Analysis of Inertia Characteristics of Direct-Drive Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Generator in Micro-Grid
Abstract
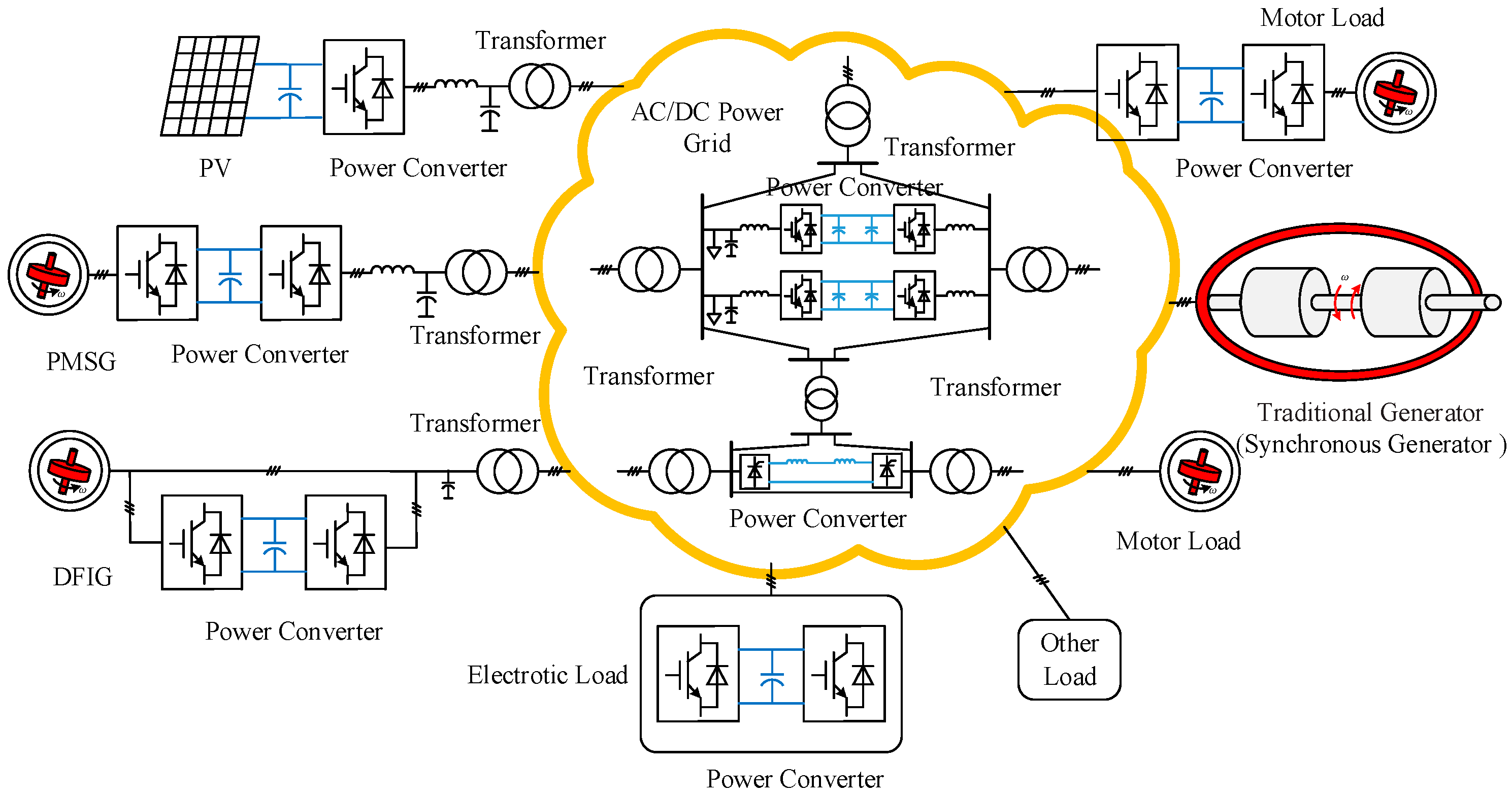
:1. Introduction
2. Inertial Source Analysis of WT Accessing Micro-Grid System
2.1. WTs Side Inertia Characteristic
2.2. DC Capacior Side Inertia Characteristic
2.3. Micro-Grid Side Inertia Characteristic
3. Analysis of Inertia Characteristics of Direct-Drive Wind Power Grid-Connected System
3.1. System Inertia Characteristic Mechanism
3.2. System Inertia Analysis
4. Simulation Result and Analysis
4.1. Simulation Settings
4.2. Inertia Characteristic Analysis and Verification
4.2.1. Analysis of Side Inertia Characteristics of WT
4.2.2. Analysis of Side Inertia Characteristics of Capacitor
4.2.3. Analysis of Inertia Characteristics under the Coordination of WT and Capacitor
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blaabjerg, F.; Teodorescu, R.; Liserre, M.; Timbus, A.V. Overview of Control and Grid Synchronization for Distributed Power Generation Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2006, 53, 1398–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, M.; Yuan, X.; Hu, J. Modeling of DFIG Wind Turbine Based on Internal Voltage Motion Equation in Power Systems Phase-Amplitude Dynamics Analysis. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2018, 33, 1484–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delille, G.; Francois, B.; Malarange, G. Dynamic frequency control support by energy storage to reduce the impact of wind and solar generation on isolated power system’s inertia. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2012, 3, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, J.M.; Franquelo, L.G.; Bialasiewicz, J.T.; Galvan, E.; Guisado, R.C.P.; Prats, M.A.M.; Leon, J.I.; Moreno-Alfonso, N. Power electronic systems for the grid integration of renewable energy sources: A survey. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2006, 53, 1002–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy, J.F.; Watson, R. Frequency Response Capability of Full Converter Wind Turbine Generators in Comparison to Conventional Generation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2008, 23, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauricioj, M.; Marano, A.; Gomez-Exposito, A. Frequency regulation contribution through variable speed wind energy conversion systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2009, 24, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Weiss, G. Synchronverters: Inverters That Mimic Synchronous Generators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Miura, Y.; Ise, T. Comparison of dynamic characteristics between virtual synchronous generator and droop control in inverter based distributed generators. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2016, 31, 3600–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, V.; Weiss, G. Synchronverters with better stability due to virtual inductors, virtual capacitors, and anti-windup. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 5994–6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping-Kwan, K.; Pei, L.; Banakar, H.; Ooi, B.T. Kinetic energy of wind-turbine generators for system frequency support. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2009, 24, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arani, M.F.M.; El-Saadany, E.F. Implementing virtual inertia in DFIG-based wind power generation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2013, 28, 1373–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, D.; Goel, L.; Ayyanar, R.; Vittal, V.; Harbour, T. Control strategy to mitigate the impact of reduced inertia due to doubly fed induction generators on large power systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2011, 26, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, V.; Zhu, X. Virtual inertia control of DFlG-based wind turbine based on the optimal power tracking. Proc. CSEE 2012, 32, 32–39. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.; Yuan, X.; Hu, J. Inertia Provision and Estimation of PLL-Based DFIG Wind Turbines. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 32, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Geng, H.; Yang, G. Phillips-Heffron model for current-controlled power electronic generation unit. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2018, 6, 582–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Qiu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Song, Z.; Thorp, J.S. Research on the impact of DFIG virtual inertia control on power system small-signal stability considering the phase-locked loop. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 32, 2094–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Li, H.; Tang, Y.; Blaabjerg, F. On the Inertia of Future More-Electronics Power Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 34, 5416–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Li, H.; Tang, Y.; Blaabjerg, F. Distributed Power System Virtual Inertia Implemented by Grid-Connected Power Converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 8488–8499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Zhuo, F.; Wang, F.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, M. Static synchronous generator model: A new perspective to investigate dynamic characteristics and stability issues of grid-tied PWM inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 6264–6280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Xiong, L.; Wang, S.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Modeling and Mechanism Investigation of Inertia and Damping Issues for Grid-Tied PV Generation Systems with Droop Control. Energies 2019, 12, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Tang, Y.; Li, H.; Li, X. A battery/ultracapacitor hybrid energy storage system for implementing the power management of virtual synchronous generators. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2018, 33, 2820–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, L.; Xiong, L.; Yang, P.; Kang, Z. Inertial and damping characteristics of DC distributed power systems based on frequency droop control. Energies 2018, 11, 2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, J.; Yuan, X.; Hu, J.; He, W. Impact of Inertia Control of DFIG-Based WTS on Electromechanical Oscillation Damping of SG. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2018, 33, 3450–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wu, K.; Huang, L.; Xin, H.; Lu, C.; Wang, H. A Coordinated Control Scheme to Realize Frequency Support of PMSG-Based Wind Turbines in Weak Grids. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Power Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Portland, OR, USA, 5–10 August 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z. A generalized droop control for grid supporting inverter based on comparison between traditional droop control and virtual synchronous generator control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 6, 5416–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundur, P.; Balu, N.J.; Lauby, M.G. Power System Stability and Control; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 1994; ISBN 9780070359581. [Google Scholar]


















| System | Parameters | Value | Parameters | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wind power | SB | 20 kVA | Udc | 1200 V |
| Cdc | 3.4 mF | kd | 1 × 104 | |
| Jw | 3.6 × 104 kg m2 | kc | 750 | |
| Grid power | P0 | 20 kW | Ls | 3 mH |
| 1/D | 1.2 × 10−5 | Cs | 50 µF | |
| U0 | 690 V | f | 50 Hz |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, D.; Wu, Y.; Xiong, L.; Zhao, C. Analysis of Inertia Characteristics of Direct-Drive Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Generator in Micro-Grid. Energies 2019, 12, 3141. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12163141
Zhang D, Wu Y, Xiong L, Zhao C. Analysis of Inertia Characteristics of Direct-Drive Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Generator in Micro-Grid. Energies. 2019; 12(16):3141. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12163141
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Donghui, Yongbin Wu, Liansong Xiong, and Chengyong Zhao. 2019. "Analysis of Inertia Characteristics of Direct-Drive Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Generator in Micro-Grid" Energies 12, no. 16: 3141. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12163141
APA StyleZhang, D., Wu, Y., Xiong, L., & Zhao, C. (2019). Analysis of Inertia Characteristics of Direct-Drive Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Generator in Micro-Grid. Energies, 12(16), 3141. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12163141





