Fintech and Financial Health in Vietnam during the COVID-19 Pandemic: In-Depth Descriptive Analysis
Abstract
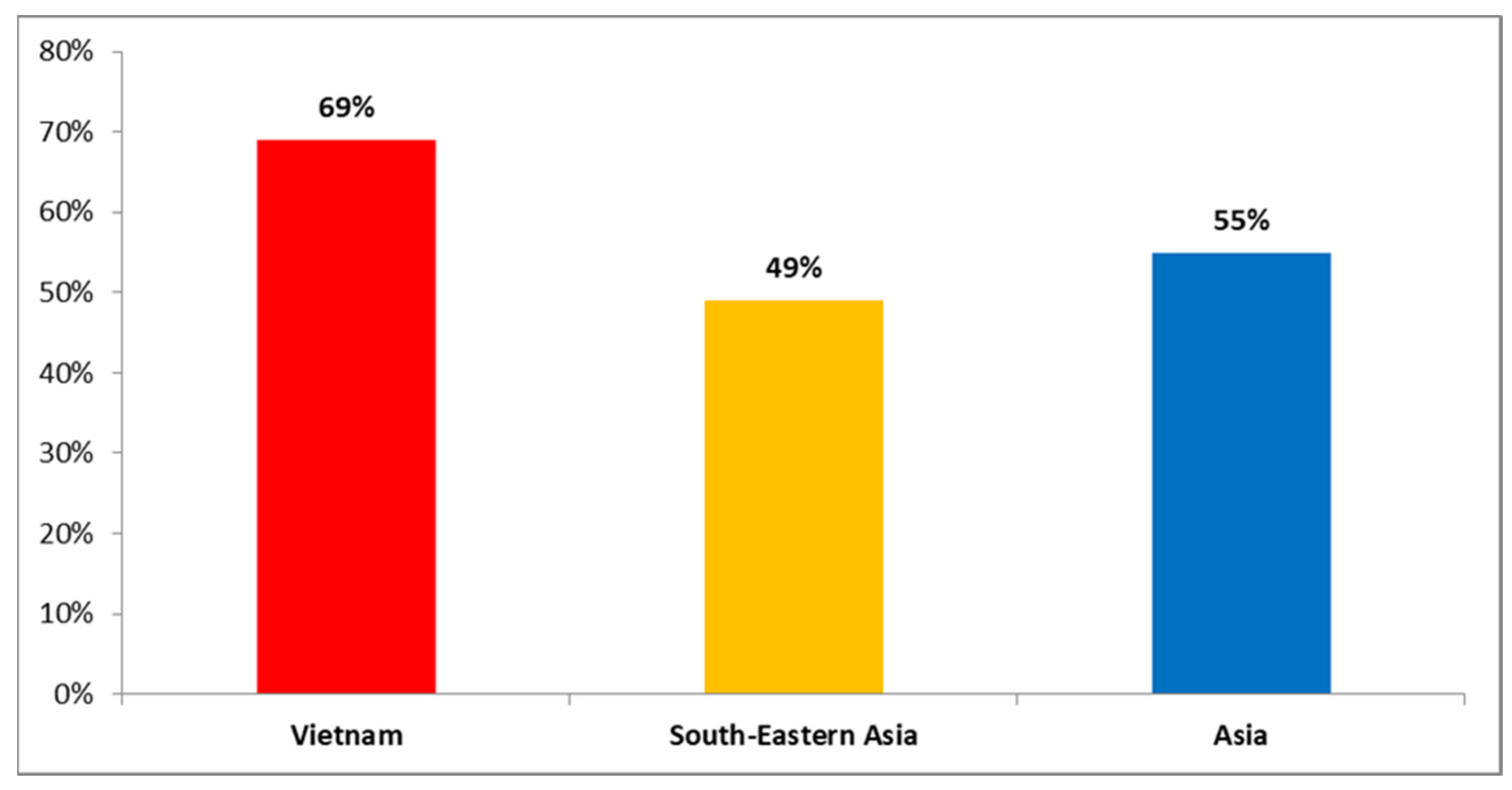
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review, Hypotheses, and Research Framework
Research Hypotheses
3. Research Methodology
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions and Recommendation
6. Limitation and Suggestions for Future Studies
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ajzen, Icek. 1993. Attitude Theory and the Attitude-Behavior Relation. In New Direction in Attitute Measurement. Edited by Dagmar Krebs and Peter Schmidt. Berlin: Walter de Gruyter, pp. 41–57. [Google Scholar]
- Anand, Swati, Kushendra Mishra, Verma Verma, and Taruna Taruna. 2020. Financial Literacy as a Mediator of Personal Financial Health during COVID-19: A Structural Equation Modelling Approach. Emerald Open Research 2: 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arner, Douglas, Janos Barberis, and Ross Buckley. 2015. The Evolution of Fintech: A New Post-Crisis Paradigm? University of Hong Kong Faculty of Law Research Paper No. 2015/047. Hong Kong: University of Hong Kong Faculty. [Google Scholar]
- Avornyo, Philip, Jiaming Fang, Ransford Okoe Odai, and Joshua Ben Vondee. 2019. Factors Affecting Continuous Intention of Mobile Banking in Tema and Kumasi. International Journal of Business and Science 10: 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barefoot, Jo Ann. 2020. Digitizing Finance: Fintech as a Solution for Consumer Financial Health and Inclusion. M-RCBG Associate Working Paper Series No. 149. Cambridge, UK: Harvard Kennedy School. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, Thorsten. 2020. Fintech and Financial Inclusion: Opportunities and Pitfalls. ADBI Working Paper Series No. 1165. Available online: https://www.adb.org/publications/fintech-financial-inclusion-opportunities-pitfalls (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- Bisht, Shailendra Singh, and Vishal Mishra. 2016. ICT-driven Financial Inclusion Initiatives for Urban Poor in a Developing Economy: Implication for Public Policies. Behavior & Information Technology 35: 817–32. [Google Scholar]
- Bongomin, George Okello Candiya, and Joseph Mpeera Ntayi. 2020. Mobile Money Adoption and Usage and Financial Inclusion: Mediating Effect of Digital Consumer Protection. In Digital Policy, Regulation and Governance. Bingley: Emerald Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Bruhn, Miriam, and Inessa Love. 2014. The Real Impact of Improved Access to Finance: Evidence from Mexico. Journal of Finance 69: 1347–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Yu-Hui, and Stuart Barnes. 2007. Initial Trust and Online Buyer Behavior. Industrial Management & Data Systems 107: 21–36. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Edwin T. C., David Y. C. Lam, and Andy C. L. Yeung. 2006. Adoption of Internet Banking: An Empirical Study in Hong Kong. Decision Support Systems 42: 1558–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chong, Alain Yee-Loong, Keng-Boon Ooi, Binshan Lin, and Boon-In Tan. 2010. Online Banking Adoption: An Empirical Analysis. In International Journal of Bank Marketing. Bingely: Emerald Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, Li-Min, Chun-Chu Liu, and Hsiao-Kuang Kao. 2015. The Adoption of Fintech Service: TAM Perspective. International Journal of Management and Administrative Sciences 3: 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- David, Dharish, Sasidaran Gopalan, and Suma Ramachandran. 2020. The Startup Government and Funding Activity in India. ADBI Working Paper Series, No. 1145. Tokyo, Japan: Asian Development Bank Institute. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, Fred D. 1985. A Technology Acceptance Model for Empirically Testing New End-User Information Systems: Theory and Result. Ph.D. thesis, MIT Sloan School of Management, Cambridge, MA, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, Fred D. 1989. Perceived Usefulness, Perceived Ease of Use, and User Acceptance of Information Technology. MIS Quarterly 13: 319–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EY. 2018. ASEAN Fintech Census 2018. Available online: https://www.ey.com/en_sg/financial-services/asean-fintech-census-2018 (accessed on 18 December 2021).
- EY. 2019. Global Fintech Adoption Index 2019. Available online: https://www.ey.com/en_hu/ey-global-fintech-adoption-index (accessed on 18 December 2021).
- Fintech Singapore. 2020. Vietnam Fintech Report 2020. Available online: https://fintechnews.sg/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/Vietnam-Fintech-Report-2020.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Goo, Jayoung James, and Joo-Yeun Heo. 2020. The Impact of the Regulatory Sandbox on the Fintech Industry, with a Discussion on the Relation between Regulatory Sandboxes and Open Innovation. MDPI-Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity 6: 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Government of Ghana. 2020. Digital Financial Services Policies. Available online: https://mofep.gov.gh/sites/default/files/acts/Ghana_DFS_Policy.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Grabner-Krauter, Sonja, and Rita Faullant. 2008. Consumer Acceptance of Internet Banking: The Influence of Internet Trust. International Journal of Bank Marketing 26: 483–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, Hong-Youl, and Helen Perks. 2005. Effects of Consumer Perceptions of Brand Experience on the Web: Brand Familiarity, Satisfaction and Brand Trust. Journal of Consumer Behaviour 4: 438–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Zhongqing, Shuai Ding, Shizheng Li, Luting Chen, and Shanlin Yang. 2019. Adoption Intention of Fintech Services for Bank Users: An Empirical Examination with an Extended Technology Acceptance Model. MDPI-Symmetry 11: 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IFC. 2020. Financial Inclusion: Creating Opportunity through Financial Services in South Asia. Available online: https://www.ifc.org/wps/wcm/connect/1116ecf6-9fdb-415f-ae2f-304a8b9dc8d8/Financial+Inclusion.pdf?MOD=AJPERES&CVID=kkIBXtL (accessed on 15 November 2021).
- Jaruwachirathanakul, Bussakorn, and Dieter Fink. 2005. Internet Banking Adoption Strategies for a Developing Country: The Case of Thailand. Internet Research 15: 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, David G, and Pedro F. Quintana-Ascencio. 2020. A solution to minimum sample size for regressions. PLoS ONE 15: e0229345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, Jihye, Juhee Kim, Hanei Son, and Dae-il Nam. 2020. The Role of Venture Capital Investment in Startups’ Sustainability Growth and Performance: Focusing on Absorptive Capacity and Venture Capitalists’ Reputation. Sustainability 12: 3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Junger, Moritz, and Mark Mietzner. 2020. Banking Goes Digital: The Adoption of Fintech Services in German Households. Finance Research Letters 34: 101260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlan, Dean, Aishwarya Lakshmi Ratan, and Jonathan Zinman. 2014. Savings by and for the Poor: A Research Review and Agenda. Review of Income and Wealth 60: 36–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Kyu, and Bipin Prabhakar. 2002. Initial Trust, Perceived Risk, and the Adoption of Internet Banking. Available online: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.5555/359640.359809 (accessed on 29 October 2021).
- Klapper, Leora, Annamaria Lusardi, and Georgios A. Panos. 2013. Financial Literacy and Its Consequences: Evidence from Russia during the Financial Crisis. Journal of Banking & Finance 37: 3904–23. [Google Scholar]
- Klapper, Leora, Annamaria Lusardi, and Peter Van Oudheusden. 2015. Financial Literacy around the World: Insights from the Standard&Poor’s Ratings Services Global Financial Literacy Survey. Available online: https://gflec.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/11/3313-Finlit_Report_FINAL-5.11.16.pdf?x21285 (accessed on 8 November 2021).
- Korynski, Piotr. 2019. The Contribution of the Fintech Sector to Financial Inclusion and Health: A Review of Opportunities and Challenges. Microfinance Centre. Available online: https://mfc.org.pl/the-contribution-of-the-fintech-sector-to-financial-inclusion-and-health-a-review-of-opportunities-and-challenges/ (accessed on 18 January 2022).
- Lins, Samuel, and Sibele Aquino. 2020. Development and initial psychometric properties of a panic buying scale during COVID-19 pandemic. Heliyon 6: e04746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, Darian, Robert Jeyakumar Nathan, Eva Gorgenyi-Hegyes, and Maria Fekete-Farkas. 2021. The Demand for Life Insurance in a Developing Country and the Mediating role of Persuasion. Journal of International Studies 14: 138–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, June, James E. Yao, and Chun-Sheng Yua. 2005. Personal Innovativeness, Social Influences and Adoption of Wireless Internet Services via Mobile Technology. Journal of Strategic Information System 14: 245–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusardi, Annamaria. 2019. Financial Literacy and the Need for Financial Inclusion: Evidence and Implications. Swiss Journal of Economics and Statistics 155: 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marakarkandy, Bijith, Nilay Yajnik, and Chandan Dasgupta. 2017. Enabling Internet Banking Adoption: An Empirical Examination with Augmented Technology Acceptance Model (TAM). Journal of Enterprise Information Management 30: 263–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, Bill. 2011. Mobile Money: Communication, Consumption and Change in the Payment Space. Journal of Development Studies 4: 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morgan, Peter J., and Long Q. Trinh. 2019. Fintech and Financial Literacy in Loa PDR. ABDI Working Paper Series. Available online: https://www.adb.org/publications/fintech-and-financial-literacy-lao-pdr (accessed on 23 December 2021).
- Morgan, Peter J., and Long Q. Trinh. 2020. Fintech and Financial Literacy in Vietnam. ADBI Working Paper Series. Available online: https://www.adb.org/publications/fintech-and-financial-literacy-viet-nam (accessed on 23 December 2021).
- Morosan, Cristian, and Agnes DeFranco. 2014. When Tradition Meets the New Technology: An Examination of the Antecedents of Attitude and Intentions to Use Mobile Devices in Private Clubs. International Journal of Hospitality Management 42: 126–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, Robert Jeyakumar. 2009. Electronic Commerce Adoption in the Arab Countries—An Empirical Study. International Arab Journal of Information Technology 1: 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Panos, Georgios A., Tatja Karkkainen, and Adele Atkinson. 2020. Financial Literacy and Attitudes to Cryptocurrencies. Working Paper. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3482083 (accessed on 12 February 2022).
- Patwardhan, Anju, Ken Singleton, and Kai Schmitz. 2018. Financial Inclusion in the Digital Age. Handbook of Blockchain, Digital Finance, and Inclusion Volume 1. Available online: https://www.ifc.org/wps/wcm/connect/0d9cffc8-a295-4e05-bf33-dca8ffa5abdf/Financial+Inclusion+in+the+Digital+Age.pdf?MOD=AJPERES&CVID=m9QAISc (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Pazarbasioglu Ceyla, Alfonso Garcia Mora, Mahesh Uttamchandani, Harish Natarajan, Erik Feyen, and Mathew Saal. 2020. Digital Financial Services. World Bank Group. Available online: http://pubdocs.worldbank.org/en/230281588169110691/Digital-Financial-Services.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2021).
- Rahman, Mahfuzur, Teoh Hui Ming, Tarannum Azim Baigh, and Moniruzzaman Sarker. 2021. Adoption of artificial intelligence in banking services: An empirical analysis. International Journal of Emerging Markets, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riyadh, Al Nahian, Deborah Bunker, and Fethi Rabhi. 2010. Barriers to E-finance Adoption in Small Medium Sized Enterprises (SMES) in Bangladesh. Paper presented at 5th Conference on Qualitative Research in IT, Brisbane, Australia, November 29–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ruparelia, Nimisha, Lesley White, and Kate Hughes. 2010. Drivers of Brand Trust in Internet Retailing. Journal of Product & Brand Management 19: 250–60. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, Hyun-Sun. 2018. Understanding Benefit and Risk Framework of Fintech Adoption: Comparison of Early Adopters and Late Adopters. Paper presented at 51st Hawai International Conference on System Sciences, Honolulu, HI, USA, January 18. [Google Scholar]
- Sahay, Ratna, Ulric Eriksson von Allmen, Amina Lahreche, Purva Khera, Sumiko Ogawa, Majid Bazarbash, and Kim Beaton. 2020. The Promise of Fintech: Financial Inclusion in the Post COVID-19 Era. Washington: International Monetary Fund. [Google Scholar]
- Salampasis, Dimitrios, and Anne-Laure Mention. 2018. Fintech: Harnessing Innovation for Financial Inclusion. In Handbook of Blockchain, Digital Finance, and Inclusion. Cambridge: Academic Press, vol. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Torres, Javier A., Francisco-Javier A. Canada, Alexander Varon Sandoval, and James-Ariel Sanchez Alzate. 2018. E-Banking in Columbia: Factors Favouring its Acceptance, Online Trust and Government Support. International Journal of Bank Marketing 36: 170–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiawan, Budi, Deni Pandu Nugraha, Atika Irawan, Robert Jeyakumar Nathan, and Zoltan Zeman. 2021. User Innovativeness and Fintech Adoption in Indonesia. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Marketing, and Complexity 7: 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, Stephen L., Lamar Reams, and Kevin Kam Fung So. 2018. Is It Worth the Price? The Role of Perceived Financial Risk, Identification, and Perceived Value in Purchasing Pay-per-view Broadcastings of Combat Sports. Sport Management Review 22: 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Shubhangi, Marshal M. Sahni, and Raj K. Kovid. 2020. What Drives Fintech Adoption? A Multi-method Evaluating using an Adapted Technology Acceptance Model. In Management Decision. Bingley: Emerald Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Troudi, Hadjer, and Djamila Bouyoucef. 2019. Predicting Purchasing Behavior of Green Food in Algerian Context. EuroMed Journal of Business 15: 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twum, Kojo Kakra, Daniel Ofori, and Bright Korang-Yeboah. 2021. Using the UTAUT, personal innovativeness and perceived financial cost to examine student’s intention to use E-learning. Journal of Science and Technology Policy Management, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UOB, PwC, and FA. 2020. Fintech in ASEAN: Get Up, Reset, Go! Available online: https://www.uobgroup.com/techecosystem/news-insights-fintech-in-asean-2020.html (accessed on 27 October 2021).
- Vasenska, Ivanka, Preslav Dimitrov, Blagovesta Koyundzhiyska-Davidkova, Vladislav Krastev, Pavol Durana, and Ioulia Poulaki. 2021. Financial transactions using fintech during the COVID-19 crisis in bulgaria. Risks 9: 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Yi-Shun, Yu-Min Wang, Hsin-Hui Lin, and Tzung-I Tang. 2003. Determinants of User Acceptance of Internet Banking: An Empirical Study. International Journal of Service Industry Management 14: 501–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, Rebecca M. 2008. Applied Statistics: From Bivariate through Multivariate Techniques. Los Angeles: Sage. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. 2017. The Global Findex Database. Available online: https://globalfindex.worldbank.org/ (accessed on 19 June 2021).
- World Economic Forum. 2020. COVID-19 Spurred a Rise in Fintech. Now Regulators are Catching Up. Available online: https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2020/10/COVID-19-financial-technology-fintech-regulation/ (accessed on 11 August 2021).
- Yoshino, Naoyuki, Peter J. Morgan, and Trinh Q. Long. 2020. Financial Literacy and Fintech Adoption in Japan. ABDI Working Paper Series. Available online: https://www.adb.org/publications/financial-literacy-fintech-adoption-japan (accessed on 17 September 2021).
- Yuen, Kum Fai, Xueqin Wang, Fei Ma, and Kevin X. Li. 2020. The psychological causes of panic buying following a health crisis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17: 3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Tingting, Can Lu, and Murat Kizildag. 2018. Banking on-the-go: Examining Consumers Adoption of Mobile Banking Services. In Journal of Quality and Service Sciences. Bingely: Emerald Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Anita Lifen, Nicole Koenig-Lewis, Stuart Hanmer-Lloyd, and Philippa Ward. 2009. Adoption of Internet Banking Services in China: Is It All about Trust? International Journal of Bank Marketing 28: 7–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolotov, Yuval, Alexander Reznik, Shmaya Bender, and Richard Isralowitz. 2020. COVID-19 Fear, Mental Health, and Substance Use Among Israeli University Students. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Countries | No. of Fintech Companies | Investment in 2020 (USD Million) | Regulatory Sandboxes | Fintech Associations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indonesia | 557 | 180.7 | Yes | Indonesia Fintech Association and Indonesia Fintech Lender Association |
| Malaysia | 407 | 72.9 | Yes | Fintech Association of Malaysia |
| Philippines | 212 | 135.5 | Yes | Fintech Philippines Association |
| Singapore | 1200 | 379.5 | Yes | Singapore Fintech Association |
| Thailand | 227 | 135.5 | Yes | Thai Fintech Association |
| Vietnam | 141 | 30 | No | Vietnam Fintech Club |
| Variable | Indicators | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Financial literary | I have knowledge of compounding interest I have knowledge of inflation I have knowledge of risk diversification | Lusardi (2019), Low et al. (2021). |
| Perceived usefulness | Using fintech can meet my financial service needs Fintech services can save time Fintech services can improve efficiency Overall, fintech services are useful to me | Davis (1989) |
| Perceived ease of use | It is easy to use fintech services It is easy to have a device to use fintech services (cellphone, APP, WiFi, et al.) | Davis (1989) |
| Trust | I believe money is secure when using fintech services Overall I believe fintech services are trustworthy I believe personal privacy is protected when using fintech services | Kim and Prabhakar (2002) |
| Brand image | I prefer to accept the fintech services provided by familiar brands I can recognize fintech services in Vietnam Fintech overall has a good reputation | Ruparelia et al. (2010) |
| Government support | The government supports and improves the use of fintech services The government has introduced favorable legislation and regulations for fintech services The government is active in setting up all kinds of infrastructure such as telecom networks which have a positive role in promoting fintech services | Marakarkandy et al. (2017) |
| User innovativeness | When I hear about a new product, I look for ways to try it Among my peers, I am usually the first one to try a new product I like to experiment with new fintech services | Zhang et al. (2018) |
| Attitude | I believe using fintech services is a good idea Using fintech services gives me a pleasant experience I am interested in fintech services | Grabner-Krauter and Faullant (2008) |
| Fintech Adoption | I will continue using fintech services I have not used but would like to use fintech services soon I will recommend fintech services to my friends | Marakarkandy et al. (2017) |
| Financial health due to COVID-19 | My earnings are reduced and savings eroded due to the COVID-19 pandemic Impulsive use of credit card is happening Forced to do panic buying and hoarding products There is a rise in prices of essential goods Tend to withdraw cash more often now There is a rise in the habit of saving money and realizing not to waste resources | Anand et al. (2020) |
| Age | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| 18–25 | 6 | 20.0% |
| 26–35 | 7 | 23.3% |
| 36–45 | 15 | 50.0% |
| >55 | 2 | 6.7% |
| Total | 30 | 100.0% |
| Employment Status | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| Student | 2 | 6.7% |
| Civil servant | 9 | 30.0% |
| Employee in private sector | 8 | 26.7% |
| Self-employed | 6 | 20.0% |
| Other | 5 | 16.7% |
| Total | 30 | 100.0% |
| Education | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| High school | 1 | 3.3% |
| Diploma | 1 | 3.3% |
| Bachelor’s degree | 18 | 60.0% |
| Master or PhD | 10 | 33.3% |
| Total | 30 | 100.0% |
| Income per Month | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| Under VND 5 M | 5 | 16.7% |
| VND 5 M–10 M | 9 | 30.0% |
| VND 10 M–20 M | 7 | 23.3% |
| Over VND 20 M | 9 | 30.0% |
| Total | 30 | 100.0% |
| Fintech Usage | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| Never | 4 | 13.3% |
| Once a week | 9 | 30.0% |
| 2–3 times a week | 7 | 23.3% |
| More than 4 times a week | 10 | 33.3% |
| Total | 30 | 100.0% |
| Gender | Frequency of Fintech Usage | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Personal Finance Needs | Business Finance Needs | Others | Total | |
| Male | 14 | 2 | 0 | 16 |
| % of total | 87.5% | 12.5% | 0 | 100% |
| Female | 13 | 0 | 1 | 14 |
| % of total | 92.9% | 0 | 7.1% | 100% |
| Gender | Frequency of Fintech Usage | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Never | Once a Week | 2–3 Times a Week | More Than 4 Times a Week | Total | |
| Male | 3 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 16 |
| % of total | 18.8% | 31.3% | 18.8% | 31.3% | 100.0% |
| Female | 1 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 14 |
| % of total | 7.1% | 28.6% | 28.6% | 35.7% | 100.0% |
| Value | df | Asymp. Sig. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (2-sided) | |||
| Pearson Chi-Square | 1.126 | 3 | 0.771 |
| Likelihood ratio | 1.168 | 3 | 0.761 |
| N of valid cases | 30 |
| Mean | Std. Dev. | |
|---|---|---|
| Financial Literacy | 3.10 | 1.09387 |
| Perceived Usefulness | 4.00 | 0.94686 |
| Perceived Ease of Use | 3.70 | 0.91539 |
| Trust | 3.03 | 0.88992 |
| Brand Image | 3.63 | 0.71840 |
| Government Support | 3.50 | 0.93772 |
| User Innovativeness | 3.06 | 0.90719 |
| User Attitude | 3.90 | 0.80301 |
| Fintech Adoption | 3.86 | 1.04166 |
| Gender | N | Mean | Std. Dev. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Literacy | Male | 16 | 2.93 | 1.1236 |
| Female | 14 | 3.28 | 1.0690 | |
| Perceived Usefulness | Male | 16 | 3.68 | 1.0144 |
| Female | 14 | 4.35 | 0.7449 | |
| Perceived Ease of Use | Male | 16 | 3.31 | 1.0144 |
| Female | 14 | 4.14 | 0.5345 | |
| Trust | Male | 16 | 2.81 | 0.9105 |
| Female | 14 | 3.28 | 0.8254 | |
| Brand Image | Male | 16 | 3.43 | 0.8139 |
| Female | 14 | 3.85 | 0.5345 | |
| Government Support | Male | 16 | 3.43 | 0.9639 |
| Female | 14 | 3.57 | 0.9376 | |
| User Innovativeness | Male | 16 | 2.93 | 0.9287 |
| Female | 14 | 3.21 | 0.8925 | |
| User Attitude | Male | 16 | 3.56 | 0.8139 |
| Female | 14 | 4.28 | 0.6112 | |
| Fintech Adoption | Male | 16 | 3.56 | 1.1528 |
| Female | 14 | 4.21 | 0.8017 |
| Fintech Adoption | ||
|---|---|---|
| Financial Literacy | Pearson Correlation | 0.133 |
| p-value | 0.483 | |
| Perceived Usefulness | Pearson Correlation | 0.699 ** |
| p-value | 0.000 | |
| Perceived Ease of Use | Pearson Correlation | 0.571 ** |
| p-value | 0.001 | |
| Fintech Trust | Pearson Correlation | 0.377 * |
| p-value | 0.040 | |
| Fintech Brand Image | Pearson Correlation | 0.531 ** |
| p-value | 0.003 | |
| Government Support | Pearson Correlation | 0.459 * |
| p-value | 0.011 | |
| User Innovative | Pearson Correlation | 0.448 * |
| p-value | 0.013 | |
| User Attitude | Pearson Correlation | 0.767 ** |
| p-value | 0.000 | |
| Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regression | 172.018 | 8 | 21.502 | 7.596 | 0.000 |
| Residual | 59.449 | 21 | 2.831 | ||
| Total | 231.467 | 29 |
| Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized | t | Sig. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | Std. Error | Coefficients Beta | |||
| (Constant) | 0.377 | 1.772 | 0.213 | 0.834 | |
| Financial literacy | −0.345 | 0.135 | −0.390 | −2.556 | 0.018 ** |
| Perceived usefulness | 0.067 | 0.242 | 0.082 | 0.279 | 0.783 |
| Perceived ease of use | 0.210 | 0.306 | 0.196 | 0.685 | 0.501 |
| Trust | −0.315 | 0.225 | −0.279 | −1.400 | 0.176 |
| Brand image | 0.266 | 0.311 | 0.207 | 0.857 | 0.401 |
| Government support | 0.007 | 0.170 | 0.007 | 0.042 | 0.967 |
| User innovativeness | 0.320 | 0.170 | 0.298 | 1.883 | 0.074 * |
| User Attitude | 0.666 | 0.308 | 0.555 | 2.164 | 0.042 ** |
| Gender | N | Mean | Std. Deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Financial literacy | Male | 16 | 2.93 | 1.12361 |
| Female | 14 | 3.28 | 1.06904 | |
| Perceived usefulness | Male | 16 | 3.68 | 1.01448 |
| Female | 14 | 4.35 * | 0.74495 | |
| Perceived ease of use | Male | 16 | 3.31 | 1.01448 |
| Female | 14 | 4.14 * | 0.53452 | |
| Trust | Male | 16 | 2.81 | 0.91059 |
| Female | 14 | 3.28 | 0.82542 | |
| Brand image | Male | 16 | 3.43 | 0.81394 |
| Female | 14 | 3.85 * | 0.53452 | |
| Government support | Male | 16 | 3.43 | 0.96393 |
| Female | 14 | 3.57 | 0.93761 | |
| User innovativeness | Male | 16 | 2.93 | 0.92871 |
| Female | 14 | 3.21 | 0.89258 | |
| Attitude | Male | 16 | 3.56 | 0.81394 |
| Female | 14 | 4.28 * | 0.61125 | |
| Fintech adoption | Male | 16 | 3.56 | 1.15289 |
| Female | 14 | 4.21 * | 0.80178 |
| t | df | p-Value | Mean Difference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Financial literacy | −0.866 | 28 | 0.394 | 0.34 |
| Perceived usefulness | −2.034 | 28 | 0.051 * | −0.66 |
| Perceived ease of use | −2.743 | 28 | 0.010 ** | −0.83 |
| Trust | −1.483 | 28 | 0.149 | 0.47 |
| Brand image | −1.642 | 28 | 0.112 | 0.41 |
| Government support | −0.384 | 28 | 0.704 | 0.13 |
| User innovativeness | −829 | 28 | 0.414 | 0.27 |
| Attitude | −2.719 | 28 | 0.011 ** | −0.72 |
| Fintech adoption | −1.772 | 28 | 0.087 * | −65 |
| Gender | Mean | Std. Dev. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| FH1: My earnings are reduced and savings eroded due to the pandemic COVID-19 | Male | 2.62 | 1.310 |
| Female | 3.21 | 1.847 | |
| Total | 2.90 | 1.583 | |
| FH2: Impulsive use of credit card is happening | Male | 3.50 | 1.211 |
| Female | 4.14 | 0.949 | |
| Total | 3.80 | 1.126 | |
| FH3: Forced to do panic buying and hoarding products | Male | 1.87 | 1.087 |
| Female | 2.85 | 1.350 | |
| Total | 2.33 | 1.295 | |
| FH4: There is a rise in prices of essential goods | Male | 3.37 | 1.087 |
| Female | 3.42 | 1.283 | |
| Total | 3.40 | 1.162 | |
| FH5: Tend to withdraw cash more often now | Male | 2.50 | 0.966 |
| Female | 2.50 | 1.091 | |
| Total | 2.50 | 1.005 | |
| FH6: There is a rise in the habit of saving money and realizing not to waste resources | Male | 4.12 | 0.885 |
| Female | 4.21 | 0.974 | |
| Total | 4.16 | 0.912 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nathan, R.J.; Setiawan, B.; Quynh, M.N. Fintech and Financial Health in Vietnam during the COVID-19 Pandemic: In-Depth Descriptive Analysis. J. Risk Financial Manag. 2022, 15, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm15030125
Nathan RJ, Setiawan B, Quynh MN. Fintech and Financial Health in Vietnam during the COVID-19 Pandemic: In-Depth Descriptive Analysis. Journal of Risk and Financial Management. 2022; 15(3):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm15030125
Chicago/Turabian StyleNathan, Robert Jeyakumar, Budi Setiawan, and Mac Nhu Quynh. 2022. "Fintech and Financial Health in Vietnam during the COVID-19 Pandemic: In-Depth Descriptive Analysis" Journal of Risk and Financial Management 15, no. 3: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm15030125
APA StyleNathan, R. J., Setiawan, B., & Quynh, M. N. (2022). Fintech and Financial Health in Vietnam during the COVID-19 Pandemic: In-Depth Descriptive Analysis. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 15(3), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm15030125








