Pediatric CNS Radiation Oncology: Recent Developments and Novel Techniques
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Proton Therapy
2.1. Planning and Delivery of Proton Therapy
2.2. Clinical Indications, Outcomes, and Challenges of Proton Therapy
3. Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Pediatric Brain Tumors
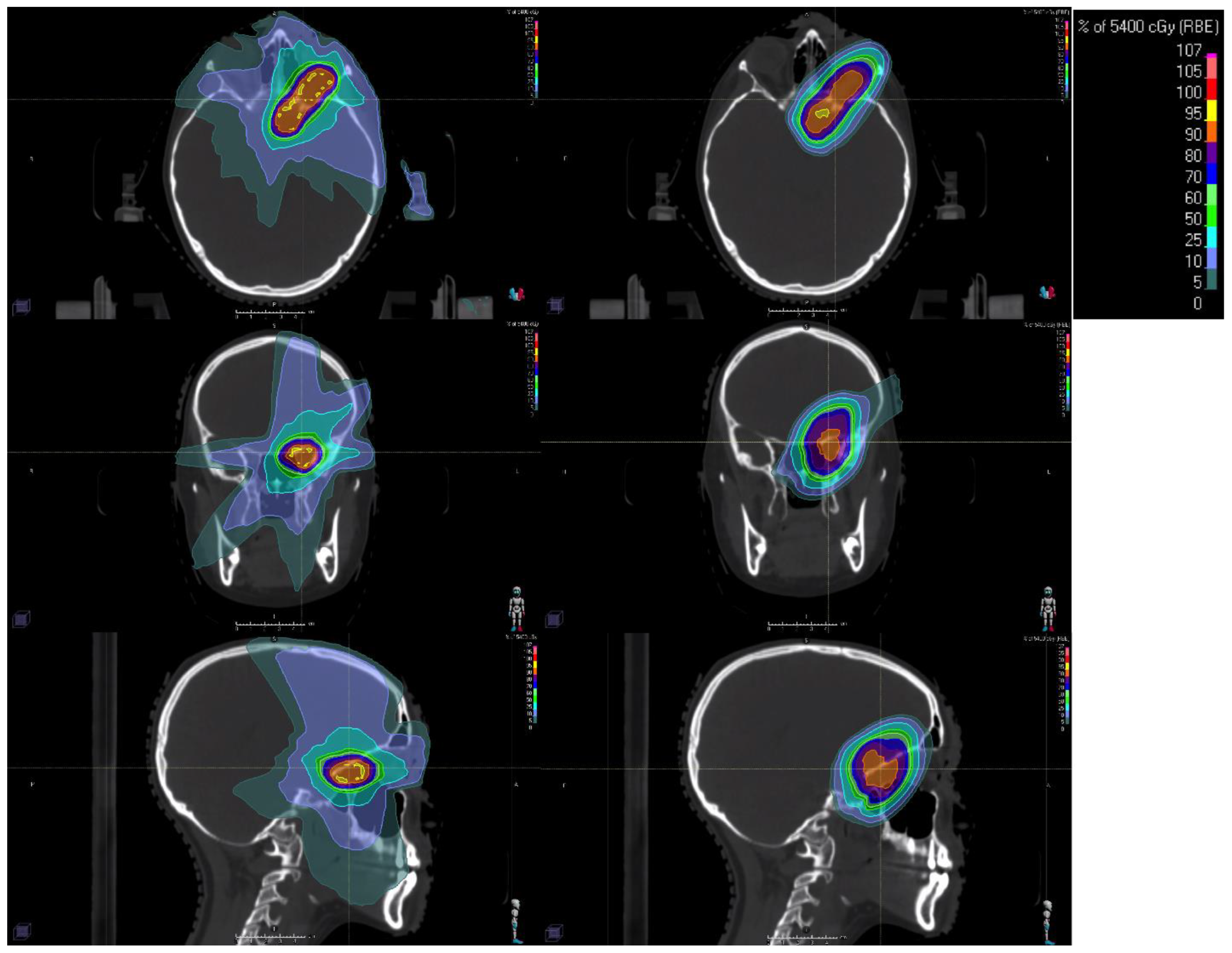
3.1. Planning and Delivery of Stereotactic Radiotherapy
3.2. Clinical Indications, Outcomes, and Challenges of Stereotactic Radiotherapy
3.2.1. Ependymoma
3.2.2. Medulloblastoma
3.2.3. Glioma
3.2.4. Craniopharyngioma
3.2.5. Brain Metastases
4. Recent Developments in Pediatric CNS Radiotherapy Volumes
4.1. CNS Germ Cell Tumors
4.1.1. Germinoma
4.1.2. Non-Germinomatous Germ Cell Tumor
4.2. Hippocampal-Sparing Technique
5. Experimental Radiation Therapies on the Horizon
5.1. FLASH Therapy
5.2. Theranostics
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Glossary
| Bragg Peak | A phenomenon in proton therapy where the radiation dose is deposited at a specific depth, minimizing exposure to surrounding healthy tissue |
| Craniospinal Irradiation (CSI) | A radiation volume that encompasses the entire brain, spinal cord, and cerebrospinal fluid |
| CyberKnife® | A frameless stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) system utilizing linear accelerator and robotic arm |
| Flash Radiotherapy (FLASH-RT) | An emerging high-dose, ultra-fast radiation therapy technique that aims to minimize normal tissue damage while effectively treating tumors |
| Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy (FSRT) | A precise stereotactic radiation delivered over multiple treatment sessions |
| Gamma Knife® | A dedicated stereotactic radiosurgery system that uses multiple cobalt-60 sources producing a narrow beam of gamma radiation |
| Hippocampal Avoidance (HA) Radiotherapy | A technique that reduces radiation exposure to the hippocampus to preserve cognitive function |
| Intensity-Modulated Proton Therapy (IMPT) | A form of proton therapy that modulates the radiation dose to better conform to the tumor shape |
| Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy (IMRT) | A photon-based radiation therapy technique that modulates the radiation dose to better conform to tumor shape |
| Linear Accelerator (LINAC) | Radiation machine that accelerates electron to generate therapeutic photon or electron |
| Linear Energy Transfer (LET) | A measure of the amount of energy deposited by radiation as it travels through tissue. |
| Passive Scatter Proton Therapy (PSPT) | A method of delivering proton therapy where a narrow beam is scattered to create a broader treatment field |
| Pencil Beam Scanning (PBS) | A method of delivering proton therapy technique that uses a magnet to steer narrow beam over treatment volume |
| Proton Arc Therapy (PAT) | A developing technique that delivers proton radiation continuously in an arc, similar to volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) with photons |
| Proton Beam Therapy (PBT) | A form of radiation therapy that uses protons instead of photons to deliver targeted radiation, reducing damage to surrounding normal tissues |
| Relative Biological Effectiveness (RBE) | A factor used to compare the effectiveness of different types of radiation in causing biological damage |
| Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) | A precise radiation technique used for tumors outside the brain, delivering high-dose radiation in fewer fractions |
| Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) | A high-dose, single-session radiation therapy technique used for treating small brain tumors with precision |
| Theranostics | A treatment approach that combines diagnostics and therapy, often using radiopharmaceuticals to both image and treat tumors |
| Volumetric-Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT) | A photon-based radiation therapy technique that delivers continuous radiation while the treatment machine rotates around the patient |
| Whole Ventricular Radiotherapy (WVRT) | A radiation approach that targets the entire ventricular system while minimizing radiation exposure to brain parenchyma |
References
- Brinkman, T.M.; Recklitis, C.J.; Michel, G.; Grootenhuis, M.A.; Klosky, J.L. Psychological Symptoms, Social Outcomes, Socioeconomic Attainment, and Health Behaviors Among Survivors of Childhood Cancer: Current State of the Literature. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2190–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otth, M.; Wyss, J.; Scheinemann, K. Long-Term Follow-Up of Pediatric CNS Tumor Survivors—A Selection of Relevant Long-Term Issues. Children 2022, 9, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte, F.; Brinkman, T.M.; Li, C.; Fay-McClymont, T.; Srivastava, D.K.; Ness, K.K.; Howell, R.M.; Mueller, S.; Wells, E.; Strother, D.; et al. Social adjustment in adolescent survivors of pediatric central nervous system tumors: A report from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. Cancer 2018, 124, 3596–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatner, R.E.; Niemierko, A.; Misra, M.; Weyman, E.A.; Goebel, C.P.; Ebb, D.H.; Jones, R.M.; Huang, M.S.; Mahajan, A.; Grosshans, D.R.; et al. Endocrine Deficiency As a Function of Radiation Dose to the Hypothalamus and Pituitary in Pediatric and Young Adult Patients With Brain Tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2854–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulino, A.C.; Lobo, M.; Teh, B.S.; Okcu, M.F.; South, M.; Butler, E.B.; Su, J.; Chintagumpala, M. Ototoxicity After Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy and Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy in Children With Medulloblastoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2010, 78, 1445–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, T.E.; Conklin, H.M.; Wu, S.; Lustig, R.H.; Xiong, X. Late Effects of Conformal Radiation Therapy for Pediatric Patients With Low-Grade Glioma: Prospective Evaluation of Cognitive, Endocrine, and Hearing Deficits. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3691–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalski, J.M.; Janss, A.J.; Vezina, L.G.; Smith, K.S.; Billups, C.A.; Burger, P.C.; Embry, L.M.; Cullen, P.L.; Hardy, K.K.; Pomeroy, S.L.; et al. Children’s Oncology Group Phase III Trial of Reduced-Dose and Reduced-Volume Radiotherapy with Chemotherapy for Newly Diagnosed Average-Risk Medulloblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 2685–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, E.; DeSantis, C.; Robbins, A.; Kohler, B.; Jemal, A. Childhood and adolescent cancer statistics, 2014. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2014, 64, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, T.E.; Bendel, A.E.; Sabin, N.D.; Burger, P.C.; Shaw, D.W.; Chang, E.; Wu, S.; Zhou, T.; Eisenstat, D.D.; Foreman, N.K.; et al. Conformal Radiation Therapy for Pediatric Ependymoma, Chemotherapy for Incompletely Resected Ependymoma, and Observation for Completely Resected, Supratentorial Ependymoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 974–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhall, G.; Grodman, H.; Ji, L.; Sands, S.; Gardner, S.; Dunkel, I.J.; McCowage, G.B.; Diez, B.; Allen, J.C.; Gopalan, A.; et al. Outcome of children less than three years old at diagnosis with non-metastatic medulloblastoma treated with chemotherapy on the “Head Start” I and II protocols. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2008, 50, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mynarek, M.; von Hoff, K.; Pietsch, T.; Ottensmeier, H.; Warmuth-Metz, M.; Bison, B.; Pfister, S.; Korshunov, A.; Sharma, T.; Jaeger, N.; et al. Nonmetastatic Medulloblastoma of Early Childhood: Results From the Prospective Clinical Trial HIT-2000 and An Extended Validation Cohort. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2028–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartels, U.; Onar-Thomas, A.; Patel, S.K.; Shaw, D.; Fangusaro, J.; Dhall, G.; Souweidane, M.; Bhatia, A.; Embry, L.; Trask, C.L.; et al. Phase II trial of response-based radiation therapy for patients with localized germinoma: A Children’s Oncology Group study. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 24, 974–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depuydt, T. Proton therapy technology evolution in the clinic: Impact on radiation protection. Ann. ICRP 2018, 47, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. A Review of the Robust Optimization Process and Advances with Monte Carlo in the Proton Therapy Management of Head and Neck Tumors. Int. J. Part. Ther. 2021, 8, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, P.C.; Zhu, X.R.; Lee, A.K.; Sahoo, N.; Melancon, A.D.; Zhang, L.; Dong, L. A Beam-Specific Planning Target Volume (PTV) Design for Proton Therapy to Account for Setup and Range Uncertainties. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 82, e329–e336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflugfelder, D.; Wilkens, J.J.; Oelfke, U. Worst case optimization: A method to account for uncertainties in the optimization of intensity modulated proton therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2008, 53, 1689–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettega, D.; Calzolari, P.; Chauvel, P.; Courdi, A.; Herault, J.; Iborra, N.; Marchesini, R.; Massariello, P.; Poli, G.L.; Tallone, L. Radiobiological studies on the 65 MeV therapeutic proton beam at Nice using human tumour cells. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2000, 76, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, S.J.; Paganetti, H.; Prise, K.M. LET-weighted doses effectively reduce biological variability in proton radiotherapy planning. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 225009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Khabazian, A.; Yepes, P.P.; Lim, G.; Poenisch, F.; Grosshans, D.R.; Mohan, R. Linear energy transfer incorporated intensity modulated proton therapy optimization. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 63, 015013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, B.A.; Korevaar, E.W.; Maring, A.; Werkman, C.I.; Scandurra, D.; Janssens, G.; Both, S.; Langendijk, J.A. Proton arc therapy increases the benefit of proton therapy for oropharyngeal cancer patients in the model based clinic. Radiother. Oncol. 2023, 184, 109670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volz, L.; Sheng, Y.; Durante, M.; Graeff, C. Considerations for Upright Particle Therapy Patient Positioning and Associated Image Guidance. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 930850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, B.; Hopper, A.; Elster, J.; Crawford, J.R.; McConnell, K.; Chang, A.; Mundt, A.J.; MacEwan, I. Volumetric de-escalation and improved acute toxicity with proton craniospinal irradiation using a vertebral body-sparing technique. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2021, 69, e29489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemura, S.; Demizu, Y.; Hasegawa, D.; Fujikawa, T.; Inoue, S.; Nishimura, A.; Tojyo, R.; Nakamura, S.; Kozaki, A.; Saito, A.; et al. The comparison of acute toxicities associated with craniospinal irradiation between photon beam therapy and proton beam therapy in children with brain tumors. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 1502–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, G.S.; Yu, J.I.; Cho, S.; Han, Y.; Oh, Y.; Lim, D.H.; Nam, H.R.; Lee, J.-W.; Sung, K.-W.; Shin, H.J. Chronological Analysis of Acute Hematological Outcomes after Proton and Photon Beam Craniospinal Irradiation in Pediatric Brain Tumors. Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 54, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldrich, K.D.; Horne, V.E.; Bielamowicz, K.; Sonabend, R.Y.; Scheurer, M.E.; Paulino, A.C.; Mahajan, A.; Chintagumpala, M.; Okcu, M.F.; Brown, A.L. Comparison of hypothyroidism, growth hormone deficiency, and adrenal insufficiency following proton and photon radiotherapy in children with medulloblastoma. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2021, 155, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.X.; Ioakeim-Ioannidou, M.; Susko, M.S.; Rao, A.D.; Yeap, B.Y.; Snijders, A.M.; Ladra, M.M.; Vogel, J.; Zaslowe-Dude, C.; Marcus, K.J.; et al. A Multi-institutional Comparative Analysis of Proton and Photon Therapy-Induced Hematologic Toxicity in Patients With Medulloblastoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 109, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, T.; Shimizu, S.; Takao, S.; Terasaka, S.; Iguchi, A.; Kobayashi, H.; Mori, T.; Yoshimura, T.; Matsuo, Y.; Tamura, M.; et al. Clinical experience of craniospinal intensity-modulated spot-scanning proton therapy using large fields for central nervous system medulloblastomas and germ cell tumors in children, adolescents, and young adults. J. Radiat. Res. 2019, 60, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Park, H.J.; Yoon, J.H.; Kim, D.W.; Park, J.; Shin, D.; Shin, S.H.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, S.-K.; Phi, J.H.; et al. Proton beam therapy reduces the incidence of acute haematological and gastrointestinal toxicities associated with craniospinal irradiation in pediatric brain tumors. Acta Oncol. 2014, 53, 1158–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLaney, T.F.; Liebsch, N.J.; Pedlow, F.X.; Adams, J.; Dean, S.; Yeap, B.Y.; McManus, P.; Rosenberg, A.E.; Nielsen, G.P.; Harmon, D.C.; et al. Phase II Study of High-Dose Photon/Proton Radiotherapy in the Management of Spine Sarcomas. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2009, 74, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralbell, R.; Lomax, A.; Cella, L.; Schneider, U. Potential reduction of the incidence of radiation-induced second cancers by using proton beams in the treatment of pediatric tumors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2002, 54, 824–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newhauser, W.D.; Fontenot, J.D.; Mahajan, A.; Kornguth, D.; Stovall, M.; Zheng, Y.; Taddei, P.J.; Mirkovic, D.; Mohan, R.; Cox, J.D.; et al. The risk of developing a second cancer after receiving craniospinal proton irradiation. Phys. Med. Biol. 2009, 54, 2277–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scorsetti, M.; Cozzi, L.; Navarria, P.; Fogliata, A.; Rossi, A.; Franceschini, D.; De Rose, F.; Franzese, C.; Carlo-Stella, C.; Santoro, A. Intensity modulated proton therapy compared to volumetric modulated arc therapy in the irradiation of young female patients with hodgkin’s lymphoma. Assessment of risk of toxicity and secondary cancer induction. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lautenschlaeger, S.; Iancu, G.; Flatten, V.; Baumann, K.; Thiemer, M.; Dumke, C.; Zink, K.; Hauswald, H.; Vordermark, D.; Mauz-Körholz, C.; et al. Advantage of proton-radiotherapy for pediatric patients and adolescents with Hodgkin’s disease. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakthivel, V.; Ganesh, K.M.; McKenzie, C.; Boopathy, R.; Selvaraj, J. Second malignant neoplasm risk after craniospinal irradiation in X-ray-based techniques compared to proton therapy. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2019, 42, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokkevåg, C.H.; Indelicato, D.J.; Herfarth, K.; Magelssen, H.; Evensen, M.E.; Ugland, M.; Nordberg, T.; Nystad, T.A.; Hægeland, C.; Alsaker, M.D.; et al. Normal tissue complication probability models in plan evaluation of children with brain tumors referred to proton therapy. Acta Oncol. 2019, 58, 1416–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernimmen, F.J.; Fredericks, S.; Wallace, N.D.; Fitzgerald, A.P. Long-Term Follow-up of Patients Treated at a Single Institution Using a Passively Scattered Proton Beam; Observations Around the Occurrence of Second Malignancies. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 103, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, D.Y.; Siddiqui, Z.; Liu, Z.A.; Dama, H.; MacDonald, S.M.; Wu, S.; Murphy, E.S.; Hall, M.D.; Malkov, V.; Onar-Thomas, A.; et al. Photon versus proton whole ventricular radiotherapy for non-germinomatous germ cell tumors: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2022, 69, e29697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, P.; Rompokos, V.; Bizzocchi, N.; Gillies, C.; Gosling, A.; Royle, G.; Chang, Y.-C.; Gaze, M.; Gains, J. Pencil Beam Scanning Proton Therapy Case Selection for Paediatric Abdominal Neuroblastoma: Effects of Tumour Location and Bowel Gas. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 33, e132–e142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Indelicato, D.J.; Mailhot, R.B.; Bradley, J.A. Impact of different treatment techniques for pediatric Ewing sarcoma of the chest wall: IMRT, 3DCPT, and IMPT with/without beam aperture. J. Appl. Clin. Med Phys. 2020, 21, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, F.; Zachiu, C.; Seravalli, E.; Ribeiro, C.O.; Janssens, G.O.; Ries, M.; de Senneville, B.D.; Maduro, J.H.; Brouwer, C.L.; Korevaar, E.W.; et al. Evaluating the benefit of PBS vs. VMAT dose distributions in terms of dosimetric sparing and robustness against inter-fraction anatomical changes for pediatric abdominal tumors. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 138, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, S.; Kharouta, M.Z.; Pidikiti, R.; Damico, N.J.; Choi, S.; Dorth, J.A.; Mansur, D.B.; Machtay, M.X.; Yao, M.; Bhatt, A.D. Proton Beam Therapy for Locally Advanced Head and Neck Tumors: An Analysis of Dosimetric and Clinical Outcomes. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 45, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bates, J.E.; Indelicato, D.J.; Morris, C.G.; Rotondo, R.L.; Bradley, J.A. Visual decline in pediatric survivors of brain tumors following radiotherapy. Acta Oncol. 2020, 59, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’oro, M.; Short, M.; Wilson, P.; Hua, C.-H.; Gargone, M.; Merchant, T.E.; Bezak, E. Influence of Target Location, Size, and Patient Age on Normal Tissue Sparing- Proton and Photon Therapy in Paediatric Brain Tumour Patient-Specific Approach. Cancers 2020, 12, 2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gram, D.; Brodin, N.P.; Björk-Eriksson, T.; Nysom, K.; Rosenschöld, P.M.A. The risk of radiation-induced neurocognitive impairment and the impact of sparing the hippocampus during pediatric proton cranial irradiation. Acta Oncol. 2023, 62, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mash, L.E.; Kahalley, L.S.; Okcu, M.F.; Grosshans, D.R.; Paulino, A.C.; Stancel, H.; De Leon, L.; Wilde, E.; Desai, N.; Chu, Z.D.; et al. Superior verbal learning and memory in pediatric brain tumor survivors treated with proton versus photon radiotherapy. Neuropsychology 2023, 37, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjæra, L.F.; Indelicato, D.J.; Handeland, A.H.; Ytre-Hauge, K.S.; Lassen-Ramshad, Y.; Muren, L.P.; Stokkevåg, C.H. A case-control study of linear energy transfer and relative biological effectiveness related to symptomatic brainstem toxicity following pediatric proton therapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2022, 175, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassaletta, Á.; Morales, J.S.; Valenzuela, P.L.; Esteso, B.; Kahalley, L.S.; Mabbott, D.J.; Unnikrishnan, S.; Panizo, E.; Calvo, F. Neurocognitive outcomes in pediatric brain tumors after treatment with proton versus photon radiation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Pediatr. 2023, 19, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, E.A.H.; Raghubar, K.P.; Cirino, P.T.; Child, A.E.; Lupo, P.J.; Grosshans, D.R.; Paulino, A.C.; Okcu, M.F.; Minard, C.G.; Ris, M.D.; et al. Cognitive predictors of social adjustment in pediatric brain tumor survivors treated with photon versus proton radiation therapy. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2022, 69, e29645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahalley, L.S.; Peterson, R.; Ris, M.D.; Janzen, L.; Okcu, M.F.; Grosshans, D.R.; Ramaswamy, V.; Paulino, A.C.; Hodgson, D.; Mahajan, A.; et al. Superior Intellectual Outcomes After Proton Radiotherapy Compared with Photon Radiotherapy for Pediatric Medulloblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-C.; Lin, S.-Y.; Tseng, C.-K. Maintenance of multidomain neurocognitive functions in pediatric patients after proton beam therapy: A prospective case-series study. Appl. Neuropsychol. Child 2018, 8, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, B.R.; Fong, G.W.; Ingerski, L.M.; Pulsifer, M.B.; Goyal, S.; Zhang, C.; Weyman, E.A.; Esiashvili, N.; Klosky, J.L.; MacDonald, T.J.; et al. Intellectual functioning among case-matched cohorts of children treated with proton or photon radiation for standard-risk medulloblastoma. Cancer 2021, 127, 3840–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahya, N.; Manan, H.A. Neurocognitive impairment following proton therapy for paediatric brain tumour: A systematic review of post-therapy assessments. Support. Care Cancer 2020, 29, 3035–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, J.P.; Powell, S.; Zelko, F.; Hartsell, W.; Goldman, S.; Fangusaro, J.; Lulla, R.R.; Smiley, N.P.; Chang, J.H.-C.; Gondi, V. Improved neuropsychological outcomes following proton therapy relative to X-ray therapy for pediatric brain tumor patients. Neuro-Oncology 2019, 21, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, L.M.; Grieco, J.A.; Evans, C.L.; Kuhlthau, K.A.; MacDonald, S.M.; Tarbell, N.J.; Yock, T.I.; Pulsifer, M.B. Executive functioning, academic skills, and quality of life in pediatric patients with brain tumors post-proton radiation therapy. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2017, 137, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonini, T.N.; Ris, M.D.; Grosshans, D.R.; Mahajan, A.; Okcu, M.F.; Chintagumpala, M.; Paulino, A.; Child, A.E.; Orobio, J.; Stancel, H.H.; et al. Attention, processing speed, and executive functioning in pediatric brain tumor survivors treated with proton beam radiation therapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 124, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, B.R.; Goldberg, S.; Tarbell, N.J.; Lawell, M.P.; Gallotto, S.L.; Weyman, E.A.; Kuhlthau, K.A.; Ebb, D.H.; MacDonald, S.M.; Yock, T.I. Long-term health-related quality of life in pediatric brain tumor survivors receiving proton radiotherapy at <4 years of age. Neuro-Oncology 2020, 22, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, M.; Bachmann, N.; Pica, A.; Bolsi, A.; De Angelis, C.; Lomax, A.J.; Weber, D.C. Early outcome after craniospinal irradiation with pencil beam scanning proton therapy for children, adolescents and young adults with brain tumors. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2022, 70, e30087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, S.; Frisch, S.; Stock, A.; Merta, J.; Bäumer, C.; Blase, C.; Schuermann, E.; Tippelt, S.; Bison, B.; Frühwald, M.; et al. Proton Beam Therapy for Pediatric Tumors of the Central Nervous System—Experiences of Clinical Outcome and Feasibility from the KiProReg Study. Cancers 2022, 14, 5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, P.S.; Tran, S.; Kroeze, S.G.; Pica, A.; Hrbacek, J.; Bachtiary, B.; Walser, M.; Leiser, D.; Lomax, A.J.; Weber, D.C. Outcomes of adolescents and young adults treated for brain and skull base tumors with pencil beam scanning proton therapy. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2020, 67, e28664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, S.; Lim, P.S.; Bojaxhiu, B.; Teske, C.; Baust, K.; Zepter, S.; Kliebsch, U.; Timmermann, B.; Calaminus, G.; Weber, D.C. Clinical outcomes and quality of life in children and adolescents with primary brain tumors treated with pencil beam scanning proton therapy. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2020, 67, e28465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Gunther, J.R.; Mahajan, A.; Jo, E.; Paulino, A.C.; Adesina, A.M.; Jones, J.Y.; Ketonen, L.M.; Su, J.M.; Okcu, M.F.; et al. Progression-free survival of children with localized ependymoma treated with intensity-modulated radiation therapy or proton-beam radiation therapy. Cancer 2017, 123, 2570–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indelicato, D.J.; Bradley, J.A.; Rotondo, R.L.; Nanda, R.H.; Logie, N.; Sandler, E.S.; Aldana, P.R.; Ranalli, N.J.; Beier, A.D.; Morris, C.G.; et al. Outcomes following proton therapy for pediatric ependymoma. Acta Oncol. 2017, 57, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalmasso, C.; Alapetite, C.; Bolle, S.; Goudjil, F.; Lusque, A.; Desrousseaux, J.; Claude, L.; Doyen, J.; Bernier-Chastagner, V.; Ducassou, A.; et al. Brainstem toxicity after proton or photon therapy in children and young adults with localized intracranial ependymoma: A French retrospective study. Radiother. Oncol. 2024, 194, 110157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, A.S.; Li, Y.; Fisher, M.J.; Minturn, J.; Paltin, I.; Belasco, J.; Phillips, P.; Kang, T.; Lustig, R.A.; Hill-Kayser, C. Tumor bed proton irradiation in young children with localized medulloblastoma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2019, 66, e27972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggi, A.; Melchionda, F.; Sardi, I.; Pavone, R.; Meneghello, L.; Kitanovski, L.; Zaletel, L.Z.; Farace, P.; Zucchelli, M.; Scagnet, M.; et al. Toxicity and Clinical Results after Proton Therapy for Pediatric Medulloblastoma: A Multi-Centric Retrospective Study. Cancers 2022, 14, 2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sienna, J.; Kahalley, L.S.; Mabbott, D.; Grosshans, D.; Santiago, A.T.; Merchant, T.E.; Manzar, G.S.; Dama, H.; Hodgson, D.C.; Chintagumpala, M.; et al. Proton therapy mediates dose reductions to brain structures associated with cognition in children with medulloblastoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2024, 119, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, S.; Phaterpekar, K.; Tsang, D.S.; Boldt, G.; Bauman, G.S. Proton Radiotherapy for Management of Medulloblastoma: A Systematic Review of Clinical Outcomes. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 8, 101189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, T.E.; Hoehn, M.E.; Khan, R.B.; Sabin, N.D.; Klimo, P.; Boop, F.A.; Wu, S.; Li, Y.; Burghen, E.A.; Jurbergs, N.; et al. Proton therapy and limited surgery for paediatric and adolescent patients with craniopharyngioma (RT2CR): A single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, R.B.; Ahmed, S.; Johnson, A.; Thomas, H.; Depauw, N.; Horick, N.; Tansky, J.; Evans, C.L.; Pulsifer, M.; Ebb, D.; et al. Proton Radiation Therapy for Pediatric Craniopharyngioma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 110, 1480–1487. [Google Scholar]
- Brisson, R.J.; Indelicato, D.J.; Bradley, J.A.; Aldana, P.R.; Klawinski, D.; Morris, C.G.; Vega, R.B.M. Long-term outcomes following proton therapy for pediatric spinal low-grade glioma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2024, 71, e31341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indelicato, D.J.; Rotondo, R.L.; Uezono, H.; Sandler, E.S.; Aldana, P.R.; Ranalli, N.J.; Beier, A.D.; Morris, C.G.; Bradley, J.A. Outcomes Following Proton Therapy for Pediatric Low-Grade Glioma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 104, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giantsoudi, D.; Adams, J.; MacDonald, S.M.; Paganetti, H. Proton Treatment Techniques for Posterior Fossa Tumors: Consequences for Linear Energy Transfer and Dose-Volume Parameters for the Brainstem and Organs at Risk. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 97, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabin, N.; Merchant, T.; Harreld, J.; Patay, Z.; Klimo, P.; Qaddoumi, I.; Armstrong, G.; Wright, K.; Gray, J.; Indelicato, D.; et al. Imaging Changes in Very Young Children with Brain Tumors Treated with Proton Therapy and Chemotherapy. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 34, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indelicato, D.J.; Flampouri, S.; Rotondo, R.L.; Bradley, J.A.; Morris, C.G.; Aldana, P.R.; Sandler, E.; Mendenhall, N.P. Incidence and dosimetric parameters of pediatric brainstem toxicity following proton therapy. Acta Oncol. 2014, 53, 1298–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas-Kogan, D.; Indelicato, D.; Paganetti, H.; Esiashvili, N.; Mahajan, A.; Yock, T.; Flampouri, S.; MacDonald, S.; Fouladi, M.; Stephen, K.; et al. National Cancer Institute Workshop on Proton Therapy for Children: Considerations Regarding Brainstem Injury. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 101, 152–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, M.S.; Yeap, B.Y.; Paganetti, H.; Goebel, C.P.; Gaudet, D.E.; Gallotto, S.L.; Weyman, E.A.; Morgan, M.L.; MacDonald, S.M.; Giantsoudi, D.; et al. Brainstem Injury in Pediatric Patients With Posterior Fossa Tumors Treated With Proton Beam Therapy and Associated Dosimetric Factors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 100, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanda, R.H.; Ganju, R.G.; Schreibmann, E.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, C.; Jegadeesh, N.; Cassidy, R.; Deng, C.; Eaton, B.R.; Esiashvili, N. Correlation of Acute and Late Brainstem Toxicities With Dose-Volume Data for Pediatric Patients With Posterior Fossa Malignancies. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 98, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojaxhiu, B.; Ahlhelm, F.; Walser, M.; Placidi, L.; Kliebsch, U.; Mikroutsikos, L.; Morach, P.; Bolsi, A.; Lomax, T.; Pica, A.; et al. Radiation Necrosis and White Matter Lesions in Pediatric Patients With Brain Tumors Treated With Pencil Beam Scanning Proton Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 100, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giantsoudi, D.; Sethi, R.V.; Yeap, B.Y.; Eaton, B.R.; Ebb, D.H.; Caruso, P.A.; Rapalino, O.; Chen, Y.-L.E.; Adams, J.A.; Yock, T.I.; et al. Incidence of CNS Injury for a Cohort of 111 Patients Treated With Proton Therapy for Medulloblastoma: LET and RBE Associations for Areas of Injury. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 95, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, J.; Grewal, A.; O’reilly, S.; Lustig, R.; Kurtz, G.; Minturn, J.E.; Shah, A.C.; Waanders, A.J.; Belasco, J.B.; Cole, K.A.; et al. Risk of brainstem necrosis in pediatric patients with central nervous system malignancies after pencil beam scanning proton therapy. Acta Oncol. 2019, 58, 1752–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baliga, S.; Gallotto, S.; Bajaj, B.; Lewy, J.; Weyman, E.; Lawell, M.P.; Yeap, B.Y.; Ebb, D.E.; Huang, M.; Caruso, P.; et al. Decade-long disease, secondary malignancy, and brainstem injury outcomes in pediatric and young adult medulloblastoma patients treated with proton radiotherapy. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 24, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, R.; Liao, K.; Grosshans, D.R.; McGovern, S.L.; McAleer, M.F.; Zaky, W.; Chintagumpala, M.M.; Mahajan, A.; Yeboa, D.N.; Paulino, A.C. Quantifying the risk and dosimetric variables of symptomatic brainstem injury after proton beam radiation in pediatric brain tumors. Neuro-Oncology 2022, 24, 1571–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunther, J.R.; Sato, M.; Chintagumpala, M.; Ketonen, L.; Jones, J.Y.; Allen, P.K.; Paulino, A.C.; Okcu, M.F.; Su, J.M.; Weinberg, J.; et al. Imaging Changes in Pediatric Intracranial Ependymoma Patients Treated With Proton Beam Radiation Therapy Compared to Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2015, 93, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine, C.A.; Liu, K.X.; Ioakeim-Ioannidou, M.; Susko, M.; Poussaint, T.Y.; Huisman, T.A.; Aboian, M.; Brown, D.; Zaslowe-Dude, C.; Rao, A.D.; et al. Brainstem Injury in Pediatric Patients Receiving Posterior Fossa Photon Radiation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 105, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, S.M.; Laack, N.N.; Terezakis, S. Humbling advances in technology: Protons, brainstem necrosis, and the self-driving car. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 97, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.; Shulkin, B.L.; Indelicato, D.J.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Boop, F.A.; Merchant, T.E. Postoperative cerebral glucose metabolism in pediatric patients receiving proton therapy for craniopharyngioma. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2015, 16, 567–573. [Google Scholar]
- Dmytriw, A.A.; Hadjinicolaou, A.; Ntolkeras, G.; Tamilia, E.; Pesce, M.; Berto, L.F.; Grant, P.E.; Pang, E.; Ahtam, B. Magnetoencephalography for the pediatric population, indications, acquisition and interpretation for the clinician. Neuroradiol. J. 2024, 12, 19714009241260801. [Google Scholar]
- PTCOG-Particle Therapy Co-Operative Group. Facilities in Operation and Facilities Under Construction. Available online: https://www.ptcog.site/index.php/facilities-under-construction (accessed on 27 November 2024).
- NHS England Specialised Services Clinical Reference Group for Radiotherapy. Clinical Commissioning Policy: Proton Beam Therapy for Children, Teenagers and Young Adults in the Treatment of Malignant and Non-Malignant Tumours; NHS England: Leeds, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cancer Australia, Strategy for Proton Beam Therapy for Cancer Patients in Australia; Cancer Australia: Surry Hills, NSW, Australia, 2023.
- American Society for Radiation Oncology. Proton Beam Therapy Model Policy. Available online: https://www.astro.org/astro/media/astro/daily%20practice/pdfs/astropbtmodelpolicy.pdf (accessed on 26 November 2024).
- Cancer Care Alberta Proton Therapy Guideline Advisory Group. Proton Beam Radiation Therapy Clinical Practice Guideline. Available online: https://www.albertahealthservices.ca/assets/info/hp/cancer/if-hp-cancer-guide-rt002-proton-beam-RT.pdf (accessed on 27 November 2024).
- Health Ontario. Proton beam therapy for cancer in children and adults: A health technology assessment. Ont. Health Technol. Assess. Ser. 2021, 21, 1–142. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, H.; Timmermann, B. Paediatric proton therapy. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20190601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawell, M.P.; Indelicato, D.J.; Paulino, A.C.; Hartsell, W.; Laack, N.N.; Ermoian, R.P.; Perentesis, J.P.; Vatner, R.; Perkins, S.; Mangona, V.S.; et al. An open invitation to join the Pediatric Proton/Photon Consortium Registry to standardize data collection in pediatric radiation oncology. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20190673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, D.S.; Timmerman, B. Improving Access to Proton Therapy in the United States and Around the World. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 119, 1078–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahgal, A.; Kellett, S.; Ruschin, M.; Greenspoon, J.; Follwell, M.; Sinclair, J.; Islam, O.; Perry, J. A Cancer Care Ontario Organizational Guideline for the Delivery of Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastasis in Ontario, Canada. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 10, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solberg, T.D.; Balter, J.M.; Benedict, S.H.; Fraass, B.A.; Kavanagh, B.; Miyamoto, C.; Pawlicki, T.; Potters, L.; Yamada, Y. Quality and safety considerations in stereotactic radiosurgery and stereotactic body radiation therapy: Executive summary. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 2, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiff, D.; Messersmith, H.; Brastianos, P.K.; Brown, P.D.; Burri, S.; Dunn, I.F.; Gaspar, L.E.; Gondi, V.; Jordan, J.T.; Maues, J.; et al. Radiation Therapy for Brain Metastases: ASCO Guideline Endorsement of ASTRO Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 2271–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehrer, E.J.; Prabhu, A.V.; Sindhu, K.K.; Lazarev, S.; Ruiz-Garcia, H.; Peterson, J.L.; Beltran, C.; Furutani, K.; Schlesinger, D.; Sheehan, J.P.; et al. Proton and Heavy Particle Intracranial Radiosurgery. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, D.; Blanck, O.; Gauer, T.; Fix, M.K.; Brunner, T.B.; Fleckenstein, J.; Loutfi-Krauss, B.; Manser, P.; Werner, R.; Wilhelm, M.L.; et al. Technological quality requirements for stereotactic radiotherapy: Expert review group consensus from the DGMP Working Group for Physics and Technology in Stereotactic Radiotherapy. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2020, 196, 421–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, H.G.; Leber, K.A.; Eustacchio, S.; Pendl, G. The role of gamma knife radiosurgery in children. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2001, 17, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, D.C.; Goumnerova, L.C.; Loeffler, J.S.; Dutton, S.; Black, P.M.; Alexander, E.; Xu, R.; Kooy, H.; Silver, B.; Tarbell, N.J. Radiosurgery in the management of pediatric brain tumors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2001, 50, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.; Bass, J.K.; Khan, R.; Kun, L.E.; Merchant, T.E. Hearing Loss After Radiotherapy for Pediatric Brain Tumors: Effect of Cochlear Dose. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2008, 72, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amendola, B.E.; Wolf, A.; Coy, S.R.; Amendola, M.A. Role of radiosurgery in craniopharyngiomas: A preliminary report. Med Pediatr. Oncol. 2003, 41, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, M.A.; Packer, R.J.; Rorke, L.B.; Zimmerman, R.A.; Goldwein, J.W.; Sutton, L.N.; Schut, L. Vascular malformation with radiation vasculopathy after treatment of chiasmatic/hypothalamic glioma. Cancer 1992, 70, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, E.S.; Sahgal, A.; Regis, J.; Levivier, M.; Fariselli, L.; Gorgulho, A.; Ma, L.; Pollock, B.; Yomo, S.; Sheehan, J.; et al. Pediatric cranial stereotactic radiosurgery: Meta-analysis and international stereotactic radiosurgery society practice guidelines. Neuro-Oncology 2024, 27, 517–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, N.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J. SU-E-T-453: Optimization of Dose Gradient for Gamma Knife Radiosurgery. Med. Phys. 2012, 39, 3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, M.; Michel-Amadry, G.; Nigoul, J.M.; Beltaifa, Y.; Regis, J. Spatial accuracy of the stereotactic Leksell® Vantage head frame in comparison with the standard stereotactic Leksell®G Frame for Gamma-Knife. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2023, 9, 035021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.S.; Chao, S.T.; Angelov, L.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; Barnett, G.; Jung, E.; Recinos, V.R.; Mohammadi, A.; Suh, J.H. Radiosurgery for Pediatric Brain Tumors. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2016, 63, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaledi, N.; Khan, R.; Gräfe, J.L. Historical Progress of Stereotactic Radiation Surgery. J. Med Phys. 2023, 48, 312–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Xu, S.; Ju, Z.; Pan, L.; Bai, J.; Liu, Y.; Qu, B.; et al. Dosimetric comparison of ZAP-X, Gamma Knife, and CyberKnife stereotactic radiosurgery for single brain metastasis. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Qu, B.; Bai, J.; Huang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Dai, X.; Weidlich, G.; Adler, J.R. The Zap-X Radiosurgical System in the Treatment of Intracranial Tumors: A Technical Case Report. Neurosurgery 2021, 88, E351–E355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendricks, B.K.; DiDomenico, J.D.; Barani, I.J.; Barranco, F.D. ZAP-X Gyroscopic Radiosurgery System: A Preliminary Analysis of Clinical Applications within a Retrospective Case Series. Ster. Funct. Neurosurg. 2021, 100, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, H.; Su, Y.-H.; Wu, H.-M.; Simonova, G.; Liscak, R.; Cohen-Inbar, O.; Sheehan, J.P.; Meola, A.; Sharma, M.; Barnett, G.H.; et al. Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Intracranial Ependymomas: An International Multicenter Study. Neurosurgery 2018, 84, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, K.H.; Marianayagam, N.J.; Park, D.J.; Persad, A.; Zamarud, A.; Shaghaghian, E.; Tayag, A.; Ustrzynski, L.; Emrich, S.C.; Gu, X.; et al. Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Ependymoma in Pediatric and Adult Patients: A Single-Institution Experience. Neurosurgery 2024, 95, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, D.S.; Burghen, E.; Klimo, P.; Boop, F.A.; Ellison, D.W.; Merchant, T.E. Outcomes After Reirradiation for Recurrent Pediatric Intracranial Ependymoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 100, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saran, F.; Baumert, B.G.; Creak, A.L.; Warrington, A.P.; Ashley, S.; Traish, D.; Brada, M. Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy in the management of recurrent or residual medulloblastoma/PNET. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2008, 50, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, M.; Tokumaru, S.; Tabuchi, K.; Kida, Y.; Takagi, M.; Imamura, J. Stereotactic Radiation Therapy with Chemotherapy in the Management of Recurrent Medulloblastomas. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2006, 42, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, C.; Stea, B.; Lulu, B.; Hamilton, A.; Cassady, J. The use of stereotactic radiosurgical boost in the treatment of medulloblastomas. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 1997, 37, 761–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somaza, S.C.; Kondziolka, D.; Lunsford, D.; Flickinger, J.C.; Bissonette, D.J.; Albright, A.L. Early Outcomes after Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Growing Pilocytic Astrocytomas in Children. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 1996, 25, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boëthius, J.; Ulfarsson, E.; Ráhn, T.; Lippitz, B. Gamma knife radiosurgery for pilocytic astrocytomas. J. Neurosurg. 2002, 97, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kano, H.; Niranjan, A.; Kondziolka, D.; Flickinger, J.C.; Pollack, I.F.; Jakacki, R.I.; Lunsford, L.D. Stereotactic radiosurgery for pilocytic astrocytomas part 2: Outcomes in pediatric patients. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2009, 95, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weintraub, D.; Yen, C.-P.; Xu, Z.; Savage, J.; Williams, B.; Sheehan, J. Gamma Knife surgery of pediatric gliomas. J. Neurosurgery: Pediatr. 2012, 10, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankinson, T.C.; Patibandla, M.R.; Green, A.; Hemenway, M.; Foreman, N.; Handler, M.; Liu, A.K. Hypofractionated Radiotherapy for Children With Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Gliomas. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2015, 63, 716–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunevicius, A.; Sheehan, J.P. Radiosurgery for Glioblastoma. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 32, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalapurakal, J.A. Radiation therapy in the management of pediatric craniopharyngiomas—A review. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2005, 21, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.J.; Cage, T.A.; Aranda, D.; Parsa, A.T.; Sun, P.P.; Auguste, K.I.; Gupta, N. A systematic review of the results of surgery and radiotherapy on tumor control for pediatric craniopharyngioma. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2012, 29, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, T.E.; Kiehna, E.N.; Sanford, R.A.; Mulhern, R.K.; Thompson, S.J.; Wilson, M.W.; Lustig, R.H.; Kun, L.E. Craniopharyngioma: The St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital experience 1984–2001. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2002, 53, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, S.; Merchant, T.E.; Boop, F.A.; Roth, J.; Constantini, S. Shifting Strategies in the Treatment of Pediatric Craniopharyngioma. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2023, 25, 1497–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, C.; Boekhoff, S.; Bischoff, M.; Beckhaus, J.; Sowithayasakul, P.; Calaminus, G.; Eveslage, M.; Valentini, C.; Bison, B.; Harrabi, S.B.; et al. Outcome after proton beam therapy versus photon-based radiation therapy in childhood-onset craniopharyngioma patients—results of KRANIOPHARYNGEOM 2007. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1180993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugawa, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Hasegawa, T.; Iwai, Y.; Matsunaga, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Hayashi, M.; Kenai, H.; Kano, T.; Mori, H.; et al. Gamma Knife Surgery for Residual or Recurrent Craniopharyngioma After Surgical Resection: A Multi-institutional Retrospective Study in Japan. Cureus 2020, 12, e6973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-C.; Yang, H.-C.; Chen, C.-J.; Hung, Y.-C.; Wu, H.-M.; Shiau, C.-Y.; Guo, W.-Y.; Pan, D.H.-C.; Chung, W.-Y.; Liu, K.-D. Gamma Knife surgery for craniopharyngioma: Report on a 20-year experience. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 121, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minniti, G.; Saran, F.; Traish, D.; Soomal, R.; Sardell, S.; Gonsalves, A.; Ashley, S.; Warrington, J.; Burke, K.; Mosleh-Shirazi, A.; et al. Fractionated stereotactic conformal radiotherapy following conservative surgery in the control of craniopharyngiomas. Radiother. Oncol. 2006, 82, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combs, S.E.; Thilmann, C.; Huber, P.E.; Hoess, A.; Debus, J.; Schulz-Ertner, D. Achievement of long-term local control in patients with craniopharyngiomas using high precision stereotactic radiotherapy. Cancer 2007, 109, 2308–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selch, M.T.; DeSalles, A.A.; Wade, M.; Lee, S.P.; Solberg, T.D.; Wallace, R.E.; Ford, J.M.; Rubino, G.; Cabatan-Awang, C.; Withers, H.R. Initial Clinical Results of Stereotactic Radiotherapy for the Treatment of Craniopharyngiomas. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2002, 1, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.D.; Jaeckle, K.; Ballman, K.V.; Farace, E.; Cerhan, J.H.; Anderson, S.K.; Carrero, X.W.; Barker, F.G., 2nd; Deming, R.; Burri, S.H.; et al. Effect of Radiosurgery Alone vs Radiosurgery with Whole Brain Radiation Therapy on Cognitive Function in Patients with 1 to 3 Brain Metastases: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2016, 316, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.D.; Ballman, K.V.; Cerhan, J.H.; Anderson, S.K.; Carrero, X.W.; Whitton, A.C.; Greenspoon, J.; Parney, I.F.; Laack, N.N.I.; Ashman, J.B.; et al. Postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery compared with whole brain radiotherapy for resected metastatic brain disease (NCCTG N107C/CEC.3): A multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondi, V.; Bauman, G.; Bradfield, L.; Burri, S.H.; Cabrera, A.R.; Cunningham, D.A.; Eaton, B.R.; Hattangadi-Gluth, J.A.; Kim, M.M.; Kotecha, R.; et al. Radiation Therapy for Brain Metastases: An ASTRO Clinical Practice Guideline. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 12, 265–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redmond, K.J.; Gui, C.; Benedict, S.; Milano, M.T.; Grimm, J.; Vargo, J.A.; Soltys, S.G.; Yorke, E.; Jackson, A.; El Naqa, I.; et al. Tumor Control Probability of Radiosurgery and Fractionated Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 110, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suki, D.; Abdulla, R.K.; Ding, M.; Khatua, S.; Sawaya, R. Brain metastases in patients diagnosed with a solid primary cancer during childhood: Experience from a single referral cancer center. J. Neurosurgery: Pediatr. 2014, 14, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, T.P.; Boyle, P.J.; Marcus, K.J.; Haas-Kogan, D.A.; Liu, K.X. Clinical outcomes for pediatric patients receiving radiotherapy for solid tumor central nervous system metastases. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2021, 68, e29331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, A.C.; Hodgson, D.; Dang, J.; Tyldesley, S.; Bouffet, E.; Bartels, U.; Cheng, S.; Hukin, J.; Bedard, P.L.; Goddard, K.; et al. Intracranial Germ Cell Tumors in Adolescents and Young Adults: A 40-Year Multi-Institutional Review of Outcomes. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 106, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, H.K.; Yoon, H.I.; Cho, J.; Shim, K.-W.; Han, J.W.; Lyu, C.J.; Kim, D.-S.; Suh, C.-O. Optimization of Intracranial Germinoma Treatment: Radiotherapy Alone with Reduced Volume and Dose. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 108, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, J.C.; Bajin, I.Y.; Marushchak, O.; McKeown, T.; Bouffet, E.; Tsang, D.S.; Laperriere, N.; Dirks, P.; Drake, J.; Ertl-Wagner, B.; et al. Time to dismiss boost? Outcomes of children with localized and metastatic germinoma. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2023, 162, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Laperriere, N.; Velec, M.; Bartels, U.; Ramaswamy, V.; Bouffet, E.; Tsang, D.S. Redefining Ventricular Target Volume in Germinoma: Is Inclusion of Temporal Horns Necessary? Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 104, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fangusaro, J.; Wu, S.; MacDonald, S.; Murphy, E.; Shaw, D.; Bartels, U.; Khatua, S.; Souweidane, M.; Lu, H.-M.; Morris, D.; et al. Phase II Trial of Response-Based Radiation Therapy for Patients With Localized CNS Nongerminomatous Germ Cell Tumors: A Children’s Oncology Group Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 3283–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calaminus, G.; Frappaz, D.; Kortmann, R.D.; Krefeld, B.; Saran, F.; Pietsch, T.; Vasiljevic, A.; Garre, M.L.; Ricardi, U.; Mann, J.R.; et al. Outcome of patients with intracranial non-germinomatous germ cell tumors—lessons from the SIOP-CNS-GCT-96 trial. Neuro-Oncology 2017, 19, 1661–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, S.; Bouffet, E.; Fisher, P.G.; Allen, J.C.; Robertson, P.L.; Chuba, P.J.; Donahue, B.; Kretschmar, C.S.; Zhou, T.; Buxton, A.B.; et al. Phase II Trial Assessing the Ability of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy With or Without Second-Look Surgery to Eliminate Measurable Disease for Nongerminomatous Germ Cell Tumors: A Children’s Oncology Group Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2464–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gondi, V.; Tomé, W.A.; Mehta, M.P. Why avoid the hippocampus? A comprehensive review. Radiother. Oncol. 2010, 97, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizumatsu, S.; Monje, M.L.; Morhardt, D.R.; Rola, R.; Palmer, T.; Fike, J.R. Extreme sensitivity of adult neurogenesis to low doses of X-irradiation. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 4021–4027. [Google Scholar]
- Monje, M.L.; Mizumatsu, S.; Fike, J.R.; Palmer, T. Irradiation induces neural precursor-cell dysfunction. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondi, V.; Pugh, S.L.; Tome, W.A.; Caine, C.; Corn, B.; Kanner, A.; Rowley, H.; Kundapur, V.; DeNittis, A.; Greenspoon, J.N.; et al. Preservation of Memory With Conformal Avoidance of the Hippocampal Neural Stem-Cell Compartment During Whole-Brain Radiotherapy for Brain Metastases (RTOG 0933): A Phase II Multi-Institutional Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3810–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondi, V.; Tolakanahalli, R.; Mehta, M.P.; Tewatia, D.; Rowley, H.; Kuo, J.S.; Khuntia, D.; Tomé, W.A. Hippocampal-Sparing Whole-Brain Radiotherapy: A “How-To” Technique Using Helical Tomotherapy and Linear Accelerator–Based Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2010, 78, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.D.; Gondi, V.; Pugh, S.; Tome, W.A.; Wefel, J.S.; Armstrong, T.S.; Bovi, J.A.; Robinson, C.; Konski, A.; Khuntia, D.; et al. Hippocampal Avoidance During Whole-Brain Radiotherapy Plus Memantine for Patients With Brain Metastases: Phase III Trial NRG Oncology CC001. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zureick, A.H.; Evans, C.L.; Niemierko, A.; Grieco, J.A.; Nichols, A.J.; Fullerton, B.C.; Hess, C.B.; Goebel, C.P.; Gallotto, S.L.; Weyman, E.A.; et al. Left hippocampal dosimetry correlates with visual and verbal memory outcomes in survivors of pediatric brain tumors. Cancer 2018, 124, 2238–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, D.S.; Kim, L.; Liu, Z.A.; Janzen, L.; Khandwala, M.; Bouffet, E.; Laperriere, N.; Dama, H.; Keilty, D.; Craig, T.; et al. Intellectual changes after radiation for children with brain tumors: Which brain structures are most important? Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, S.; Wu, S.; Ashford, J.M.; Tinkle, C.L.; Lucas, J.T.; Qaddoumi, I.; Gajjar, A.; Krasin, M.J.; Conklin, H.M.; Merchant, T.E. Association between hippocampal dose and memory in survivors of childhood or adolescent low-grade glioma: A 10-year neurocognitive longitudinal study. Neuro-Oncology 2019, 21, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goda, J.S.; Dutta, D.; Krishna, U.; Goswami, S.; Kothavade, V.; Kannan, S.; Maitre, M.; Bano, N.; Gupta, T.; Jalali, R. Hippocampal radiotherapy dose constraints for predicting long-term neurocognitive outcomes: Mature data from a prospective trial in young patients with brain tumors. Neuro-Oncology 2020, 22, 1677–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, T.E.; Schreiber, J.E.; Wu, S.; Lukose, R.; Xiong, X.; Gajjar, A. Critical Combinations of Radiation Dose and Volume Predict Intelligence Quotient and Academic Achievement Scores After Craniospinal Irradiation in Children With Medulloblastoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 90, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmond, K.J.; Mahone, E.M.; Terezakis, S.; Ishaq, O.; Ford, E.; McNutt, T.; Kleinberg, L.; Cohen, K.J.; Wharam, M.; Horska, A. Association between radiation dose to neuronal progenitor cell niches and temporal lobes and performance on neuropsychological testing in children: A prospective study. Neuro-Oncology 2013, 15, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, R.; MacDonald, S. Hippocampus avoidance in pediatric patients. Neuro-Oncology 2019, 21, 1093–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherlow, J.M.; Shaw, D.W.; Margraf, L.R.; Bowers, D.C.; Huang, J.; Fouladi, M.; Onar-Thomas, A.; Zhou, T.; Pollack, I.F.; Gajjar, A.; et al. Conformal Radiation Therapy for Pediatric Patients with Low-Grade Glioma: Results from the Children’s Oncology Group Phase 2 Study ACNS0221. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 103, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tensaouti, F.; Ducassou, A.; Chaltiel, L.; Bolle, S.; Muracciole, X.; Coche-Dequeant, B.; Alapetite, C.; Bernier, V.; Claude, L.; Supiot, S.; et al. Patterns of failure after radiotherapy for pediatric patients with intracranial ependymoma. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 122, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, B.; Khakoo, Y.; Souweidane, M.M.; Dunkel, I.J.; Patel, S.H.; Gilheeney, S.W.; De Braganca, K.C.; Karajannis, M.A.; Wolden, S.L. Patterns of relapse for children with localized intracranial ependymoma. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2018, 138, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baliga, S.; Adams, J.A.; Bajaj, B.V.M.; Van Benthuysen, L.; Daartz, J.; Gallotto, S.L.; Lewy, J.R.; DeNunzio, N.; Weyman, E.A.; Lawell, M.P.; et al. Patterns of failure in pediatric medulloblastoma and implications for hippocampal sparing. Cancer 2022, 129, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padovani, L.; Chapon, F.; André, N.; Boucekine, M.; Geoffray, A.; Bourdeau, F.; Masliah-Planchon, J.; Claude, L.; Huchet, A.; Laprie, A.; et al. Hippocampal Sparing During Craniospinal Irradiation: What Did We Learn About the Incidence of Perihippocampus Metastases? Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 100, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vozenin, M.-C.; Bourhis, J.; Durante, M. Towards clinical translation of FLASH radiotherapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montay-Gruel, P.; Acharya, M.M.; Jorge, P.G.; Petit, B.; Petridis, I.G.; Fuchs, P.; Leavitt, R.; Petersson, K.; Gondré, M.; Ollivier, J.; et al. Hypofractionated FLASH-RT as an Effective Treatment against Glioblastoma that Reduces Neurocognitive Side Effects in Mice. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 27, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montay-Gruel, P.; Acharya, M.M.; Petersson, K.; Alikhani, L.; Yakkala, C.; Allen, B.D.; Ollivier, J.; Petit, B.; Jorge, P.G.; Syage, A.R.; et al. Long-term neurocognitive benefits of FLASH radiotherapy driven by reduced reactive oxygen species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 10943–10951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montay-Gruel, P.; Petersson, K.; Jaccard, M.; Boivin, G.; Germond, J.-F.; Petit, B.; Doenlen, R.; Favaudon, V.; Bochud, F.; Bailat, C.; et al. Irradiation in a flash: Unique sparing of memory in mice after whole brain irradiation with dose rates above 100 Gy/s. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 124, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, D.A.; Lartey, F.M.; Schüler, E.; Rafat, M.; King, G.; Kim, A.; Ko, R.; Semaan, S.; Gonzalez, S.; Jenkins, M.; et al. Reduced cognitive deficits after FLASH irradiation of whole mouse brain are associated with less hippocampal dendritic spine loss and neuroinflammation. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 139, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, B.D.; Alaghband, Y.; Kramár, E.A.; Ru, N.; Petit, B.; Grilj, V.; Petronek, M.S.; Pulliam, C.F.; Kim, R.Y.; Doan, N.-L.; et al. Elucidating the neurological mechanism of the FLASH effect in juvenile mice exposed to hypofractionated radiotherapy. Neuro-Oncology 2022, 25, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugherty, E.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Mascia, A.; Sertorio, M.; Woo, J.; McCann, C.; Russell, K.; Sharma, R.; Khuntia, D.; et al. FLASH radiotherapy for the treatment of symptomatic bone metastases in the thorax (FAST-02): Protocol for a prospective study of a novel radiotherapy approach. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascia, A.E.; Daugherty, E.C.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, E.; Xiao, Z.; Sertorio, M.; Woo, J.; Backus, L.R.; McDonald, J.M.; McCann, C.; et al. Proton FLASH Radiotherapy for the Treatment of Symptomatic Bone Metastases: The FAST-01 Nonrandomized Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2023, 9, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitkreutz, D.Y.; Shumail, M.; Bush, K.K.; Tantawi, S.G.; Maxime, P.G.; Loo, B.W. Initial Steps Towards a Clinical FLASH Radiotherapy System: Pediatric Whole Brain Irradiation with 40 MeV Electrons at FLASH Dose Rates. Radiat. Res. 2020, 194, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VIDEO: FLASH Radiotherapy ‘Transformative’ in Treating Pediatric Brain Tumors. Available online: https://www.healio.com/news/hematology-oncology/20240719/video-flash-radiotherapy-transformative-in-treating-pediatric-brain-tumors (accessed on 26 November 2024).
- Jo, H.-J.; Oh, T.; Lee, Y.-R.; Kang, G.-S.; Park, H.-J.; Ahn, G.-O. FLASH Radiotherapy: A FLASHing Idea to Preserve Neurocognitive Function. Brain Tumor Res. Treat. 2023, 11, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolboom, N.; Verger, A.; Albert, N.L.; Fraioli, F.; Guedj, E.; Traub-Weidinger, T.; Morbelli, S.; Herrmann, K.; Zucchetta, P.; Plasschaert, S.L.; et al. Theranostics in Neurooncology: Heading Toward New Horizons. J. Nucl. Med. 2023, 65, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Rangarajan, V.; Shah, S.; Puranik, A.; Purandare, N. MIBG (metaiodobenzylguanidine) theranostics in pediatric and adult malignancies. Br. J. Radiol. 2018, 91, 20180103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBois, S.G.; Granger, M.M.; Groshen, S.; Tsao-Wei, D.; Ji, L.; Shamirian, A.; Czarnecki, S.; Goodarzian, F.; Berkovich, R.; Shimada, H.; et al. Randomized Phase II Trial of MIBG Versus MIBG, Vincristine, and Irinotecan Versus MIBG and Vorinostat for Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Neuroblastoma: A Report From NANT Consortium. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3506–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souweidane, M.M.; Kramer, K.; Pandit-Taskar, N.; Zhou, Z.; Haque, S.; Zanzonico, P.; Carrasquillo, J.A.; Lyashchenko, S.K.; Thakur, S.B.; Donzelli, M.; et al. Convection-enhanced delivery for diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma: A single-centre, dose-escalation, phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1040–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menda, Y.; Sue O’Dorisio, M.; Kao, S.; Khanna, G.; Michael, S.; Connolly, M.; Babich, J.; O’Dorisio, T.; Bushnell, D.; Madsen, M. Phase I Trial of 90Y-DOTA0-Tyr3-Octreotide Therapy in Children and Young Adults with Refractory Solid Tumors That Express Somatostatin Receptors. J. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51, 1524–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Author and Study Type | Photon/ Proton | Patient Population | Median Follow Up | Treatment Dose | Injury Rate | Identified Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indelicanto et al., 2014 [74] Single institution retrospective | Proton | 313 children Median age 5.9 years All brain tumors | 2 years | Median prescribed dose 54 Gy | 2-year cumulative brainstem toxicity 3.8% 2-year grade 3+ toxicity 2.1% | V55 and Dmax to brainstem |
| Giantsoudi et al., 2016 [79] Single-institution retrospective | Proton | 111 children Median age 7 years Medulloblastoma | 4.2 years | Median CSI 23.4 Gy, boost 54 Gy | 3.6% for any grade, 2.7% for grade 3+ at 5 years | N/A |
| Gentile et al., 2018 [76] Single-institution retrospective | Proton | 216 children Median age 6.6 years IF tumors | 4.2 years | Median dose 54 Gy Median brainstem Dmax 53.6 Gy | 2% for any grade at 5 years | Higher brainstem Dmax and V55 |
| Haas-Kogan et al., 2018 [75] Multi-institutional retrospective | Proton | 671 children Median age 5.4 years IF tumors | 3 years | Variable—54–59.4 Gy depending on institution and histology | 2.4% for grade 2+ necrosis, 1.3% for grade 3+ Fatal brainstem injury 0.4% | Higher prescription dose and higher doses to the brainstem |
| Vogel et al., 2019 [80] Single-institution retrospective | Proton | 166 children Median age 10 years All brain tumors, 50% IF | 19.6 months | Median dose 54 Gy Median brainstem Dmax 55.4 Gy | 0.7% symptomatic necrosis | N/A |
| Baliga et al., 2022 [81] Single-institution retrospective | Proton | 178 children Median age 8.1 years Medulloblastoma | 9.3 years | 18–36 Gy CSI, boost to cavity or posterior fossa 54–55.8 Gy | 1.9% at 10 years | N/A |
| Upadhyay et al., 2022 [82] Single-institution retrospective | Proton | 595 children Median age 6.3 years All brain tumors, 76% IF | 39.6 months | Median prescribed dose 54 Gy | 3.2% symptomatic brain injury | Higher V50–52 to brainstem, female gender, pre-RT high dose chemotherapy, lack of CSI |
| Gunther et al., 2015 [83] Single-institution retrospective | Proton | 37 children Median age 4.4 years Ependymoma | 40.6 months | Median dose 59.4 Gy | 11% symptomatic brainstem injury | N/A |
| Gunther et al., 2015 [83] Single-institution retrospective | Photon | 35 children Median age 6.9 years, ependymoma | 40.6 months | Median dose 54 Gy | 9% symptomatic brainstem injury | N/A |
| Nanda et al., 2017 [77] Single-institution retrospective | Photon | 60 children Median age 6.2 years IF tumors | 2.8 years | CSI 18–36 Gy, Boost 54–59.4 Gy | 23% for any brainstem toxicity, 3% for grade 3+ | N/A |
| Devine et al., 2019 [84] Multi-institution retrospective | Photon | 107 children Median age 8.3 years IF tumors | 4.7 years | Median CSI 23.4 Gy, boost 55.8 Gy. Median brainstem Dmax 57.6 Gy | 1.9% for any brainstem toxicity | N/A |
| SIOP-GCT-96 [148] | ACNS0122 [149] | ACNS1123 [147] | ACNS2021 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RT field | Focal RT | CSI | WVRT | WVRT + Spinal RT |
| RT field prescription dose | 54 Gy | 36 Gy | 30.6 Gy | 30.6 Gy |
| Boost | - | Focal RT | Focal RT | Focal RT |
| Boost volume total dose | - | 54 Gy | 54 Gy | 54 Gy |
| Timepoint | 5 years | 5 years | 3 years | Accruing as of January 2025 |
| PFS | 72% | 84%/92% * | 77%/88% ** | |
| OS | 82% | 93%/98% * | 88%/92% ** |
| Author and Study Type | Patient Population | Median Follow Up | Radiotherapy Technique | Frequency of Neurocognitive Assessment | Hippocampal Dosimetric Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Archarya et al., 2019 [158] Prospective longitudinal observation study | 80 patients from 6–21 years old with low grade glioma | 9.8 years | 54 Gy 3D conformal or intensity modulated radiotherapy | Baseline, 6-month, yearly through year 5, year 7 or 8, then at 10 years | Volume receiving 40 Gy or higher to the right of left hippocampus associated with short-delay recall. |
| Goda et al., 2020 [159] Prospective longitudinal observation study | 48 patients less than 13 years old with benign or low-grade tumors | 5 years | 54 Gy stereotactic conformal radiotherapy | Baseline, 6- month, then annually | Age < 13 years and mean left hippocampal dose > 30 Gy associated with worse FSIQ Mean left hippocampus dose > 25 Gy associated with >10% of the PQ subdomain |
| Zureick et al., 2018 [156] Retrospective review | 70 patients less than 22 years old with primary brain tumor | 3 years | Variable dose using proton therapy | Not specified | Volume receiving 20 Gy or higher to the left hippocampus associated with decline in delayed and immediate verbal and visual memory, FSIQ |
| Merchant et al., 2014 [160] Prospective longitudinal observation study | 58 patients less than 21 years old with medulloblastoma | Not specified (upto 5 years) | 23.4 Gy CSI 55.8 Gy primary site for average risk 36–39.6 Gy CSI 55.8 Gy primary site for high risk | Baseline then annually | Higher left or right hippocampi associated with lower IQ, WIAT reading, spelling, math |
| Redmond et al., 2013 [161] Prospective longitudinal observation study | 19 patients aged 1–18 years with various brain tumors | Not specified (upto 26 months) | 12 Gy–59.4 Gy using various techniques | Baseline, 6-month, 15-month, 27-month | Increasing mean dose to left or right hippocampus associated with worse motor speed and dexterity but not verbal learning or memory |
| Tsang et al., 2020 [157] Prospectively collected retrospective study | 56 patients age 1–17 years old with various brain tumros | 3.2 years | 23.4 Gy–59.4 Gy using photon | Baseline and then every 2–3 years | Dose to 50% of left or right hippocampus associated with lower verbal comprehension index |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, J.; Patel, S.; Schlosser, M.-P.; Arifin, A.J.; Oliveira, C.; Charpentier, A.-M.; Tsang, D.S. Pediatric CNS Radiation Oncology: Recent Developments and Novel Techniques. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32030180
Oh J, Patel S, Schlosser M-P, Arifin AJ, Oliveira C, Charpentier A-M, Tsang DS. Pediatric CNS Radiation Oncology: Recent Developments and Novel Techniques. Current Oncology. 2025; 32(3):180. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32030180
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Justin, Samir Patel, Mary-Pat Schlosser, Andrew J. Arifin, Carol Oliveira, Anne-Marie Charpentier, and Derek S. Tsang. 2025. "Pediatric CNS Radiation Oncology: Recent Developments and Novel Techniques" Current Oncology 32, no. 3: 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32030180
APA StyleOh, J., Patel, S., Schlosser, M.-P., Arifin, A. J., Oliveira, C., Charpentier, A.-M., & Tsang, D. S. (2025). Pediatric CNS Radiation Oncology: Recent Developments and Novel Techniques. Current Oncology, 32(3), 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32030180





