Model of Optimizing Correspondence Risk-Return Marketing for Short-Term Lending
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Related Works
2.2. Research Methodology
3. Results
3.1. Expected Return Analysis and Triad “Risk–Return-Marketing” Optimization
- (1)
- The increasing of segment A profitability;
- (2)
- Management risk improvement in segment D;
- (3)
- The improving management risk in segment C;
- (4)
- The increasing of segment B profitability.
3.2. The CLV Based Optimization Based for Repeated Loans
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anandanatarajan, K. 2019. Customer Reationship Management–A Strategic Tool for Marketing. IJRAR 6. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3676830 (accessed on 17 August 2022).
- Babenko, Vitalina, Andriy Panchyshyn, Larysa Zomchak, Maryna Nehrey, Zoriana Artym-Drohomyretska, and Taras Lahotskyi. 2021. Classical machine learning methods in economics research: Macro and micro level example. WSEAS Transactions on Business and Economics 18: 209–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bédard-Pagé, Guillaume. 2019. Non-Bank Financial Intermediation in Canada: An Update. Bank of Canada Staff Discussion Paper No. 2. Ottawa: Bank of Canada. [Google Scholar]
- Caputo, Francesco, Armando Papa, Valentina Cillo, and Manlio Del Giudice. 2019. Technology readiness for education 4.0: Barriers and opportunities in the digital world. In Opening Up Education for Inclusivity Across Digital Economies and Societies. Hershey: IGI Global, pp. 277–96. [Google Scholar]
- Chappell, Gerald, Holger Harreis, Andras Havas, Andrea Nuzzo, Theo Pepanides, and Kayvaun Rowshankish. 2018. The Lending Revolution: How Digital Credit is Changing Banks from the Inside. McKinsey & Company, August. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/risk/our-insights/the-lending-revolution-how-digitalcredit-is-changing-banks-from-the-inside (accessed on 10 August 2022).
- Chernenko, Sergey, Isil Erel, and Robert Prilmeier. 2019. Nonbank lending. Dice Center Working Paper 2018-13. National Bureau of Economic Research. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3220527 (accessed on 22 August 2022).
- d’Avernas, Adrien, Quentin Vandeweyer, and Matthieu Darracq-Pariès. 2020. The growth of non-bank finance and new monetary policy tools. Research Bulletin 69: 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Eichholtz, Piet, Nagihan Mimiroglu, Steven Ongena, and Erkan Yönder. 2020. Banks, Non-Banks, and the Incorporation of Local Information in CMBS Loan Pricing. Swiss Finance Institute Research Paper No. 19–58. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3481034 (accessed on 2 September 2022).
- Fleckenstein, Quirin, Manasa Gopal, German Gutierrez Gallardo, and Sebastian Hillenbrand. 2020. Nonbank Lending and Credit Cyclicality. New York: NYU Stern School of Business. [Google Scholar]
- Fogoros, Teodora Elena, Mihaela Maftei, Stelian Mircea Olaru, and Gabriela Elena Bitan. 2020. From Traditional to Digital: A Study on Business Models in The Context of Digitalization. Paper presented at the 3rd International Conference on Economics and Social Sciences, Bucharest, Romania, October 15–16; pp. 749–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guryanova, Lidiya, Roman Yatsenko, Nadija Dubrovina, and Vitalina Babenko. 2020. Machine Learning Methods and Models, Predictive Analytics and Applications. In Paper presented at the Machine Learning Methods and Models, Predictive Analytics and Applications 2020: Proceedings of the Workshop on the XII International Scientific Practical Conference Modern Problems of Social and Economic Systems Modelling (MPSESM-W 2020), Kharkiv, Ukraine, June 25; vol. 2649, pp. 1–5. Available online: http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2649/ (accessed on 5 September 2022).
- Hacioglu, Umit, ed. 2019. Blockchain Economics and Financial Market Innovation: Financial Innovations in the Digital Age. Belin: Springer Nature. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Joong Ho. 2017. Does Lending by banks and non-banks differ? Evidence from small business financing. Banks & Bank Systems 12: 98–104. [Google Scholar]
- Harvard Business Review Analytic Service. 2019. In the Game: Traditional Financial Institutions Embrace Fintech Disruption. Available online: https://hbr.org/resources/pdfs/comm/mastercard/Fintech.pdf (accessed on 14 July 2022).
- Insider Intelligence. 2022. A look at Nonbank Loans and the Alternative Lending Industry Business Model in 2021. Available online: https://www.businessinsider.com/alternative-lending-nonbank-industry (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- Kaminskyi, Andrii, and Maryna Nehrey. 2021. Clustering approach to analysis of the credit risk and profitability for nonbank lenders. Paper presented at the CEUR Workshop Proceedings, Machine Learning Methods and Models, Predictive Analytics and Applications—13th Workshop on the International Scientific Practical Conference Modern Problems of Social and Economic Systems Modelling, MPSESM-W 2021, Kharkiv, Ukraine, April 9; vol. 2927, pp. 125–36. [Google Scholar]
- Kondova, Galia, and Trishit Bandyopadhyay. 2019. The Impact of Non-bank Lending on Bank Efficiency: Data Envelopment Analysis of European Banks. International Journal of Trade, Economics and Finance 10: 108–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Mihye. 2018. Non-Bank Lending to Firms: Evidence from Korean Firm-Level Data. The Journal of Industrial Distribution & Business 9: 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Monil, Patel, Patel Darshan, Rana Jecky, Chauhan Vimarsh, and B. R. Bhatt. 2020. Customer Segmentation Using Machine Learning. International Journal for Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology (IJRASET) 8: 2104–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opare, Edwin Ayisi, and Kwangjo Kim. 2020. A compendium of practices for central bank digital currencies for multinational financial infrastructures. IEEE Access 8: 110810–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patalano, Robert, and Caroline Roulet. 2020. Structural Developments in Global Financial Intermediation: The Rise of Debt and Non-Bank Credit Intermediation. OECD Working Papers on Finance, Insurance and Private Pensions, No. 44. Paris: OECD Publishing. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pobric, Amira. 2014. Measuring customer profitability: The applicability of different concepts in practice. Ekonomika Preduzeća 62: 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rateiwa, Ronald, and Meshach J. Aziakpono. 2017. Non-bank financial institutions and economic growth: Evidence from Africa’s three largest economies. South African Journal of Economic and Management Sciences 20: 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, Wendell R. 1995. Product differentiation and market segmentation as alternative marketing strategies. Marketing Management 4: 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soukal, Ivan, Eva Hamplová, and Jiri Haviger. 2021. Effectiveness of Regulation of Educational Requirements for Non-Bank Credit Providers in Czech Republic. Social Sciences 10: 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storbacka, Kaj. 1997. Segmentation based on customer profitability—Retrospective analysis of retail bank customer bases. Journal of Marketing Management 13: 479–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Lili. 2019. The Roles of Information Technology in Customer Relationship Performance, Employee User Satisfaction, Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction. Oxford: Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Vasileva, Valya. 2019. Development of Consumer Lending by Non-Bank Credit Companies in Bulgaria. Economic Archive 1: 65–76. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Jinlei, Yuanjun Zhao, Chunjia Han, Yanghui Liu, and Mu Yang. 2021. Big data, big challenges: Risk management of financial market in the digital economy. Journal of Enterprise Information Management 35: 1288–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
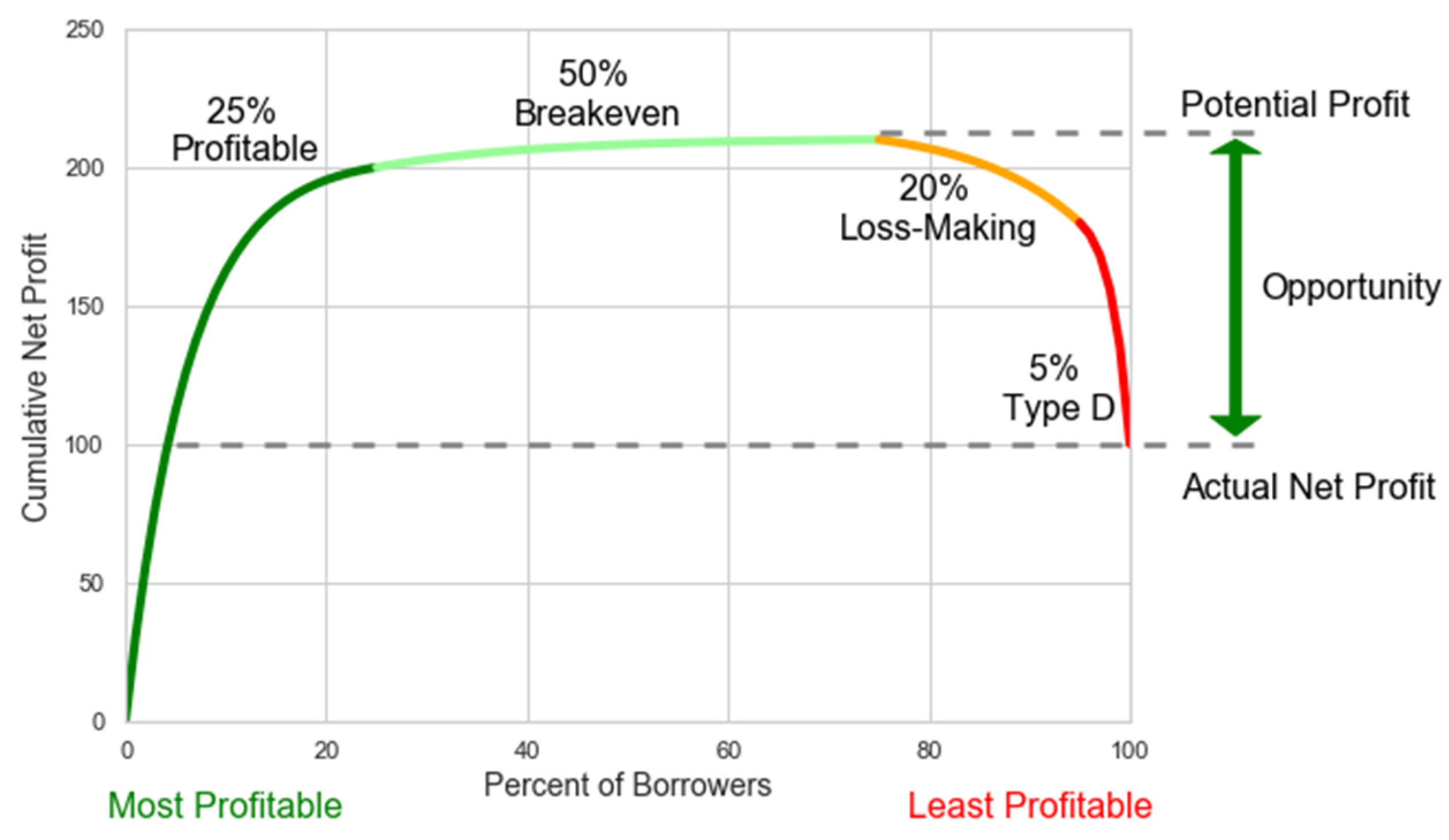
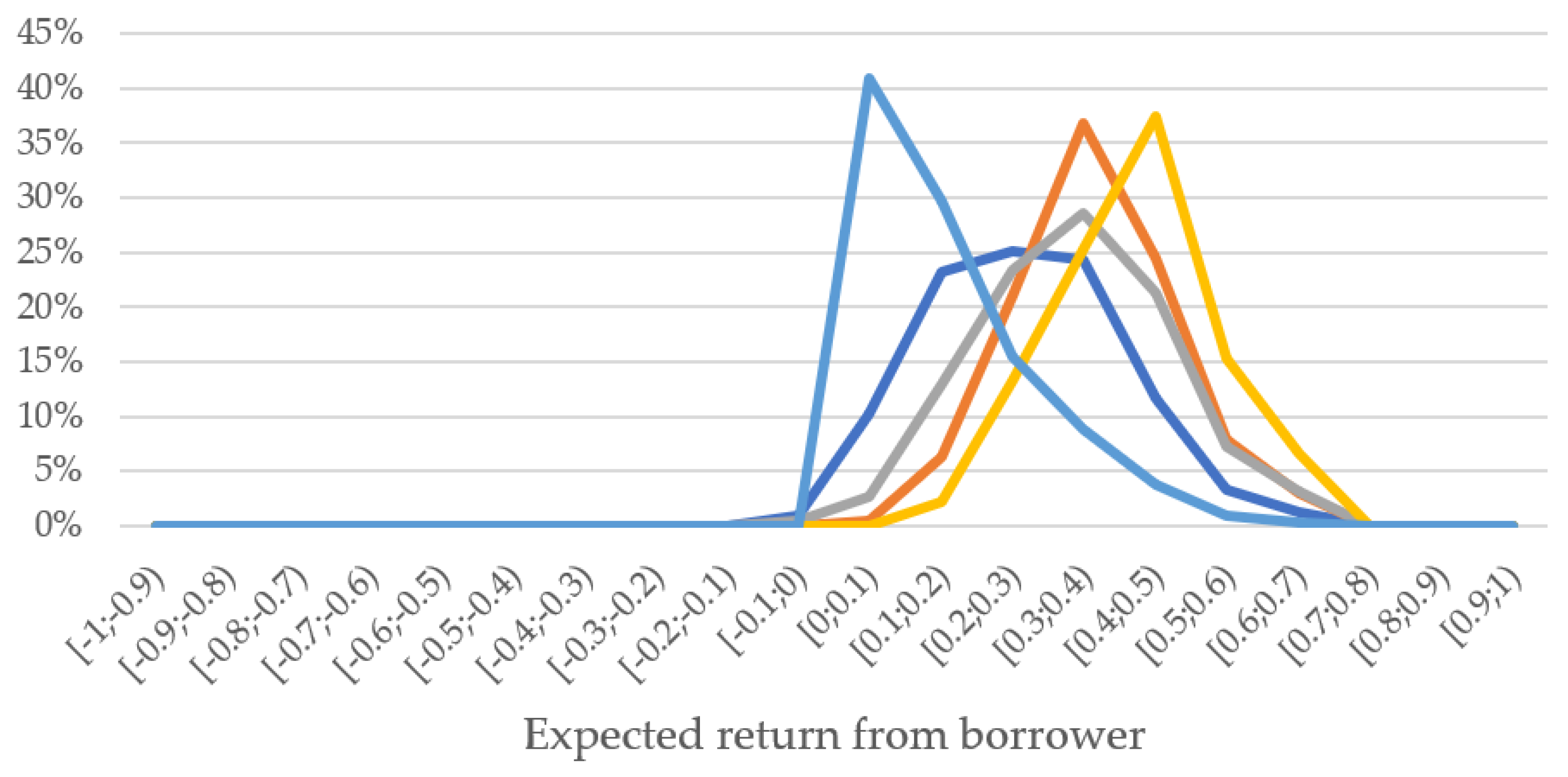
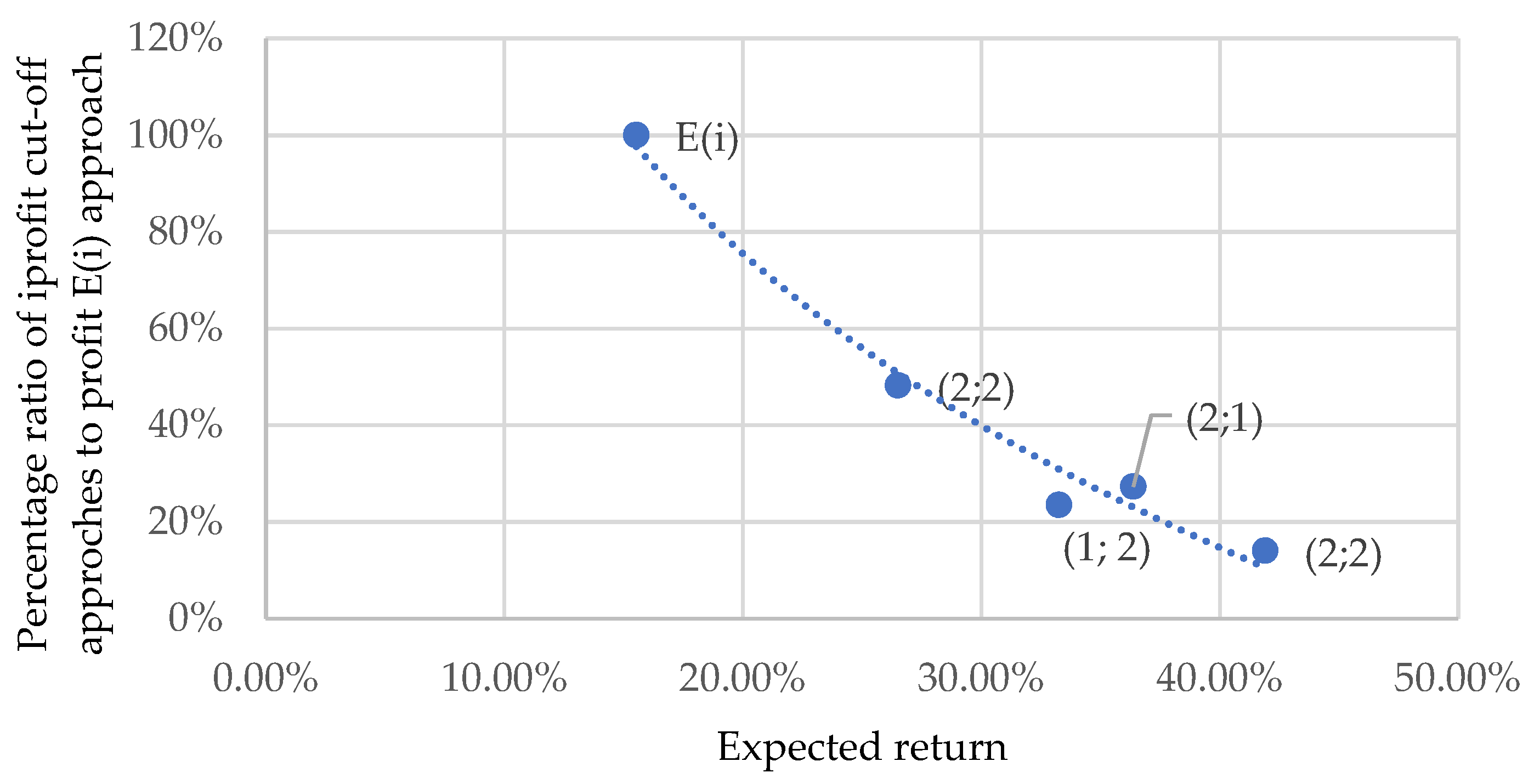


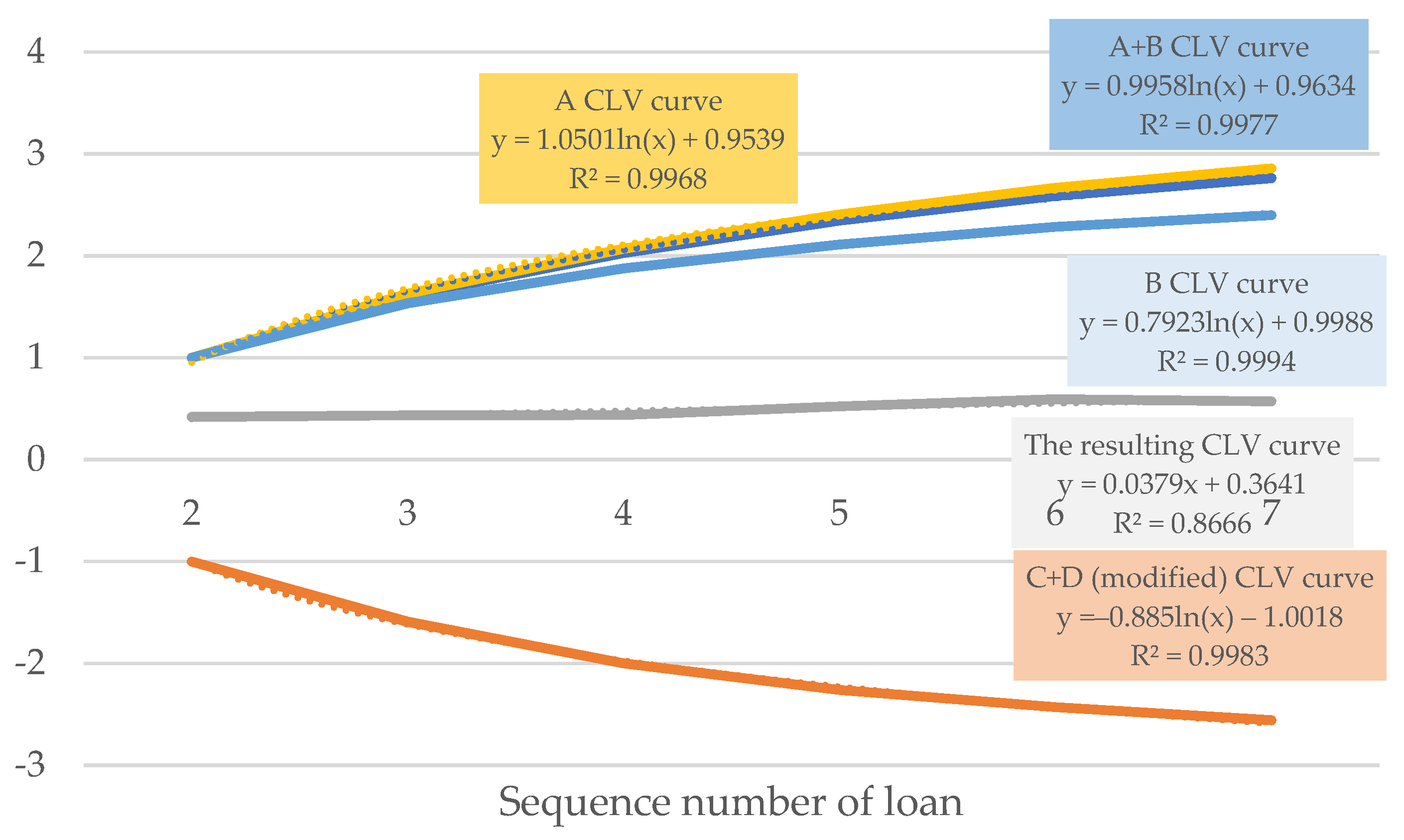
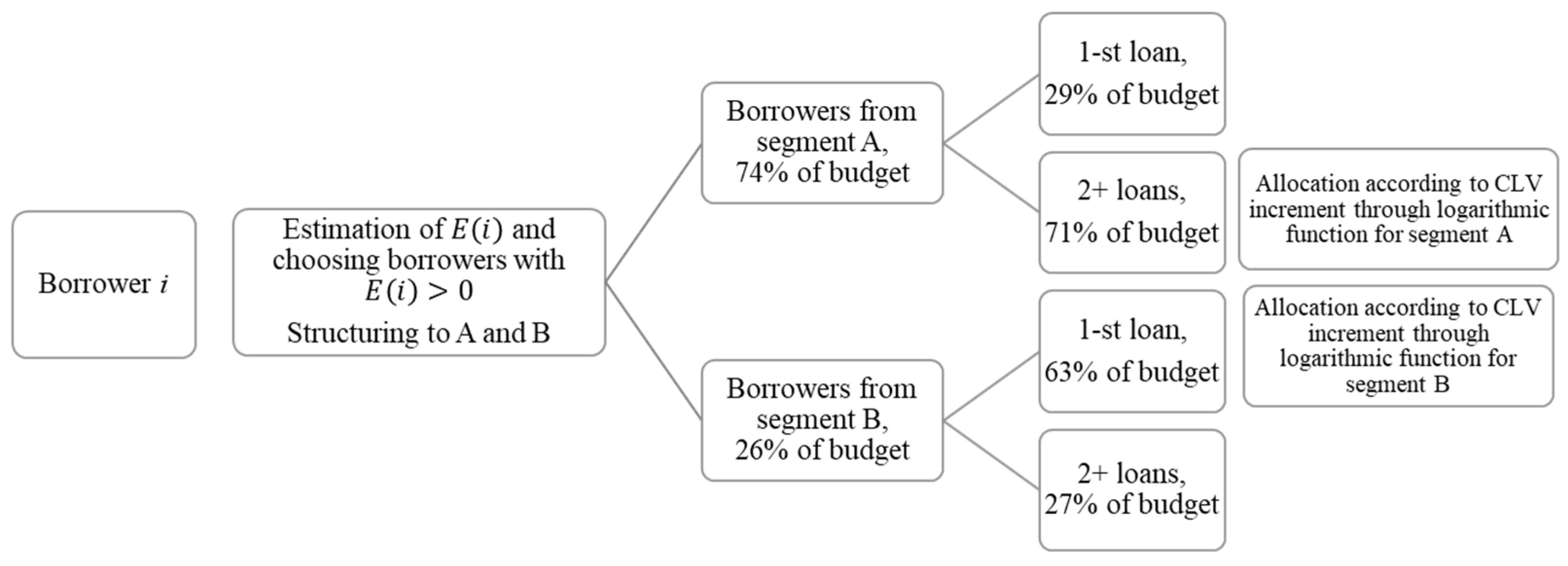
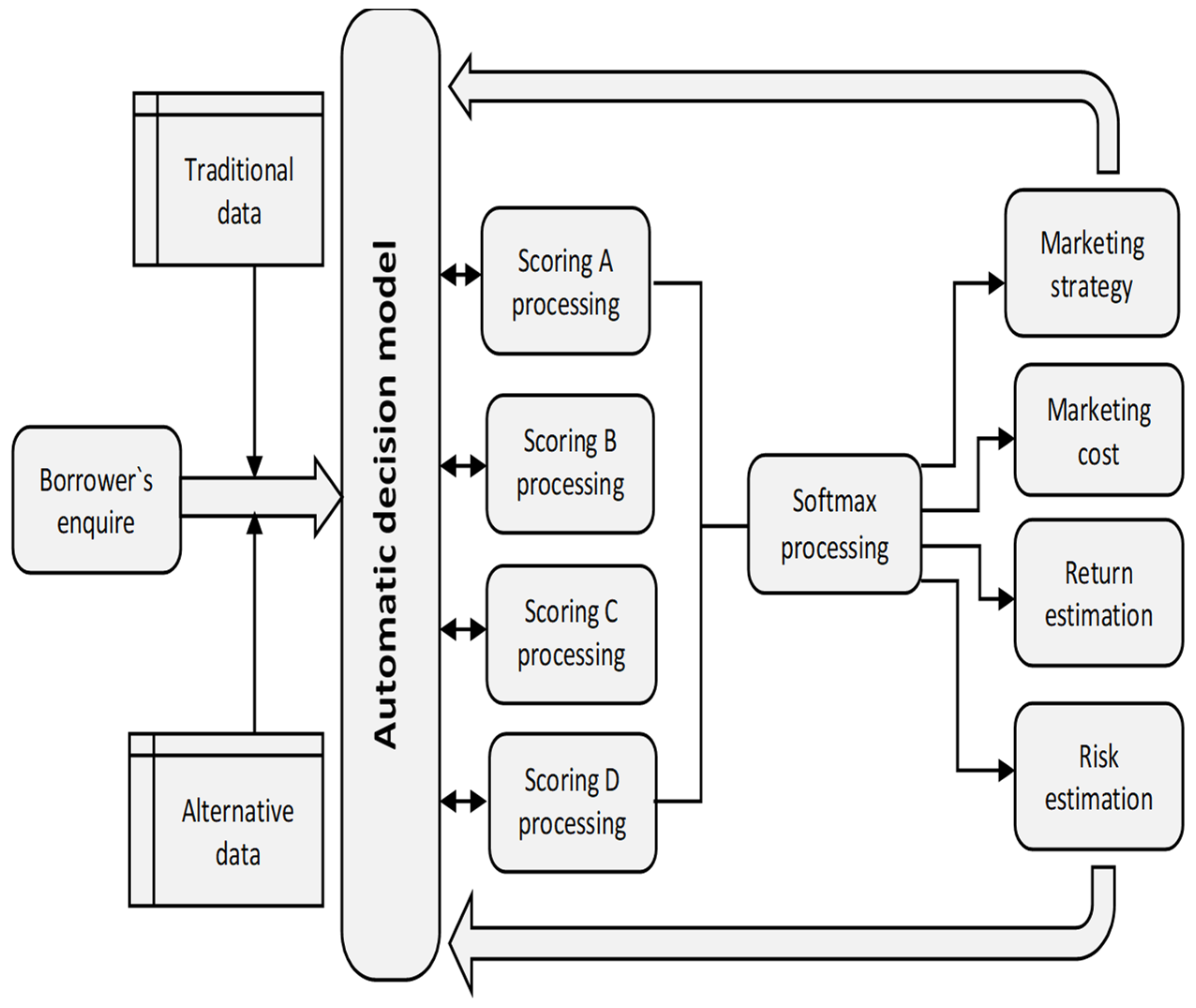
| Segment | Description |
|---|---|
| A | A total of 20% of the borrowers make the most money. Research shows that in the PDL segment, 20% of the income can be 200–400% of the total income of the lender during this period. |
| B | Borrowers who pay all necessary payments fully and on time, but are not included in A. |
| C | Borrowers pay some payments but do not generate profit. Therefore, they provide only part of the necessary payments, but they have paid some payments (payments more than 0). |
| D | First payment default (any payments). Arrears are 100%. |
| Segment | Risk | Return | Marketing Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Higher than average | Very high | Focus on repeater loans. The increasing amount of loans. |
| B | Lower than average | Low | The increasing amount of loans. Discounts for repeater loans. |
| C | Higher than average | Negative | Minimize loan amount. |
| D | Very high | −100% | - |
| Scoring Characteristics (Traditional) | Information Values | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | |
| Credit-bureau rating | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.12 |
| Borrower’s age | 0.13 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.03 |
| The specified goal of loan inquiry (including unspecified goal case) | 0.41 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.02 |
| Loan in order from this lender | 0.67 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.03 |
| Required term of the loan | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.24 |
| Existence of a promotional code | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.02 |
| Loan amount | 0.44 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.04 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaminskyi, A.; Nehrey, M.; Babenko, V.; Zimon, G. Model of Optimizing Correspondence Risk-Return Marketing for Short-Term Lending. J. Risk Financial Manag. 2022, 15, 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm15120583
Kaminskyi A, Nehrey M, Babenko V, Zimon G. Model of Optimizing Correspondence Risk-Return Marketing for Short-Term Lending. Journal of Risk and Financial Management. 2022; 15(12):583. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm15120583
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaminskyi, Andrii, Maryna Nehrey, Vitalina Babenko, and Grzegorz Zimon. 2022. "Model of Optimizing Correspondence Risk-Return Marketing for Short-Term Lending" Journal of Risk and Financial Management 15, no. 12: 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm15120583
APA StyleKaminskyi, A., Nehrey, M., Babenko, V., & Zimon, G. (2022). Model of Optimizing Correspondence Risk-Return Marketing for Short-Term Lending. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 15(12), 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm15120583







