Injectable Synthetic Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate/Calcium Sulfate (GeneX) for the Management of Contained Defects Following Curettage of Benign Bone Tumours
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, C.J.; Brien, E.W. Early postoperative compilations of bone filling in curettage defects. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2019, 14, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goulet, J.A.; Senunas, L.E.; DeSilva, G.L.; Greenfield, M.L. Autogenous iliac crest bone graft. Complications and functional assessment. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1997, 339, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Graham, S.M.; Leonidou, A.; Aslam-Pervez, N.; Hamza, A.; Panteliadis, P.; Heliotis, M.; Mantalaris, A.; Tsiridis, E. Biological therapy of bone defects: The immunology of bone allo-transplantation. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2010, 10, 885–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeets, R.; Kolk, A.; Gerressen, M.; Driemel, O.; Maciejewski, O.; Hermanns-Sachweh, B.; Riediger, D.; Stein, J.M. A new biphasic osteoinductive calcium composite material with a negative Zeta potential for bone augmentation. Head Face Med. 2009, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gava, N.F.; Engel, E.E. Treatment alternatives and clinical outcomes of bone filling after benign tumour curettage. A systematic review. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2022, 108, 102966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogose, A.; Hotta, T.; Kawashima, H.; Kondo, N.; Gu, W.; Kamura, T.; Endo, N. Comparison of hydroxyapatite and beta tricalcium phosphate as bone substitutes after excision of bone tumors. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2005, 72, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A.C.; Smith, J.K.; Courtney, H.S.; Haggard, W.O. Evaluation of two sources of calcium sulfate for a local drug delivery system: A pilot study. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2011, 469, 3008–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hung, Y.W.; Ko, W.S.; Liu, W.H.; Chow, C.S.; Kwok, Y.Y.; Wong, C.W.; Tse, W.L.; Ho, P.C. Local review of treatment of hand enchondroma (artificial bone substitute versus autologous bone graft) in a tertiary referral centre: 13 years’ experience. Hong Kong Med. J. 2015, 21, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galois, L.; Mainard, D.; Delagoutte, J.P. Beta-tricalcium phosphate ceramic as a bone substitute in orthopaedic surgery. Int. Orthop. 2002, 26, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirata, M.; Murata, H.; Takeshita, H.; Sakabe, T.; Tsuji, Y.; Kubo, T. Use of purified beta-tricalcium phosphate for filling defects after curettage of benign bone tumours. Int. Orthop. 2006, 30, 510–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, H.; Kim, S.; Chung, S.H. Clinical Outcome of Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate Use for Bone Defects after Operative Treatment of Benign Tumors. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2019, 11, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholas, R.W.; Lange, T.A. Granular tricalcium phosphate grafting of cavitary lesions in human bone. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1994, 306, 197–203. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Oh, J.H.; Han, I.; Kim, H.S.; Chung, S.W. Grafting using injectable calcium sulfate in bone tumor surgery: Comparison with demineralized bone matrix-based grafting. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2011, 3, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, L.J.; Clayer, M. Aqueous calcium sulphate as bone graft for voids following open curettage of bone tumours. ANZ J. Surg. 2013, 83, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.; Xiao, L.; Fu, H.; Bi, D.; Ma, H.; Tong, P. Study on injectable and degradable cement of calcium sulphate and calcium phosphate for bone repair. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, S.; Hannink, G. Injectable bone-graft substitutes: Current products, their characteristics and indications, and new developments. Injury 2011, 42 (Suppl. S2), S30–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillingham, Y.A.; Lenart, B.A.; Gitelis, S. Function after injection of benign bone lesions with a bioceramic. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2012, 470, 2014–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, V.; Evaniew, N.; Finlay, K.; Jurriaans, E.; Ghert, M.; Deheshi, B.; Parasu, N. Chronology of the Radiographic Appearances of the Calcium Sulfate-Calcium Phosphate Synthetic Bone Graft Composite Following Resection of Bone Tumors: A Follow-up Study of Postoperative Appearances. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2016, 67, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesenbichler, J.; Maurer-Ertl, W.; Sadoghi, P.; Pirker-Fruehauf, U.; Bodo, K.; Leithner, A. Adverse reactions of artificial bone graft substitutes: Lessons learned from using tricalcium phosphate geneX®. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2014, 472, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friesenbichler, J.; Maurer-Ertl, W.; Sadoghi, P.; Pirker-Fruehauf, U.; Bodo, K.; Leithner, A. Reply to the Letter to the Editor: Adverse reactions of artificial bone graft substitutes: Lessons learned from using tricalcium phosphate geneX®. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2014, 472, 767–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lowery, K.; Chaturvedi, A.; Blomfield, M.; Sharma, H. Effectiveness of the management of bony articular collapse with bony defects in tibial plateau fractures with the use of GeneX: An absorbable calcium composite synthetic bone graft. J. Limb Lengthen. Recon. 2018, 4, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, W.C.; Jang, J.H.; Jeong, J.Y.; Suh, K.T.; Moon, N.H. Effect of a synthetic osteoconductive bone graft substitute with zeta potential control (geneX®ds) in the treatment of intertrochanteric fracture: A single center experience of 115 consecutive proximal femoral nail antirotations. J. Orthop. Sci. 2019, 24, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, T.W.; Lee, E.S.; Kim, O.G.; Heo, K.S.; Shon, W.Y. Usefulness of Synthetic Osteoconductive Bone Graft Substitute with Zeta Potential Control for Intramedullary Fixation with Proximal Femur Nail Antirotation in Osteoporotic Unstable Femoral Intertrochanteric Fracture. Hip Pelvis 2021, 33, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.L.; Zhu, X.S.; Chen, L.; Chen, C.M.; Mangham, D.C.; Coulton, L.A.; Aiken, S.S. Bone healing response to a synthetic calcium sulfate/β-tricalcium phosphate graft material in a sheep vertebral body defect model. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2012, 100, 1911–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhan, B.L.; Ye, Z. Significance of percutaneous vertebroplasty with Genex in the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures. Zhongguo Gu Shang 2011, 24, 223–226. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Saadoun, S.; Macdonald, C.; Bell, B.A.; Papadopoulos, M.C. Dangers of bone graft substitutes: Lessons from using GeneX. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2011, 82, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welkerling, H.; Raith, J.; Kastner, N.; Marschall, C.; Windhager, R. Painful soft-tissue reaction to injectable Norian SRS calcium phosphate cement after curettage of enchondromas. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2003, 85, 238–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottalorda, J.; Bourelle, S. Current treatments of primary aneurysmal bone cysts. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B 2006, 15, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.Y.; Yang, S.K.; Sheppard, W.L.; Hegde, V.; Zoller, S.D.; Nelson, S.D.; Federman, N.; Bernthal, N.M. Current management of aneurysmal bone cysts. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2016, 9, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibbs, C.P., Jr.; Hefele, M.C.; Peabody, T.D.; Montag, A.G.; Aithal, V.; Simon, M.A. Aneurysmal bone cyst of the extremities. Factors related to local recurrence after curettage with a high-speed burr. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1999, 81, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walden, M.J.; Murphey, M.D.; Vidal, J.A. Incidental enchondromas of the knee. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2008, 190, 1611–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubahn, J.D.; Bachoura, A. Enchondroma of the Hand: Evaluation and Management. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2016, 24, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altay, M.; Bayrakci, K.; Yildiz, Y.; Erekul, S.; Saglik, Y. Secondary chondrosarcoma in cartilage bone tumors: Report of 32 patients. J. Orthop. Sci. 2007, 12, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.Y.; Joo, M.W.; Choi, Y.H.; Chung, Y.G.; Park, C.J. Simple curettage and allogeneic cancellous bone chip impaction grafting in solitary enchondroma of the short tubular bones of the hand. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvai, A.; Unni, K.K. Premalignant conditions of bone. J. Orthop. Sci. 2006, 11, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kushchayeva, Y.S.; Kushchayev, S.V.; Glushko, T.Y.; Tella, S.H.; Teytelboym, O.M.; Collins, M.T.; Boyce, A.M. Fibrous dysplasia for radiologists: Beyond ground glass bone matrix. Insights Imaging 2018, 9, 1035–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feller, L.; Wood, N.H.; Khammissa, R.A.; Lemmer, J.; Raubenheimer, E.J. The nature of fibrous dysplasia. Head Face Med. 2009, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riddle, N.D.; Bui, M.M. Fibrous dysplasia. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2013, 137, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diah, E.; Morris, D.E.; Lo, L.J.; Chen, Y.R. Cyst degeneration in craniofacial fibrous dysplasia: Clinical presentation and management. J. Neurosurg. 2007, 107, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanton, R.P. Surgery for fibrous dysplasia. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2006, 21 (Suppl. S2), P105–P109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keijser, L.C.; Van Tienen, T.G.; Schreuder, H.W.; Lemmens, J.A.; Pruszczynski, M.; Veth, R.P. Fibrous dysplasia of bone: Management and outcome of 20 cases. J. Surg. Oncol. 2001, 76, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiCaprio, M.R.; Enneking, W.F. Fibrous dysplasia. Pathophysiology, evaluation, and treatment. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2005, 87, 1848–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamad, A.T.; Kumar, A.; Anand Kumar, C. Intraosseous epidermoid cyst of the finger phalanx: A case report. J. Orthop. Surg. 2006, 14, 340–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.Y.; Eisler, J.; Springfield, D.; Klein, M.J. Intraosseous epidermoid inclusion cyst in a great toe. A case report and review of the literature. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2003, 127, e298–e300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Bhuiya, T.; Chen, S.; Kenan, S.; Kahn, L. Epidermal inclusion cyst of phalanx: A case report and review of the literature. Skeletal. Radiol. 2006, 35, 861–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, F.; Panjwani, T.R.; Patankar, H. Intraosseous Epidermoid Inclusion Cyst of Distal Phalanx: A Rare Entity. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, RJ01–RJ02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Case | Age/Sex | ASA | Lesion Site | Diameter (mm) | Tissue Diagnosis | Follow-Up (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
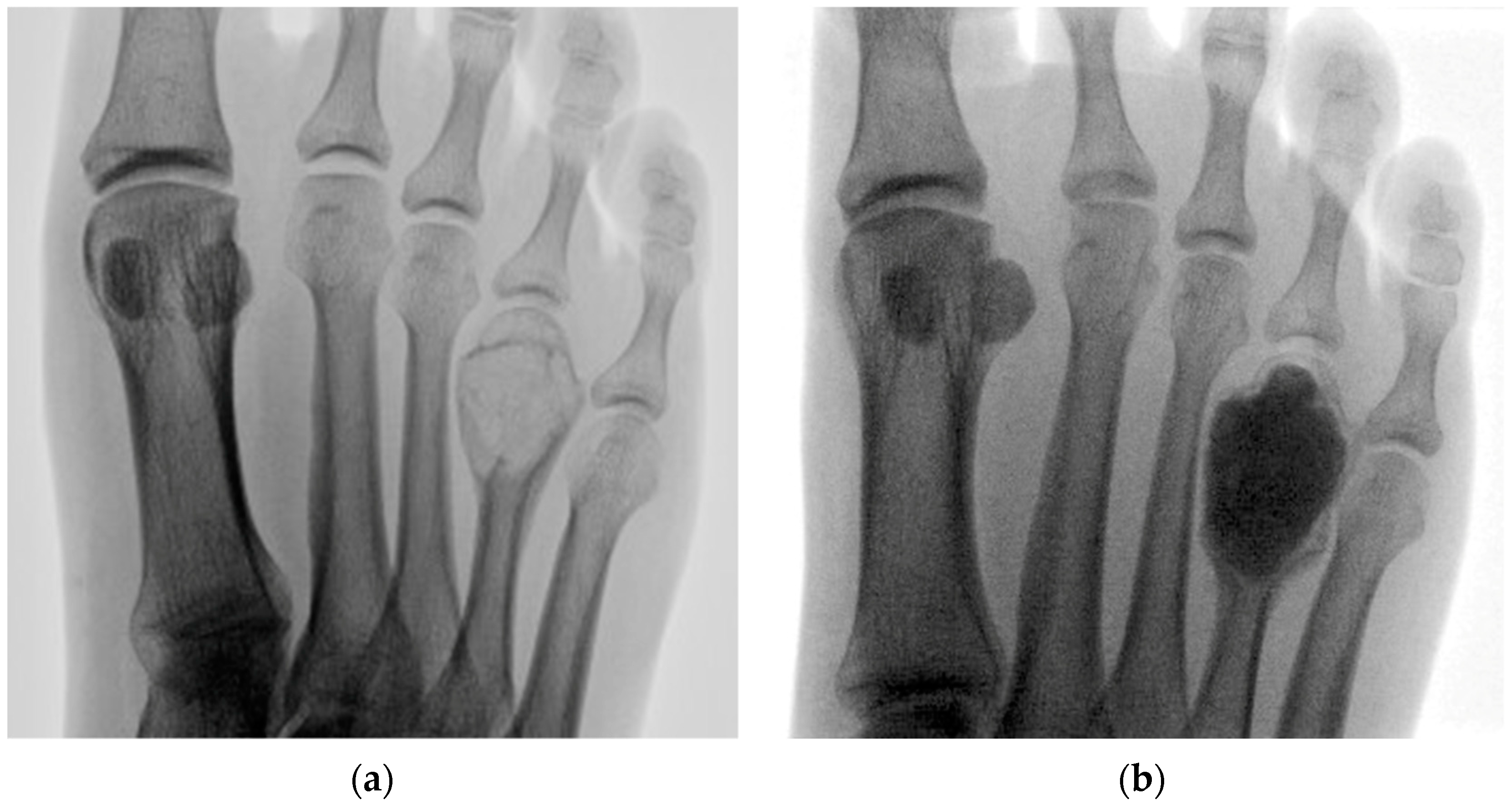
| 1 | 23 M | 2 | Right foot 4th metatarsal | 20 | Aneurysmal bone cyst | 30 |
| 2 | 34 M | 1 | Left middle finger P1 | 32 | Enchondroma | 24 |
| 3 | 17 F | 1 | Right proximal tibia | 58 | Fibrous dysplasia | 22 |
| 4 | 27 F | 2 | Left foot 2nd metatarsal | 24 | Enchondroma | 23 |
| 5 | 36 M | 1 | Left little finger P3 | 10 | Enchondroma | 25 |
| 6 | 25 F | 2 | Right os calcis | 33 | Aneurysmal bone cyst | 28 |
| 7 | 71 M | 2 | Right middle finger P3 | 20 | Epidermoid cyst | 27 |
| 8 | 23 F | 1 | Left hand 2nd metacarpal | 27 | Aneurysmal bone cyst | 23 |
| 9 | 27 F | 1 | Left tibial diaphysis | 41 | Fibrous dysplasia | 23 |
| 10 | 75 F | 2 | Right medial femoral condyle | 20 | Enchondroma | 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Razii, N.; Docherty, L.M.; Halai, M.; Mahendra, A.; Gupta, S. Injectable Synthetic Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate/Calcium Sulfate (GeneX) for the Management of Contained Defects Following Curettage of Benign Bone Tumours. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 3697-3707. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30040281
Razii N, Docherty LM, Halai M, Mahendra A, Gupta S. Injectable Synthetic Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate/Calcium Sulfate (GeneX) for the Management of Contained Defects Following Curettage of Benign Bone Tumours. Current Oncology. 2023; 30(4):3697-3707. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30040281
Chicago/Turabian StyleRazii, Nima, Laura M. Docherty, Mansur Halai, Ashish Mahendra, and Sanjay Gupta. 2023. "Injectable Synthetic Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate/Calcium Sulfate (GeneX) for the Management of Contained Defects Following Curettage of Benign Bone Tumours" Current Oncology 30, no. 4: 3697-3707. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30040281
APA StyleRazii, N., Docherty, L. M., Halai, M., Mahendra, A., & Gupta, S. (2023). Injectable Synthetic Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate/Calcium Sulfate (GeneX) for the Management of Contained Defects Following Curettage of Benign Bone Tumours. Current Oncology, 30(4), 3697-3707. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30040281





