water sources in southern Brazil. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agric. Ambient. 2008, 12, 367–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griza, F.T.; Ortiz, K.S.; Geremias, D.; Thiesen, F.V. Avaliação da contaminação por organofosforados em águas superficiais no município de Rondinha—Rio Grande do Sul. Quim. Nova 2008, 31, 1631–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, C.L.F.; Volcão, L.M.; Ramires, P.F.; de Moura, R.R.; da Silva Júnior, F.M.R. Distribution of pesticides in agricultural and urban soils of Brazil: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2020, 22, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isenring, R. Pesticides and the Loss of Biodiversity. 2010. Available online: https://www.pan-europe.info/old/Resources/Briefings/Pesticides_and_the_loss_of_biodiversity.pdf (accessed on 16 December 2024).
- Marinowic, D.R.; Mergener, M.; Pollo, T.A.; Maluf, S.W.; da Silva, L.B. In vivo Genotoxicity of the Pyrethroid Pesticide β-Cyfluthrin Using the Comet Assay in the Fish Bryconamericus Iheringii. Z. Für Naturforschung C 2012, 67, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, F. Agrotóxicos Podem ter Causado a Morte de 480 Milhões de Abelhas no RS. 2019. Available online: https://www.ufrgs.br/jornal/agrotoxicos-podem-ter-causado-a-morte-de-480-milhoes-de-abelhas-no-rs/ (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Colussi, J. Agrotóxicos Causaram Morte de Abelhas em 27 Municípios do RS. 2019. Available online: https://gauchazh.clicrbs.com.br/campo-e-lavoura/noticia/2019/08/agrotoxicos-causaram-morte-de-abelhas-em-27-municipios-do-rs-cjz34x3eg00pa01qmo1fenwci.html (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Wingen, N.M.A.; Cubas, G.K.; Oliveira, G.T. A preliminary approach to the Impact of a commercial formulation of glyphosate (Roundup®) in ecologically relevant concentrations on Pseudis minuta tadpoles. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Contam. 2022, 17, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, J.; Bai, X.; Liverman, D.M.; Rockström, J.; Qin, D.; Stewart-Koster, B.; Rocha, J.C.; Jacobson, L.; Abrams, J.F.; Andersen, L.S.; et al. A just world on a safe planet: A Lancet Planetary Health-Earth Commission report on Earth-system boundaries, translations, and transformations. Lancet Planet Health 2024, 8, e813–e873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcellos, F.C.S.; Iganci, J.R.V.; Ribeiro, G.A. Qualidade microbiológica da água do rio São Lourenço, São Lourenço do Sul, Rio Grande do Sul. Arq. Inst. Biol. 2006, 73, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodré, N.S.; Périco, E.; Schröder, N.T.; da Silveira, E.F. Sanitation and public health: Space-temporal analysis of morbidity and mortality in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Cuad. Educ. Desarro. 2024, 16, e3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-Filho, P.R.; Croda, J.; Araújo, A.A.S.; Correia, D.; Quintans-Júnior, L.J. Catastrophic Floods in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil: The Need for Public Health Responses to Potential Infectious Disease Outbreaks. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2024, 57, e006032024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziliotto, M.; Chies, J.A.B.; Ellwanger, J.H. Extreme Weather Events and Pathogen Pollution Fuel Infectious Diseases: The 2024 Flood-Related Leptospirosis Outbreak in Southern Brazil and Other Red Lights. Pollutants 2024, 4, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, P.O.; Guasselli, L.A.; Oliveira, G.G.; Nascimento, V.F. Relação entre casos de hepatite A e áreas de inundação, município de Encantado, Rio Grande do Sul, Brasil. Cien. Saude Colet. 2021, 26, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silveira, R.D.; Neto, J.L.S. As repercussões dos eventos climáticos extremos nas regiões socioeconômicas do Rio Grande do Sul. Bol. Gaúcho Geogr. 2015, 42, 234–244. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, L.P.; Rodrigues-Filho, S.; Marengo, J.A.; Santos, D.V.; Mikosz, L. Mudanças climáticas e desastres: Análise das desigualdades regionais no Brasil. Sustain. Debate 2020, 11, 278–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesan, J.; Alba, E.; Tabarelli, C.; Mello, E.P.; Honnef, D.H.; Pereira, R.S. Risco de incêndios na Estação Ecológica do Taim, Rio Grande do Sul. Nativa 2020, 8, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beal-Neves, M.; Chiarani, E.; Ferreira, P.M.A.; Fontana, C.S. The role of fire disturbance on habitat structure and bird communities in South Brazilian Highland Grasslands. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiarani, E.; Bettio, M.; Fontana, C.S. Temporal changes in bird communities in areas with different histories of fire disturbance in highland grasslands of Brazil. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braz, N.G.S.; Cascais, L.B.; da Silva, L.H.G.; Miura, A.K. Detecção de áreas queimadas na Estação Ecológica do Taim (RS), causada pelos incêndios de 2008 e 2013. Anais XVII Simpósio Brasileiro de Sensoriamento Remoto—SBSR, João Pessoa-PB, Brazil. 2015, pp. 6735–6742. Available online: http://www.dsr.inpe.br/sbsr2015/files/p1476.pdf (accessed on 26 November 2024).
- Justino, G. Mortandade de Animais Devido a Incêndio no Taim Preocupa Ecologistas. Available online: https://www.terra.com.br/planeta/sustentabilidade/mortandade-de-animais-devido-a-incendio-no-taim-preocupa-ecologistas,9c024331a47cd310VgnVCM20000099cceb0aRCRD.html?utm_source=clipboard (accessed on 26 November 2024).
- Eppley, T.M.; Hoeks, S.; Chapman, C.A.; Ganzhorn, J.U.; Hall, K.; Owen, M.A.; Adams, D.B.; Allgas, N.; Amato, K.R.; Andriamahaihavana, M.; et al. Factors influencing terrestriality in primates of the Americas and Madagascar. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2121105119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zank, C.; Becker, F.G.; Abadie, M.; Baldo, D.; Maneyro, R.; Borges-Martins, M. Climate change and the distribution of neotropical red-bellied toads (Melanophryniscus, Anura, Amphibia): How to prioritize species and populations? PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luedtke, J.A.; Chanson, J.; Neam, K.; Hobin, L.; Maciel, A.O.; Catenazzi, A.; Borzée, A.; Hamidy, A.; Aowphol, A.; Jean, A.; et al. Ongoing declines for the world’s amphibians in the face of emerging threats. Nature 2023, 622, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.P.; Quevedo, P.S.; Schild, A.L. Intoxicação por larvas de Perreyia flavipes em bovinos na região sul do Rio Grande do Sul. Pesq. Vet. Bras. 2008, 28, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanches, F.; Verdum, R.; Fisch, G.; Gass, S.L.B.; Rocha, V.M. Extreme Rainfall Events in the Southwest of Rio Grande do Sul (Brazil) and Its Association with the Sandization Process. Am. J. Clim. Change 2019, 8, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, R.C.; Fan, F.M.; Collischonn, W. Scenarios of climate change effects in water availability within the patos Lagoon’s Basin. Rev. Bras. De Recur. Hídricos 2020, 25, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jornal Nacional. RS: Excesso de água doce na Lagoa dos Patos Prejudica a Reprodução de Espécies Marinhas. Available online: https://g1.globo.com/jornal-nacional/noticia/2024/06/05/rs-excesso-de-agua-doce-na-lagoa-dos-patos-prejudica-a-reproducao-de-especies-marinhas.ghtml (accessed on 26 November 2024).
- Margonar, G. Jornal do Comércio, Fauna da Lagoa dos Patos Sofre Alterações no pós-Enchente. Available online: https://www.jornaldocomercio.com/geral/2024/07/1157504-fauna-da-lagoa-dos-patos-sofre-alteracoes-no-pos-enchente.html (accessed on 26 November 2024).
- Fontoura, N.F.; Vieira, J.P.; Becker, F.G.; Rodrigues, L.R.; Malabarba, L.R.; Schulz, U.H.; Möller, O.O.; Garcia, A.M.; Vilella, F.S. Aspects of fish conservation in the upper Patos Lagoon basin. J. Fish. Biol. 2016, 89, 315–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasil, Presidência da República, Casa Civil, Subchefia Para Assuntos Jurídicos. Lei nº 12.305, de 2 de Agosto de 2010. Available online: https://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/_ato2007-2010/2010/lei/l12305.htm (accessed on 21 November 2024).
- Brasil, Presidência da República Secretaria-Geral Subchefia para Assuntos Jurídicos. Decreto nº 10.936, de 12 de Janeiro de 2022. Available online: https://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/_Ato2019-2022/2022/Decreto/D10936.htm (accessed on 21 November 2024).
- Chen, S.; Redkar-Palepu, V. United Nations Development Programme. Umuganda: Rwanda’s Audacity of Hope to End Plastic Pollution. 2023. Available online: https://www.undp.org/blog/umuganda-rwandas-audacity-hope-end-plastic-pollution (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- Jones, N. How to stop plastic pollution: Three strategies that actually work. Nature 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peplow, M. A new answer to the plastics pollution crisis? Nature 2025, 638, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil, Casa Civil, Secretaria Especial para Assuntos Jurídicos. Lei nº 14.850, de 2 de Maio de 2024: Institui a Política Nacional de Qualidade do Ar. Available online: https://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/_ato2023-2026/2024/lei/L14850.htm (accessed on 30 October 2024).
- Tavella, R.A.; de Moura, F.R.; Miraglia, S.G.E.K.; da Silva Júnior, F.M.R. A New Dawn for Air Quality in Brazil. Lancet Planet Health. 2024, 8, e717–e718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CONAMA—Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente, Ministério do Meio Ambiente e Mudança do Clima, Brasil. Resolução nº 506, de 5 de julho de 2024. Available online: https://conama.mma.gov.br/?option=com_sisconama&task=arquivo.download&id=827 (accessed on 21 November 2024).
- Guttikunda, S.K. Northern India and Pakistan are yet again engulfed in a haze of pollution—But a lasting solution is possible. Nature 2024, 636, 569–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United Nations Environment Programme; International Union for Conservation of Nature. Nature-Based Solutions for Climate Change Mitigation; United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), Nairobi and International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), Gland. 2021. Available online: https://wedocs.unep.org/xmlui/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/37318/NBSCCM.pdf (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- Fraga, J.M.L.; Pinto, M. Governança e litígios climáticos no contexto da proteção e da resiliência ambiental no Rio Grande do Sul. HomaPublica 2024, 8, e119. [Google Scholar]
- Secretaria do Meio Ambiente e Infraestrutura, Governo do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul. ProClima2050: Estratégias para o Enfrentamento das Mudanças Climáticas do Rio Grande do Sul. Available online: https://www.proclima2050.rs.gov.br/upload/arquivos/202404/11130802-am-0001-23-plano-de-ac-a-o-clima-tica-digital-a4-3-1.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2024).
- Murphy, T.W., Jr.; Murphy, D.J.; Love, T.F.; LeHew, M.L.A.; McCall, B.J. Modernity is incompatible with planetary limits: Developing a PLAN for the future. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2021, 81, 102239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickel, J. Less is More: How Degrowth Will Save the World; Cornerstone: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pillar, V.D.; Overbeck, G.E. Grazing can reduce wildfire risk amid climate change. Science 2025, 387, eadu7471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QGIS Development Team, QGIS Geographic Information System, Version 3.28.9, Open Source Geospatial Foundatio. 2025. Available online: https://qgis.org (accessed on 5 February 2025).
- IBGE—Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. Available online: https://www.ibge.gov.br/geociencias/cartas-e-mapas/informacoes-ambientais/15842-biomas.html (accessed on 22 November 2024).
- FEPAM—Fundação Estadual de Proteção Ambiental. Geoprocessamento, Serviço de Inteligência Geoespacial. Available online: https://www.fepam.rs.gov.br/geoprocessamento (accessed on 22 November 2024).
- Google, Google Satellite, Google Maps, 2025. Data Processed Using QGIS Desktop 3.28.9. Available online: https://www.google.com/maps (accessed on 5 February 2025).






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ellwanger, J.H.; Ziliotto, M.; Kulmann-Leal, B.; Chies, J.A.B. Environmental Challenges in Southern Brazil: Impacts of Pollution and Extreme Weather Events on Biodiversity and Human Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22020305
Ellwanger JH, Ziliotto M, Kulmann-Leal B, Chies JAB. Environmental Challenges in Southern Brazil: Impacts of Pollution and Extreme Weather Events on Biodiversity and Human Health. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2025; 22(2):305. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22020305
Chicago/Turabian StyleEllwanger, Joel Henrique, Marina Ziliotto, Bruna Kulmann-Leal, and José Artur Bogo Chies. 2025. "Environmental Challenges in Southern Brazil: Impacts of Pollution and Extreme Weather Events on Biodiversity and Human Health" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 22, no. 2: 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22020305
APA StyleEllwanger, J. H., Ziliotto, M., Kulmann-Leal, B., & Chies, J. A. B. (2025). Environmental Challenges in Southern Brazil: Impacts of Pollution and Extreme Weather Events on Biodiversity and Human Health. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 22(2), 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22020305






