Response Surface Methodology (RSM) Powered Formulation Development, Optimization and Evaluation of Thiolated Based Mucoadhesive Nanocrystals for Local Delivery of Simvastatin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of SIM-NCs
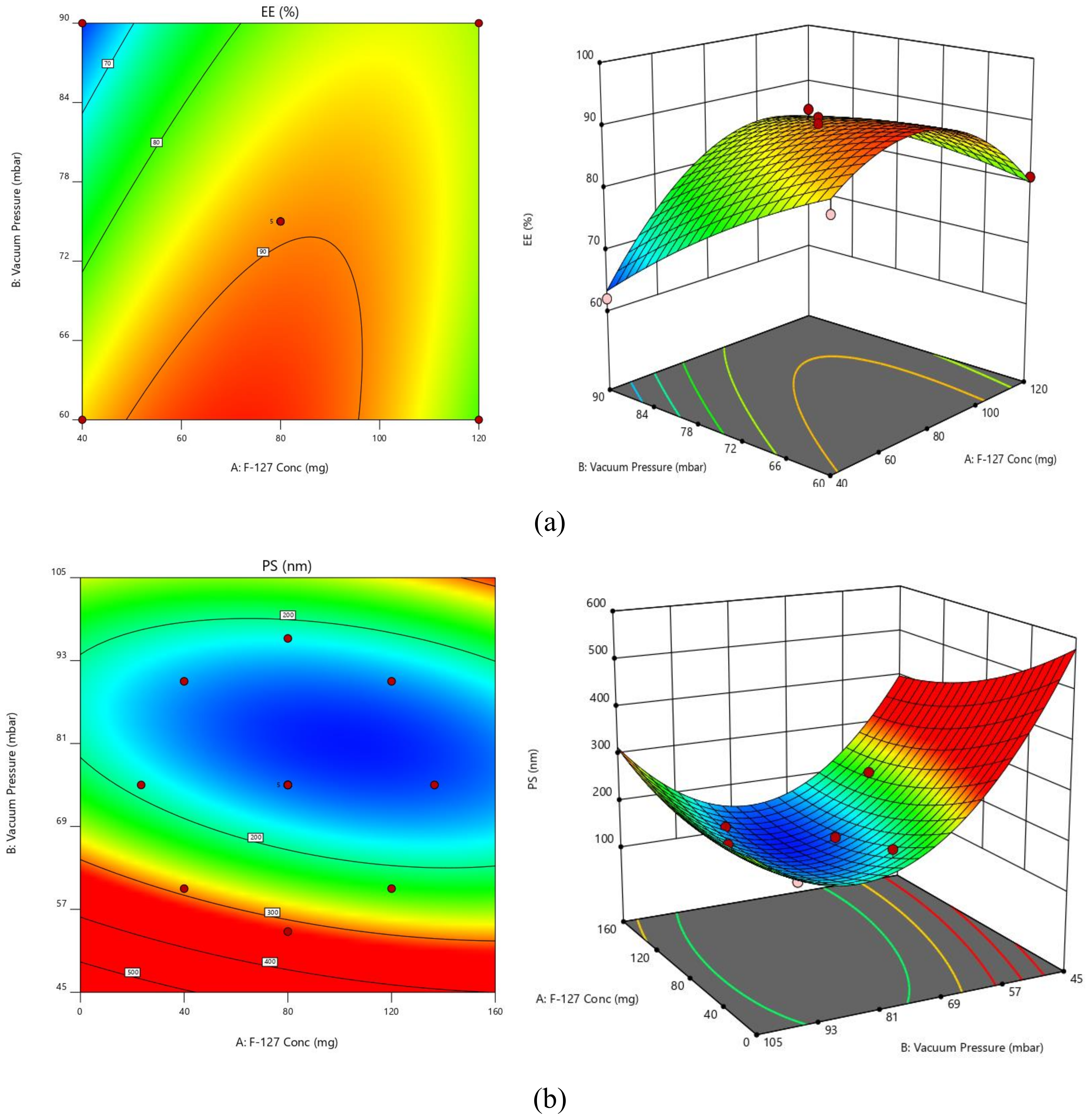
2.3. Experimental Design
2.3.1. PS
2.3.2. EE
2.4. Standardization and Validation of Optimization Outcome
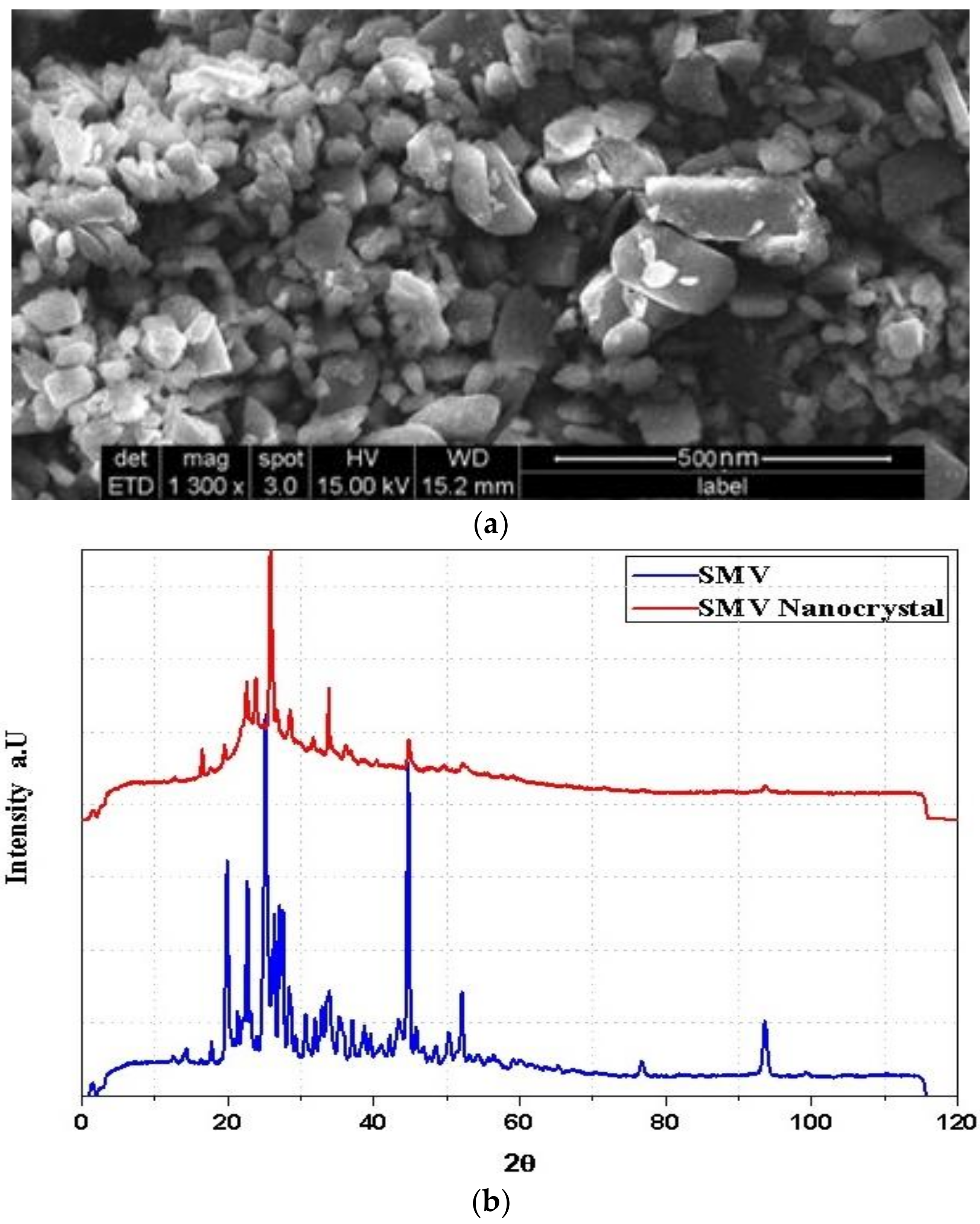
2.5. SIM-NC Morphology
X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
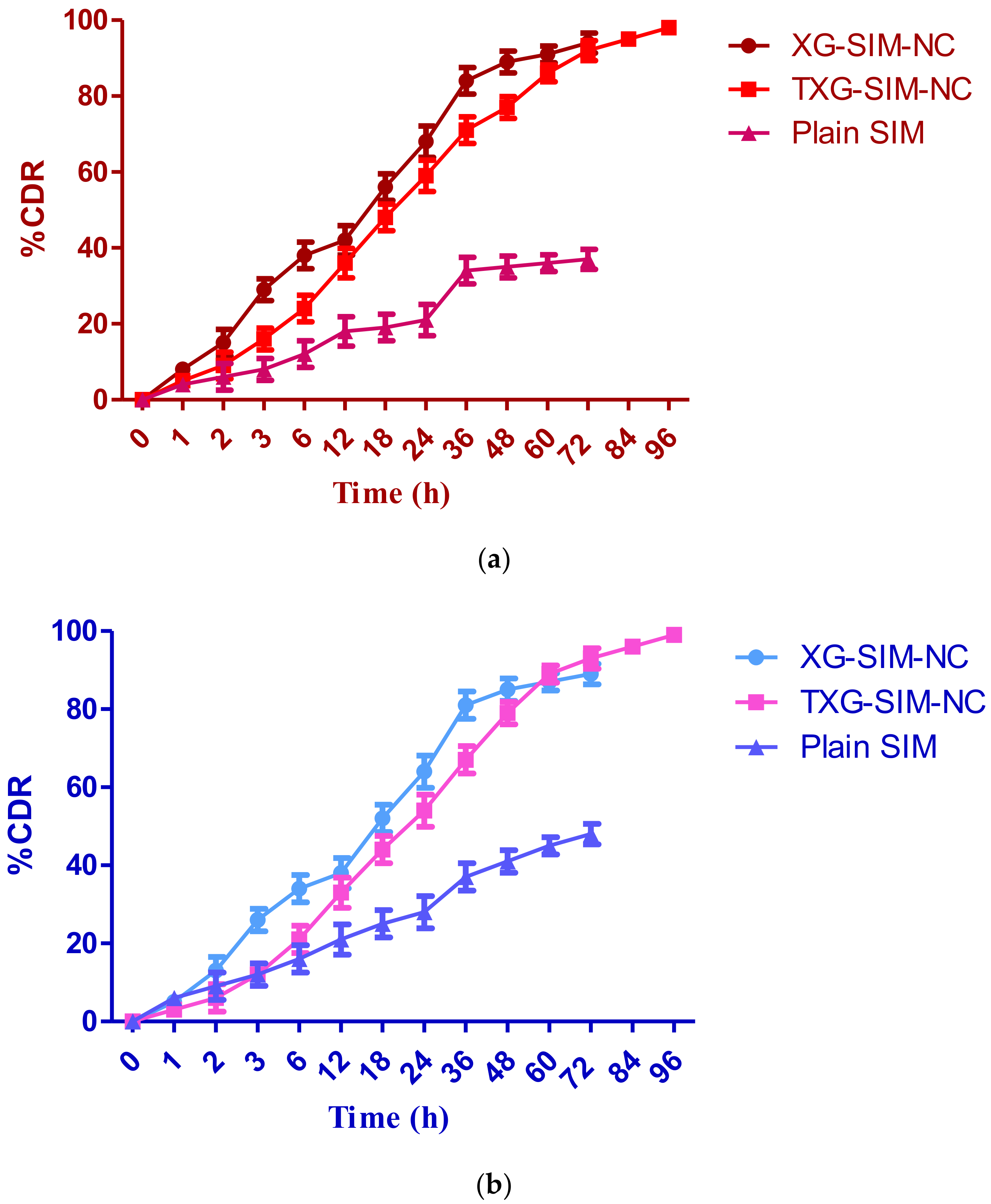
2.6. Drug Release Study
2.7. Mucoadhesive Evaluation of SIM-NC: Zeta Potential Determination and Turbidimetric Measurement
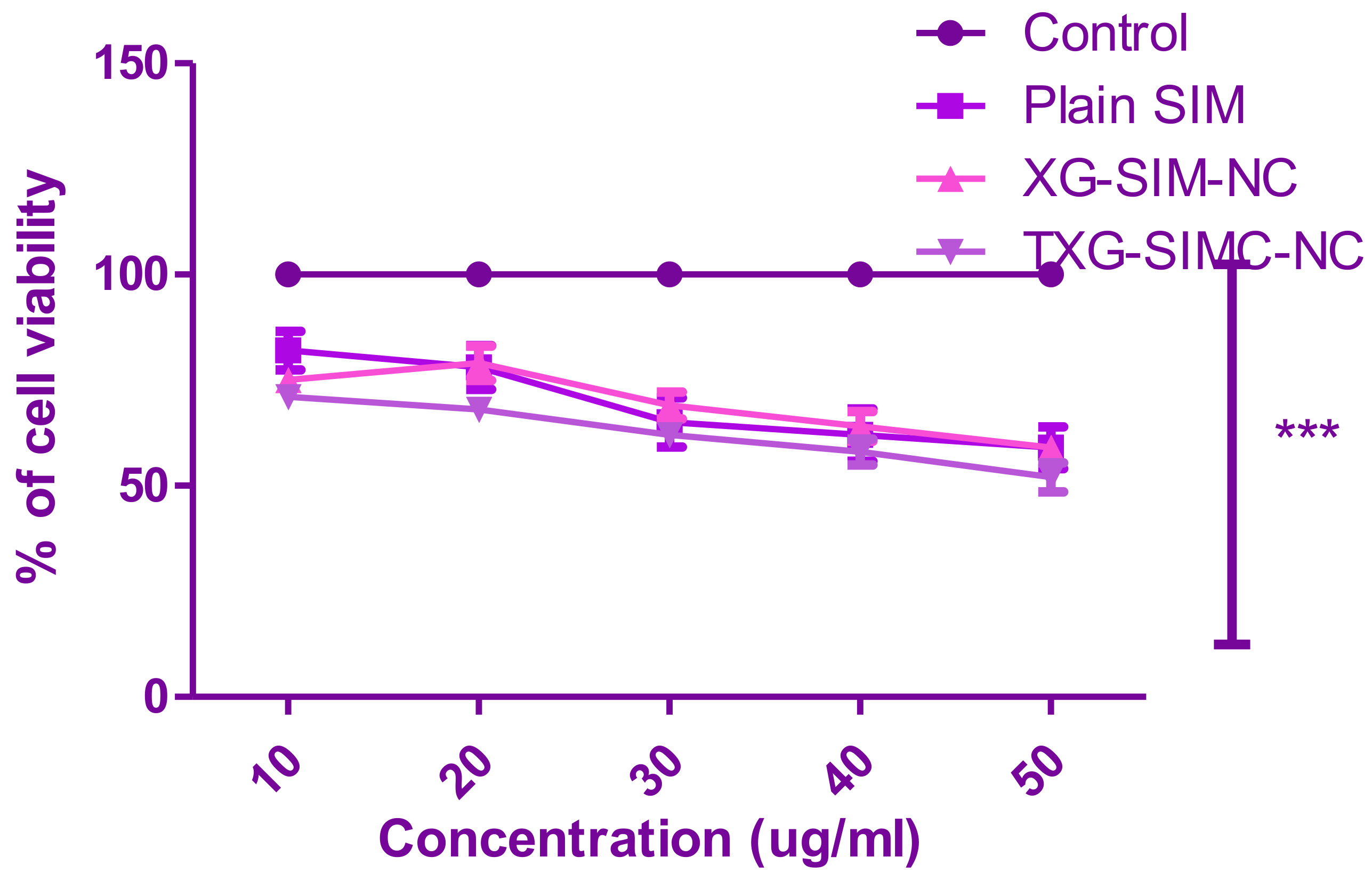
2.8. In Vitro Cell Viability Assay
2.9. In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Studies
2.9.1. Sample Preparation and Simvastatin Medication Concentration Measurement
2.9.2. Analyzing Pharmacokinetics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Surface Morphology
3.2. Drug Release Study
3.3. Mucoadhesion Study
3.4. Cytotoxic Study
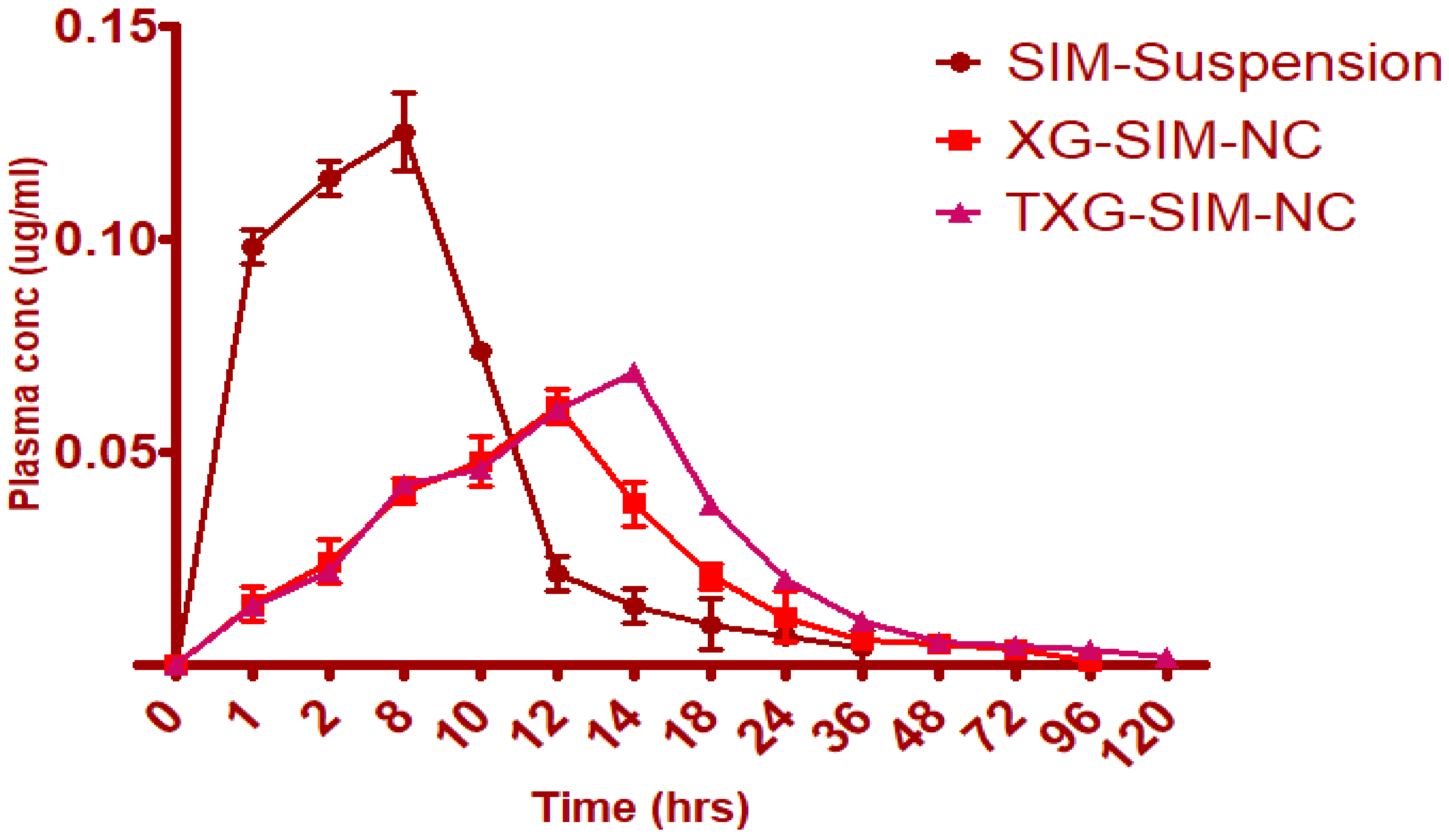
3.5. Pharmacokinetic Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tyagi, P.; Subramony, J.A. Nanotherapeutics in oral and parenteral drug delivery: Key learnings and future outlooks as we think small. J. Control. Release 2018, 272, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borkowska, M.; Siek, M.; Kolygina, D.V.; Sobolev, Y.I.; Lach, S.; Kumar, S.; Cho, Y.-K.; Kandere-Grzybowska, K.; Grzybowski, B.A. Targeted crystallization of mixed-charge nanoparticles in lysosomes induces selective death of cancer cells. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peer, D.; Karp, J.M.; Hong, S.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Margalit, R.; Langer, R. Nanocarriers as an emerging platform for cancer therapy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Kantoff, P.W.; Wooster, R.; Farokhzad, O.C. Cancer nanomedicine: Progress, challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Meel, R.; Sulheim, E.; Shi, Y.; Kiessling, F.; Mulder, W.J.M.; Lammers, T. Smart cancer nanomedicine. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawar, V.K.; Singh, Y.; Meher, J.G.; Gupta, S.; Chourasia, M.K. Engineered nanocrystal technology: In-vivo fate, targeting and applications in drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2014, 183, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Geng, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, J.; Yan, Z.; Yu, L. Nanocrystal Technology as a Strategy to Improve Drug Bioavailability and Antitumor Efficacy for the Cancer Treatment. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 2416–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Lv, Y.; Li, T. Hybrid drug nanocrystals. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 143, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jermain, S.V.; Brough, C.; Williams, R.O., 3rd. Amorphous solid dispersions and nanocrystal technologies for poorly water-soluble drug delivery—An update. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 535, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, O.P.; Patel, V.; Mehta, T. Nanocrystal for ocular drug delivery: Hope or hype. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2016, 6, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, W. Injected nanocrystals for targeted drug delivery. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2016, 6, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Dai, T.; Feng, N. A Novel Solubility-Enhanced Rubusoside-Based Micelles for Increased Cancer Therapy. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreeharsha, N.; Naveen, N.R.; Anitha, P.; Goudanavar, P.S.; Ramkanth, S.; Fattepur, S.; Telsang, M.K.; Habeebuddin, M.; Answer, K. Development of Nanocrystal Compressed Minitablets for Chronotherapeutic Drug Delivery. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danhier, F. To exploit the tumor microenvironment: Since the EPR effect fails in the clinic, what is the future of nanomedicine? J. Control. Release 2016, 244, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netsomboon, K.; Laffleur, F.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. P-glycoprotein inhibitors: Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of a preactivated thiomer. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2016, 42, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghori, M.U.; Alba, K.; Smith, A.M.; Conway, B.R.; Kontogiorgos, V. Okra extracts in pharmaceutical and food applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 42, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, V.M.; Walker, G.F.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Thiolated polymers: Evidence for the formation of disulphide bonds with mucus glycoproteins. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2003, 56, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhakamy, N.A.; Naveen, N.R.; Gorityala, S.; Kurakula, M.; Hosny, K.M.; Safhi, A.Y.; Bukhary, D.M.; Bukhary, H.A.; Sabei, F.Y.; Mushtaq, R.Y.; et al. Development of Novel S-Protective Thiolated-Based Mucoadhesive Tablets for Repaglinide: Pharmacokinetic Study. Polymers 2022, 14, 3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netsomboon, K.; Jalil, A.; Laffleur, F.; Hupfauf, A.; Gust, R.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Thiolated chitosans: Are Cys-Cys ligands key to the next generation? Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 242, 116395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, V.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, P.; Singh, I. Thiolation of Biopolymers for Developing Drug Delivery Systems with Enhanced Mechanical and Mucoadhesive Properties: A Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balata, G.F.; Zidan, A.S.; Abourehab, M.A.; Essa, E.A. Rapid disintegrating tablets of simvastatin dispersions in polyoxyethylene–polypropylene block copolymer for maximized disintegration and dissolution. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 3211–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naveen, N.R.; Gopinath, C.; Rao, D.S. Design expert supported mathematical optimization of repaglinide gastroretentive floating tablets: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Futur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 3, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Arnold, R.S.; Sun, C.Q.; Petros, J.A. A mitochondrial DNA mutation influences the apoptotic effect of statins on prostate cancer. Prostate 2015, 75, 1916–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanae, M.; Tsubaki, M.; Satou, T.; Itoh, T.; Imano, M.; Yamazoe, Y.; Nishida, S. Statin-induced apoptosis via the suppression of ERK1/2 and Akt activation by inhibition of the geranylgeranyl-pyrophosphate biosynthesis in glioblastoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 30, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, A.; Verma, S.; Verma, P.R.P.; Singh, S.K.; Chakraborty, A. Fabrication of liquid and solid self-double emulsifying drug delivery system of atenolol by response surface methodology. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 41, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Ramesh, V.H.; Bhavani, P.D.; Goudanavar, P.S.; Naveen, N.R.; Ramesh, B.; Fattepur, S.; Shiroorkar, P.N.; Habeebuddin, M.; Meravanige, G.; et al. Optimization of process parameters for fabrication of electrospun nanofibers containing neomycin sulfate and Malva sylvestris extract for a better diabetic wound healing. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 3370–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreeharsha, N.; Prasanthi, S.; Mahalakshmi, S.V.V.N.S.; Goudanavar, P.S.; Naveen, N.R.; Gowthami, B.; Fattepur, S.; Meravanige, G.; Asdaq, S.M.B.; Anwer, K.; et al. Enhancement of Anti-Tumoral Properties of Paclitaxel Nano-Crystals by Conjugation of Folic Acid to Pluronic F127: Formulation Optimization, In Vitro and In Vivo Study. Molecules 2022, 27, 7914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, K.; Jindal, R.; Jindal, D. RSM-CCD optimized microwave-assisted synthesis of chitosan and gelatin-based pH sensitive, inclusion complexes incorporated hydrogels and their use as controlled drug delivery systems. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 48, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Park, J.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Conwell, C.; Liu, Y.; Bathula, S.R.; Huang, L. Targeted Cancer Therapy With Novel High Drug-Loading Nanocrystals. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 3542–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizg, W.Y.; Naveen, N.R.; Kurakula, M.; Bukhary, H.A.; Safhi, A.Y.; Alfayez, E.; Sindi, A.M.; Ali, S.; Murshid, S.S.; Hosny, K.M. QbD Supported Optimization of the Alginate-Chitosan Nanoparticles of Simvastatin in Enhancing the Anti-Proliferative Activity against Tongue Carcinoma. Gels 2022, 8, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldawsari, H.M.; Naveen, N.R.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Goudanavar, P.S.; Rao, G.K.; Budha, R.R.; Nair, A.B.; Badr-Eldin, S.M. Compression-coated pulsatile chronomodulated therapeutic system: QbD assisted optimization. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 2258–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naveen, N.R.; Kurakula, M.; Gowthami, B. Process optimization by response surface methodology for preparation and evaluation of methotrexate loaded chitosan nanoparticles. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 33, 2716–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurakula, M.; Naveen, N.R.; Patel, B.; Manne, R.; Patel, D.B. Preparation, Optimization and Evaluation of Chitosan-Based Avanafil Nanocomplex Utilizing Antioxidants for Enhanced Neuroprotective Effect on PC12 Cells. Gels 2021, 7, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naveen, N.R. Design and characterization of sustained release matrix tablets of glimepiride by using synthetic and natural polymers. Int. J. drug Discov. Herb. Res. 2013, 3, 573–578. [Google Scholar]
- Dadashpour, M.; Ganjibakhsh, M.; Mousazadeh, H.; Nejati, K. Increased Pro-Apoptotic and Anti-Proliferative Activities of Simvastatin Encapsulated PCL-PEG Nanoparticles on Human Breast Cancer Adenocarcinoma Cells. J. Clust. Sci. 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, O.A.A.; Kurakula, M.; Banjar, Z.M.; Afouna, M.I.; Zidan, A.S. Quality by Design Coupled with Near Infrared in Formulation of Transdermal Glimepiride Liposomal Films. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 2062–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Kapil, R.; Nandi, M.; Ahuja, N. Developing oral drug delivery systems using formulation by design: Vital precepts, retrospect and prospects. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2011, 8, 1341–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Campos, A.M.; Diebold, Y.; Carvalho, E.L.S.; Sánchez, A.; Alonso, M.J. Chitosan Nanoparticles as New Ocular Drug Delivery Systems: In Vitro Stability, in Vivo Fate, and Cellular Toxicity. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, R.; Chandasana, H.; Chhonker, Y.; Rathi, C.; Kumar, D.; Mitra, K.; Shukla, P. Mucoadhesive nanoparticles for prolonged ocular delivery of natamycin: In vitro and pharmacokinetics studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 432, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rençber, S.; Karavana, S.Y.; Yılmaz, F.F.; Eraç, B.; Nenni, M.; Ozbal, S.; Pekçetin, Ç.; Gurer-Orhan, H.; Limoncu, M.H.; Güneri, P.; et al. Development, characterization, and in vivo assessment of mucoadhesive nanoparticles containing fluconazole for the local treatment of oral candidiasis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 2641–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurakula, M.; Naveen, N.R. In Situ Gel Loaded with Chitosan-Coated Simvastatin Nanoparticles: Promising Delivery for Effective Anti-Proliferative Activity against Tongue Carcinoma. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manjunath, K.; Venkateswarlu, V. Pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution and bioavailability of clozapine solid lipid nanoparticles after intravenous and intraduodenal administration. J. Control. Release 2005, 107, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raju, K.K.; Sudhakar, B.; Murthy, K.V.R. Factorial Design Studies and Biopharmaceutical Evaluation of Simvastatin Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Improving the Oral Bioavailability. ISRN Nanotechnol. 2014, 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.; Warsi, M.H.; Mallick, N.; Akhter, S.; Gahoi, S.; Jain, G.K.; Talegaonkar, S.; Ahmad, F.J.; Khar, R.K. Enhanced bioavailability of nano-sized chitosan–atorvastatin conjugate after oral administration to rats. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 44, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, S.B.; Chandrasekhar, K.B.; Reddy, K.B. Formulation, in-vitro and in-vivo pharmacokinetic evaluation of simvastatin nanostructured lipid carrier loaded transdermal drug delivery system. Futur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveen, N.R.; Gopinath, C.; Kurakula, M. Okra-Thioglycolic acid conjugate—Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation as a mucoadhesive polymer. Processes 2020, 8, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.H.; Kwon, Y.S.; Kim, I.Y. Pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics and clinical efficacy of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2016, 13, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ho, P.C. Formulation optimization of scutellarin-loaded HP-β-CD/chitosan nanoparticles using response surface methodology with Box–Behnken design. Asian, J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 12, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeirani, Z.; Jan, B.M.; Ali, B.S.; Noor, I.M.; Hwa, S.C.; Saphanuchart, W. The optimal mixture design of experiments: Alternative method in optimizing the aqueous phase composition of a microemulsion. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2012, 112, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Gong, W.; Liang, Z. Quantifying the effects of fuel compositions on GDI-derived particle emissions using the optimal mixture design of experiments. Fuel 2015, 154, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, A.K.; Pal, D.; Santra, K. Ispaghula mucilage-gellan mucoadhesive beads of metformin HCl: Development by response surface methodology. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 107, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooda, A.; Nanda, A.; Jain, M.; Kumar, V.; Rathee, P. Optimization and evaluation of gastroretentive ranitidine HCl microspheres by using design expert software. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 51, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, A.; Sindhu, K.; Giri, K.; Umera, F.; Gauthami, G.; Kumar, J.V.; Naveen, N.; Rao, K.N.V.; Ali, S.S.; Sri, K. Pharmacognostical and physio-chemical evaluation of Indian Asparagus officinalis Linn family Lamiaceae. Int. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. Res. 2017, 9, 327–336. [Google Scholar]
- Naveen, N.R.; Nagaraja, T.S.; Bharathi, D.R.; Reddy, J.N.S. Formulation Design and In Vitro Evaluation for Stomach Specific Drug Delivery System of Anti Retroviral drug–Acyclovir. Int. J. Pharm. Life Sci. 2013, 4, 2506–2510. [Google Scholar]


| Factors/Independent Variables | Levels | Responses/Dependent Variables | Constraints | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1.414 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +1.414 | |||
| F-127 Conc.—X1 | 23.4315 | 40 | 80 | 120 | 136.569 | EE | Maximum |
| Vacuum Pressure—X2 | 53.7868 | 60 | 75 | 90 | 96.2132 | PS | Minimum |
| Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Response 1 | Response 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Std | Run | A: F-127 Conc | B: Vacuum Pressure | EE | PS |
| mg | mbar | % | nm | ||
| 3 | 1 | 40 | 90 | 62 | 147 |
| 8 | 2 | 80 | 96.2132 | 78 | 185 |
| 10 | 3 | 80 | 75 | 91 | 165 |
| 4 | 4 | 120 | 90 | 85 | 165 |
| 9 | 5 | 80 | 75 | 88 | 144 |
| 11 | 6 | 80 | 75 | 89 | 148 |
| 5 | 7 | 23.4315 | 75 | 69 | 207 |
| 7 | 8 | 80 | 53.7868 | 94 | 321 |
| 6 | 9 | 136.569 | 75 | 74 | 130 |
| 13 | 10 | 80 | 75 | 89 | 145 |
| 1 | 11 | 40 | 60 | 85 | 278 |
| 12 | 12 | 80 | 75 | 90 | 142 |
| 2 | 13 | 120 | 60 | 81 | 239 |
| Response | Models | R2 | Adju. R2 | Pred. R2 | Adequate Precision | Sequential p-Value | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EE | Linear | 0.2780 | 0.1336 | −0.3744 | ---- | 0.1962 | |
| 2 FI | 0.4460 | 0.2613 | −0.2797 | 23.1661 | 0.1329 | ||
| Quadratic | 0.9768 | 0.9603 | 0.8618 | --- | <0.0001 | Suggested | |
| Cubic | 0.9947 | 0.9874 | 0.9630 | --- | 0.0245 | ||
| PS | Linear | 0.5163 | 0.4196 | 0.1086 | --- | 0.0265 | |
| 2 FI | 0.5355 | 0.3807 | −0.0348 | --- | 0.5570 | ||
| Quadratic | 0.9679 | 0.9450 | 0.8174 | 18.7863 | <0.0001 | Suggested | |
| Cubic | 0.9912 | 0.9789 | 0.9501 | --- | 0.0392 |
| Intercept | A | B | AB | A2 | B2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EE | 89.4 | 3.25888 | −5.20343 | 6.75 | −9.075 | −1.825 |
| p-values | 0.0018 | 0.0001 | 0.0002 | <0.0001 | 0.0386 | |
| PS | 148.8 | −16.2368 | −49.6666 | 14.25 | 8.975 | 51.225 |
| p-values | 0.0132 | <0.0001 | 0.0799 | 0.1329 | <0.0001 |
| Parameter | SIM Suspension | XG-SIM-NC | TXG-SIM-NC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tmax (h) | 8 | 12 | 14 |
| Cmax (µg/mL) | 0.1254 | 0.061 | 0.069 |
| AUC0-∞ (µg/mL h) | 84.6528 | 1453.0478 | 1847.0654 |
| MRT0-v (h) | 23 | 72 | 96 |
| Frel | -- | 17.16% enhanced bioavailability | 21.82% enhanced bioavailability |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bakhaidar, R.B.; Naveen, N.R.; Basim, P.; Murshid, S.S.; Kurakula, M.; Alamoudi, A.J.; Bukhary, D.M.; Jali, A.M.; Majrashi, M.A.; Alshehri, S.; et al. Response Surface Methodology (RSM) Powered Formulation Development, Optimization and Evaluation of Thiolated Based Mucoadhesive Nanocrystals for Local Delivery of Simvastatin. Polymers 2022, 14, 5184. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235184
Bakhaidar RB, Naveen NR, Basim P, Murshid SS, Kurakula M, Alamoudi AJ, Bukhary DM, Jali AM, Majrashi MA, Alshehri S, et al. Response Surface Methodology (RSM) Powered Formulation Development, Optimization and Evaluation of Thiolated Based Mucoadhesive Nanocrystals for Local Delivery of Simvastatin. Polymers. 2022; 14(23):5184. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235184
Chicago/Turabian StyleBakhaidar, Rana B., Nimbagal Raghavendra Naveen, Pratap Basim, Samar S. Murshid, Mallesh Kurakula, Abdulmohsin J. Alamoudi, Deena M. Bukhary, Abdulmajeed M. Jali, Mohammed A. Majrashi, Sameer Alshehri, and et al. 2022. "Response Surface Methodology (RSM) Powered Formulation Development, Optimization and Evaluation of Thiolated Based Mucoadhesive Nanocrystals for Local Delivery of Simvastatin" Polymers 14, no. 23: 5184. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235184
APA StyleBakhaidar, R. B., Naveen, N. R., Basim, P., Murshid, S. S., Kurakula, M., Alamoudi, A. J., Bukhary, D. M., Jali, A. M., Majrashi, M. A., Alshehri, S., Alissa, M., & Ahmed, R. A. (2022). Response Surface Methodology (RSM) Powered Formulation Development, Optimization and Evaluation of Thiolated Based Mucoadhesive Nanocrystals for Local Delivery of Simvastatin. Polymers, 14(23), 5184. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235184









