Usage of FTA® Classic Cards for Safe Storage, Shipment, and Detection of Arboviruses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Viruses
2.2. Whatman® FTA® Classic Cards
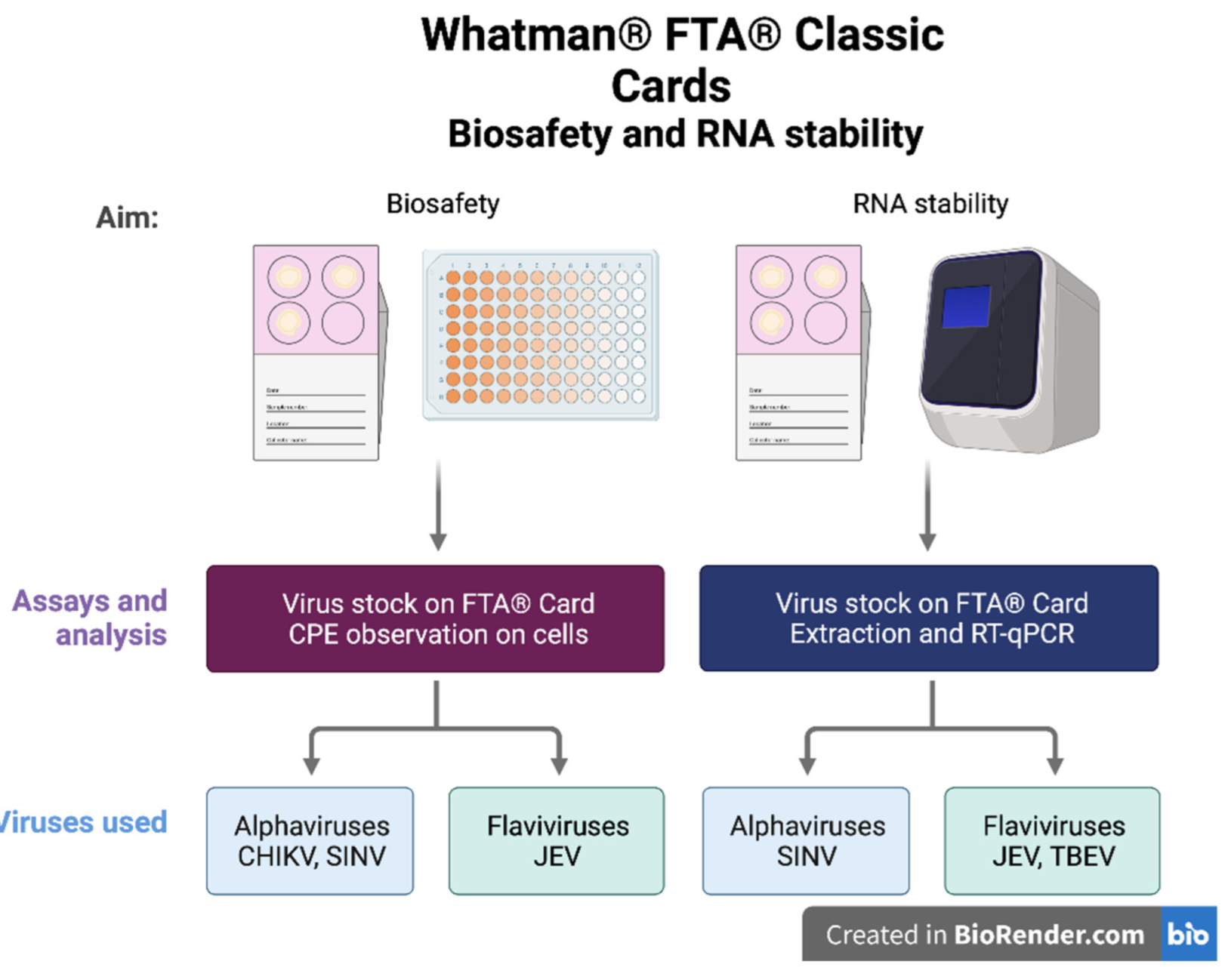
2.3. Biosafety Using FTA® Cards
2.4. RNA Stability on FTA® Cards
2.5. Extraction of Viral RNA from FTA® Cards
2.6. Reverse Transcription Quantitative PCR
2.7. Data Visualization
3. Results
3.1. Cell Viability Assay to Determine the Inactivation of Samples Eluted from the FTA® Cards
3.2. Investigation of the Stability of Alpha- and Flavivirus Viral RNA on the FTA® Cards
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Braack, L.; De Almeida, A.P.G.; Cornel, A.J.; Swanepoel, R.; De Jager, C. Mosquito-borne arboviruses of African origin: Review of key viruses and vectors. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Abbasi, A.B.; Illingworth, C.J.R. Mutational load causes stochastic evolutionary outcomes in acute RNA viral infection. Virus Evol. 2019, 5, vez008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanjuan, R.; Domingo-Calap, P. Mechanisms of viral mutation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 4433–4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McMichael, A.J.; Haines, J.A.; Slooff, R.; Sari Kovats, R.; World Health Organization, Office of Global and Integrated Environmental Health; WHO/WMO/UNEP Task Group on Health Impact Assessement of Climate Change. Climate Change and Human Health: An Assessment/Prepared by a Task Group on Behalf of the World Health Organization, the World Meteorological Association and the United Nations Environment Programme; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996.
- Watson, R.T.; Zinyowera, M.C.; Moss, R.H. Climate Change 1995 Impacts, Adaptations and Mitigation of Climate Change: Scientific-Technical Analyses; IPCC: Cambridge, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, R.T.; Zinyowera, M.C.; Moss, R.H. The Regional Impacts of Climate Change: An Assesment of Vunerability; IPCC: Cambridge, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl, J.F.; Grace, D. The consequences of human actions on risks for infectious diseases: A review. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2015, 5, 30048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Relova, D.; Rios, L.; Acevedo, A.M.; Coronado, L.; Perera, C.L.; Perez, L.J. Impact of RNA Degradation on Viral Diagnosis: An Understated but Essential Step for the Successful Establishment of a Diagnosis Network. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paz, S.; Semenza, J.C. Environmental drivers of West Nile fever epidemiology in Europe and Western Asia—A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 3543–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ziegler, U.; Lühken, R.; Keller, M.; Cadar, D.; van der Grinten, E.; Michel, F.; Albrecht, K.; Eiden, M.; Rinder, M.; Lachmann, L.; et al. West Nile virus epizootic in Germany, 2018. Antivir. Res. 2019, 162, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeller, H.; Van Bortel, W.; Sudre, B. Chikungunya: Its History in Africa and Asia and Its Spread to New Regions in 2013–2014. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 214, S436–S440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, J.H.-O.; Eldholm, V.; Seligman, S.J.; Lundkvist, Å.; Falconar, A.K.; Gaunt, M.W.; Musso, D.; Nougairède, A.; Charrel, R.; Gould, E.A.; et al. Erratum for Pettersson et al. How Did Zika Virus Emerge in the Pacific Islands and Latin America? MBio 2018, 9, e00386-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Go, Y.Y.; Balasuriya, U.B.; Lee, C.K. Zoonotic encephalitides caused by arboviruses: Transmission and epidemiology of alphaviruses and flaviviruses. Clin. Exp. Vaccine Res. 2014, 3, 58–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siengsanan-Lamont, J.; Blacksell, S.D. A Review of Laboratory-Acquired Infections in the Asia-Pacific: Understanding Risk and the Need for Improved Biosafety for Veterinary and Zoonotic Diseases. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2018, 3, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wille, M.; Yin, H.; Lundkvist, A.; Xu, J.; Muradrasoli, S.; Jarhult, J.D. RNAlater® is a viable storage option for avian influenza sampling in logistically challenging conditions. J. Virol. Methods 2018, 252, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, P.H.; Sokeechand, B.S.H.; Garver, K.A.; Jones, G.; Lumsden, J.S.; Bols, N.C. Fish viruses stored in RNAlater can remain infectious and even be temporarily protected from inactivation by heat or by tissue homogenates. J. Virol. Methods 2018, 253, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraus, R.H.; van Hooft, P.; Waldenstrom, J.; Latorre-Margalef, N.; Ydenberg, R.C.; Prins, H.H. Avian influenza surveillance with FTA cards: Field methods, biosafety, and transportation issues solved. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 54, e2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haglund, M.; Vene, S.; Forsgren, M.; Gunther, G.; Johansson, B.; Niedrig, M.; Plyusnin, A.; Lindquist, L.; Lundkvist, A. Characterisation of human tick-borne encephalitis virus from Sweden. J. Med. Virol. 2003, 71, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melik, W.; Nilsson, A.S.; Johansson, M. Detection strategies of tick-borne encephalitis virus in Swedish Ixodes ricinus reveal evolutionary characteristics of emerging tick-borne flaviviruses. Arch. Virol. 2007, 152, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfield, K.L.; Johnson, N.; Phipps, L.P.; Stephenson, J.R.; Fooks, A.R.; Solomon, T. Tick-borne encephalitis virus—A review of an emerging zoonosis. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 1781–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, J.S.; Gurley, E.S.; Pulliam, J.R. Rethinking Japanese Encephalitis Virus Transmission: A Framework for Implicating Host and Vector Species. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0004074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bogovic, P.; Strle, F. Tick-borne encephalitis: A review of epidemiology, clinical characteristics, and management. World J. Clin. Cases 2015, 3, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veje, M.; Studahl, M.; Johansson, M.; Johansson, P.; Nolskog, P.; Bergstrom, T. Diagnosing tick-borne encephalitis: A re-evaluation of notified cases. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurkela, S.; Manni, T.; Myllynen, J.; Vaheri, A.; Vapalahti, O. Clinical and laboratory manifestations of Sindbis virus infection: Prospective study, Finland, 2002–2003. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 191, 1820–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albinsson, B.; Vene, S.; Rombo, L.; Blomberg, J.; Lundkvist, A.; Ronnberg, B. Distinction between serological responses following tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) infection vs. vaccination, Sweden 2017. Eurosurveillance 2018, 23, 17-00838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laine, M.; Luukkainen, R.; Toivanen, A. Sindbis viruses and other alphaviruses as cause of human arthritic disease. J. Intern. Med. 2004, 256, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.; Smura, T.; Lundstrom, J.O.; Pettersson, J.H.; Sironen, T.; Vapalahti, O.; Lundkvist, A.; Hesson, J.C. Introduction and Dispersal of Sindbis Virus from Central Africa to Europe. J. Virol 2019, 93, e00620-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- CDC. Chikungunya Virus. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/chikungunya/index.html (accessed on 1 April 2022).
- Maw, M.T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Kasanga, C.J.; Terasaki, K.; Fukushi, H. A practical tissue sampling method using ordinary paper for molecular detection of infectious bursal disease virus RNA by RT-PCR. Avian Dis. 2006, 50, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelwhab, E.M.; Luschow, D.; Harder, T.C.; Hafez, H.M. The use of FTA® filter papers for diagnosis of avian influenza virus. J. Virol. Methods 2011, 174, 120–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, J.E.; Easterbrook, L.; Pitman, J.; Anderson, D.; Roddy, S.; Bailey, D.; Vipond, R.; Bruce, C.B.; Roberts, A.D. The effect of a non-denaturing detergent and a guanidinium-based inactivation agent on the viability of Ebola virus in mock clinical serum samples. J. Virol. Methods 2017, 250, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines on Viral Inactivation and Removal Procedures Intended to Assure the Viral Safety of Human Blood Plasma Products; Technical Report Series No. 924, Annex 4; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004.
- Patel, P.; Landt, O.; Kaiser, M.; Faye, O.; Koppe, T.; Lass, U.; Sall, A.A.; Niedrig, M. Development of one-step quantitative reverse transcription PCR for the rapid detection of flaviviruses. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jost, H.; Bialonski, A.; Storch, V.; Gunther, S.; Becker, N.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J. Isolation and phylogenetic analysis of Sindbis viruses from mosquitoes in Germany. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 1900–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Team, R. RStudio: Integrated Development for R, version 1.1.453; RStudio Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2015; Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 1 April 2022).
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.A.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healthcare, G. FTA Cards Available online. Available online: https://www.gelifesciences.co.jp/tech_support/manual/pdf/28984354%20AA_FTA%20CardsDataSheet.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2022).
- Ramirez, A.L.; Hall-Mendelin, S.; Hewitson, G.R.; McMahon, J.L.; Staunton, K.M.; Ritchie, S.A.; van den Hurk, A.F. Stability of West Nile Virus (Flaviviridae: Flavivirus) RNA in Mosquito Excreta. J. Med. Entomol. 2019, 56, 1135–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankamp, B.; Sein, C.; Simbu, E.P.; Anderson, R.; Abernathy, E.; Chen, M.-H.; Tamfum, J.-J.M.; Wannemuehler, K.A.; Waku-Kouomou, D.; Lopareva, E.N.; et al. Use of FTA Cards To Transport Throat Swabs and Oral Fluid Samples for Molecular Detection and Genotyping of Measles and Rubella Viruses. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e00048-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De la Torre, D.; Astolfi-Ferreira, C.S.; Chacon, R.D.; Piantino Ferreira, A.J. Sensitive SYBR Green-Real Time PCR for the Detection and Quantitation of Avian Rotavirus A. Vet. Sci. 2018, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kurucz, N.; Minney-Smith, C.A.; Johansen, C.A. Arbovirus surveillance using FTA™ cards in modified CO2 -baited encephalitis virus surveillance traps in the Northern Territory, Australia. J. Vector Ecol. 2019, 44, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hall-Mendelin, S.; Ritchie, S.A.; Johansen, C.A.; Zborowski, P.; Cortis, G.; Dandridge, S.; Hall, R.A.; van den Hurk, A.F. Exploiting mosquito sugar feeding to detect mosquito-borne pathogens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11255–11259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rogers, C.; Burgoyne, L. Bacterial typing: Storing and processing of stabilized reference bacteria for polymerase chain reaction without preparing DNA--an example of an automatable procedure. Anal. Biochem. 1997, 247, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona-Ospina, J.A.; Villalba-Miranda, M.F.; Palechor-Ocampo, L.A.; Mancilla, L.I.; Sepulveda-Arias, J.C. A systematic review of FTA cards(R) as a tool for viral RNA preservation in fieldwork: Are they safe and effective? Prev. Vet. Med. 2019, 172, 104772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water. LT1ESWTR Disinfection Profiling and Benchmarking: Technical Guidance Manual; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 2003.
- Appassakij, H.; Khuntikij, P.; Kemapunmanus, M.; Wutthanarungsan, R.; Silpapojakul, K. Viremic profiles in asymptomatic and symptomatic chikungunya fever: A blood transfusion threat? Transfusion 2013, 53, 2567–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco-Lauth, A.; Mason, G.; Bowen, R. Pathogenesis of Japanese encephalitis virus infection in a golden hamster model and evaluation of flavivirus cross-protective immunity. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011, 84, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murgue, B.; Roche, C.; Chungue, E.; Deparis, X. Prospective study of the duration and magnitude of viraemia in children hospitalised during the 1996–1997 dengue-2 outbreak in French Polynesia. J. Med. Virol. 2000, 60, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricou, V.; Minh, N.N.; Farrar, J.; Tran, H.T.; Simmons, C.P. Kinetics of Viremia and NS1 Antigenemia Are Shaped by Immune Status and Virus Serotype in Adults with Dengue. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Libraty, D.H.; Young, P.R.; Pickering, D.; Endy, T.P.; Kalayanarooj, S.; Green, S.; Vaughn, D.W.; Nisalak, A.; Ennis, F.A.; Rothman, A.L. High circulating levels of the dengue virus nonstructural protein NS1 early in dengue illness correlate with the development of dengue hemorrhagic fever. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 186, 1165–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matangkasombut, P.; Manopwisedjaroen, K.; Pitabut, N.; Thaloengsok, S.; Suraamornkul, S.; Yingtaweesak, T.; Duong, V.; Sakuntabhai, A.; Paul, R.; Singhasivanon, P. Dengue viremia kinetics in asymptomatic and symptomatic infection. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 101, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, H.A.; MacLeod, E.T.; Hide, G.; Welburn, S.C.; Picozzi, K. The best practice for preparation of samples from FTA®cards for diagnosis of blood borne infections using African trypanosomes as a model system. Parasites Vectors 2011, 4, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, E.H.; Velez, J.O.; Russell, B.J.; Basile, A.J.; Brault, A.C.; Hughes, H.R. Evaluation of Whatman FTA cards for the preservation of yellow fever virus RNA for use in molecular diagnostics. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, T.; Ishii, A.; Segawa, T.; Takagi, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Itou, T. Establishing conditions for the storage and elution of rabies virus RNA using FTA® cards. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2015, 77, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mackay, I.M.; Arden, K.E.; Nitsche, A. Real-time PCR in virology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 1292–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernandez, R.; Brown, D.T.; Paredes, A. Structural differences observed in arboviruses of the alphavirus and flavivirus genera. Adv. Virol. 2014, 2014, 259382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, R.; Wang, M.; Yin, Z.; Cheng, A. Structure and function of capsid protein in flavivirus infection and its applications in the development of vaccines and therapeutics. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| (A) Vero E6 cells | |||||||||||||||
| FTA® | FTA® | FTA® | FTA® JEV | FTA® JEV | FTA® JEV | FTA® CHIKV | FTA® CHIKV | FTA® CHIKV | JEV | JEV | JEV | CHIKV | CHIKV | CHIKV | |
| 1 | ! | ! | ! | ! | ! | ! | ! | ! | ! | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 10−1 | ! | ! | ! | ! | ! | ! | ! | ! | ! | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 10−2 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 10−3 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 10−4 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | − | + | + | + |
| 10−5 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | + |
| 10−6 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | + |
| 10−7 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| (B) Vero cells | |||||||||||||||
| FTA® | FTA® | FTA® | FTA® SINV | FTA® SINV | FTA® SINV | SINV | SINV | SINV | |||||||
| 1 | ! | ! | ! | ! | ! | ! | + | + | + | ||||||
| 10−1 | ! | ! | ! | ! | ! | ! | + | + | + | ||||||
| 10−2 | ! | ! | ! | ! | ! | ! | + | + | + | ||||||
| 10−3 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | + | ||||||
| 10−4 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | + | ||||||
| 10−5 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | ||||||
| 10−6 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | ||||||
| 10−7 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krambrich, J.; Bringeland, E.; Hesson, J.C.; Hoffman, T.; Lundkvist, Å.; Lindahl, J.F.; Ling, J. Usage of FTA® Classic Cards for Safe Storage, Shipment, and Detection of Arboviruses. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10071445
Krambrich J, Bringeland E, Hesson JC, Hoffman T, Lundkvist Å, Lindahl JF, Ling J. Usage of FTA® Classic Cards for Safe Storage, Shipment, and Detection of Arboviruses. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(7):1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10071445
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrambrich, Janina, Emelie Bringeland, Jenny C. Hesson, Tove Hoffman, Åke Lundkvist, Johanna F. Lindahl, and Jiaxin Ling. 2022. "Usage of FTA® Classic Cards for Safe Storage, Shipment, and Detection of Arboviruses" Microorganisms 10, no. 7: 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10071445
APA StyleKrambrich, J., Bringeland, E., Hesson, J. C., Hoffman, T., Lundkvist, Å., Lindahl, J. F., & Ling, J. (2022). Usage of FTA® Classic Cards for Safe Storage, Shipment, and Detection of Arboviruses. Microorganisms, 10(7), 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10071445







