A Bibliometric Analysis of Research Trends in Geopolymer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
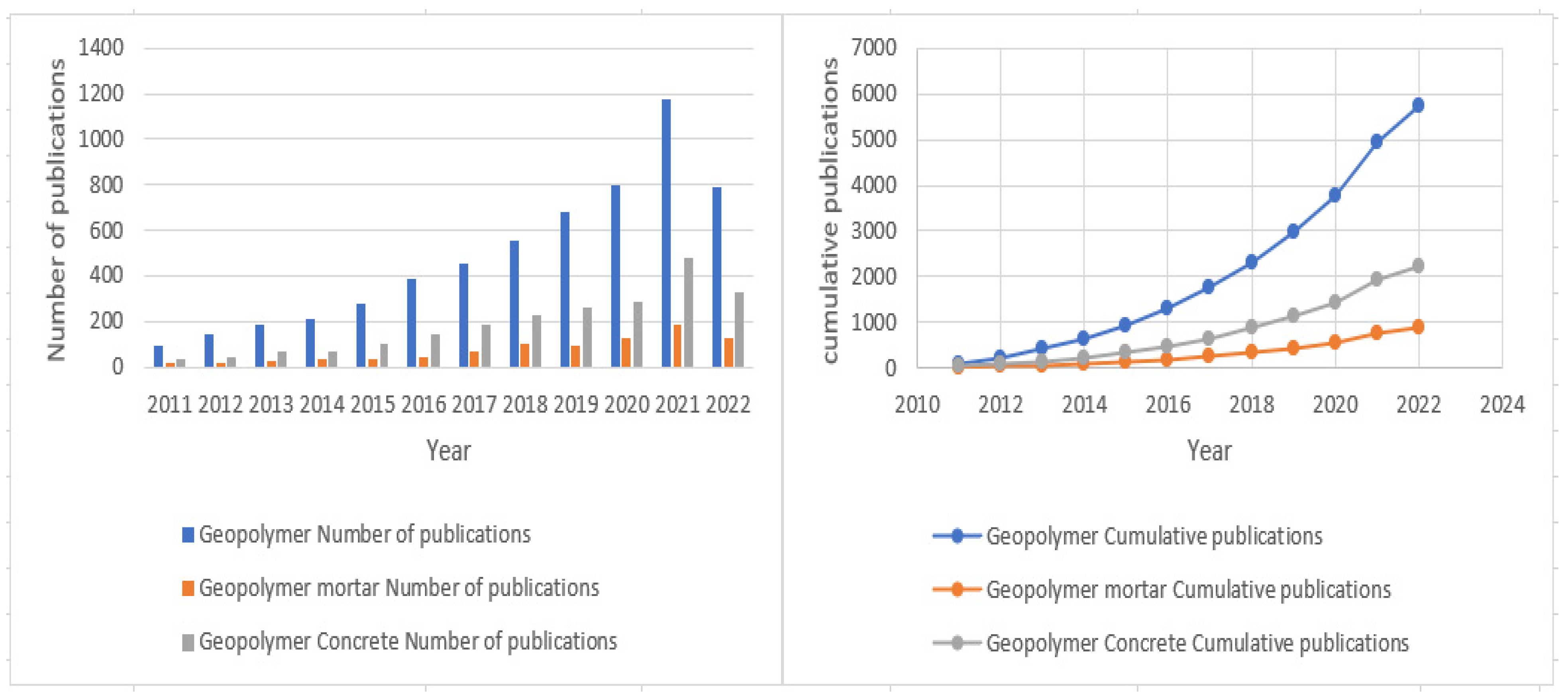
3.1. Yearly Distribution and Growth Trends
3.2. Publication Sources Contribution
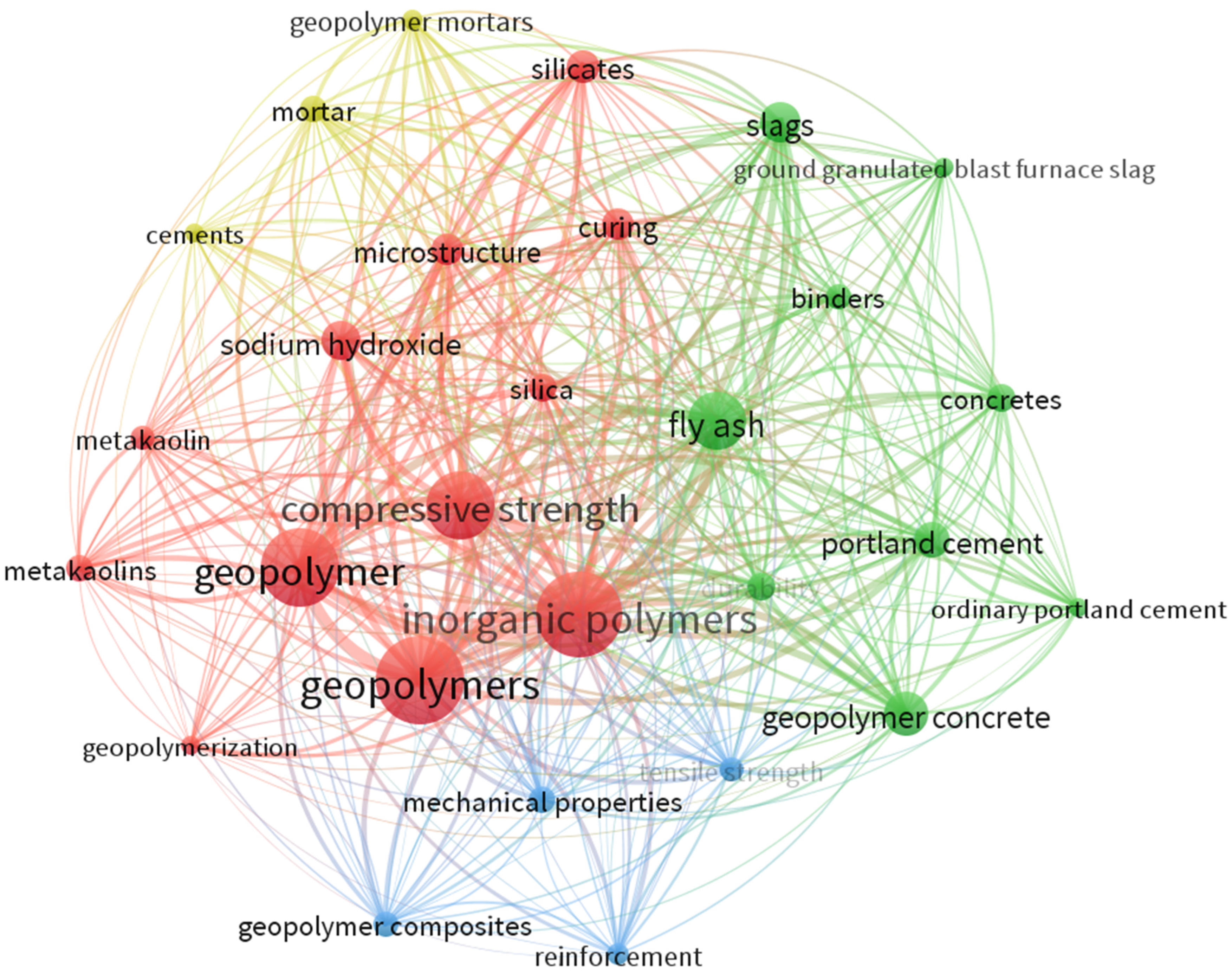
3.3. Keyword Co-Occurrence
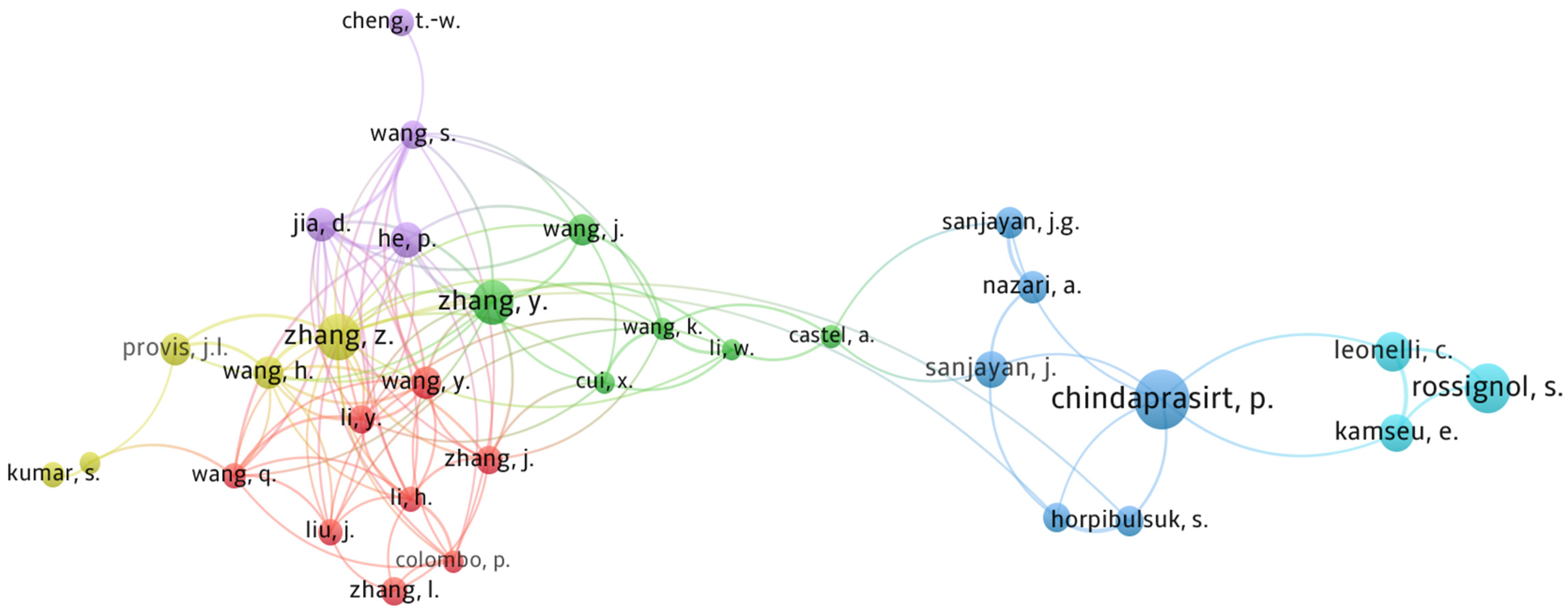
3.4. Authors’ Contribution
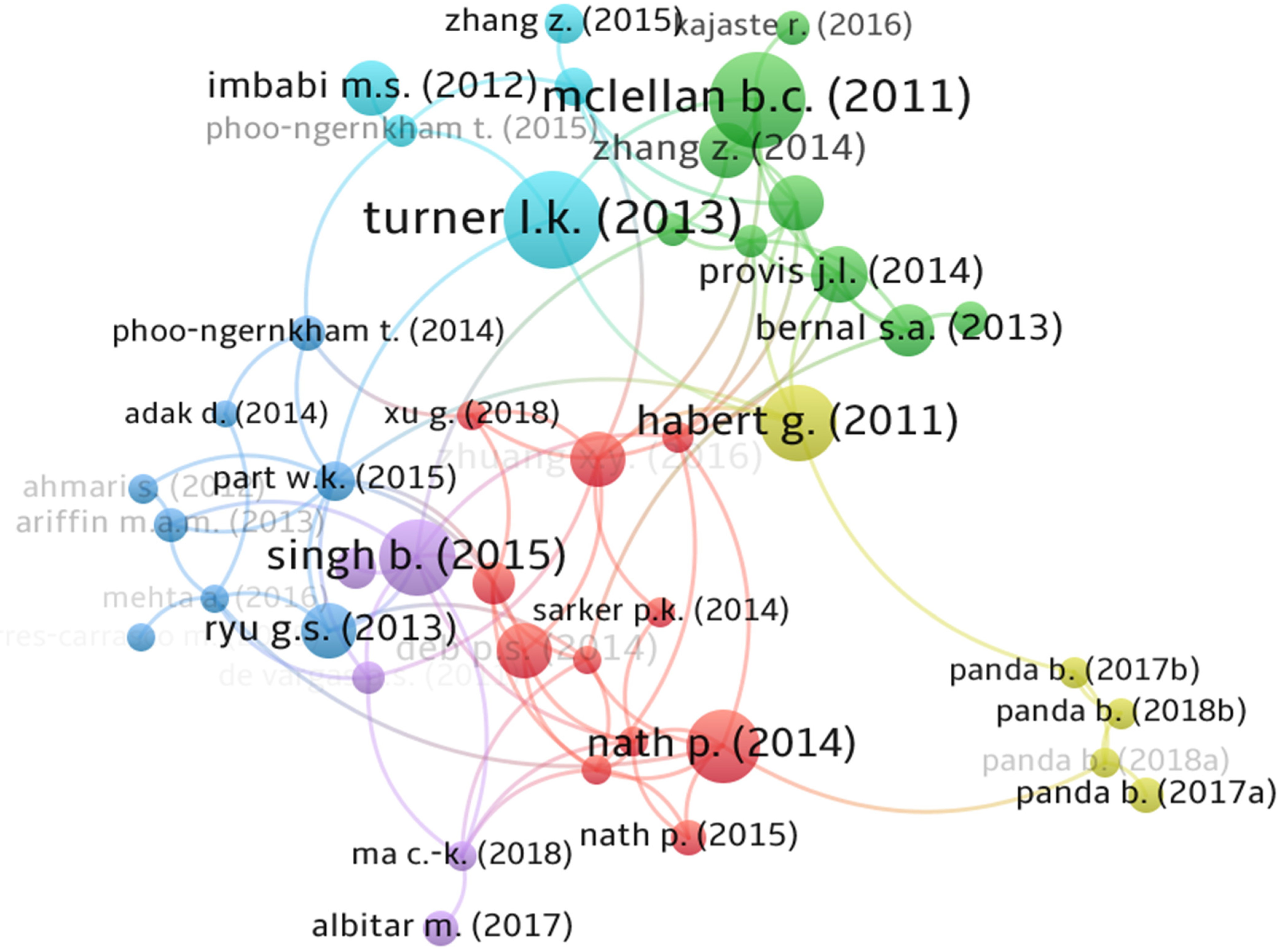
3.5. Publication Contribution
3.6. Countries’ Contribution
4. Future Research Trends
- A synchronized standard geopolymer mix design and test method incorporating various ranges of NaOH, Na2SiO3/NaOH, SiO2/Na2O, SiO2/Al2O3, CaO/SiO2, CaO/(SiO2 + Al2O3), L/B, curing temperature and time, and aggregates to achieve better geopolymerization and give better strength output.
- The harmonized utilization of the different waste materials to obtain geopolymers with high performance. The properties of the waste materials vary making it difficult to develop geopolymers with consistent properties.
- Predictive models for mechanical strength and durability properties of geopolymer to guide preliminary mix design and achieve the required performance without conducting tedious and costly trial and error mix formulations.
- Techniques to enhance the reactivity of precursor materials.
- Low-temperature curing conditions to replace the high-temperature curing conditions, save on energy costs, and adopt in situ casting of geopolymer.
- Low-cost user-friendly activating solutions to replace the expensive user-hostile alkaline and acidic solutions.
- Large-scale treatment technology for phosphogypsum and its reaction mechanism in unary or binary geopolymer systems.
- The application and implementation of geopolymer binder, mortar, concrete, brick, etc., in the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry.
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
- In terms of publication sources, the journals Construction and Building Materials, Journal of Cleaner Production, Ceramics International, and Materials are the top four most preferred for geopolymer publications. Most of the sources were citing articles from the journals Construction and Building Materials, Cement and Concrete Composites, Cement and Concrete Research, and the Journal of Cleaner Production.
- In terms of keyword co-occurrence, the most used keywords are geopolymers, inorganic polymer, and geopolymer. The findings can assist future researchers to choose keywords for easy identification of a particular research field in search engines.
- In terms of author contribution, the authors Jay Sanjayan, Prinya Chindaprasirt, and Mustafa Al Bakri Abdullah have the most documents, whilst John Provis has the most total citations. The analysis shows that researchers from different geographical areas are interconnected through citations in the field of geopolymer.
- In terms of countries’ contribution, the highest number of publications were from China, India, Australia, and the United States of America. The country cooperation network depicts that there is a robust research collaboration of most of the countries with India, Australia, and China. The African countries leading in geopolymer research consist of Egypt, Cameroon, Nigeria, and Morocco; hence the need to scale up geopolymer research in sub-Saharan Africa.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, C.; Jiménez, A.F.; Palomo, A. New cements for the 21st century: The pursuit of an alternative to Portland cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 750–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovits, J. Geopolymer Chemistry and Applications, 5th ed.; Institut Géopolymère: Saint-Quentin, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- McLellan, B.C.; Williams, R.P.; Lay, J.; van Riessen, A.; Corder, G.D. Costs and carbon emissions for geopolymer pastes in comparison to ordinary portland cement. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 1080–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheimi, M.; Aziz, I.H.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Almadani, M.; Abd Razak, R. Waste Material via Geopolymerization for Heavy-Duty Application: A Review. Materials 2022, 15, 3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nodehi, M.; Taghvaee, V.M. Alkali-Activated Materials and Geopolymer: A Review of Common Precursors and Activators Addressing Circular Economy. Circ. Econ. Sustain. 2021, 2, 165–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Provis, J.L.; Reid, A.; Wang, H. Mechanical, thermal insulation, thermal resistance and acoustic absorption properties of geopolymer foam concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2015, 62, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Hechmi El Ouni, M.; Azab, M.; Ali, K.; Haider, H.; Rashedi, A. A scientometric review on mechanical and durability performance of geopolymer Paste: Effect of various raw materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 345, 128297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.S. Durability Performance of Geopolymer Concrete: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huseien, G.F.; Asaad, M.A.; Abadel, A.A.; Ghoshal, S.K.; Hamzah, H.K.; Benjeddou, O.; Mirza, J. Drying Shrinkage, Sulphuric Acid and Sulphate Resistance of High-Volume Palm Oil Fuel Ash-Included Alkali-Activated Mortars. Sustainability 2022, 14, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhu, H.; Feng, P.; Zhang, P. A review on shrinkage-reducing methods and mechanisms of alkali-activated/geopolymer systems: Effects of chemical additives. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 49, 104056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amran, M.; Al-Fakih, A.; Chu, S.H.; Fediuk, R.; Haruna, S.; Azevedo, A.; Vatin, N. Long-term durability properties of geopolymer concrete: An in-depth review. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 15, e00661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, W.; Ahmad, A.; Ostrowski, K.A.; Aslam, F.; Joyklad, P. A scientometric review of waste material utilization in concrete for sustainable construction. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 15, e00683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burduhos Nergis, D.D.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Vizureanu, P.; Tahir, M.F. Geopolymers and Their Uses: Review. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 374, 012019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habert, G.; d’Espinose de Lacaillerie, J.B.; Roussel, N. An environmental evaluation of geopolymer based concrete production: Reviewing current research trends. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA. GlobalABC Roadmap for Building and Construction 2020–2050: Towards a Zero-Emission, Efficient and Resilient Buildings and Construction Sector. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/globalabc-roadmap-for-buildings-and-construction-2020-2050, (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- IEA. Cement Technology Roadmap Plots Path to Cutting CO2 Emissions 24% by 2050. International Energy Agency. 2018. Available online: https://www.iea.org/news/cement-technology-roadmap-plots-path-to-cutting-co2-emissions-24-by-2050 (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- Cao, Y.; Cui, Y.; Yu, X.; Li, T.; Chang, I.S.; Wu, J. Bibliometric analysis of phosphogypsum research from 1990 to 2020 based on literatures and patents. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 66845–66857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, A.; Jain, M.K. Fly ash—Waste management and overview: A Review. Recent Res. Sci. Technol. 2014, 6, 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Sett, R. Fly ash: Characteristics, Problems and Possible Utilization. Environ. Sci. Adv. Appl. Sci. Res. 2017, 8, 32–50. [Google Scholar]
- Alabi, S.A.; Mahachi, J. Chloride ion penetration performance of recycled concrete with different geopolymers. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 38, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, A.L.; Tayeh, B.A.; Adesina, A.; Isleem, H.F.; Zeyad, A.M. Potential applications of geopolymer concrete in construction: A review. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 15, e00733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.; Arif, M.; Shariq, M. Use of geopolymer concrete for a cleaner and sustainable environment—A review of mechanical properties and microstructure. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 223, 704–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, A.M. Potential use of phosphogypsum in alkali-activated fly ash under the effects of elevated temperatures and thermal shock cycles. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 87, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovits, J. Geopolymers—Inorganic polymeric new materials. J. Therm. Anal. 1991, 37, 1633–16556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhir, M.R.; Chen, S.; Rai, S.; Jain, D. An Empirical Model for Geopolymer Reactions Involving Fly Ash and GGBS. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 2022, 8801294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebana, M.V.; Ziat, K.; Semlal, N.; Saidi, M. Modeling compressive strength of Moroccan fly ash–phosphogypsum geopolymer bricks. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, I.H.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Mohd Salleh, M.A.A.; Azimi, E.A.; Chaiprapa, J.; Sandu, A.V. Strength development of solely ground granulated blast furnace slag geopolymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 250, 118720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suksiripattanapong, C.; Krosoongnern, K.; Thumrongvut, J.; Sukontasukkul, P.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Chindaprasirt, P. Properties of cellular lightweight high calcium bottom ash-portland cement geopolymer mortar. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2020, 12, e00337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falayi, T. A comparison between fly ash- and basic oxygen furnace slag-modified gold mine tailings geopolymers. Int. J. Energy Environ. Eng. 2020, 11, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basri, M.S.M.; Mustapha, F.; Mazlan, N.; Ishak, M.R. Rice Husk Ash-Based Geopolymer Binder: Compressive Strength, Optimize Composition, FTIR Spectroscopy, Microstructural, and Potential as Fire-Retardant Material. Polymers 2021, 13, 4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukor Lim, N.H.A.; Samad, M.; Ariffin, N.F.; Hussin, M.W.; Bhutta, M.A.R.; Sarbini, N.R.; Khalid, N.H.A.; Aminuddin, E. Effect of Curing Conditions on Compressive Strength of FA-POFA-based Geopolymer Mortar. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 431, 092007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, J.J.; Rao, H.S.; Ghorpade, V.G. XRD & SEM studies of Fly-ash and Phosphogypsum based Geopolymer Bricks. Int. J. Eng. Trends Technol. 2021, 69, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Tang, Q.; Xakalashe, B.S.; Fan, X.; Gan, M.; Chen, X.; Ji, Z.; Huang, X.; Friedrich, B. Mechanical and environmental characteristics of red mud geopolymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 321, 125564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhi, M.A.; Rodríguez, E.D.; Walkley, B.; Zhang, Z.; Kirchheim, A.P. Metakaolin-based geopolymers: Relation between formulation, physicochemical properties and efflorescence formation. Compos. B Eng. 2020, 182, 107671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaze, C.R.; Lemougna, P.N.; Alomayri, T.; Assaedi, H.; Adesina, A.; Das, S.K.; Nana, G.L.L.; Kamseu, E.; Melo, U.C.; Leonelli, C. Characterization and performance evaluation of laterite based geopolymer binder cured at different temperatures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 270, 121443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchadjié, L.N.; Ekolu, S.O.; Quainoo, H.; Tematio, P. Incorporation of activated bauxite to enhance engineering properties and microstructure of volcanic ash geopolymer mortar composites. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 41, 102384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özen, S.; Alam, B. Compressive Strength and Microstructural Characteristics of Natural Zeolite-based Geopolymer. Period. Polytech. Civ. Eng. 2017, 62, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabie, M.; Irshidat, M.R.; Al-Nuaimi, N. Ambient and Heat-Cured Geopolymer Composites: Mix Design Optimization and Life Cycle Assessment. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchakouté, H.K.; Rüscher, C.H.; Kong, S.; Kamseu, E.; Leonelli, C. Geopolymer binders from metakaolin using sodium waterglass from waste glass and rice husk ash as alternative activators: A comparative study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 114, 276–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Ma, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Huang, B.; He, Q. Strength, microstructure, efflorescence behavior and environmental impacts of waste glass geopolymers cured at ambient temperature. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghizadeh, A.; Ekolu, S.O. Investigation of mixture factors influencing alkali-silica reaction in fly ash-based geopolymer mortars. In Proceedings of the 71st RILEM Annual Week ICACMS, Chennai, India, 3–8 September 2017; pp. 95–400. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Shi, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y. A review on mixture design methods for geopolymer concrete. Compos. B Eng. 2019, 178, 107490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, W.; Khan, M.; Smarzewski, P. Effect of Short Fiber Reinforcements on Fracture Performance of Cement-Based Materials: A Systematic Review Approach. Materials 2021, 14, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donthu, N.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Pandey, N.; Lim, W.M. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 133, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Pei, Y. Bibliographic and visualized analysis of geopolymer research and its application in heavy metal immobilization: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakka, W.P.; Abdul Shukor Lim, N.H.; Chau Khun, M. A scientometric review of geopolymer concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 124353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, L.; Yang, W.; Liu, H.; Ahmad, W.; Ahmwa, A.; Aslam, F.; Joyklad, P. A comprehensive overview of geopolymer composites: A bibliometric analysis and literature review. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e00830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Pan, Y.; Bai, Y.; Yao, S.; Sun, S. A Bibliometric Analysis of Research Progress and Trends on Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer. Materials 2022, 15, 4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadegani, A.A.; Salehi, H.; Yunus, M.M.; Farhadi, H.; Fooladi, M.; Farhadi, M.; Ebrahim, N.A. A Comparison between Two Main Academic Literature Collections: Web of Science and Scopus Databases. Asian Soc. Sci. 2013, 9, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, E.L. Finding Citations to Social Work Literature: The Relative Benefits of Using Web of Science, Scopus, or Google Scholar. J. Acad. Librariansh. 2012, 38, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meho, L.I. Using Scopus’s CiteScore for assessing the quality of computer science conferences. J. Informetr. 2019, 13, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzard, M.H.; El-Hassan, H.; El-Maaddawy, T.; Alsalami, M.; Abdulrahman, F.; Hassan, A.A. A Bibliometric Analysis of the Studies on Self-Healing Concrete Published between 1974 and 2021. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabour, M.R.; Amiri, E.A.; Akbari, M.; Sadeghi-Sheshdeh, A. A bibliometric analysis of research trends in life cycle assessment of fresh concrete and mortar during 1997–2021. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 71894–71910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrvar, A.; Batagelj, V. Analysis and visualization of large networks with program package Pajek. Complex Adapt. Syst. Modeling 2016, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Citation-based clustering of publications using CitNetExplorer and VOSviewer. Scientometrics 2017, 111, 1053–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luhar, I.; Luhar, S.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Razak, R.A.; Vizureanu, P.; Sandu, A.V.; Matasaru, P.D. A State-of-the-Art Review on Innovative Geopolymer Composites Designed for Water and Wastewater Treatment. Materials 2021, 14, 7456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco-Torgal, F.; Labrincha, J.A.; Leonelli, C.; Palomo, A.; Chindaprasirt, P. Handbook of Alkali-Activated Cements, Mortars, and Concretes; Woodhead Publishing Series in Civil and Structural Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Azevedo, A.R.G.; Marvila, M.T.; de Oliveira, L.B.; Ferreira, W.M.; Colorado, H.; Teixeira, S.R.; Viera, C.M.F. Circular economy and durability in geopolymers ceramics pieces obtained from glass polishing waste. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2021, 18, 1891–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, N.; Mohamed, O.A.; Sayed, E.T.; Abdelkareem, M.A.; Olabi, A.G. Geopolymer concrete as green building materials: Recent applications, sustainable development and circular economy potentials. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stats, S.A. Sustainable Development Goals: Baseline Report. 2017. Available online: http://www.statssa.gov.za/MDG/SDG_Baseline_Report_2017.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2022).
- Ahmad, S.; Sohail, M.; Waris, A.; Elginaid, A.; Magid, I. SCImago, Eigenfactor Score, and H5 Index Journal Rank Indicator:A Study of Journals in the area of Construction and Building Technologies. J. Libr. Inf. Technol. 2018, 38, 278. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, S.A.J.; Abdel-Magid, I.M.; Hussain, A. Comparison among journal impact factor, SCimago journal rank indicator, eigenfactor score and h5-index of environmental engineering journals. COLLNET J. Scientometr. Inf. Manag. 2017, 11, 133–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, A.; Sudalaimani, K.; Vijayakumar, C.T.; Saravanakumar, S.S. Effect of bio-additives on physico-chemical properties of fly ash-ground granulated blast furnace slag based self cured geopolymer mortars. J. Hazard Mater. 2019, 361, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amran, M.; Debbarma, S.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. Fly ash-based eco-friendly geopolymer concrete: A critical review of the long-term durability properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 270, 121857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuni, I.Y.; Shen, G.Q.P.; Osei-Kyei, R. Scientometric review of global research trends on green buildings in construction journals from 1992 to 2018. Energy Build. 2019, 190, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhao, Y. Bibliometric analysis of global environmental assessment research in a 20-year period. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2015, 50, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, H.; Hu, J.; Kim, Y.R. Effect of slag, silica fume, and metakaolin on properties and performance of alkali-activated fly ash cured at ambient temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 197, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phummiphan, I.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Rachan, R.; Arulrajah, A.; Shen, S.L.; Chindaprasirt, P. High calcium fly ash geopolymer stabilized lateritic soil and granulated blast furnace slag blends as a pavement base material. J. Hazard Mater. 2018, 341, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashifana, T.P.; Okonta, F.N.; Ntuli, F. Geotechnical Properties and Microstructure of Lime-Fly Ash-Phosphogypsum-Stabilized Soil. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2018, 2018, 3640868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askarian, M.; Tao, Z.; Samali, B.; Adam, G.; Shuaibu, R. Mix composition and characterisation of one-part geopolymers with different activators. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 225, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Zhu, Z.; Peng, Y.; Wan, Y.; Xu, X.; Pu, S.; Song, S.; Wei, W. Effect of steel slag on fresh, hardened and microstructural properties of high-calcium fly ash based geopolymers at standard curing condition. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 229, 116933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colangelo, F.; Farina, I.; Travaglioni, M.; Salzano, C.; Cioffi, R.; Petrillo, A. Eco-efficient industrial waste recycling for the manufacturing of fibre reinforced innovative geopolymer mortars: Integrated waste management and green product development through LCA. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 312, 127777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukontasukkul, P.; Chindaprasirt, P.; Pongsopha, P.; Phoo-Ngernkham, T.; Tangchirapat, W.; Banthia, N. Effect of fly ash/silica fume ratio and curing condition on mechanical properties of fiber-reinforced geopolymer. J. Sustain. Cem. Based Mater. 2020, 9, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacob, N.S.; ElGawady, M.A.; Sneed, L.H.; Said, A. Shear strength of fly ash-based geopolymer reinforced concrete beams. Eng. Struct. 2019, 196, 109298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, S.J.; Hsiao, Y.H.; Wang, T.T.; Cheng, T.W.; Ueng, T.-H. Microstructure of geopolymer accounting for associated mechanical characteristics under various stress states. Cem. Concr. Res. 2013, 54, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, L.K.; Collins, F.G. Carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2-e) emissions: A comparison between geopolymer and OPC cement concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 43, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Ishwarya, G.; Gupta, M.; Bhattacharyya, S.K. Geopolymer concrete: A review of some recent developments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 85, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, P.; Sarker, P.K. Effect of GGBFS on setting, workability and early strength properties of fly ash geopolymer concrete cured in ambient condition. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 66, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, I.; Bernal, S.A.; Provis, J.L.; Hamdan, S.J.; van Deventer, S.J. Microstructural changes in alkali activated fly ash/slag geopolymers with sulfate exposure. Mater. Struct. 2013, 46, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, T.; Abdollahnejad, Z.; Yliniemi, J.; Kinnunen, P.; Illikainen, M. One-part alkali-activated materials: A review. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 103, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provis, J.L. Geopolymers and other alkali activated materials: Why, how, and what. Mater. Struct. 2014, 47, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, P.S.; Nath, P.; Sarker, P.K. The effects of ground granulated blast-furnace slag blending with fly ash and activator content on the workability and strength properties of geopolymer concrete cured at ambient temperature. Mater. Des. 2014, 62, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Deventer, J.S.J.; Provis, J.L.; Duxson, P. Technical and commercial progress in the adoption of geopolymer cement. Miner. Eng. 2012, 29, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Provis, J.L.; Reid, A.; Wang, H. Geopolymer foam concrete: An emerging material for sustainable construction. Constr. Build Mater. 2014, 56, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, G.S.; Lee, Y.B.; Koh, K.T.; Chung, Y.S. The mechanical properties of fly ash-based geopolymer concrete with alkaline activators. Constr. Build Mater. 2013, 47, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbabi, M.S.; Carrigan, C.; McKenna, S. Trends and developments in green cement and concrete technology. Int. J. Sustain. Built Environ. 2012, 1, 194–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.Y.; Chen, L.; Komarneni, S.; Zhou, C.H.; Tong, D.S.; Yang, H.M.; Yu, W.H.; Wang, H. Fly ash-based geopolymer: Clean production, properties and applications. J. Clean Prod. 2016, 125, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, S.A.; Provis, J.L.; Walkley, B.; Nicolas, R.S.; Gehman, J.D.; Brice, D.G.; Kilcullen, A.R.; Duxson, P.; van Deventer, J.S.J. Gel nanostructure in alkali-activated binders based on slag and fly ash, and effects of accelerated carbonation. Cem. Concr. Res. 2013, 53, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Jie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, G. Synthesis and characterization of red mud and rice husk ash-based geopolymer composites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 37, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasby, T.; Day, J.; Genrich, R.; Kemp, M. Commercial Scale Geopolymer Concrete Construction. In Proceedings of the Saudi International Building and Constructions Technology Conference, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 11–12 May 2015; Available online: https://www.wagner.com.au/media/1516/geopolymer-concrete_saudi-conference_2015.pdf (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Whyte, C.; de Bres, D. Geopolymer Concrete: Concrete from Waste Materials. 2016. Available online: https://sustainabletech.co.za/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/Geo-Polymer-Concrete-Systems.pdf2016 (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Schmidt, W. Why Africa can spearhead innovative and sustainable cement and concrete technologies globally. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium Knowledge Exchange for Young Scientists Proceedings, Accra, Ghana, 7–9 June 2016; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchins, B.I.; Yuan, X.; Anderson, J.M.; Santangelo, G.M. Relative Citation Ratio (RCR): A New Metric That Uses Citation Rates to Measure Influence at the Article Level. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, C.; Colledge, L.; Meester, W.; Azoulay, N.; Plume, A. CiteScore metrics: Creating journal metrics from the Scopus citation index. Learn. Publ. 2019, 32, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Option | Inclusion Criteria Applied |
|---|---|
| Language | English |
| Publication date | April 2011–2022 |
| Subject area | Engineering; Material Science; Environmental Science |
| Source type | Journal |
| Document type | Article, Review |
| S/N | Keywords Searched | Article Results | Article Results after Limits |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Geopolymer | 9887 | 5186 |
| 2 | Geopolymer mortar | 1374 | 866 |
| 3 | Geopolymer concrete | 3721 | 2253 |
| S/N | Source | Publications | Citation | Average Citation per Publication | JIF | H-Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Construction and Building Materials | 1030 | 40,671 | 39.49 | 7.693 | 198 |
| 2 | Journal of Cleaner Production | 239 | 7611 | 31.85 | 11.072 | 232 |
| 3 | Ceramics International | 232 | 7388 | 31.84 | 5.532 | 126 |
| 4 | Materials | 230 | 3240 | 14.09 | 3.748 | 128 |
| 5 | Cement and Concrete Composites | 163 | 11,141 | 68.35 | 9.93 | 174 |
| 6 | Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering | 136 | 3518 | 25.87 | 3.266 | 114 |
| 7 | Journal of Building Engineering | 124 | 2077 | 16.75 | 5.318 | 54 |
| 8 | Materials Letters | 82 | 3567 | 43.50 | 3.574 | 155 |
| 9 | Case Studies in Construction Materials | 81 | 806 | 9.95 | 4.934 | 36 |
| 10 | Cement and Concrete Research | 73 | 9910 | 135.75 | 11.958 | 239 |
| 11 | Journal of the American Ceramic Society | 67 | 2859 | 42.67 | 3.784 | 203 |
| 12 | Sustainability | 60 | 342 | 5.70 | 3.889 | 109 |
| 13 | Journal of Hazardous Materials | 59 | 1328 | 22.51 | 14.224 | 307 |
| 14 | Composites Part B Engineering | 56 | 3412 | 60.93 | 9.078 | 163 |
| 15 | Polymers | 53 | 285 | 5.38 | 4.967 | 89 |
| 16 | Materials and Design | 52 | 3900 | 75.00 | 9.417 | 187 |
| S/N | Keyword | Occurrences | S/N | Keyword | Occurrences |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Geopolymers | 4082 | 15 | Binders | 546 |
| 2 | Inorganic Polymer | 4045 | 16 | Silica | 529 |
| 3 | Geopolymer | 3067 | 17 | Mortar | 518 |
| 4 | Compressive Strength | 2587 | 18 | Metakaolins | 484 |
| 5 | Fly Ash | 2211 | 19 | Polymer | 463 |
| 6 | Geopolymer Concrete | 1102 | 20 | Metakaolin | 457 |
| 7 | Slags | 989 | 21 | Cement | 433 |
| 8 | Silicates | 877 | 22 | Durability | 427 |
| 9 | Portland Cement | 857 | 23 | Tensile Strength | 375 |
| 10 | Sodium Hydroxide | 827 | 24 | Geopolymer Composites | 368 |
| 11 | Curing | 813 | 25 | Reinforcement | 352 |
| 12 | Concretes | 774 | 26 | Geopolymerization | 343 |
| 13 | Microstructure | 695 | 27 | Binders | 546 |
| 14 | Mechanical Properties | 653 | 28 | Silica | 529 |
| S/N | Author | Publications | Citations | Average Citation | Total Link Strength |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jay Sanjayan | 104 | 4311 | 41.45 | 182 |
| 2 | Prinya Chindaprasirt | 99 | 5626 | 56.83 | 181 |
| 3 | Mohd Mustafa Al Bakri Abdullah | 91 | 1010 | 11.10 | 377 |
| 4 | Sylvie Rossignol | 80 | 1778 | 22.23 | 239 |
| 5 | Cristina Leonelli | 61 | 1579 | 25.89 | 220 |
| 6 | Elie Kamseu | 59 | 1236 | 20.95 | 228 |
| 7 | Zuhua Zhang | 53 | 3376 | 63.70 | 246 |
| 8 | Peigang He | 50 | 1130 | 22.60 | 338 |
| 9 | Dechang Jia | 50 | 1119 | 22.38 | 332 |
| 10 | Ali Nazari | 48 | 1708 | 35.58 | 67 |
| 11 | John Provis | 48 | 6377 | 132.85 | 106 |
| 12 | Suksun Horpibulsuk | 44 | 2458 | 55.86 | 112 |
| 13 | Xue-min Cui | 44 | 1549 | 35.20 | 147 |
| 14 | Arul Arulrajah | 43 | 2009 | 46.72 | 107 |
| 15 | Ta-Wui Cheng | 39 | 797 | 20.44 | 97 |
| 16 | Yingwu Zhou | 39 | 924 | 23.69 | 283 |
| 17 | Joao Labrincha | 38 | 1559 | 41.03 | 132 |
| 18 | Andrei Victor Sandu | 38 | 565 | 14.87 | 168 |
| 19 | Faiz Ahmed Shaikh | 37 | 2238 | 60.49 | 63 |
| 20 | Vanchai Sata | 36 | 2829 | 78.58 | 85 |
| 21 | Arnaud Castel | 33 | 1389 | 42.09 | 30 |
| 22 | Claudio Ferone | 33 | 1202 | 36.42 | 121 |
| 23 | Jian-Guo Dai | 32 | 624 | 19.50 | 53 |
| 24 | Xiafeng Duan | 32 | 579 | 18.09 | 246 |
| 25 | Yan He | 32 | 927 | 28.97 | 83 |
| 25 | Paolo Colombo | 31 | 1083 | 34.94 | 78 |
| S/N | Publication | Citations |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | McLellan et al. [3] | 884 |
| 2 | Turner & Collins [77] | 878 |
| 3 | Habert et al. [14] | 675 |
| 4 | Singh et al. [78] | 649 |
| 5 | Nath & Sarker [79] | 626 |
| 6 | Ismail et al. [80] | 537 |
| 7 | Luukkonen et al. [81] | 462 |
| 8 | Provis, [82] | 455 |
| 9 | Deb et al. [83] | 445 |
| 10 | van Deventer et al. [84] | 445 |
| 11 | Zhang et al. [85] | 439 |
| 12 | Ryu et al. [86] | 437 |
| 13 | Imbabi et al. [87] | 435 |
| 14 | Zhuang et al. [88] | 419 |
| 15 | Bernal et al. [89] | 411 |
| 16 | He et al. [90] | 406 |
| S/N | Country | Publications | Percentage (%) | Citations | Average Citation per Publication | Nominal GDP Rank (IMF 2022) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | China | 1124 | 16.10 | 24,008 | 21.36 | 2 |
| 2 | India | 890 | 12.75 | 11,234 | 12.62 | 5 |
| 3 | Australia | 651 | 9.33 | 21,231 | 32.61 | 13 |
| 4 | United States | 451 | 6.46 | 11,609 | 25.74 | 1 |
| 5 | Malaysia | 333 | 4.77 | 8777 | 26.36 | 34 |
| 6 | Italy | 299 | 4.28 | 7903 | 26.43 | 9 |
| 7 | UK | 238 | 3.41 | 5971 | 25.09 | 6 |
| 8 | Thailand | 234 | 3.35 | 7515 | 32.12 | 28 |
| 9 | Turkey | 215 | 3.08 | 3746 | 17.42 | 23 |
| 10 | France | 212 | 3.04 | 2936 | 13.85 | 7 |
| 11 | Saudi Arabia | 201 | 2.88 | 3209 | 15.97 | 18 |
| 12 | Brazil | 181 | 2.59 | 3748 | 20.71 | 10 |
| 13 | Germany | 153 | 2.19 | 4131 | 27.00 | 4 |
| 14 | Iran | 153 | 2.19 | 2707 | 17.69 | 14 |
| 15 | Spain | 144 | 2.06 | 3550 | 24.65 | 15 |
| 16 | Egypt | 141 | 2.02 | 2428 | 17.22 | 35 |
| 17 | South Korea | 124 | 1.78 | 1736 | 14.00 | 12 |
| 18 | Cameroon | 118 | 1.69 | 2644 | 22.41 | 95 |
| 19 | Canada | 115 | 1.65 | 3105 | 27.00 | 8 |
| 20 | Czech Republic | 100 | 1.43 | 681 | 6.81 | 48 |
| 21 | Pakistan | 97 | 1.39 | 877 | 9.04 | 44 |
| 22 | Indonesia | 96 | 1.38 | 588 | 6.13 | 17 |
| 23 | Portugal | 95 | 1.36 | 1113 | 11.72 | 51 |
| 24 | Iraq | 88 | 1.26 | 1339 | 15.22 | 47 |
| 25 | Taiwan | 80 | 1.15 | 1177 | 14.71 | 21 |
| 26 | Romania | 72 | 1.03 | 784 | 10.89 | 49 |
| 27 | Hong Kong | 58 | 0.83 | 1283 | 22.12 | 42 |
| 28 | Finland | 55 | 0.79 | 3416 | 62.11 | 46 |
| 29 | Russia | 55 | 0.79 | 321 | 5.84 | 11 |
| 30 | Viet Nam | 53 | 0.76 | 1350 | 25.47 | 39 |
| 31 | Belgium | 52 | 0.74 | 563 | 10.83 | 25 |
| 32 | Nigeria | 52 | 0.74 | 692 | 13.31 | 31 |
| 33 | Singapore | 50 | 0.72 | 3044 | 60.88 | 37 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matsimbe, J.; Dinka, M.; Olukanni, D.; Musonda, I. A Bibliometric Analysis of Research Trends in Geopolymer. Materials 2022, 15, 6979. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196979
Matsimbe J, Dinka M, Olukanni D, Musonda I. A Bibliometric Analysis of Research Trends in Geopolymer. Materials. 2022; 15(19):6979. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196979
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatsimbe, Jabulani, Megersa Dinka, David Olukanni, and Innocent Musonda. 2022. "A Bibliometric Analysis of Research Trends in Geopolymer" Materials 15, no. 19: 6979. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196979
APA StyleMatsimbe, J., Dinka, M., Olukanni, D., & Musonda, I. (2022). A Bibliometric Analysis of Research Trends in Geopolymer. Materials, 15(19), 6979. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196979







