Research on Design, Simulation, and Experiment of Separation Mechanism for Micro-Nano Satellites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mission Analysis
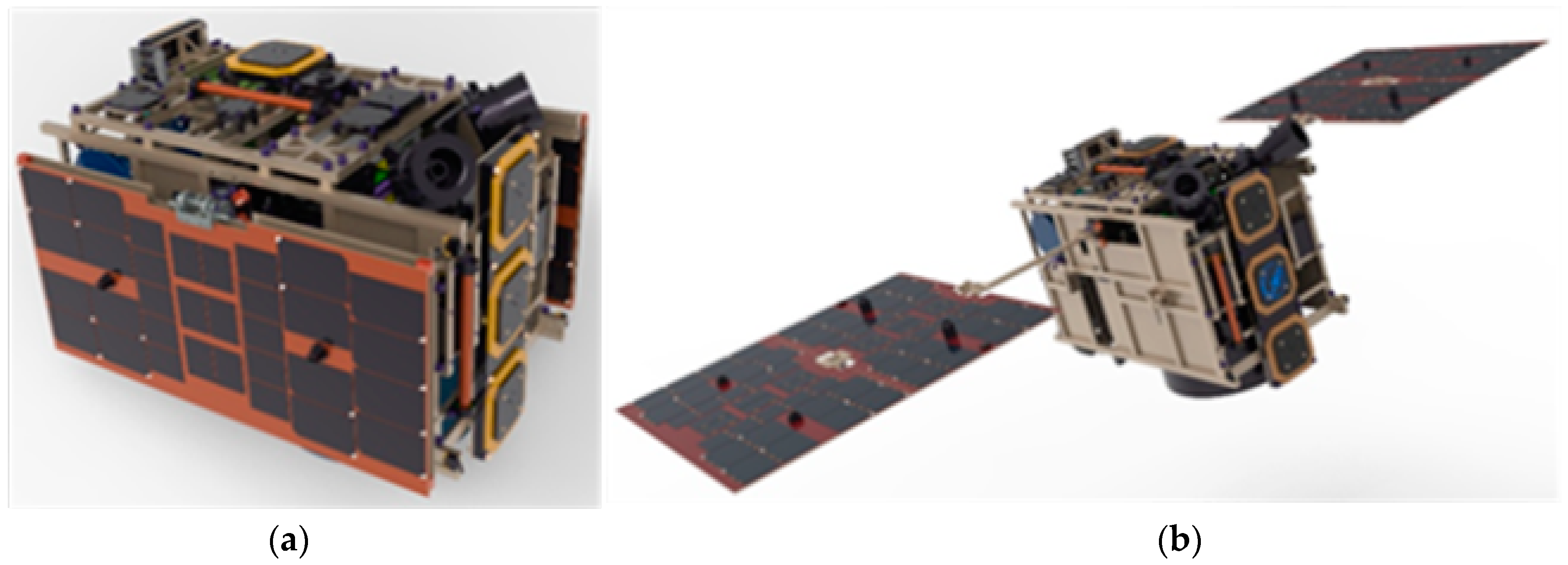
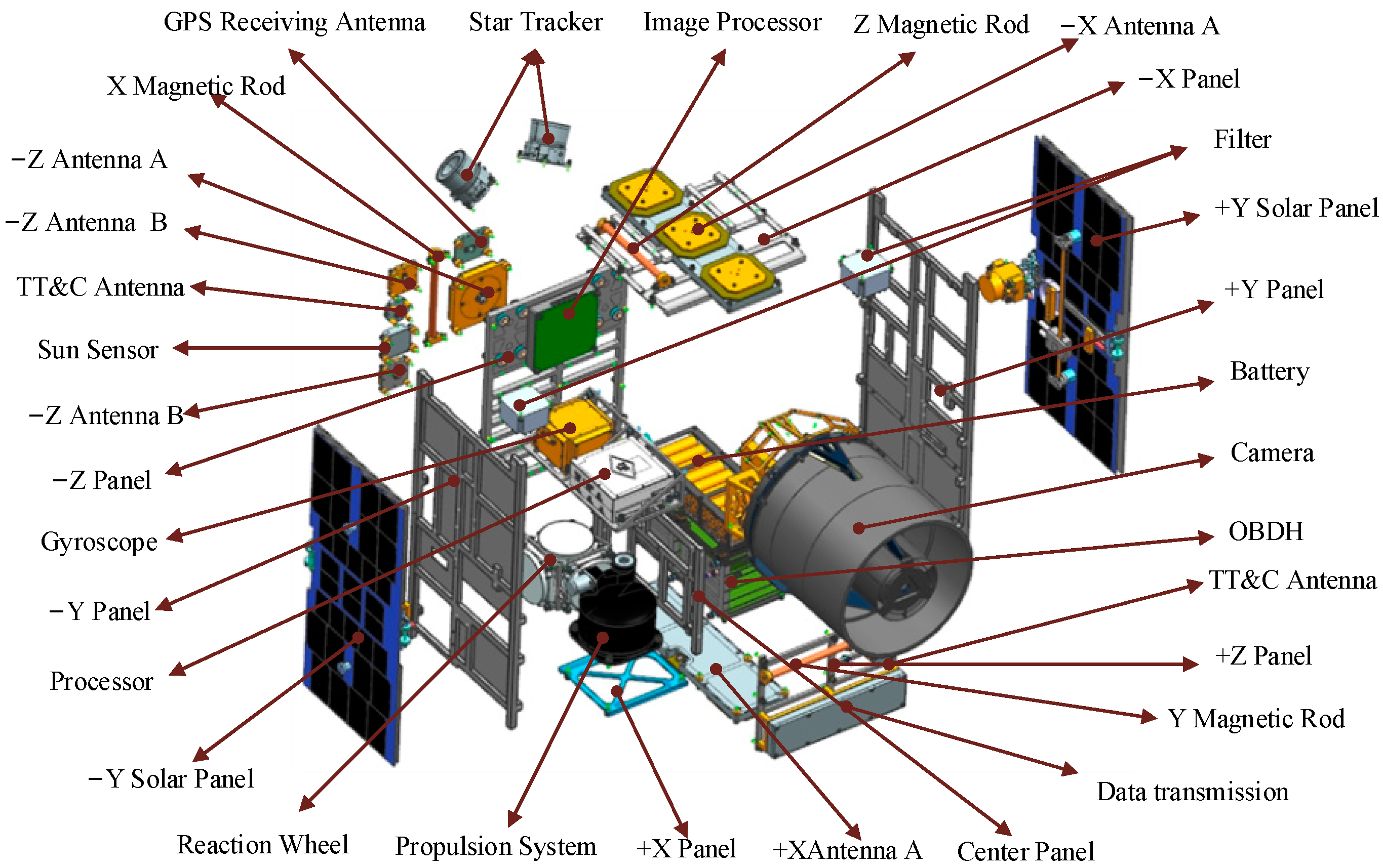
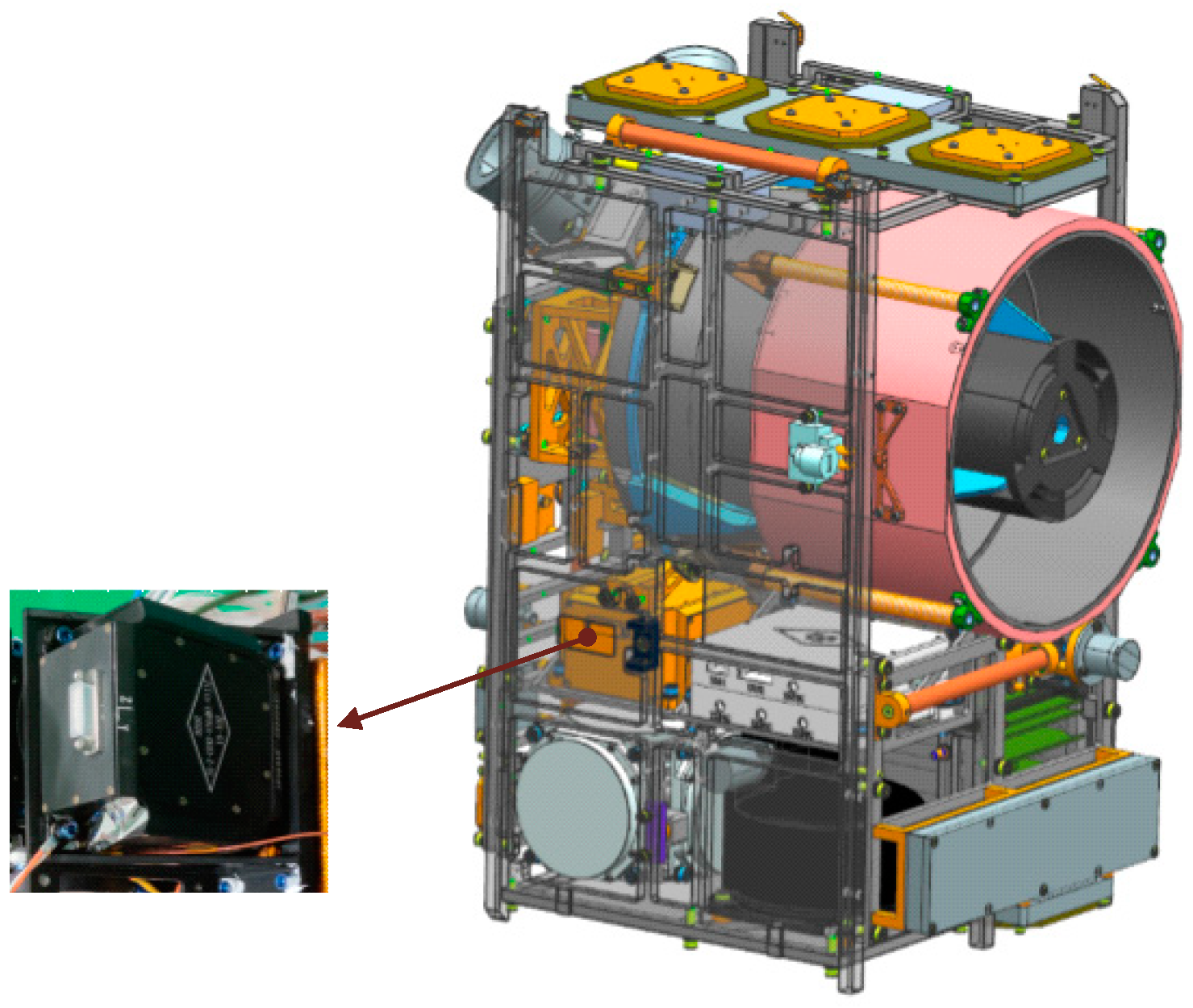
2.1. Satellite Description
2.2. Separation Mechanism Design Requirements
3. Design of the Separation Mechanism
3.1. Overall Design
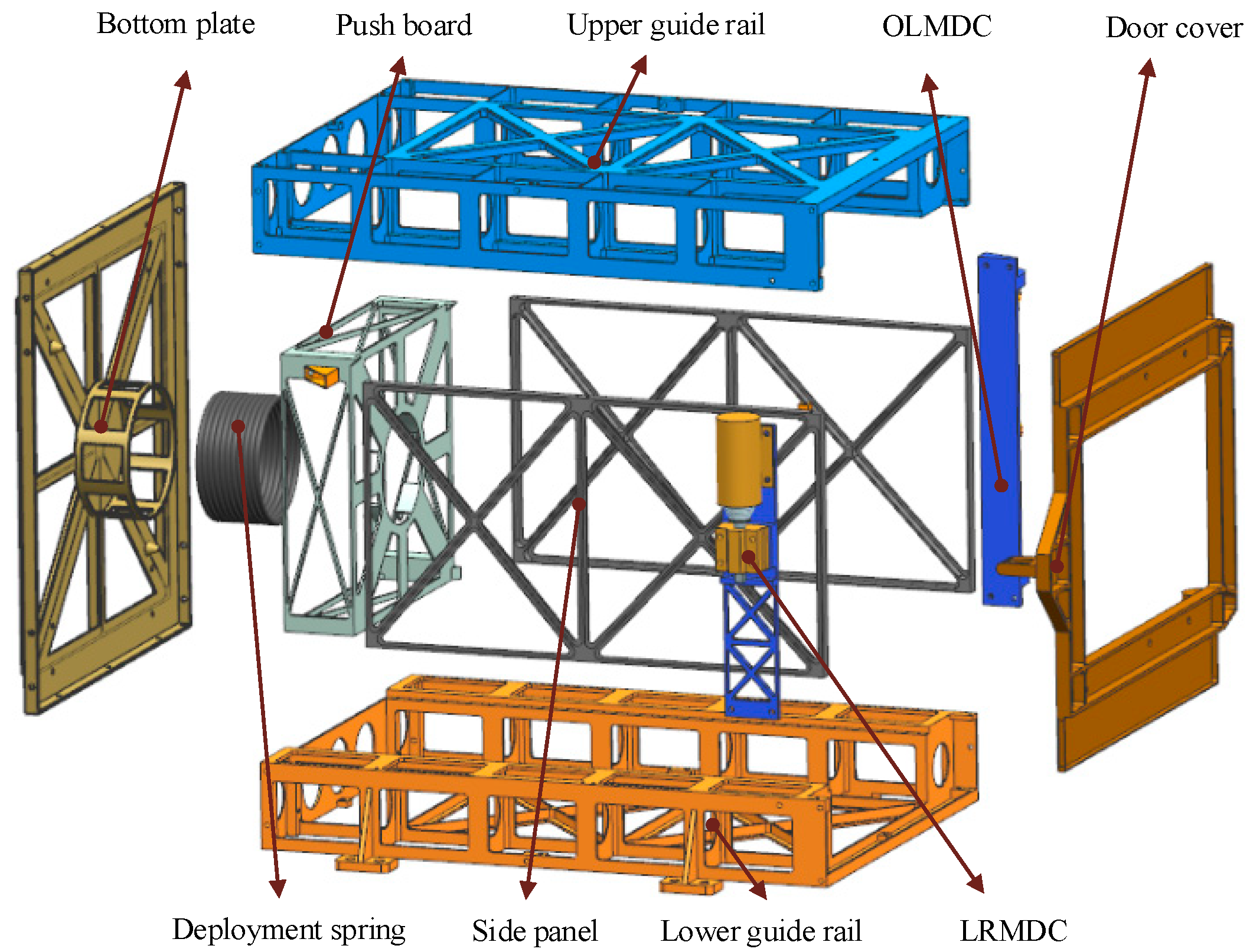
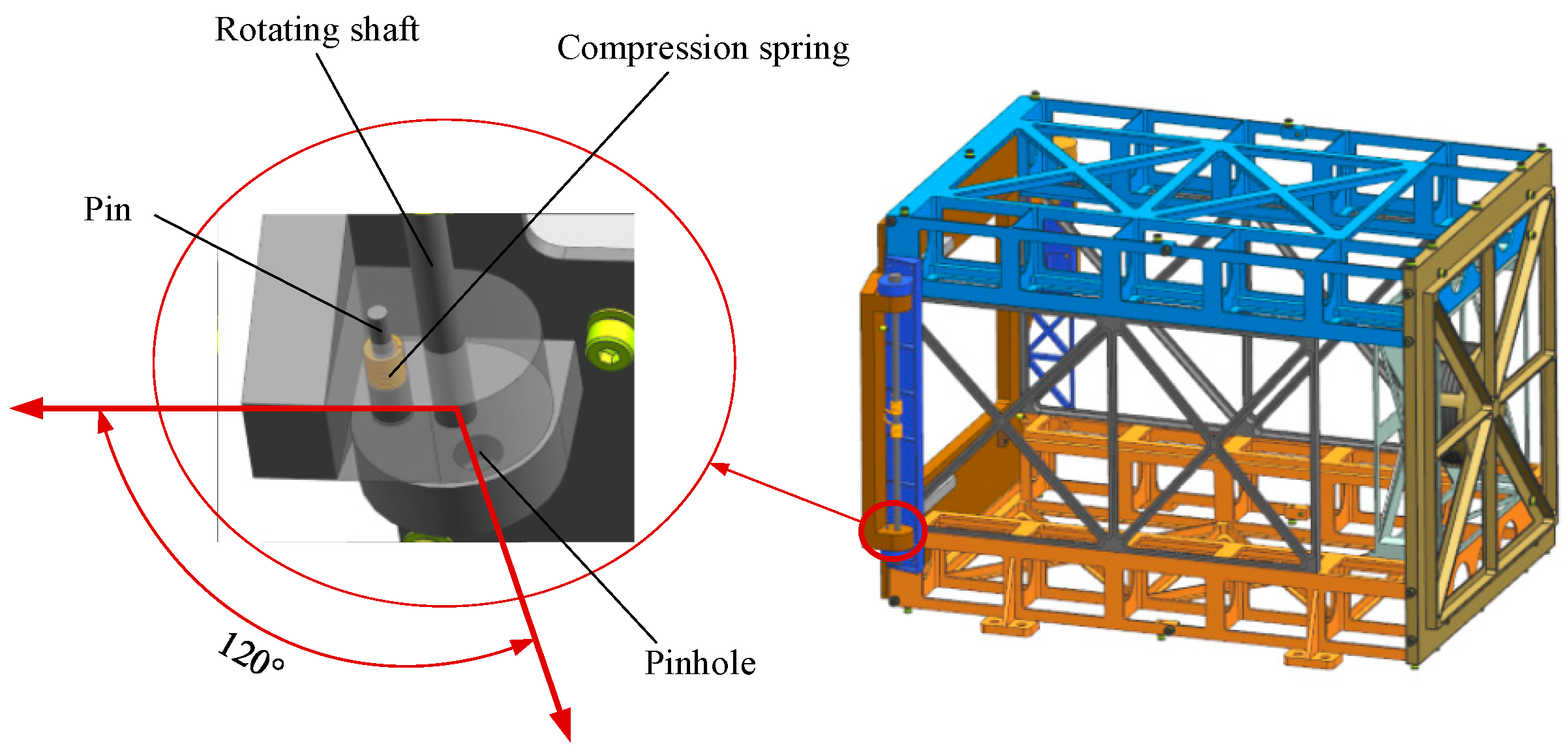
3.2. Mechanism Design
- Ejection system
- k—stiffness coefficient of the deployment spring;
- —maximum displacement of the deployment spring;
- —mass of the MF satellite;
- —initial ejecting velocity of the MF satellite.
- H0—free height of the deployment spring;
- D—mean diameter of the deployment spring.
- G—shear modulus of the deployment spring material;
- —mean diameter of the deployment spring;
- —active coil number of the deployment spring;
- —wire diameter of the deployment spring.
- OLMDC
4. Analysis
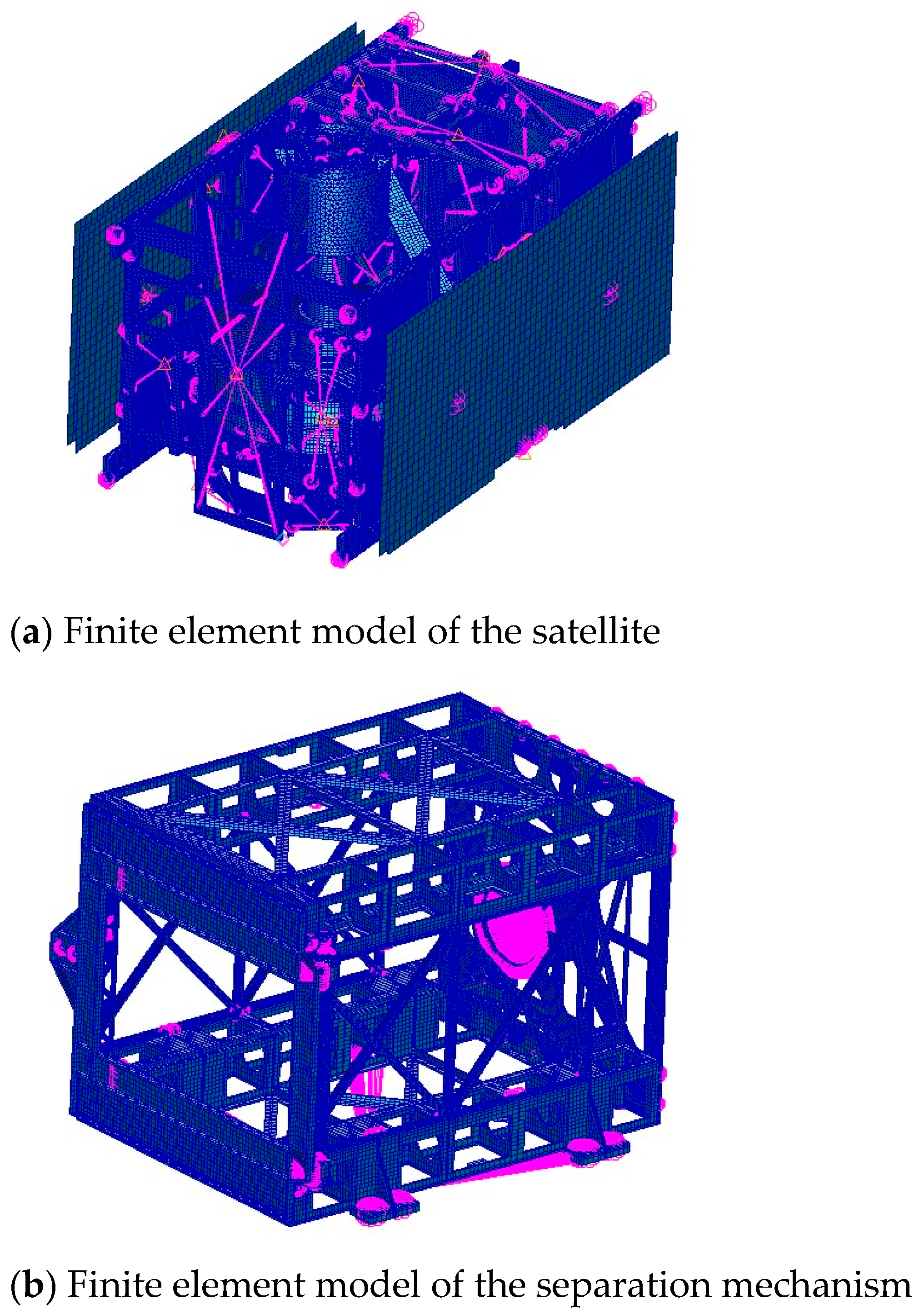
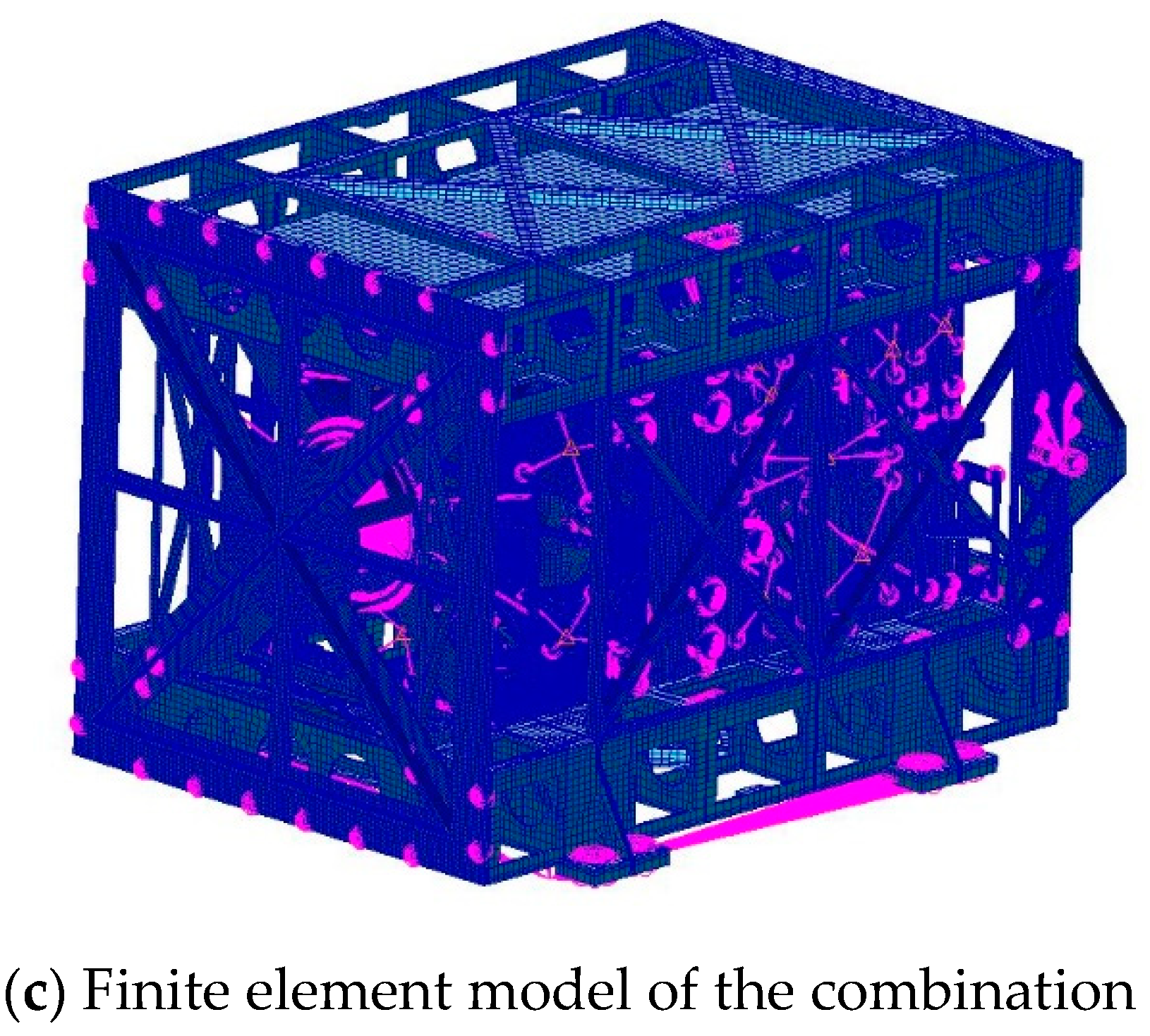
4.1. Model Description
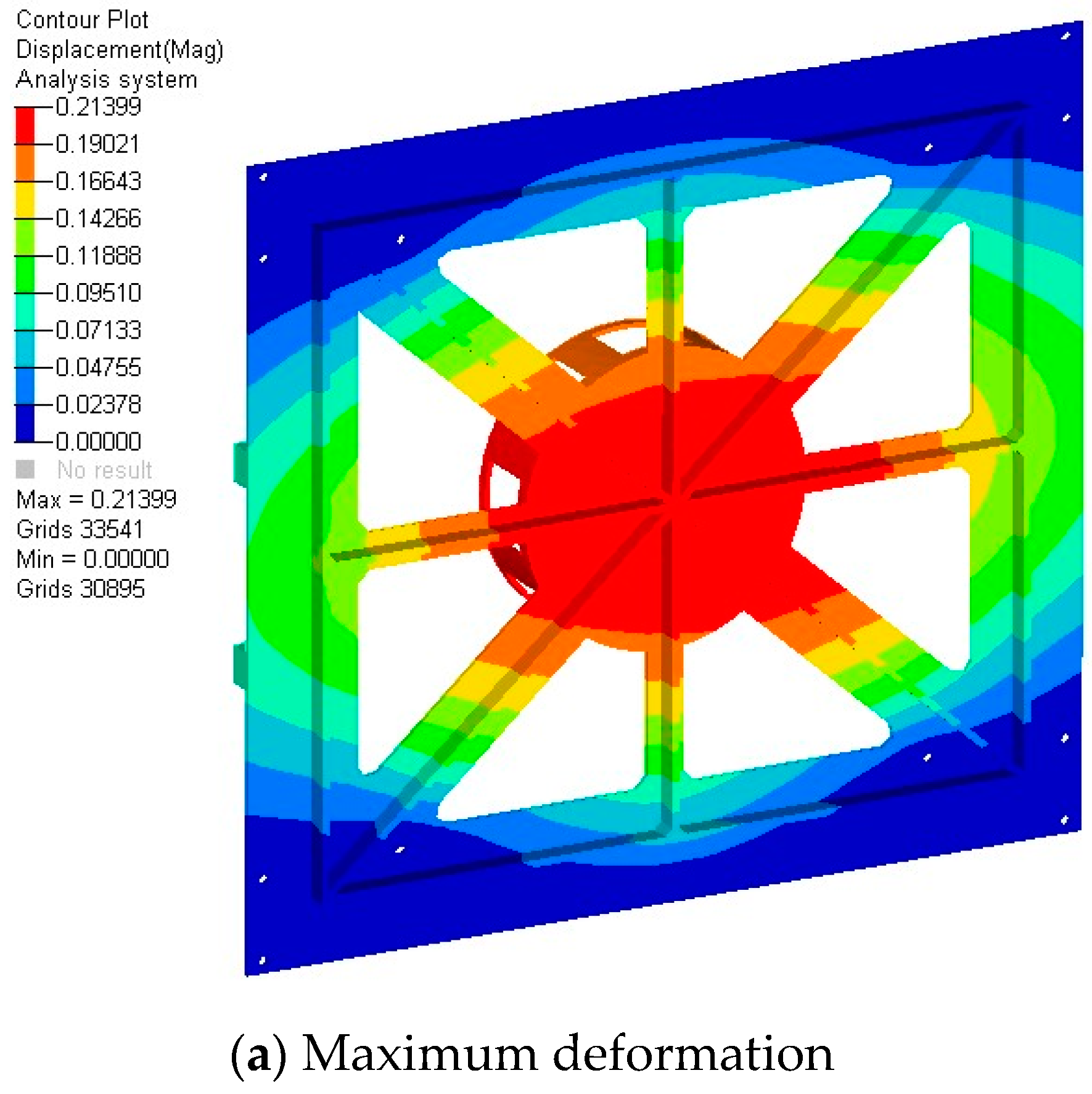
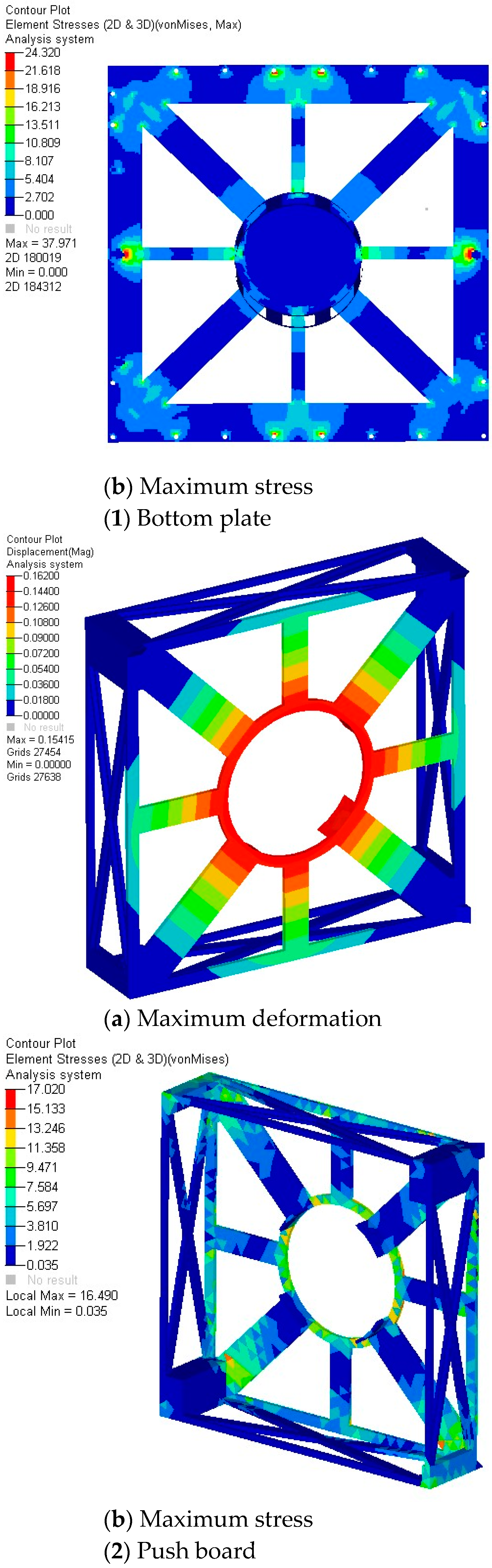
4.2. Quasi-Static Acceleration Analysis
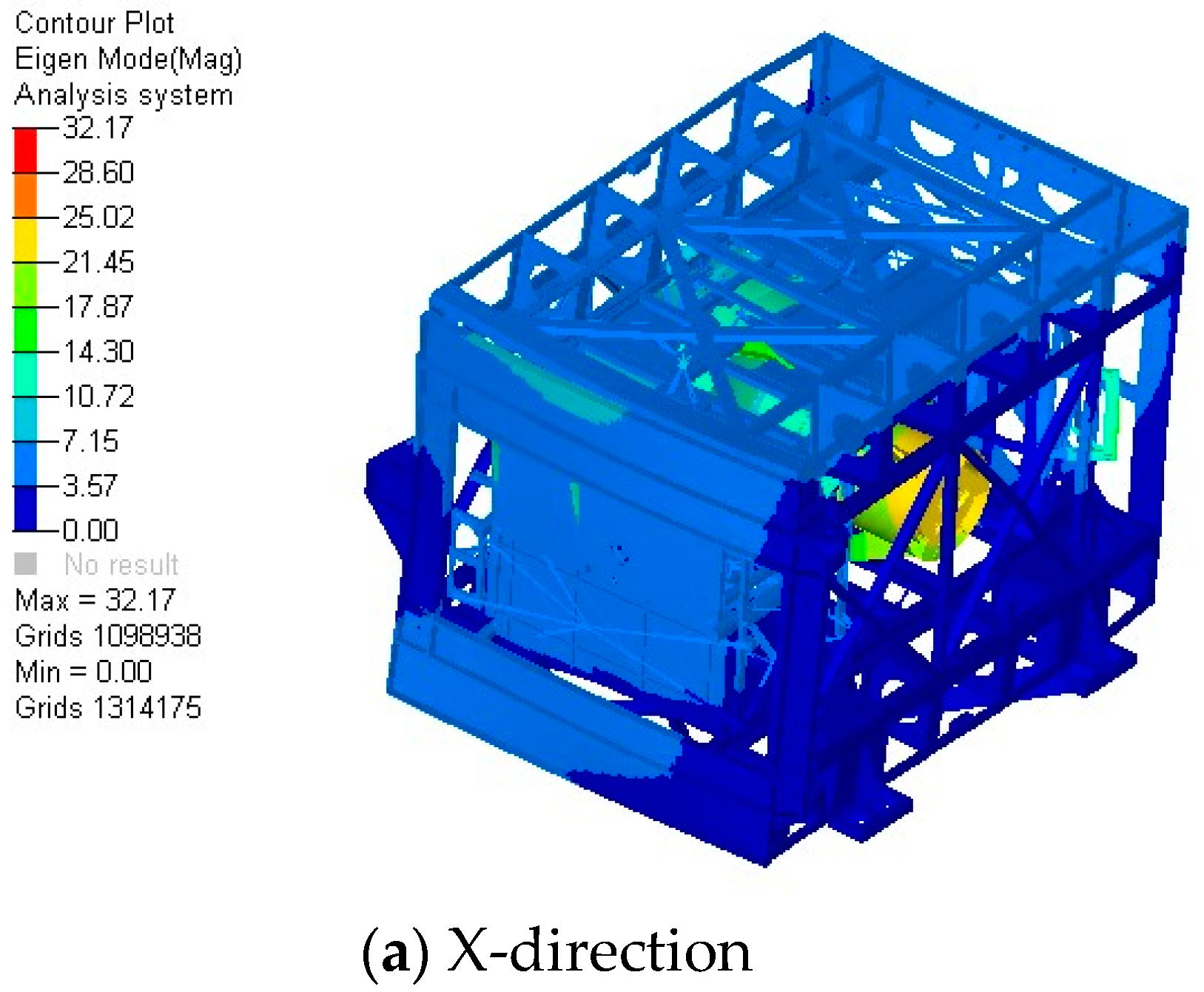
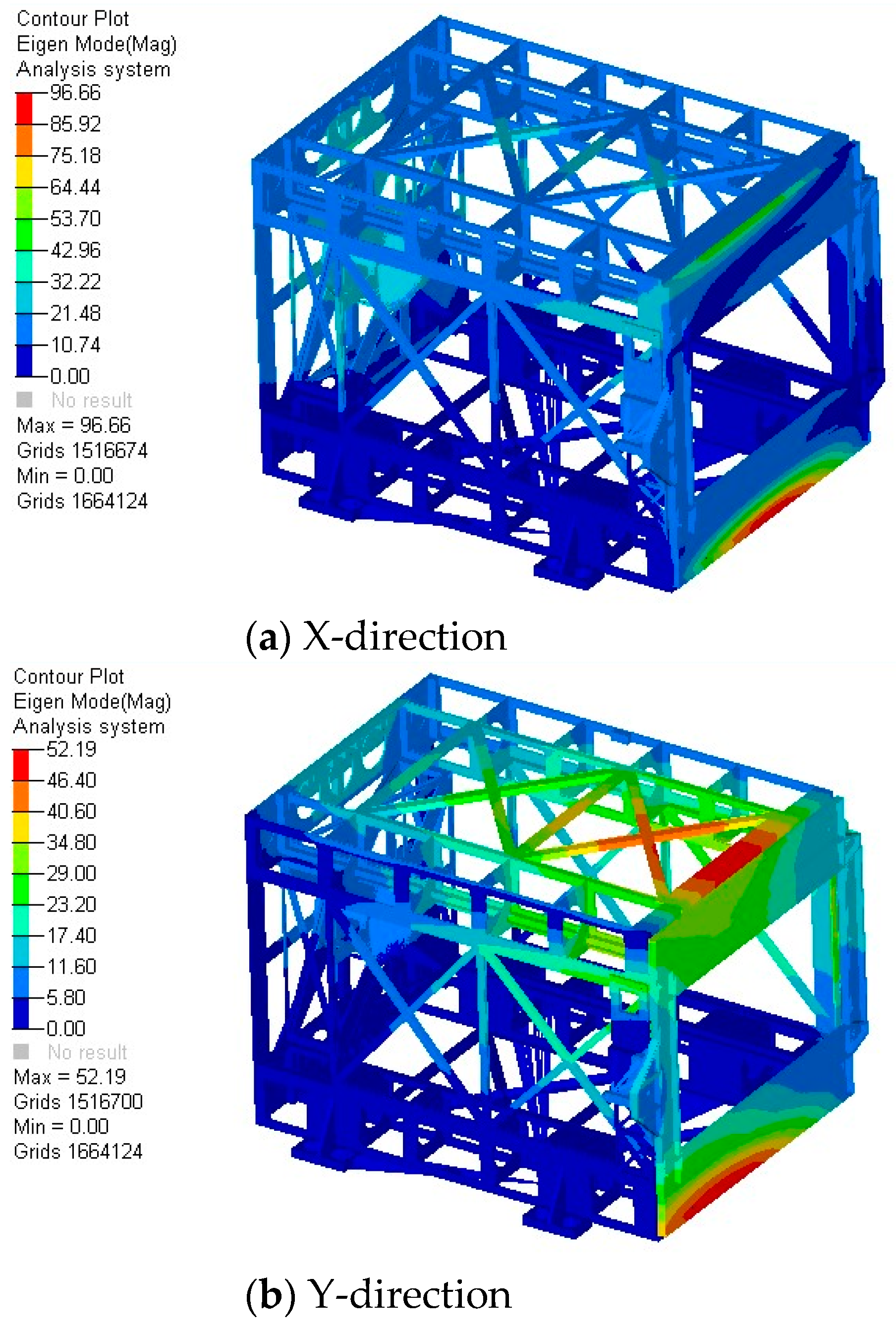
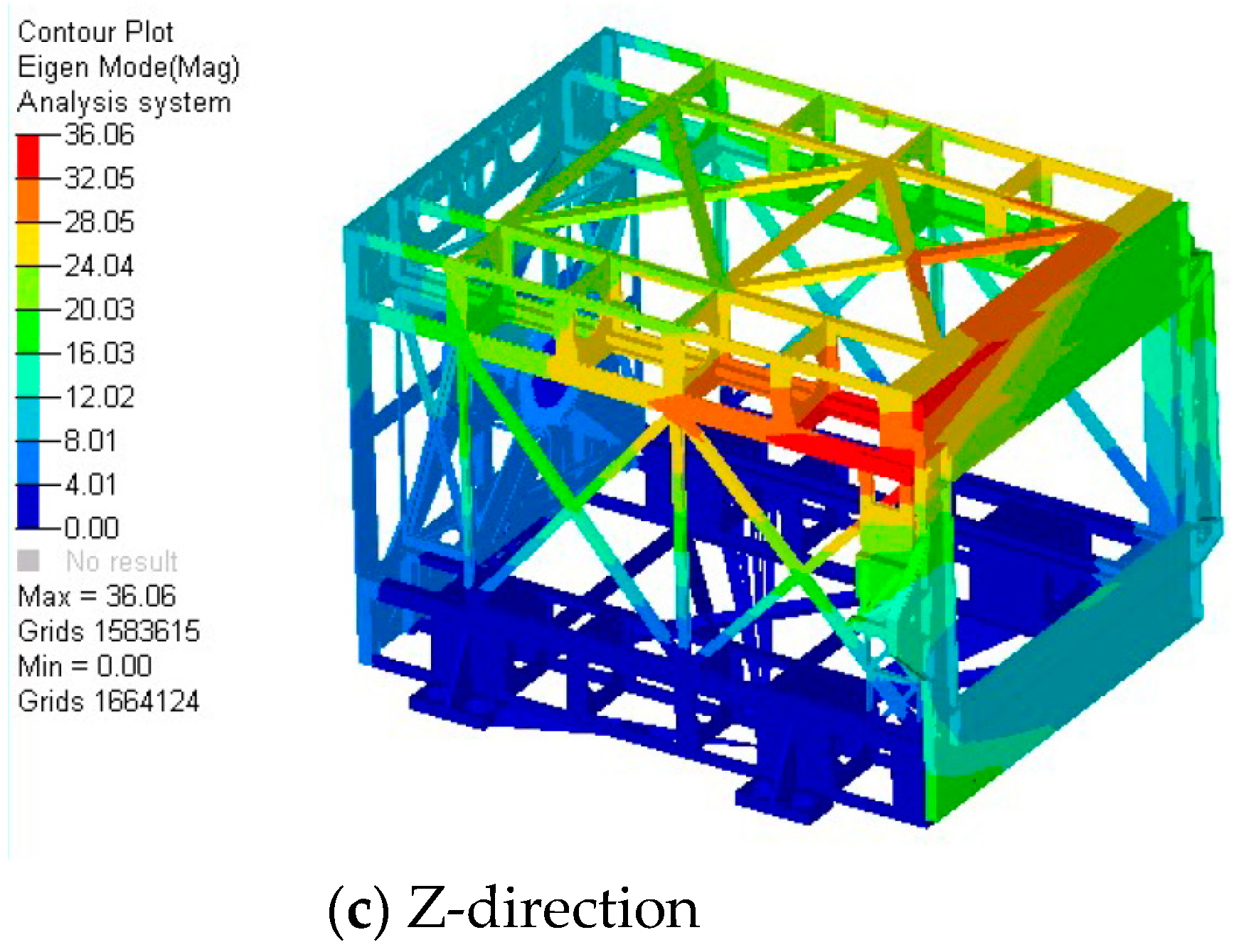
4.3. Modal Analysis
4.4. Random Vibration Analysis
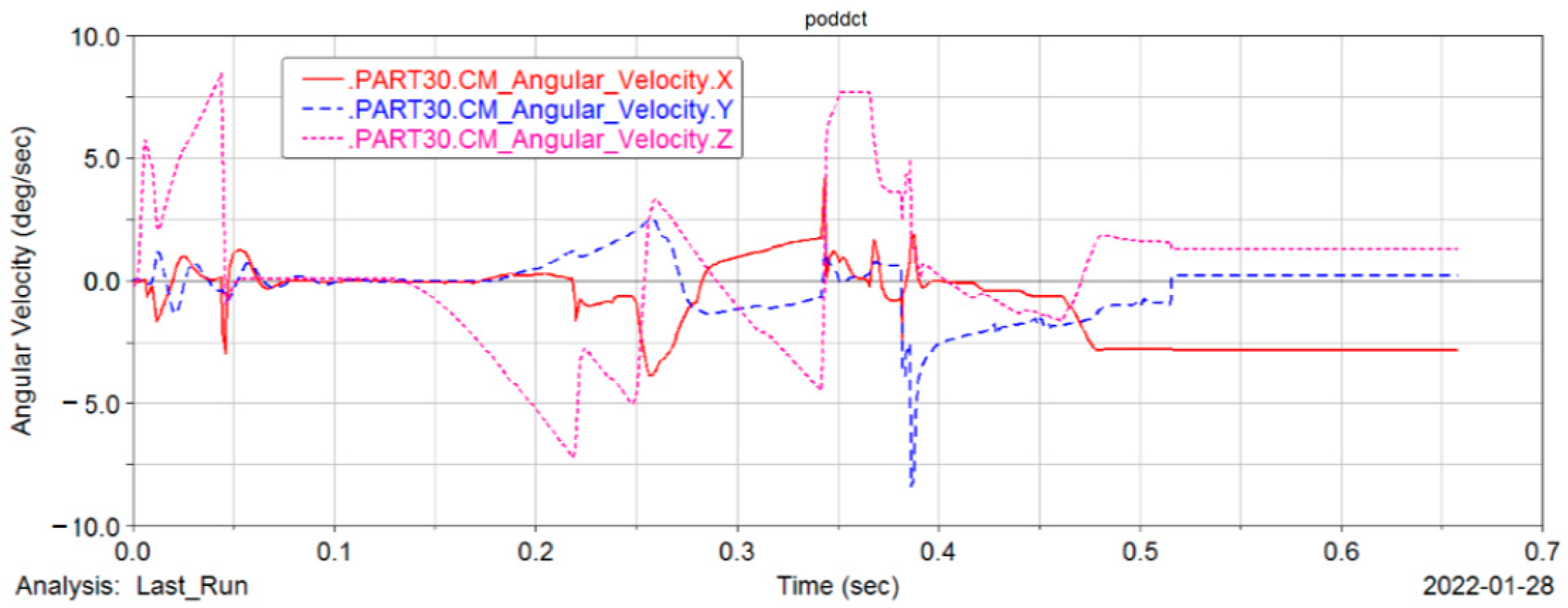
4.5. Kinematic Analysis
- Ejecting velocity
- Ejecting angular velocity
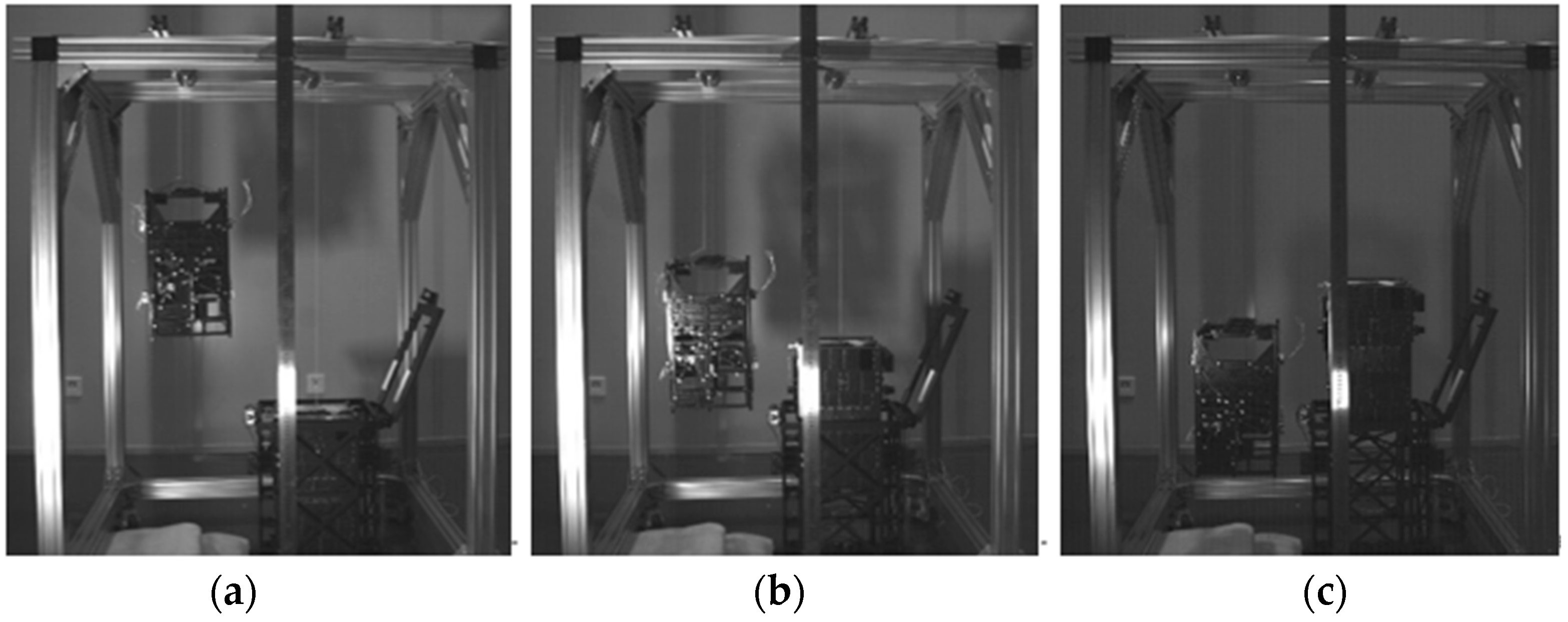
5. Experimental Verification
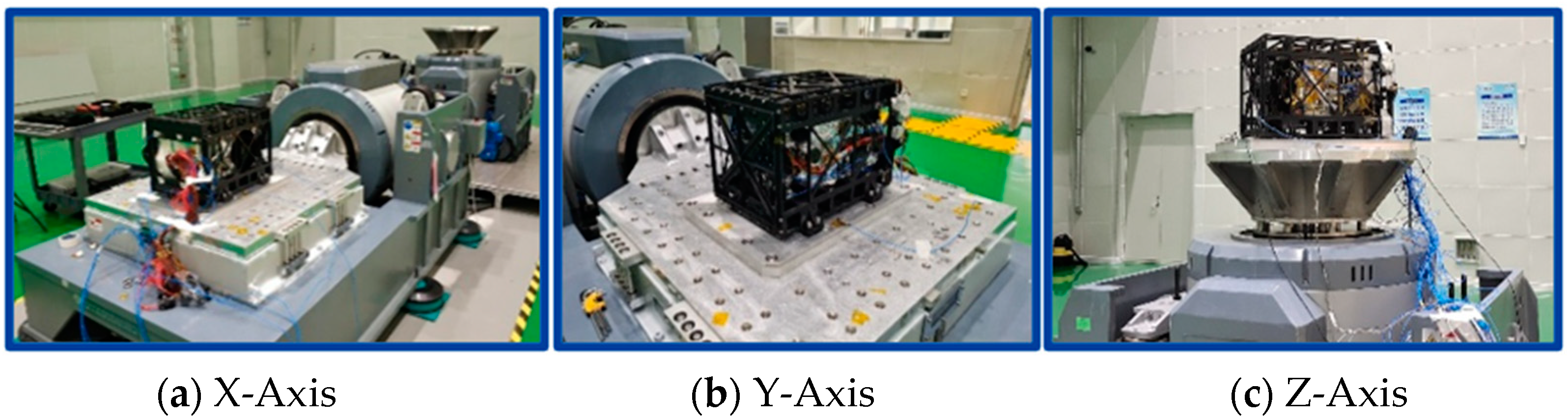
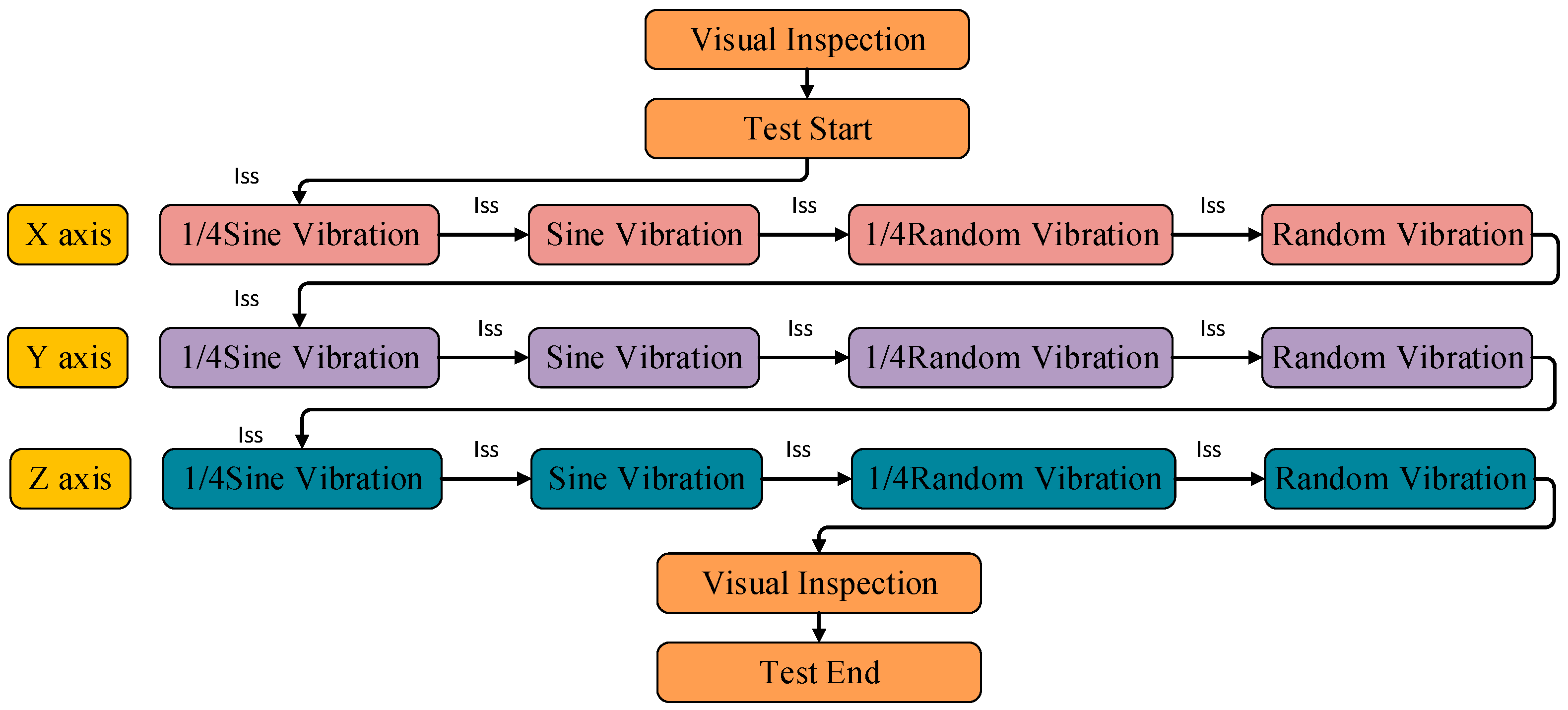
5.1. Vibration Test
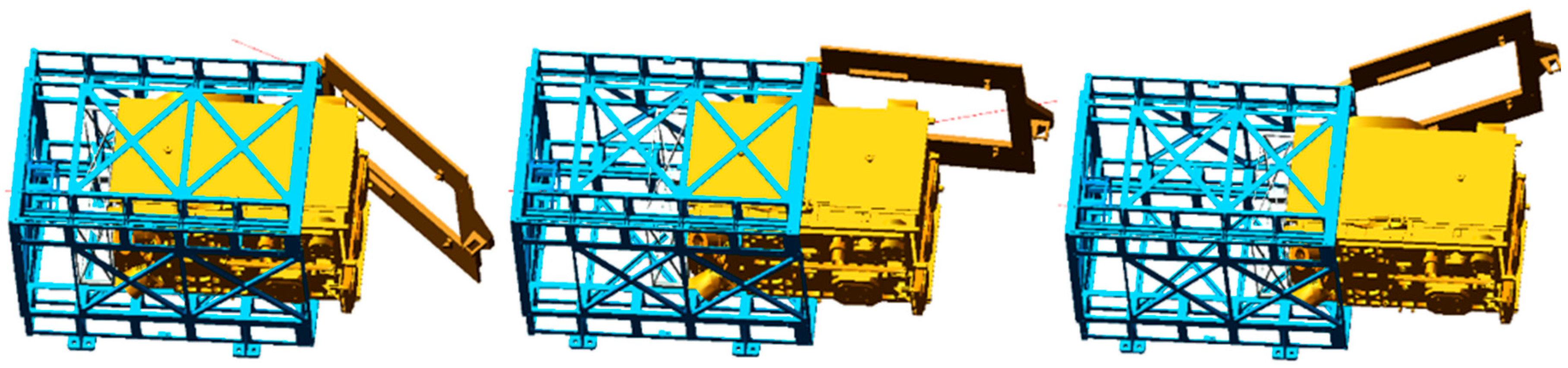
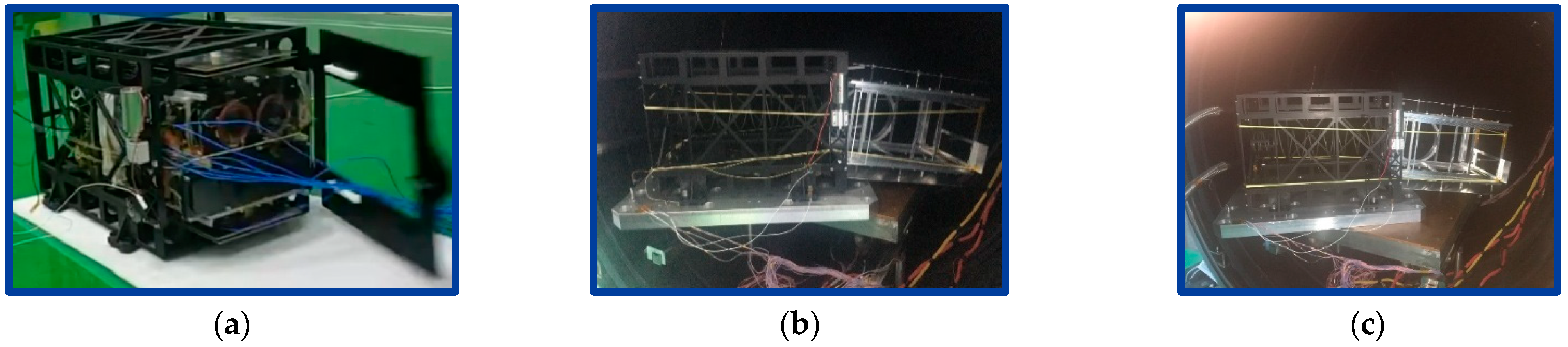
5.2. Separation Test
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nieto-Peroy, C.; Emami, M.R. CubeSat Mission: From Design to Operation. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, O.-J.; Shim, H.; Yu, S.; Bae, Y.; Kee, C.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.; Han, J.; Han, S.; Choi, Y. In-Orbit Results and Attitude Analysis of the Snuglite Cube-Satellite. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, P.; Wu, C.; Chen, K.; Ren, W.; Liu, L.; Tang, Y.; Ji, C.; Sang, X. SIASAIL-I Solar Sail: From System Design to On-Orbit Demonstration Mission. Acta Astronaut. 2022, 192, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, S.; Go, J.-S.; Oh, H.-U. Experimental Cansat Platform for Functional Verification of Burn Wire Triggering-Based Holding and Release Mechanisms. Aerospace 2021, 8, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, S.; Go, J.-S.; Kim, H.; Oh, H.-U. Development of a Novel Deployable Solar Panel and Mechanism for 6U CubeSat of STEP Cube Lab-II. Aerospace 2021, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Song, C.-M.; Lee, S.-H.; Song, S.-C.; Oh, H.-U. Design and Performance of X-Band SAR Payload for 80 kg Class Flat-Panel-Type Microsatellite Based on Active Phased Array Antenna. Aerospace 2022, 9, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, L.; Jin, Z. Structural Performance Optimization and Verification of an Improved Thin-Walled Storage Tank for a Pico-Satellite. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teng, L.; Yang, H.; Jin, Z. Novel Measurement Method for Determining Mass Characteristics of Pico-Satellites. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, S.-C.; Son, J.-H.; Song, S.-C.; Park, J.-H.; Koo, K.-R.; Oh, H.-U. Innovative Mechanical Design Strategy for Actualizing 80 kg-Class X-Band Active SAR Small Satellite of S-STEP. Aerospace 2021, 8, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoolcraft, J.; Klesh, A.; Werne, T. MarCO: Interplanetary Mission Development on a CubeSat Scale. In Space Operations: Contributions from the Global Community; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017; pp. 221–231. [Google Scholar]
- Poghosyan, A.; Golkar, A. CubeSat evolution: Analyzing CubeSat Capabilities for Conducting Science Missions. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2017, 88, 59–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.; Crisp, N.; Hollingsworth, P. Launch and Deployment of Distributed Small Satellite Systems. In Proceedings of the 65th International Astronautical Congress (IAC), Toronto, ON, Canada, 29 September–3 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrparvar, A.; Carnahan, J. CubeSat Design Specification Revision 13. In The CubeSat Program; California Polytechnic State University: San Luis Obispo, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Morettini, G.; Zucca, G.; Braccesi, C.; Cianetti, F.; Dionigi, M. CubeSat Spatial Expedition: An Overview from Design to Experimental Verification. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1038, 012026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashida, H.; Fujihashi, K.; Inagawa, S.; Miura, Y.; Omagari, K.; Miyashita, N.; Matunaga, S.; Toizumi, T.; Kataoka, J.; Kawai, N. Design of Tokyo Tech nano-satellite Cute-1.7+ APD II and its operation. Acta Astronaut. 2010, 66, 1412–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capovilla, G.; Cestino, E.; Reyneri, L.M.; Romeo, G. Modular Multifunctional Composite Structure for CubeSat Applications: Preliminary Design and Structural Analysis. Aerospace 2020, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.-J.; Lee, Y.-K.; Oh, H.-U. Performance Evaluation of Hinge Driving Separation Nut-Type Holding and Releasing Mechanism Triggered by Nichrome Burn Wire. Int. J. Aeronaut. Space Sci. 2015, 16, 602–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, H.-S.; Kim, B.; Choi, J.-W. A Compact Non-explosive Separation Device for High Preload and Low Shock. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2014, 15, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Hao, D.; Gong, W. Design and Analysis of an Integrated Device for Launch Adapter and Resettable Orbital Deployer for Picosatellites. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part G J. Aerosp. Eng. 2020, 234, 818–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Xu, Y.; Fu, J.; Wu, C.; Chen, Z. Kinematic System Design of the Pico-Satellite Separation Mechanism. J. Astronaut. 2014, 35, 626–632. [Google Scholar]
- Grimm, C.D.; Lange, C.; Lange, M.; Mierheim, O.; Witte, L.; Sasaki, K.; Chand, S.; Ksenik, E.; Grundmann, J.-T.; Ho, T.-M. The MASCOT Separation Mechanism. CEAS Space J. 2020, 12, 343–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glücksberg, A.; Soul, H.; Yawny, A. Releasing Systems for Aerospace Industry Based upon Shape Memory Alloys: Characterization of Materials for Actuators. Matéria 2018, 23, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nohmi, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Itose, O.; Saitou, J. Rocket Separation Mechanism for Pico Mother and Daughter satellite “KUKAI”. J. Syst. Des. Dyn. 2010, 4, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Li, X.; Sun, Y. The Shock Response Prediction of Spacecraft Structure Based on Hybrid FE-SEA Method. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Tu, H.; Dong, H.; Yan, N. Separation Reliability Analysis for the Low-Shock Separation Nut with Mechanism Motion Failure Mode. Aerospace 2022, 9, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honghao, Y.; Yifei, Y.; Yifan, L.; Fei, Y.; Jun, W.; Qi, R.; Zongquan, D. Research Progress of Space Non-Pyrotechnic Low-Shock Connection and Separation Technology (SNLT): A review. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2021; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.; Munakata, R. Dnepr 2 Satellite Identification and the Mk. III P-POD. In Proceedings of the CubeSat Developers’ Workshop, San Luis Obispo, CA, USA, 10 April 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Q.; Jiang, M.; Qi, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. The Design and Analysis of Picosatellite Orbital Deployer Based on Shape Memory Alloy Release. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Computer Systems, Electronics and Control (ICCSEC), Dalian, China, 25–27 December 2017; pp. 1689–1694. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M. Design and Implementation of Ground Support Equipment for Characterizing the Performance of XPOD and CNAPS & Thermal Analysis of CNAPS Pressure Regulator Valve; University of Toronto: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Akagi, H.; Takata, M.; Watanabe, H.; Sano, T.; Oikawa, K. Kibo’s Contribution to Broadening the Possibilities for Micro-Satellite. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Space Operations, Daejeon, Korea, 16–20 May 2016; p. 2517. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrowolski, M.; Grygorczuk, J.; Kedziora, B.; Tokarz, M.; Borys, M. DRAGON-8U Nanosatellite Orbital Deployer. In Proceedings of the 42nd Aerospace Mechanism Symposium, Baltimore, MD, USA; 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Roemer, S.; Stoltz, S. SPL Light Weight Deployment Mechanism for Single CubeSats and DPL for double CubeSats. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Small Satellite Systems and Services (4S), Funchal, Madeira, Portugal, 31 May–4 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Aslan, A.R.; Bernal, C.; Puig-Suari, J. I-4b: Deployment Systems. In Nanosatellites Space and Ground Technologies, Operations and Economics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 375–397. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Development of the New Approach of Formation Initialization Using Spring Separation Mechanism Considering J2 Perturbation. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 55, 2616–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, S.R.; Sahay, D.; Sandya, S.; Sandeep, G.; Nikhilesh, K. Design and Development of Inter-Satellite Separation Mechanism for Twin Nano Satellite—STUDSAT-2. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Sky, MT, USA, 5–12 March 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Puig-Suari, J.; Turner, C.; Ahlgren, W. Development of the Standard CubeSat Deployer and a CubeSat class PicoSatellite. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Aerospace Conference Proceedings (Cat. No. 01TH8542), Sky, MT, USA, 10–17 March 2001; Volume 341, pp. 1, 341–347, 353. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.-K.; Kim, G.-N.; Park, S.-Y. Novel Structure and Thermal Design and Analysis for CubeSats in Formation Flying. Aerospace 2021, 8, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| NO | Index Name | Index Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Structural parameters | Size (mm) | ≤400 × 500 × 550 |
| Mass (kg) | ≤6 | ||
| 2 | Separation attitude | Separation velocity (m/s) | 0.5–2 |
| Separation angular velocity(°/s) | ≤3 | ||
| 3 | Natural frequency | 3 axis (Hz) | ≥50 |
| 4 | Overload | Lateral direction(g) | 3 |
| Vertical direction(g) | 10 | ||
| Location | Maximum Deformation | Maximum Stress | Failure Stress | Safety Coefficient | Safety Margin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bottom plate | 0.214 mm | 24.3 MPa | 410 MPa | 2.0 | 7.4 |
| Push board | 0.162 mm | 17 MPa | 410 MPa | 2.0 | 11.1 |
| Young’s Modulus (MPa) | Poisson’s Ratio | Density (kg/mm3) | Failure Stress (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 70,000 | 0.33 | 2.7 | 410 MPa |
| No | Frequency (Hz) | Mode Shape |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 77.7 | X-Direction |
| 2 | 70.8 | Y-Direction |
| 3 | 82.6 | Z-Direction |
| No | Frequency (Hz) | Mode Shape |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 243.6 | X-Direction |
| 2 | 168.8 | Y-Direction |
| 3 | 116.5 | Z-Direction |
| Frequency (Hz) | Acceptance Conditions | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Spectrum Density (g2/Hz) | Total RMS of Acceleration (g) | ||
| Value | 20~150 | +3 dB/oct | 7.19 |
| 150~280 | 0.04 | ||
| 280~320 | 0.15 | ||
| 320~380 | 0.10 | ||
| 380~850 | 0.05 | ||
| 850~1000 | 0.02 | ||
| 1000~2000 | 0.005 | ||
| Direction | 3 directions | ||
| Time | 1 min for each direction | ||
| No. | Location | X-Response/grms | Y-Response/grms | Z-Response/grms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | Camera mounting point | 4.3 | 5.6 | 6.3 |
| A2 | Camera backplate | 4.2 | 5.0 | 5.7 |
| A3 | Primary mirror of the camera | 3.7 | 5.1 | 5.5 |
| A4 | Secondary mirror of the camera | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.6 |
| A5 | OBHD | 4.9 | 4.4 | 5.4 |
| A6 | Solar panel | 5.6 | 9.3 | 11.6 |
| B1 | Cover door | 14.9 | 8.7 | 12.0 |
| B2 | Side panel | 6.5 | 4.6 | 12.1 |
| Direction | X | Y | Z | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st mode natural frequency | Numerical analysis | 77.7 | 70.8 | 82.6 |
| First Iss test | 71.3 | 63.9 | 78.4 | |
| Final Iss test | 72.1 | 62.8 | 72.7 | |
| Natural frequency change | Numerical analysis/First ISS test | −8.2% | −9.7% | −5.1% |
| First/Final Iss test | +1.1% | −1.8% | −7.2% | |
| No. | Location | X-Response/grms | Y-Response/grms | Z-Response/grms | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analysis | Test | Analysis | Test | Analysis | Test | ||
| A1 | Camera mounting point | 4.3 | 2.2 | 5.6 | 2.6 | 6.3 | 3.1 |
| A2 | Camera backplate | 4.2 | 2.1 | 5.0 | 1.6 | 5.7 | 2.1 |
| A3 | Primary mirror of the camera | 3.7 | 1.6 | 5.1 | 2.1 | 5.5 | 1.8 |
| A4 | Secondary mirror of the camera | 5.5 | 4.2 | 5.5 | 2.1 | 5.6 | 5.6 |
| A5 | OBHD | 4.9 | 2.9 | 4.4 | 1.9 | 5.4 | 2.3 |
| A6 | Solar panel | 5.6 | 4.2 | 9.3 | 7.3 | 11.6 | 11.7 |
| B1 | Cover door | 14.9 | 15.4 | 8.7 | 8.4 | 12.0 | 11.5 |
| B2 | Side panel | 6.5 | 6.7 | 4.6 | 4.2 | 12.1 | 12.8 |
| No | X (°/s) | Y (°/s) | Z (°/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.09 | 0.32 | 0.58 |
| 2 | 0.15 | 0.35 | 0.57 |
| 3 | 0.13 | 0.30 | 0.61 |
| 4 | 0.11 | 0.33 | 0.63 |
| 5 | 0.08 | 0.39 | 0.59 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.; Zhao, C.; Li, J.; Guan, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, L. Research on Design, Simulation, and Experiment of Separation Mechanism for Micro-Nano Satellites. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5997. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12125997
Zhao X, Zhao C, Li J, Guan Y, Chen S, Zhang L. Research on Design, Simulation, and Experiment of Separation Mechanism for Micro-Nano Satellites. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(12):5997. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12125997
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xiangyu, Chunjuan Zhao, Jiale Li, Yongliang Guan, Shanbo Chen, and Lei Zhang. 2022. "Research on Design, Simulation, and Experiment of Separation Mechanism for Micro-Nano Satellites" Applied Sciences 12, no. 12: 5997. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12125997
APA StyleZhao, X., Zhao, C., Li, J., Guan, Y., Chen, S., & Zhang, L. (2022). Research on Design, Simulation, and Experiment of Separation Mechanism for Micro-Nano Satellites. Applied Sciences, 12(12), 5997. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12125997






