Systemic Risk Modeling with Lévy Copulas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Review of Literature
3. The Methodology
- estimation of the marginal process by an ARMA-GARCH-NTS model,
- estimation of the various copula functions by marginal innovations, and
- computation of the CoVaR and CoCVaR from the estimated copulas.
3.1. Copula
3.1.1. The Archimedean Copula
3.1.2. The NTS Copula
3.2. CoVaR
3.2.1. CoVaR
3.2.2. Calculation of CoVaR by a Copula
- estimate the marginal CDFs and from the available data,
- estimate the parameters of the copula function ,
- solve u from Equation (14), and
- obtain CoVaR by inverting the marginal CDF: =.
3.3. CoCVaR
CoCVaR
4. The GARCH Model with NTS Innovations and Copula
4.1. The ARMA-GARCH-NTS (AGNTS) Model
- Fit the ARMA-GARCH-T process with Student’s t innovations and generate a large number of scenarios from the fitted Student’s t distribution.
- Fit the generated scenarios with an NTS distribution and generate the same size of scenarios from the fitted NTS distribution.
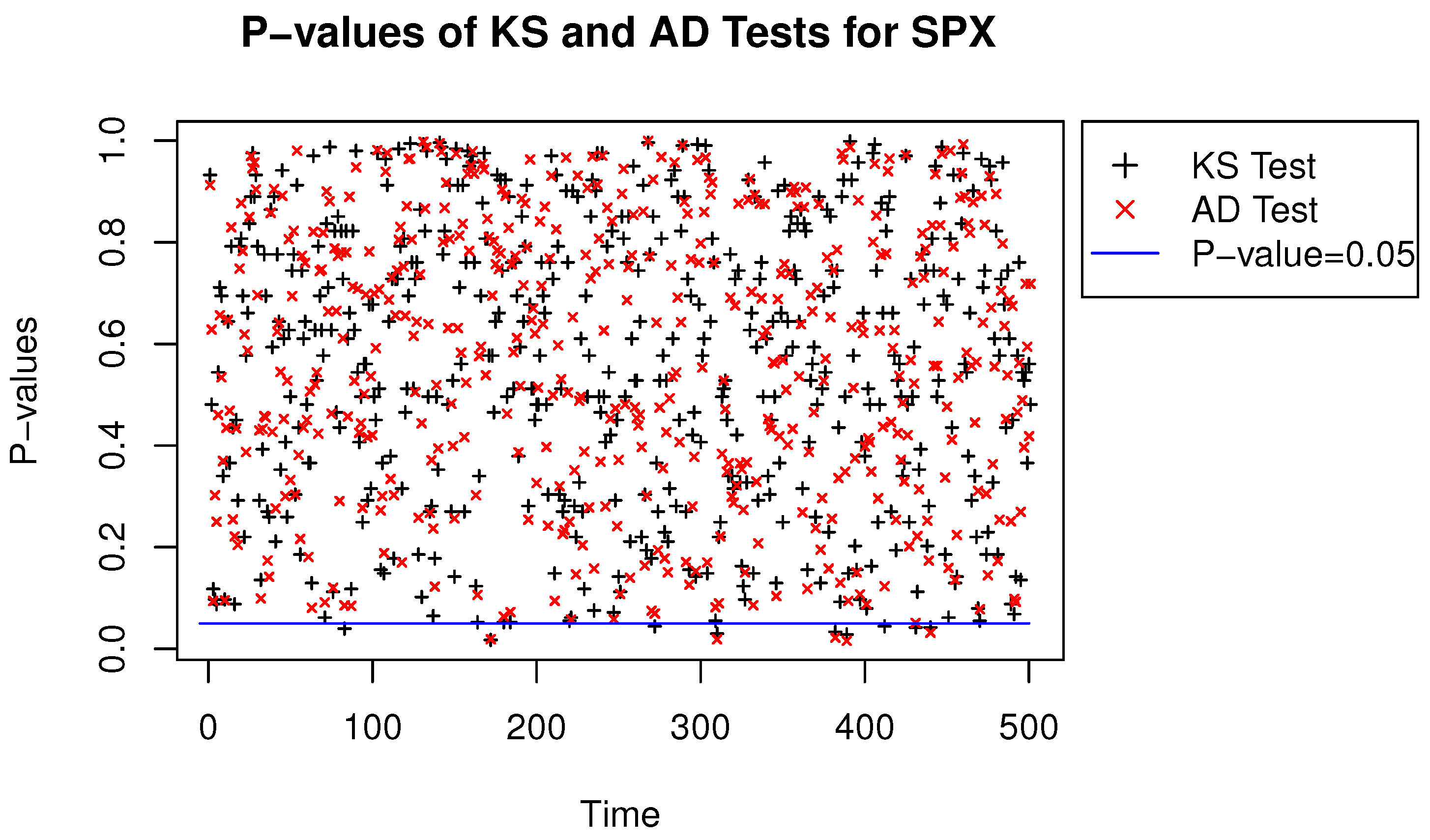
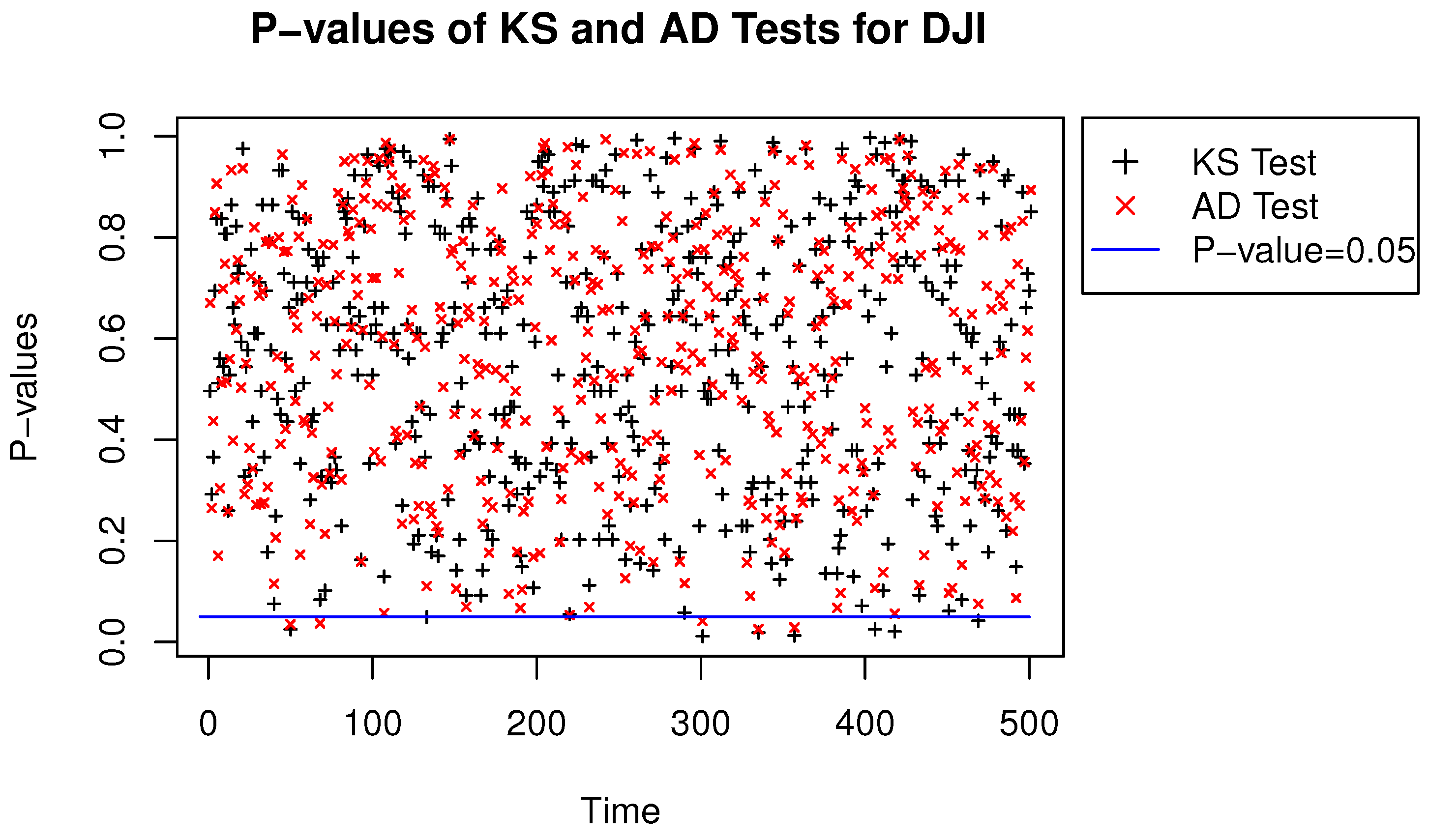
- Use the Kolmogorov–Smirnov (KS) and Anderson-Darling (AD) two-sample tests to confirm that these two sets of scenarios are indistinguishable.
4.2. Calculation of CoVaR and CoCVaR by AGNTS
5. Backtesting and Goodness of Fit
5.1. The Generalized Kupiec’s Test
5.2. Modification of the Generalized Kupiec’s Test
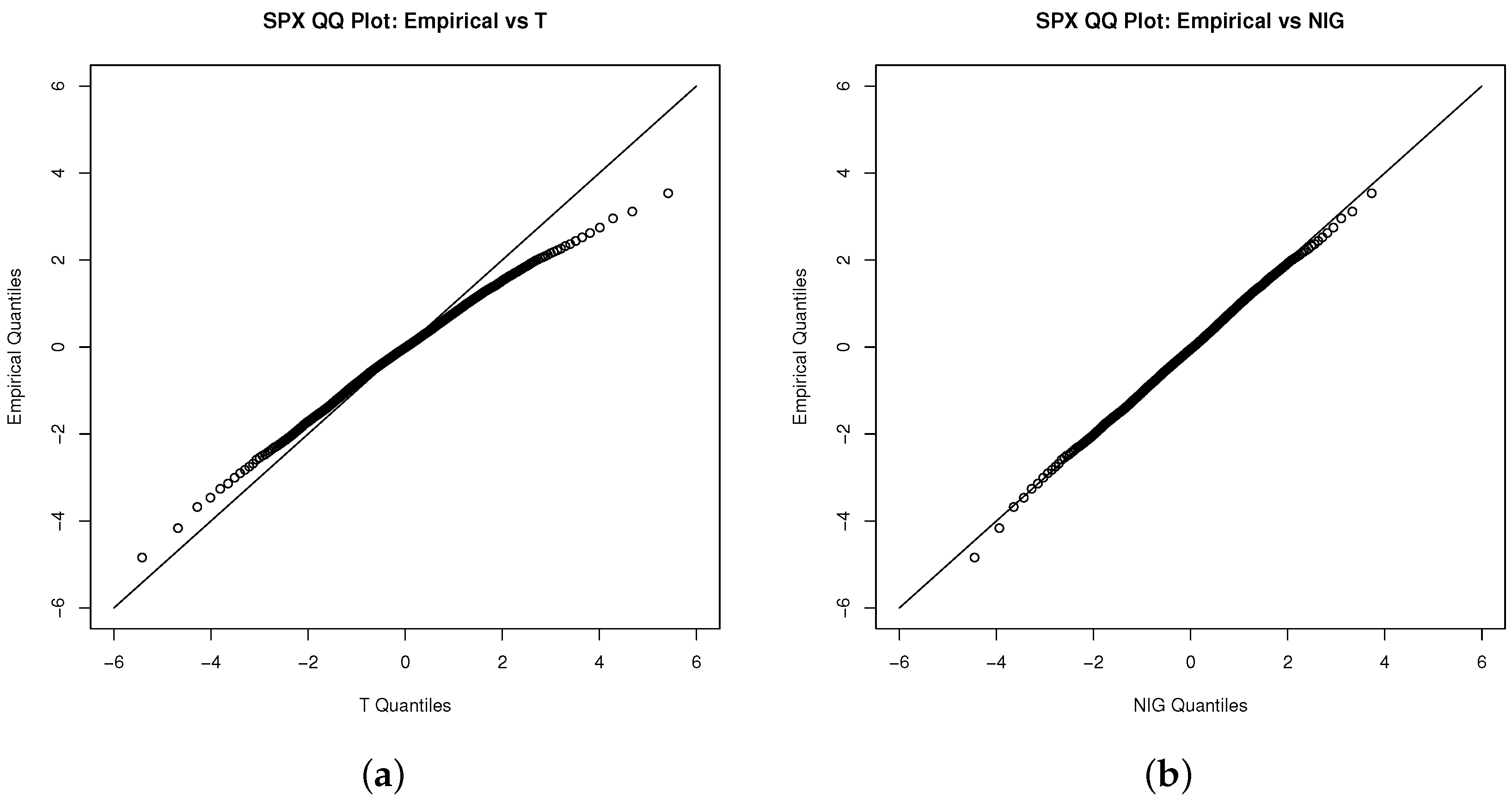
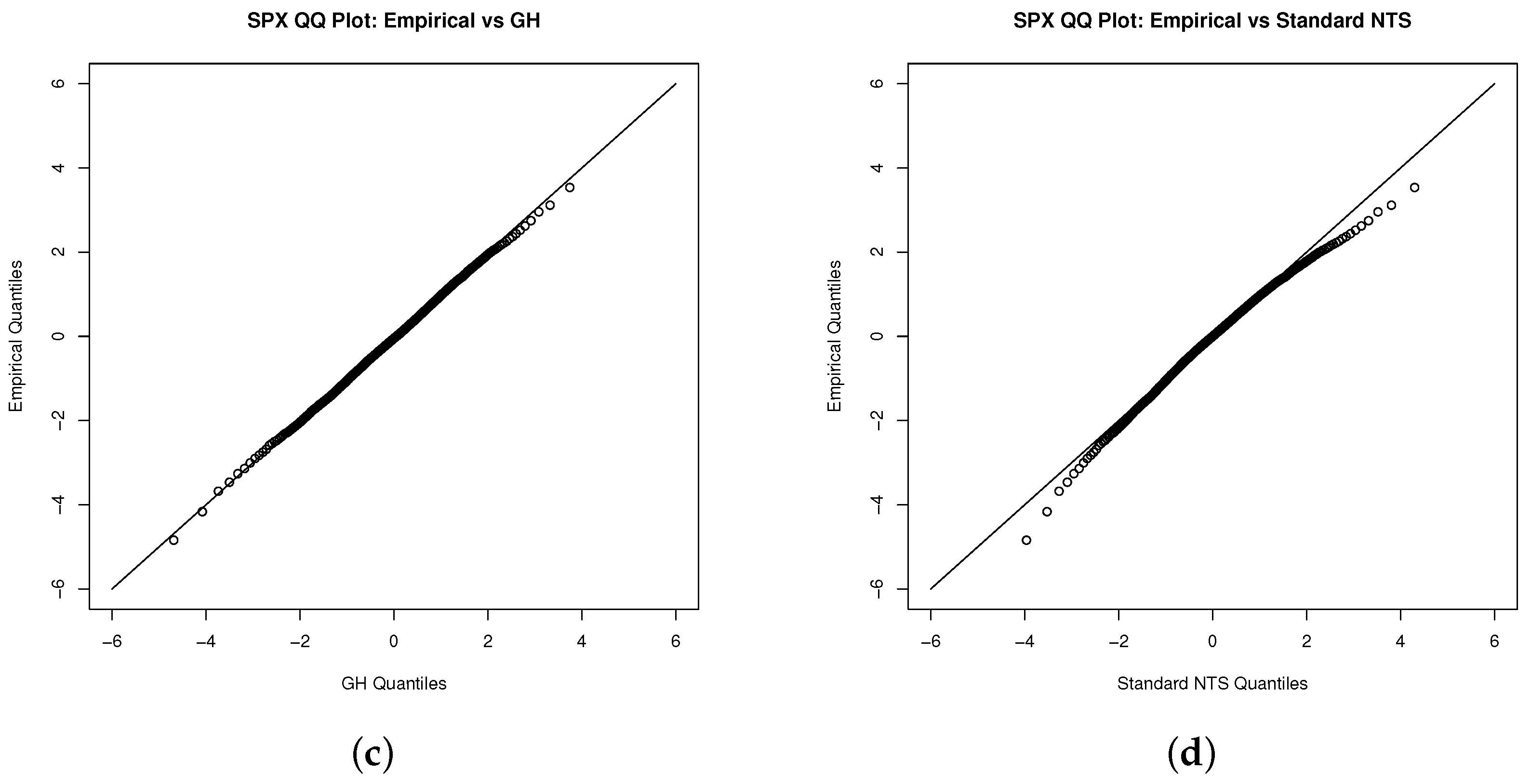
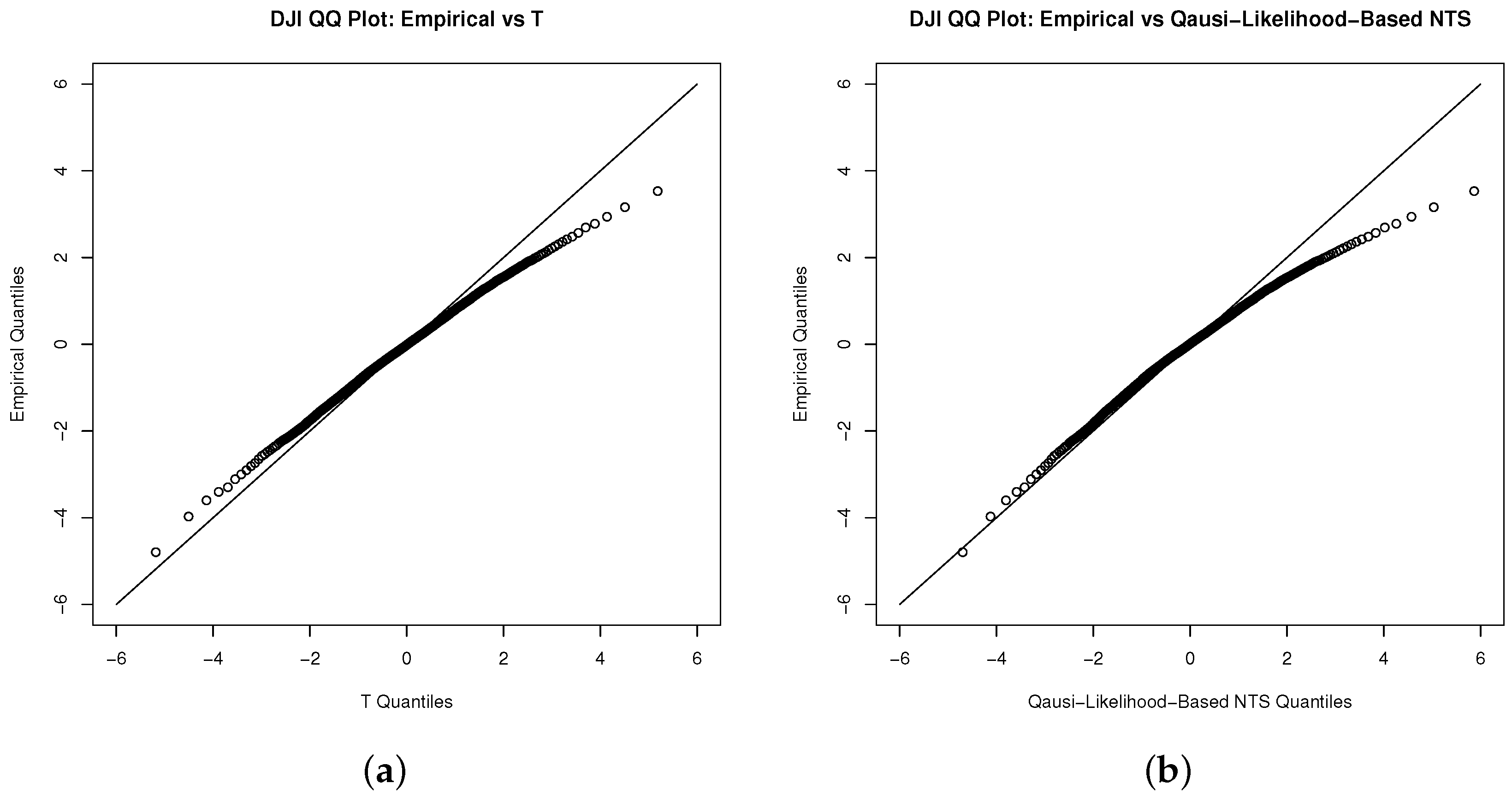
5.3. Goodness of Fit
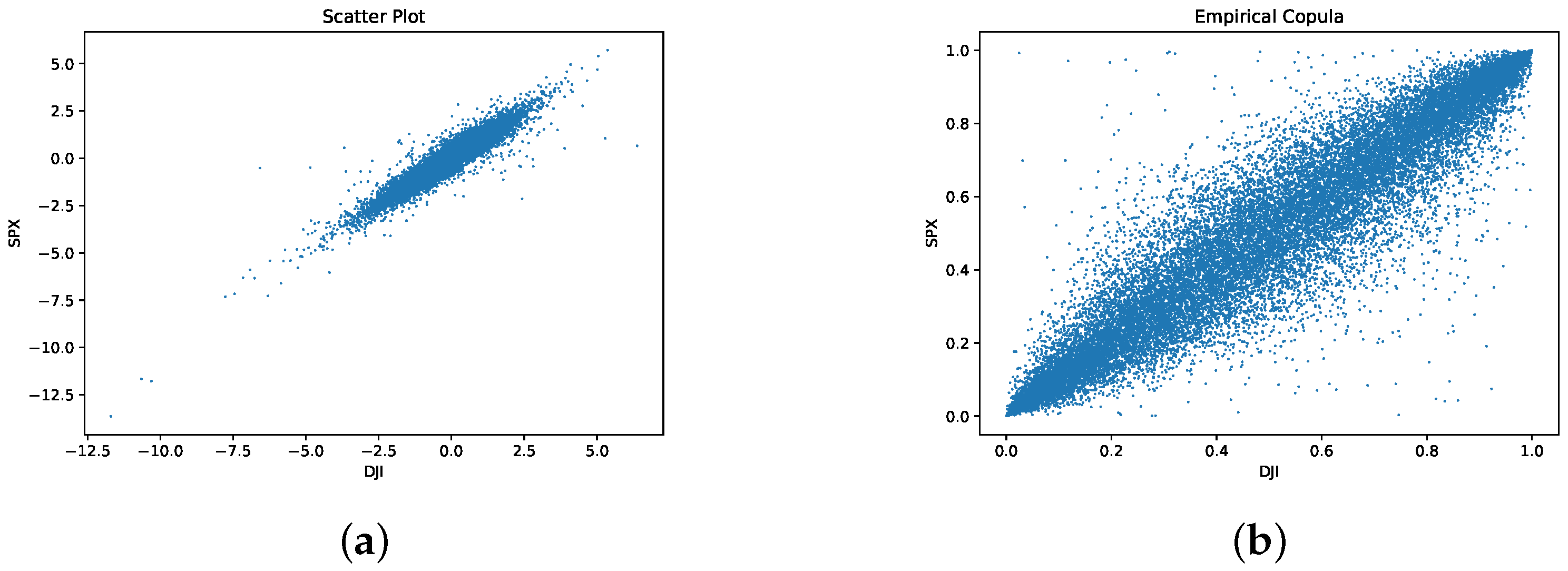
6. Data
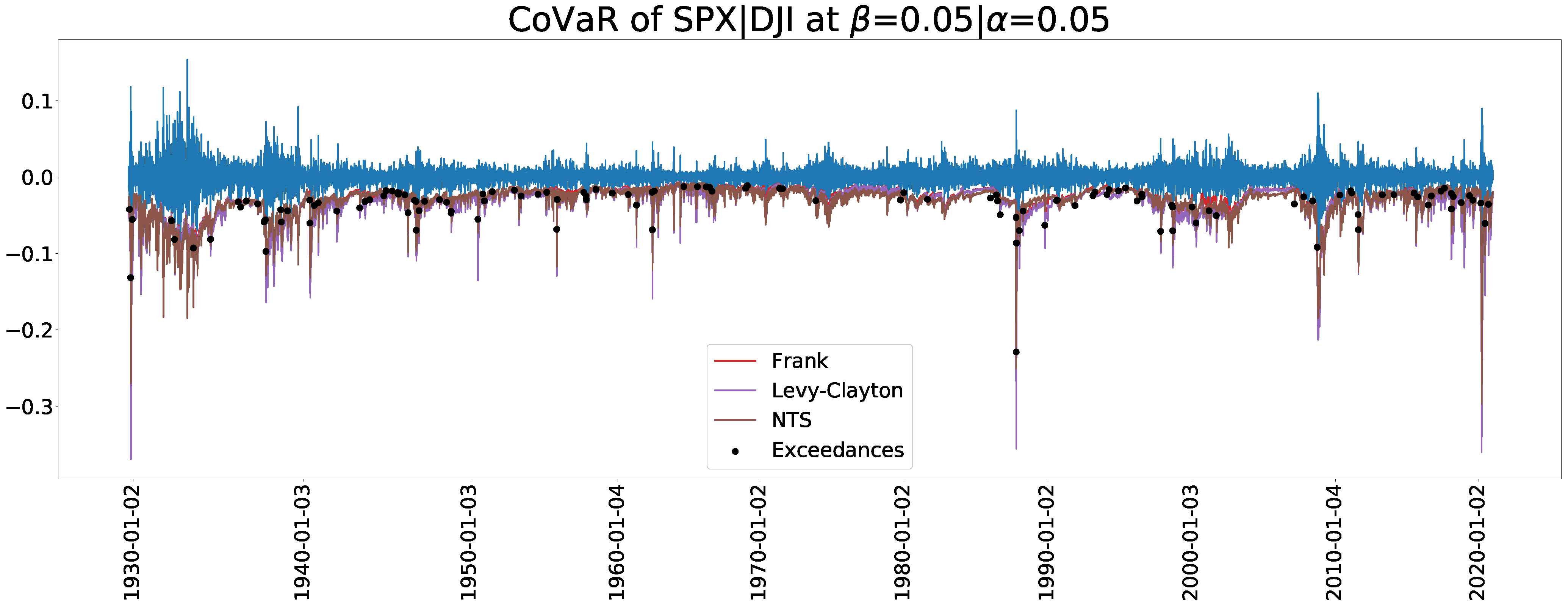
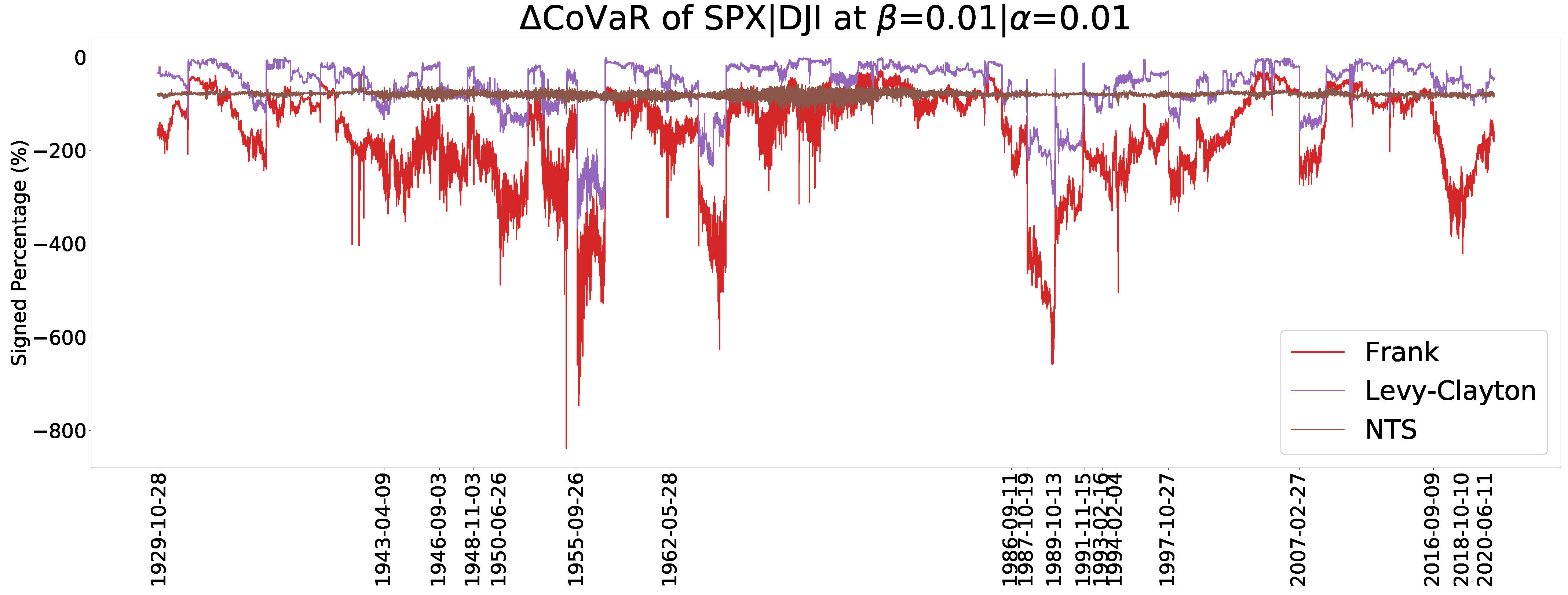
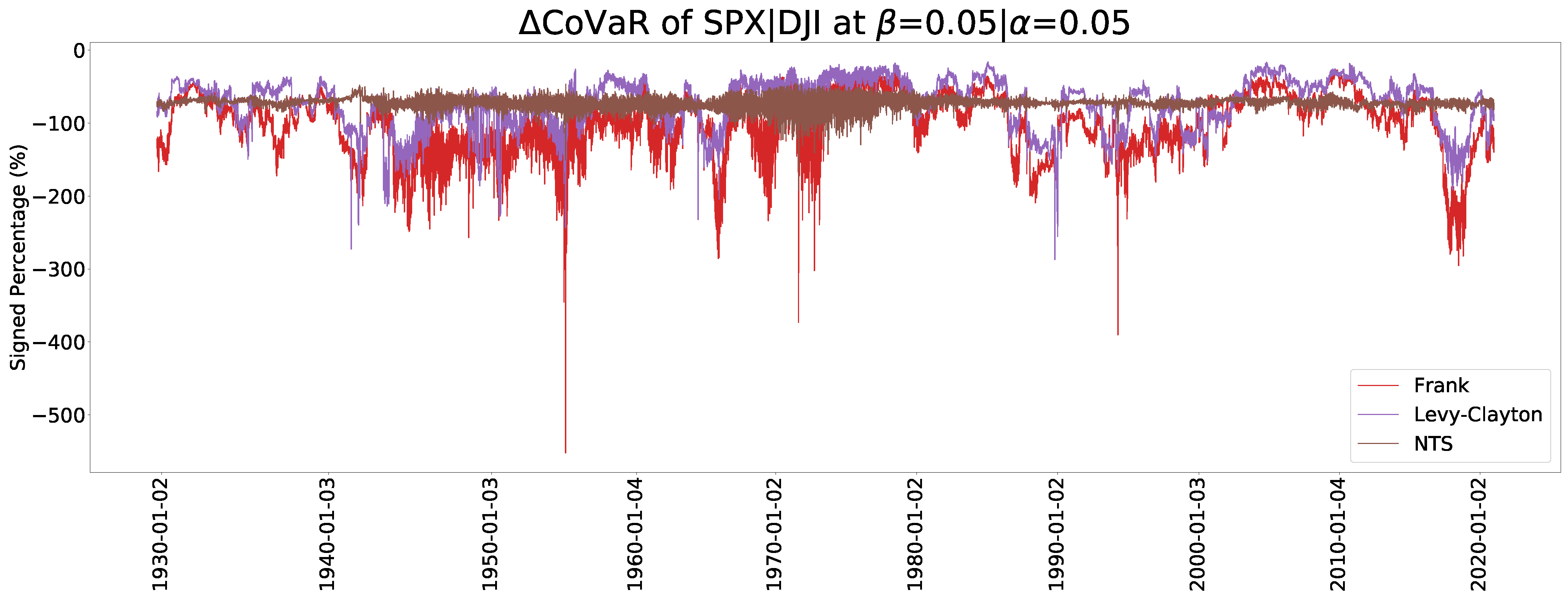
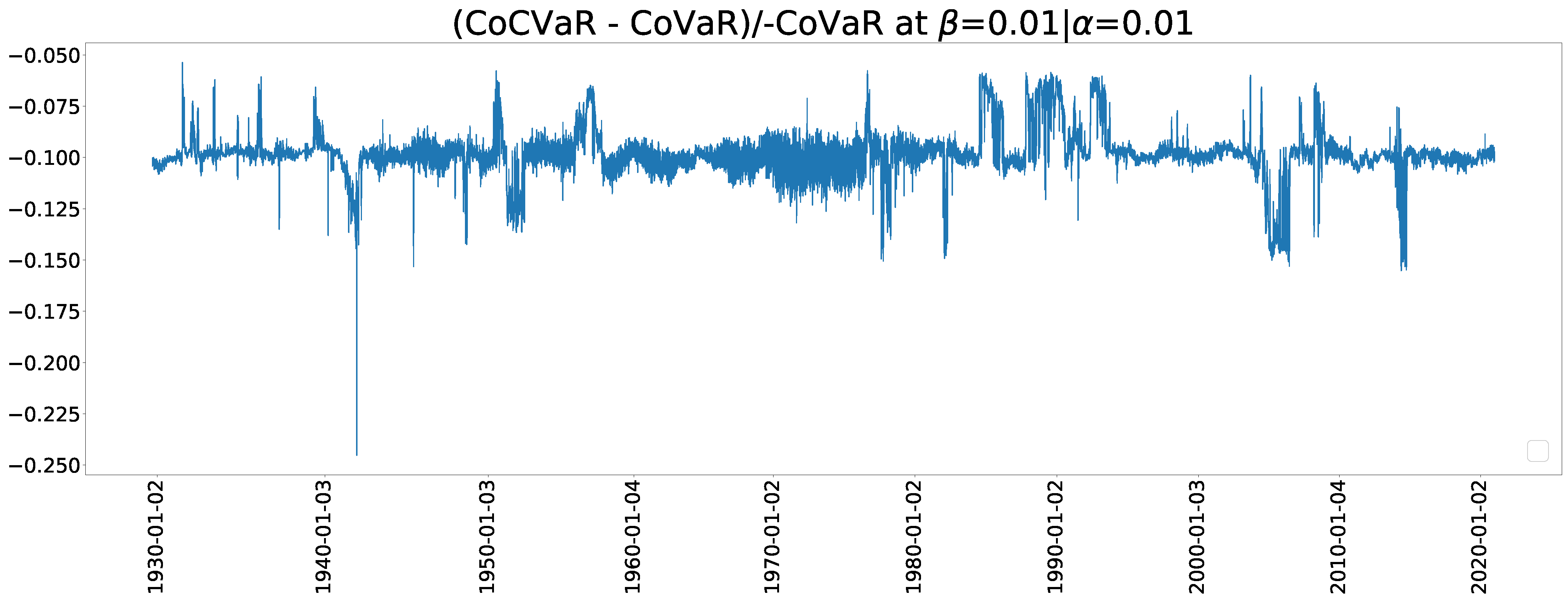
7. Results
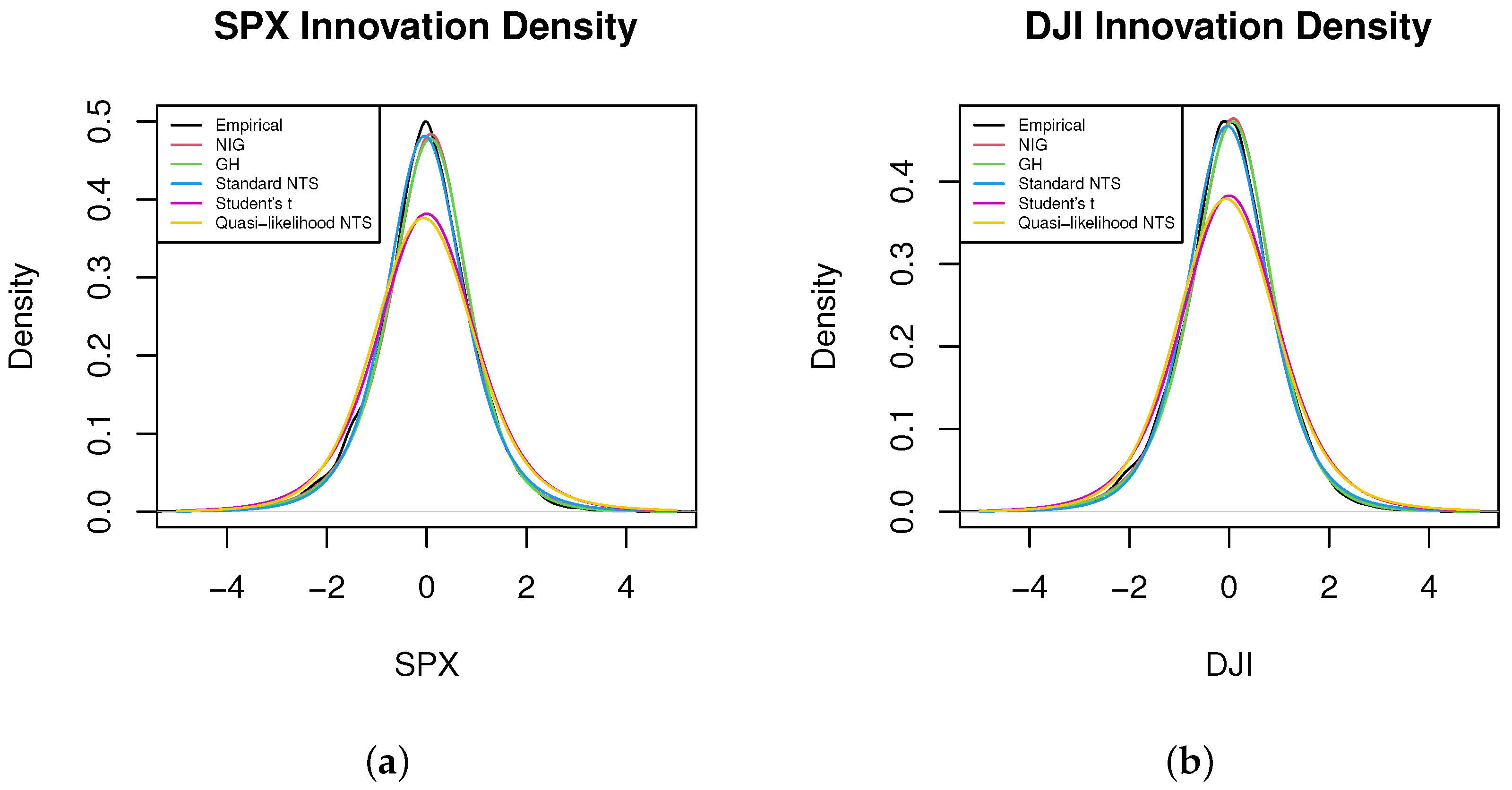
7.1. Test for Copulas
7.2. Backtesting
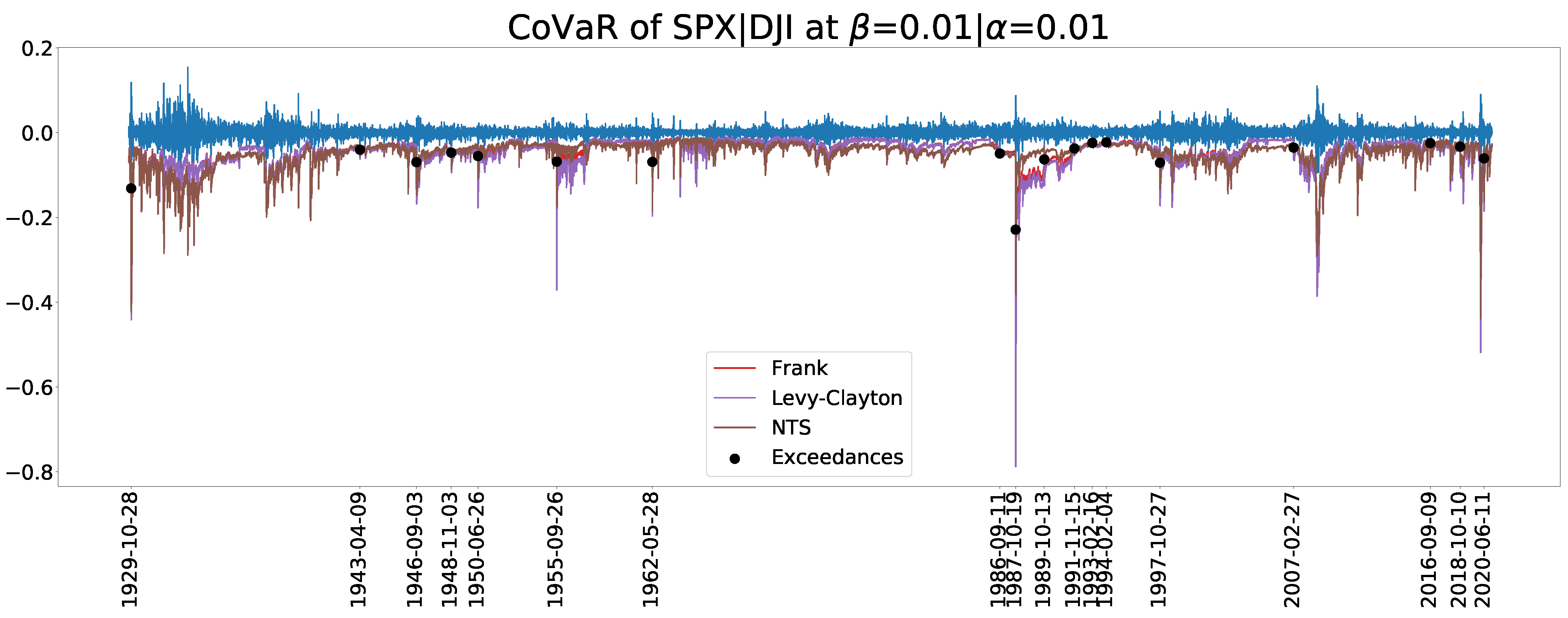
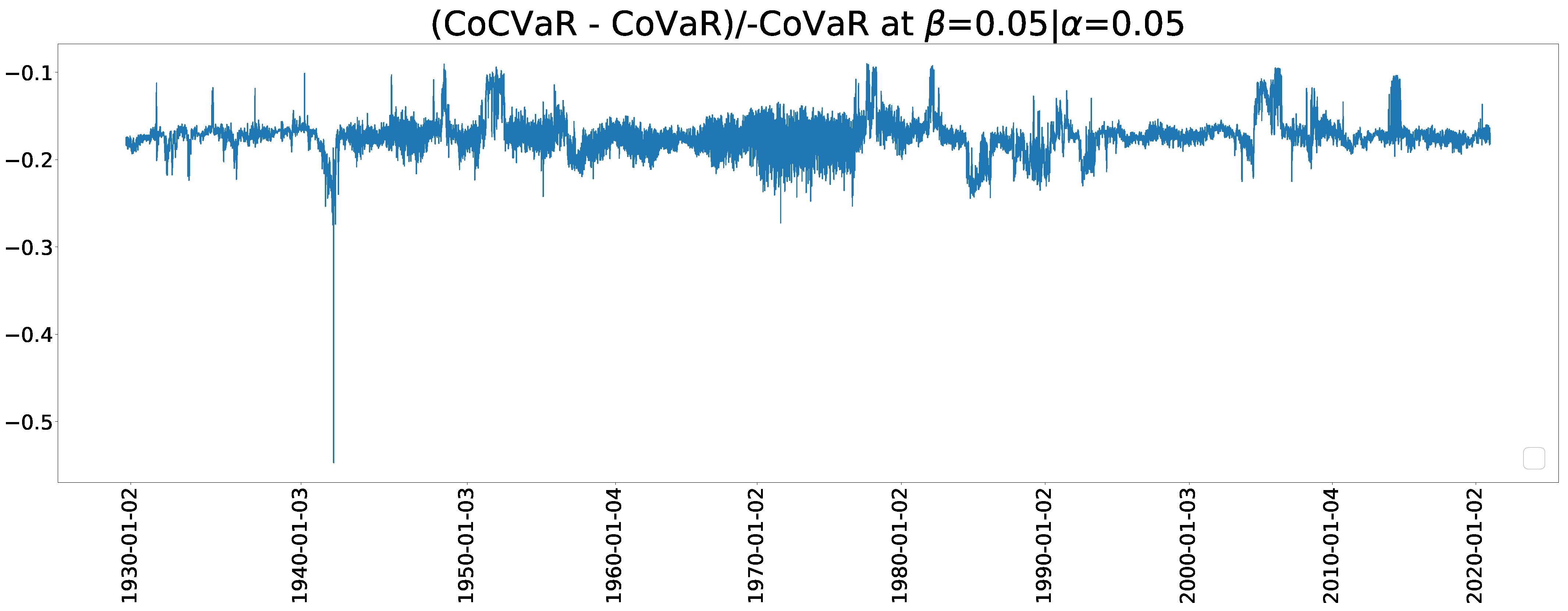
7.3. CoVaR and CoVaR
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
| 1. | https://rdrr.io/github/aaron9011/temStaR-v0.814/ (accessed on 4 June 2021) |
References
- Acharya, Viral V., Lasse H. Pedersen, Thomas Philippon, and Matthew Richardson. 2017. Measuring systemic risk. The Review of Financial Studies 30: 2–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, Viral V., Hyun Song Shin, and Tanju Yorulmazer. 2011. Crisis resolution and bank liquidity. The Review of Financial Studies 24: 2166–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, Tobias, and Markus K. Brunnermeier. 2011. CoVaR. Technical Report. Cambridge: National Bureau of Economic Research. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, Linda, Turan G. Bali, and Yi Tang. 2012. Does systemic risk in the financial sector predict future economic downturns? The Review of Financial Studies 25: 3000–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, Abhinav, Tiantian Li, Tetsuo Kurosaki, and Young Shin Kim. 2016. Foster–hart optimal portfolios. Journal of Banking & Finance 68: 117–30. [Google Scholar]
- Barndorff-Nielsen, Ole E. 1997. Normal inverse gaussian distributions and stochastic volatility modelling. Scandinavian Journal of Statistics 24: 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barndorff-Nielsen, Ole Eiler, and Sergei Z. Levendorskii. 2001. Feller processes of normal inverse gaussian type. Quantitative Finance 1: 318–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barndorff-Nielsen, Ole E., and Neil Shephard. 2001. Normal Modified Stable Processes. Oxford: Citeseer. [Google Scholar]
- Basel Committee on Banking Supervision. 2009. Principles for Sound Stress Testing Practices and Supervision. Available online: https://www.bis.org/publ/bcbs155.htm (accessed on 4 June 2021).
- Bernardi, Mauro, Fabrizio Durante, and Piotr Jaworski. 2017. Covar of families of copulas. Statistics & Probability Letters 120: 8–17. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, Michele Leonardo, and Alberto Maria Sorrentino. 2020. Measuring covar: An empirical comparison. Computational Economics 55: 511–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braiek, Sana, Rihab Bedoui, and Lotfi Belkacem. 2020. Islamic portfolio optimization under systemic risk: Vine copula-covar based model. International Journal of Finance & Economics. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownlees, Christian, and Robert F. Engle. 2017. Srisk: A conditional capital shortfall measure of systemic risk. The Review of Financial Studies 30: 48–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerutti, Eugenio, Stijn Claessens, and Patrick McGuire. 2012. Systemic Risks in Global Banking: What Available Data Can Tell Us and What More Data Are Needed? Technical Report. Cambridge: National Bureau of Economic Research. [Google Scholar]
- Chollete, Lorán, Andréas Heinen, and Alfonso Valdesogo. 2009. Modeling international financial returns with a multivariate regime-switching copula. Journal of Financial Econometrics 7: 437–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, Joel E., Richard A. Davis, and Gennady Samorodnitsky. 2020. Heavy-tailed distributions, correlations, kurtosis and taylor’s law of fluctuation scaling. Proceedings of the Royal Society A 476: 20200610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danielsson, Jon, Bjørn N. Jorgensen, Sarma Mandira, Gennady Samorodnitsky, and Casper G. De Vries. 2005. Subadditivity Re-Examined: The Case for Value-at-Risk. Technical Report. Ithaca: Cornell University, Operations Research and Industrial Engineering. [Google Scholar]
- De Luca, Giovanni, and Giorgia Rivieccio. 2012. Multivariate tail dependence coefficients for archimedean copulae. In Advanced Statistical Methods for the Analysis of Large Data-Sets. Berlin and Heidelberg: Springer, pp. 287–96. [Google Scholar]
- Delbaen, Freddy, and Walter Schachermayer. 1999. The Fundamental Theorem of Asset Pricing for Unbounded Stochastic Processes. Vienna: SFB Adaptive Information Systems and Modelling in Economics and Management. [Google Scholar]
- Di Bernardino, Elena, Véronique Maume-Deschamps, and Clémentine Prieur. 2013. Estimating a bivariate tail: A copula based approach. Journal of Multivariate Analysis 119: 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Zaichao, and Juan Carlos Escanciano. 2017. Backtesting expected shortfall: Accounting for tail risk. Management Science 63: 940–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eberlein, Ernst, and Dilip B. Madan. 2009. On correlating Lévy processes. Robert H. Smith School Research Paper No. RHS, 6–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eberlein, Ernst, and Fehmi Özkan. 2005. The lévy libor model. Finance and Stochastics 9: 327–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embrechts, Paul, Hansjorg Furrer, and Roger Kaufmann. 2003. Quantifying regulatory capital for operational risk. Derivatives Use, Trading and Regulation 9: 217–33. [Google Scholar]
- Emmer, Susanne, Marie Kratz, and Dirk Tasche. 2015. What is the best risk measure in practice? A comparison of standard measures. Journal of Risk 18: 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forbes, Kristin, and Roberto Rigobon. 2001. Measuring contagion: Conceptual and empirical issues. In International Financial Contagion. Berlin and Heidelberg: Springer, pp. 43–66. [Google Scholar]
- Frahm, Gabriel. 2004. Generalized Elliptical Distributions: Theory and Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität zu Köln, Köln, Germany. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, René, Eric Renault, and David Veredas. 2011. Estimation of stable distributions by indirect inference. Journal of Econometrics 161: 325–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, René, and Georges Tsafack. 2008. Dependence Structure and Extreme Comovements in International Equity and Bond Markets with Portfolio Diversification Effects. Working Paper. Risk Asset Management Research Centre: Available online: http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.1107718 (accessed on 4 June 2021).
- Giglio, Stefano, Bryan Kelly, and Seth Pruitt. 2016. Systemic risk and the macroeconomy: An empirical evaluation. Journal of Financial Economics 119: 457–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardi, Giulio, and A. Tolga Ergün. 2013. Systemic risk measurement: Multivariate garch estimation of covar. Journal of Banking & Finance 37: 3169–80. [Google Scholar]
- Härdle, Wolfgang K., Ostap Okhrin, and Weining Wang. 2012. HMM in Dynamic HAC Models. Available online: http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2894223 (accessed on 4 June 2021).
- Heffernan, Janet E. 2000. A directory of coefficients of tail dependence. Extremes 3: 279–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Wei-Qiang, and Stanislav P. Uryasev. 2018. The cocvar approach: Systemic risk contribution measurement. Journal of Risk 20: 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaworski, Piotr. 2017. On conditional value at risk (covar) for tail-dependent copulas. Dependence Modeling 5: 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaworski, Piotr, Fabrizio Durante, Wolfgang Karl Hardle, and Tomasz Rychlik. 2010. Copula Theory and Its Applications. Berlin and Heidelberg: Springer, vol. 198. [Google Scholar]
- Kanas, Angelos, and Panagiotis D. Zervopoulos. 2020. Systemic risk-shifting in us commercial banking. Review of Quantitative Finance and Accounting 54: 517–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimalis, Emmanouil N., and Nikos K. Nomikos. 2018. Measuring systemic risk in the european banking sector: A copula covar approach. The European Journal of Finance 24: 944–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Young Shin, Svetlozar T. Rachev, Michele Leonardo Bianchi, Ivan Mitov, and Frank J. Fabozzi. 2011. Time series analysis for financial market meltdowns. Journal of Banking & Finance 35: 1879–91. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Young Shin, and David S. Volkmann. 2013. Normal tempered stable copula. Applied Mathematics Letters 26: 676–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritzman, Mark, Yuanzhen Li, Sebastien Page, and Roberto Rigobon. 2011. Principal components as a measure of systemic risk. The Journal of Portfolio Management 37: 112–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liebscher, Eckhard. 2008. Construction of asymmetric multivariate copulas. Journal of Multivariate analysis 99: 2234–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lien, Donald, Gerui Lim, Li Yang, and Chunyang Zhou. 2013. Dynamic dependence between liquidity and the s&p 500 index futures-cash basis. Journal of Futures Markets 33: 327–42. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Edward M. H., Edward W. Sun, and Min-Teh Yu. 2018. Systemic risk, financial markets, and performance of financial institutions. Annals of Operations Research 262: 579–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, Rand Kwong Yew, Jamie Alcock, Robert Faff, and Timothy Brailsford. 2013. Canonical vine copulas in the context of modern portfolio management: Are they worth it? Journal of Banking & Finance 37: 3085–99. [Google Scholar]
- Low, Rand Kwong Yew, Robert Faff, and Kjersti Aas. 2016. Enhancing mean–variance portfolio selection by modeling distributional asymmetries. Journal of Economics and Business 85: 49–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mainik, Georg, and Eric Schaanning. 2014. On dependence consistency of CoVaR and some other systemic risk measures. Statistics & Risk Modeling 31: 49–77. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, Tilo, and Gennady Samorodnitsky. 2013. Multivariate tail estimation with application to analysis of covar. Astin Bulletin 43: 245–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pourkhanali, Armin, Jong-Min Kim, Laleh Tafakori, and Farzad Alavi Fard. 2016. Measuring systemic risk using vine-copula. Economic Modelling 53: 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritsker, Matt. 2001. The channels for financial contagion. In International Financial Contagion. Berlin and Heidelberg: Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Reboredo, Juan C., and Andrea Ugolini. 2015. Systemic risk in european sovereign debt markets: A covar-copula approach. Journal of International Money and Finance 51: 214–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rémillard, Bruno, Nicolas Papageorgiou, and Frédéric Soustra. 2012. Copula-based semiparametric models for multivariate time series. Journal of Multivariate Analysis 110: 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rivera-Castro, Miguel A., Andrea Ugolini, and Juan Arismendi Zambrano. 2018. Tail systemic risk and contagion: Evidence from the brazilian and latin america banking network. Emerging Markets Review 35: 164–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Ken-Iti. 1999. Lévy Processes and Infinitely Divisible Distributions. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Schoutens, Wim. 2003. Lévy Processes in Finance: Pricing Financial Derivatives. Leuven: KU LEUVEN. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segoviano Basurto, Miguel, and Charles Goodhart. 2009. Banking Stability Measures. IMF Working Paper. Washington: International Monetary Fund, pp. 1–54. [Google Scholar]
- Shiryaev, Albert N. 1999. Essentials of Stochastic Finance: Facts, Models, Theory. Singapore: World Scientific, vol. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Sklar, M. 1959. Fonctions de repartition an dimensions et leurs marges. Publications de L Institut de Statistique de L Universite de Paris. 8: 229–31. [Google Scholar]
- Smaga, Pawel. 2014. The Concept of Systemic Risk. London: Systemic Risk Centre, London School of Economics and Political Science. [Google Scholar]
- Tankov, Peter. 2016. Lévy copulas: Review of recent results. In The Fascination of Probability, Statistics and Their Applications. Edited by Mark Podolskij, Robert Stelzer, Steen Thorbjørnsen and Almut E. D. Veraart. Cham: Springer, pp. 127–51. [Google Scholar]
- Targino, Rodrigo S., Gareth W. Peters, and Pavel V. Shevchenko. 2015. Sequential Monte Carlo samplers for capital allocation under copula-dependent risk models. Insurance: Mathematics and Economics 61: 206–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tobias, Adrian, and Markus K. Brunnermeier. 2016. CoVaR. The American Economic Review 106: 1705. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Lu, Jason Z. Ma, and Shigeyuki Hamori. 2018. Dependence structures and systemic risk of government securities markets in central and eastern europe: A covar-copula approach. Sustainability 10: 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Jianlin. 2015. Systemic Risk Measure: CoVaR and Copula. Master’s Thesis, Humboldt University at Berlin, Berlin. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Jin, and Dietmar Maringer. 2010. Asset Pair-Copula Selection with Downside Risk Minimization. Technical Report. Available online: https://ideas.repec.org/p/com/wpaper/037.html (accessed on 4 June 2021).




| Family | ||
|---|---|---|
| Clayton | ||
| Frank | ||
| Gumbel | ||
| Lévy-Clayton |
| Copulas | Clayton | L-C | Gumbel | Frank | NTS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1604 | 0.2356 | 0.1184 | 0.0169 | 0.0091 | |
| 0.3722 | 0.5551 | 0.3610 | 0.2368 | 0.0954 | |
| 1834.7888 | 1131.3683 | 1255.0111 | 35.1158 | 4.6477 | |
| MAE | 0.0968 | 0.0750 | 0.0700 | 0.0069 | 0.0039 |
| MSE | 0.1069 | 0.1003 | 0.0778 | 0.0081 | 0.0041 |
| Quantile | Clayton | Frank | Gumbel | L-C | NTS | Expected |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| = 0.01, = 0.01 | 47 | 55 | 61 | 47 | 18 | 2.3943 |
| = 0.05, = 0.05 | 163 | 156 | 333 | 110 | 132 | 59.8575 |
| = 0.01, = 0.50 | 1679 | 1152 | 4264 | 190 | 243 | 119.715 |
| = 0.05, = 0.50 | 4105 | 1416 | 5207 | 731 | 898 | 598.575 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Djurić, P.M.; Kim, Y.S.; Rachev, S.T.; Glimm, J. Systemic Risk Modeling with Lévy Copulas. J. Risk Financial Manag. 2021, 14, 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm14060251
Liu Y, Djurić PM, Kim YS, Rachev ST, Glimm J. Systemic Risk Modeling with Lévy Copulas. Journal of Risk and Financial Management. 2021; 14(6):251. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm14060251
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yuhao, Petar M. Djurić, Young Shin Kim, Svetlozar T. Rachev, and James Glimm. 2021. "Systemic Risk Modeling with Lévy Copulas" Journal of Risk and Financial Management 14, no. 6: 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm14060251
APA StyleLiu, Y., Djurić, P. M., Kim, Y. S., Rachev, S. T., & Glimm, J. (2021). Systemic Risk Modeling with Lévy Copulas. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 14(6), 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm14060251









