Application of the New Importance–Performance Analysis Method to Explore the Strategies of Rural Outdoor Dining Experiences in Taiwan
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- To explore the background and recreational characteristics of consumers participating in rural outdoor dining experiences.
- (2)
- To explore the discrepancy between demographic variables and customer satisfaction.
- (3)
- To explore development strategies for rural outdoor dining experiences through NIPA.
- (4)
- To provide practical suggestions for the development of outdoor dining experiences in rural communities in Taiwan.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Rural Outdoor Dining
2.2. Dining Experience
2.3. New Importance–Performance Analysis
- Service quality is developed, as are the questionnaire items.
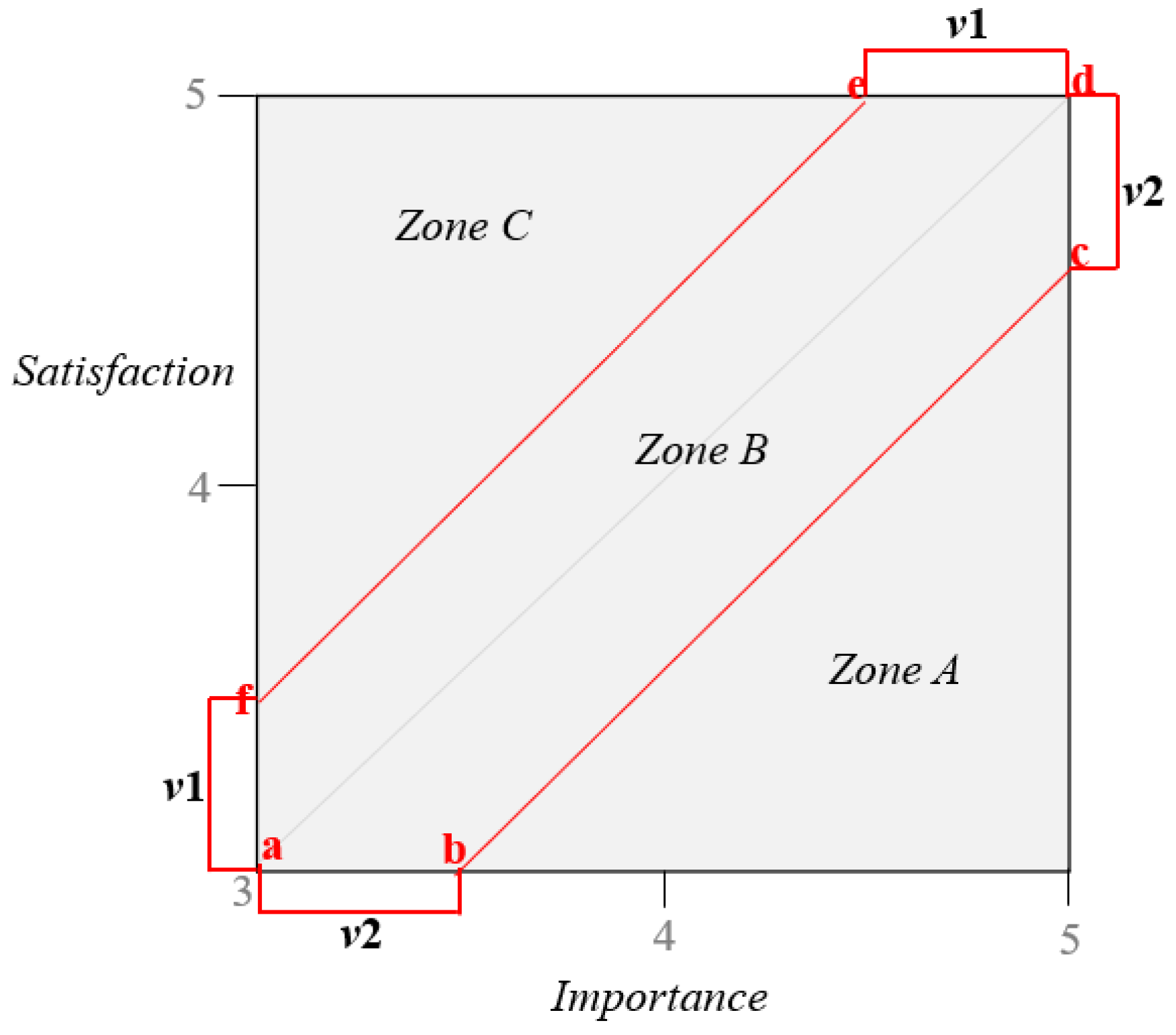
- Customers are invited to evaluate the degrees of these properties in terms of “importance”, “performance”, and “tolerance”. “Importance” refers to the perceived importance of the properties of a product or service for the preferences of customers. “Performance” refers to the product or service of performance for the supplier. “Tolerance” refers to the level that customers can allow between “importance” and “performance”.
- Compute the mean of the items; importance is on the horizontal axis, and performance is on the vertical axis. The degree of service quality is a coordinate, and the value is represented in a two-dimensional space.
3. Research Methods
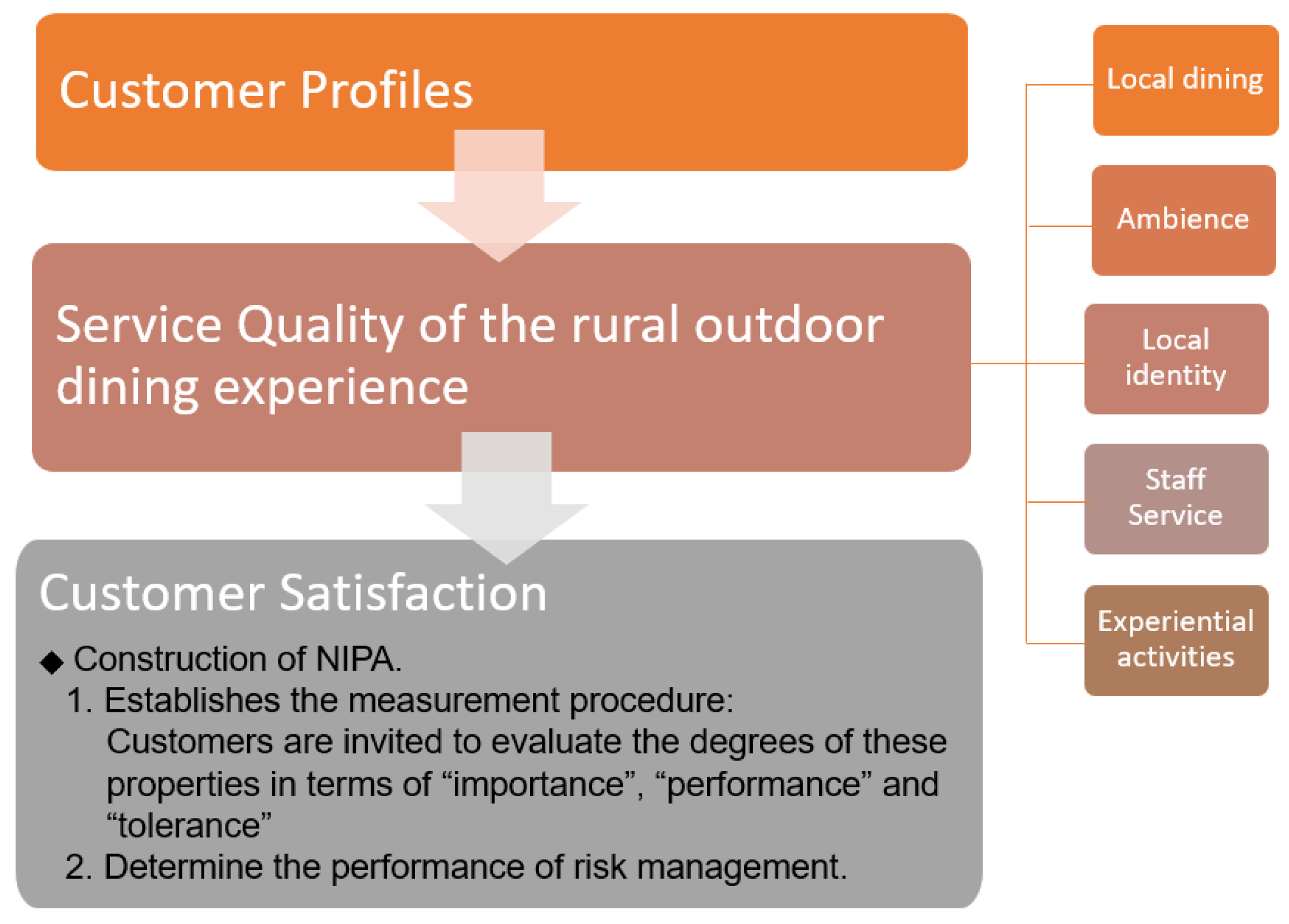
3.1. Conceptual Model
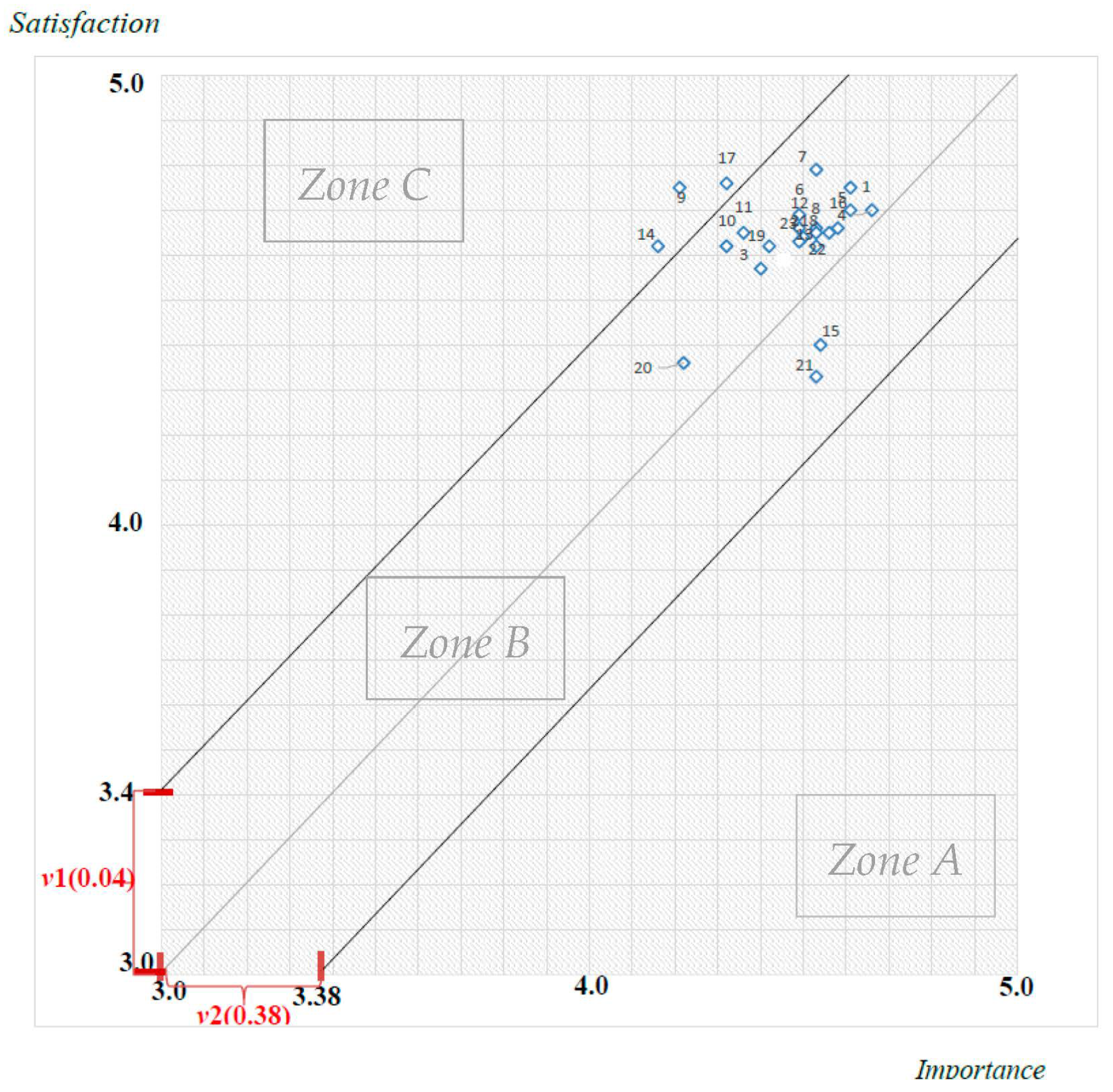
- Zone A: primary improvement, high importance, and low satisfaction.
- 2.
- Zone B: maintenance, and scores of importance and performance are high.
- 3.
- Zone C: excessive development, lower importance, and higher satisfaction.
3.2. Instruments and Measures
- (1)
- If PS − ES > 0, positive, customers are satisfied, which means excessive supply to demand and satisfied with quality.
- (2)
- If PS − ES < 0, negative, customers cannot accept it, which means it is lower than expected, and the quality should be improved.
- (3)
- If PS − ES = 0, equal, customers are satisfied, which means their expectation of service matches their need.
4. Results
4.1. Sampling
4.2. Empirical Analysis and Results
4.3. NIPA of Satisfaction with Service
5. Conclusions and Suggestions
6. Limitations and Future Research Directions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Anderson, Eugene W., Claes Fornell, and Donald R. Lehmann. 1994. Customer satisfaction, market share, and profitability: Findings from Sweden. Journal of Marketing 58: 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacon, Donald R. 2003. A comparison of approaches to importance-performance analysis. International Journal of Market Research 45: 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtiar, Arfan, Mega Aulia Silviadara, and Aries Susanty. 2017. Perbandingan Kualitas Layanan Ritel Swalayan Menggunakan Competitive Zone of Tolerance Based dan Importance-Performance Analysis. Jurnal Ilmiah Teknik Industri 16: 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bessière, Jacinthe. 1998. Local Development and Heritage: Traditional Food and Cuisine as Tourist Attractions in Rural Areas. Sociologia Ruralis 38: 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouder, Patrick, Svante Karlsson, and Linda Lundmark. 2015. Hyper-production: A new metric of multifunctionality. European Countryside 7: 134–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruyere, Brett L., Donald A. Rodriguez, and Jerry J. Vaske. 2002. Enhancing Importance-Performance Analysis through Segmentation. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing 12: 81–95. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Yang, Xiang Robert Li, Robin DiPietro, and Kevin Kam Fung So. 2019. The creation of memorable dining experiences: Formative index construction. International Journal of Hospitality Management 82: 308–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpio, Carlos E., Michael K. Wohlgenant, and Tullaya Boonsaeng. 2008. The demand for agritourism in the United States. Journal of Agricultural and Resource Economics 33: 254–69. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Kuan-Yu. 2014. Improving importance-performance analysis: The role of the zone of tolerance and competitor performance. The case of Taiwan’s hot spring hotels. Tourism Management 40: 260–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Li-Fei, Szu-Chi Chen, and Chao-Ton Su. 2018. An innovative service quality evaluation and improvement model. The Service Industries Journal 38: 228–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Zueng-Sang, Zeng-Yei Hseu, and Chen-Chi Tsai. 2015. The Soils of Taiwan. Dordrecht: Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Ching-Chan, Hung-Che Wu, Ming-Chun Tsai, Ya-Yuan Chang, and Cheng-Ta Chen. 2021. Identifying the strategic implications of service attributes of wedding banquet halls for market competition and risk management. International Journal of Hospitality Management 92: 102732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csurgó, Bernadett, and Melanie K. Smith. 2022. Cultural heritage, sense of place and tourism: An analysis of cultural ecosystem services in rural Hungary. Sustainability 14: 7305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewey, John. 1925. Experience and Nature, Rev. ed. LaSalle: Open Court. [Google Scholar]
- El-Said, Osman Ahmed, Michael Smith, and Wijdan Al Ghafri. 2021. Antecedents and outcomes of dining experience satisfaction in ethnic restaurants: The moderating role of food neophobia. Journal of Hospitality Marketing & Management 30: 799–824. [Google Scholar]
- Findlay, Allan M., David Short, and Aileen Stockdale. 2000. The labour-market impact of migration to rural areas. Applied Geography 20: 333–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, Igy. 2013. Modified importance-performance analysis of airport facilities-A case study of cochin international airport limited. IOSR Journal of Humanities and Social Science 17: 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grönroos, Christian. 1984. A service quality model and its marketing implications. European Journal of Marketing 18: 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzel, Ozlem, and Taylan Dortyol. 2016. Exploring the multi-sensory based memorable tourism experiences: A study of Adam &Eve hotel in Turkey. Journal of Marketing and Consumer Behaviour in Emerging Markets 2: 28–39. [Google Scholar]
- Hanaysha, Jalal. 2016. Testing the effects of food quality, price fairness, and physical environment on customer satisfaction in fast food restaurant industry. Journal of Asian Business Strategy 6: 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, Kai Victor. 2014. Development of SERVQUAL and DINESERV for measuring meal experiences in eating establishments. Scandinavian Journal of Hospitality and Tourism 14: 116–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawes, Jon M., and C. P. Rao. 1985. Using Importance-Performance Analysis to Develop Health Care Marketing Strategies. Journal of Health Care Marketing 5: 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Chih-Cheng, Shang-Pin Li, Jiin-Chyuan Mark Lai, Yung-Kuan Chan, and Ming-Yuan Hsieh. 2023. Research on the international sustainable practice of the taiwanese food and agricultural education law under the current global food security challenges. Foods 12: 2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Chih-Cheng, Ying-Hsiang Lin, Chun-Nan Lin, and Shang-Pin Li. 2019. Research on Assessment of Service Satisfaction by Innovation Model: Using iBike as an Example. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology 124: 357–58. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, Ananda Sabil. 2018. Revisiting the importance of casual dining experience quality: An empirical study. International Journal of Quality and Service Sciences 10: 233–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, EunHa, and SooCheong Shawn Jang. 2011. Restaurant experiences triggering positive electronic word-of-mouth (eWOM) motivations. International Journal of Hospitality Management 30: 356–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Mingjie, IpKin Anthony Wong, Anita Eves, and Aliana Man Wai Leong. 2018. A multilevel investigation of china’s regional economic conditions on cocreation of dining experience and outcomes. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management 30: 2132–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, Robert. 1995. The zone of tolerance: Exploring the relationship between service transactions and satisfaction with the overall service. International Journal Service Industry Management 6: 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassarjian, Harold H. 1977. Content analysis in consumer research. Journal of Consumer Research 4: 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiatkawsin, Kiattipoom, and Ian Sutherland. 2020. Examining luxury restaurant dining experience towards sustainable reputation of the Michelin restaurant guide. Sustainability 12: 2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinhans, Elsabe Hendrina, C. H. Van Heerden, and I. C. Kleynhans. 2016. A review of dining experience dimensions over two decades. African Journal of Hospitality, Tourism and Leisure 35: 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Konuk, Faruk Anıl. 2019. The influence of perceived food quality, price fairness, perceived value and satisfaction on customers’ revisit and word-of-mouth intentions towards organic food restaurants. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services 50: 103–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Wen-Hwa, and Ching-Chan Cheng. 2018. Less is more: A new insight for measuring service quality of green hotels. International Journal of Hospitality Management 68: 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Shang-Pin, Ying-Hsiang Lin, and Chih-Cheng Huang. 2022. Application of the Innovative Model NIPA to Evaluate Service Satisfaction. Sustainability 14: 10036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundmark, Linda. 2006. Restructuring and employment change in sparsely populated areas. In Examples from northern Sweden and Finland. Umeå: Gerum, Kulturgeografiska Institutionen, Umeå Universitet. [Google Scholar]
- Matzler, Kurt, Elmar Sauerwein, and Kenneth Heischmidt. 2003. Importance-performance analysis revisited: The role of the factor structure of customer satisfaction. The Service Industries Journal 23: 112–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabian, Albert, and James A. Russell. 1974. An Approach to Environmental Psychology. Cambridge: MIT Press. [Google Scholar]
- Namin, Aidin. 2017. Revisiting customers’ perception of service quality in fast food restaurants. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services 34: 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natori, Yoji, and Richard Chenoweth. 2008. Differences in rural landscape perceptions and preferences between farmers and naturalists. Journal of Environmental Psychology 28: 250–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Munhyang Moon, and Seongseop Sam Kim. 2020. Dimensionality of ethnic food fine dining experience: An application of semantic network analysis. Tourism Management Perspectives 35: 100719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, Anantharanthan, Valarie A. Zeithaml, and Leonard L. Berry. 1985. A conceptual model of service quality and its implications for future research. Journal of Marketing 49: 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, Arun. 2004. Assessing and improving service performance for maximum impact: Insights from a two-decade-long research journey. Performance Measurement and Metrics 5: 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, Arun, Leonard L. Berry, and Valarie A. Zeithaml. 1991. Understanding customer expectations of service. Sloan Management Review 32: 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Parasuraman, Arun, Valarie A. Zeithaml, and Leonard L. Berry. 1994. Alternative scales for measuring service quality: A comparative assessment based on psychometric and diagnostic criteria. Journal of Retailing 70: 201–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Eerang, and Andy Widyanta. 2022. Food tourism experience and changing destination foodscape: An exploratory study of an emerging food destination. Tourism Management Perspectives 42: 100964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piqueras-Fiszman, Betina, and Sara R. Jaeger. 2015. What makes meals ‘memorable’? A consumer-centric exploration. Food Research International 76: 233–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privitera, Donatella, Adrian Nedelcu, and Virgil Nicula. 2018. Gastronomic and food tourism as an economic local resource: Case studies from Romania and Italy. GeoJournal of Tourism and Geosites 21: 143–57. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Hailian, Minglong Li, Boyang Shu, and Billy Bai. 2020. Enhancing hospitality experience with service robots: The mediating role of rapport building. Journal of Hospitality Marketing and Management 29: 247–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, Scott, Mohammed Lefrid, Shiva Jahani, Matthew D. Munyon, and S. Mostafa Rasoolimanesh. 2019. Effect of dining experience on future intention in quick service restaurants. British Food Journal 121: 2620–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, Kisang, and Heesup Han. 2010. Influence of the quality of food, service, and physical environment on customer satisfaction and behavioral intention in quick-casual restaurants: Moderating role of perceived price. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Research 34: 310–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, Bernd. 1999. Experiential Marketing. New York: The Free Press. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, Bernd, and Lia Zarantonello. 2013. Consumer experience and experiential marketing: A critical review. Review of Marketing Research 10: 25–61. [Google Scholar]
- Scozzafava, Gabriele, Caterina Contini, Caterina Romano, and Leonardo Casini. 2017. Eating out: Which restaurant to choose. Food 119: 1870–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shobri, Nor Diyana M. 2018. Blending functional and emotional experience with the experience economy model to understand resort experience. International Journal of Innovation and Business 9: 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Taiwanese Food and Agricultural Education Law (TFAEL). 2022. Available online: https://law.moj.gov.tw/ENG/LawClass/LawAll.aspx?pcode=M0090039 (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Tarrant, Michael A., and Erin K. Smith. 2002. The use of a modified importance–performance framework to examine visitor satisfaction with attributes of outdoor recreation settings. Managing Leisure 7: 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonge, Joanna, and Susan A. Moore. 2007. Importance-satisfaction analysis for marine-park hinterlands: A western Australian case study. Tourism Management 28: 768–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torquati, Biancamaria, Tiziano Tempesta, Daniel Vecchiato, Sonia Venanzi, and Chiara Paffarini. 2017. The value of traditional rural landscape and nature protected areas in tourism demand: A study on agritourists’ preferences. Landscape Online 53: 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Ming-Chun, Shu-Ping Lin, and Ching-Chan Cheng. 2022. A comprehensive quality improvement model: Integrating internal and external information. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence 33: 548–65. [Google Scholar]
- Tsaur, Sheng-Hshiung, and Pei-Chun Lo. 2020. Measuring memorable dining experiences and related emotions in fine dining restaurants. Journal of Hospitality Marketing & Management 29: 887–910. [Google Scholar]
- Tussyadiah, Iis P. 2016. Factors of satisfaction and intention to use peer-to-peer accommodation. International Journal of Hospitality Management 55: 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Mian, and Shixian Luo. 2021. Effects of rural restaurants’ outdoor dining environment dimensions on customers’ satisfaction: A consumer perspective. Foods 10: 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Mian, Wenjie Fan, Jian Qiu, Sining Zhang, and Jinting Li. 2022. The Evaluation of Rural Outdoor Dining Environment from Consumer Perspective. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19: 13767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Tuan Lo, Rahmah Awang Siti, Jusoh Ahmad, Md Nor Khalil, and Soehod Khairiah. 2018. The role of patron dining experience and emotions on relationship quality in chain restaurant industry. Intangible Capital 14: 357–69. [Google Scholar]
- Zeithaml, Valarie A., Leonard L. Berry, and Arantharanthan Parasuraman. 1993. The nature and determinants of customer expectations of service. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science 21: 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Constructs | Measurement Items |
|---|---|
| Local dining |
|
| Ambience |
|
| Local identity |
|
| Staff service |
|
| Experiential activities |
|
| Variables | Categories | N | Percentage % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 222 | 56.1 |
| Female | 174 | 43.9 | |
| Age | Under 25 | 36 | 9.1 |
| 26–35 | 136 | 34.3 | |
| 36–45 | 53 | 13.4 | |
| 46–55 | 87 | 22.0 | |
| Above 50 | 84 | 21.2 | |
| Education | Below high school | 87 | 22.0 |
| College | 172 | 43.4 | |
| Master | 137 | 34.6 | |
| Income | Below 20,000 | 17 | 4.3 |
| 20,001–30,000 | 19 | 4.8 | |
| 30,001–40,000 | 51 | 12.8 | |
| 40,001–50,000 | 167 | 42.2 | |
| Above 50,001 | 142 | 35.9 | |
| Companions | Alone | 38 | 9.6 |
| Couples | 84 | 21.2 | |
| Family | 51 | 12.9 | |
| Friends | 223 | 56.3 |
| Construct | Number of Items | Cronbach’s α Value |
|---|---|---|
| Dining | 5 | 0.825 |
| Ambience | 4 | 0.834 |
| Local identity | 4 | 0.828 |
| Staff service | 5 | 0.955 |
| Experiential activities | 5 | 0.889 |
| Variables | Gender | Age | Education | Income | Companions | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F-Value | p-Value | F-Value | p-Value | F-Value | p-Value | F-Value | p-Value | F-Value | p-Value | |
| Local dining | 1.375 | 0.875 | 45.936 | 0.000 * | 13.711 | 0.000 * | 34.714 | 0.000 * | 7.705 | 0.000 * |
| Ambience | 108.668 | 0.002 * | 74.668 | 0.000 * | 11.043 | 0.000 * | 39.864 | 0.000 * | 22.705 | 0.000 * |
| Local identity | 0.452 | 0.916 | 13.861 | 0.000 * | 5.561 | 0.004 * | 22.846 | 0.000 * | 10.986 | 0.000 * |
| Staff service | 3.198 | 0.163 | 20.690 | 0.000 * | 0.830 | 0.437 | 11.640 | 0.000 * | 11.608 | 0.000 * |
| Experiential activities | 6.440 | 0.146 | 64.161 | 0.000 * | 2.331 | 0.099 | 41.881 | 0.000 * | 21.495 | 0.000 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.-P. Application of the New Importance–Performance Analysis Method to Explore the Strategies of Rural Outdoor Dining Experiences in Taiwan. J. Risk Financial Manag. 2024, 17, 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17050208
Li S-P. Application of the New Importance–Performance Analysis Method to Explore the Strategies of Rural Outdoor Dining Experiences in Taiwan. Journal of Risk and Financial Management. 2024; 17(5):208. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17050208
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shang-Pin. 2024. "Application of the New Importance–Performance Analysis Method to Explore the Strategies of Rural Outdoor Dining Experiences in Taiwan" Journal of Risk and Financial Management 17, no. 5: 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17050208
APA StyleLi, S.-P. (2024). Application of the New Importance–Performance Analysis Method to Explore the Strategies of Rural Outdoor Dining Experiences in Taiwan. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 17(5), 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm17050208






