A Novel Design Method for the Geometric Shapes of Flux Modulation Poles in the Surface-Mounted Permanent Magnet Vernier Machines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Analytical Modeling for the Armature Magnetic Field
2.1. Winding MMF Function
- (1)
- The flux density, MMF, and permeance in the air-gap are uniform with the axial direction.
- (2)
- The values of the winding MMF are varied linearly in the regions in front of the slot opening.
- (3)
- The three-phase currents are symmetric and sinusoidal as follows.
2.2. Air-Gap Permeance Function
- (1)
- The stator and rotor cores possess infinite permeability.
- (2)
- The relative permeability of the PM is unity.
- (3)
- FMPs formed on the tooth are in symmetry with respect to the central axis of the tooth.
- (4)
- All teeth are of the same shape.
- (5)
- The height of the FMPs is high enough to have no influence on the air-gap permeance distribution.
2.3. Flux Density Distribution by the Windings
2.4. Flux Density Distribution by the Windings
3. Optimization of the FMP Shape
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Chau, K.T.; Cheng, M. Analysis, design and experimental verification of a field-modulated permanent-magnet machine for direct-drive wind turbines. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2015, 9, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Qu, R.; Li, D.; Li, J.; Zhou, G. Design of a dual-stator LTS vernier machine for direct-drive wind power generation. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2016, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ho, S.L.; Fu, W.N.; Zhang, X. Design optimization of a novel doubly fed dual-rotor flux-modulated machine for hybrid electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Yang, J.; Zhao, W.; Ji, J.; Chen, Q.; Gong, W. Design and analysis of a new fault-tolerant permanent-magnet vernier machine for electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 4176–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Qu, R.; Li, D.; Li, J. A high torque density vernier PM machines for hybrid electric vehicle applications. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference (VPPC), Hangzhou, China, 17–20 October 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, Y.; Ishiguro, H.; Kitani, K.; Fujimoto, T.; Hirata, K. Development and control of a novel cylindrical IPM linear vernier motor for compliant robot actuation. In Proceedings of the 2013 IECON—39th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Vienna, Austria, 10–13 November 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.S.; Lipo, T.A. Torque performance comparison between a ferrite magnet vernier motor and an industrial interior permanent magnet machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 2088–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukotić, M.; Miljavec, D. Design of a permanent-magnet flux-modulated machine with a high torque density and high power factor. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2016, 10, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Qu, R.; Li, J.; Xiao, L.; Wu, L.; Xu, W. Analysis of torque capability and quality in vernier permanent-magnet machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, K.; Niguchi, N.; Hirata, K. Analysis of a vernier motor with concentrated windings. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 2241–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Liu, G.; Zhao, W.; Yang, X.; Cheng, R. Hybrid stator design of fault-tolerant permanent-magnet vernier machines for direct-drive applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 64, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toba, A.; Lipo, T.A. Generic torque-maximizing design methodology of surface permanent-magnet vernier machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2000, 36, 1539–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Cheng, M.; Chau, K.T.; Liu, X.; Xiao, F.; Zhao, W. Linear primary permanent magnet vernier machine for wave energy conversion. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2015, 9, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Chang, J. Design of a vernier machine with PM on both sides of rotor and stator. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 877–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Qu, R.; Xu, W.; Li, J.; Lipo, T.A. Design procedure of dual-stator spoke-array vernier permanent-magnet machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 2972–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Niu, S.; Ho, S.L.; Fu, W.; Zuo, S. Design and analysis of novel magnetic flux-modulated mnemonic machines. IET Electr. Power Appl 2015, 9, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Liu, G.; Zhao, W.; Ji, J.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, W.; Jiang, T. Quantitative comparison of integral and fractional slot permanent magnet vernier motors. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2015, 30, 1483–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Lipo, T.A. Analysis of a PM vernier motor with spoke structure. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Chang, J. Influences of winding MMF harmonics on torque characteristics in surface-mounted permanent magnet vernier machines. Energies 2017, 10, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Chang, J. Effects of flux modulation poles on the radial magnetic forces in surface-mounted permanent magnet vernier machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.; Li, D.; Qu, R.; Jiang, D.; Li, J. Advanced high torque density PM vernier machine with multi working harmonics. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Torres, C.; Garcia, A.; Riba, J.; Romeral, L. Design and optimization for vehicle driving cycle of rare-earth-free SynRM based on coupled lumped thermal and magnetic networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Kwon, J.; Wang, X.; Lipo, T.A.; Kwon, B. Optimal design of a spoke-type permanent magnet motor with phase-group concentrated-coil windings to minimize torque pulsations. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Q.; Howe, D. Instantaneous magnetic field distribution in brushless permanent magnet dc motors. III. Effect of stator slotting. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1993, 29, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



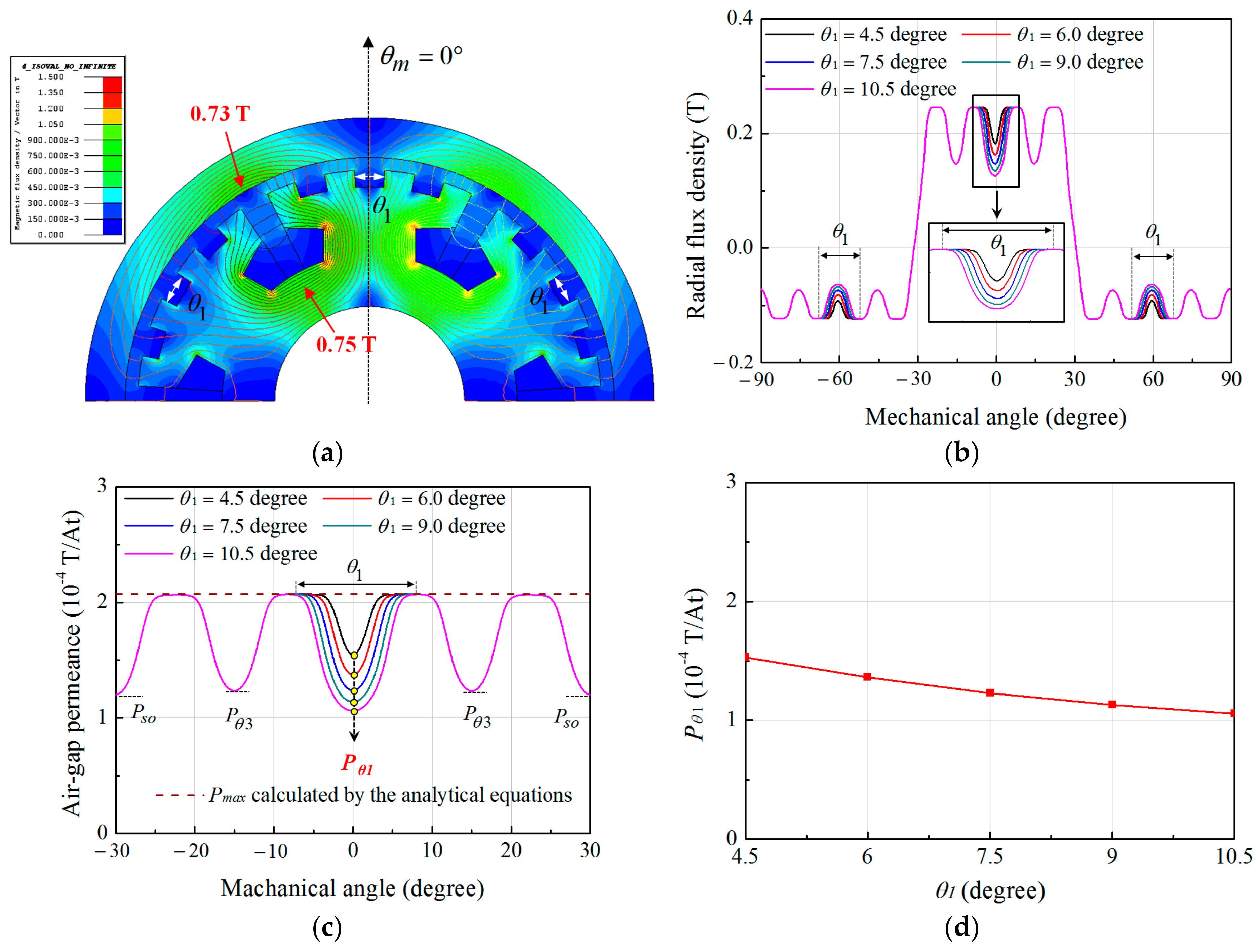



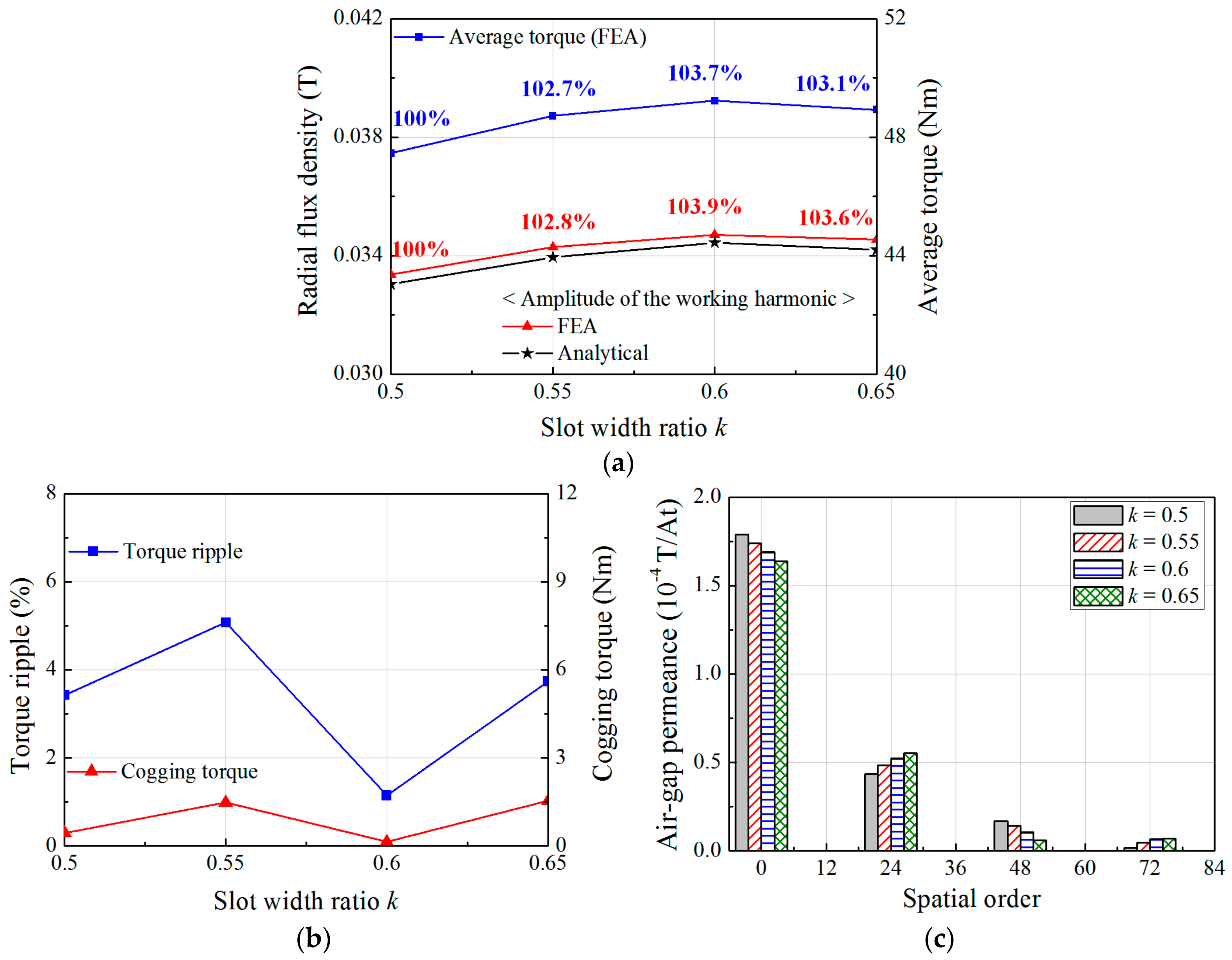




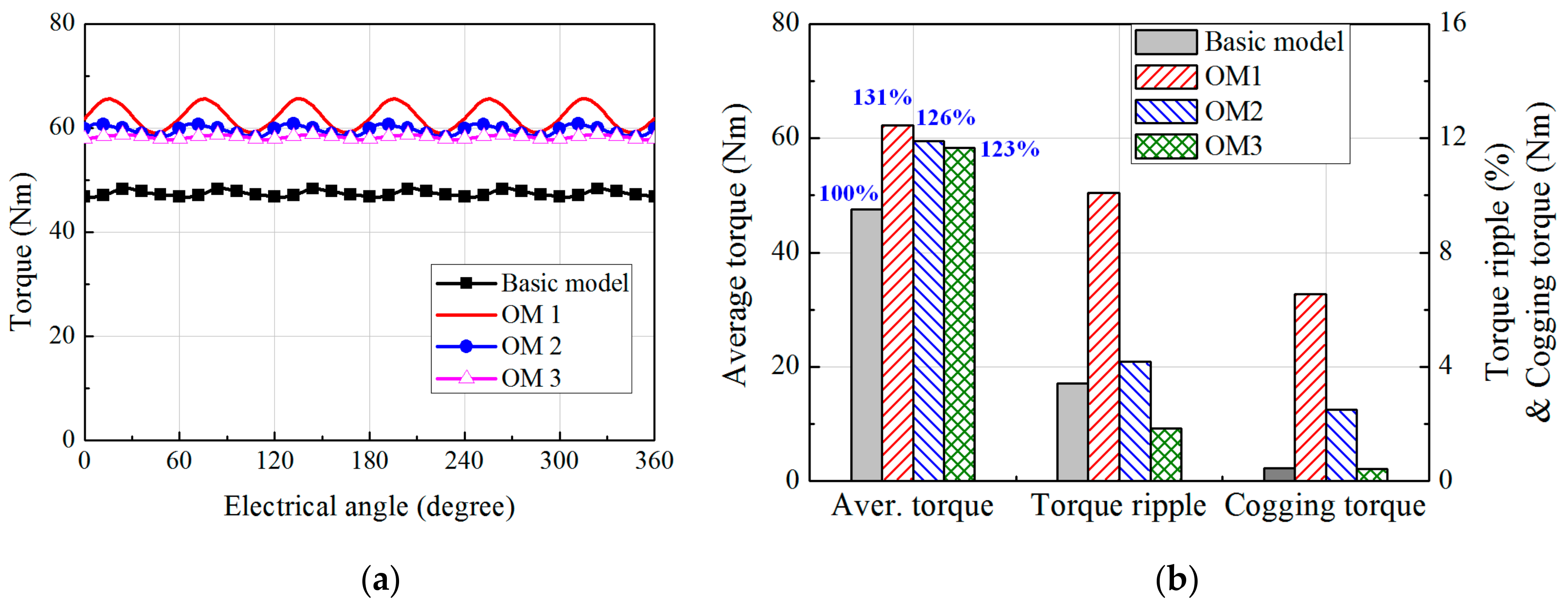
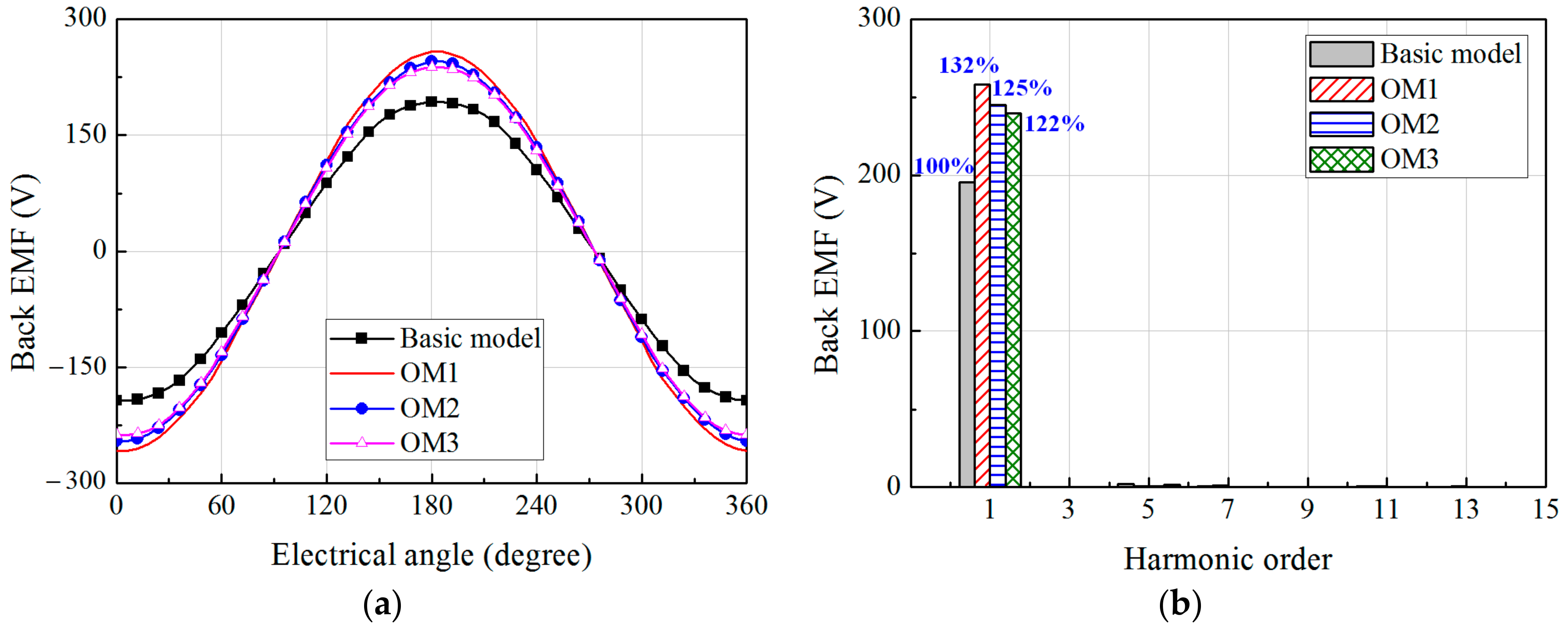
| Quantity | Value | Quantity | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rotor Outer Diameter | 260 mm | Height of FMPs | 8 mm |
| Stack Length | 30 mm | Number of turns per coil | 140 |
| Air-Gap Length | 1 mm | PM residual flux density | 1.2 T |
| PM Thickness | 5 mm | Armature phase current | 6 A |
| Slot Width Ratio | Design Variables (°) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k | θ1 | θ2 | θ3 | θ4 | θs |
| 0.5 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 7.5 |
| 0.55 | 8.25 | 6.75 | 8.25 | 6.75 | 8.25 |
| 0.6 | 9 | 6 | 9 | 6 | 9 |
| 0.65 | 9.75 | 5.25 | 9.75 | 5.25 | 9.75 |
| Model | Design Variables (Degree) | |B22(x)| (T) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| θ1 | θ2 | θ3 | θ4 | θs | Analytical | FEA | |
| Basic Model | 7.5 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 0.034 | 0.033 |
| OM1 | 11.66 | 4.7 | 11.72 | 5.86 | 3.78 | 0.045 | 0.044 |
| OM2 | 9.17 | 6.25 | 12.09 | 4.35 | 5.45 | 0.043 | 0.042 |
| OM3 | 13.06 | 5.27 | 9.97 | 4.98 | 6.49 | 0.042 | 0.041 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, D.; Chang, J. A Novel Design Method for the Geometric Shapes of Flux Modulation Poles in the Surface-Mounted Permanent Magnet Vernier Machines. Energies 2017, 10, 1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10101551
Jang D, Chang J. A Novel Design Method for the Geometric Shapes of Flux Modulation Poles in the Surface-Mounted Permanent Magnet Vernier Machines. Energies. 2017; 10(10):1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10101551
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Daekyu, and Junghwan Chang. 2017. "A Novel Design Method for the Geometric Shapes of Flux Modulation Poles in the Surface-Mounted Permanent Magnet Vernier Machines" Energies 10, no. 10: 1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10101551
APA StyleJang, D., & Chang, J. (2017). A Novel Design Method for the Geometric Shapes of Flux Modulation Poles in the Surface-Mounted Permanent Magnet Vernier Machines. Energies, 10(10), 1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10101551





