Design Methodology, Modeling, and Comparative Study of Wireless Power Transfer Systems for Electric Vehicles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Convenience: eliminating the need for power cables and the effect of the bad weather;
- Safety: eliminating the danger of sparking and electrical shock risk;
- Reliability: eliminating the components with the greatest possibility of failure in most electronic systems, namely, the power cords and connectors.
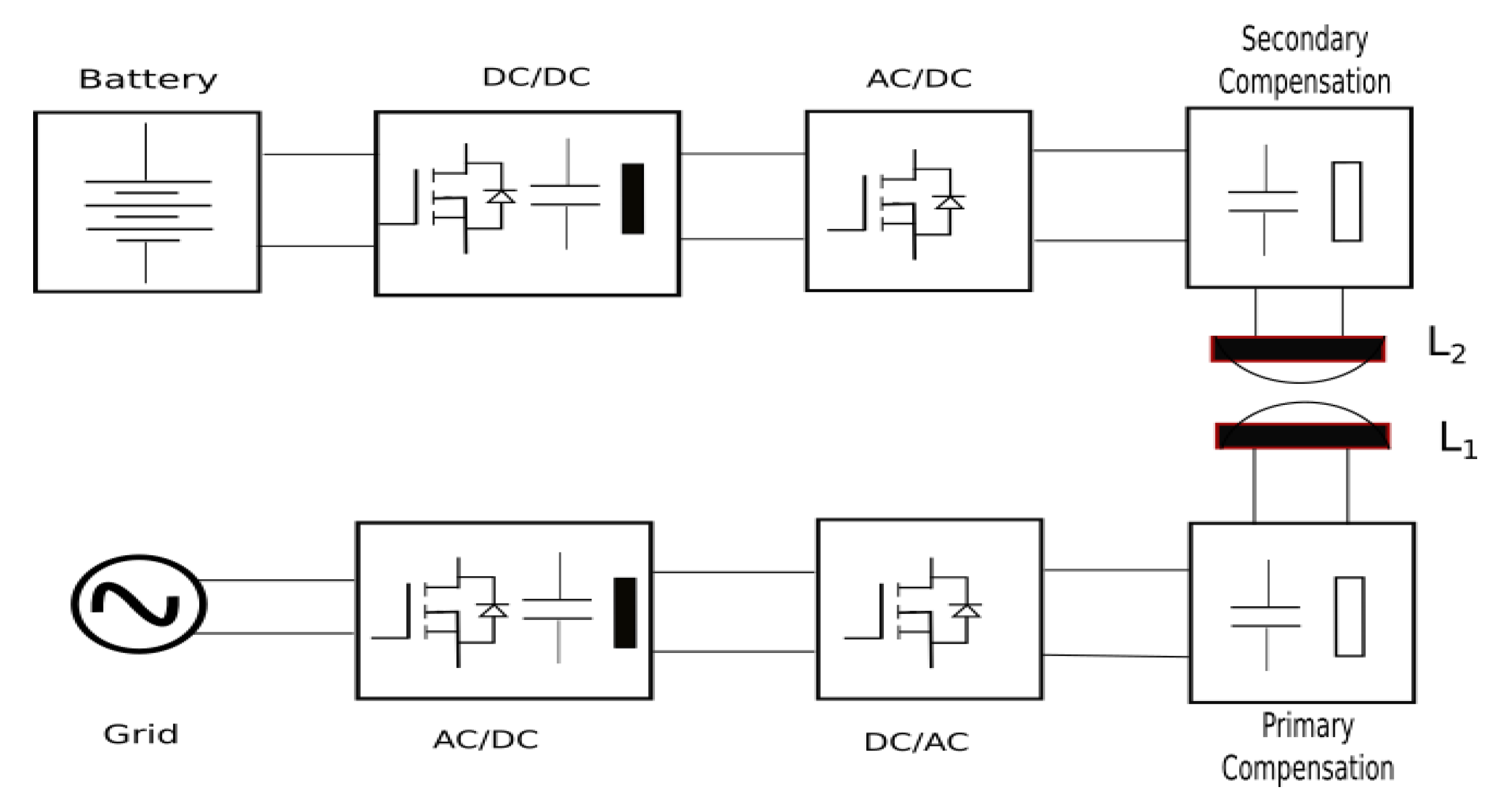
2. Design Sizing Methodology for the SS Topology of the WPT System
2.1. Resonant Wireless Power Transfer System
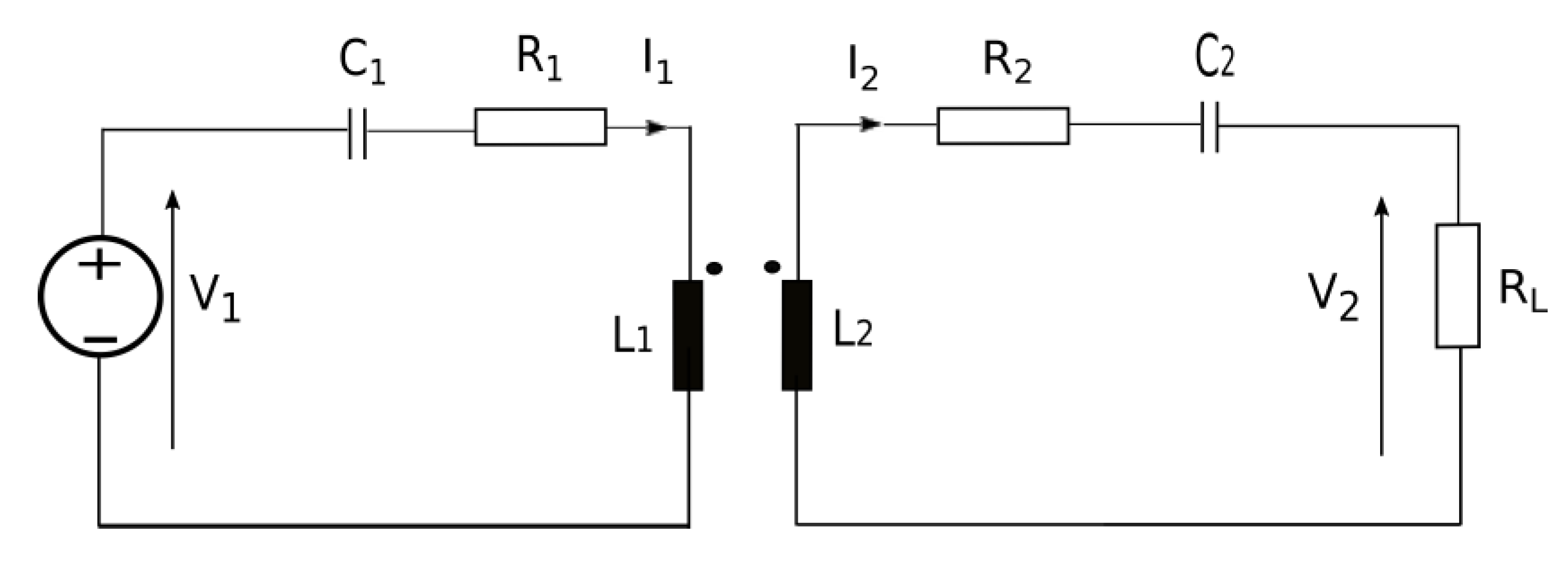
2.2. WPT System Model for SS Topology
2.3. Windings Sizing Calculation
2.4. Self and Mutual Inductance Calculation
2.5. Design Steps for the SS Topology WPT System
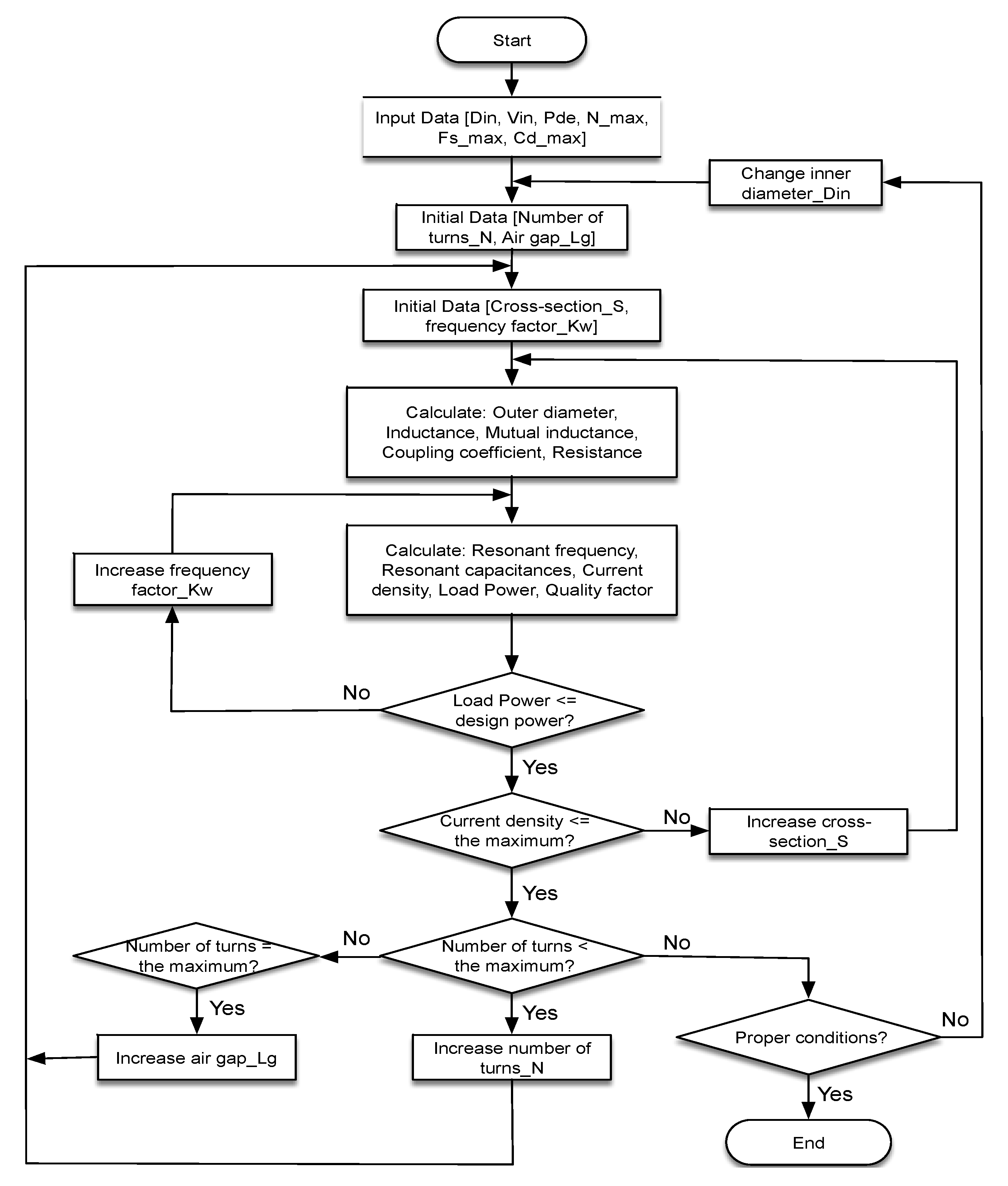
3. Design Optimization for SS Topology of WPT System
3.1. Flow Chart of Coil Sizing Optimization
3.2. Optimal Parameters and Coil Dimensions
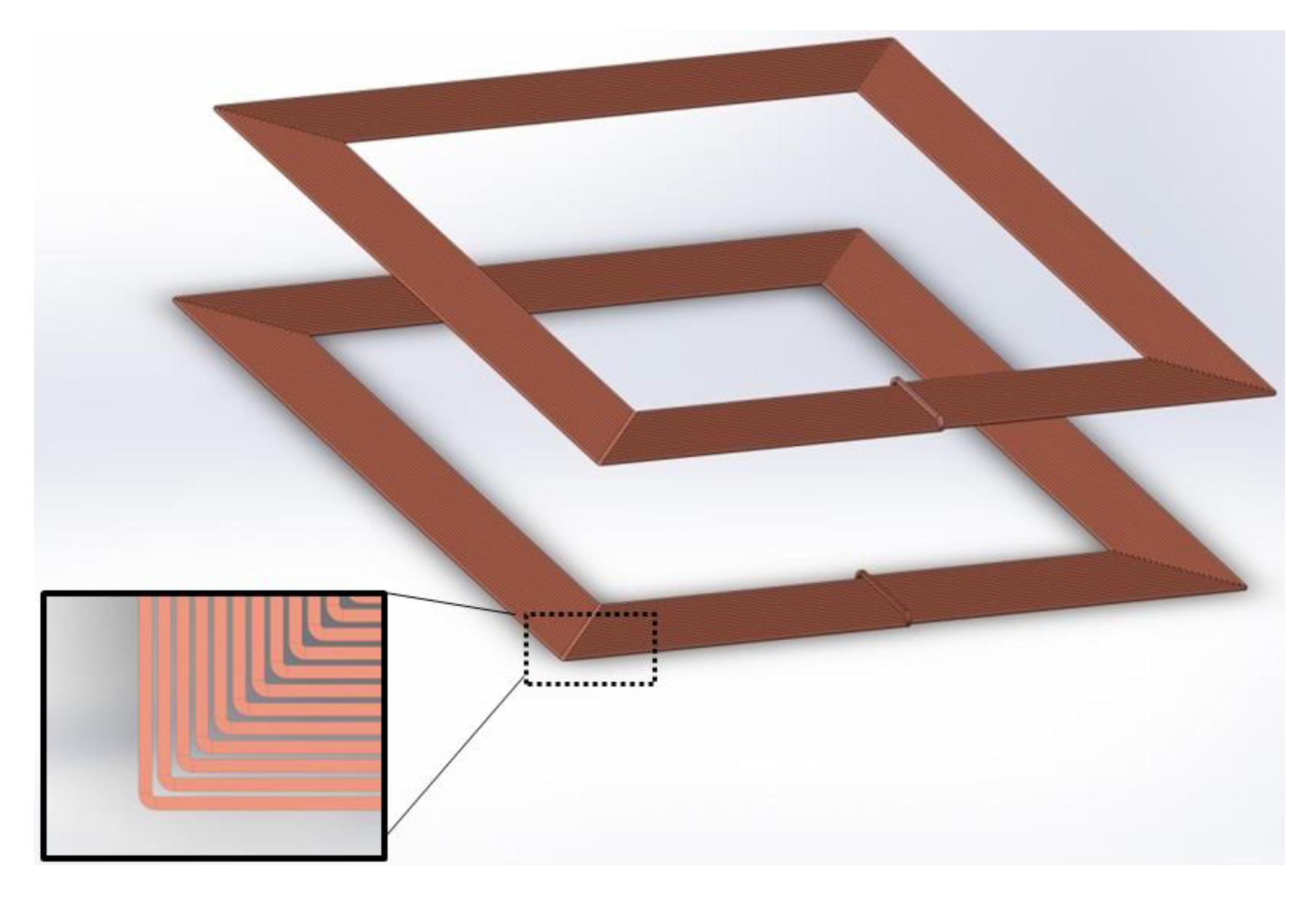
4. Magnetic Design and Verification
Magnetic Design and Verification of Coils Parameters
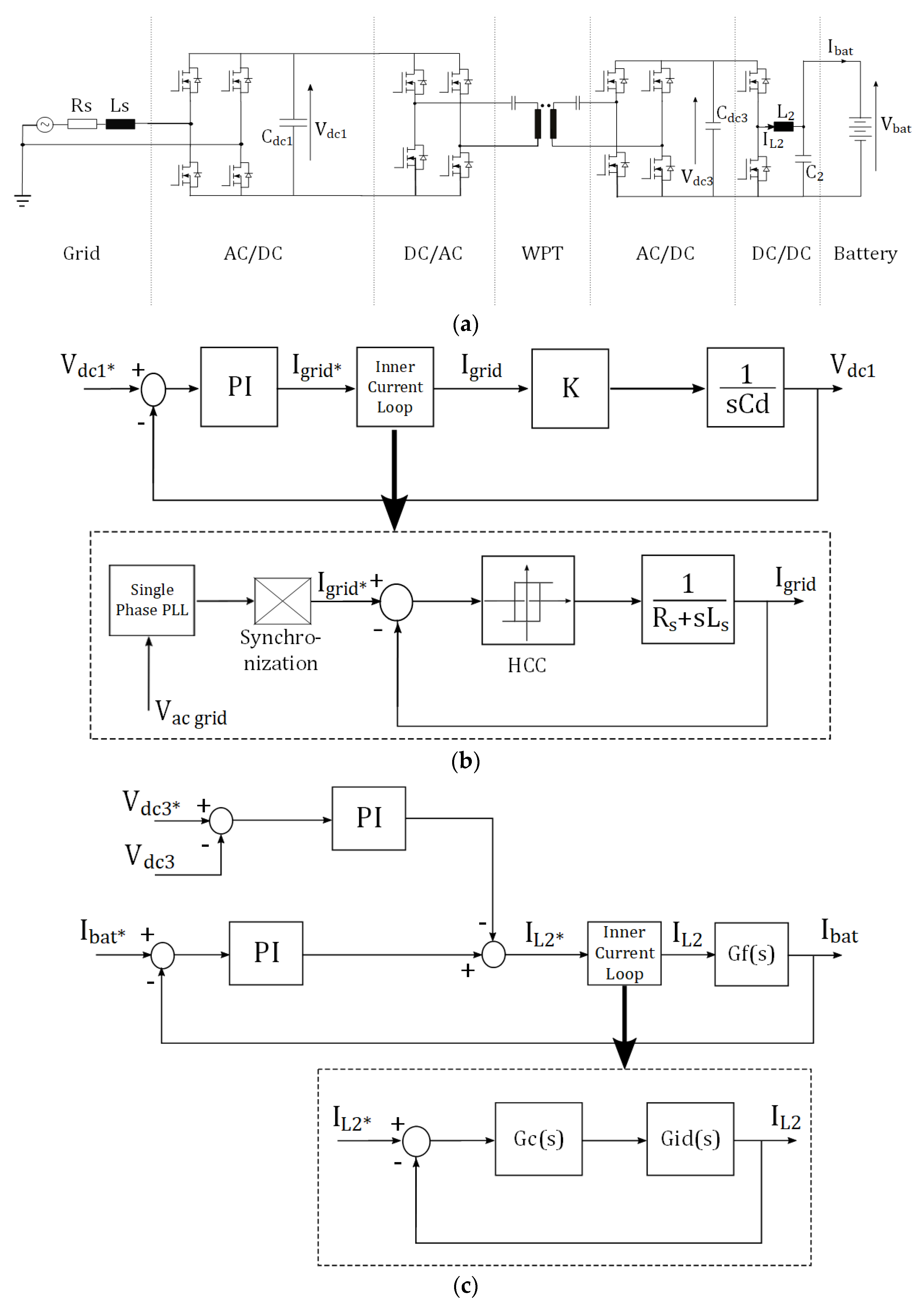
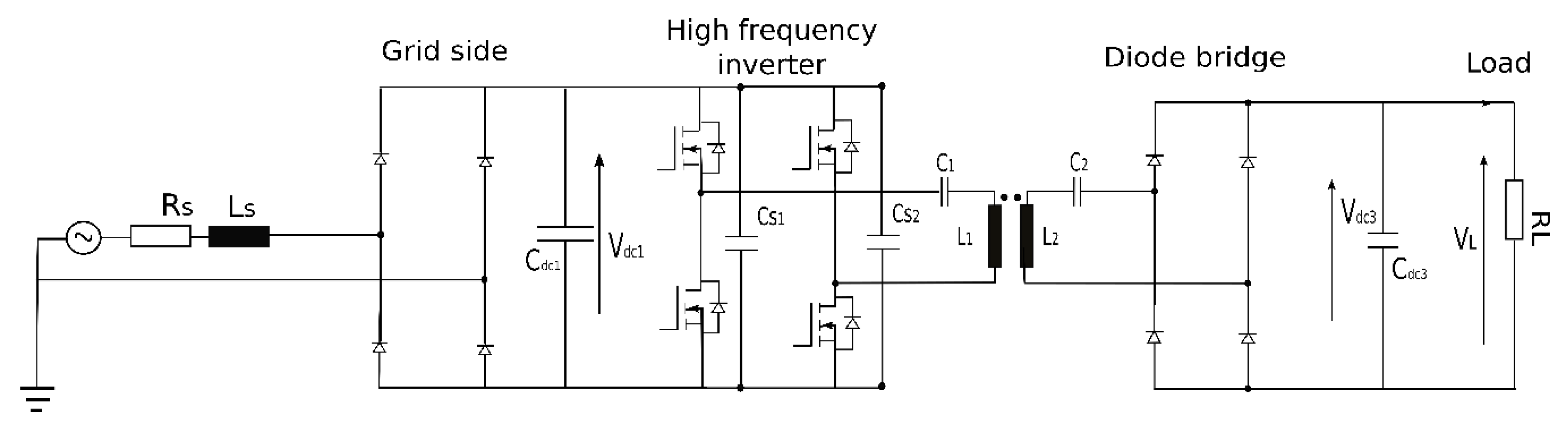
5. Design of Control System for a Bidirectional SS WPT System
5.1. WPT System Control for Low-Voltage Battery
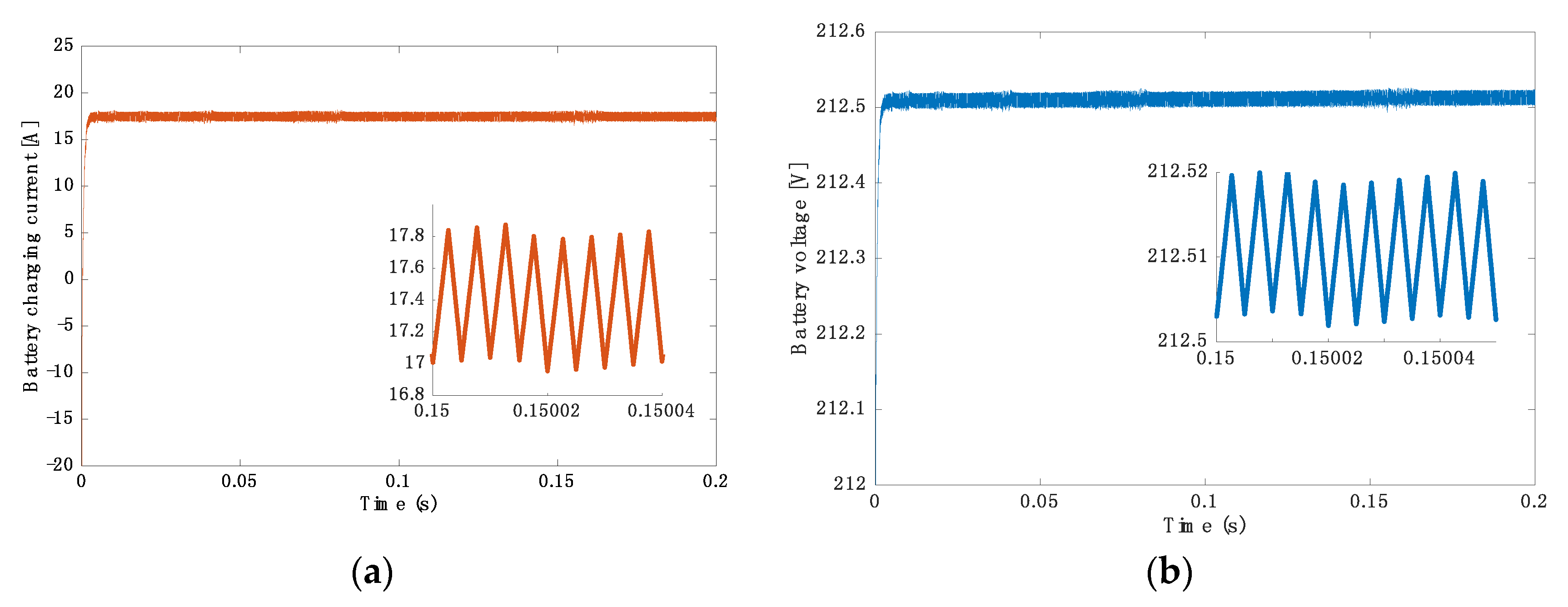
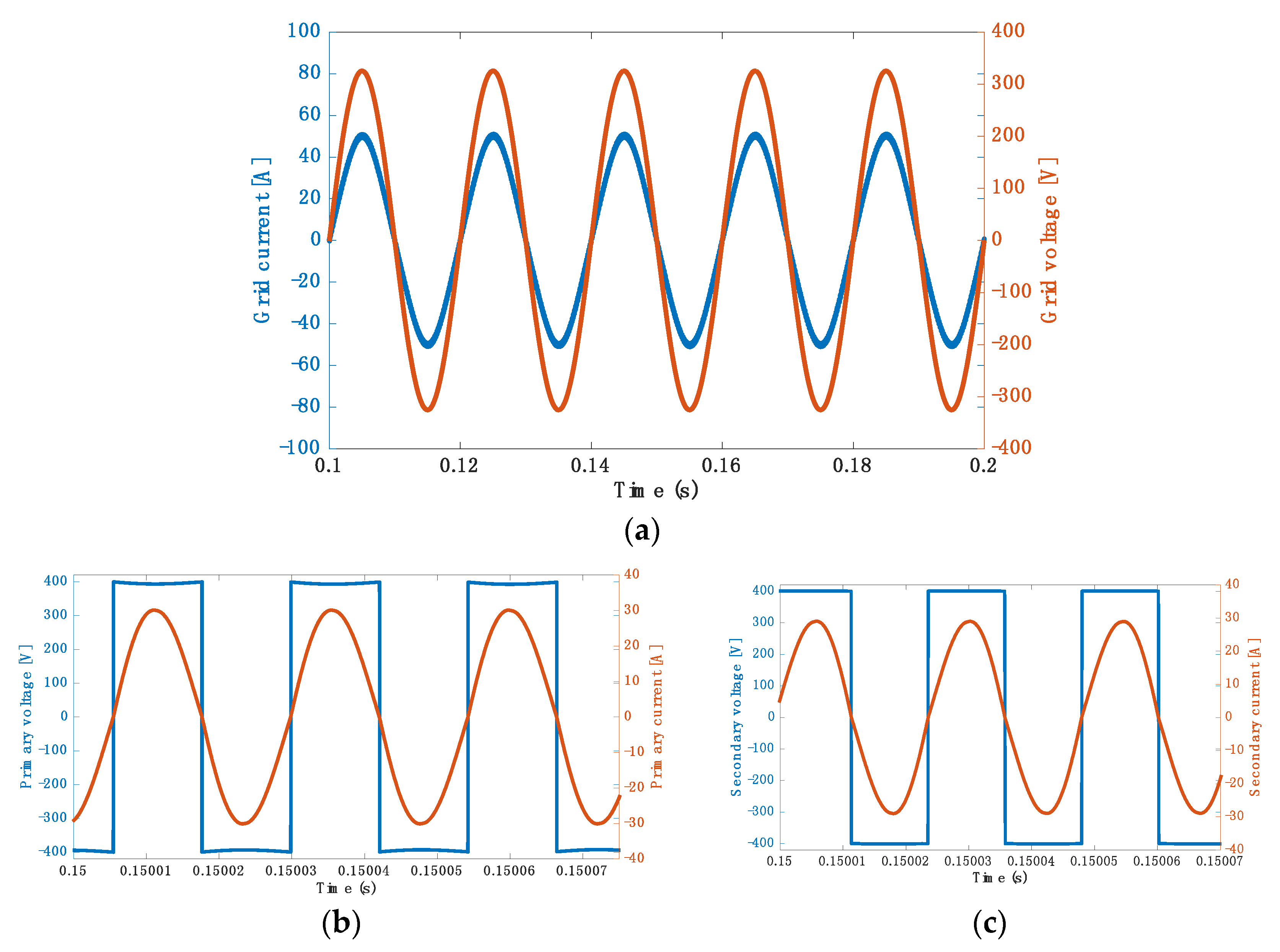
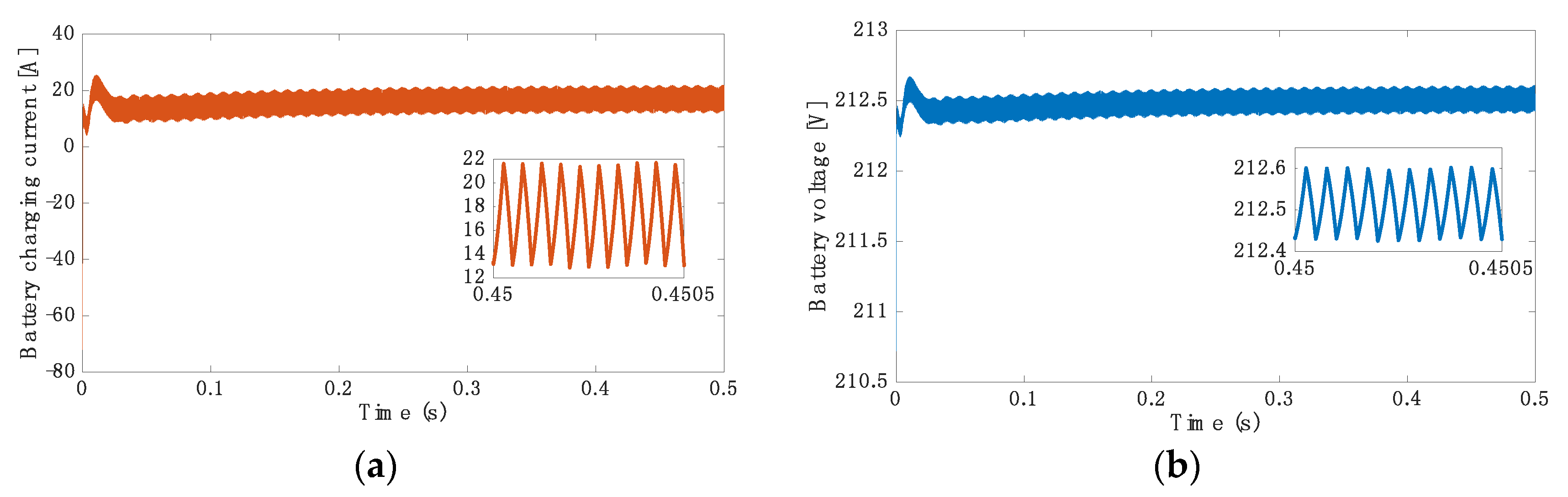
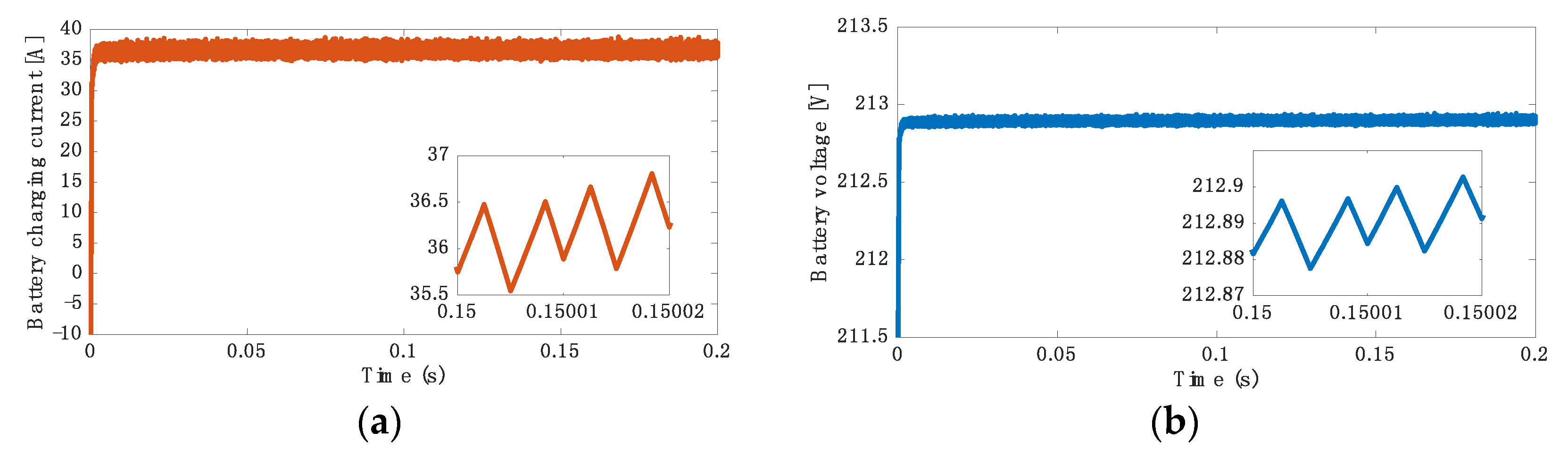
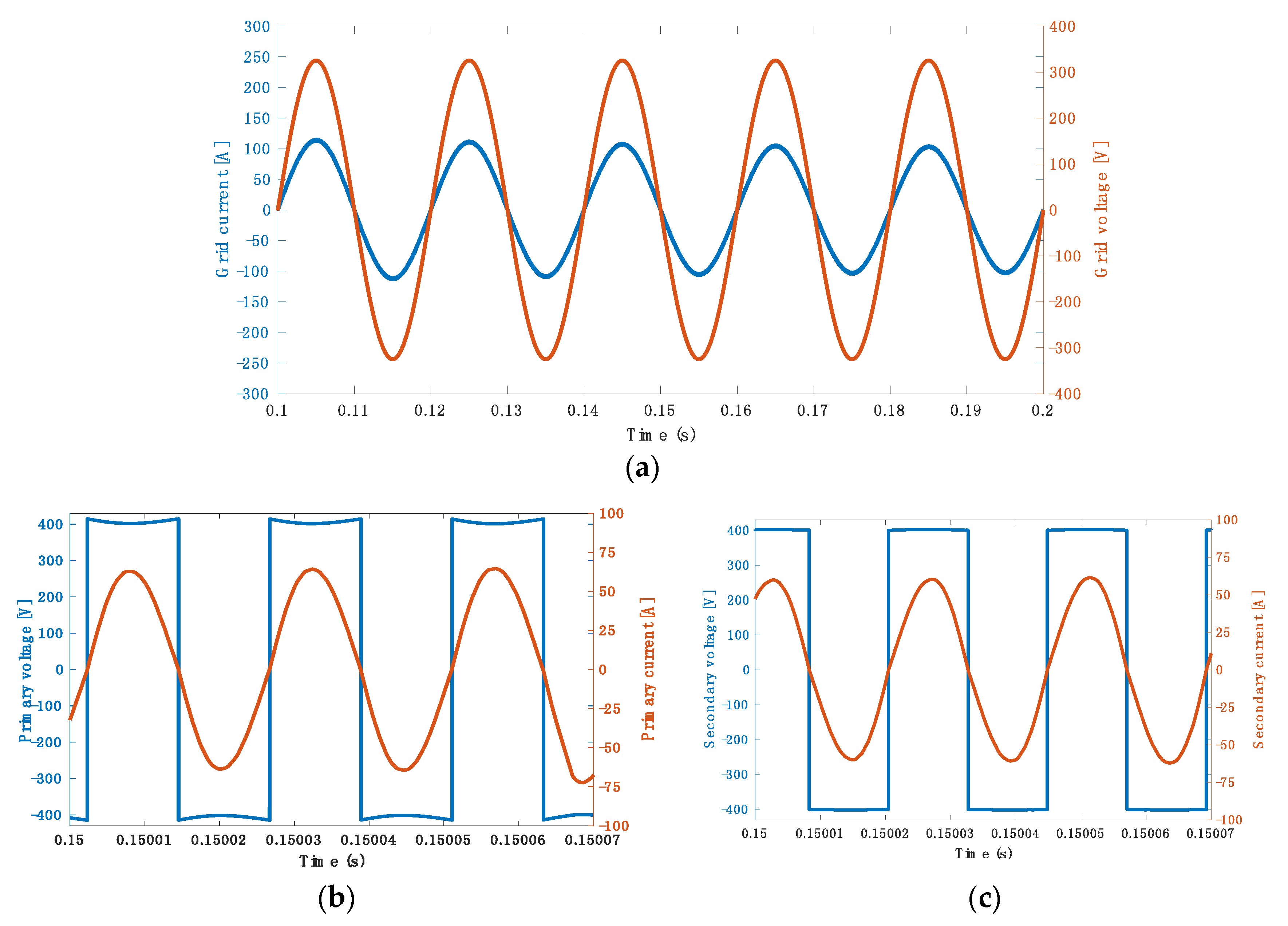
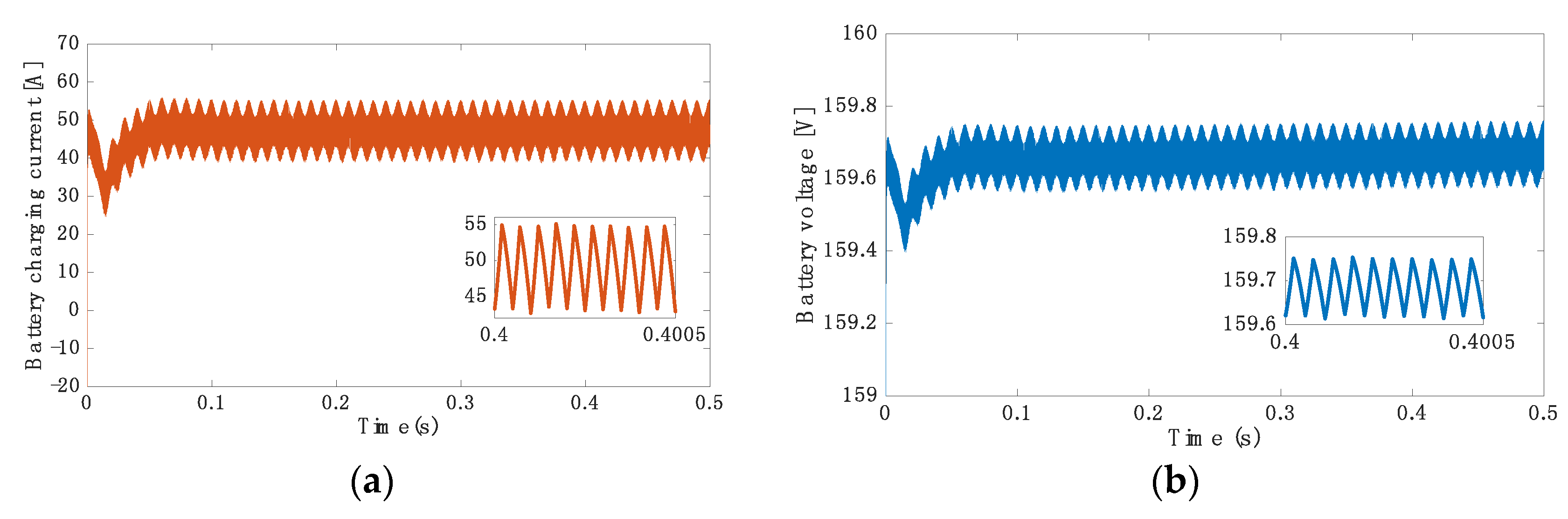
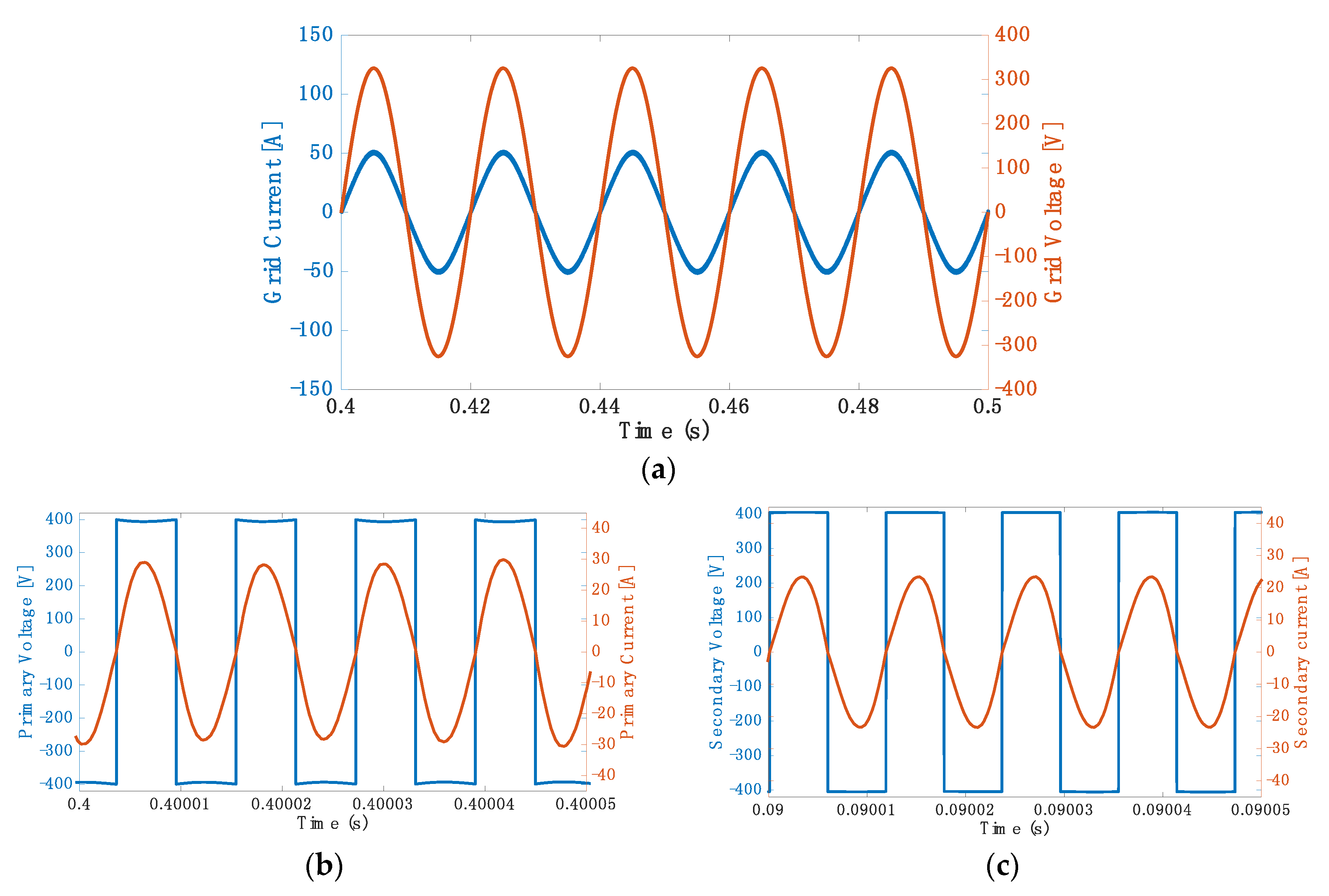
5.2. Simulation Results for 3.7 kW at 40 kHz
5.3. Simulation Results for 3.7 kW at 85 kHz
5.4. Simulation Results for 7.7 kW at 40 kHz
5.5. Simulation Results for 7.7 kW at 85 kHz
6. Experimental Validation
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hegazy, O.; Barrero, R.; Van Mierlo, J.; Lataire, P.; Omar, N.; Coosemans, T. An advanced power electronics interface for electric vehicles applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 5508–5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACEA—European Automobile Manufacturers’ Association. ACEA Report. Available online: http://www.acea.be/publications (accessed on 12 June 2018).
- Miceli, R.; Viola, F. Designing a sustainable university recharge area for electric vehicles: Technical and economic analysis. Energies 2017, 10, 1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenna, M.; Dolara, A.; Foiadelli, F.; Leva, S.; Longo, M. Urban scale photovoltaic charging stations for electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2014, 5, 1234–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, M.; Zaninelli, D.; Viola, F.; Romano, P.; Miceli, R.; Caruso, M.; Pellitteri, F. Recharge stations: A review. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Ecological Vehicles and Renewable Energies, EVER 2016, Monte Carlo, Monaco, 6–8 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Covic, G.A.; Boys, J.T. Inductive Power Transfer. Proc. IEEE 2013, 101, 1276–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covic, G.A.; Boys, J.T. Modern Trends in Inductive Power Transfer for Transportation Applications. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2013, 1, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalwar, K.A.; Aamir, M.; Mekhilef, S. Inductively coupled power transfer (ICPT) for electric vehicle charging—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 47, 462–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosshard, R.; Kolar, J.W. Inductive Power Transfer for Electric Vehicle Charging: Technical challenges and tradeoffs. IEEE Power Electron. Mag. 2016, 3, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogge, M.; Wollny, S.; Sauer, D. Fast Charging Battery Buses for the Electrification of Urban Public Transport—A Feasibility Study Focusing on Charging Infrastructure and Energy Storage Requirements. Energies 2015, 8, 4587–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersson, M. Energy Storage Solutions for Electric Bus Fast Charging Stations. Master’s Thesis, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, P.; Miller, J.M.; Onar, O.C.; White, C.P. A Compact Wireless Charging System for ElectricVehicles. In Proceedings of the Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Denver, CO, USA, 15–19 September 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 3629–3634. [Google Scholar]
- Garcés Quílez, M.; Abdel-Monem, M.; El Baghdadi, M.; Yang, Y.; Van Mierlo, J.; Hegazy, O. Modelling, Analysis and Performance Evaluation of Power Conversion Unit in G2V/V2G Application—A Review. Energies 2018, 11, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.M.; Jones, P.T.; Li, J.M.; Onar, O.C. ORNL experience and challenges facing dynamic wireless power charging of EV’s. IEEE Circuits Syst. Mag. 2015, 15, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, L.; Shuai, C.; Chen, Z. Wireless Power Transfer by Electric Field Resonance and Its Application in Dynamic Charging. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 6602–6612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhao, H.; Deng, J.; Li, S.; Mi, C.C. Comparison Study on SS and double-sided LCC compensation topologies for EV/PHEV Wireless Chargers. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 65, 4429–4439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, Y.H.; Choi, B.H.; Lee, E.S.; Lim, G.C.; Cho, G.H.; Rim, C.T. General Unified Analyses of Two-Capacitor Inductive Power Transfer Systems: Equivalence of Current-Source SS and SP Compensations. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 6030–6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditya, K.; Williamson, S.S. Comparative Study of Series-Series and Series-Parallel Compensation Topologies for Electric Vehicle Charging. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 23rd International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), Istanbul, Turkey, 1–4 June 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 426–430. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Wong, S.C.; Tse, C.K.; Chen, Q. Analysis and comparison of secondary series-and parallel-compensated inductive power transfer systems operating for optimal efficiency and load-independent voltage-transfer ratio. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 2979–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stielau, O.H.; Covic, G.A. Design of loosely coupled inductive power transfer systems. In Proceedings of the 2000 International Conference on Power System Technology, Perth, WA, Australia, 4–7 December 2000; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X.; Liao, Y. Compensation topology for flat spiral coil inductive power transfer systems. IET Power Electron. 2015, 8, 1893–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neath, M.J.; Swain, A.K.; Madawala, U.K.; Thrimawithana, D.J. An optimal PID controller for a bidirectional inductive power transfer system using multiobjective genetic algorithm. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 1523–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.H.; Covic, G.A.; Boys, J.T.; Robertson, D.J. A series-tuned inductive-power-transfer pickup with a controllable AC-voltage output. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 26, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wong, S.C.; Tse, C.K.; Chen, Q. A study of sectional tracks in roadway inductive power transfer system. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 17–22 September 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 822–826. [Google Scholar]
- Chopra, S. Contactless Power Transfer for Electric Vehicle Charging Application. Master’s Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Prasanth, V. Wireless Power Transfer for E-Mobility. Master’s Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Liu, S.; Zhou, Y.C.; Cui, T.J. An optimizable circuit structure for high-efficiency wireless power transfer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, J.L.; Sallán, J.; Sanz Osorio, J.F.; Llombart, A. High-misalignment tolerant compensation topology for ICPT systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosshard, R.; Kolar, J.W. Fundamentals and Multi-Objective Design of Inductive Power Transfer Systems. In Proceedings of the 30th Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC 2015), Charlotte, NC, USA, 15–19 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.; Lai, J.S.; Chen, R.; Faraci, W.E.; Zahid, Z.U.; Gu, B.; Zhang, L.; Lisi, G.; Anderson, D. High Efficiency Contactless Power Transfer System for Electric Vehicle Battery Charging Application. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2014, 6777, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Rodriguez, F.J.; Hernández, J.C.; Jurado, F. Voltage behaviour in radial distribution systems under the uncertainties of photovoltaic systems and electric vehicle charging loads. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2018, 28, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, J.C.; Ruiz-Rodriguez, F.J.; Jurado, F. Modelling and assessment of the combined technical impact of electric vehicles and photovoltaic generation in radial distribution systems. Energy 2017, 141, 316–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Sutil, F.; Hernández, J.C.; Tobajas, C. Overview of electrical protection requirements for integration of a smart DC node with bidirectional electric vehicle charging stations into existing AC and DC railway grids. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2015, 122, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, J.C.; Sutil, F.S.; Vidal, P.G. Protection of a multiterminal DC compact node feeding electric vehicles on electric railway systems, secondary distribution networks, and PV systems. Turkish J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2016, 24, 3123–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Mi, C. Wireless Power Transfer for Electric Vehicle Applications. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2015, 3, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigerwald, R.L. Comparison of Half-Bridge Resonant Converter Topologies. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 1988, 3, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallan, J.; Villa, J.L.; Llombart, A.; Sanz, J.F. Optimal Design of ICPT Systems Applied to Electric Vehicle Battery Charge. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 2140–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditya, K.; Williamson, S.S. Design considerations for loosely coupled inductive power transfer (IPT) system for electric vehicle battery charging—A comprehensive review. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), Dearborn, MI, USA, 15–18 June 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Benomar, Y.; El Baghdadi, M.; Hegazy, O.; Yang, Y.; Messagie, M.; Mierlo, J. Van Design and modeling of V2G inductive charging system for light-duty Electric Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2017 Twelfth International Conference on Ecological Vehicles and Renewable Energies (EVER), Monte Carlo, Monaco, 11–13 April 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- El Baghdadi, M.; Benomar, Y.; Hegazy, O.; Yang, Y.; Van Mierlo, J. Design approach and interoperability analysis of wireless power transfer systems for vehicular applications. In Proceedings of the 2016 18th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE’16 ECCE Europe), Karlsruhe, Germany, 5–9 September 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Benomar, Y.; El Baghdadi, M.; Hegazy, O.; Van Mierlo, J. Design, Modeling and Control of a Bidirectional Wireless Power Transfer for Light-Duty Vehicles: G2V and V2G Systems. In Proceedings of the 2017 19th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE’17 ECCE Europe), Warsaw, Poland, 11–14 September 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]


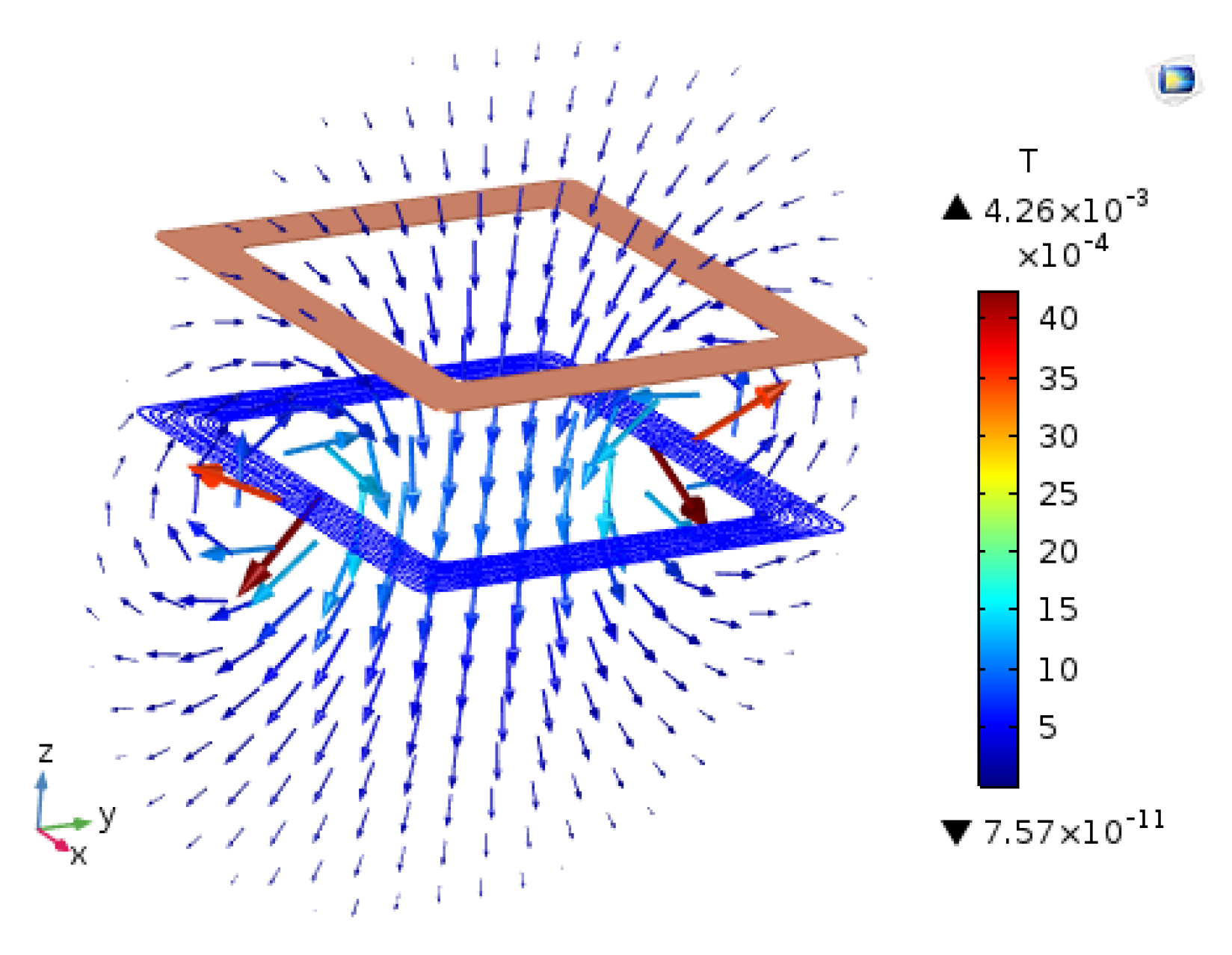

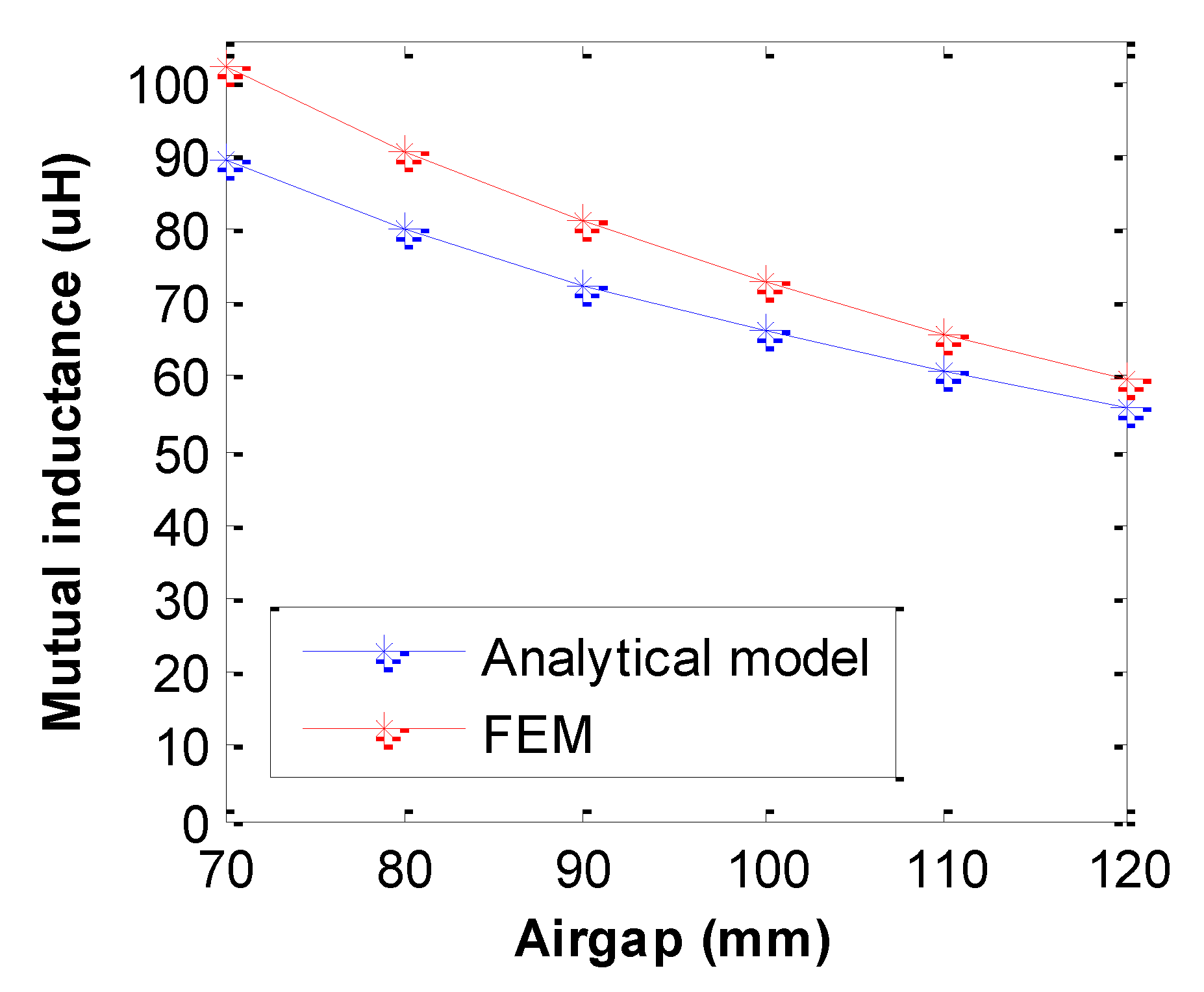
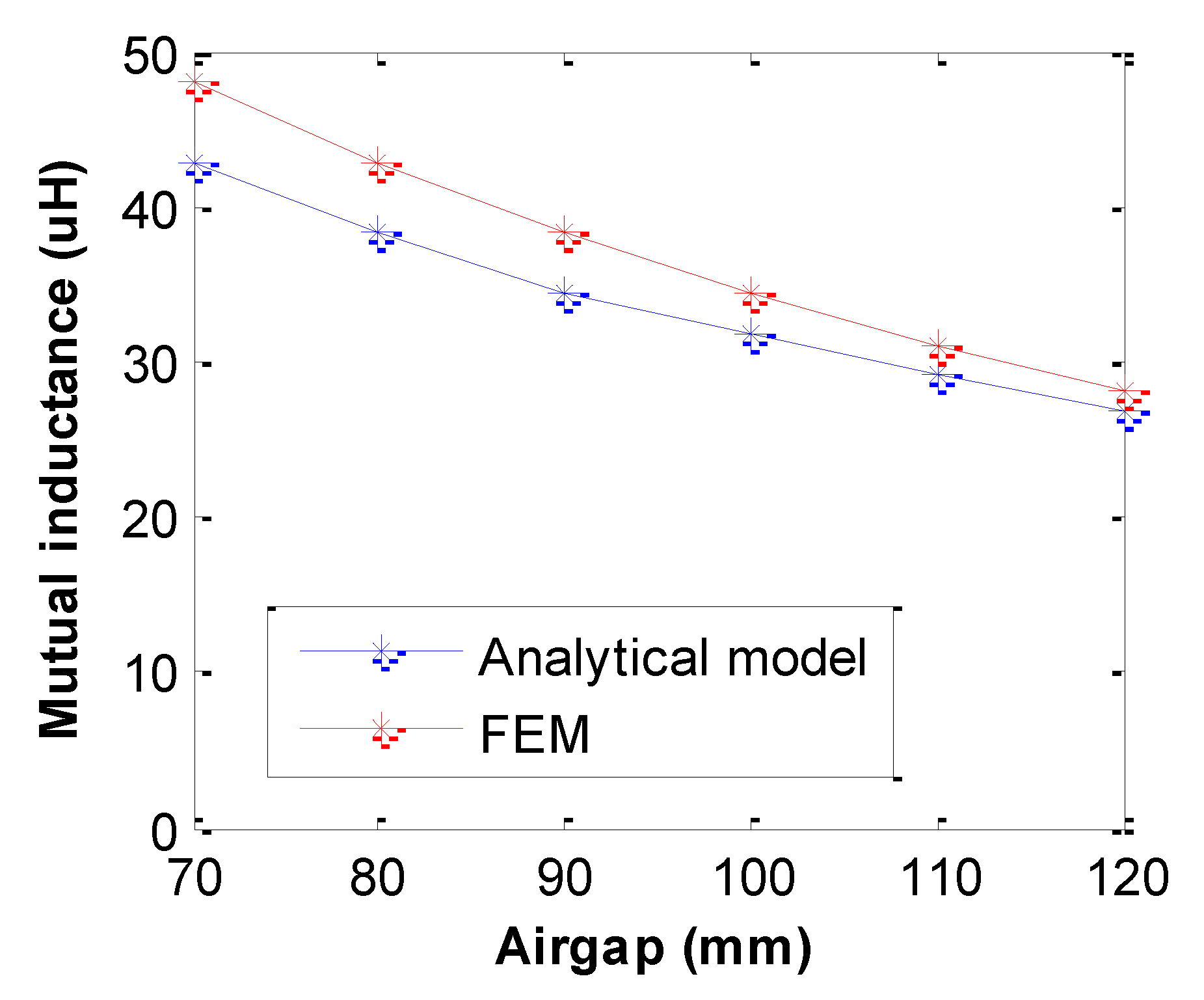



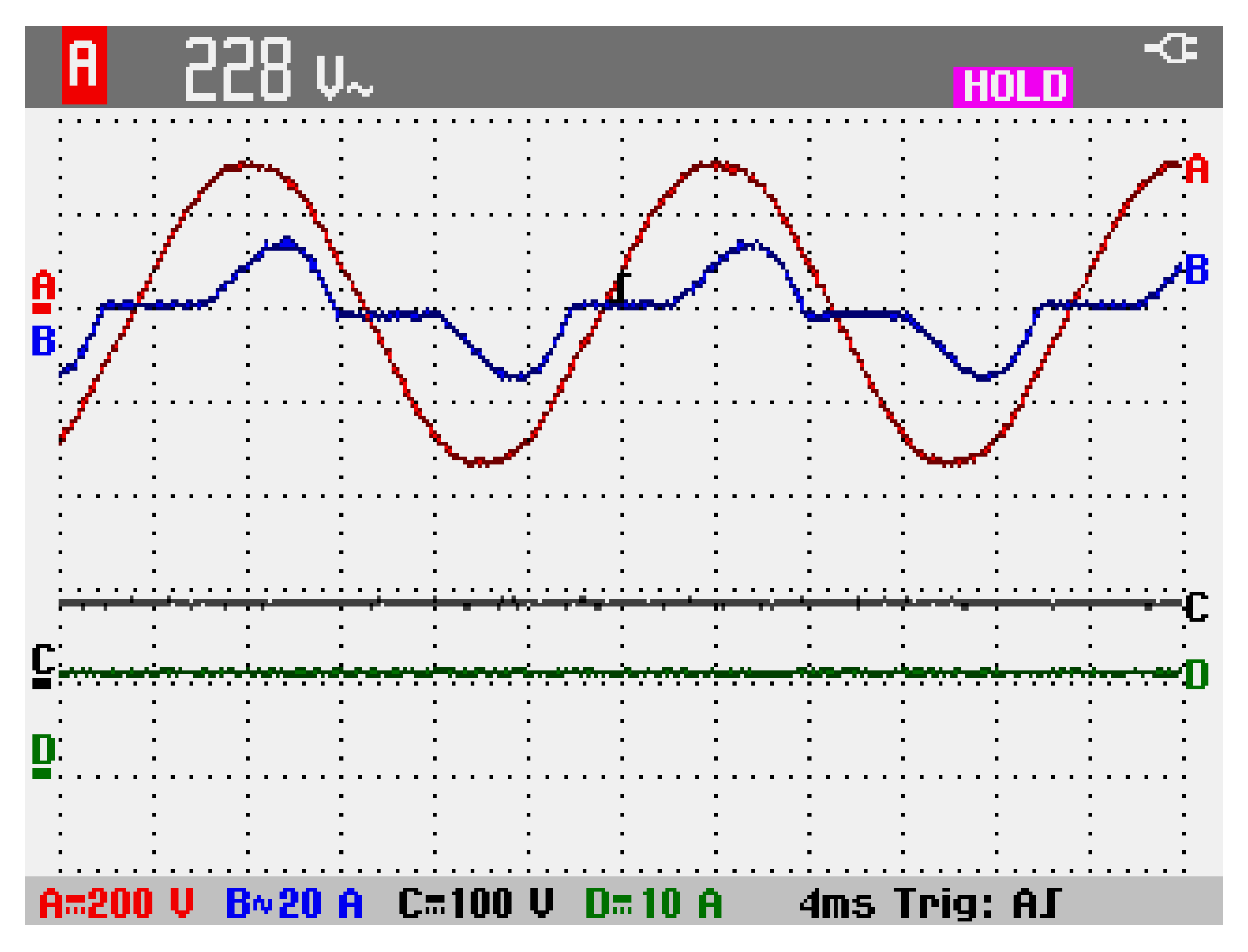
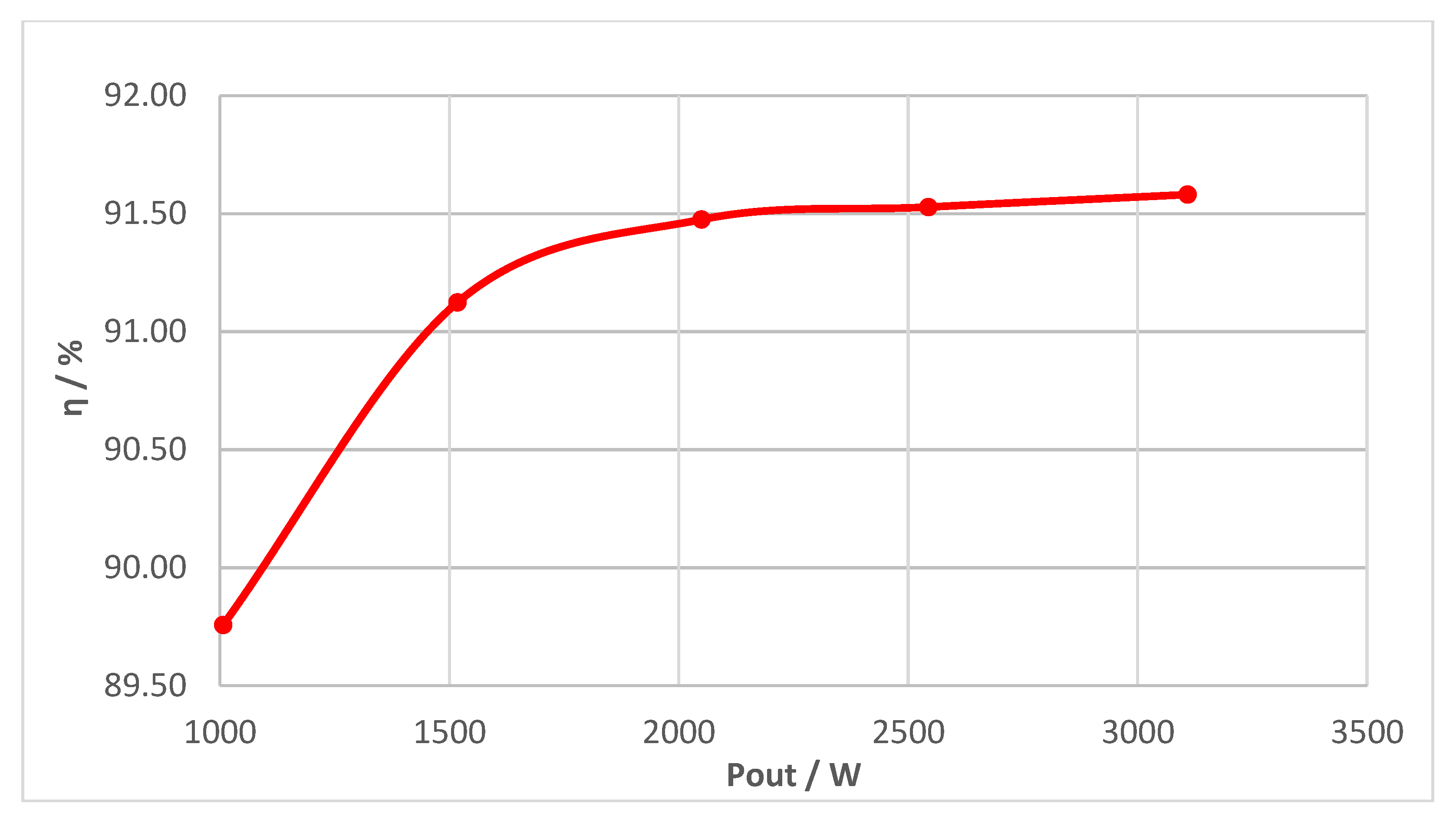
| Frequency (kHz) | Power Level (kW) | Number of Turns | Winding Cross-Sectional Area (mm2) | Primary Coil Outer Size (mm) | Secondary Coil Outer Size (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | N2 | S1 | S2 | ||||
| 40/85 | 3.7 | 23 | 22 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 334 × 334 | 330 × 330 |
| 7.7 | 16 | 15 | 5.4 | 5.4 | 364 × 364 | 329 × 329 | |
| Frequency (kHz) | Power Level (kW) | L1 (μH) | L2 (μH) | C1 (nF) | C2 (nF) | R1 (mΩ) | R2 (mΩ) | Lg (mm) | M (μH) | k |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | 3.7 | 332.41 | 302.24 | 47.63 | 52.37 | 203 | 192 | 100 | 68.45 | 0.22 |
| 7.7 | 160.80 | 140.06 | 98.45 | 113.03 | 68 | 63 | 100 | 33.05 | 0.22 | |
| 85 | 3.7 | 332.41 | 302.24 | 10.69 | 11.76 | 203 | 192 | 100 | 68.45 | 0.22 |
| 7.7 | 160.80 | 140.06 | 22.17 | 25.45 | 68 | 63 | 100 | 33.05 | 0.22 |
| 3.7 kW | 7.7 kW | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analytical Model | FEM | Error (%) | Analytical Model | FEM | Error (%) | |
| L1 (μH) | 332.41 | 323.65 | 3 | 160.80 | 159.62 | 1 |
| L2 (μH) | 302.24 | 298.38 | 1 | 140.06 | 138.98 | 1 |
| M (μH) | 68.45 | 72.99 | 7 | 33.05 | 34.51 | 4 |
| k | 0.22 | 0.23 | - | 0.22 | 0.23 | - |
| Parameter | L1 (μH) | L2 (μH) | C1 (nF) | C2 (nF) | Cs1 (uF) | Cs2 (uF) | Cdc3 (uF) | RL (Ω) | fsw (kHz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simulation | 332.41 | 302.24 | 47.63 | 52.37 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 4700 | 8.3 | 40 |
| Lab Measurement | 336.91 | 299.28 | 47 | 50 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 4700 | 8.3 | 37 |
| Components | Manufacturer | Part Number |
|---|---|---|
| Primary SiC MOSFET | ROHM | SCT3030KL |
| Diode Rectifies | IXYS | DSEP2x31-06A |
| Snubber Film Capacitors | KEMET | C4BSPBX4150ZBLJ |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; El Baghdadi, M.; Lan, Y.; Benomar, Y.; Van Mierlo, J.; Hegazy, O. Design Methodology, Modeling, and Comparative Study of Wireless Power Transfer Systems for Electric Vehicles. Energies 2018, 11, 1716. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11071716
Yang Y, El Baghdadi M, Lan Y, Benomar Y, Van Mierlo J, Hegazy O. Design Methodology, Modeling, and Comparative Study of Wireless Power Transfer Systems for Electric Vehicles. Energies. 2018; 11(7):1716. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11071716
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yang, Mohamed El Baghdadi, Yuanfeng Lan, Yassine Benomar, Joeri Van Mierlo, and Omar Hegazy. 2018. "Design Methodology, Modeling, and Comparative Study of Wireless Power Transfer Systems for Electric Vehicles" Energies 11, no. 7: 1716. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11071716
APA StyleYang, Y., El Baghdadi, M., Lan, Y., Benomar, Y., Van Mierlo, J., & Hegazy, O. (2018). Design Methodology, Modeling, and Comparative Study of Wireless Power Transfer Systems for Electric Vehicles. Energies, 11(7), 1716. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11071716









