Cloning and Characterization of Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate Aldolase from Euphausia superba
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Cloning and Bioinformatics Analysis
2.2. Protein Expression and Purification
2.3. Expression Optimization of Recombinant Vectors
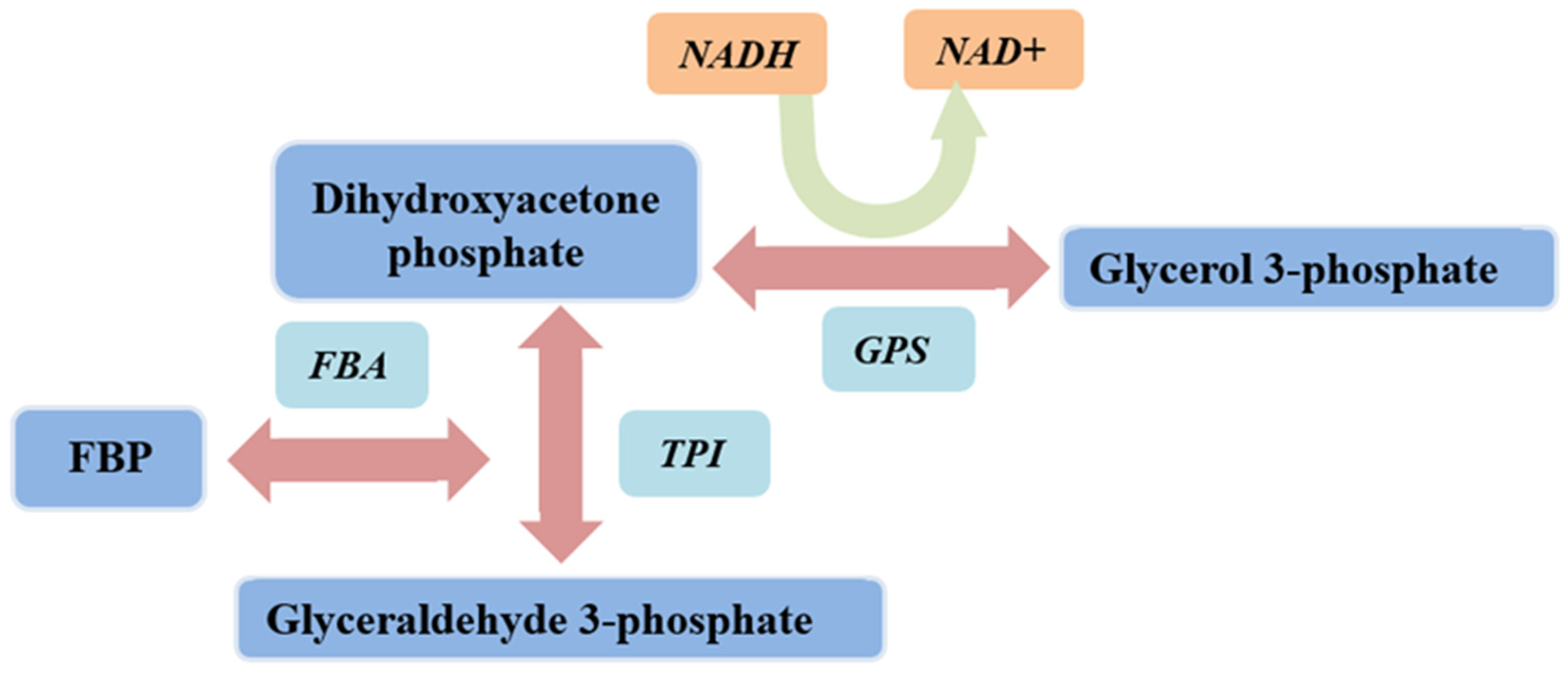
2.4. Activity Analysis
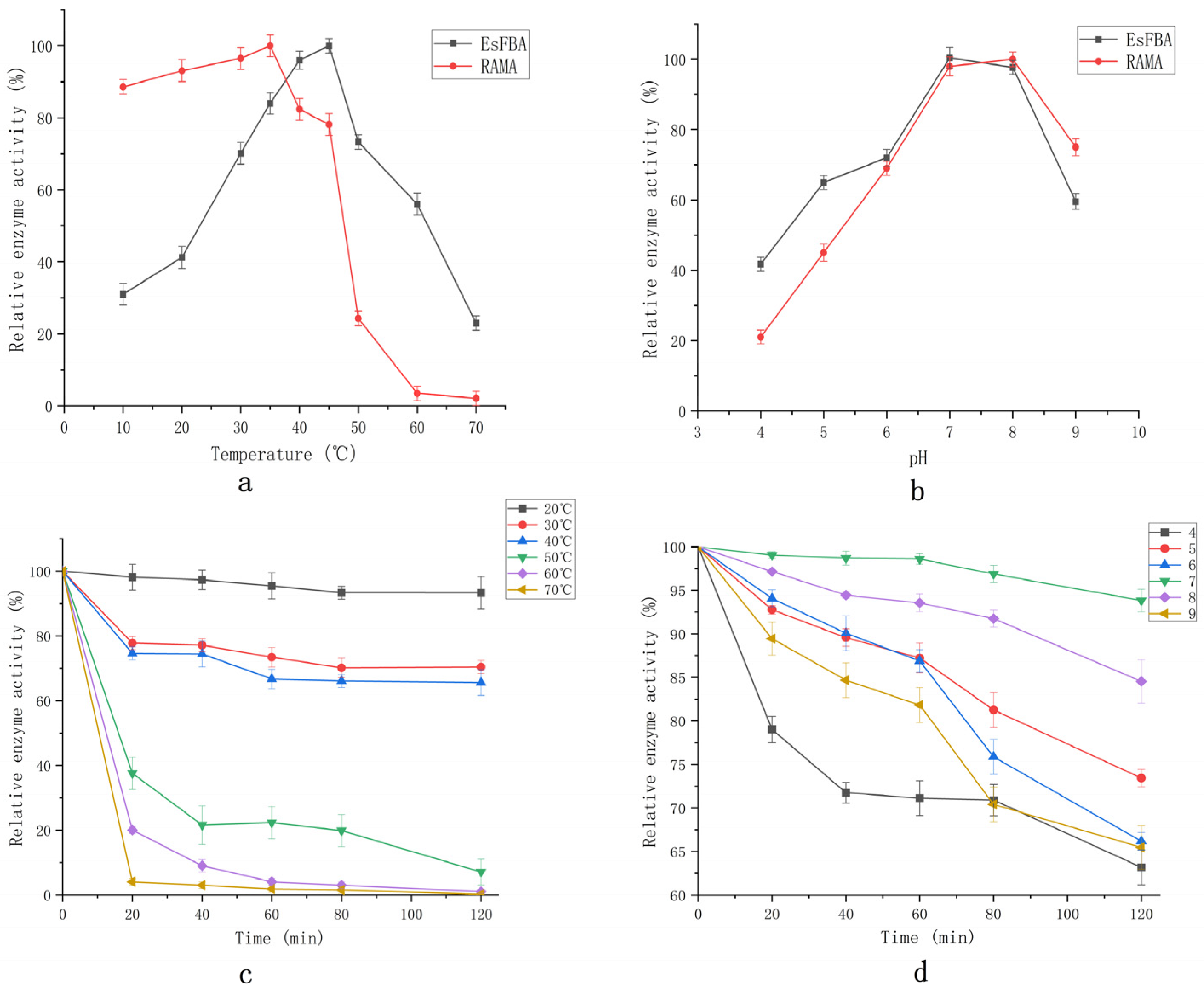
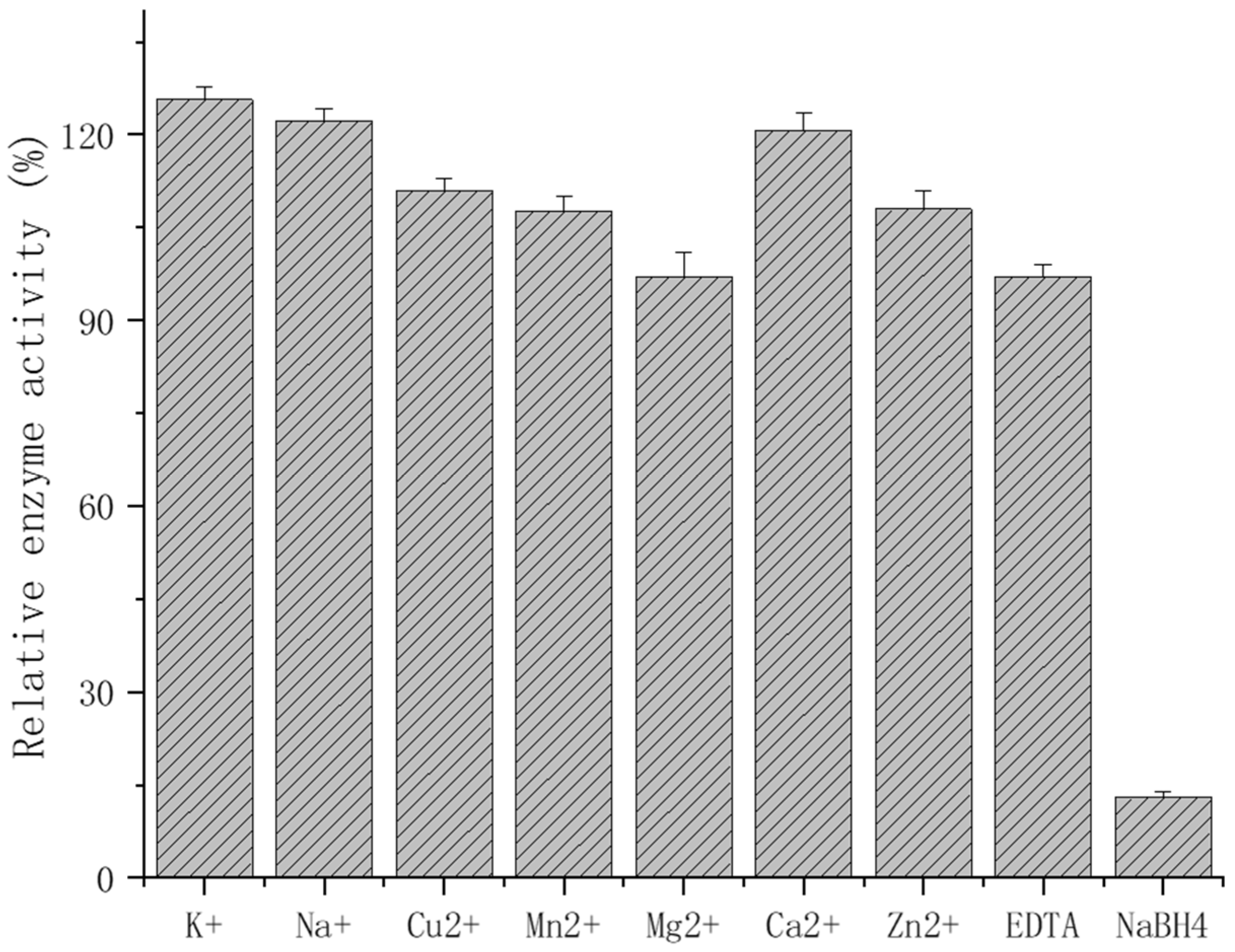
2.5. Biochemical Characterization
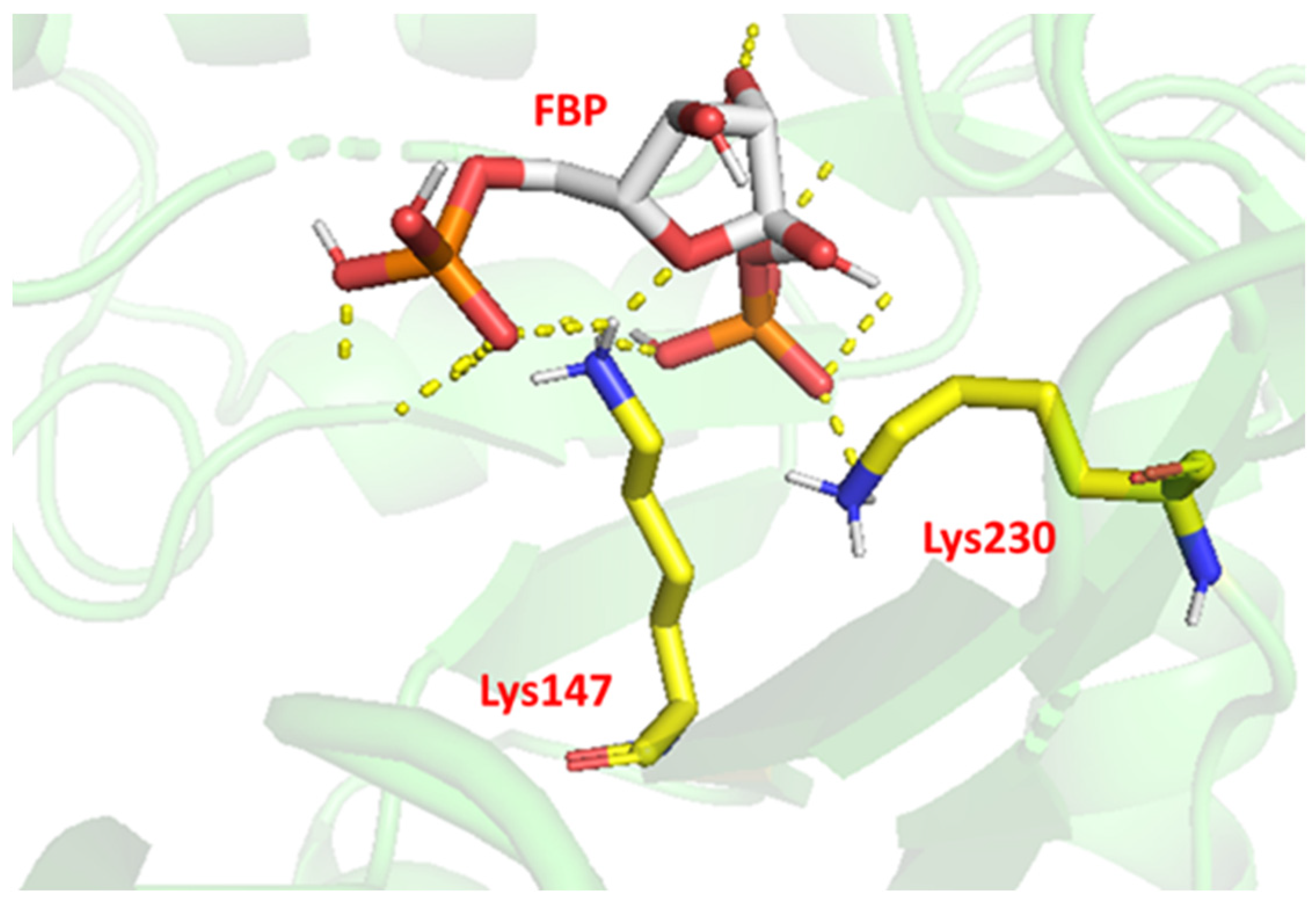
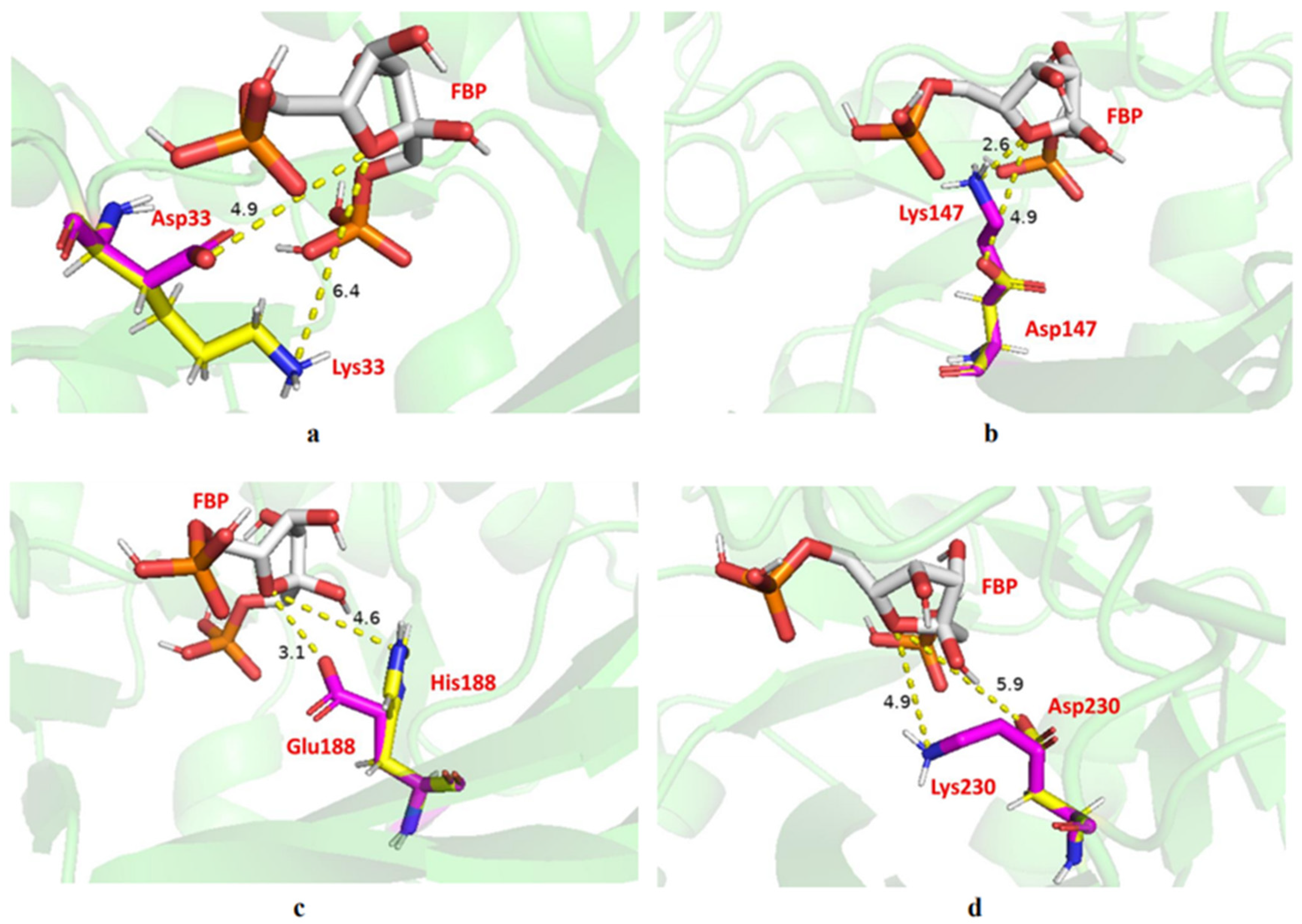
2.6. Site-Directed Mutagenesis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Instruments
3.2. Cloning and Bioinformatics Analysis
3.3. Construction of Recombinant Plasmid
3.4. Protein Expression and Purification
3.5. Optimization of Induction Conditions
3.6. Activity Assay
3.7. Biochemical Characterization
3.8. Site-Directed Mutagenesis
3.9. Molecular Modeling
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campanella, M.E.; Chu, H.; Low, P.S. Assembly and regulation of a glycolytic enzyme complex on the human erythrocyte membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 2402–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazurek, S.; Zwerschke, W.; Jansen-DüRR, P.; Eigenbrodt, E. Effects of the human papilloma virus HPV-16 E7 oncoprotein on glycolysis and glutaminolysis: Role of pyruvate kinase type M2 and the glycolytic-enzyme complex. Biochem. J. 2001, 356, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, S.P.J.; Storey, K.B. Reevaluation of the “glycolytic complex” in muscle: A multitechnique approach using trout white muscle. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1988, 267, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Salih, M.; Leddy, J.J.; Tuana, B.S. The Muscle-specific Calmodulin-dependent Protein Kinase Assembles with the Glycolytic Enzyme Complex at the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum and Modulates the Activity of Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase in a Ca2+/Calmodulin-dependent Manner. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 35176–35182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutter, W.J.; Hunsley, J.R.; Groves, W.E.; Calder, J.; Woodfin, B.M. Fructose diphosphate aldolase. Methods Enzymol. 1966, 9, 479–498. [Google Scholar]
- Ocampos, D.; Bacila, M. Purification and properties of fructose-1,6-diphosphate aldolase from beef heart muscle. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 1975, 47, 551–556. [Google Scholar]
- Gamblin, S.J.; Cooper, B.; Millar, J.R.; Davies, G.J.; Littlechild, J.A.; Watson, H.C. The crystal structure of human muscle aldolase at 3.0 resolution. FEBS Lett. 1990, 262, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hester, G.; Brenner-Holzach, O.; Rossi, F.A.; Struck-Donatz, M.; Piontek, K. The crystal structure of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase from Drosophila melanogaster at 2.5 A resolution. FEBS Lett. 1991, 292, 237–242. [Google Scholar]
- Sygusch, J.; Beaudry, D.; Allaire, M. Molecular architecture of rabbit skeletal muscle aldolase at 2.7-A resolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 7846–7850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, C.S.; Gupta, S.; Kumar, H.; Tiwari, M. Evolutionary and functional analysis of fructose bisphosphate aldolase of plant parasitic nematodes. Bioinformation 2013, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochman, M.; Krzywda, U.; Kwiatkowska, D.; Baranowski, T. Multiple molecular forms of fructose diphosphate aldolase in ontogeny and phylogeny. Int. J. Biochem. 1971, 2, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Sautin, Y.Y.; Holliday, L.S.; Gluck, S.L. The Glycolytic Enzyme Aldolase Mediates Assembly, Expression, and Activity of Vacuolar H+-ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 8732–8739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tochio, T.; Tanaka, H.; Nakata, S.; Hosoya, H. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase A is involved in HaCaT cell migration by inducing lamellipodia formation. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2010, 58, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiquete-Felix, N.; Hernandez, J.M.; Mendez, J.A.; Zepeda-Bastida, A.; Chagolla-Lopez, A.; Mujica, A. In guinea pig sperm, aldolase A forms a complex with actin, WAS, and Arp2/3 that plays a role in actin polymerization. Reproduction 2009, 137, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorentzen, E.; Pohl, E.; Zwart, P.; Stark, A.; Russell, R.B.; Knura, T.; Hensel, R.; Siebers, B. Crystal structure of an archaeal class I aldolase and the evolution of (betaalpha)8 barrel proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 47253–47260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorentzen, E.; Siebers, B.; Hensel, R. Structure, function and evolution of the Archaeal class I fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2004, 32, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarski, M.D.; Simon, E.S.; Bischofberger, N.; Fessner, W.D.; Kim, M.J.; Lees, W.; Saito, T.; Waldmann, H.; Whitesides, G.M. Rabbit muscle aldolase as a catalyst in organic synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cai, L.; Wei, M.; Peng, G.W. One-pot four-enzyme synthesis of ketoses with fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolases from Staphylococcus carnosus and rabbit muscle. Carbohydr. Res. 2012, 357, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, N.J.; Neal, J.; Dawson; Kyle, K.; Biggar; Kenneth, B.; Storey. Characterization of Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate Aldolase during Anoxia in the Tolerant Turtle, Trachemys scripta elegans: An Assessment of Enzyme Activity, Expression and Structure. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, S.; Cerdán, M.E.; Siso, M. Isolation and transcriptional regulation of the Kluyveromyces lactis FBA1 (fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase) gene. Can. J. Microbiol. 2004, 50, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xue, C.; Wang, Y.; Yang, B. Extraction of Proteins with Low Fluoride Level from Antarctic Krill (Euphausia superba) and Their Composition Analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 6108–6112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaafsma, F.L.; David, C.L.; Kohlbach, D.; Ehrlich, J.; Castellani, G.; Lange, B.A.; Vortkamp, M.; Meijboom, A.; Fortuna-Wünsch, A.; Immerz, A.; et al. Allometric relationships of ecologically important Antarctic and Arctic zooplankton and fish species. Polar Biol. 2022, 45, 203–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Tao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, G.; Sun, S.; Li, C.; Le, F. Feeding strategies of Euphausia superba in the eastern South Shetland Islands in austral summer. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2019, 38, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yan, Z.; Li, Z.; Fu, M.; Xue, C.; Wang, J. A low proportion n-6/n-3 PUFA diet supplemented with Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) oil protects against osteoarthritis by attenuating inflammation in ovariectomized mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 6766–6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Wu, J.; Zhu, B.; Du, M.; Wu, C.; Yu, C.; Song, L.; Xu, X. Low oil emulsion gel stabilized by defatted Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) protein using high-intensity ultrasound. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 70, 105294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.H.; Mao, X.Z.; Wang, K.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhao, M.H. Phosphorylated peptides from Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) ameliorated osteoporosis by activation of osteogenesis-related MAPKs and PI3K/AKT/GSK-3 beta pathways in dexamethasone-treated mice. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 47, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Zhao, G.X.; Suo, S.K.; Wang, Y.M.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Purification, Identification, Activity Evaluation, and Stability of Antioxidant Peptides from Alcalase Hydrolysate of Antarctic Krill (Euphausia superba) Proteins. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.; Li, J.; Chunhong, L.; Zhang, R.Y.; Sieber, H.C.; Li, Y.H.; Loers, G.; Petridis, A.K.; Xia, Z.Y.; Dong, H.J.; et al. An antarctic krill oil-based diet elicits neuroprotective effects by inhibiting oxidative stress and rebalancing the M1/M2 microglia phenotype in a cuprizone model for demyelination. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 76, 104309. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, I.; Kalfas, S.; Malmsten, M.; Arnebrant, T. Proteolytic degradation of oral biofilms in vitro and in vivo: Potential of proteases originating from Euphausia superba for plaque control. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2010, 109, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, X.; Yan, J.; Li, Y. Gene analysis and structure prediction for the cold-adaption mechanism of trypsin from the krill Euphausia superba (Dana, 1852). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 3049–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellingsen, T.E.; Mohr, V. Biochemistry of the autolytic processes in Antarctic krill postmortem. Biochem. J. 1987, 246, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjödahl, J.; Emmer, A.; Vincent, J.; Roeraade, J. Characterization of proteinases from Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba). Protein Expr. Purif. 2002, 26, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziveri, J.; Tros, F.; Guerrera, I.C.; Chhuon, C.; Audry, M.; Dupuis, M.; Barel, M.; Korniotis, S.; Fillatreau, S.; Gales, L.; et al. The metabolic enzyme fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase acts as a transcriptional regulator in pathogenic. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mccarthy, J.S.; Wieseman, M.; Tropea, J.; McCarthy, J.S.; Wieseman, M.; Tropea, J.; Kaslow, D.; Abraham, D.; Lustigman, S.; Tuan, R.; et al. Onchocerca volvulus glycolytic enzyme fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase as a target for a protective immune response in humans. Infect. Immun. 2019, 70, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, K.; Wang, B.; Zhou, H.; Luo, Q.L.; Zhong, Z.R. Amelioration of type 1 diabetes by recombinant fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase and cystatin derived from Schistosoma japonicum in a murine model. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 1753–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezerra, M.A.; Santelli, R.E.; Oliveira, E.P.; Villar, L.S.; Escaleira, L.A. Response surface methodology (RSM) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry. Talanta 2008, 76, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochman, M.; Kwiatkowska, D. Purification and properties of fructose diphosphate aldolase from Ascaris suum muscle. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1972, 152, 856–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götz, F.; Fischer, S.; Schleifer, K.H. Purification and characterisation of an unusually heat-stable and acid/base-stable class I fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase from Staphylococcus aureus. FEBS J. 2010, 108, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willard, M.J.; Gibbs, M. Fructose-diphosphate aldolase from blue-green algae. Methods Enzymol. 1975, 42, 228–231. [Google Scholar]
- Dalby, A.; Dauter, Z.; Littlechild, J.A. Crystal structure of human muscle aldolase complexed with fructose 1,6-bisphosphate: Mechanistic implications. Protein Sci. 2010, 8, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorentzen, E.; Siebers, B.; Hensel, R.; Pohl, E. Mechanism of the Schiff base forming fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase: Structural analysis of reaction intermediates. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rellos, P.; Sygusch, J.; Cox, T.M. Expression, purification, and characterization of natural mutants of human aldolase B. Role of quaternary structure in catalysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pédelacq, J.D.; Cabantous, S.; Tran, T.; Terwilliger, T.C.; Waldo, G.S. Engineering and characterization of a superfolder green fluorescent protein. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Tang, R.; Zhu, D.; Wang, W.; Yi, L.; Ma, L. Non-peptide guided auto-secretion of recombinant proteins by super-folder green fluorescent protein in. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurady, A.; Zdanov, A.; Moissac, D.D.; Beaudry, D.; Sygusch, J. A conserved glutamate residue exhibits multifunctional catalytic roles in D-fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolases. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 9474–9483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morris, A.J.; Tolan, D.R. Site-directed mutagenesis identifies aspartate 33 as a previously unidentified critical residue in the catalytic mechanism of rabbit aldolase A. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, A.J.; Tolan, D.R. Lysine-146 of rabbit muscle aldolase is essential for cleavage and condensation of the C3-C4 bond of fructose 1,6-bis(phosphate). Biochemistry 1994, 33, 12291–12297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



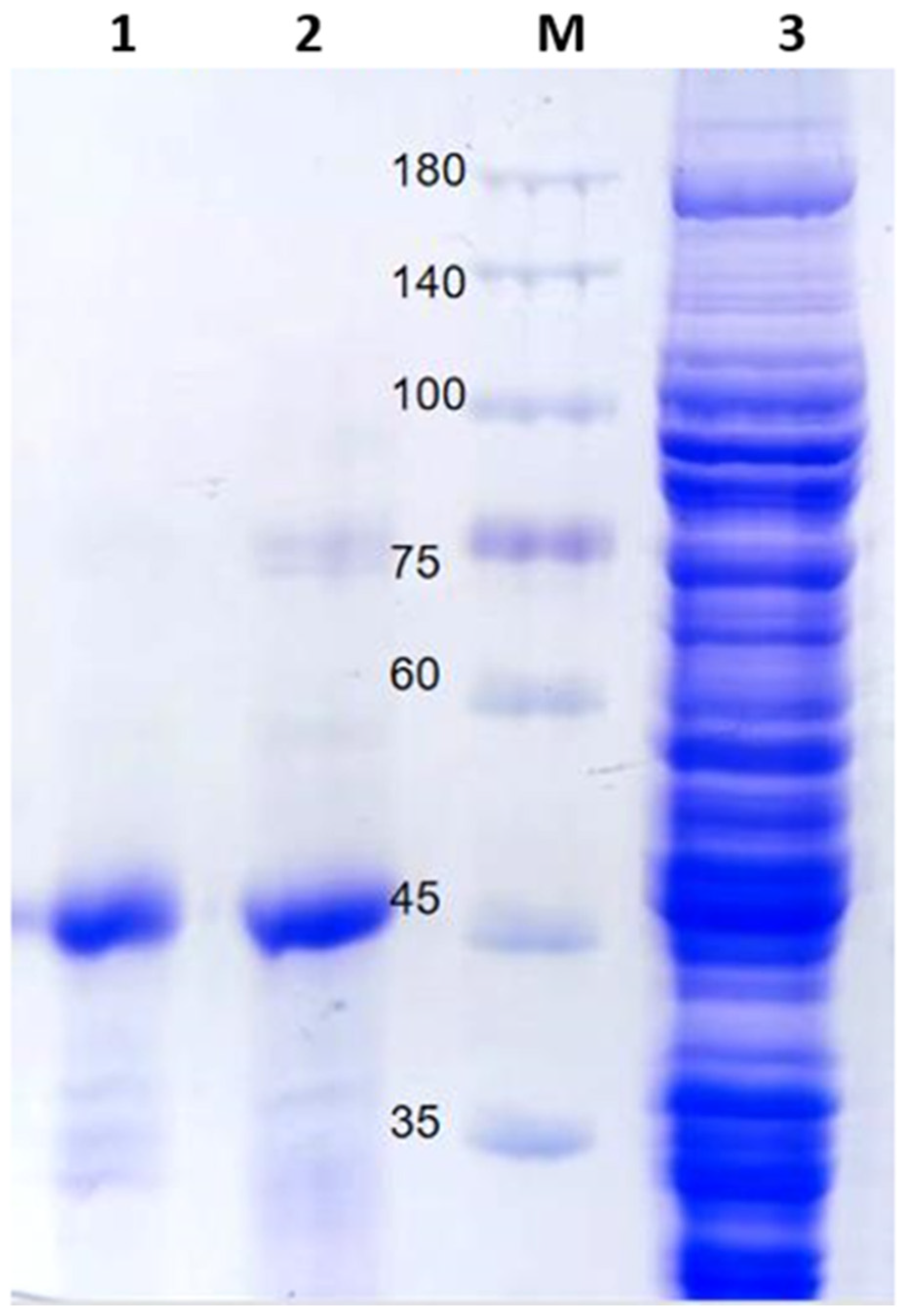
| Total Activity (U) | Protein Concentration (mg/mL) | Specific Activity (U/mg) | Purification Fold | Yield (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude enzyme | 799.8 | 8.1 | 9.5 | 1 | 100 |
| Ni2+-NTA | 280.4 | 0.7 | 193.5 | 20.4 | 35.1 |
| Enzyme Activity (U/mg) | Relative Enzyme Activity | |
|---|---|---|
| Wild type | 193.5 ± 0.37 | 100% |
| D34K | 191.9 ± 1.05 | 99% |
| K147D | 93.2 ± 1.34 | 48% |
| E188H | 143.7 ± 0.98 | 74% |
| K230D | 101.7 ± 0.72 | 53% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, J.; Xin, W.; Wang, F.; Xie, W.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J. Cloning and Characterization of Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate Aldolase from Euphausia superba. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810478
Xia J, Xin W, Wang F, Xie W, Liu Y, Xu J. Cloning and Characterization of Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate Aldolase from Euphausia superba. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(18):10478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810478
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Jikun, Wanmeng Xin, Fang Wang, Wancui Xie, Yi Liu, and Jiakun Xu. 2022. "Cloning and Characterization of Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate Aldolase from Euphausia superba" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 18: 10478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810478
APA StyleXia, J., Xin, W., Wang, F., Xie, W., Liu, Y., & Xu, J. (2022). Cloning and Characterization of Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate Aldolase from Euphausia superba. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(18), 10478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810478






