The Added Value of Intraventricular Hemorrhage on the Radiomics Analysis for the Prediction of Hematoma Expansion of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Ethical Considerations
2.3. Clinical Parameters and Clinical Outcomes
2.4. CT Imaging Protocol
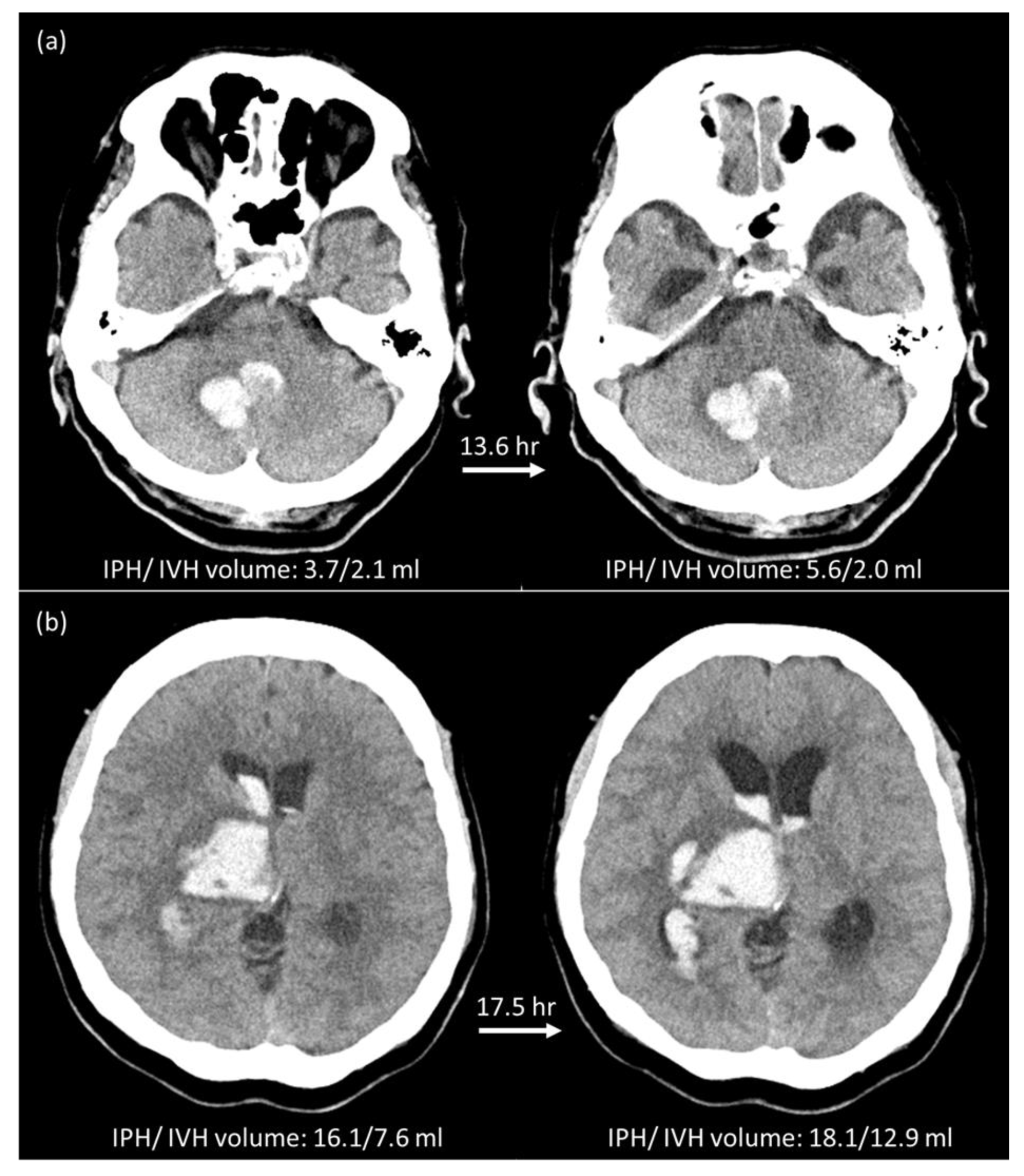
2.5. Manual Hematoma Segmentation and HE Definition
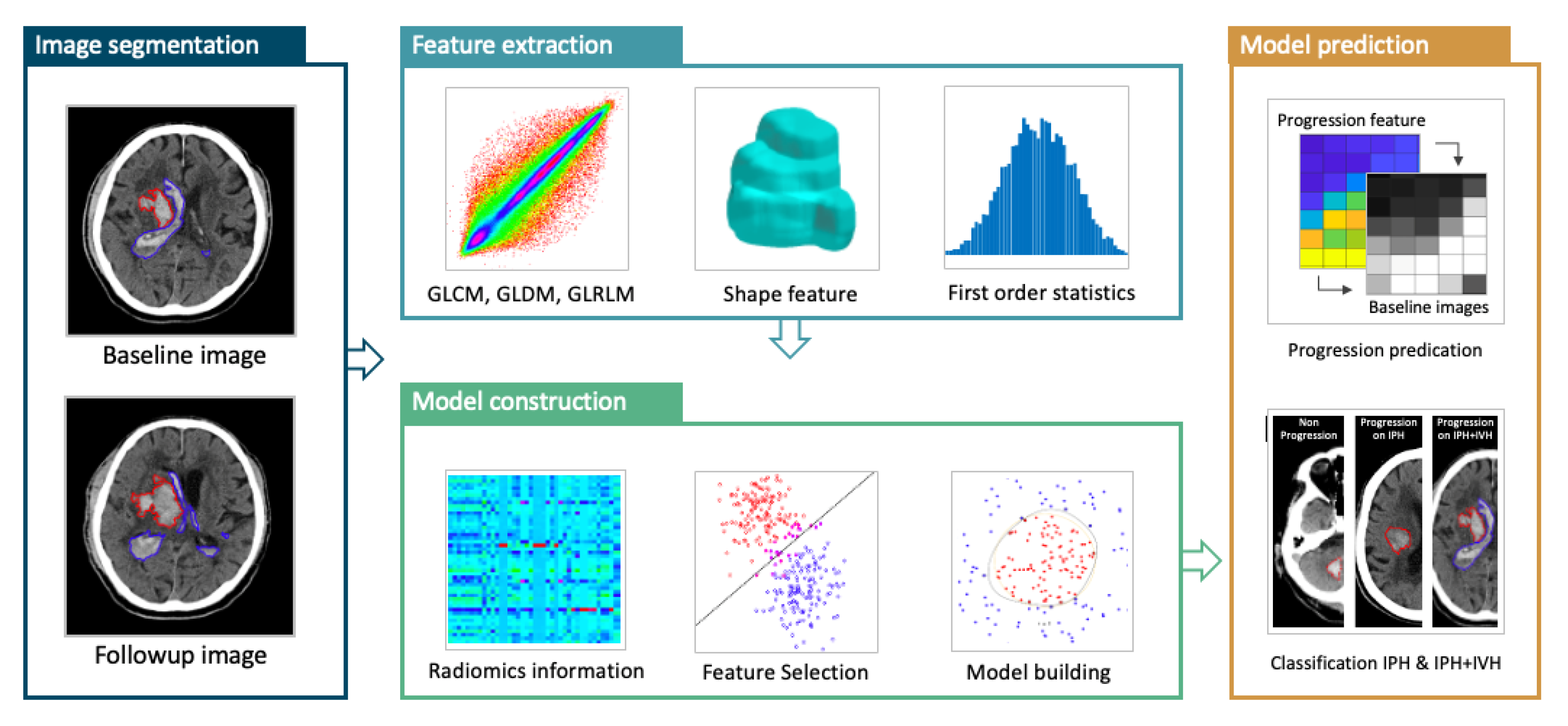
2.6. Feature Extraction and Feature Selection
2.7. Model Building and Radiomics Score (RS)
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
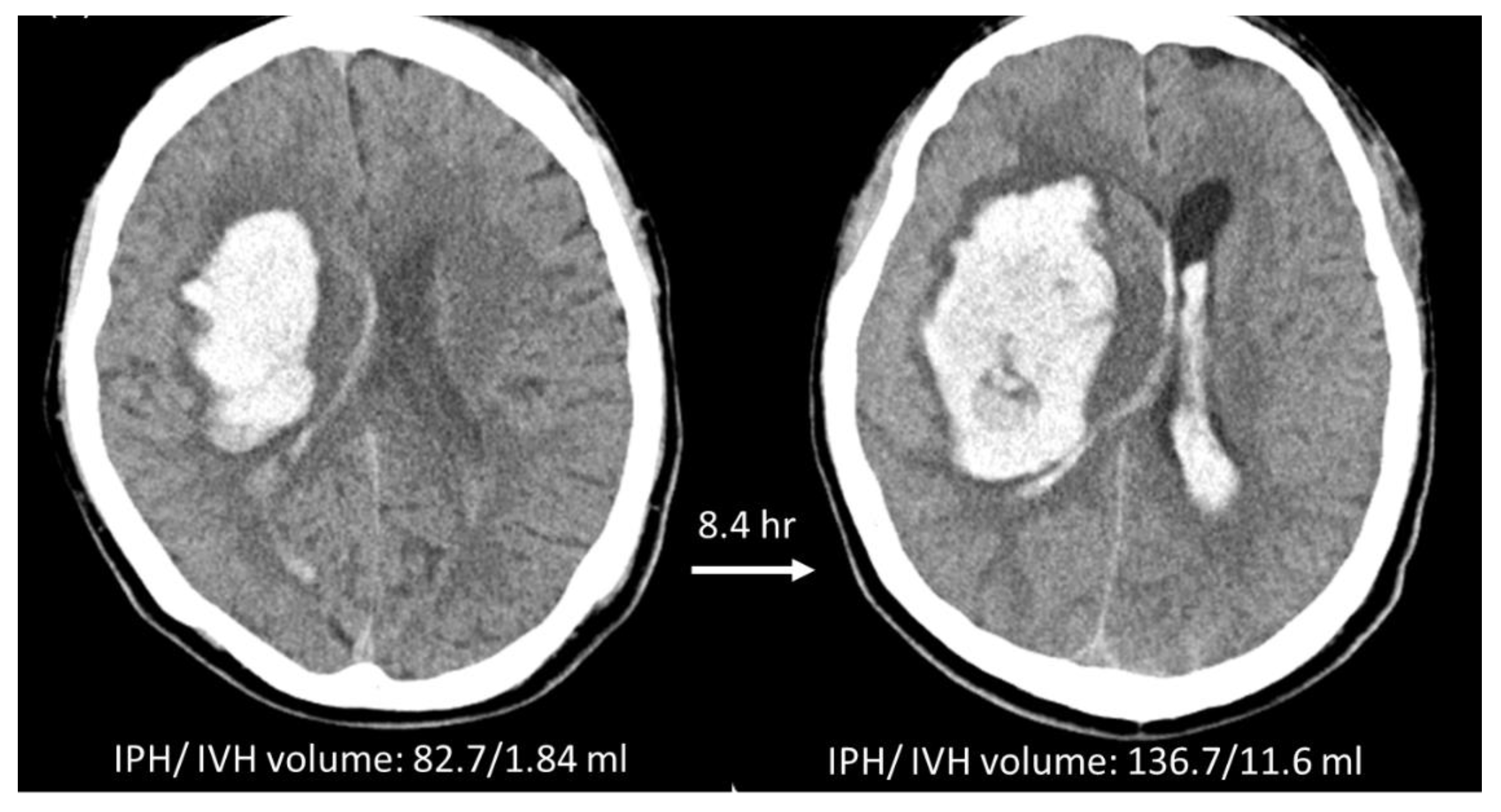
3.1. Hematoma Expansion Status Defined by IPH (HEP)
3.2. Hematoma Expansion Status Defined by IPH + IVH (HEP+V)
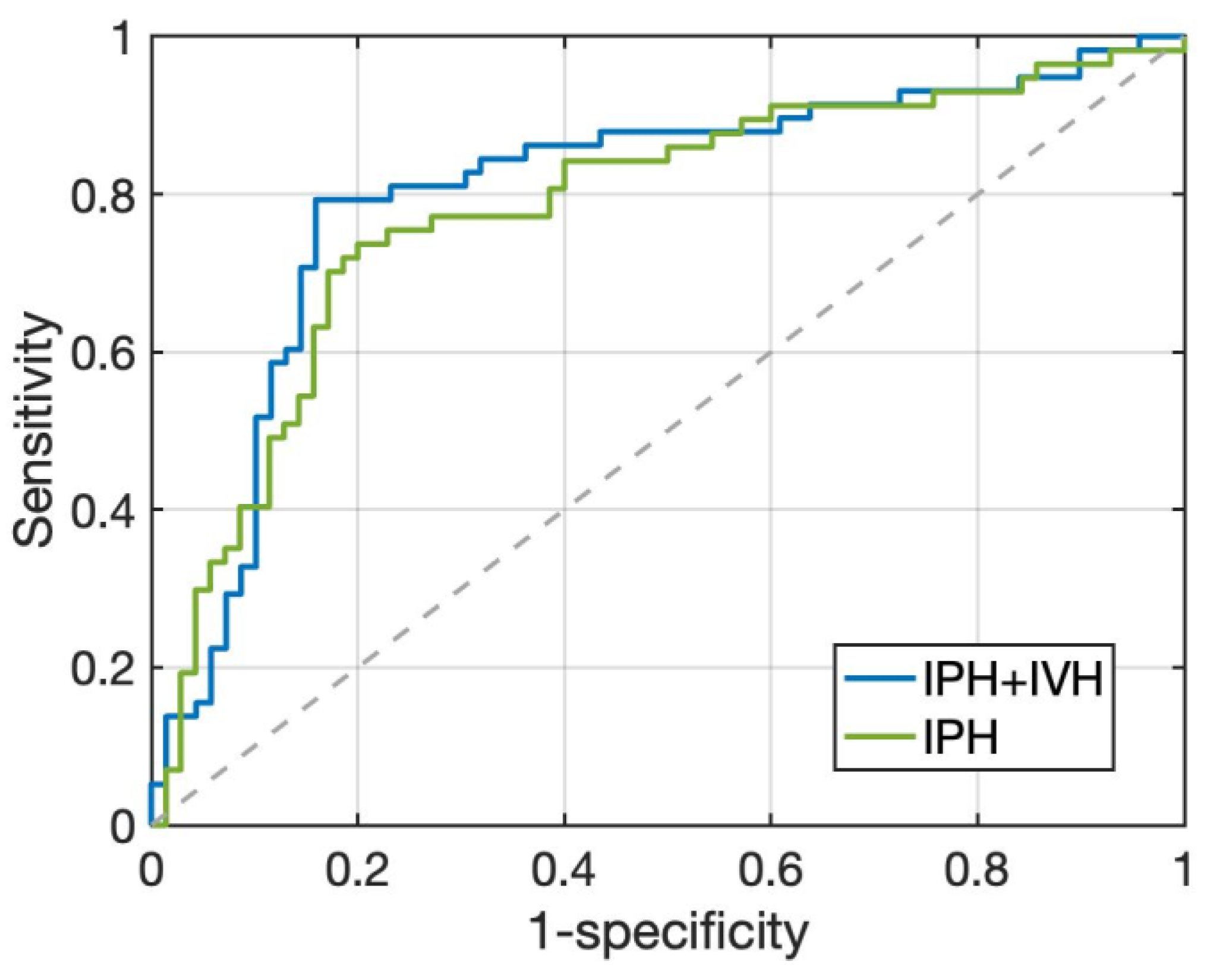
3.3. HE Prediction Performance of Two Radiomics Models
3.4. Radiologic Parameters and Early Outcome of Two Radiomics Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AUC | Area Under the ROC Curve |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| GCS | Glasgow Coma Scale |
| HE | Hematoma Expansion |
| ICH | Intracerebral Hemorrhage |
| IPH | Intraparenchymal Hemorrhage |
| IVH | Intraventricular Hemorrhage |
| mRS | modified Rankin Scale |
| NCCT | Non-Contrast Computed Tomography |
| NIHSS | National Institute of Health Stroke Scale |
| RM | Radiomics Model |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| ROI | Region of Interest |
| ICHP | ROI of intraparenchymal component of intracerebral hemorrhage |
| ICHP+V | ROI of intraventricular component of intracerebral hemorrhage |
| RS | Radiomics Score |
| sICH | spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage |
References
- Qureshi, A.I.; Tuhrim, S.; Broderick, J.P.; Batjer, H.H.; Hondo, H.; Hanley, D.F. Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1450–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Asch, C.J.; Luitse, M.J.; Rinkel, G.J.; van der Tweel, I.; Algra, A.; Klijn, C.J. Incidence, case fatality, and functional outcome of intracerebral haemorrhage over time, according to age, sex, and ethnic origin: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.M.; Broderick, J.; Hennerici, M.; Brun, N.C.; Diringer, M.N.; Mayer, S.A.; Begtrup, K.; Steiner, T. Hematoma growth is a determinant of mortality and poor outcome after intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurology 2006, 66, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brott, T.; Broderick, J.; Kothari, R.; Barsan, W.; Tomsick, T.; Sauerbeck, L.; Spilker, J.; Duldner, J.; Khoury, J. Early hemorrhage growth in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 1997, 28, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demchuk, A.M.; Dowlatshahi, D.; Rodriguez-Luna, D.; Molina, C.A.; Blas, Y.S.; Dzialowski, I.; Kobayashi, A.; Boulanger, J.M.; Lum, C.; Gubitz, G.; et al. Prediction of haematoma growth and outcome in patients with intracerebral haemorrhage using the CT-angiography spot sign (PREDICT): A prospective observational study. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravani, H.; Mayer, S.A.; Demchuk, A.; Jahromi, B.S.; Gladstone, D.J.; Flaherty, M.; Broderick, J.; Aviv, R.I. Emergency noninvasive angiography for acute intracerebral hemorrhage. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 1481–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dowlatshahi, D.; Demchuk, A.M.; Flaherty, M.L.; Ali, M.; Lyden, P.L.; Smith, E.E. Defining hematoma expansion in intracerebral hemorrhage: Relationship with patient outcomes. Neurology 2011, 76, 1238–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barras, C.D.; Tress, B.M.; Christensen, S.; Collins, M.; Desmond, P.M.; Skolnick, B.E.; Mayer, S.A.; Davis, S.M. Quantitative CT Densitometry for Predicting Intracerebral Hemorrhage Growth. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 1139–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boulouis, G.; Morotti, A.; Brouwers, H.B.; Charidimou, A.; Jessel, M.J.; Auriel, E.; Pontes-Neto, O.; Ayres, A.; Vashkevich, A.; Schwab, K.M.; et al. Association Between Hypodensities Detected by Computed Tomography and Hematoma Expansion in Patients With Intracerebral Hemorrhage. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, G.; Huang, Y.J.; Dong, M.X.; Lv, F.J.; Wei, X.; Chen, J.J.; Zhang, L.J.; Qin, X.Y.; Xie, P. Blend Sign on Computed Tomography: Novel and Reliable Predictor for Early Hematoma Growth in Patients With Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stroke 2015, 46, 2119–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blacquiere, D.; Demchuk, A.M.; Al-Hazzaa, M.; Deshpande, A.; Petrcich, W.; Aviv, R.I.; Rodriguez-Luna, D.; Molina, C.A.; Silva Blas, Y.; Dzialowski, I.; et al. Intracerebral Hematoma Morphologic Appearance on Noncontrast Computed Tomography Predicts Significant Hematoma Expansion. Stroke 2015, 46, 3111–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ng, D.; Churilov, L.; Mitchell, P.; Dowling, R.; Yan, B. The CT swirl sign is associated with hematoma expansion in intracerebral hemorrhage. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulouis, G.; Morotti, A.; Charidimou, A.; Dowlatshahi, D.; Goldstein, J.N. Noncontrast Computed Tomography Markers of Intracerebral Hemorrhage Expansion. Stroke 2017, 48, 1120–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Xie, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, F.; Sun, J.; Jiang, X. Radiomics features on non-contrast computed tomography predict early enlargement of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2019, 185, 105491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Zhang, Y.; Niyazi, T.; Wei, J.; Guocai, G.; Liu, J.; Liang, S.; Liang, F.; Yan, P.; Wang, K.; et al. Radiomics for predicting hematoma expansion in patients with hypertensive intraparenchymal hematomas. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 115, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Ma, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X. Noncontrast computer tomography-based radiomics model for predicting intracerebral hemorrhage expansion: Preliminary findings and comparison with conventional radiological model. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Ding, Z.; Shan, Y.; Chen, W.; Feng, Z.; Pang, P.; Shen, Q. A Nomogram Model of Radiomics and Satellite Sign Number as Imaging Predictor for Intracranial Hematoma Expansion. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Shan, Y.; Hu, Z.; Chen, W.; Yang, B.; Han, J.; Huang, Y.; Xu, W.; Feng, Z. Quantitative parameters of CT texture analysis as potential markers for early prediction of spontaneous intracranial hemorrhage enlargement. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 4389–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhu, D.; Liu, J.; Zhang, M.; Xu, H.; Xiang, Y.; Zhan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.; Yang, Y. Clinical-radiomics Nomogram for Risk Estimation of Early Hematoma Expansion after Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Acad. Radiol. 2021, 28, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemphill, J.C., III; Bonovich, D.C.; Besmertis, L.; Manley, G.T.; Johnston, S.C. The ICH score: A simple, reliable grading scale for intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 2001, 32, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, T.; Diringer, M.N.; Schneider, D.; Mayer, S.A.; Begtrup, K.; Broderick, J.; Skolnick, B.E.; Davis, S.M. Dynamics of intraventricular hemorrhage in patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: Risk factors, clinical impact, and effect of hemostatic therapy with recombinant activated factor VII. Neurosurgery 2006, 59, 767–773; discussion 773–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maas, M.B.; Nemeth, A.J.; Rosenberg, N.F.; Kosteva, A.R.; Prabhakaran, S.; Naidech, A.M. Delayed intraventricular hemorrhage is common and worsens outcomes in intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurology 2013, 80, 1295–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Witsch, J.; Bruce, E.; Meyers, E.; Velazquez, A.; Schmidt, J.M.; Suwatcharangkoon, S.; Agarwal, S.; Park, S.; Falo, M.C.; Connolly, E.S.; et al. Intraventricular hemorrhage expansion in patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurology 2015, 84, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yogendrakumar, V.; Ramsay, T.; Fergusson, D.A.; Demchuk, A.M.; Aviv, R.I.; Rodriguez-Luna, D.; Molina, C.A.; Silva, Y.; Dzialowski, I.; Kobayashi, A.; et al. Redefining Hematoma Expansion With the Inclusion of Intraventricular Hemorrhage Growth. Stroke 2020, 51, 1120–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogendrakumar, V.; Ramsay, T.; Fergusson, D.; Demchuk, A.M.; Aviv, R.I.; Rodriguez-Luna, D.; Molina, C.A.; Silva, Y.; Dzialowski, I.; Kobayashi, A.; et al. New and expanding ventricular hemorrhage predicts poor outcome in acute intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurology 2019, 93, e879–e888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, J.P.; Adams, H.P.; Barsan, W.; Feinberg, W.; Feldmann, E.; Grotta, J.; Kase, C.; Krieger, D.; Mayberg, M.; Tilley, B.; et al. Guidelines for the Management of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stroke 1999, 30, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huynh, T.J.; Aviv, R.I.; Dowlatshahi, D.; Gladstone, D.J.; Laupacis, A.; Kiss, A.; Hill, M.D.; Molina, C.A.; Rodriguez-Luna, D.; Dzialowski, I.; et al. Validation of the 9-Point and 24-Point Hematoma Expansion Prediction Scores and Derivation of the PREDICT A/B Scores. Stroke 2015, 46, 3105–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morotti, A.; Brouwers, H.B.; Romero, J.M.; Jessel, M.J.; Vashkevich, A.; Schwab, K.; Afzal, M.R.; Cassarly, C.; Greenberg, S.M.; Martin, R.H.; et al. Intensive Blood Pressure Reduction and Spot Sign in Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 950–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado Almandoz, J.E.; Yoo, A.J.; Stone, M.J.; Schaefer, P.W.; Goldstein, J.N.; Rosand, J.; Oleinik, A.; Lev, M.H.; Gonzalez, R.G.; Romero, J.M. Systematic characterization of the computed tomography angiography spot sign in primary intracerebral hemorrhage identifies patients at highest risk for hematoma expansion: The spot sign score. Stroke 2009, 40, 2994–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morotti, A.; Boulouis, G.; Charidimou, A.; Schwab, K.; Kourkoulis, C.; Anderson, C.D.; Gurol, M.E.; Viswanathan, A.; Romero, J.M.; Greenberg, S.M.; et al. Integration of Computed Tomographic Angiography Spot Sign and Noncontrast Computed Tomographic Hypodensities to Predict Hematoma Expansion. Stroke 2018, 49, 2067–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwers, H.B.; Chang, Y.; Falcone, G.J.; Cai, X.; Ayres, A.M.; Battey, T.W.; Vashkevich, A.; McNamara, K.A.; Valant, V.; Schwab, K.; et al. Predicting hematoma expansion after primary intracerebral hemorrhage. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morotti, A.; Dowlatshahi, D.; Boulouis, G.; Al-Ajlan, F.; Demchuk, A.M.; Aviv, R.I.; Yu, L.; Schwab, K.; Romero, J.M.; Gurol, M.E.; et al. Predicting Intracerebral Hemorrhage Expansion With Noncontrast Computed Tomography. Stroke 2018, 49, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, H.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, T.; Sheng, W.; Huang, Q.; Song, J.; Huang, D.; Lan, L.; Li, Y.; et al. Prediction of hematoma expansion in spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage using support vector machine. EBioMedicine 2019, 43, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Arima, H.; Salman, R.A.-S.; Woodward, M.; Heeley, E.; Stapf, C.; Lavados, P.M.; Robinson, T.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Clinical Prediction Algorithm (BRAIN) to Determine Risk of Hematoma Growth in Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stroke 2015, 46, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, Z.; Guo, D.; Tang, Z.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Luo, S.; Yao, X.; Song, W.; Song, J.; Zhou, Z. Noncontrast Computed Tomography-Based Radiomics Analysis in Discriminating Early Hematoma Expansion after Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Korean J. Radiol. 2021, 22, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.Q.; Chen, Q.; Xiang, Y.L.; Zhan, C.Y.; Zhang, M.Y.; Chen, C.; Zhuge, Q.C.; Chen, W.J.; Yang, X.M.; Yang, Y.J. Predicting intraventricular hemorrhage growth with a machine learning-based, radiomics-clinical model. Aging 2021, 13, 12833–12848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.D.; Kuoy, E.; Grinband, J.; Weinberg, B.D.; Thompson, M.; Homo, R.; Chen, J.; Abcede, H.; Shafie, M.; Sugrue, L.; et al. Hybrid 3D/2D Convolutional Neural Network for Hemorrhage Evaluation on Head CT. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, J.; Park, K.-S.; Karki, M.; Lee, E.; Ko, S.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, D.; Choe, J.; Son, J.; Kim, M.; et al. Improving Sensitivity on Identification and Delineation of Intracranial Hemorrhage Lesion Using Cascaded Deep Learning Models. J. Digit. Imaging 2019, 32, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Schreuder, F.H.B.M.; Klijn, C.J.M.; Prokop, M.; Ginneken, B.v.; Marquering, H.A.; Roos, Y.B.W.E.M.; Baharoglu, M.I.; Meijer, F.J.A.; Manniesing, R. Intracerebral Haemorrhage Segmentation in Non-Contrast CT. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phaphuangwittayakul, A.; Guo, Y.; Ying, F.; Dawod, A.Y.; Angkurawaranon, S.; Angkurawaranon, C. An optimal deep learning framework for multi-type hemorrhagic lesions detection and quantification in head CT images for traumatic brain injury. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 7320–7338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Song, N.; Liu, L.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, B.; Yang, W.; Chen, Z. Efficiency of a deep learning-based artificial intelligence diagnostic system in spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage volume measurement. BMC Med. Imaging 2021, 21, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Luna, D.; Boyko, M.; Subramaniam, S.; Klourfeld, E.; Jo, P.; Diederichs, B.J.; Kosior, J.C.; Dowlatshahi, D.; Aviv, R.I.; Molina, C.A.; et al. Magnitude of Hematoma Volume Measurement Error in Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stroke 2016, 47, 1124–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dowlatshahi, D.; Kosior, J.C.; Idris, S.; Eesa, M.; Dickhoff, P.; Joshi, M.; Subramaniam, S.; Tymchuk, S.; Hill, M.D.; Aviv, R.I.; et al. Planimetric hematoma measurement in patients with intraventricular hemorrhage: Is total volume a preferred target for reliable analysis? Stroke 2012, 43, 1961–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, C.; Gong, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wu, S.; Wu, G.; Deng, Y.; Xia, C.; et al. Deep Network for the Automatic Segmentation and Quantification of Intracranial Hemorrhage on CT. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 541817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chan, S.; Chen, J.H.; Chang, K.T.; Lin, C.Y.; Pan, H.B.; Lin, W.C.; Kwong, T.; Parajuli, R.; Mehta, R.S.; et al. Development of U-Net Breast Density Segmentation Method for Fat-Sat MR Images Using Transfer Learning Based on Non-Fat-Sat Model. J. Digit Imaging 2021, 34, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, Y.; Takeuchi, S.; Sasaki, O.; Minakawa, T.; Tanaka, R. Multivariate analysis of predictors of hematoma enlargement in spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 1998, 29, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Hematoma Expansion Based on ICHP | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes (57 Cases) | No (70 Cases) | p Value | |
| Sex | 0.681 | ||
| Male/Female | 41/16 (72%/28%) | 48/22 (69%/31%) | |
| Age (years) | 60.6 (51, 69) | 60.4 (51, 67) | 0.921 |
| Interval from onset to CT scan (min) | 165 (60, 168) | 200 (76, 207) | 0.379 |
| Interval between CT scans (h) | 19.9 (4.6, 24.8) | 23.8 (9.9, 35.9) | 0.327 |
| Initial IPH volume (mL) | 17.2 (7.2,23.4) | 22.7 (9.8, 28.8) | 0.064 |
| Initial IVH volume (mL) | 4.5 (0, 4.4) | 1.8 (0, 2) | 0.097 |
| Initial IPH + IVH volume (mL) | 21.7 (10.6, 28.1) | 24.5 (10.5, 34.2) | 0.423 |
| IPH volume change (mL) | 38.6 (10.6, 63.3) | −0.4 (−1.8, 1.3) | <0.001 * |
| IVH volume change (mL) | 5.6 (0, 9.4) | 0.1 (0, 0) | <0.001 * |
| IPH + IVH volume change (mL) | 44.2 (11.9, 72.8) | −0.4 (−2.6, 1.4) | <0.001 * |
| IVH at baseline CT scan | 23 (40.4%) | 26 (37.1%) | 0.712 |
| DM | 15 (26.3%) | 20 (28.6%) | 0.777 |
| HTN | 45 (78.9%) | 58 (82.8%) | 0.576 |
| Smoking | 26 (45.6%) | 22 (31.4%) | 0.101 |
| Alcohol | 21 (36.8%) | 12 (17.1%) | 0.012 * |
| Antiplatelet/Anticoagulation | 13 (22.8%) | 10 (14.3%) | 0.215 |
| Bleeding diathesis # | 12 (21.1%) | 4 (5.7%) | 0.010 * |
| SBP at ER > 180 mmHg | 31 (54.4%) | 35 (50.0%) | 0.623 |
| DBP at ER > 100 mmHg | 36 (63.2%) | 40 (57.1%) | 0.492 |
| GCS 3–12 | 24 (42.1%) | 31 (44.3%) | 0.805 |
| Location | 0.071 | ||
| basal ganglia | 34 (59.6%) | 31 (44.3%) | |
| thalamus | 9 (15.8%) | 22 (31.4%) | |
| lobar | 6 (10.5%) | 12 (17.1%) | |
| posterior fossa | 8 (14.0%) | 5 (7.1%) | |
| Hospital stay (days) | 20 (11, 41.5) | 19.5 (12, 26) | 0.034 * |
| In-hospital mortality | 20 (35.1%) | 3 (4.3%) | <0.001 * |
| Brain surgery during hospitalization | 31 (54.4%) | 21 (30.0%) | 0.005 * |
| Poor outcome (mRS > 3 at discharge) | 54 (94.7%) | 44 (62.9%) | <0.001 * |
| RMP+V | RMp | |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 81.9% (104/127) | 76.4% (97/127) |
| Sensitivity | 79.3% (46/58) | 71.9% (41/57) |
| Specificity | 84.1% (58/69) | 80.0% (56/70) |
| False Positive Rate | 19.3% (11/57) | 25.5% (14/55) |
| False Negative Rate | 17.1% (12/70) | 22.2% (16/72) |
| Positive Predictive Value | 80.7% (46/57) | 74.5% (41/55) |
| Negative Predictive Value | 82.9% (58/70) | 77.8% (56/72) |
| Labelled Hematoma Expansion | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | p Value | |
| RMP+V | 53 cases | 74 cases | |
| Median interval from onset to CT scan (min) | 141 (55, 149) | 215 (80, 221) | 0.068 |
| Median interval between CT scans (h) | 18.1 (5.1, 22.9) | 24.9 (9.5, 40.2) | 0.087 |
| Median initial IPH volume (mL) | 22.5 (9.8, 25.8) | 17.6 (6.9, 26.4) | 0.103 |
| Median initial IVH volume (mL) | 3.5 (0, 4.8) | 0 (0, 4.8) | 0.737 |
| Median initial IPH + IVH volume (mL) | 25.5 (9.8, 26.7) | 21.1 (10.9, 30.6) | 0.223 |
| Median IPH volume change (mL) | 31.3 (4.3, 51.7) | 7.0 (−1.2, 2.9) | <0.001 |
| Median IVH volume change (mL) | 4.2 (0, 5.0) | 1.4 (−0.1, 0.6) | 0.029 |
| Median IPH + IVH volume change (mL) | 35.5 (4.8, 65.4) | 0.9 (−1.3, 5.7) | <0.001 |
| Intraventricular extension | 16 (30.2%) | 33 (44.6%) | 0.100 |
| GCS 3–13 | 20 (37.7%) | 35 (47.3%) | 0.284 |
| Hospital stay (days) | 19 (11.5, 27) | 21 (12, 30.3) | 0.747 |
| Brain surgery during hospitalization | 26 (49.1%) | 26 (35.1%) | 0.116 |
| In-hospital mortality | 16 (30.2%) | 7 (9.5%) | 0.003 |
| mRS at discharge > 3 | 49 (92.5%) | 57 (77.0%) | 0.021 |
| RMP | 52 cases | 75 cases | |
| Median interval from onset to CT scan (min) | 156 (62, 168) | 204 (72, 217) | 0.237 |
| Median interval between CT scans (h) | 18.6 (4.2, 23.6) | 24.4 (8.9, 40.0) | 0.145 |
| Median initial IPH volume (mL) | 22.5 (10.4, 30.2) | 17.7 (7.0, 23.0) | 0.108 |
| Median initial IVH volume (mL) | 2.9 (0, 2.6) | 3.5 (0, 4.1) | 0.718 |
| Median initial IPH + IVH volume (mL) | 25.4 (10.4, 36.8) | 21.2 (10.7, 28.0) | 0.235 |
| Median IPH volume change (mL) | 32.7 (4.1, 48.6) | 6.3 (−1.3, 4.3) | <0.001 |
| Median IVH volume change (mL) | 4.6 (0, 7.8) | 1.2 (0, 1.0) | 0.010 |
| Median IPH + IVH volume change (mL) | 37.3 (4.4, 57.5) | 7.4 (−1.4, 5.5) | <0.001 |
| Intraventricular extension | 20 (38.5%) | 29 (38.7%) | 0.981 |
| GCS 3–13 | 20 (38.5%) | 35 (46.7%) | 0.359 |
| Hospital stay (days) | 22 (12.3, 39) | 19 (12, 26) | 0.087 |
| Brain surgery during hospitalization | 28 (53.4%) | 24 (32%) | 0.014 |
| In-hospital mortality | 13 (25%) | 10 (13.3%) | 0.093 |
| mRS at discharge > 3 | 48 (92.3%) | 58 (77.3%) | 0.026 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, T.-C.; Liu, Y.-L.; Chen, J.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, T.-Y.; Ko, C.-C.; Su, M.-Y. The Added Value of Intraventricular Hemorrhage on the Radiomics Analysis for the Prediction of Hematoma Expansion of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2755. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112755
Wu T-C, Liu Y-L, Chen J-H, Zhang Y, Chen T-Y, Ko C-C, Su M-Y. The Added Value of Intraventricular Hemorrhage on the Radiomics Analysis for the Prediction of Hematoma Expansion of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(11):2755. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112755
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Te-Chang, Yan-Lin Liu, Jeon-Hor Chen, Yang Zhang, Tai-Yuan Chen, Ching-Chung Ko, and Min-Ying Su. 2022. "The Added Value of Intraventricular Hemorrhage on the Radiomics Analysis for the Prediction of Hematoma Expansion of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage" Diagnostics 12, no. 11: 2755. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112755
APA StyleWu, T.-C., Liu, Y.-L., Chen, J.-H., Zhang, Y., Chen, T.-Y., Ko, C.-C., & Su, M.-Y. (2022). The Added Value of Intraventricular Hemorrhage on the Radiomics Analysis for the Prediction of Hematoma Expansion of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Diagnostics, 12(11), 2755. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12112755






