Detection of Inter-Turn Faults in Multi-Phase Ferrite-PM Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Machines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
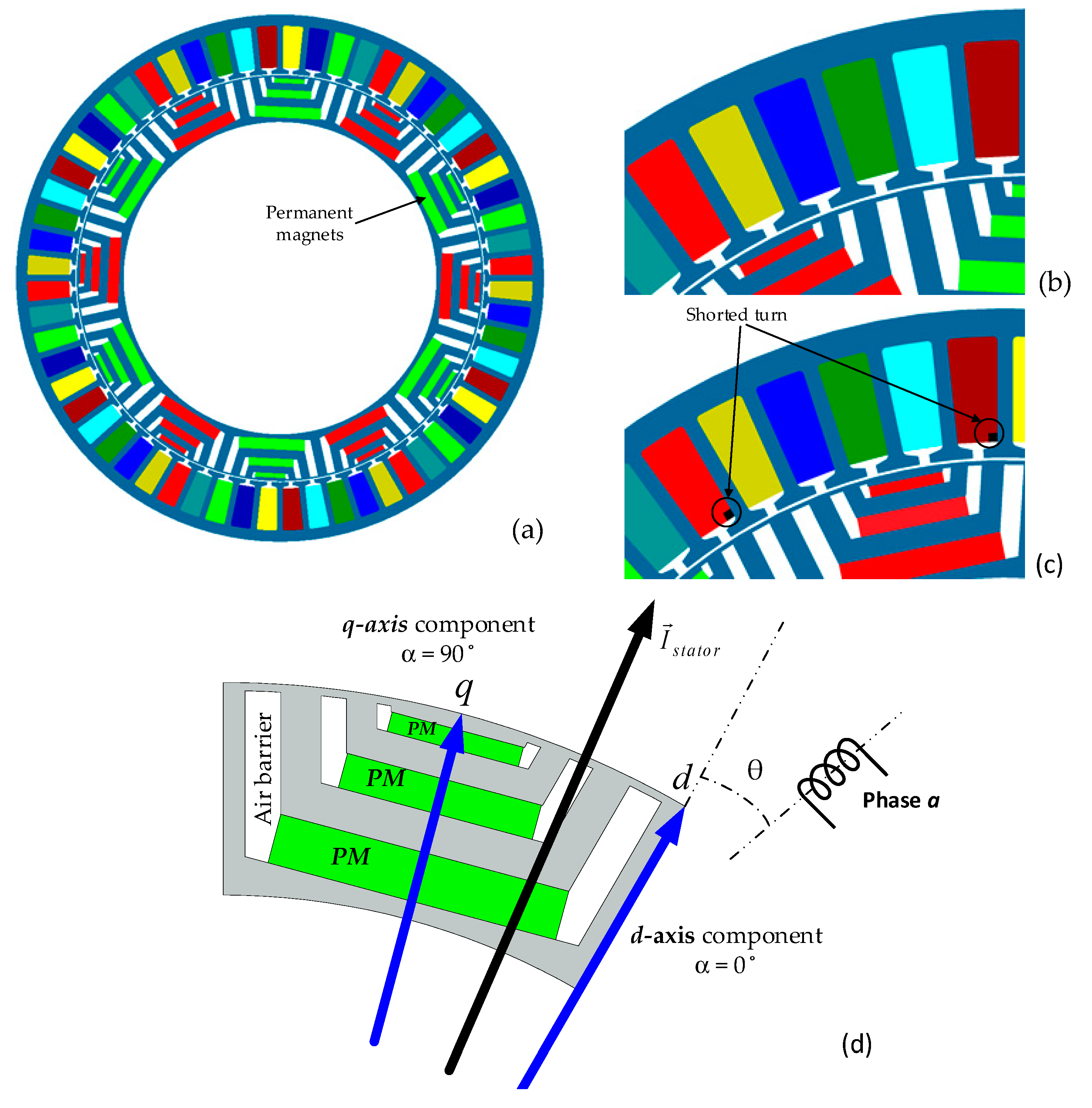
2. The Analyzed fPMa-SynRM
3. Validation of the FEM Model
4. Detection of Inter-Turn Faults in fPMa-SynRMs by Analyzing the Spectra of the Stator Currents and the ZSVC
5. Results
5.1. The Analyzed Machine Operating under Low-Load Conditions
5.2. The Analyzed Machine Operating under Rated Conditions
5.3. Summary of the Results Obtained
6. Indicators to Diagnose Early Inter-Turn Faults
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| ia,b,c,d,e | Instantaneous value of the phase current (A) |
| if | Instantaneous value of the fault current (A) |
| id | d-axis current (A) |
| iq | q-axis current (A) |
| iline,rated,peak,1 | Rated peak value of the fundamental harmonic of the line current (A) |
| iFFT | Spectral data of the line current provided by the FFT algorithm (A) |
| iline,peak,1 | Peak value of the fundamental harmonic of the line current (A) |
| iFFT,1 | Peak value of the fundamental harmonic of the line current (A) |
| va,b,c,d,e | Instantaneous value of the phase voltage (V) |
| vZSVC | Instantaneous value of the homopolar voltage (V) |
| vZSVC,FFT | Spectral data of the vZSVC provided by the FFT algorithm (V) |
| vZSVC,FFT,1 | Peak value of the fundamental harmonic of the vZSVC (V) |
| fs | Electrical frequency (Hz) |
| k | Harmonic number (-) |
| p | Pole pairs (-) |
| λPM | Instantaneous value of the zero-sequence component of the flux linkage due to the permanent magnets (Wb) |
| λa,b,c,d,c | Instantaneous value of the flux linkage in phases a,b,c,d,e due to permanent magnets (Wb) |
| Ra,b,c,d,e | Phase resistance (Ω) |
| θ | Rotor position (electrical °) |
| α | Current angle (electrical °) |
| FFT | Fast Fourier transform |
| fPMa-SynRM | Ferrite-assisted synchronous reluctance motor |
| IPM | Interior-PM motor |
| MCSA | Motor current signature analysis |
| PM | Permanent magnet |
| ZSVC | Zero-sequence voltage component |
| back-emf | Back-electromotive force |
| mmf | Magnetomotive force |
References
- Riba, J.-R.; López-Torres, C.; Romeral, L.; Garcia, A. Rare-earth-free propulsion motors for electric vehicles: A technology review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Wu, W.; Quan, L.; Xiang, Z.; Gu, W. Design and Multi-Objective Stratified Optimization of a Less-rare-earth Hybrid Permanent Magnets Motor with High Torque Density and Low Cost. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimiabeigi, M.; Sheridan, R.S.; Widmer, J.D.; Walton, A.; Farr, M.; Scholes, B.; Harris, I.R. Production and Application of HPMS Recycled Bonded Permanent Magnets for a Traction Motor Application. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 3795–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Chen, D.; Lipo, T.A.; Kwon, B.-I. Performance Improvement of Ferrite-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Machines Using Asymmetrical Rotor Configurations. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Bonthu, S.S.R.; Choi, S.; Baek, J. Design of five-phase permanent magnet assisted synchronous reluctance motor for low output torque ripple applications. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2016, 10, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Torres, C.; Riba, J.-R.; Garcia, A.; Romeral, L. Detection of eccentricity faults in five-phase ferrite-PM assisted synchronous reluctance machines. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognani, S.; Mahmoud, H.; Bianchi, N. Fast synthesis of permanent magnet assisted synchronous reluctance motors. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2016, 10, 312–318. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, H.; Bianchi, N. Eccentricity in Synchronous Reluctance Motors-Part I: Analytical and Finite-Element Models. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2015, 30, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.A.; Wadhwani, A.K.; Kapoor, S.R. Early Estimation of Faults in Induction Motors Using Symbolic Dynamic-Based Analysis of Stator Current Samples. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2011, 26, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Jeong, H.; Kim, S.W. Diagnosis of Interturn Short-Circuit Fault in PMSM by Residual Voltage Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Symposium on Power Electronics, Electrical Drives, Automation and Motion (SPEEDAM), Amalfi, Italy, 20–22 June 2018; pp. 160–164. [Google Scholar]
- Akar, M. Detection of a static eccentricity fault in a closed loop driven induction motor by using the angular domain order tracking analysis method. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2013, 34, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiz, J.; Jafari, A. Interturn fault diagnosis in brushless direct current motors—A review. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Lyon, France, 20–22 Feburary 2018; pp. 437–444. [Google Scholar]
- Urresty, J.-C.; Riba, J.-R.; Romeral, L. Application of the zero-sequence voltage component to detect stator winding inter-turn faults in PMSMs. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2012, 89, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romary, R.; Demian, C.; Schlupp, P.; Roger, J.-Y. Offline and Online Methods for Stator Core Fault Detection in Large Generators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 4084–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraaba, L.; Al-Hamouz, Z.; Abido, M.; Maraaba, L.; Al-Hamouz, Z.; Abido, M. An Efficient Stator Inter-Turn Fault Diagnosis Tool for Induction Motors. Energies 2018, 11, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ma, G.; Wu, Y.; Ma, G. Anti-Interference and Location Performance for Turn-to-Turn Short Circuit Detection in Turbo-Generator Rotor Windings. Energies 2019, 12, 1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-C.; Jheng, Y.-M.; Kuo, C.-C.; Hsueh, Y.-M.; Chang, H.-C.; Jheng, Y.-M.; Kuo, C.-C.; Hsueh, Y.-M. Induction Motors Condition Monitoring System with Fault Diagnosis Using a Hybrid Approach. Energies 2019, 12, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-K.; Jeong, C.-L.; Lee, S.-T.; Hur, J. Early Detection Technique for Stator Winding Inter-Turn Fault in BLDC Motor Using Input Impedance. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giantomassi, A.; Ferracuti, F.; Iarlori, S.; Ippoliti, G.; Longhi, S. Electric Motor Fault Detection and Diagnosis by Kernel Density Estimation and Kullback-Leibler Divergence Based on Stator Current Measurements. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 1770–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Haque, M.S.; Arafat, A.; Toliyat, H. Detection and Estimation of Extremely Small Fault Signature by Utilizing Multiple Current Sensor Signals in Multiphase Electric Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 2805–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzida, A.; Touhami, O.; Ibtiouen, R.; Belouchrani, A.; Fadel, M.; Rezzoug, A. Fault Diagnosis in Industrial Induction Machines Through Discrete Wavelet Transform. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 4385–4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Feng, G.; Tang, X.; Gu, J.X.; Xu, G.; Cattley, R.; Gu, F.; Ball, A.D.; Huang, B.; Feng, G.; et al. A Performance Evaluation of Two Bispectrum Analysis Methods Applied to Electrical Current Signals for Monitoring Induction Motor-Driven Systems. Energies 2019, 12, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilamparithi, T.; Nandi, S. Analysis, modeling and simulation of static eccentric reluctance synchronous motor. In Proceedings of the 8th IEEE Symposium on Diagnostics for Electrical Machines, Power Electronics & Drives, Bologna, Italy, 5–8 September 2011; pp. 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Saavedra, H.; Urresty, J.-C.; Riba, J.-R.; Romeral, L. Detection of interturn faults in PMSMs with different winding configurations. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 79, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.B.; Hyun, D.; Kang, T.; Yang, C.; Shin, S.; Kim, H.; Park, S.; Kong, T.-S.; Kim, H.-D. Identification of False Rotor Fault Indications Produced by Online MCSA for Medium-Voltage Induction Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urresty, J.-C.; Riba, J.-R.; Romeral, L.; Ortega, J.A. Mixed resistive unbalance and winding inter-turn faults model of permanent magnet synchronous motors. Electr. Eng. 2014, 97, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saavedra, H.; Riba, J.-R.; Romeral, L. Detection of inter-turn faults in five-phase permanent magnet synchronous motors. Adv. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2014, 14, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urresty, J.-C.; Riba, J.-R.; Romeral, L. Influence of the stator windings configuration in the currents and zero-sequence voltage harmonics in permanent magnet synchronous motors with demagnetization faults. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 4885–4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solodkiy, E.; Dadenkov, D.; Salnikov, S. Detection Of Stator Inter-turn Short Circuit In Three-Phase Induction Motor Using Current Coordinate Transformation. In Proceedings of the 2019 26th International Workshop on Electric Drives: Improvement in Efficiency of Electric Drives (IWED), Moscow, Russia, 30 January–2 Feburary 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Caicedo-Narvaez, C.; Li, Y.; Maharjan, L.; Cosoroaba, E.; Fahimi, B.; Kiani, M.; Moallem, M. Thermal signature analysis of an 8/6 switched reluctance motor under inter-turn short circuit fault. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Lyon, France, 20–22 Feburary 2018; pp. 1859–1864. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.-T.; Hur, J. Detection Technique for Stator Inter-Turn Faults in BLDC Motors Based on Third-Harmonic Components of Line Currents. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welchko, B.A.; Lipo, T.A.; Jahns, T.M.; Schulz, S.E. Fault Tolerant Three-Phase AC Motor Drive Topologies: A Comparison of Features, Cost, and Limitations. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2004, 19, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallmark, O.; Harnefors, L.; Carlson, O. Control Algorithms for a Fault-Tolerant PMSM Drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2007, 54, 1973–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urresty, J.C.; Riba, J.R.; Romeral, L. A back-emf based method to detect magnet failures in PMSMs. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of phases | 5 |
| Rated power (kW) | 3.5 |
| Rated voltage (VRMS) | 240 |
| Rated current (ARMS) | 4 |
| Rated torque (N·m) | 5.7 |
| Rated speed (rev/min) | 5000 |
| Number of pole pairs (p) | 6 |
| Outer Stator diameter (mm) | 162.8 |
| Outer Rotor diameter (mm) | 114 |
| Stack Length (mm) | 26 |
| Airgap width (mm) | 0.3 |
| Number of slots | 60 |
| Conductors per slot | 60 |
| Slots/pole/phase (q) | 1 |
| Layer type | Double layer |
| Permanent magnets | Ferrite HF 30/26 |
| Magnetic steel | M330-35A |
| d-axis inductance (Ld, mH) | 59.7 under no current (id = iq = 0) 15.9 under maximum current (id = iline,rated,peak,1, iq = 0) |
| q-axis inductance (Lq, mH) | 15.2 under no current (id = iq = 0) 11.8 under maximum current (id = 0, iq = iline,rated,peak,1) |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of nodes | 151,469 |
| Number of line elements | 24,672 |
| Number of surface elements | 75,718 |
| Mesh order | 2nd order |
| Number of excellent quality elements | 96.16% |
| Number of good quality elements | 3.44% |
| Harmonic Order | 1 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 11 | 13 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rated operating conditions | |||||||
| Healthy (dB) | 0 | –16.4 | –152.8 | –34.5 | –29.5 | –37.0 | –45.6 |
| Faulty (dB) | 0 | –16.4 | –68.6 | –34.4 | –29.5 | –37.0 | –45.5 |
| ∆dB1st harmonic | –68.6 * | ||||||
| Low-saturation conditions | |||||||
| Healthy (dB) | 0 | –11.9 | −143.1 | –28.4 | –31.6 | –34.8 | –35.1 |
| Faulty (dB) | 0 | –12.0 | –66.71 | –28.4 | –31.9 | –34.9 | –35.3 |
| ∆dB1st harmonic | –66.71 * | ||||||
| Harmonic Order | 1 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 11 | 13 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rated operating conditions | |||||||
| Healthy (dB) | –144.3 | –131.7 | 0 | –130.8 | –140.8 | –138.9 | –127.4 |
| Faulty (dB) | –43.9 | –40.9 | 0 | –49.9 | –48.5 | –53.0 | –52.4 |
| ∆dB5th harmonic | –43.9 * | ||||||
| Low-saturation conditions | |||||||
| Healthy (dB) | –144.8 | –132 | 0 | –130 | –137.2 | –139.9 | –131.3 |
| Faulty (dB) | –37.0 | –59.9 | 0 | –63.7 | –63.7 | –66.3 | –67.9 |
| ∆dB5th harmonic | –37.0 * | ||||||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Candelo-Zuluaga, C.; Riba, J.-R.; López-Torres, C.; Garcia, A. Detection of Inter-Turn Faults in Multi-Phase Ferrite-PM Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Machines. Energies 2019, 12, 2733. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12142733
Candelo-Zuluaga C, Riba J-R, López-Torres C, Garcia A. Detection of Inter-Turn Faults in Multi-Phase Ferrite-PM Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Machines. Energies. 2019; 12(14):2733. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12142733
Chicago/Turabian StyleCandelo-Zuluaga, Carlos, Jordi-Roger Riba, Carlos López-Torres, and Antoni Garcia. 2019. "Detection of Inter-Turn Faults in Multi-Phase Ferrite-PM Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Machines" Energies 12, no. 14: 2733. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12142733
APA StyleCandelo-Zuluaga, C., Riba, J.-R., López-Torres, C., & Garcia, A. (2019). Detection of Inter-Turn Faults in Multi-Phase Ferrite-PM Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Machines. Energies, 12(14), 2733. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12142733






