Firm Performance of Saudi Manufacturers: Does the Management of Cash Conversion Cycle Components Matter?
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The primary goal of this study is to examine how the cash conversion cycle impacts the performance of manufacturing companies in Saudi Arabia. This overarching objective is further divided into four sub-objectives, which are delineated as follows:
- To inspect the link between the aggregate cash conversion cycle and the firm’s performance.
- To explore the link of the inventory policy with the firm’s performance.
- To explore the link of the accounts receivable policy with the firm’s performance.
- To consider the link of the accounts payable policy with the firm’s performance.
2. Literature Review and Hypotheses Development
2.1. Cash Conversion Cycle Management and Firm Performance
2.2. Inventory Management and Firm Performance
2.3. Accounts Receivable Management and Firm Performance
2.4. Accounts Payable Management and Firm Performance
3. Research Design and Methodology
3.1. Sample Selection and Model Specifications
3.2. Variables Measurement
3.2.1. Dependent Variable: Firm Performance Measurement
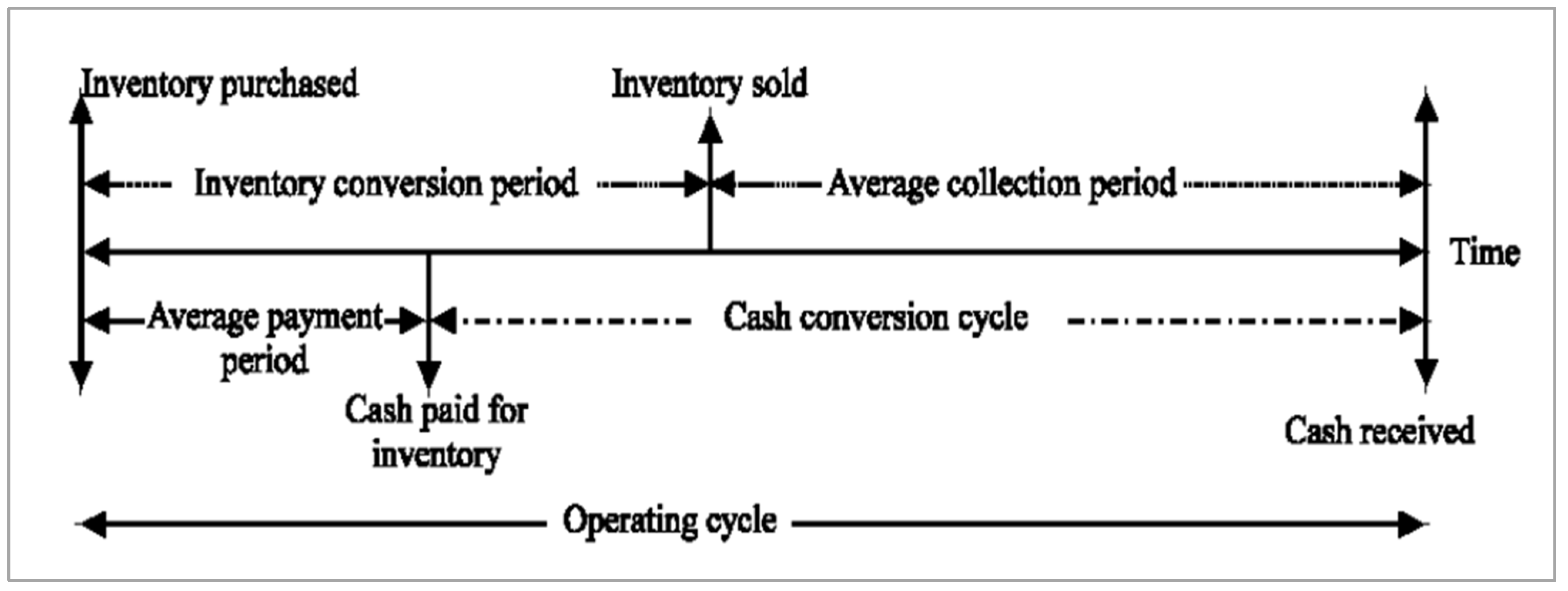
3.2.2. CCC Variables Measurement
3.2.3. Control Variables
4. Main Findings
4.1. Descriptive Statistics
4.2. Multicollinearity Test
4.3. Panel Tests
4.4. Hypotheses Validation and Discussion
4.5. Robustness Checks and Further Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Variable | Symbol | Measure | Reference | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Return on assets | ROA | Book value of net profit after tax/total assets | Kim (2005) | Datastream |
| Inventory conversion period | ICP | (Average inventory/cost of goods sold) × 365 | Gitman et al. (2015) | Datastream |
| Accounts receivable collection period | ARCP | (Average receivables/sales) × 365 | Brigham (1995) | Datastream |
| Days payable outstanding | DPO | (Average payables/cost of goods sold) × 365 | Brigham (1995) | Datastream |
| Cash conversion cycle | CCC | CCC = ICP + ARCP − DPO | Keown et al. (2003) | Datastream |
| Firm size | FSIZE | Natural logarithm of total assets. | Fama and French (1995) | Datastream |
| Debt ratio | DEBT | Long-term liabilities divided by lagged total assets. | Datastream | |
| Board size | BSIZE | Number of members in the board. | Beiner et al. (2004) and Alves (2011) | Datastream |
| Big4 auditor | BIG | Indicator that takes the value of 1 if the company is audited by at least one of the Big4 audit firm, and 0 otherwise. | Annual reports | |
| COVID-19 | COVID | Indicator that takes a value of 1 for the firm-year observations that fall in the coronavirus pandemic (2020–2021), and 0 otherwise. | Authors |
References
- Ali, Khurshid, Numaira Showkat, and Khaled Achraf Chisti. 2022. Impact of inventory management on operating profits: Evidence from India. Journal of Finance and Economics 10: 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnaim, Musab, and Amel Kouaib. 2023. Inventory turnover and firm profitability: A Saudi Arabian Investigation. Processes 11: 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, Sandra Maria Geraldes. 2011. The effect of the board structure on earnings management: Evidence from Portugal. Journal of Financial Reporting and Accounting 9: 141–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attari, Muneeb, and Kashif Raza. 2012. The optimal relationship of cash conversion cycle with firm size and profitability. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences 2: 189–203. [Google Scholar]
- Beiner, Stefan, Wolfgang Drobetz, Frank Schmid, and Heinz Zimmermann. 2004. Is board size an independent corporate governance mechanism? Kyklos 57: 327–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigham, Eugene. 1995. Fundamentals of Financial Management. Mason Ohio: The Dryden Press. [Google Scholar]
- Charitou, Melita Stephanou, Maria Elfani, and Petros Lois. 2010. The effect of working capital management on firm profitability: Empirical evidence from an emerging market. Journal of Business & Economics Research 8: 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deloof, Marc. 2003. Does working capital management affect profitability of Belgian firms? Journal of Business Finance and Accounting 30: 573–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demiraj, Rezart, Suzan Dsouza, and Mohammad Abiad. 2022. Working Capital Management Impact on Profitability: Pre-Pandemic and Pandemic Evidence from the European Automotive Industry. Risks 10: 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebben, Jay, and Alec Johnson. 2011. Cash conversion cycle management in small firms: Relationships with liquidity. Journal of Small Business & Entrepreneurship 24: 381–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enqvista, Julius, Michael Graham, and Jussi Nikkinen. 2014. The impact of working capital management on firm profitability in different business cycles: Evidence from Finland. Research in International Business and Finance 32: 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroglu, Cuneyt, and Christian Hofer. 2011. Lean, leaner, too lean? The inventory–performance link revisited. Journal of Operations Management 29: 356–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fama, Eugene, and Kenneth French. 1995. Size and book-to-market factors in earnings and returns. Journal of Finance 50: 131–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, Vishal, Marshall Fisher, and Ananth Raman. 2005. An econometric analysis of inventory turnover performance in retail services. Management Science 51: 181–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, Amarjit, Nahum Biger, and Neil Arun Mathur. 2010. The relationship between working capital management and profitability: Evidence from the United States. Business and Economics Journal 10: 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Gitman, Lawrence. 1974. Estimating corporate liquidity requirements: A simplified approach. The Financial Review 9: 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitman, Lawrence, Juchau Roger, and Flanagan Jack. 2015. Principles of Managerial Finance. Boston: Pearson Education International. [Google Scholar]
- Gujarati, Damodar. 2003. Basic Econometrics, 4th ed. New York: McGraw Hill. [Google Scholar]
- Hashed, Abdul Wahid Ahmed, and Abdul Rahman Shaik. 2022. The nexus between inventory management and firm performance: A Saudi Arabian perspective. Journal of Asian Finance Economics and Business 9: 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, Debabrata. 2018. Impact of working capital management on profitability of the selected listed FMCG companies in India. International Research Journal of Business Studies 11: 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, Randolph Westerfield. 2003. Fundamentals of Corporate Finance, 6th ed. Boston: McGraw-Hill Companies. [Google Scholar]
- Jose, Manuel, Carol Lancaster, and Jerry Stevens. 1996. Corporate returns and cash conversion cycles. Journal of Economics and Finance 20: 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, Norazira, Anuar Nawawi, and Ahmad Saiful Azlin Puteh Salin. 2018. Inventory management effectiveness of a manufacturing Company—Malaysian evidence. International Journal of Law and Management 60: 1163–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, Rejaul, Md Abdullah Al Mamun, and Abu Sadeque Md. Kamruzzaman. 2023. Cash conversion cycle and financial performance: Evidence from manufacturing firms of Bangladesh. Asian Journal of Economics and Banking, ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keown, Arthur, John Martin, William Petty, and David Scott. 2003. Foundations of Finance: The Logic and Practice of Financial Management, 4th ed. London: Pearson Education. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, Mohammad Nauman, and Imran Khokhar. 2015. The effect of selected financial ratios on profitability: An empirical analysis of listed firms of cement sector in Saudi Arabia. Quarterly Journal of Econometrics Research 1: 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Yangmin. 2005. Board network characteristics and firm performance in Korea. Corporate Governance An International Review 13: 800–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, Andrew, and Michael Lenox. 2011. Lean and green? An Empirical examination of the relationship between lean production and environmental performance. Production and Operations Management 10: 244–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouaib, Amel. 2022. Corporate sustainability disclosure and investment efficiency: The Saudi Arabian context. Sustainability 14: 13984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koumanakos, Dimitrios. 2008. The effect of inventory management on firm performance. International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management 57: 355–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, Jin Kyung. 2019. Analysis of inventory turnover as a performance measure in manufacturing industry. Processes 7: 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Qi, and Xi Lin. 2021. Cash conversion cycle and aggregate stock returns. Journal of Financial Markets 52: 100560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louw, Elmarie, John Hall, and Rudra Pradhan. 2022. The relationship between working capital management and profitability: Evidence from South African retail and construction firms. Global Business Review 23: 313–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathuva, David. 2010. The Influence of Working Capital Management Components on Corporate Profitability: A Survey on Kenyan Listed Firms. Research Journal of Business Management 4: 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, Umakanta, Jei-Zheng Wu, and Biswajit Sarkar. 2021. Optimum sustainable inventory management with backorder and deterioration under controllable carbon emissions. Journal of Cleaner Production 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muchaendepi, Wiseman, Charles Mbohwa, T. Hamandishe, and James Kanyepe. 2019. Inventory management and performance of SMEs in the Manufacturing sector of Harare. Procedia Manufacturing 23: 454–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niresh, Aloy. 2012. Working capital management & financial performance of manufacturing sector in Sri Lanka. European Journal of Business and Management 4: 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Peel, Michael, Nicholas Wilson, and Carole Howorth. 2000. Late payment and credit management in the small firm sector: Some empirical evidence. International Small Business Journal 18: 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, Jeffrey, and Gerald Salancik. 1978. The External Control of Organizations: A Resource Dependence Perspective. New York: Harper and Row. [Google Scholar]
- Raheman, Abdul, and Mohamed Nasr. 2007. Working capital management and profitability-case of Pakistani firms. International Review of Business Research Papers 3: 279–300. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, Mohammed Ziaur, Muhammad Nauman Khan, and Imran Khokhar. 2014. Select financial ratios as a determinant of profitability evidence from petrochemical industry in Saudi Arabia. European Journal of Business and Management 6: 187–96. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, Verlyn, and Eugene Laughlin. 1980. A cash conversion cycle approach to liquidity analysis. Financial Management 9: 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, W. L. M., Sakunika Rathnayake, and C. Pathirawasam. 2020. Effect of inventory management on financial performance of listed manufacturing companies in Sri Lanka. IAR Journal of Business Management 1: 383–89. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, Stephen, Randolph Westerfield, and Bradford Jordan. 2003. Fundamentals of Corporate Finance, 6th ed. New York: The McGraw-Hill Companies. [Google Scholar]
- Schonberger, Richard. 2007. Japanese production management: An evolution—With mixed success. Journal of Operations Management 25: 403–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, Rachna, and Hojung Shin. 2007. Relationships among information technology, inventory, and profitability: An investigation of level invariance using sector level data. Journal of Operations Management 25: 768–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, Abdul Rahman. 2021a. COVID-19 pandemic and the reaction of Asian stock markets: Empirical evidence from Saudi Arabia. Journal of Asian Finance, Economics, and Business 8: 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, Abdul Rahman. 2021b. Components of working capital and profitability in Saudi Arabian companies. Investment Management and Financial Innovations 18: 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, Keith. 1980. Profitability Versus Liquidity Tradeoffs in Working Capital Management, Readings on the Movement of Working Capital. New York: West Publishing Company, St. Paul. [Google Scholar]
- Vahid, Taghizadeh Khanqah, Ghanavati Elham, Akbari Khosroshahi Mohsen, and Ebrati Mohammadreza. 2012. Working capital management and corporate performance: Evidence from Iranian companies. Procedia—Social and Behavioral Sciences 62: 1313–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnani, Sushma, and Bhupesh Kr Shah. 2007. Impact of working capital management policies on corporate performance—An empirical study. Global Business Review 8: 267–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Yung-Jang. 2002. Liquidity management, operating performance, and corporate value: Evidence from Japan and Taiwan. Journal of Multinational Financial Management 12: 159–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangari, Kamau Lucy. 2015. Influence of inventory management practices on organizational competitiveness: A case of Safaricom Kenya LTD. International Academic Journal of Procurement and Supply Chain Management 1: 72–98. [Google Scholar]
- White, Richard, John Pearson, and Jeffrey Wilson. 1999. JIT manufacturing survey of implementations in small and large U.S. manufacturers. Management Science 45: 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sector | Industry Group | Firms | Obs. | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Energy | Energy | 4 | 20 | 5 |
| 2 | Materials | Materials Industry Group | 46 | 230 | 52 |
| 3 | Industrials | Capital Goods | 16 | 80 | 18 |
| 4 | Consumer Discretionary | Consumer Durables and Apparel | 7 | 35 | 8 |
| 5 | Consumer Staples | Food and Beverages | 15 | 75 | 17 |
| Total | 88 | 440 | 100 |
| Mean | Median | St. Dev. | Kurtosis | Skewness | Minimum | Maximum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panel A. Summary statistics | |||||||
| ROA | 8.8716 | 8.9734 | 5.2891 | 2.5528 | 1.5990 | 0.0510 | 30.1357 |
| CCC (days) | 52.6971 | 41.6284 | 145.1492 | 3.1855 | 0.0942 | 8.4300 | 110.3149 |
| ICP (days) | 103.4313 | 74.9566 | 142.7498 | 28.5379 | 4.8279 | 5.1728 | 1106.0606 |
| ARCP (days) | 81.0069 | 35.1963 | 21.0878 | 82.9970 | 8.4962 | 29.0526 | 150.9347 |
| DPO (days) | 59.1641 | 60.0000 | 26.8383 | 1.9355 | −0.0524 | 10.0000 | 104.0000 |
| FSIZE | 17.1270 | 15.9473 | 2.1495 | −0.8242 | 0.5016 | 14.0411 | 20.5364 |
| DEBT | 1.5898 | 0.5301 | 3.6516 | 19.1304 | 5.0047 | 0.1142 | 19.3150 |
| BSIZE | 8.3570 | 9.0000 | 3.2514 | 12.0651 | 3.8229 | 4.0000 | 24.0000 |
| Panel B. Frequencies statistics | Obs. | Freq (1) | % | Freq (0) | % | ||
| BIG | 440 | 215 | 49 | 225 | 51 | ||
| COVID | 440 | 176 | 40 | 264 | 60 | ||
| ROA | CCC | ICP | ARCP | DPO | FSIZE | DEBT | BSIZE | VIF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ROA | 1.0000 | −0.1478 *** | −0.0861 * | −0.0687 * | 0.0709 * | 0.0795 ** | −0.0330 * | 0.0542 | - |
| CCC | −0.2568 ** | 1.0000 | 0.4673 ** | 0.5981 ** | 0.4042 *** | 0.1225 | 0.0120 * | 0.1475 | 1.50 |
| ICP | −0.1030 ** | 0.4394 ** | 1.0000 | −0.0265 | 0.0137 *** | 0.0012 | −0.0016 | 0.0309 *** | 1.15 |
| ARCP | −0.0084 ** | 0.4977 ** | −0.0455 | 1.0000 | 0.0173 | 0.3050 *** | −0.0427 | 0.0913 * | 1.66 |
| DPO | 0.0813 * | 0.4113 *** | 0.1822 *** | 0.0384 | 1.0000 | −0.0768 | 0.2778 *** | −0.0435 | 1.24 |
| FSIZE | 0.0885 ** | 0.2892 | 0.0058 * | 0.3050 *** | −0.0809 | 1.0000 | −0.2196 *** | 0.3901 *** | 1.57 |
| DEBT | −0.0237 * | 0.0208 | −0.0042 | −0.0427 * | 0.0933 *** | −0.0804 *** | 1.0000 | −0.0411 *** | 1.39 |
| BSIZE | 0.0366 | 0.1310 | 0.1614 *** | 0.0862 * | −0.0364 | 0.0640 *** | −0.0455 *** | 1.0000 | 1.46 |
| Panel A Equation (1) | Panel B Equation (2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coef. | T | Coef. | T | |
| Constant | −3.672 *** | −2.94 | −3.2569 *** | −2.56 |
| CCC | −0.145 ** | −2.39 | ||
| ICP | −0.211 ** | −2.15 | ||
| ARCP | −0.035 ** | −2.04 | ||
| DPO | 0.017 * | 1.70 | ||
| FSIZE | 0.754 ** | 1.95 | 0.772 ** | 1.93 |
| DEBT | −0.268 * | −1.69 | −0.270 * | −1.70 |
| BSIZE | 0.059 | 0.42 | 0.063 | 0.48 |
| BIG | 0.146 | 1.57 | 0.150 | 1.55 |
| COVID | 0.115 * | 1.72 | 0.127 * | 1.74 |
| FIRMS | Included | Included | ||
| YEARS | Included | Included | ||
| Observations | 440 | 440 | ||
| R-sq (%) | 7.587 | 7.619 | ||
| Adjusted R-sq (%) | 7.302 | 7.496 | ||
| F-stat | 55.841 *** | 53.110 *** | ||
| Prob (F-stat) | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kouaib, A.; Bu Haya, M.I. Firm Performance of Saudi Manufacturers: Does the Management of Cash Conversion Cycle Components Matter? J. Risk Financial Manag. 2024, 17, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17010016
Kouaib A, Bu Haya MI. Firm Performance of Saudi Manufacturers: Does the Management of Cash Conversion Cycle Components Matter? Journal of Risk and Financial Management. 2024; 17(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleKouaib, Amel, and Mohammed Ibrahim Bu Haya. 2024. "Firm Performance of Saudi Manufacturers: Does the Management of Cash Conversion Cycle Components Matter?" Journal of Risk and Financial Management 17, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17010016
APA StyleKouaib, A., & Bu Haya, M. I. (2024). Firm Performance of Saudi Manufacturers: Does the Management of Cash Conversion Cycle Components Matter? Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 17(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17010016






