Multilayer Perceptron-Based Real-Time Intradialytic Hypotension Prediction Using Patient Baseline Information and Heart-Rate Variation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
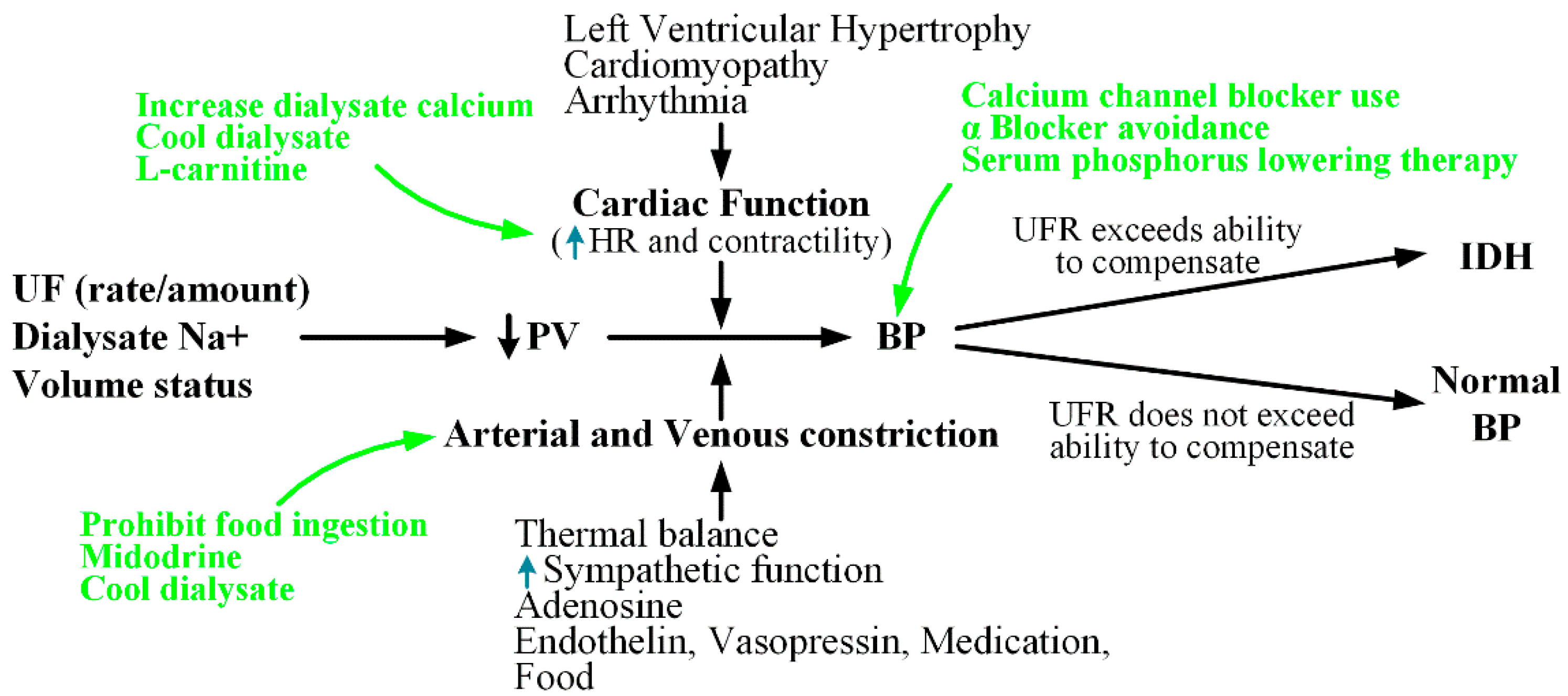
2. Pathogenesis and Medical Treatment for IDH
2.1. Maintenance of Cardiac Output
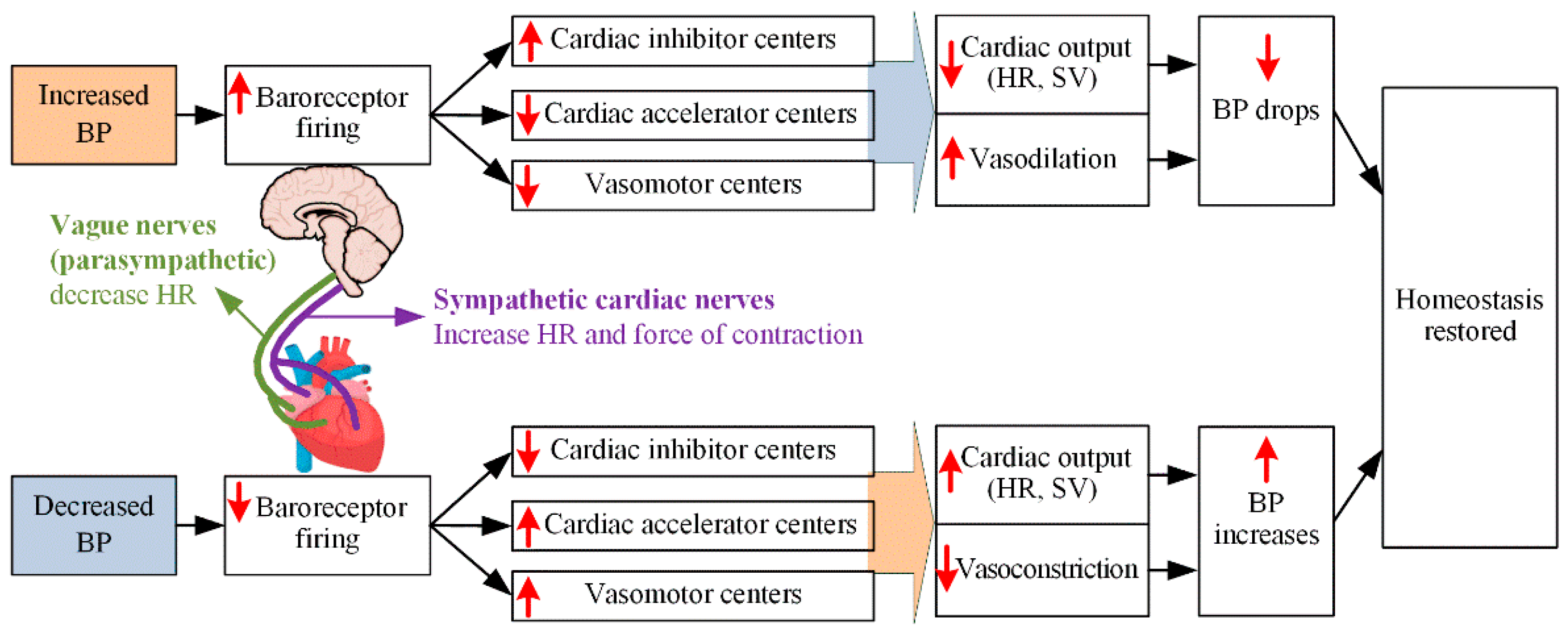
2.1.1. HR
2.1.2. Contractility
2.2. Cardiac Preload
2.3. Arteriolar Vasoconstriction
2.3.1. ANS
2.3.2. Vasopressor Hormones
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Participants
3.2. Proposed Multilayer Perceptron Model for IDH Prediction
4. Results
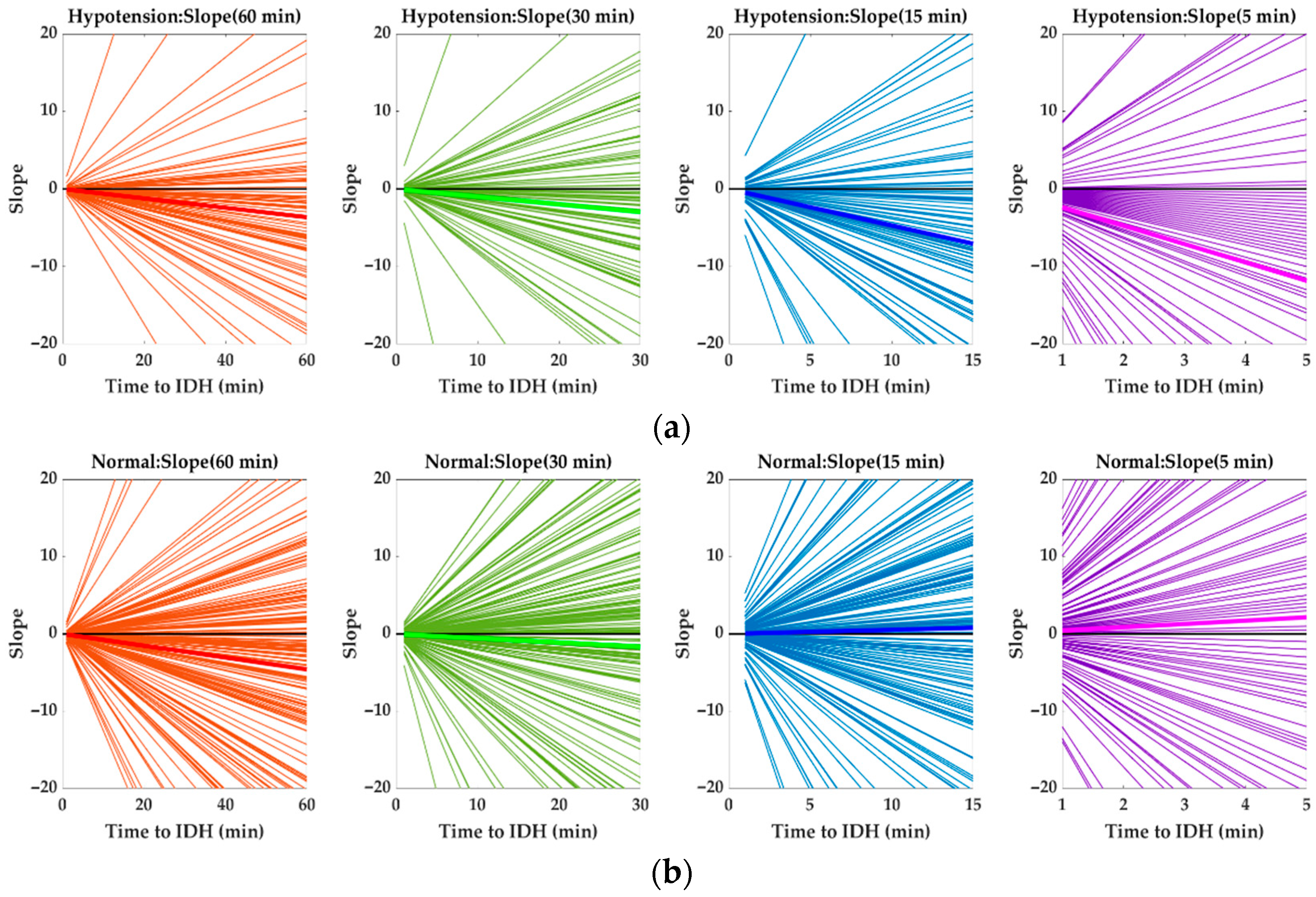
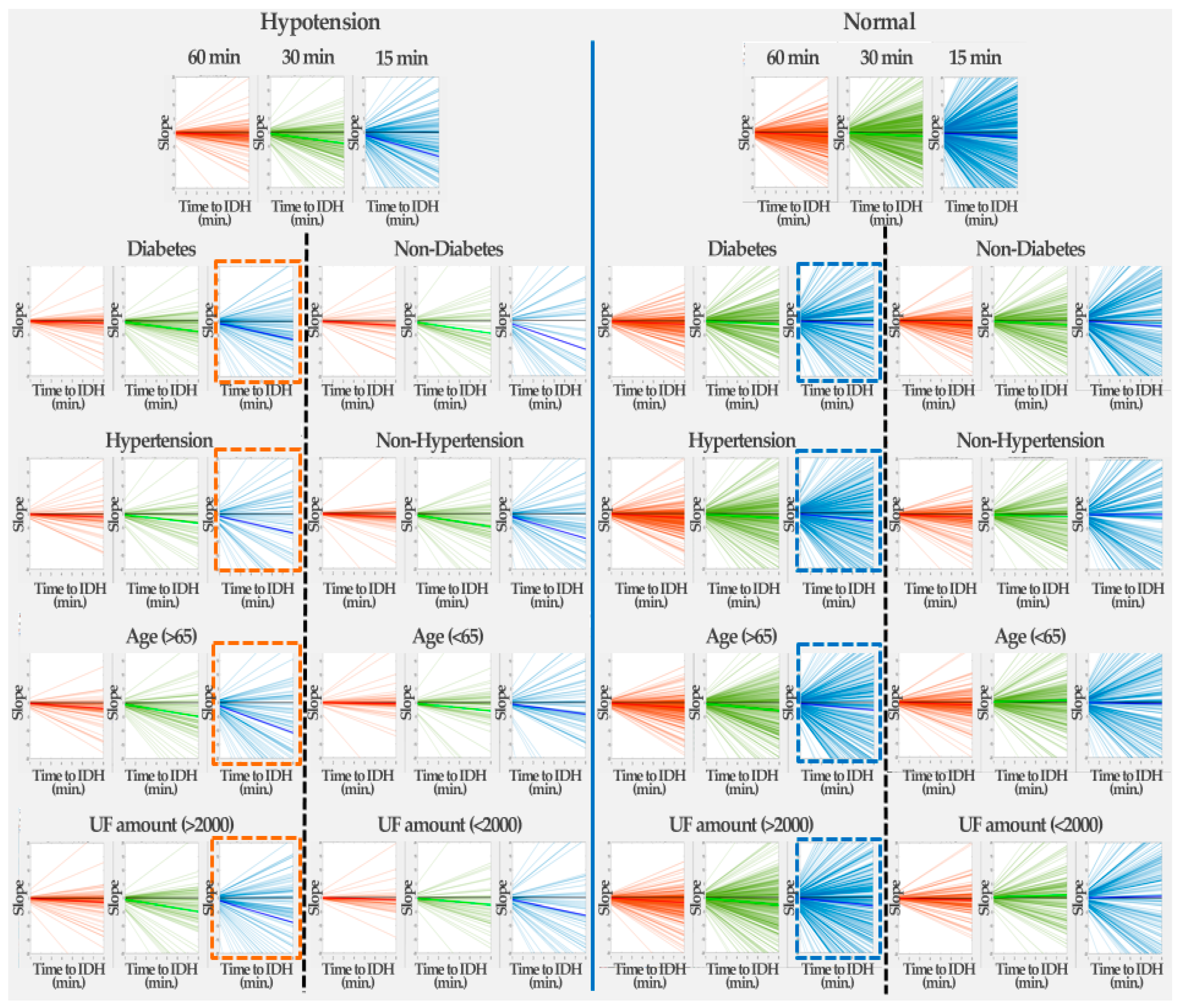
4.1. Changes in HR Slope before IDH
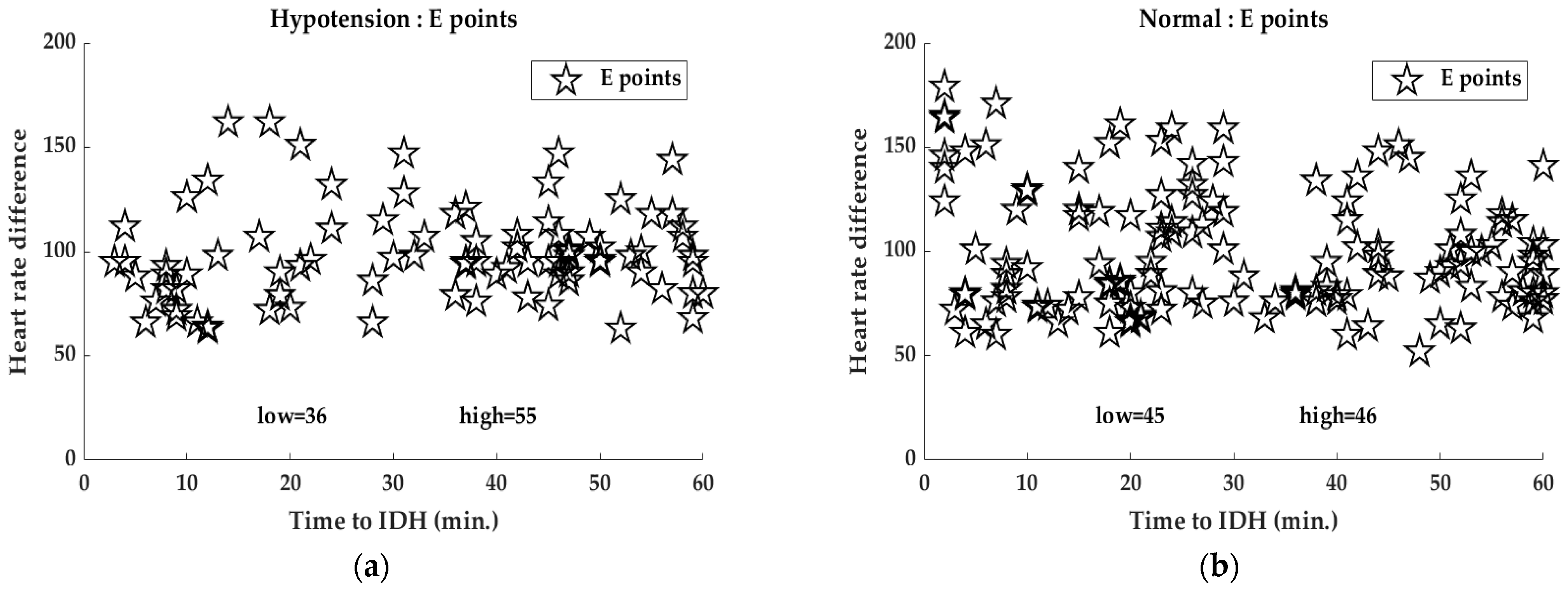
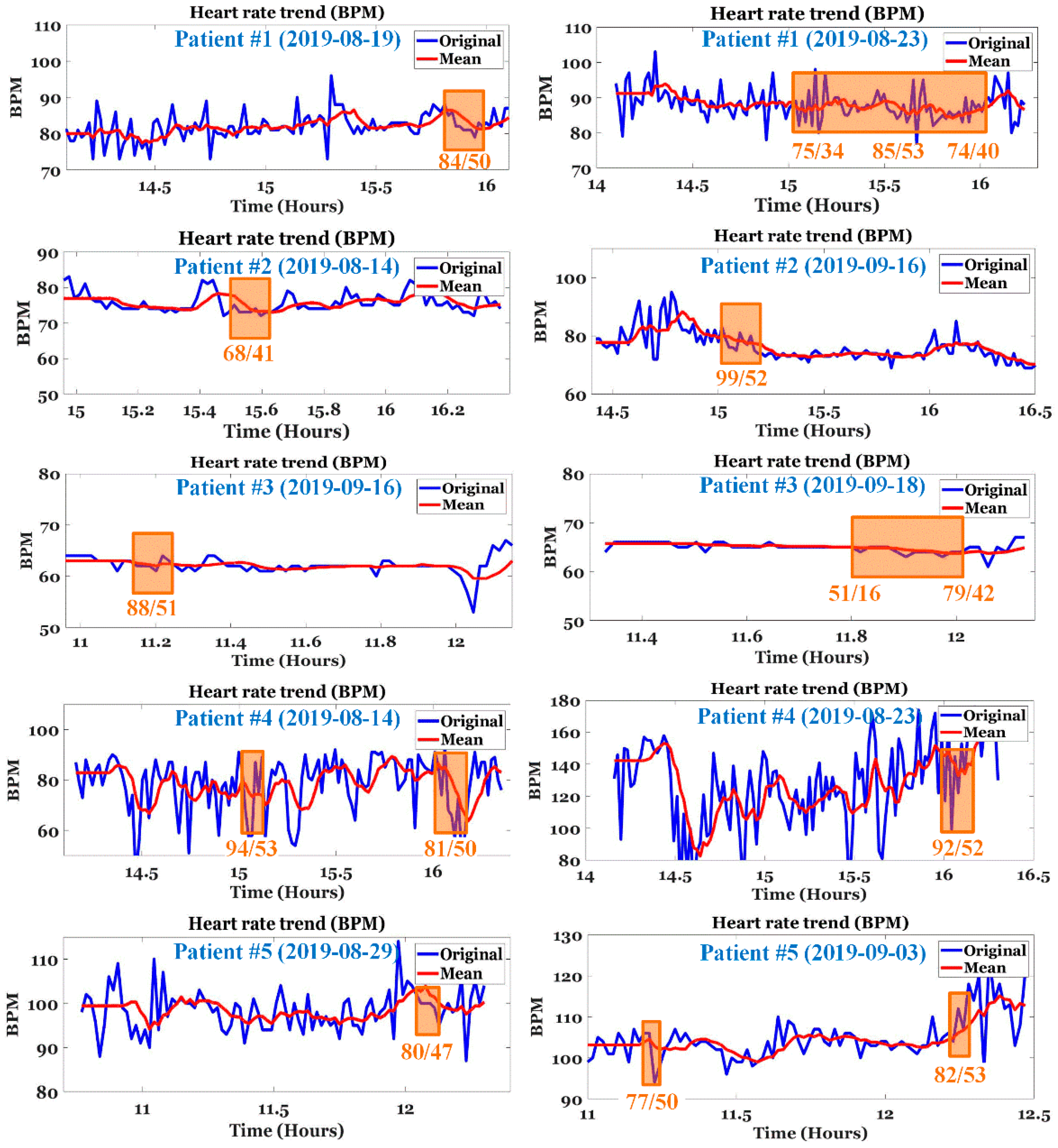
4.2. Analysis of E-Point
4.3. Analysis of HR Slope
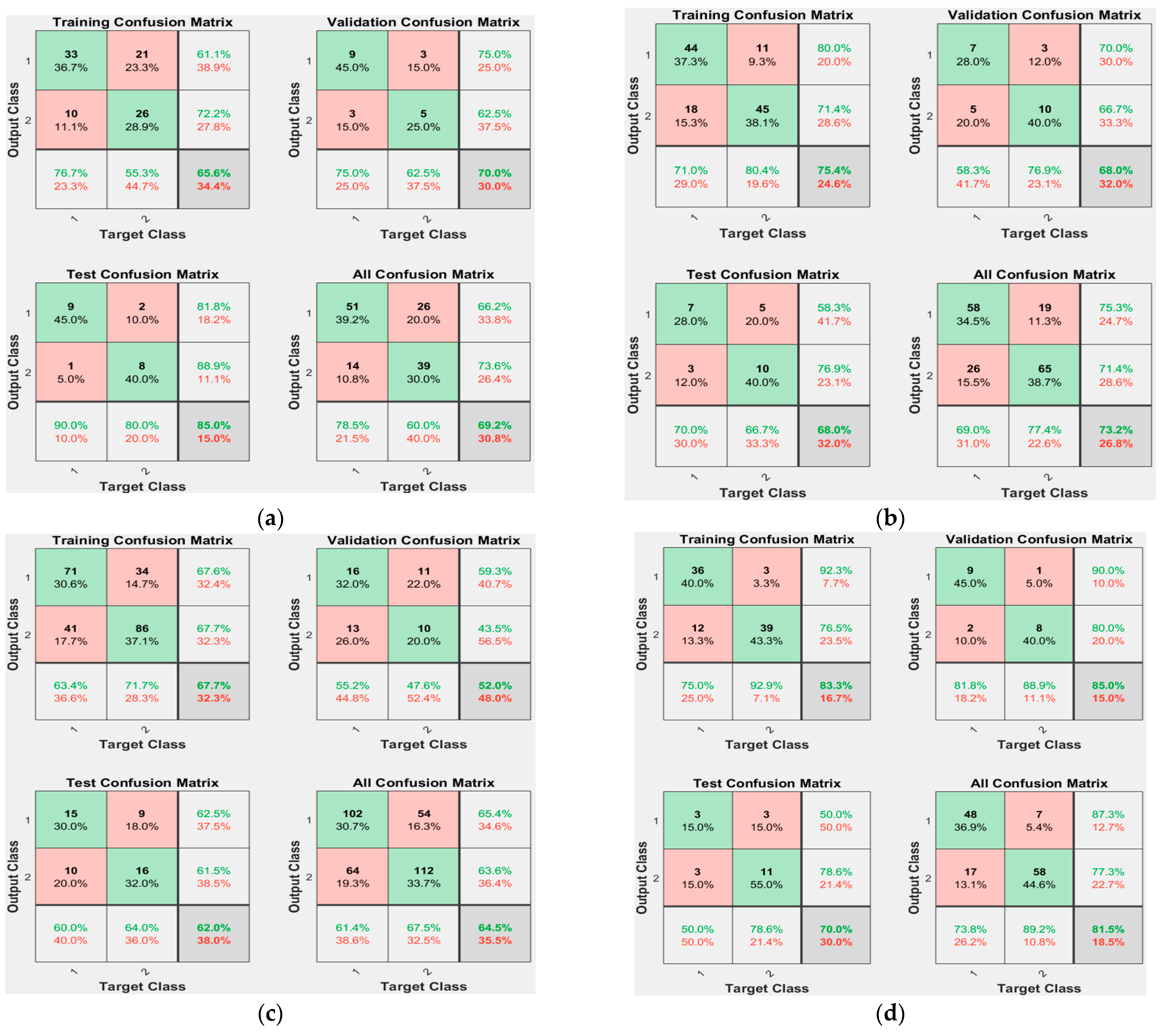
4.4. Model Results
5. Discussion
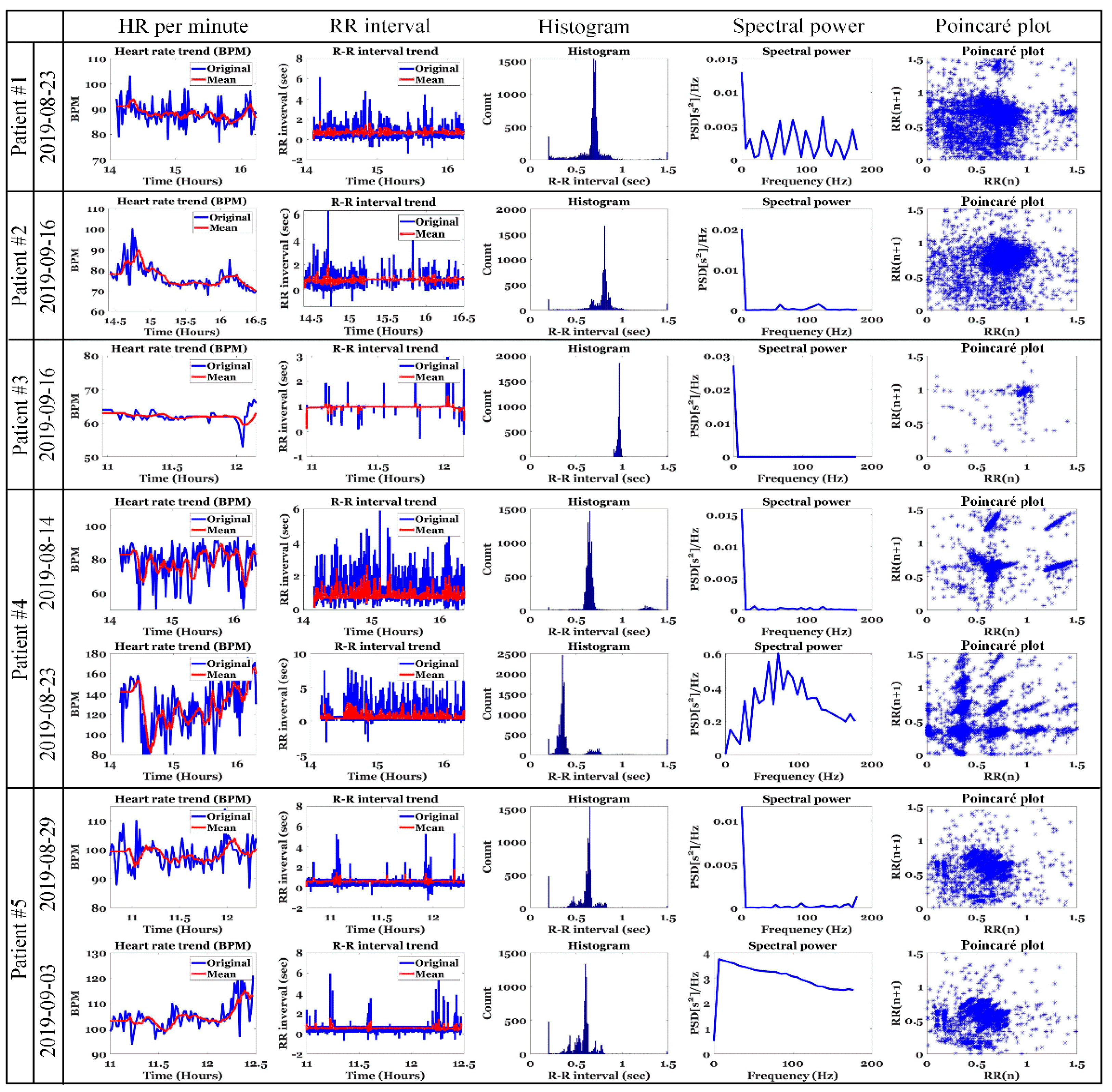
5.1. ECG Analysis of Patients with IDH
5.2. Real-Time Prediction of IDH
5.3. Data and Clinical Issues of IDH
6. Conclusions
7. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daugirdas, J.T. Measuring intradialytic hypotension to improve quality of care. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 512–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, R. How can we prevent intradialytic hypotension? Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2012, 21, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assimon, M.M.; Flythe, J.E. Definitions of intradialytic hypotension. Semin. Dial. 2017, 30, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, M.J. Clinical dilemmas in dialysis: Managing the hypotensive patient. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2001, 38, S1–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanbay, M.; Ertuglu, L.A.; Afsar, B.; Ozdogan, E.; Siriopol, D.; Covic, A.; Basile, C.; Ortiz, A. An update review of intradialytic hypotension: Concept, risk factors, clinical implications and management. Clin. Kidney J. 2020, 13, 981–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tislér, A.; Akócsi, K.; Borbás, B.; Fazakas, L.; Ferenczi, S.; Görögh, S.; Kulcsár, I.; Nagy, L.; Sámik, J.; Szegedi, J.; et al. The effect of frequent or occasional dialysis-associated hypotension on survival of patients on maintenance haemodialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2003, 18, 2601–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shoji, T.; Tsubakihara, Y.; Fujii, M.; Imai, E. Hemodialysis-associated hypotension as an independent risk factor for two-year mortality in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2004, 66, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selby, N.M.; McIntyre, C.W. The acute cardiac effects of dialysis. Semin. Dial. 2007, 20, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, F.; Bailón, R.; Hernando, D.; Laguna, P.; Martínez, J.P.; Solem, K.; Sörnmo, L. Prediction of hypotension in hemodialysis patients. Physiol. Meas. 2014, 35, 1885–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.B.; Wu, K.C.; Moi, S.H.; Chuang, L.Y.; Yang, C.H. Deep learning for intradialytic hypotension prediction in hemodialysis patients. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 82382–82390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, A. Can Advances in Hemodialysis Machine Technology Prevent Intradialytic Hypotension? Semin. Dial. 2009, 22, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reilly, R.F. Attending rounds: A patient with intradialytic hypotension. Clin. J. Amer. Soc. Nephrology 2014, 9, 798–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Kim, W.J.; Cho, N.J.; Choi, C.Y.; Heo, N.H.; Gil, H.W.; Lee, E.Y. Predicting intradialytic hypotension using heart rate variability. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reeves, P.B.; Causland, F.R. Mechanisms, clinical implications, and treatment of intradialytic hypotension. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 13, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kersh, E.S.; Kronfield, S.J.; Unger, A.; Popper, R.W.; Cantor, S.; Cohn, K. Autonomic insufficiency in uremia as a cause of hemodialysis-induced hypotension. N. Engl. J. Med. 1974, 290, 650–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Converse, R.L.; Jacobsen, T.N.; Jost, C.M.; Toto, R.D.; Grayburn, P.A.; Obregon, T.M.; Tarazi, F.F.; Victor, R.G. Paradoxical withdrawal of reflex vasoconstriction as a cause of hemodialysis-induced hypotension. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 90, 1657–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimizu, K.; Kurosawa, T.; Sanjo, T. Effect of hyperosmolality on vasopressin secretion in intradialytic hypotension: A mechanistic study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2008, 52, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, E.; Corazza, L.; Cannarile, D.C.; Soverini, M.L.; Cavalcanti, S.; Cavani, S.; Fiorenzi, A.; Santoro, A. Short term variability of oxygen saturation during hemodialysis is a warning parameter for hypotension appearance. In Proceedings of the 2008 Computers in Cardiology, Bologna, Italy, 14–17 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Solem, K.; Olde, B.; Sörnmo, L. Prediction of intradialytic hypotension using photoplethysmography. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 57, 1611–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sörnmo, L.; Sandberg, F.; Gil, E.; Solem, K. Noninvasive techniques for prevention of intradialytic hypotension. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 5, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, C.; Maule, S.; Mecca, F.; Quadri, R.; Martina, G.; Perin, P.C. The influence of autonomic neuropathy on hypotension during hemodialysis. Clin. Auton. Res. 2002, 12, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabi, M.; Nafisi, V.R.; Pak, F. Prediction of intradialytic hypotension using PPG signal features. In Proceedings of the 22nd Iranian Conference on Biomedical Engineering (ICBME), Tehran, Iran, 25–27 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pelosi, G.; Emdin, M.; Carpeggiani, C.; Morales, M.A.; Piacenti, M.; Dattolo, P.; Cerrai, T.; Macerata, A. Impaired sympathetic response before intradialytic hypotension: A study based on spectral analysis of heart rate and pressure variability. Clin. Sci. 1999, 96, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossola, M.; Laudisio, A.; Antocicco, M.; Panocchia, N.; Tazza, L.; Colloca, G.; Tosato, M.; Zuccalà, G. Intradialytic hypotension is associated with dialytic age in patients on chronic hemodialysis. Ren. Fail. 2013, 35, 1260–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.J.; Chen, C.Y.; Wu, P.C.; Pan, C.F.; Shih, H.M.; Huang, M.Y.; Chou, L.H.; Tang, J.S.; Wu, C.J. Intelligent system to predict intradialytic hypotension in chronic hemodialysis. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2018, 117, 888–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Yun, D.; Yoo, J.; Yoo, K.; Kim, Y.C.; Kim, D.K.; Oh, K.H.; Joo, K.W.; Kim, Y.S.; Kwak, N.; et al. Deep learning model for real-time prediction of intradialytic hypotension. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 16, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.W.; Yang, J.Y.; Un, C.H.; Chen, K.Y.; Huang, C.C.; Tsaih, R.H. The New method of feature selection for intradialytic hypotension prediction using machine learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE 3rd Eurasia Conference on Biomedical Engineering, Healthcare and Sustainability (ECBIOS), Tainan, Taiwan, 28–30 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.Y.; Hu, H.W.; Liu, C.H.; Chen, K.Y.; Un, C.H.; Huang, C.C.; Chen, C.C.; Lin, C.C.K.; Chang, H.; Lin, H.M. Differencing time series as an important feature extraction for intradialytic hypotension prediction using machine learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE 3rd Eurasia Conference on Biomedical Engineering, Healthcare and Sustainability (ECBIOS), Tainan, Taiwan, 28–30 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Flythe, J.E.; Xue, H.; Lynch, K.E.; Curhan, G.C.; Brunelli, S.M. Association of mortality risk with various definitions of intradialytic hypotension. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harnett, J.D.; Foley, R.N.; Kent, G.M.; Barre, P.E.; Murray, D.; Parfrey, P.S. Congestive heart failure in dialysis patients: Prevalence, incidence, prognosis and risk factors. Kidney Int. 1995, 47, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rothe, C.F. Physiology of venous return. An unappreciated boost to the heart. Arch. Intern. Med. 1986, 146, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettema, E.M.; Zittema, D.; Kuipers, J.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Vart, P.; Jong, P.E.; Westerhuis, R.; Franssen, C.F. Dialysis hypotension: A role for inadequate increase in arginine vasopressin levels? A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Nephrol. 2014, 39, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.F.F.; Peixoto, A.J.; Perazella, M.A. How should we manage adverse intradialytic blood pressure changes? Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2012, 19, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, N. Seasonal variation and predictors of intradialytic hypotension. Hypertens. Res. 2021, 44, 1551–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, T.W.; Lee, S.H.; Kwon, K.K. An adaptive median filter based on sampling rate for R-peak detection and major-arrhythmia analysis. Sensors 2020, 20, 6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, T.W.; Kwon, K.K. Efficient real-time R and QRS detection method using a pair of derivative filters and max filter for portable ECG device. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bae, T.W.; Kwon, K.K.; Kim, K.H. Vital block and vital sign server for ECG and vital sign monitoring in a portable u-Vital system. Sensors 2020, 20, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wehrwein, E.A.; Orer, H.S.; Barman, S.M. Overview of the anatomy, physiology, and pharmacology of the autonomic nervous system. Compr. Physiol. 2016, 6, 1239–1278. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Control of Heart Rate. Available online: https://teachmephysiology.com/cardiovascular-system/cardiac-output/control-heart-rate (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Your Parasympathetic Nervous System Explained. Available online: https://www.healthline.com/health/parasympathetic-nervous-system#cranial-nerves (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Plotconfusion. Available online: https://kr.mathworks.com/help/deeplearning/ref/plotconfusion.html (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Plot Classification Confusion Matrix. Available online: https://lost-contact.mit.edu/afs/inf.ed.ac.uk/group/teaching/matlab-help/R2016b/nnet/ref/plotconfusion.html (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Bae, T.W.; Kwon, K.K. ECG PQRST complex detector and heart rate variability analysis using temporal characteristics of fiducial points. Biomed. Signal Processing Control. 2021, 66, 102291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, T.-W.; Kwon, K.-K.; Kim, K.-H. Electrocardiogram fiducial point detector using a bilateral filter and symmetrical point-filter structure. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, F.K.; Jochen, G.R.; Hanjie, Z.; Joanna, W.; Stephan, T.; Peter, K. The time of onset of intradialytic hypotension during a hemodialysis session associates with clinical parameters and mortality. Kidney Int. 2021, 99, 1408–1417. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.J.; Chen, Y.Y.; Pan, C.F.; Wu, V.; Wu, C.J. Dataset supporting blood pressure prediction for the management of chronic hemodialysis. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| References | Factors Used | Model Used | Data Source | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solem et al. [19], 2010 | Amplitude of PPG | Hypothesis based statistical model | 11 patients 25 treatments | 57~65% |
| Bossola et al. [24], 2013 | Age, Sex, CCIS, Hemoglobin, Serum creatinine, Serum albumin, DSC, Blood flow, IWG, ACE-Inhibitors or Sartans, Predialysis SBP, Dialytic age | Linear and logistic regression model | 82 patients | - |
| Sandberg et al. [9], 2014 | PPG envelope, LF/HF ratio of ECG | Bayes’ rule | 28 sessions from 11 hypotension-prone patients, 20 sessions from 7 patients | 9/14 (symptomatic IDH), 5/5 (acute symptomatic IDH) |
| Shahabi et al. [22], 2015 | Time domain features and LF/HF ratio of PPG | Genetic algorithm and AdaBoost | 10 patients 217 Normal, 22 Pre-IDH episode, 90 IDH episode | Accuracy of 90.68 %) |
| Lin et al. [25], 2018 |
| Time-dependent logistic regression model | 653 HD outpatients, 55,516 HD treatment sessions | Sensitivity of 86% and specificity of 81% |
| Park et al. [13], 2019 | Diabetes mellitus, CAD, CHF, Age, UFR, iPTH, ARB, CCB, β-blocker, RRI, HF, TP, AIC | Multivariate negative binomial model | 28 patients, 85 cases (10% of a total 852 dialysis sessions) | - |
| Chen et al. [10], 2020 | Age, BMI, Gender, Comorbidity of hypertension, UF coefficient, UF amount, UFR, Ca, Cardiothoracic ratio | Deep Neural Network | 279 participants, 780 hemodialysis sessions | - |
| Comorbidity of hypertension, UF coefficient, UF amount, UFR | Deep Neural Network | |||
| Lee et al. [26], 2021 | Age, Male, Hemodialysis type, Vascular access, Anticoagulant, Blood findings, Dialysate finding | Recurrent Neural Network | 9292 patients, 261,647 sessions | AUC of 0.94 |
| Hu et al. [27], 2021 | Blood draw data, Physiological measurement data, Time series | Long Short-Term Memory | 593 dialysis sessions | AUC of 0.97 |
| Yang et al. [28], 2021 | Time-relevant difference | Light Gradient Boosting Machine | 593 hemodialysis sessions | Sensitivity of 88.9% |
| Total | Male, n (%) | Female, n (%) | Age > 65 y, n (%) | Age < 65 y, n (%) | Diabetes, n (%) | Non-Diabetes, n (%) | Hypertension, n (%) | Non-Hypertension, n (%) | UF Amount | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 89 | 48 (53.9) | 41 (41.6) | 52 (58.4) | 37 (41.6) | 47 (52.8) | 33 (37.1) | 51 (57.3) | 38 (42.7) | 2182.7 |
| IDH | 67 | 30 (44.8) | 37 (55.2) | 41 (61.2) | 26 (38.8) | 35 (52.2) | 28 (41.8) | 29 (43.3) | 29 (43.3) | 2127.4 |
| Non-IDH | 22 | 18 (81.8) | 4 (18.2) | 11 (50.0) | 11 (50.0) | 12 (54.5) | 5 (22.7) | 9 (40.9) | 9 (40.9) | 2350.9 |
| Hypotension | Normal | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60 min | 30 min | 15 min | 5 min | 60 min | 30 min | 15 min | 5 min | |
| Mean slope | −0.0608 | −0.0987 | −0.4706 | −2.3681 | −0.0764 | −0.0555 | 0.0526 | 0.4310 |
| Num. of positive slopes | 25 | 33 | 24 | 18 | 73 | 103 | 108 | 95 |
| Num. of negative slopes | 66 | 58 | 67 | 73 | 111 | 81 | 76 | 89 |
| % of negative slopes | 72.5 | 63.7 | 73.6 | 80.2 | 60.3 | 44.0 | 41.3 | 48.4 |
| Hypotension | Normal | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 min | 15 min | 8 min | 30 min | 15 min | 8 min | 30 min | 15 min | 8 min | 30 min | 15 min | 8 min | |
| Underlying disease | Diabetes | Non-diabetes | Diabetes | Non-diabetes | ||||||||
| Mean slope | −0.136 | −0.489 | −0.808 | −0.207 | −0.558 | −1.303 | −0.159 | −0.155 | −0.179 | −0.224 | −0.185 | −0.259 |
| Num. of positive slopes | 27 | 21 | 44 | 13 | 16 | 32 | 94 | 132 | 209 | 85 | 127 | 201 |
| Num. of negative slopes | 76 | 82 | 59 | 50 | 47 | 31 | 261 | 223 | 146 | 258 | 216 | 142 |
| % of negative slopes | 73.79 | 79.61 | 57.28 | 79.37 | 74.60 | 49.21 | 73.52 | 62.82 | 41.13 | 75.22 | 62.97 | 41.40 |
| Underlying disease | Hypertension | Non-hypertension | Hypertension | Non-hypertension | ||||||||
| Mean slope | −0.154 | −0.429 | −0.862 | −0.171 | −0.587 | −0.109 | −0.198 | −0.215 | −0.374 | −0.182 | −0.104 | 0.007 |
| Num. of positive slopes | 17 | 18 | 37 | 23 | 19 | 39 | 93 | 145 | 233 | 86 | 114 | 177 |
| Num. of negative slopes | 59 | 58 | 39 | 67 | 71 | 51 | 320 | 268 | 180 | 199 | 171 | 108 |
| % of negative slopes | 77.63 | 76.32 | 51.32 | 74.44 | 78.89 | 56.67 | 77.48 | 64.89 | 43.58 | 69.82 | 60 | 37.89 |
| Underlying disease | Age | Non-age | Age | Non-age | ||||||||
| Mean slope | −0.254 | −0.6198 | −1.353 | −0.045 | −0.379 | −0.529 | −0.221 | −0.357 | −0.332 | −0.151 | 0.087 | −0.064 |
| Num. of positive slopes | 14 | 16 | 42 | 26 | 21 | 34 | 89 | 116 | 242 | 90 | 143 | 168 |
| Num. of negative slopes | 80 | 78 | 52 | 46 | 51 | 38 | 314 | 287 | 161 | 205 | 152 | 127 |
| % of negative slopes | 85.11 | 82.98 | 55.32 | 63.89 | 70.83 | 52.78 | 77.92 | 71.22 | 39.95 | 69.49 | 51.53 | 43.05 |
| Underlying disease | UF | Non-UF | UF | Non-UF | ||||||||
| Mean slope | −0.190 | −0.607 | −1.094 | −0.107 | −0.325 | −0.792 | −0.240 | −0.335 | −0.377 | −0.103 | 0.134 | 0.072 |
| Num. of positive slopes | 27 | 23 | 54 | 13 | 14 | 22 | 101 | 149 | 253 | 78 | 110 | 157 |
| Num. of negative slopes | 85 | 89 | 58 | 41 | 40 | 32 | 351 | 303 | 199 | 168 | 136 | 89 |
| % of negative slopes | 75.89 | 79.46 | 51.79 | 75.93 | 74.07 | 59.26 | 77.65 | 67.04 | 44.03 | 68.29 | 55.28 | 36.18 |
| Combinations | Model Ranking | ACC (%) | TPR (%) | PPV (%) | MCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 layer, 60 min | 4 | 69.2 % | 78.5 % | 66.2 % | 0.391 |
| 1 layer, 45 min | 2 | 73.2 % | 69.0 % | 75.3 % | 0.496 |
| 1 layer, 30 min | 5 | 64.5 % | 61.4 % | 65.4 % | 0.290 |
| 2 layers, 60 min | 1 | 81.5 % | 73.8 % | 87.3 % | 0.638 |
| 2 layers, 45 min | 3 | 70.2 % | 66.7 % | 71.8 % | 0.370 |
| 2 layers, 30 min | 6 | 59.6 % | 68.1 % | 58.2 % | 0.195 |
| Patient Data | Session Data |
|---|---|
| Male sex, Dialysis vintage, Race (White, Black), Peripheral artery disease, Peripheral vascular disease, Antihypertensive use, Body temperature | Interdialytic weight gain, Blood flow, Dialysate temperature, Dialysate conductivity, Dialysate sodium, Dialysate calcium, Body weight before and after HD |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bae, T.W.; Kim, M.S.; Park, J.W.; Kwon, K.K.; Kim, K.H. Multilayer Perceptron-Based Real-Time Intradialytic Hypotension Prediction Using Patient Baseline Information and Heart-Rate Variation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191610373
Bae TW, Kim MS, Park JW, Kwon KK, Kim KH. Multilayer Perceptron-Based Real-Time Intradialytic Hypotension Prediction Using Patient Baseline Information and Heart-Rate Variation. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(16):10373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191610373
Chicago/Turabian StyleBae, Tae Wuk, Min Seong Kim, Jong Won Park, Kee Koo Kwon, and Kyu Hyung Kim. 2022. "Multilayer Perceptron-Based Real-Time Intradialytic Hypotension Prediction Using Patient Baseline Information and Heart-Rate Variation" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 16: 10373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191610373
APA StyleBae, T. W., Kim, M. S., Park, J. W., Kwon, K. K., & Kim, K. H. (2022). Multilayer Perceptron-Based Real-Time Intradialytic Hypotension Prediction Using Patient Baseline Information and Heart-Rate Variation. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(16), 10373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191610373






