Ligands of Therapeutic Utility for the Liver X Receptors
Abstract
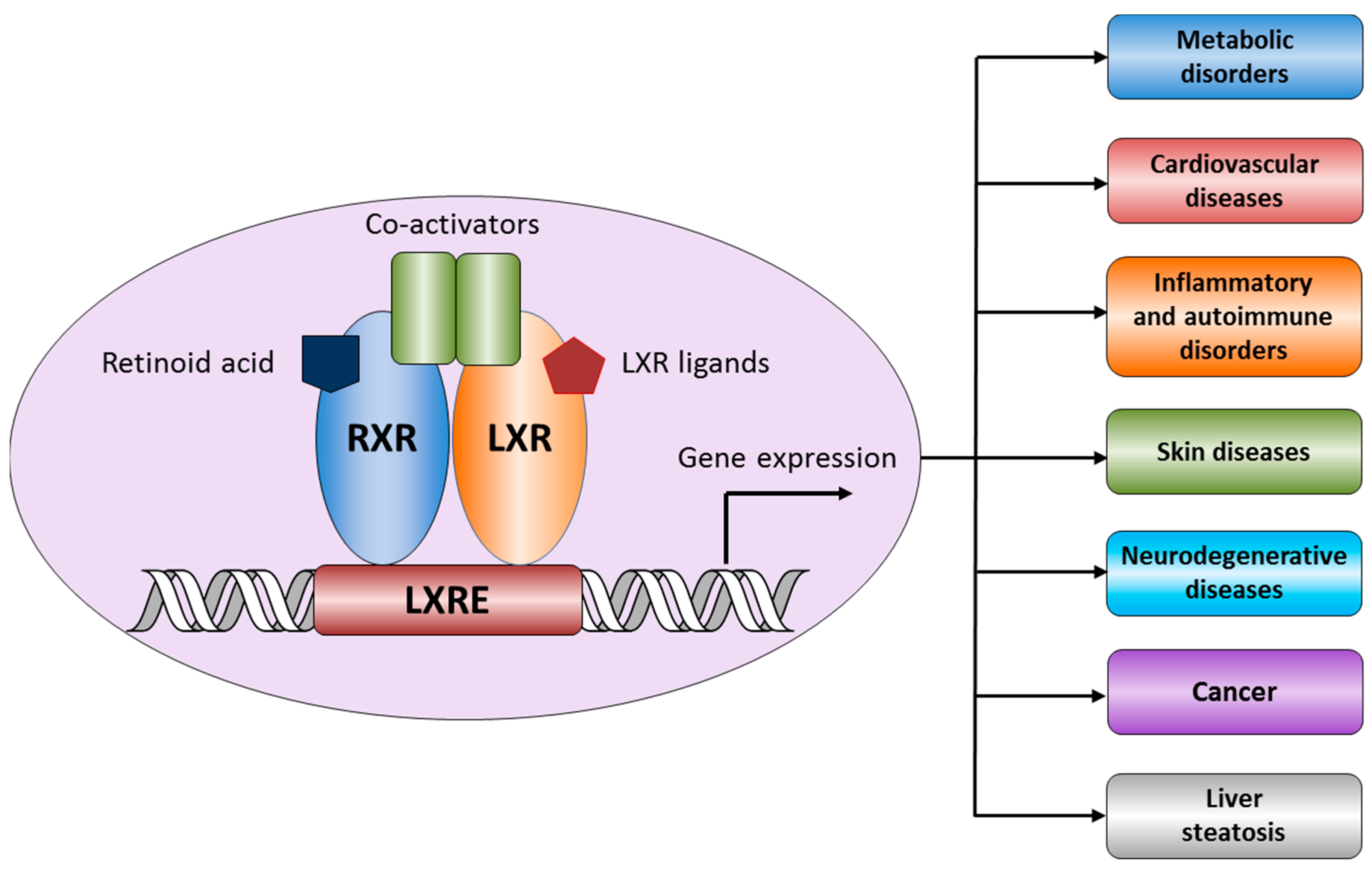
:1. Structure and Functions of Liver X Receptors
1.1. LXR and Atherosclerosis
1.2. LXR and Cancer
1.3. LXR and Alzheimer’s Disease (AD)
2. Ligands of Liver X Receptors
2.1. Endogenous Agonists
2.2. Endogenous Antagonists
2.3. Natural Products and Derivatives
2.3.1. Natural Agonists
2.3.2. Natural Antagonists
2.3.3. Synthetic LXR Ligands
3. LXR Ligand Design Considerations—A Molecular Modeling Perspective
4. Summary
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laudet, V.; Gronemeyer, H. The Nuclear Receptor FactsBook; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Janowski, B.A.; Grogan, M.J.; Jones, S.A.; Wisely, G.B.; Kliewer, S.A.; Corey, E.J.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. Structural requirements of ligands for the oxysterol liver X receptors LXRα and LXRβ. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apfel, R.; Benbrook, D.; Lernhardt, E.; Ortiz, M.A.; Salbert, G.; Pfahl, M. A novel orphan receptor specific for a subset of thyroid hormone-responsive elements and its interaction with the retinoid/thyroid hormone receptor subfamily. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1994, 14, 7025–7035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willy, P.J.; Umesono, K.; Ong, E.S.; Evans, R.M.; Heyman, R.A.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. LXR, a nuclear receptor that defines a distinct retinoid response pathway. Genes Dev. 1995, 9, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Hiipakka, R.A.; Kokontis, J.M.; Liao, S. Ubiquitous Receptor: Structures, Immunocytochemical Localization, and Modulation of Gene Activation by Receptors for Retinoic Acids and Thyroid Hormonesa. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1995, 761, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinar, D.M.; Endo, N.; Rutledge, S.J.; Vogel, R.; Rodan, G.A.; Schmidt, A. NER, a new member of the gene family encoding the human steroid hormone nuclear receptor. Gene 1994, 147, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson-Rechavi, M.; Escriva Garcia, H.; Laudet, V. The nuclear receptor superfamily. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 585–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tice, C.M.; Noto, P.B.; Fan, K.Y.; Zhuang, L.; Lala, D.S.; Singh, S.B. The Medicinal Chemistry of Liver X Receptor (LXR) Modulators. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 7182–7205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, S.; Ostberg, T.; Jacobsson, M.; Norstrom, C.; Stefansson, K.; Hallen, D.; Johansson, I.C.; Zachrisson, K.; Ogg, D.; Jendeberg, L. Crystal structure of the heterodimeric complex of LXRalpha and RXRbeta ligand-binding domains in a fully agonistic conformation. EMBO J. 2003, 2, 4625–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Li, S.; Wu, J.; Xia, C.; Lala, D.S. Liver X receptors interact with corepressors to regulate gene expression. Mol. Endocrinol. 2003, 17, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, P.A.; Kennedy, M.A.; Mak, P.A. LXRs; Oxysterol-activated nuclear receptors that regulate genes controlling lipid homeostasis. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2002, 38, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.D.; Tontonoz, P. Liver X receptors at the intersection of lipid metabolism and atherogenesis. Atherosclerosis 2015, 242, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Gross, K.W. Transcriptional regulation of renin: An update. Hypertension 2005, 45, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoval-Hernandez, A.G.; Buitrago, L.; Moreno, H.; Cardona-Gomez, G.P.; Arboleda, G. Role of Liver X Receptor in AD Pathophysiology. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummins, C.L.; Volle, D.H.; Zhang, Y.; McDonald, J.G.; Sion, B.; Lefrancois-Martinez, A.M.; Caira, F.; Veyssiere, G.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Lobaccaro, J.M. Liver X receptors regulate adrenal cholesterol balance. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1902–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmuth, M.; Moosbrugger-Martinz, V.; Blunder, S.; Dubrac, S. Role of PPAR, LXR, and PXR in epidermal homeostasis and inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabitova, L.; Gorin, A.; Astsaturov, I. Molecular pathways: Sterols and receptor signaling in cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codina, A.; Love, J.D.; Li, Y.; Lazar, M.A.; Neuhaus, D.; Schwabe, J.W. Structural insights into the interaction and activation of histone deacetylase 3 by nuclear receptor corepressors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 6009–6014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, J.R.; Ballesteros, I.; Deniz, J.M.; Hurtado, O.; Vivancos, J.; Nombela, F.; Lizasoain, I.; Castrillo, A.; Moro, M.A. Activation of liver X receptors promotes neuroprotection and reduces brain inflammation in experimental stroke. Circulation 2008, 118, 1450–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sironi, L.; Mitro, N.; Cimino, M.; Gelosa, P.; Guerrini, U.; Tremoli, E.; Saez, E. Treatment with LXR agonists after focal cerebral ischemia prevents brain damage. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 3396–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bensinger, S.J.; Bradley, M.N.; Joseph, S.B.; Zelcer, N.; Janssen, E.M.; Hausner, M.A.; Shih, R.; Parks, J.S.; Edwards, P.A.; Jamieson, B.D.; et al. LXR signaling couples sterol metabolism to proliferation in the acquired immune response. Cell 2008, 134, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geyeregger, R.; Shehata, M.; Zeyda, M.; Kiefer, F.W.; Stuhlmeier, K.M.; Porpaczy, E.; Zlabinger, G.J.; Jager, U.; Stulnig, T.M. Liver X receptors interfere with cytokine-induced proliferation and cell survival in normal and leukemic lymphocytes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 86, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, S.B.; Castrillo, A.; Laffitte, B.A.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Tontonoz, P. Reciprocal regulation of inflammation and lipid metabolism by liver X receptors. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castrillo, A.; Joseph, S.B.; Marathe, C.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Tontonoz, P. Liver X receptor-dependent repression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 10443–10449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.; Langmann, T.; Schmitz, G.; Zhu, Y. Native LDL upregulation of ATP-binding cassette transporter-1 in human vascular endothelial cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002, 22, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norata, G.D.; Ongari, M.; Uboldi, P.; Pellegatta, F.; Catapano, A.L. Liver X receptor and retinoic X receptor agonists modulate the expression of genes involved in lipid metabolism in human endothelial cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2005, 16, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bradley, M.N.; Hong, C.; Chen, M.; Joseph, S.B.; Wilpitz, D.C.; Wang, X.; Lusis, A.J.; Collins, A.; Hseuh, W.A.; Collins, J.L.; et al. Ligand activation of LXR beta reverses atherosclerosis and cellular cholesterol overload in mice lacking LXR alpha and apoE. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 2337–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.Y.; Ou, X.; Hao, X.R.; Cao, D.L.; Tang, Y.L.; Hu, Y.W.; Li, X.X.; Tang, C.K. The effect of T0901317 on ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 and Niemann-Pick type C1 in apoE−/− mice. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2008, 51, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, S.B.; Laffitte, B.A.; Patel, P.H.; Watson, M.A.; Matsukuma, K.E.; Walczak, R.; Collins, J.L.; Osborne, T.F.; Tontonoz, P. Direct and indirect mechanisms for regulation of fatty acid synthase gene expression by liver X receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 11019–11025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repa, J.J.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. The liver X receptor gene team: Potential new players in atherosclerosis. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1243–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Hao, M.; Luo, Y.; Liang, C.P.; Silver, D.L.; Cheng, C.; Maxfield, F.R.; Tall, A.R. Stearoyl-CoA desaturase inhibits ATP-binding cassette transporter A1-mediated cholesterol efflux and modulates membrane domain structure. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 5813–5820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kratzer, A.; Buchebner, M.; Pfeifer, T.; Becker, T.M.; Uray, G.; Miyazaki, M.; Miyazaki-Anzai, S.; Ebner, B.; Chandak, P.G.; Kadam, R.S.; et al. Synthetic LXR agonist attenuates plaque formation in apoE−/− mice without inducing liver steatosis and hypertriglyceridemia. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 312–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, N.; Bischoff, E.D.; Daige, C.L.; Thomas, D.; Vu, C.T.; Heyman, R.A.; Tangirala, R.K.; Schulman, I.G. Macrophage liver X receptor is required for antiatherogenic activity of LXR agonists. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, D.; Hiipakka, R.A.; Dai, Q.; Guo, J.; Reardon, C.A.; Getz, G.S.; Liao, S. Antiatherosclerotic effects of a novel synthetic tissue-selective steroidal liver X receptor agonist in low-density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 327, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, D.; Hiipakka, R.A.; Reardon, C.A.; Getz, G.S.; Liao, S. Differential anti-atherosclerotic effects in the innominate artery and aortic sinus by the liver X receptor agonist T0901317. Atherosclerosis 2009, 203, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinet, E.M.; Basso, M.D.; Halpern, A.R.; Yates, D.W.; Steffan, R.J.; Clerin, V.; Resmini, C.; Keith, J.C.; Berrodin, T.J.; Feingold, I.; et al. LXR ligand lowers LDL cholesterol in primates, is lipid neutral in hamster, and reduces atherosclerosis in mouse. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 2358–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terasaka, N.; Hiroshima, A.; Koieyama, T.; Ubukata, N.; Morikawa, Y.; Nakai, D.; Inaba, T. T-0901317, a synthetic liver X receptor ligand, inhibits development of atherosclerosis in LDL receptor-deficient mice. FEBS Lett. 2003, 536, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, A.J.; Sheu, M.Y.; Schmuth, M.; Kao, J.; Fluhr, J.W.; Rhein, L.; Collins, J.L.; Willson, T.M.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Elias, P.M.; et al. Liver X receptor activators display anti-inflammatory activity in irritant and allergic contact dermatitis models: Liver-X-receptor-specific inhibition of inflammation and primary cytokine production. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 120, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatano, Y.; Man, M.Q.; Uchida, Y.; Crumrine, D.; Mauro, T.M.; Feingold, K.R.; Elias, P.M.; Holleran, W.M. Murine atopic dermatitis responds to peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors alpha and beta/delta (but not gamma) and liver X receptor activators. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuchi, J.; Kokontis, J.M.; Hiipakka, R.A.; Chuu, C.P.; Liao, S. Antiproliferative effect of liver X receptor agonists on LNCaP human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7686–7689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuu, C.P.; Hiipakka, R.A.; Kokontis, J.M.; Fukuchi, J.; Chen, R.Y.; Liao, S. Inhibition of tumor growth and progression of LNCaP prostate cancer cells in athymic mice by androgen and liver X receptor agonist. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 6482–6486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rough, J.J.; Monroy, M.A.; Yerrum, S.; Daly, J.M. Anti-proliferative effect of LXR agonist T0901317 in ovarian carcinoma cells. J. Ovarian Res. 2010, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vedin, L.L.; Lewandowski, S.A.; Parini, P.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Steffensen, K.R. The oxysterol receptor LXR inhibits proliferation of human breast cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuu, C.P.; Lin, H.P. Antiproliferative effect of LXR agonists T0901317 and 22(R)-hydroxycholesterol on multiple human cancer cell lines. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 3643–3648. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Noghero, A.; Perino, A.; Seano, G.; Saglio, E.; Lo Sasso, G.; Veglio, F.; Primo, L.; Hirsch, E.; Bussolino, F.; Morello, F. Liver X receptor activation reduces angiogenesis by impairing lipid raft localization and signaling of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 2280–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pages, G.; Pouyssegur, J. Transcriptional regulation of the Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor gene—A concert of activating factors. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005, 65, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Roz, A.; Bard, J.M.; Valin, S.; Huvelin, J.M.; Nazih, H. Macrophage apolipoprotein E and proliferation of MCF-7 breast cancer cells: Role of LXR. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 3783–3789. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pencheva, N.; Buss, C.G.; Posada, J.; Merghoub, T.; Tavazoie, S.F. Broad-spectrum therapeutic suppression of metastatic melanoma through nuclear hormone receptor activation. Cell 2014, 156, 986–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strittmatter, W.J.; Saunders, A.M.; Schmechel, D.; Pericak-Vance, M.; Enghild, J.; Salvesen, G.S.; Roses, A.D. Apolipoprotein E: High-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 1977–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellano, J.M.; Kim, J.; Stewart, F.R.; Jiang, H.; DeMattos, R.B.; Patterson, B.W.; Fagan, A.M.; Morris, J.C.; Mawuenyega, K.G.; Cruchaga, C.; et al. Human apoE isoforms differentially regulate brain amyloid-beta peptide clearance. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 89ra57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suon, S.; Zhao, J.; Villarreal, S.A.; Anumula, N.; Liu, M.; Carangia, L.M.; Renger, J.J.; Zerbinatti, C.V. Systemic treatment with liver X receptor agonists raises apolipoprotein E, cholesterol, and amyloid-beta peptides in the cerebral spinal fluid of rats. Mol. Neurodegener. 2010, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahrle, S.E.; Jiang, H.; Parsadanian, M.; Legleiter, J.; Han, X.; Fryer, J.D.; Kowalewski, T.; Holtzman, D.M. ABCA1 is required for normal central nervous system ApoE levels and for lipidation of astrocyte-secreted apoE. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 40987–40993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koldamova, R.; Lefterov, I. Role of LXR and ABCA1 in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease—Implications for a new therapeutic approach. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2007, 4, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stachel, S.J.; Zerbinatti, C.; Rudd, M.T.; Cosden, M.; Suon, S.; Nanda, K.K.; Wessner, K.; DiMuzio, J.; Maxwell, J.; Wu, Z.; et al. Identification and in Vivo Evaluation of Liver X Receptor beta-Selective Agonists for the Potential Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 3489–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janowski, B.A.; Willy, P.J.; Devi, T.R.; Falck, J.R.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. An oxysterol signalling pathway mediated by the nuclear receptor LXR alpha. Nature 1996, 383, 728–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, J.M.; Kliewer, S.A.; Moore, L.B.; Smith-Oliver, T.A.; Oliver, B.B.; Su, J.L.; Sundseth, S.S.; Winegar, D.A.; Blanchard, D.E.; Spencer, T.A.; et al. Activation of the nuclear receptor LXR by oxysterols defines a new hormone response pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 3137–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorkhem, I. Rediscovery of cerebrosterol. Lipids 2007, 42, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorkhem, I. Crossing the barrier: Oxysterols as cholesterol transporters and metabolic modulators in the brain. J. Intern. Med. 2006, 260, 493–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pikuleva, I.A. Cholesterol-metabolizing cytochromes P450. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2006, 34, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Liao, S. Cholestenoic acid is a naturally occurring ligand for liver X receptor alpha. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 4180–4184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Menke, J.G.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, G.; MacNaul, K.L.; Wright, S.D.; Sparrow, C.P.; Lund, E.G. 27-hydroxycholesterol is an endogenous ligand for liver X receptor in cholesterol-loaded cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 38378–38387. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Chen, G.; Head, D.L.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Russell, D.W. Enzymatic reduction of oxysterols impairs LXR signaling in cultured cells and the livers of mice. Cell Metab. 2007, 5, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, J.; Quinn, C.M.; Gelissen, I.C.; Brown, A.J. Endogenous 24(S),25-epoxycholesterol fine-tunes acute control of cellular cholesterol homeostasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; McDonald, J.G.; Patel, A.; Zhang, Y.; Umetani, M.; Xu, F.; Westover, E.J.; Covey, D.F.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Cohen, J.C.; et al. Sterol intermediates from cholesterol biosynthetic pathway as liver X receptor ligands. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 27816–27826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byskov, A.G.; Baltsen, M.; Andersen, C.Y. Meiosis-activating sterols: Background, discovery, and possible use. J. Mol. Med. 1998, 76, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, J.; Tu, H.; Shan, B.; Luk, A.; DeBose-Boyd, R.A.; Bashmakov, Y.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. Unsaturated fatty acids inhibit transcription of the sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) gene by antagonizing ligand-dependent activation of the LXR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 6027–6032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, T.; Shimano, H.; Yahagi, N.; Ide, T.; Amemiya-Kudo, M.; Matsuzaka, T.; Nakakuki, M.; Tomita, S.; Okazaki, H.; Tamura, Y.; et al. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Suppress Sterol Regulatory Element-binding Protein 1c Promoter Activity by Inhibition of Liver X Receptor (LXR) Binding to LXR Response Elements. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 1705–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, R.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Shen, X. Regulation of prostaglandin F2α against β amyloid clearance and its inflammation induction through LXR/RXR heterodimer antagonism in microglia. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2013, 106, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.M.; Gang, G.T.; Kim, D.K.; Kim, Y.D.; Koo, S.H.; Lee, C.H.; Choi, H.S. Ursodeoxycholic acid inhibits liver X receptor alpha-mediated hepatic lipogenesis via induction of the nuclear corepressor SMILE. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 1079–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrodin, T.J.; Shen, Q.; Quinet, E.M.; Yudt, M.R.; Freedman, L.P.; Nagpal, S. Identification of 5α,6α-Epoxycholesterol as a Novel Modulator of Liver X Receptor Activity. Mol. Pharmacol. 2010, 78, 1046–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C. Natural modulators of liver X receptors. J. Integr. Med. 2014, 12, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plat, J.; Mensink, R.P. Increased intestinal ABCA1 expression contributes to the decrease in cholesterol absorption after plant stanol consumption. FASEB J. 2002, 16, 1248–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plat, J.; Nichols, J.A.; Mensink, R.P. Plant sterols and stanols: Effects on mixed micellar composition and LXR (target gene) activation. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 2468–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plosch, T.; Kruit, J.K.; Bloks, V.W.; Huijkman, N.C.; Havinga, R.; Duchateau, G.S.; Lin, Y.; Kuipers, F. Reduction of cholesterol absorption by dietary plant sterols and stanols in mice is independent of the Abcg5/8 transporter. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 2135–2140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoang, M.H.; Jia, Y.; Jun, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, B.Y.; Lee, S.J. Fucosterol is a selective liver X receptor modulator that regulates the expression of key genes in cholesterol homeostasis in macrophages, hepatocytes, and intestinal cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 11567–11575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, E.; Matsuda, M.; Yamada, Y.; Tachibana, Y.; Shimomura, I.; Makishima, M. Induction of intestinal ATP-binding cassette transporters by a phytosterol-derived liver X receptor agonist. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 36091–36098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, T.; Yao, Y.-L.; Jin, X.-J.; Lian, L.-H.; Li, Q.; Yang, N.; Jin, Q.; Wu, Y.-L.; Nan, J.-X. Acanthoic acid, a diterpene in Acanthopanax koreanum, ameliorates the development of liver fibrosis via LXRs signals. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 218, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traves, P.G.; Hortelano, S.; Zeini, M.; Chao, T.H.; Lam, T.; Neuteboom, S.T.; Theodorakis, E.A.; Palladino, M.A.; Castrillo, A.; Bosca, L. Selective activation of liver X receptors by acanthoic acid-related diterpenes. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 71, 1545–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayasuriya, H.; Herath, K.B.; Ondeyka, J.G.; Guan, Z.; Borris, R.P.; Tiwari, S.; de Jong, W.; Chavez, F.; Moss, J.; Stevenson, D.W.; et al. Diterpenoid, steroid, and triterpenoid agonists of liver X receptors from diversified terrestrial plants and marine sources. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.H.; Razmovski-Naumovski, V.; Salam, N.K.; Duke, R.K.; Tran, V.H.; Duke, C.C.; Roufogalis, B.D. A novel LXR-alpha activator identified from the natural product Gynostemma pentaphyllum. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 70, 1298–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherwood, I.R.; Short, W.F. 192. Podocarpic acid. Part I. J. Chem. Soc. Resumed 1938, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.B.; Ondeyka, J.G.; Liu, W.; Chen, S.; Chen, T.S.; Li, X.; Bouffard, A.; Dropinski, J.; Jones, A.B.; McCormick, S.; et al. Discovery and development of dimeric podocarpic acid leads as potent agonists of liver X receptor with HDL cholesterol raising activity in mice and hamsters. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 2824–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, C.G.; Horike, H.; Cha, B.Y.; Uhm, K.O.; Yamauchi, R.; Yamaguchi, T.; Hosono, T.; Iida, K.; Woo, J.T.; Michikawa, M. Honokiol increases ABCA1 expression level by activating retinoid X receptor beta. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 33, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotani, H.; Tanabe, H.; Mizukami, H.; Makishima, M.; Inoue, M. Identification of a naturally occurring rexinoid, honokiol, that activates the retinoid X receptor. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1332–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.R. Paeoniflorin acts as a liver X receptor agonist. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 15, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, H.J.; Hoang, M.H.; Lee, J.W.; Yaoyao, J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, H.J.; Seo, W.D.; Hwang, B.Y.; Lee, S.J. Iristectorigenin B isolated from Belamcanda chinensis is a liver X receptor modulator that increases ABCA1 and ABCG1 expression in macrophage RAW 264.7 cells. Biotechnol. Lett. 2012, 3, 2213–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, M.H.; Jia, Y.; Jun, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, D.H.; Hwang, B.Y.; Kim, W.J.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, S.J. Ethyl 2,4,6-trihydroxybenzoate is an agonistic ligand for liver X receptor that induces cholesterol efflux from macrophages without affecting lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 4094–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Hoang, M.H.; Jun, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.J. Cyanidin, a natural flavonoid, is an agonistic ligand for liver X receptor alpha and beta and reduces cellular lipid accumulation in macrophages and hepatocytes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 4185–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, H.J.; Hoang, M.H.; Yeo, S.K.; Jia, Y.; Lee, S.J. Induction of ABCA1 and ABCG1 expression by the liver X receptor modulator cineole in macrophages. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bramlett, K.S.; Houck, K.A.; Borchert, K.M.; Dowless, M.S.; Kulanthaivel, P.; Zhang, Y.; Beyer, T.P.; Schmidt, R.; Thomas, J.S.; Michael, L.F.; et al. A natural product ligand of the oxysterol receptor, liver X receptor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 307, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herath, K.; Jayasuriya, H.; Ondeyka, J.G.; Guan, Z.; Borris, R.P.; Stijfhoorn, E.; Stevenson, D.; Wang, J.; Sharma, N.; Macnaul, K.; et al. Guttiferone I, a new prenylated benzophenone from Garcinia humilis as a liver X receptor ligand. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 6, 617–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamehiro, N.; Sato, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Asakawa, Y.; Yokoyama, S.; Kawanishi, T.; Ohno, Y.; Inoue, K.; Nagao, T.; et al. Riccardin C: A natural product that functions as a liver X receptor (LXR)alpha agonist and an LXRbeta antagonist. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 5299–5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldwasser, J.; Cohen, P.Y.; Yang, E.; Balaguer, P.; Yarmush, M.L.; Nahmias, Y. Transcriptional regulation of human and rat hepatic lipid metabolism by the grapefruit flavonoid naringenin: Role of PPARalpha, PPARgamma and LXRalpha. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Granillo, M.; Steffensen, K.R.; Granados, O.; Torres, N.; Korach-Andre, M.; Ortiz, V.; Aguilar-Salinas, C.; Jakobsson, T.; Diaz-Villasenor, A.; Loza-Valdes, A.; et al. Soy protein isoflavones differentially regulate liver X receptor isoforms to modulate lipid metabolism and cholesterol transport in the liver and intestine in mice. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 2469–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, M.H.; Jia, Y.; Jun, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Hwang, K.Y.; Choi, D.W.; Um, S.J.; Lee, B.Y.; You, S.G.; Lee, S.J. Taurine is a liver X receptor-alpha ligand and activates transcription of key genes in the reverse cholesterol transport without inducing hepatic lipogenesis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 900–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, X.; Wang, M.; Lu, M.; Xi, B.; Sheng, H.; Zang, Y.Q. Rhein ameliorates fatty liver disease through negative energy balance, hepatic lipogenic regulation, and immunomodulation in diet-induced obese mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 300, E886–E893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanaya, N.; Kubo, M.; Liu, Z.; Chu, P.; Wang, C.; Yuan, Y.C.; Chen, S. Protective effects of white button mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) against hepatic steatosis in ovariectomized mice as a model of postmenopausal women. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, N.; Sun, Q.; Ding, X.; Li, G.; Zheng, B.; Gu, M.; Huang, F.; Sun, Y.Q.; et al. Extract of Kuding tea prevents high-fat diet-induced metabolic disorders in C57BL/6 mice via liver X receptor (LXR) beta antagonism. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Yang, B.; Huang, C. Okra polysaccharide improves metabolic disorders in high-fat diet-induced obese C57BL/6 mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 2075–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, T.S.; Oh, W.K.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, J.B. Selective LXRalpha inhibitory effects observed in plant extracts of MEH184 (Parthenocissua tricuspidata) and MEH185 (Euscaphis japonica). Biochem. Biophys Res. Commun. 2006, 349, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.; Bledsoe, R.K.; Collins, J.L.; Boggs, S.; Lambert, M.H.; Miller, A.B.; Moore, J.; McKee, D.D.; Moore, L.; Nichols, J.; et al. X-ray crystal structure of the liver X receptor beta ligand binding domain: Regulation by a histidine-tryptophan switch. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 27138–27143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viennois, E.; Mouzat, K.; Dufour, J.; Morel, L.; Lobaccaro, J.M.; Baron, S. Selective liver X receptor modulators (SLiMs): What use in human health? Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 351, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farnegardh, M.; Bonn, T.; Sun, S.; Ljunggren, J.; Ahola, H.; Wilhelmsson, A.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Carlquist, M. The three-dimensional structure of the liver X receptor beta reveals a flexible ligand-binding pocket that can accommodate fundamentally different ligands. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 38821–38828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fradera, X.; Vu, D.; Nimz, O.; Skene, R.; Hosfield, D.; Wynands, R.; Cooke, A.J.; Haunso, A.; King, A.; Bennett, D.J.; et al. X-ray structures of the LXRalpha LBD in its homodimeric form and implications for heterodimer signaling. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 399, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, S.B.; McKilligin, E.; Pei, L.; Watson, M.A.; Collins, A.R.; Laffitte, B.A.; Chen, M.; Noh, G.; Goodman, J.; Hagger, G.N.; et al. Synthetic LXR ligand inhibits the development of atherosclerosis in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7604–7609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaye, M.C.; Krawiec, J.A.; Campobasso, N.; Smallwood, A.; Qiu, C.; Lu, Q.; Kerrigan, J.J.; De Los Frailes Alvaro, M.; Laffitte, B.; Liu, W.S.; et al. Discovery of substituted maleimides as liver X receptor agonists and determination of a ligand-bound crystal structure. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 5419–5422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, E.Y.; Caravella, J.A.; Watson, M.A.; Campobasso, N.; Ghisletti, S.; Billin, A.N.; Galardi, C.; Wang, P.; Laffitte, B.A.; Iannone, M.A.; et al. Structure-guided design of N-phenyl tertiary amines as transrepression-selective liver X receptor modulators with anti-inflammatory activity. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 5758–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Yamazaki, T.; Yoshida, M.; Arai, M.; Terasaka, N.; Honzumi, S.; Wakabayashi, K.; Hayashi, S.; Nakai, D.; et al. Discovery and structure-guided optimization of tert-butyl 6-(phenoxymethyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzoates as liver X receptor agonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 3914–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopecky, D.J.; Jiao, X.Y.; Fisher, B.; McKendry, S.; Labelle, M.; Piper, D.E.; Coward, P.; Shiau, A.K.; Escaron, P.; Danao, J.; et al. Discovery of a new binding mode for a series of liver X receptor agonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 2407–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernotas, R.C.; Singhaus, R.R.; Kaufman, D.H.; Travins, J.M.; Ullrich, J.W.; Unwalla, R.; Quinet, E.; Evans, M.; Nambi, P.; Olland, A.; et al. 4-(3-Aryloxyaryl)quinoline sulfones are potent liver X receptor agonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kick, E.; Martin, R.; Xie, Y.; Flatt, B.; Schweiger, E.; Wang, T.L.; Busch, B.; Nyman, M.; Gu, X.H.; Yan, G.; et al. Liver X receptor (LXR) partial agonists: Biaryl pyrazoles and imidazoles displaying a preference for LXRbeta. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhuang, L.; Fan, K.Y.; Tice, C.M.; Zhao, W.; Dong, C.; Lotesta, S.D.; Leftheris, K.; Lindblom, P.R.; Liu, Z.; et al. Discovery of a Novel, Orally Efficacious Liver X Receptor (LXR) beta Agonist. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 3264–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tice, C.M.; Noto, P.B.; Fan, K.Y.; Zhao, W.; Lotesta, S.D.; Dong, C.; Marcus, A.P.; Zheng, Y.J.; Chen, G.; Wu, Z.; et al. Brain penetrant liver X receptor (LXR) modulators based on a 2,4,5,6-tetrahydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrazole core. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 5044–5050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gronemeyer, H.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Laudet, V. Principles for modulation of the nuclear receptor superfamily. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 950–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuercher, W.J.; Buckholz, R.G.; Campobasso, N.; Collins, J.L.; Galardi, C.M.; Gampe, R.T.; Hyatt, S.M.; Merrihew, S.L.; Moore, J.T.; Oplinger, J.A.; et al. Discovery of tertiary sulfonamides as potent liver X receptor antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 3412–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, J.R.; Tu, H.; Luk, A.; Repa, J.J.; Medina, J.C.; Li, L.; Schwendner, S.; Wang, S.; Thoolen, M.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; et al. Role of LXRs in control of lipogenesis. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 2831–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, W.R., Jr.; Shenk, J.L.; Snaith, M.R.; Russell, C.S.; Plunket, K.D.; Bodkin, N.L.; Lewis, M.C.; Winegar, D.A.; Sznaidman, M.L.; Lambert, M.H.; et al. A selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta agonist promotes reverse cholesterol transport. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 5306–5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurecka, P.; Cerny, J.; Hobza, P.; Salahub, D.R. Density functional theory augmented with an empirical dispersion term. Interaction energies and geometries of 80 noncovalent complexes compared with ab initio quantum mechanics calculations. J. Comput. Chem. 2007, 28, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neese, F. The ORCA program system. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2012, 2, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezac, J. Cuby: An integrative framework for computational chemistry. J. Comput. Chem. 2016, 37, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klamt, A. Conductor-like Screening Model for Real Solvents: A New Approach to the Quantitative Calculation of Solvation Phenomena. J. Phys. Chem. 1995, 99, 2224–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, K.E.; Merz, K.M., Jr. Role of solvation in the energy stabilization inside the hydrophobic core of the protein rubredoxin. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 15650–15653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheiner, S.; Kar, T. Effect of solvent upon CH...O hydrogen bonds with implications for protein folding. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 3681–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












| Phytosterol | EC50 (nM) | |
|---|---|---|
| LXRα | LXRβ | |
| Sitosterol | 42 | 26 |
| Campesterol | 43 | 28 |
| Fucosterol | 33 | 42 |
| Sitostanol | 136 | 110 |
| Campestenol | 122 | 124 |
| GW3965A | 197 | 41 |
| Name | LXR SPA Binding IC50 (µM) | Cofactor Association HTRF * Assay, EC50 (µM) | Transactivation Max. Fold Induction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LXRα | LXRβ | LXRα | LXRβ | LXRα | LXRβ | |
| Acanthoic acid | 0.25 | 1.49 | 0.18 | ≥50 | 15.9 (100 µM) | 5.6 (100 µM) |
| Viperidone | 0.10 | --- | ≥15 | ----- | ---- | ---- |
| Polycarpol | 0.12 | ≥15 | 0.030 | ≥50 | ----- | ----- |
| Gorgostone Derivative | 0.07 | 0.2 | 0.05 | ---- | 13 (10 µM) | 2.2 (10 µM) |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Komati, R.; Spadoni, D.; Zheng, S.; Sridhar, J.; Riley, K.E.; Wang, G. Ligands of Therapeutic Utility for the Liver X Receptors. Molecules 2017, 22, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010088
Komati R, Spadoni D, Zheng S, Sridhar J, Riley KE, Wang G. Ligands of Therapeutic Utility for the Liver X Receptors. Molecules. 2017; 22(1):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010088
Chicago/Turabian StyleKomati, Rajesh, Dominick Spadoni, Shilong Zheng, Jayalakshmi Sridhar, Kevin E. Riley, and Guangdi Wang. 2017. "Ligands of Therapeutic Utility for the Liver X Receptors" Molecules 22, no. 1: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010088
APA StyleKomati, R., Spadoni, D., Zheng, S., Sridhar, J., Riley, K. E., & Wang, G. (2017). Ligands of Therapeutic Utility for the Liver X Receptors. Molecules, 22(1), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010088







