Abstract
To date, effectively controlling resistant weeds has been a great challenge in modern agricultural production. Developing new modes of action of herbicides would be an efficient, convenient, and timely means of controlling resistant weeds. In particular, new modes of herbicide action do not appear to have evolutionary resistance or cross-resistance with existing herbicides. However, a few successful herbicides with new modes of action (MoAs) have been marketed in the past 20 years. In this paper, we analyzed limiting factors for the slow development of novel herbicide MoAs. We then summarized the positive herbicide targets for the herbicides that have been discovered in recent years, such as Solanyl Diphosphate Synthase (SPS), Fatty Acid Thioesterase (FAT), Plastid Peptide Deformylase (PDEF), and Dihydroxy-Acid Dehydratase (DHAD). Some commercial herbicide varieties have been obtained based on novel herbicide targets, such as Homogentisate Solanesyltransferase (HST) and Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenase (DHODH). This provides a new reference and idea for herbicide molecular design in the future. In addition, some practical and efficient methods were mentioned for the rational design, discovery, and development of targeted herbicides development. In order to overcome the adverse conditions of compound druggability, prodrug strategies are also used in herbicide development, which can optimize the administration, permeability, absorption, and distribution of the original drug molecule or a candidate compound and may provide more possibilities for the development of new herbicides. The development of new herbicides is fascinating, the challenges and rewards are great, and the path to success is becoming more apparent.
1. Introduction
Since the 1870s, the rise of organic chemistry prompted agrochemical research to enter the era of organic agrochemicals. Organic agrochemicals display the advantages of having a wide range of applications and good crop safety. For example, glyphosate, the low-use rate sulfonylurea and imidazolinone herbicides, as well as the aryloxyphenoxypropionate and cyclohexanediones families display these advantages. Agrochemicals are an efficient and convenient method to reduce food production losses [1,2,3]. It is undeniable that agrochemicals have brought about an increase in food production, but the disadvantages that cannot be ignored have gradually emerged through their indiscriminate use [4]. In particular, some herbicide varieties that were developed early, such as paraquat, showed high toxicity to humans and other beneficial organisms. The good news is that most of them have been banned. In modern agricultural production, scientists focus on developing new green agrochemicals with high selectivity and low-use rates, that are environmentally friendly and low-cost [5,6].
The current development of new herbicides still faces major challenges [7,8]. The development of herbicides with new MoAs is urgently needed in order to combat the growing number of herbicide-resistant weeds. As we know, weed populations have evolved resistance under herbicide exposure. Thus, the development of herbicides with novel mechanisms of action is an important way to control resistant weeds. However, despite the discovery of a few novel herbicide targets, to minimize the risk of failure, most scientists remain focused on existing herbicide targets. After the year 2000, the discovery of new agrochemical varieties usually required the screening of more than 100,000 compounds, which takes 8–10 years and costs more than 200 million dollars, which significantly increases the risk and cost of drug development [6]. Thus, a good herbicide target is key to the development of new herbicides. Rational molecular design methods can improve the efficiency of herbicide development, reduce the risk of failure, and save unnecessary costs. The main goals of this paper are to outline the novel targets for herbicide development and to provide an efficient method for herbicide discovery. Obviously, this review does not cover all the known targets or rational drug design approaches. We just present a representative example and hope that this research will be helpful for the development of new herbicides in the future.
2. Herbicide Resistance Risk
The first synthetic auxin herbicide (2,4-D) was commercially released in the 1940s, which opened a new era of weed control in modern crop production and was used for the selective control of broadleaf weeds in cereal grain crops [9,10]. Subsequently, a series of highly effective selective herbicides were developed based on specific herbicide targets. Herbicides are becoming most widely used in agriculture. Although the existing herbicides play an important role in agricultural production, the herbicide-resistant weeds are still at risk of getting out of control. The rapid development of weed resistance due to the long-term use of a single type of herbicide resulted in the control effect of herbicides, that is, a significant reduction or even loss of control effectiveness [8]. Since 1956, when the first resistant weed Daucus carota L. was identified, the number of resistant weeds has increased by leaps and bounds. Statistics from the International Survey of Herbicide Resistance Weeds show that more than 500 species of weeds worldwide have evolved resistance to one or two known herbicides. Of all the herbicides, weeds have developed severe resistance to targeted acetolactate synthase (ALS) herbicides, and the number of resistant weeds has reached 171 (Table 1). Existing research shows that resistance to the herbicides that target ALS is mainly caused by amino acid mutations on the target [11].

Table 1.
Major herbicide targets and the number of herbicide-resistant weeds by site of action (including cross-resistant weeds).
Herbicide-resistant weeds are difficult to manage once they are established. There is no timely and effective way to stop the increasing number of resistant weeds. In particular, the number of cross-resistant weeds and multiple-resistant weeds is increasing year by year. Generally, the cross-resistant weed is conferred by a single mechanism and is normally restricted to two or more herbicides with the same mode of action. The herbicide-resistant mechanism can be target-site-based, or non-target-site-based. For example, weeds that develop resistance to targeted ALS herbicides are mainly produced by target mutations (A122G, P197T, and W574L). For non-target-site-based resistance, the insensi-tivity of the weeds to the herbicides results from enhancing their metabolism and reducing translocation. Unlike this, multiple-resistant weeds usually involve two or more mechanisms of herbicide action [12]. One of the most successful strategies for managing herbicide-resistant weeds is interchangeably applying multiple types of herbicides, especially herbicides with a totally new mechanism of action. However, lack of effective, alternative, and novel herbicide MoAs has resulted in resistant weeds spreading across major farmlands, complicating weed management. For example, resistant Echinochloa crusgalli (L.), which looks very similar to rice, has strong adaptability and a wide distribution, and is quickly becoming the most serious type of weed in rice fields. Thus, there is an urgent need for the development of herbicides with novel modes of action for agricultural production.
3. Limiting Factors in Studying Novel Herbicide MoAs
Many specific proteins that take part in plant biochemical and/or physiological pathways are used as targets for herbicide development. This mainly includes the following categories: the photosynthesis process, cell division and growth, cellular metabolism, and the material transportation process. However, just a few new successful herbicide targets have been used to develop herbicides over the past two decades. Longer development times and decreased success rates, the rising cost of development [13], agrochemical industry consolidation, and escalating regulatory and environmental requirements [2] have all lead to a halt in research on novel herbicide modes of action. Another important factor is the use of a transgenic crop [14] and bioagrochemicals [15]. For example, the commercialization of glyphosate-resistant (GR) crops has further exacerbated the dominant product of glyphosate in herbicides worldwide [16,17]. The adoption of genetically modified (GM) crops has revolutionized weed management and reduced investments in research on new targets [18]. In particular, the main crops, including glyphosate-resistant (GR) crops, soybean, maize, canola, and cotton, have been commercialized and have carried out large-scale promotion [19], further compressing the market space for other herbicides. Considering that the herbicide market for the three major GR crops has been devalued, the profit margin of the new herbicides is getting smaller and smaller. Most importantly, GR wheat [20] and rice [21] will eventually be introduced into the market in the future, which will further cut down the efforts for the discovery of new herbicide targets. Secondly, the influence of industry consolidation occurred even before the introduction of GR crops. Agrochemical industry consolidation has resulted in tremendous attrition in the number of scientists engaged in this field of research [22]. A few remaining research groups have focused on individual promising targets, leading to fewer studies on the targets of diverse herbicides. The attention of weed scientists has largely been directed towards finding new herbicides based on existing targets due to a dramatic increase in the use of herbicides around the globe. Both reasons have probably contributed to the stagnation seen in the development of novel herbicide modes of action. On the other hand, the risk of developing novel herbicide MoAs has significantly increased because that new product requires not only excellent biological activity, but must also conform to the envi-ronmental requirements and toxicological regulations. Thus, it is also more attractive to introduce familiar compounds with old modes of action for agrochemical research and development institutions [23].
In recent years, the exploration of new MoAs has become a popular area, mainly due to the increasingly serious problem of weed resistance. All over the world, more and more resistant weed biotypes have appeared and the number of resistant weeds is continuing to grow. The most common way to effectively control resistant weeds is to alternate the use of different herbicides with different MoAs. However, multiple-resistant weeds, which tolerate two or more types of herbicides simultaneously, are becoming more and more widespread. Furthermore, they make weed management more challenging [24]. Therefore, the development of herbicides with novel mechanisms of action is urgently needed in order to control multiple-resistant weeds. In the long run, herbicide-resistant weeds are inevitable, and scientific and rational weed management is the primary solution. The efficient way is to develop herbicides with new modes of action, with no further resistance or cross-resistance to the existing herbicides.
4. Novel Potential Herbicide Targets
Research into herbicide targets began in the middle of the last century. There is no clear definition to describe a good herbicide target site. As Duke, S. O. mentioned [23], the crucial consideration is that blocking the function of a target is fatal and, as a result, plant survival is unrecoverable. Inhibition of a relatively small percentage of the target will cause serious injury to plants, followed by death. The biological function of the target is irreplaceable in the organism. Last cntury, using physiological and biochemical technology, many herbicide targets were determined. Later, high-throughput in vitro screening was used to discover potential herbicide targets. More recently, ‘omics’ approaches have been used to determine the targets of natural products or other bioactive molecules [23]. Using a molecular probe to study plant physiological and biochemical processes is becoming a more and more popular method to confirm potential herbicide targets [25].
4.1. The Discovery of New Targets Based on Known Herbicides
4.1.1. Solanyl Diphosphate Synthase (SPS)
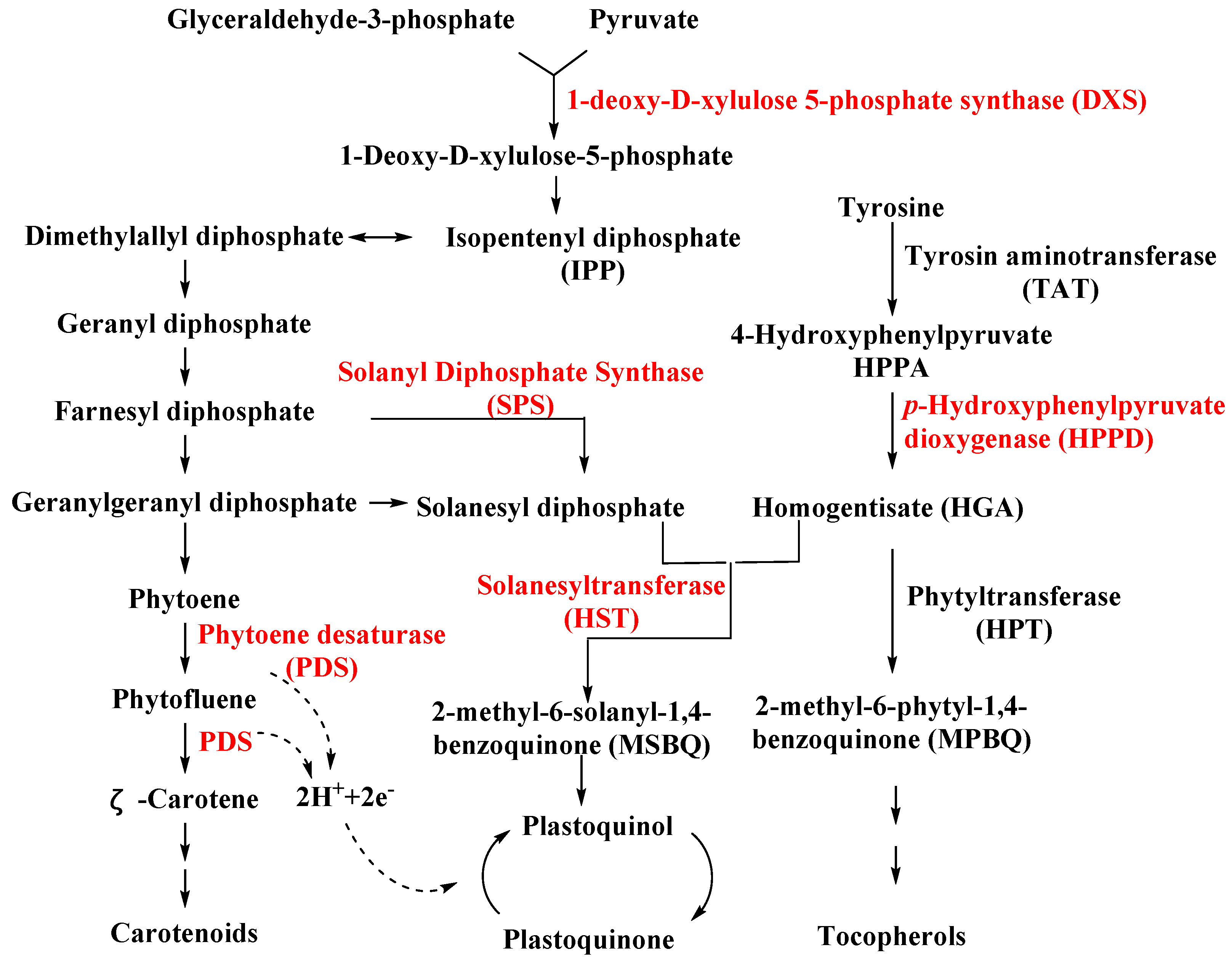
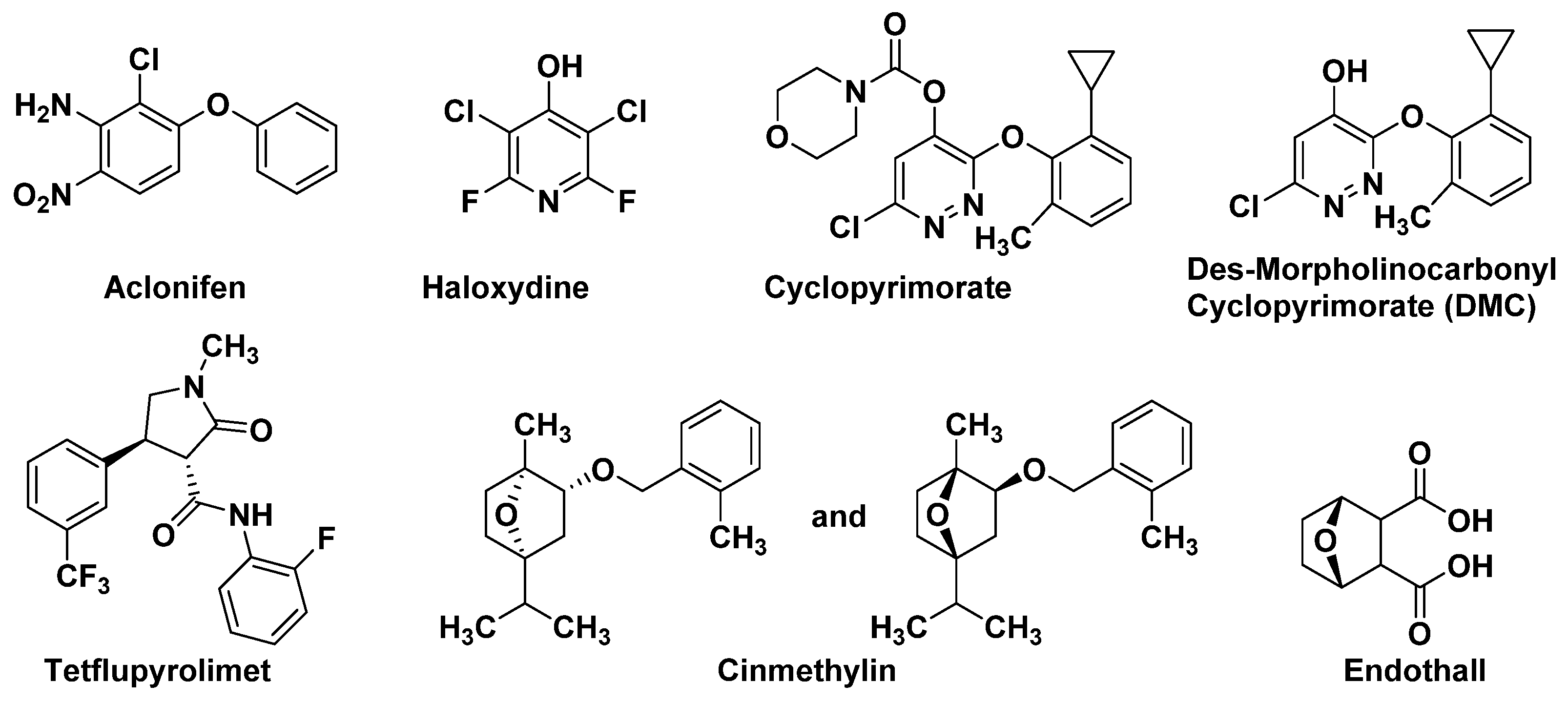
SPS is an important enzyme for plastoquinone synthesis, which catalyzes the multi-step condensation reaction of isopentenyl diphosphate and farnesyl diphosphate to form solanesyl diphosphate (Figure 1) [26]. Aclonifen (Figure 2), a relatively old diphenylether herbicide, caused the bleaching of treated plants. Recently, the binding site of aclonifen was confirmed via the inhibition of SPS and by blocking the biosynthesis of geranyl diphosphate [27,28]. A plant possesses three subtypes of SPS encoded by three genes: SPS1 and SPS2, which are localized in the chloroplast and involved in plastoquinone synthesis, and SPS3, which is involved in ubiquinone synthesis [29,30]. Existing research results show that aclonifen only inhibits SPS1 and SPS2, and has no response to SPS3. Herbicides that target HPPD have been used for many years and have achieved remarkable results in terms of herbicidal efficacy and safety. However, there has been not a significant breakthrough over the years for herbicides that target SPS. The main reason for this is that, for a long time in the past, the mechanism of action of SPS was not clear, and it was uncertain whether SPS would become a new herbicide target. Now that these problems have been solved, there will be more novel inhibitors targeting SPS based on the Aclonifen compound.
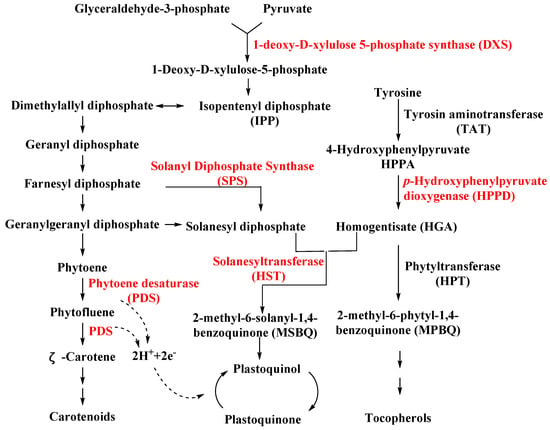
Figure 1.
Biosynthesis pathways for carotenoids, plastoquinone, and tocopherols in plant. The herbicide target is indicated by the red color.
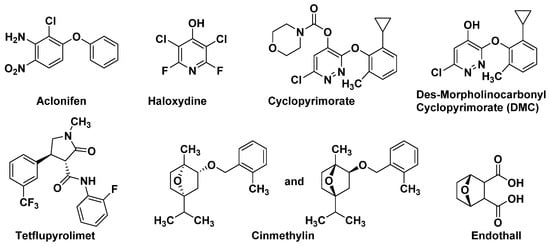
Figure 2.
The structures of the inhibitors with new MOAs.
4.1.2. Homogentisate Solanesyltransferase (HST)
HST is another novel bleaching herbicide target that catalyzes the prenylation and decarboxylation of homogentisate (HGA) to form 2-methyl-6-solanesyl-1,4-benzoquinol (MSBQ) in the plastoquinone biosynthesis pathway (Figure 1) [31,32,33]. Plastoquinone, as the important cofactor, takes part in the biosynthesis process of carotenoids. Blocking the biosynthesis of carotenoids will interrupt the normal photosynthesis of plants, which leads to bleaching and death. Haloxydine (Figure 2) is a well-known HST inhibitor. Nevertheless, it has not yet been used commercially. Another HST inhibitor, cyclopyrimorate (Figure 2) as a rice herbicide, was invented by Mitsui Chemicals Agro Inc. and was launched in 2019 in Japan. Its metabolite product, cyclopyrimorate, strongly inhibited HST in crude E. coli extracts [34]. As a downstream protein of SPS and HPPD, with the successful launch of cyclopyrimorate, more efficient targeting of the HTS inhibitor can be quickly obtained using targeted herbicide molecular rational design methods. With the extensive use of HPPD herbicides, we cannot prevent the emergence of HPPD-resistant weeds, so herbicides that target HTS may be used as an alternative agent in order to control resistant weeds in the future.
4.1.3. Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenase (DHODH)
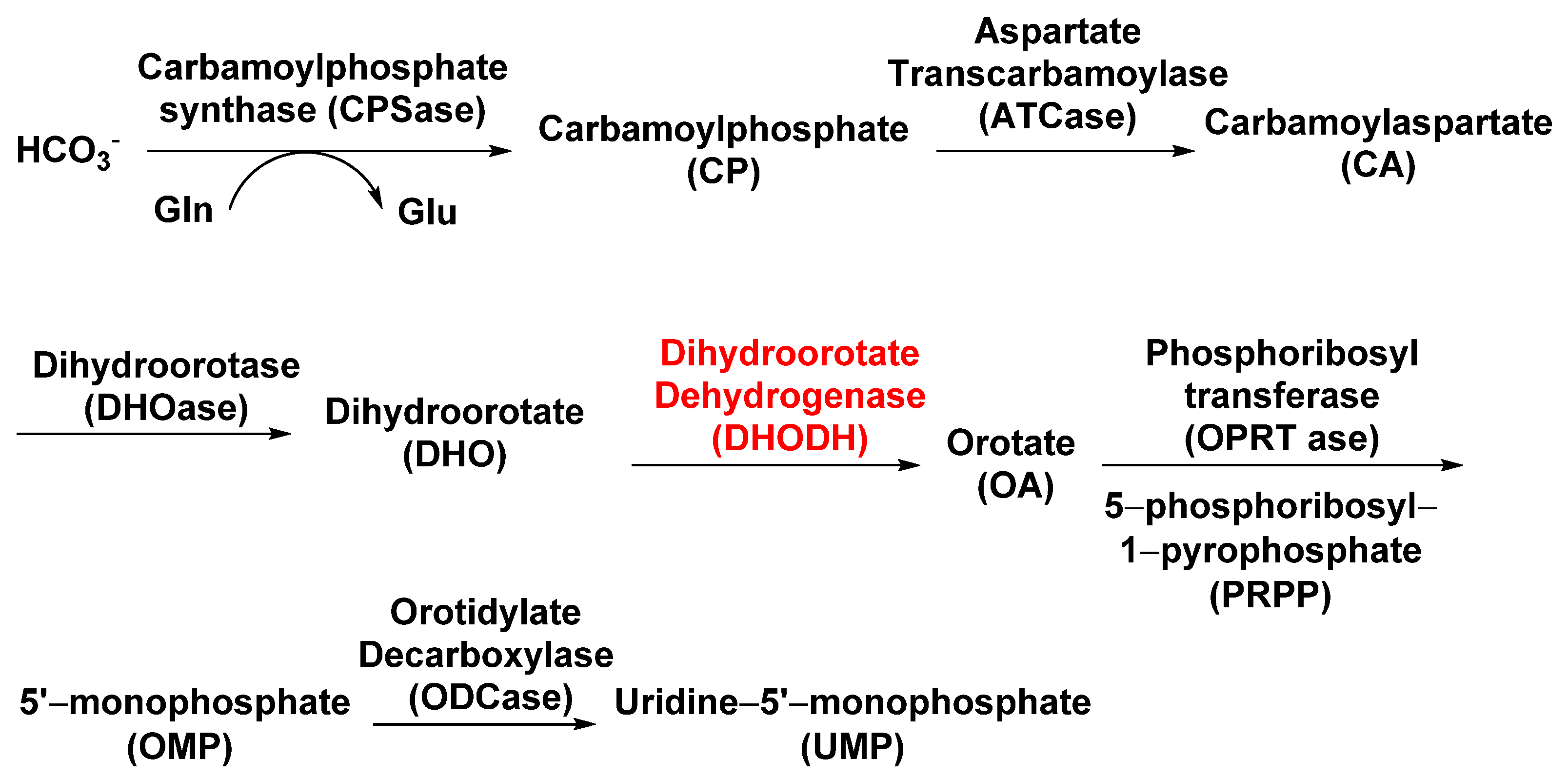
Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH; EC 1.3.99.11), located on the outer surface of the inner mitochondrial membrane, catalyzes the fourth step of pyrimidine biosynthesis [35]. De novo pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthesis consists of six enzymatic steps (Figure 3), which are evolutionarily conserved in all the species examined [36]. Inhibition of this pathway is lethal to most organisms. Tetflupyrolimet (Figure 2) is a novel targeting DHODH inhibitor that can interfere with de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis, and is expected to be commercialized in 2024. The target site of tetflupyrolimet was identified by adopting a combination of forwarding genetic screens and metabolomics approaches, and by testing the intrinsic affinities of analogs with the enzyme in vitro using biochemical methods [29]. The successful development of DHODH-targeted drugs will bring more selectivity to the management of resistant weeds.
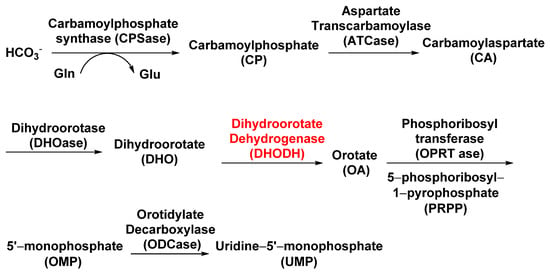
Figure 3.
The biosynthesis pathway of the pyrimidine nucleotide. The potential herbicide target is indicated by the red color.
4.1.4. Fatty Acid Thioesterase (FAT)
In plants, fatty acid thioesterase (FAT) acts on the lipid biosynthesis pathway by mediating the release of fatty acids (FA) from its acyl carrier protein (ACP) and transferring them to the endoplasmic reticulum [37,38]. Cinmethylin (Figure 2), a natural product-like benzyl ether derivative of 1,4-cineole, is an old herbicide that was commercialized in 1989 [39]. The mode action of cinmethylin was not clear at first. Later, Campe R., et.al. confirmed that cinmethylin binds to FAT proteins from Lemna and Arabidopsis. using a fluorescence-based thermal shift assay. They also demonstrated the co-crystallization of cinmethylin within the FAT enzyme [37].
4.1.5. Serine/Threonine Protein Phosphatases (PPs)
Phosphorylation plays a vital role in almost every aspect of cell life, and is one of the dominant means of controlling protein function and regulating most biological processes. PPs were divided into three subclasses—phosphoprotein phosphatases, metal-dependent protein phosphatases, and aspartate-based phosphatases. In plants, serine/threonine protein phosphatase belongs to the phosphoprotein phosphatase sub-class [40]. Endothall (Figure 2) was developed in the 1950s. Endothall inhibits the activity of alfalfa serine/threonine PP2A, and to a lesser extent, inhibits serine/threonine PP1, which further affects the coordination of chromosomal and microtubule events during plant cell mitosis [25,41].
4.2. Exploring New Herbicide MoAs Based on Natural Products
4.2.1. Dihydroxy-Acid Dehydratase (DHAD)
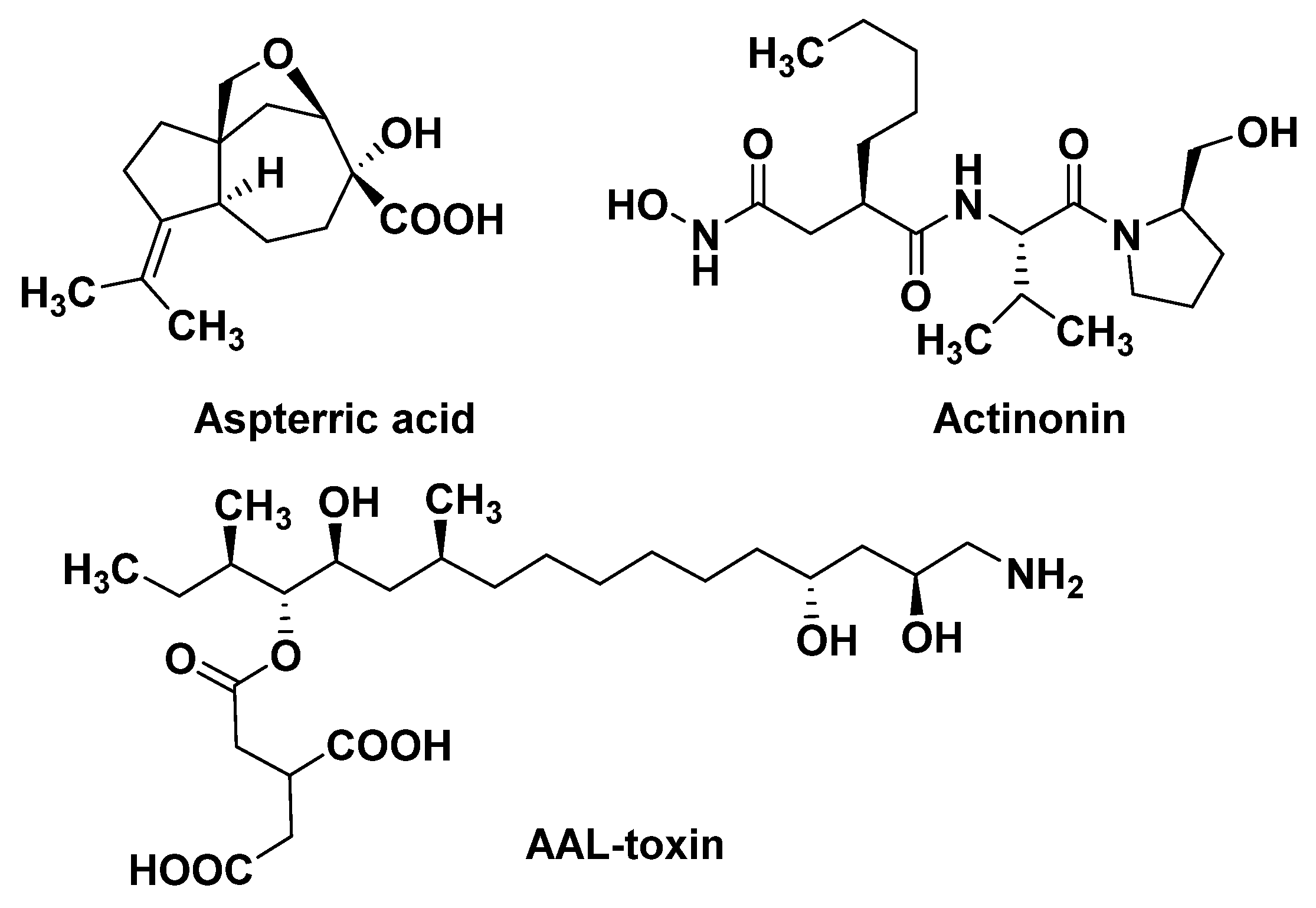
The branched chain amino acid (BCAA) biosynthetic pathway consists of three common enzymes: acetolactate synthase (ALS), acetohydroxy acid isoreductase (KARI), and dihydroxy acid dehydratase (DHAD). DHAD is involved in the synthesis of essential amino acids in plants. It catalyzes the dehydration reaction of α, β-dihydroxy acid to generate the precursor α-keto acid of leucine, isoleucine, and valine in the BCAA pathway. DHAD is highly conserved in different plant species and is not present in animals. Therefore, DHAD is considered to be an ideal broad-spectrum herbicide target. Further work has demonstrated that aspterric acid (Figure 4) targets DHAD by an innovative resistant-gene-directed discovery approach [42,43].
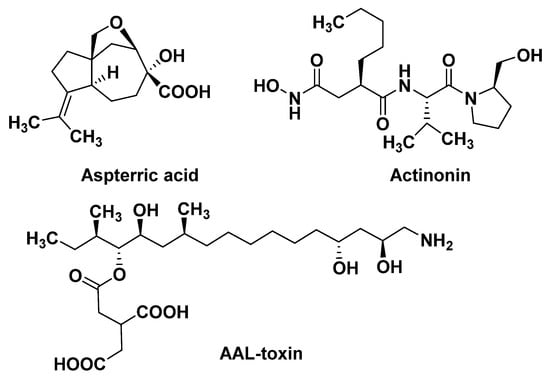
Figure 4.
The structures of natural products with new MOAs.
4.2.2. Plastid Peptide Deformylase (PDEF)
Peptide deformylase mainly exists in prokaryotes and higher plants, but is absent in mammalian cells. PDEF acts on the translation process of new proteins, and its function is to catalyze the hydrolysis of the N-formyl group from the initiating methionine. Actinonin (Figure 4), a target PDEF inhibitor, leads to stunting, bleaching, and necrosis of the treated weed [44,45,46]. Since the Adams group first discovered PDEF from the initial extracts of Escherichia coli and Bacillus stearothermophilus in 1968 [47], it has been widely studied by drug molecular designers, and has also been used as a target for crop antimicrobial drugs, which have been thoroughly studied. However, the recent report that the natural product Actinonin can act as a herbicide to inhibit plant growth clearly pushes the study of PDEF into new areas. Of course, studying it as a weed control target, as opposed to an antibiotic target, raises a lot of different questions. For example, it has been reported that the isoenzyme of PDEF is found in human mitochondria [48], and PDEF inhibitors may have inhibitory effects on it, which indicates the potential safety risk of targeting PDEF inhibitors.
4.2.3. Ceramide Synthase
Ceramide synthase not only forms a complex lipid skeleton for sphingolipid biosynthesis, but also serves as a target for many microbial toxins [49]. Ceramide synthase catalyzes the acylation of sphinganine, sphingosine, and other long chain sphingoids to form their N-acyl derivatives. The AAL-toxin (Figure 4) can inhibit ceramide synthase, leading to the rapid accumulation of sphingosine and its substrate derivative phytosphingosine. Sphinganine and phytosphingosine are both highly phytotoxic. They cause similar symptoms to the AAL-toxin, and also affect plasma membrane integrity [50]. In addition, at lower concentrations, AAL-toxin may induce cell apoptosis caused by plasma membrane dysfunction. However, AAL-toxin, as an analogue of the fumonisins, is highly toxic to mammals [51].
To date, more than 200,000 secondary metabolites have been identified. Only a small number of compounds have determined modes of action, and many potential herbicide targets have been found. In this short chapter, we provide some brief examples of natural phytotoxins with novel MoAs, such as Trp synthase [52], Enoyl reductase [53], Orn carbamoyl transferase [54], CF1 ATPase [55,56], Peptide deformylase [57], Golgi assembly [58], H+-ATPase [59], and RNA polymerase [60]. Natural products are an important source of herbicides with new MoAs, and we believe that there will be more efficient and safer herbicides developed based on the natural products soon.
4.3. Exploration of Potential Herbicide MoAs Based on Their Biochemical Mechanisms
4.3.1. DNA Gyrase
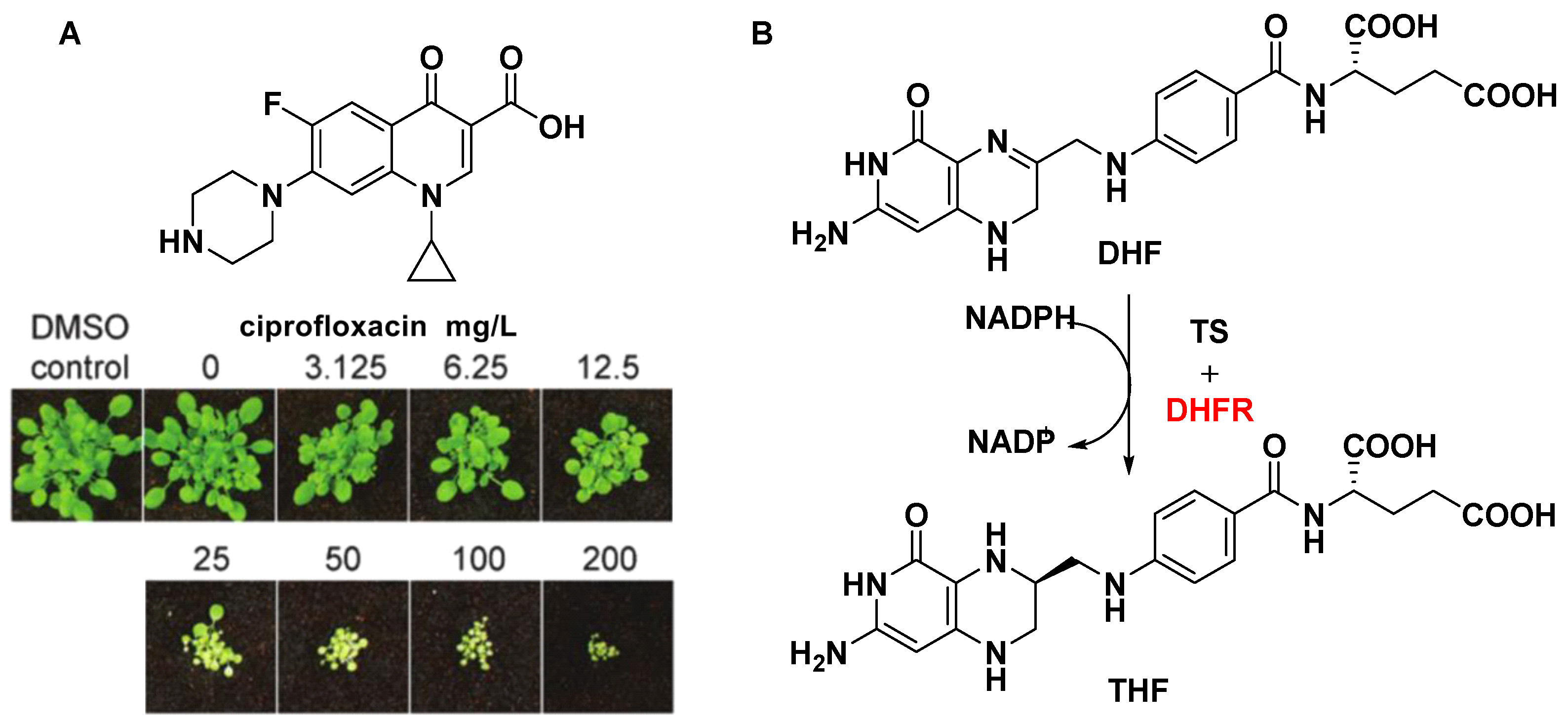
DNA topoisomerases, a key target for anticancer drugs and antibiotics, are classified as type I and II according to whether their reactions proceed via transient single (I)- or double (II)-stranded breaks in DNA. DNA gyrase is an indispensable type II topoisomerase, and affects proper plant growth. Michael D. W. [61] and Anthony M. [62] have shown that ciprofloxacin and its analogues inhibited DNA gyrase and displayed post-emergent herbicidal activity (Figure 5A). Although DNA topoisomerases are present in both animals and plants, and the concentration of the drug required to achieve plant death is high, there is no denying that DNA topoisomerases are attractive targets for the design of novel drug molecules based on biochemical mechanisms.
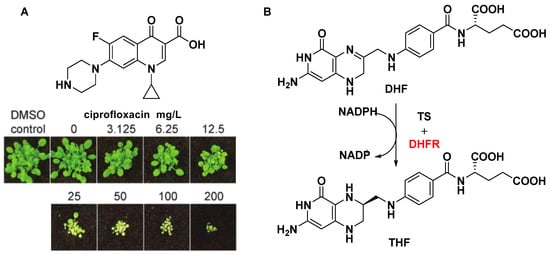
Figure 5.
(A) Post-emergent herbicidal activity of ciprofloxacin. (B) Part of the folate biosynthesis pathway. The potential herbicide target is indicated by the red color.
4.3.2. Dihydrofolate Reductase (DHFR)
Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) is another key enzyme in the folate biosynthetic pathway, relating to the synthesis of DNA precursors and some amino acids [63]. Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) catalyzes the reduction of dihydrofolate (DHF) into THF using NADPH as the reducing agent (Figure 5B). Unlike most prokaryotes and eukaryotes, DHFRs encodes a gene for a bifunctional protein composed in protozoa and plants. Another domain is thymidylate synthase (TS), which also plays an important role in the folate pathway [64]. Using a genetic knockout analysis, a recent study showed that DHFR can be regarded as a potential herbicide target due to the necessity of two isoforms of DHFR for seed development [65].
Since the rapid development of functional genomics, proteomics, structural biology, and gene-editing technology, many potential herbicide targets have been discovered, such as Mg protoporphyrin monomethylester [66], imadazoleglycerol phosphate dehydratase [45], cystathionine β-lyase [67], carbonic anhydrase [68], transketolase [69], and flavanone 3-hydroxylase [70].
5. Targeted Herbicide Discovery and Development
More and more researchers are focusing on targeted drug discovery and development. In recent years, the rapid development of life sciences has greatly promoted research into and the development of new agrochemicals, which has established a series of potential herbicide targets. The reasonable design and optimization of lead compounds are crucial steps for the development of targeted herbicides. The discovery of lead compounds is usually optimized through many rounds of a design–synthesis–test–analysis cycle [6]. Through the re-optimization of the lead structure, active tests in vivo and in vitro have obtained candidate compounds with practical applications to complete the development of commercial products. Throughout the process, a good lead structure often determines the success rate of herbicide development. So, our first concern is how to obtain the leading structure.
First, natural products are an important source for new lead compounds [6,71]. Natural products are advantageous due to their wide source, novel structure, unique mode of action, good environmental compatibility, lesser toxicity and fewer side effects. Statistics show that the proportion of agrochemical molecules that are related to natural products reached more than 60% [72]. Despite the fact that there are few successful cases of natural products being used directly as herbicides, in the past, investigators were developing many herbicides by modifying natural products. For example, herbicides that target HPPD, including mesotrione, control the widest possible range of weed species, and the key skeleton of mesotrione comes from leptospermone which is separated from bottlebrush plant extracts [73].
Random synthesis and screening [74] is also a practical strategy to discover new lead compounds. Random synthesis screening is usually based on existing active herbicide molecules, and employs rational structural derivation in order to obtain lead compounds with similar or better biological activities. The other well-known methods, such as the “Me too” strategy, scaffold hopping, and bio-isostere, obtain the lead structure with the same mechanism of action. Although they have been proven to be the most successful new drug discovery methods at present, a significant disadvantage of these methods is the high research and development costs, lower research and development success rates, and the difficulty in obtaining competitive new products with novel MoAs. Besides this, the intermediate derivatization method (IDM) is also used to apply various synthetic methods utilizing key intermediates to construct compounds with novel structures, and to obtain lead compounds combined with biological activity screening, which also plays an important role in the development of drug molecules [75]. Depending on the functionality and structural characteristics of the intermediates, in general, the intermediate derivatization method (IDM) contains three types, i.e., Common Intermediate Method (CIM), Terminal Group Replacement Method (TRM), and Active compound Derivatization Method (ADM).
Second, computer-aided drug design (CADD) is an effective technology for drug research and discovery, including structure-based drug design (SBDD) and ligand-based drug design (LBDD) [76,77]. The effect of the herbicide on the weed is a consequence of the interaction of the ligand (herbicide) and the target. That is to say, when the herbicide is absorbed by the weeds and transported to a specific site of action to exert its efficacy, the pharmacological activity of herbicide is related to the spatial arrangement and electronic nature of the atoms and the way these atoms interact with their action target [76]. Because of this, we can computationally simulate the binding mode of the inhibitor to the specific site of the target (Figure 6). Computer-aided drug design can be used to identify new inhibitors via pharmacophore derivatization, molecular dynamics analysis, quantum chemical (QM), and combined QM, or high-throughput virtual screening can be used to identify new inhibitors based on large and available molecular databases.
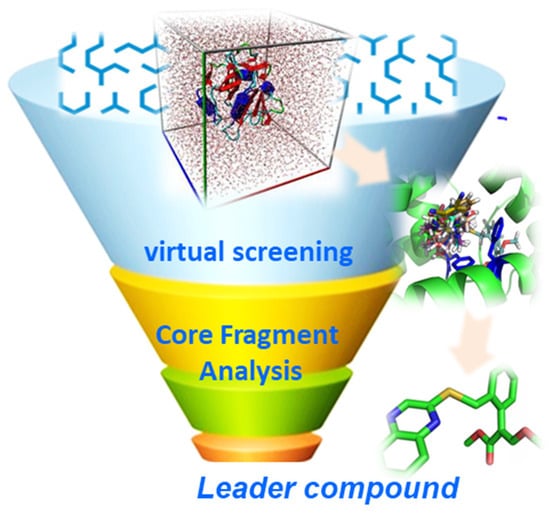
Figure 6.
The method of computer-aided drug design (CADD).
In recent years, more and more unknown proteins have been identified and may become positive herbicide targets. Although the detailed 3D structures of these proteins are still unknown, we can use homology modeling or AlphaFold to predict the structure of the protein [78], or an online server to predict the structure of the protein (swiss-mode). With the rapid development of biotechnology and AI technology, clarifying the biological function and the mechanisms of the protein, analyzing the three-dimensional structure of the protein, identifying the specific action sites of the protein, and establishing a fast and accurate activity evaluation system in vitro, and faciliting the rational design of targeted drug molecules is possible, all of which can significantly improve the success rates of lead structure discovery [79].
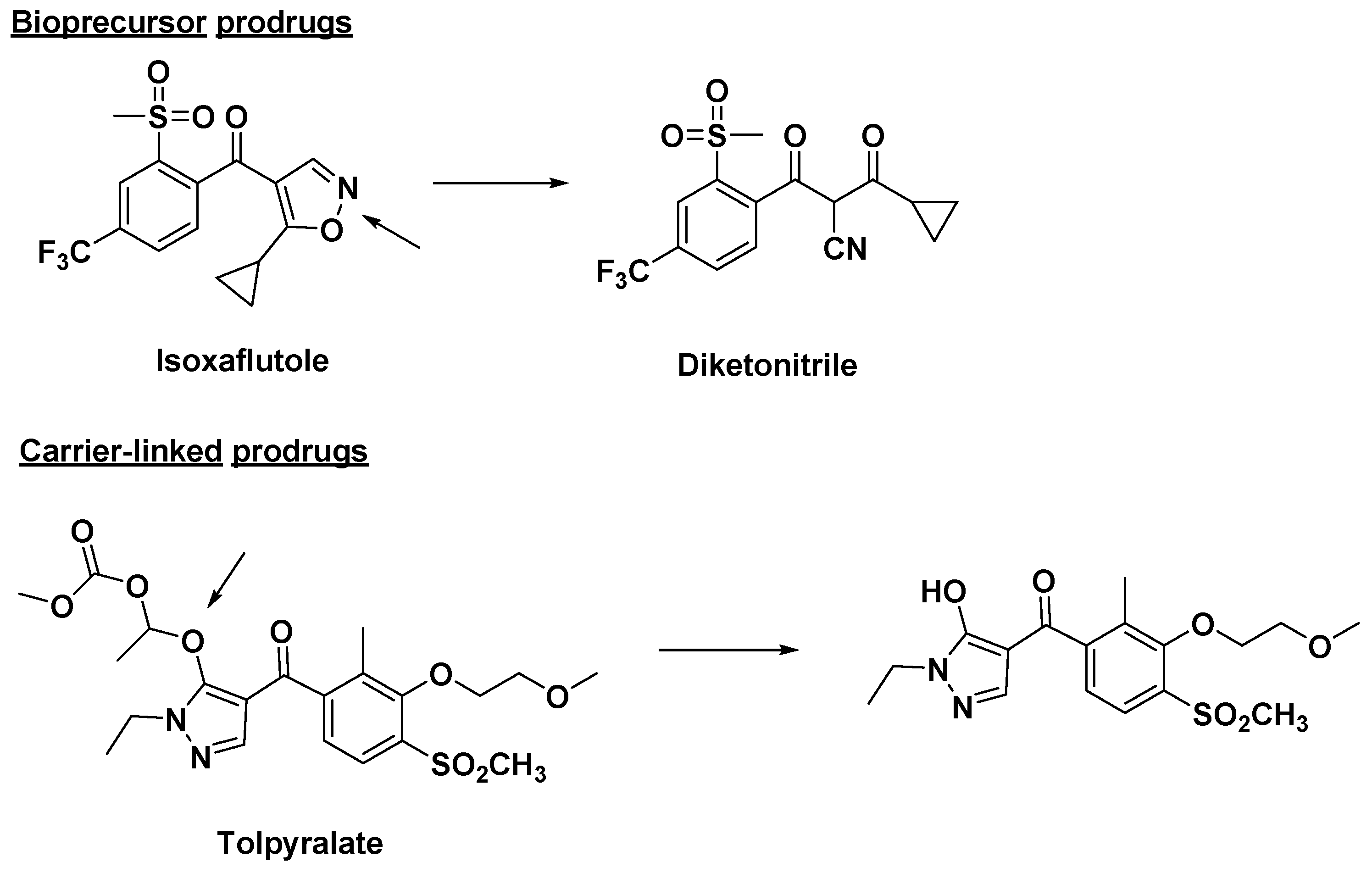
In addition, prodrug strategy during drug development has become an established tool for improving the pharmacological activity of compounds. The first intentionally designed prodrug was probably methenamine, which was designed by Schering in 1899. Until 1958, Adrien Albert first proposed the concept of a “Prodrug” when studying the selective toxicity of drug molecules [80]. The concept of prodrugs was further improved in 2008 by Jarkko Rautio based on Adrien Albert’s prodrug theory. In Rautio’s opinion, prodrugs are bioreversible derivatives of drug molecules that undergo enzymatic and/or chemical transformations in vivo in order to release drug molecules that are capable of exerting their intended pharmacological activity [81]. Later, the definition given by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) was developed. They stated that a prodrug is a chemically modified active drug that must undergo biological and chemical transformation before it can exert a pharmacological response [82]. Prodrugs are mainly divided into bioprecursor prodrugs and carrier-linked prodrugs [83,84]. Bioprodrugs are the result of the intramolecular modifications of the active pharmaceutical ingredients. The bioprecursor prodrugs do not contain carriers and yield ultimate active agents upon biotransformation through hydration (lactone or lactam), oxidation or reduction, or metabolic activity [81,85,86,87]. For example, a broad-spectrum herbicide, such as isoxaflutole, does not have a promoiety or carrier, but after biotransformation, diketonitrile is the metabolite of isoxaflutole which is the actual inhibitor and herbicide (Figure 7). For the carrier-linked prodrug, once it enters the organism, it undergoes enzymatic or non-enzymatic cleavage to release the originally active agent and carrier [82,88,89]. Types of carrier-linked prodrugs include esters, amides, phosphates, carbamates, carbonates, oximes, imines, and N-Mannich bases.
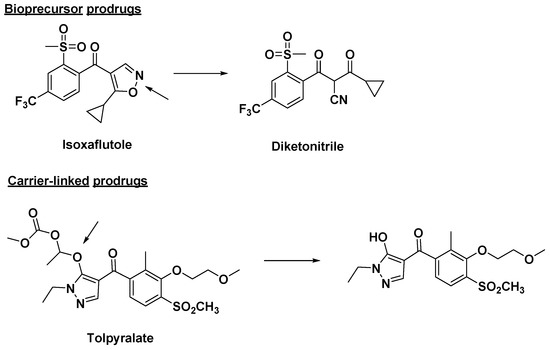
Figure 7.
Some bioprecursor pro-herbicides and carrier-linked pro-herbicides. Arrows indicate reaction sites for biological and chemical transformation.
Prodrug strategy has also attracted much attention in the field of agrochemical research. It was mainly used to optimize the administration, permeability, absorption, and distribution of the original drug molecule or a candidate compound. For example, appropriately increasing aqueous solubility or lipid solubility would be a mode of passive transport through biological membranes. Introducing a special functional group may change the absorption, conduction, or metabolism of drug molecules between organisms, which may also increase the selectivity of drug molecules, and prolong biological half-life time, as well as achieving tissue-targeted delivery [87,90,91]. At present, prodrug strategy can overcome the adverse conditions of compound druggability and has been widely used in the research and development of agrochemicals.
6. Conclusions and Outlook
The high risk of failure in developing new agrochemicals and commercialized glyphosate-resistant crops has limited the progress of the development of new herbicides. Using herbicides with new modes of action with no evolved resistance and no cross-resistance to existing herbicides is still a scientific and rational weed management strategy to slow down the rate of evolution of resistant weeds and effectively control existing resistant weeds. The demand for herbicides with new MoAs is driven by the emergence of more and more serious herbicide-resistant weeds and the environmental safety issues surrounding some older herbicides. Therefore, scientists are starting to pay more attention to developing new herbicide MoAs that are environmentally friendly with no evolved resistance. Fortunately, many novel targets for herbicide development have been obtained and introduced into the market, such as SPS, HST, DHODH, and FAT, as well as herbicides with new action targets. In addition, based on active natural products, many potential herbicide targets have been discovered using omics research methods.
With the development of organic pesticides in the green direction, with low toxicity and high efficiency, targets that differ from species to species will be most desirable. For example, DHAD is found only in plants and microbes, not in mammals. Therefore, an inhibitor that selectively targets DHAD would be safe for mammals. Generally, highly effective herbicides require targets that are irreplaceable and very sensitive to the inhibitor even at very low concentrations, which is also the reason why many enzymes in plants cannot be regarded as ideal targets. Moreover, the rapid development of GM crops also limits the progress of research into and the development of new MoA molecules. GM crops have made significant breakthroughs, but they also face ongoing controversy and the continued use of existing herbicides has further exacerbated the crisis of resistant weeds. Therefore, the government, scientific research institutions, enterprises, and growers should work together to vigorously encourage and support the research and development of new MoA herbicides, which will bring more options for the management of resistant weeds.
The identification of novel and effective herbicide targets is an important step in the development of targeted herbicides. Now, there are many ways to solve this problem. For example, the comprehensive use of bioinformatics, molecular biology, and pharmacology have unique advantages for the discovery of original targets. Most importantly, resolving the three-dimensional structure of the target protein is conducive to the realization of precise targeted drug molecular design. Combining computer-aided drug design technology, random synthesis and screening, and the intermediate derivatization method, the success rate of drug development, based on new herbicide MoAs, will be significantly improved. Furthermore, using a prodrug to optimize the administration, permeability, absorption, and distribution of the original drug molecules or a candidate compound may overcome the adverse conditions of compound druggability. Despite the remarkable progress made in the field of prodrug design, many key issues remain unresolved, especially how to choose a rational prodrug carrier in a targeted manner in the early stages. We predict that, in the future, more MoAs will be unearthed, more safer herbicides will be developed, and better solutions for the management of weeds and resistant weeds will be achieved.
Author Contributions
Investigation and data curation, B.H., Y.H., W.W. and W.Y.; writing—review and editing, B.H. and Y.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work has been supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2021YFD1700101) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20221002).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
References
- Mascarelli, A. Growing up with pesticides. Science 2013, 341, 740–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparks, T.C.; Lorsbach, B.A. Perspectives on the agrochemical industry and agrochemical discovery. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godfray, H.C.; Beddington, J.R.; Crute, I.R.; Haddad, L.; Lawrence, D.; Muir, J.F.; Pretty, J.; Robinson, S.; Thomas, S.M.; Toulmin, C. Food security: The challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Science 2010, 327, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enserink, M.; Hines, P.J.; Vignieri, S.N.; Wigginton, N.S.; Yeston, J.S. Smarter pest control. The pesticide paradox. Introduction. Science 2013, 341, 728–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Dong, J.; Lin, H.Y.; Wang, M.Y.; Li, X.K.; Zheng, B.F.; Chen, Q.; Hao, G.F.; Yang, W.C.; Yang, G.F. Pyrazole-isoindoline-1,3-dione hybrid: A promising scaffold for 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase inhibitors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 10844–10852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberth, C.; Jeanmart, S.; Luksch, T.; Plant, A. Current challenges and trends in the discovery of agrochemicals. Science 2013, 341, 742–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, S.O.; Owens, D.K.; Dayan, F.E. The growing need for biochemical bioherbicides. ACS Symp. Ser. 2014, 1172, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Service, R.F. Agriculture. What happens when weed killers stop killing? Science 2013, 341, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, G.E. The discovery and development of 2,4-D. Agric. Hist. Soc. 1967, 41, 243–254. [Google Scholar]
- Sterling, T.M.; Hall, J.C. Mechanism of action of auxins and the kinetics of cellular growth. In Herbicide Activity: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology; Roe, R.M., Burton, J.D., Kuhr, R.J., Eds.; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997; pp. 111–141. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Ge, L.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, L.; You, L.; Wang, D.; Liu, W.; Wang, J. A Trp-574-Leu mutation in the acetolactate synthase (ALS) gene of Lithospermum arvense L. confers broad-spectrum resistance to ALS inhibitors. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 158, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckie, H.J.; Tardif, F.J. Herbicide cross resistance in weeds. Crop Prot. 2012, 35, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, T.C. Insecticide discovery: An evaluation and analysis. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2013, 107, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, E.D.; Ciliberto, F.; Hennessy, D.A.; Moschini, G. Genetically engineered crops and pesticide use in U.S. maize and soybeans. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copping, L.G.; Menn, J.J. Biopesticides: A review of their action, applications and efficacy. Pest Manag. Sci. 2000, 56, 651–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, S.O.; Powles, S.B. Glyphosate: A once-in-a-century herbicide. Pest Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, G.; Barfoot, P. Environmental impacts of genetically modified (GM) crop use 1996–2015: Impacts on pesticide use and carbon emissions. GM Crops Food 2017, 8, 117–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, S.O. The history and current status of glyphosate. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, M.D.; Zelaya, I.A. Herbicide-resistant crops and weed resistance to herbicides. Pest Manag. Sci. 2005, 61, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.N. Weed control and species shift in bromoxynil- and glyphosate-resistant cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) rotation systems. Weed Technol. 2004, 18, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.X.; Huang, J.Q.; Wei, Z.M.; Yao, Q.H.; Wan, C.Z.; Lu, J.A. Engineering higher yield and herbicide resistance in rice by agrobacterium-mediated multiple gene transformation. Crop Sci. 2004, 44, 2206–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleby, A.P. A history of weed control in the United States and Canada—A sequel. Weed Sci. 2005, 53, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, S.O. Why have no new herbicide modes of action appeared in recent years? Pest Manag. Sci. 2012, 68, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranel, P.J.; Riggins, C.W.; Bell, M.S.; Hager, A.G. Herbicide resistances in Amaranthus tuberculatus: A call for new options. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 5808–5812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tresch, S.; Schmotz, J.; Grossmann, K. Probing mode of action in plant cell cycle by the herbicide endothall, a protein phosphatase inhibitor. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2011, 99, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlau, S.; Schroder, F.; Freigang, J.; Laber, B.; Lange, G.; Passon, D.; Kleessen, S.; Lohse, M.; Schulz, A.; von Koskull-Doring, P.; et al. Aclonifen targets solanesyl diphosphate synthase, representing a novel mode of action for herbicides. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 3377–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Lu, S. Plastoquinone and ubiquinone in plants: Biosynthesis, physiological function and metabolic engineering. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohara, K.; Sasaki, K.; Yazaki, K. Two solanesyl diphosphate synthases with different subcellular localizations and their respective physiological roles in Oryza sativa. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 2683–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, F.E.; Haesaert, G.; van Leeuwen, T.; Holden-Dye, L.; Crossthwaite, A.; Nauen, R. Pesticides modes of action and resistance: A perspective from the 2019 IUPAC congress. Outlooks Pest Manag. 2019, 30, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, L.; Saiki, R.; Tatsumi, K.; Nakagawa, T.; Kawamukai, M. Identification and subcellular localization of two solanesyl diphosphate synthases from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004, 45, 1882–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadre, R.; Frentzen, M.; Saeed, M.; Hawkes, T. Catalytic reactions of the homogentisate prenyl transferase involved in plastoquinone-9 biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 18191–18198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collakova, E.; DellaPenna, D. Homogentisate phytyltransferase activity is limiting for tocopherol biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2003, 131, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collakova, E.; DellaPenna, D. Isolation and functional analysis of homogentisate phytyltransferase from Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 and arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2001, 127, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shino, M.; Hamada, T.; Shigematsu, Y.; Hirase, K.; Banba, S. Action mechanism of bleaching herbicide cyclopyrimorate, a novel homogentisate solanesyltransferase inhibitor. J. Pestic. Sci. 2018, 43, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullrich, A.; Knecht, W.; Piskur, J.; Löffler, M. Plant dihydroorotate dehydrogenase differs significantly in substrate specificity and inhibition from the animal enzymes. FEBS Lett. 2002, 529, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zrenner, R.; Stitt, M.; Sonnewald, U.; Boldt, R. Pyrimidine and purine biosynthesis and degradation in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 805–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campe, R.; Hollenbach, E.; Kammerer, L.; Hendriks, J.; Hoffken, H.W.; Kraus, H.; Lerchl, J.; Mietzner, T.; Tresch, S.; Witschel, M.; et al. A new herbicidal site of action: Cinmethylin binds to acyl-ACP thioesterase and inhibits plant fatty acid biosynthesis. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 148, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umetsu, N.; Shirai, Y. Development of novel pesticides in the 21st century. J. Pestic. Sci. 2020, 45, 54–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, F.E.; Romagni, J.G.; Duke, S.O. Herbicides, cinmethylin. In Encyclopedia of Agrochemicals; Plimmer, J.R., Gammon, D.W., Ragsdale, N.N., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 754–757. [Google Scholar]
- Uhrig, R.G.; Labandera, A.M.; Moorhead, G.B. Arabidopsis PPP family of serine/threonine protein phosphatases: Many targets but few engines. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajsa, J.; Pan, Z.; Dayan, F.E.; Owens, D.K.; Duke, S.O. Validation of serine/threonine protein phosphatase as the herbicide target site of endothall. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2012, 102, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, S.O.; Stidham, M.A.; Dayan, F.E. A novel genomic approach to herbicide and herbicide mode of action discovery. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zang, X.; Yuan, S.; Bat-Erdene, U.; Nguyen, C.; Gan, J.; Zhou, J.; Jacobsen, S.E.; Tang, Y. Resistance-gene-directed discovery of a natural-product herbicide with a new mode of action. Nature 2018, 559, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.Z.; Patel, D.V.; Hackbarth, C.J.; Wang, W.; Dreyer, G.; Young, D.C.; Margolis, P.S.; Wu, C.; Ni, Z.J.; Trias, J.; et al. Actinonin, a naturally occurring antibacterial agent, is a potent deformylase inhibitor. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisson, C.; Britton, K.L.; Sedelnikova, S.E.; Rodgers, H.F.; Eadsforth, T.C.; Viner, R.C.; Hawkes, T.R.; Baker, P.J.; Rice, D.W. Crystal structures reveal that the reaction mechanism of imidazoleglycerol-phosphate dehydratase is controlled by switching Mn(II) coordination. Structure 2015, 23, 1236–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayan, F.E.; Duke, S.O. Natural compounds as next-generation herbicides. Plant Physiol. 2014, 166, 1090–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.M. On the release of the formyl group from nascent protein. J. Mol. Biol. 1968, 33, 571–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serero, A.; Giglione, C.; Sardini, A.; Martinez-Sanz, J.; Meinnel, T. An unusual peptide deformylase features in the human mitochondrial N-terminal methionine excision pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 52953–52963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, E.; Merrill, A.H. Ceramide synthase. Methods Enzymol. 2000, 311, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gechev, T.S.; Gadjev, I.Z.; Hille, J. An extensive microarray analysis of AAL-toxin-induced cell death in Arabidopsis thaliana brings new insights into the complexity of programmed cell death in plants. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 1185–1197. [Google Scholar]
- Duke, S.O.; Dayan, F.E. Clues to new herbicide mechanisms of action from natural sources. ACS Symp. Ser. 2013, 1141, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, P.; Sanjaya; Su, R.C.; Teixeira da Silva, J.A.; Chan, M.T. Plant native tryptophan synthase beta 1 gene is a non-antibiotic selection marker for plant transformation. Planta 2007, 225, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, F.E.; Ferreira, D.; Wang, Y.H.; Khan, I.A.; McInroy, J.A.; Pan, Z. A pathogenic fungi diphenyl ether phytotoxin targets plant enoyl (acyl carrier protein) reductase. Plant Physiol. 2008, 147, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Templeton, M.D.; Reinhardt, L.A.; Collyer, C.A.; Mitchell, R.E.; Cleland, W.W. Kinetic analysis of the L-ornithine transcarbamoylase from Pseudomonas savastanoi pv. phaseolicola that is resistant to the transition state analogue (R)-N delta-(N′-sulfodiaminophosphinyl)-L-ornithine. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 4408–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groth, G. Structure of spinach chloroplast F1-ATPase complexed with the phytopathogenic inhibitor tentoxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 3464–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meiss, E.; Konno, H.; Groth, G.; Hisabori, T. Molecular processes of inhibition and stimulation of ATP synthase caused by the phytotoxin tentoxin. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 24594–24599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.X.; Dirk, L.M.; Pattanaik, S.; Das, N.C.; Maiti, I.B.; Houtz, R.L.; Williams, M.A. Plant peptide deformylase: A novel selectable marker and herbicide target based on essential cotranslational chloroplast protein processing. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2007, 5, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driouich, A.; Jauneau, A.; Staehelin, L.A. 7-Dehydrobrefeldin A, a naturally occurring brefeldin a derivative, inhibits secretion and causes a cis-to-trans breakdown of golgi stacks in plant cells. Plant Physiol. 1997, 113, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hejli, A.M.; Koster, K.L. The allelochemical sorgoleone inhibits root H+-ATPase and water uptake. J. Chem. Ecol. 2004, 30, 2181–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielsen, E.M. Tagetitoxin inhibits RNA synthesis directed by RNA polymerases from chloroplasts and Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 29, 493–498. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, M.D.; Waraich, N.F.; Debowski, A.W.; Corral, M.G.; Maxwell, A.; Mylne, J.S.; Stubbs, K.A. Developing ciprofloxacin analogues against plant DNA gyrase: A novel herbicide mode of action. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 1869–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans-Roberts, K.M.; Mitchenall, L.A.; Wall, M.K.; Leroux, J.; Mylne, J.S.; Maxwell, A. DNA gyrase is the target for the quinolone drug ciprofloxacin in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 3136–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, F.E. Current Status and Future Prospects in Herbicide Discovery. Plants 2019, 8, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, P.M.; Danenberg, P.V.; Johnston, P.G.; Lenz, H.J.; Ladner, R.D. Standing the test of time: Targeting thymidylate biosynthesis in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 11, 282–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corral, M.G.; Haywood, J.; Stehl, L.H.; Stubbs, K.A.; Murcha, M.W.; Mylne, J.S. Targeting plant DIHYDROFOLATE REDUCTASE with antifolates and mechanisms for genetic resistance. Plant J. 2018, 95, 727–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peter, E.; Rothbart, M.; Oelze, M.L.; Shalygo, N.; Dietz, K.J.; Grimm, B. Mg protoporphyrin monomethylester cyclase deficiency and effects on tetrapyrrole metabolism in different light conditions. Plant Cell Physiol. 2010, 51, 1229–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maimann, S.; Wagner, C.; Kreft, O.; Zeh, M.; Willmitzer, L.; Hofgen, R.; Hesse, H. Transgenic potato plants reveal the indispensable role of cystathionine beta-lyase in plant growth and development. Plant J. 2000, 23, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverman, D.N.; Lindskog, S. The catalytic mechanism of carbonic anhydrase: Implications of a rate-limiting protolysis of water. Acc. Chem. Res. 2002, 21, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochetov, G.A.; Solovjeva, O.N. Structure and functioning mechanism of transketolase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1844, 1608–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Tian, L.; Liu, H.; Pan, Q.; Zhan, J.; Huang, W. Sugars induce anthocyanin accumulation and flavanone 3-hydroxylase expression in grape berries. Plant Growth Regul. 2009, 58, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Morris-Natschke, S.L.; Lee, K.H. Strategies for the optimization of natural leads to anticancer drugs or drug candidates. Med. Res. Rev. 2016, 36, 32–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantrell, C.L.; Dayan, F.E.; Duke, S.O. Natural products as sources for new pesticides. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudegnies, R.; Edmunds, A.J.F.; Fraser, T.E.M.; Hall, R.G.; Hawkes, T.R.; Mitchell, G.; Schaetzer, J.; Wendeborn, S.; Wibley, J. Herbicidal 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase inhibitors—A review of the triketone chemistry story from a Syngenta perspective. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 4134–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, R.; Nagaoka, M.; Hirai, K.; Uchida, A.; Kochi, S.-i.; Yamada, O.; Tokumura, J. Synthesis and insecticidal activity of novel 1-alkyl-3-sulfonyloxypyrazole-4-carboxamide derivatives. J. Pestic. Sci. 2010, 35, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, A.; Liu, C.; Yang, X.; Dekeyser, M. Application of the intermediate derivatization approach in agrochemical discovery. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 7079–7107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taft, C.A.; Da Silva, V.B.; Da Silva, C.H. Current topics in computer-aided drug design. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuntz, I.D. Structure-based strategies for drug design and discovery. Science 1992, 257, 1078–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Zidek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olliaro, P.L.; Gottlieb, M.; Wirth, D.F. Plasmodium falciparum proteinases: Targeted drug development. Parasitol. Today 1996, 12, 413–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, A. Chemical aspects of selective toxicity. Nature 1958, 182, 421–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautio, J.; Kumpulainen, H.; Heimbach, T.; Oliyai, R.; Oh, D.; Jarvinen, T.; Savolainen, J. Prodrugs: Design and clinical applications. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.P.; Chandra, S.; Tiwari, R.; Srivastava, A.; Tiwari, G. Therapeutic Potential of Prodrugs towards Targeted Drug Delivery. Open Med. Chem. J. 2018, 12, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawilska, J.B.; Wojcieszak, J.; Olejniczak, A.B. Prodrugs: A challenge for the drug development. Pharmacol. Rep. 2013, 65, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttunen, K.M.; Raunio, H.; Rautio, J. Prodrugs—From serendipity to rational design. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 750–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, N.; Lippard, S.J. Redox activation of metal-based prodrugs as a strategy for drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.P.; Joshi, S.; Russell, P.J.; Verma, N.D.; Wang, X.; Khatri, A. Molecular chemotherapy and chemotherapy: A new front against late-stage hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 4006–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokil, G.R.; Rewatkar, P.V. Bioprecursor prodrugs: Molecular modification of the active principle. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 1316–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivas, N.R. The rationality for using prodrug approach in drug discovery programs for new xenobiotics: Opportunities and challenges. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2011, 36, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kratz, F.; Müller, I.A.; Ryppa, C.; Warnecke, A. Prodrug strategies in anticancer chemotherapy. ChemMedChem 2008, 3, 20–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, P.W.; Hung, C.F.; Fang, J.Y. Current prodrug design for drug discovery. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 2236–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, S.; Mandlekar, S.; Marathe, P. Prodrug design to improve pharmacokinetic and drug delivery properties: Challenges to the discovery scientists. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 3874–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).