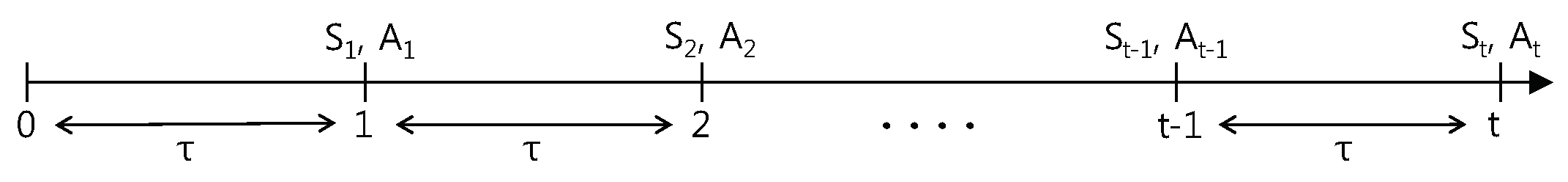Abstract
The limited battery capacity of Internet of Things (IoT) devices is a major deployment barrier for IoT-based computing systems. In this paper, we propose an energy efficient cooperative computation algorithm (EE-CCA). In an EE-CCA, a pair of IoT devices decide whether to offload some parts of the task to the opponent by considering their energy levels and the task deadline. To minimize the energy outage probability while completing most of tasks before their deadlines, we formulate a constraint Markov decision process (CMDP) problem and the optimal offloading strategy is obtained by linear programming (LP). Meanwhile, an optimization problem of finding pairs of IoT devices (i.e., IoT device pairing problem) is formulated under the optimal offloading strategy. Evaluation results demonstrate that the EE-CCA can reduce the energy outage probability up to compared with the random offloading scheme while completing tasks before their deadlines with high probability.
1. Introduction
From the recent advancement of Internet of Things (IoT) devices with high computing power, complicated computation can be handled without remote servers [1]. However, the development speed of batteries for IoT devices is inferior to that of computing module, and thus the limited battery capacity of IoT devices is being a major deployment barrier for IoT-based computing systems. Therefore, there is an increasing interest on the energy harvesting technique that converts wasted energy to electricity [2,3]. With this technique, IoT devices do not need to recharge and/or replace their batteries anymore, and thus the operating expenditure of IoT-based computing systems can be reduced [4]. However, the energy that can be harvested from external energy sources is generally uncontrollable and intermittent. Moreover, the harvested energy volume has temporal and spatial variations. Therefore, it is difficult to provide a reliable power supply to IoT devices. In this situation, if an IoT device cannot harvest energy for a long time and it processes lots of tasks requiring high computing power, its energy can be depleted. To mitigate this problem and improve the energy efficiency of harvesting IoT devices, a number of works (e.g., sleep scheduling, CPU cycle adjustment, and so on) have been investigated in the literature [5,6,7,8,9,10]. One of the possible solutions is offloading tasks to nearby IoT devices [5,6,7]. IoT-based computing systems have advantages compared to remote servers-based offloading systems. For example, offloading to remote servers consumes huge resources in networks when IoT devices generate lots of tasks. In addition, longer latency is needed when offloading to remote servers. Especially when an energy-scarce IoT device offloads tasks to a nearby energy-abundant IoT device, energy depletion of the energy-scarce IoT devices probably does not occur. However, unplanned offloading can cause another energy depletion. For example, when an offloader (i.e., an energy-scarce IoT device) always offloads all tasks to an offloadee (i.e., an energy-abundant IoT device) having lots of own tasks and/or small harvesting rate, the energy of the offloadee can be depleted within a short duration. Moreover, tasks cannot be completed within their deadlines due to the high load of the offloadee. Therefore, a sophisticated offloading algorithm should be devised.
In this paper, we propose an energy efficient cooperative computation algorithm (EE-CCA). In an EE-CCA, each IoT device is paired to its partner and a pair of IoT devices conduct cooperative computing. Specifically, a centralized controller collects information such as the distribution about temporal and spatial variations of external energy sources, the task occurrence rates of IoT devices, and the energy levels of IoT devices. Based on this information, the controller can construct and distribute offloading decision tables to IoT devices. Then, when a task occurs in IoT devices, they decide whether to offload some parts of the task to the opponent by following the decision tables. To minimize the energy outage probability while completing most of the tasks before their deadlines, we formulate a constraint Markov decision process (CMDP) problem, and the optimal offloading strategy is obtained by linear programming (LP). Meanwhile, an optimization problem of finding pairs of IoT devices (i.e., IoT device pairing problem) is formulated under the optimal offloading strategy. Evaluation results demonstrate that the EE-CCA can reduce the energy outage probability up to compared with the random offloading scheme while completing tasks before their deadlines with high probability. In addition, the EE-CCA operates adaptively even when the operating environment (e.g., inter-task occurrence rate) changes.
The contribution of this paper can be summarized as follows: (1) we develop the cooperative computation algorithm called EE-CCA for IoT devices, while optimizing the EE-CCA by means of CMDP formulation; (2) optimal pairs of IoT devices are decided based on the optimization problem; and (3) extensive evaluation results are presented and analyzed under various environments, providing valuable guidelines for the design of cooperative computing in energy harvesting IoT.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Related works are summarized in Section 2, and the EE-CCA is described in Section 3. The CMDP model for cooperative computing and the optimization problem for the IoT device pairing are developed in Section 4. Evaluation results are given in Section 5, and followed by the concluding remarks in Section 6.
2. Related Works
A number of studies on the computation offloading have been conducted to improve the energy efficiency of energy-constraint devices [11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. These can be categorized into: (1) framework design [11,12,13,14,15,16]; and (2) algorithm design [17,18,19,20,21,22].
Wang et al. [11] proposed an evolutionary mobile network architecture called MobiScud that integrates the cloud services into the mobile networks by means of software defined networking (SDN) and network function virtualization (NFV) technologies in a backwards compatible fashion. Tong et al. [12] organized edge cloud servers into a hierarchical architecture which enables aggregation of the peak loads across different tiers of cloud servers. Specifically, when the loads exceed the capacities of lower tiers of edge cloud servers, they can be aggregated and offloaded by other servers at higher tiers in the edge cloud hierarchy to maximize the amount of mobile workloads being served. Taleb and Ksentini [13] introduced a follow me cloud concept that enables mobile cloud services to follow their respective mobile devices by migrating services to the optimal cloud. Liu et al. [14] proposed convergence of cloud and cellular systems, abbreviated as CONCERT, based on a concept of control/data plane decoupling and hierarchically placement of the resources within the network to manage flexibly and elastically networks and cloud services. Puente et al. [15] presented a seamless approach for the deployment of edge clouds where conventional mobile traffic and computing related traffic are segregated and handled individually at base stations. However, since these works do not consider the device-to-device offloading, IoT devices with high computing power cannot be exploited efficiently. Shukla and Munir [16] proposed a computation offloading architecture where an IoT device first tries to offload tasks to another IoT device instead of directly offloading to the cloud to process the huge amount of data while guaranteeing the task completion before the deadline. However, they did not provide any optimization method.
Ko et al. [17] proposed a spatial and temporal computation offloading decision algorithm where an energy-constraint device decides where and when to process tasks by means of a Markov decision process (MDP) by considering the energy consumption and the transmission cost. Zhao et al. [18] developed an optimization problem whose objective function is to maximize the probability that task execution satisfies the given delay bound. The problem was proved to be concave, and an optimal algorithm was proposed. Tang and Chen [19] studied a social-aware computation offloading game and designed a distributed computation offloading algorithm to achieve the Nash equilibrium. Similarly, Chen et al. [20] modeled a multi-user computation offloading game and designed a distributed computation offloading algorithm that can achieve the Nash equilibrium of the game. Zheng et al. [21] formulated the mobile users’ offloading decision process under a dynamic environment as a stochastic game. Then, they proposed a multi-agent stochastic learning algorithm that can run in a fully distributed manner without any information exchange. Yu et al. [22] developed an optimal collaborative offloading strategy under a distributed caching scenario. Specifically, they formulated a problem of users’ allocation as a coalition formation game with the consideration of relationships between the offloading and caching and then proposed an optimal offloading with a caching-enhancement scheme. These works improve the performance of computation offloading; however, no previous studies optimize the performance of IoT-based computing systems.
3. Energy Efficient Cooperative Computation Algorithm (EE-CCA)
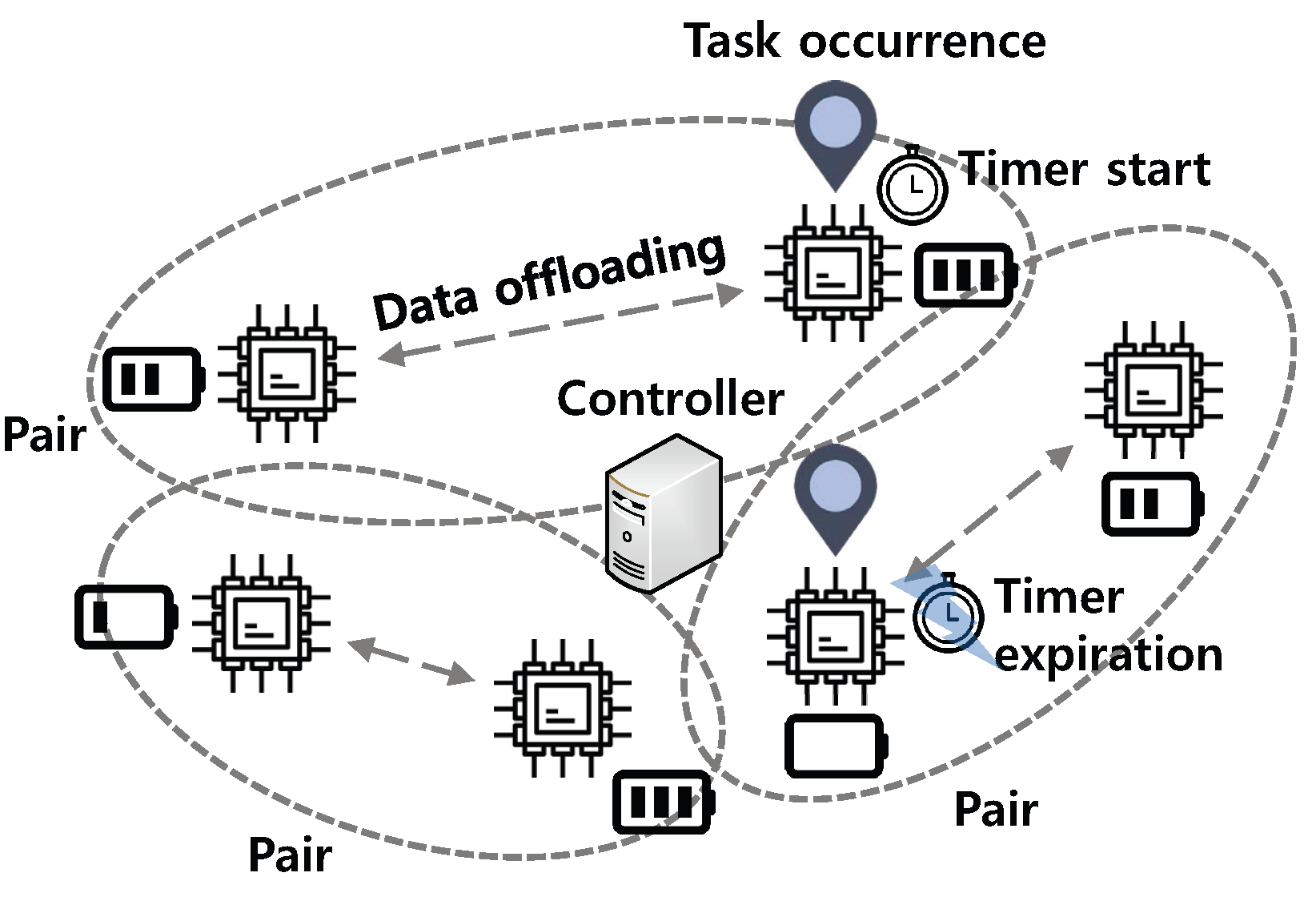
Figure 1 shows the system model of this paper. In our system model, there are N IoT devices with the energy harvesting capability. We assume heterogeneous IoT environment, where IoT devices have different computing power and current energy level. In real systems, some IoT devices may not have sufficient computing power and/or harvesting capability. To support this situation, a study on the robustness of the proposed algorithm (e.g., a resilient multiscale coordination control [23]) should be conducted, which is one of our future works. In addition, since they are installed at different spots and the condition of external energy sources is volatile, energy volumes that can be harvested at each IoT device are different from each other. In addition, with different rates, these IoT devices periodically generate tasks that can be abstracted into the input data and the completion deadline before which the task should be completed [24]. In addition, we consider an application where the input data do not have dependency, e.g., binomial classification that determines whether each input is larger than a given threshold or not, and therefore the input data can be partitioned and offloaded. When the task occurs in a particular IoT device, it decides whether to offload some parts of the task (i.e., input data) to a neighbor IoT device or not with the consideration of the energy level and the deadline of the task. Note that, even though the formulation of this paper is based on the assumption where IoT devices can offload all or half of the tasks, it can be easily extended to consider other portions of the task.
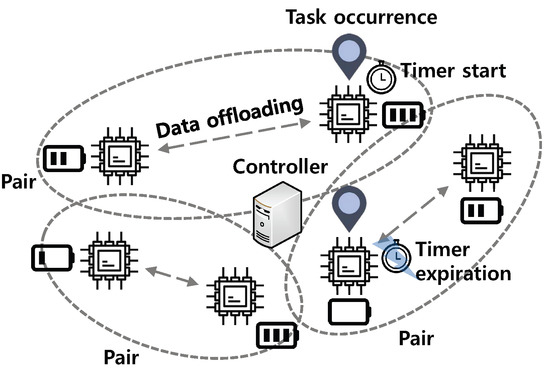
Figure 1.
System model.
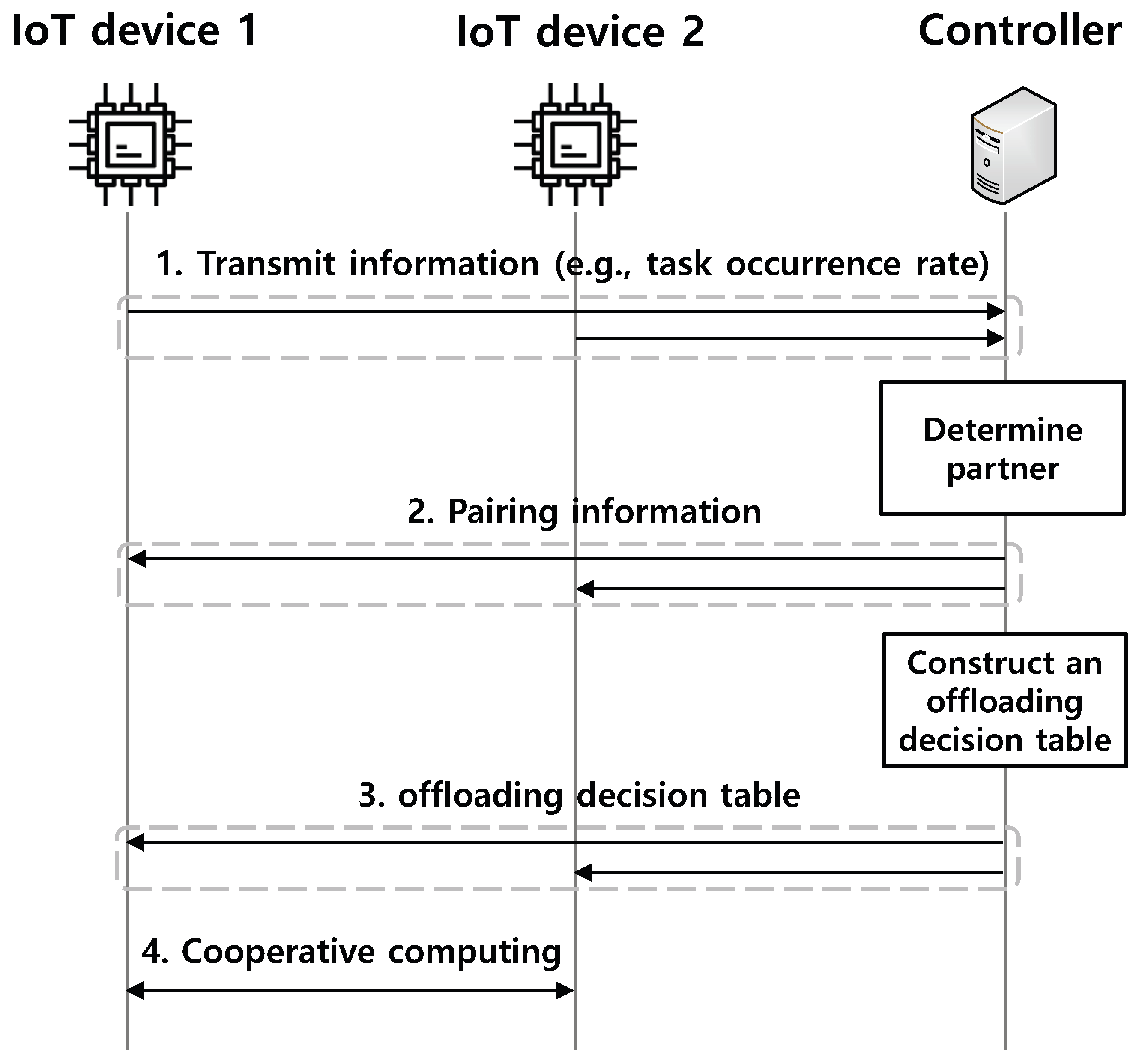
Intuitively, when an IoT device offloads some parts of the task to a neighbor IoT device, the task can be processed in a distributed manner, which can reduce the energy consumption of the task owner. Since IoT devices offload their tasks to nearby IoT devices by exploiting transmission technologies with low power consumption (e.g., Bluetooth), the energy consumption for transmission of the task can be neglected compared to that for processing the task. Moreover, if the neighbor IoT device does not have its own task, the task completion time can be shortened. However, if the task is offloaded to an energy-scarce IoT device, it causes the energy depletion of the IoT device, and then the offloaded task cannot be processed due to the energy depletion. In addition, when the neighbor IoT device has its own task, it should process its own task and the offloaded task simultaneously, and thus its processing time can increase. Then, both tasks may not be completed within their deadlines. To prevent these situations, we propose the EE-CCA and its flow chart is shown in Figure 2. First, the controller collects and/or maintains information such as the distribution about temporal and spatial variations of external energy sources, the task occurrence rates of IoT devices, and the energy levels of IoT devices (Step 1 in Figure 2). Based on this information, the controller determines appropriate partners of IoT devices for cooperative computation and transmits the pairing information to IoT devices (Step 2 in Figure 2). In addition, the controller constructs an offloading decision table consisting of the current status and the operation in a centralized manner. If some parameters (e.g., the task occurrence rates of IoT devices) are changed, the offloading decision table can be reconstructed by the controller and transmitted to IoT devices again. Therefore, if the parameters are frequently changed, extra signaling overhead can occur. To mitigate the signaling overhead, several techniques such as aggregation and delta encoding can be exploited [25]. Note that the offloading decision table can be obtained by CMDP, which will be elaborated in Section 4. After that, the controller transmits the optimal offloading decision table to IoT devices (Step 3 in Figure 2). On the basis of this table, IoT devices can conduct the cooperative computing (i.e., decide whether to offload some parts of the task or not) (Step 4 in Figure 2). By means of table deployments in IoT devices, the CMDP model can be applied to resource-constrained IoT devices without any high computation overhead in IoT devices [26].
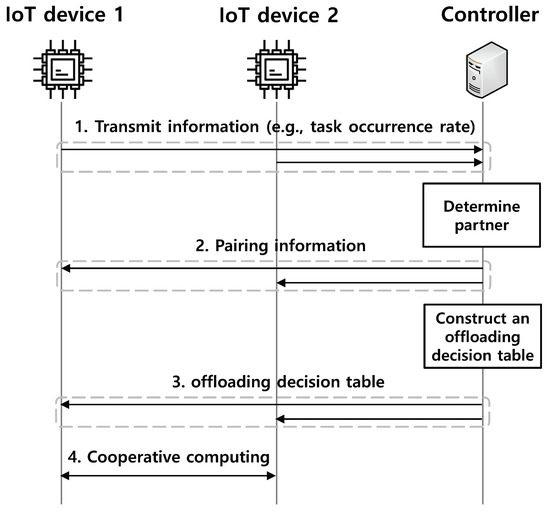
Figure 2.
Flow chart.
4. Constraint Markov Decision Process (CMDP)
To obtain the optimal offloading strategy, we formulate a CMDP model with five elements. (Since the CMDP model that is a mathematical framework to model decision-making when outcomes need to be constrained, and they are partially random and under the control of the decision maker [27], it is suitable to construct the optimal offloading decision table.): (1) decision epoch; (2) state; (3) action; (4) transition probability; and (5) cost and constraint functions. Subsequently, we convert the CMDP model to an equivalent LP problem to obtain the optimal policy. After that, the IoT device pairing problem is formulated under the optimal offloading policy. Important notations for the CMDP model and IoT device pairing problem are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Summary of notations.
4.1. Decision Epoch
Figure 3 shows the timing diagram for the CMDP model. A sequence represents the time epochs when successive decisions are made [28]. and denote the state and the action chosen at the decision epoch , respectively. represents the duration of each decision epoch.
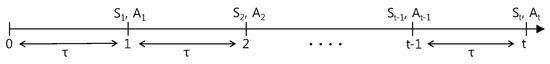
Figure 3.
Timing diagram.
4.2. State Space
We define the overall state space as (The state space is constructed based on the assumption where IoT devices can offload all or half of the task. However, it can be easily extended to consider other portions of the task to add elements to , , , and .)
where and are the states for representing the occurrence and processing status for the task of IoT devices i and j, respectively. and denote the states for the processing status of the offloaded task of IoT devices i and j, respectively. and are the states for the energy level of IoT devices i and j, respectively. and represent the states for denoting whether the timers for the deadline of the task of IoT devices i and j expire or not, respectively.
, , , and are the states for IoT device i, and these states are defined as follows.
First, is given by
where represents the occurrence and processing status for the task of IoT device i. In other words, denotes that the task does not occur in IoT device i, whereas refers to the situation immediately after the task occurs in IoT device i. represents the situation where IoT device i processes all of the task by itself. Meanwhile, and represent the situations where half of the task and all of the tasks are offloaded to IoT device j, respectively. Note that, when , IoT device i processes the remaining half of the task.
is represented by
where represents the processing status of the offloaded task of IoT device i. Specifically, describes the situation where any task is not offloaded to its partner (i.e., IoT device j). Meanwhile, and represent the situation where half of the task and all of the tasks are offloaded to IoT device j, respectively, and it is being processed in IoT device j.
is represented as [29]
where is the maximum battery capacity of an IoT device.
where denotes whether the timer for the deadline of the task of IoT device i expires or not. In other words, and represent that the timer for the deadline of the task of IoT device i does not expire and expires, respectively.
, , , and are the states for IoT device j, and these states can be defined as similar with the states for IoT device i. These definitions are omitted in this paper due to the page limitation and for simple descriptions, which can be found in [30].
4.3. Action Space
When the task occurs in IoT devices, each IoT device can decide whether to offload to its partner or not and the portion to be offloaded based on the current state information. The action set is constructed based on the assumption where IoT devices can offload all or half of the task. However, it can be easily extended to consider other portions of the task to define additional actions. Therefore, the action set can be described by
where and are the action spaces for IoT devices i and j, respectively, which can be defined as
and
where and represent that IoT devices i and j do not offload its task, respectively. and denote that IoT devices i and j offload half of the task to its partner, respectively. In addition, and are the actions where IoT devices i and j offload all of the task to its partner, respectively.
4.4. Transition Probability
The state transition probability of IoT device i is affected by the state of IoT device j. Specifically, the processing speed of the task occurring in IoT device i (i.e., the transition probability of ) is dependent on whether the task occurring at IoT device j is processed in IoT device i or not (i.e., ). In addition, the transition probability of is affected by whether IoT device j processes its own task or not (i.e., ). Similar to that, the state transition probability of IoT device j is also influenced by the state of IoT device i (especially and ). Therefore, the transition probability with the chosen action A from the current state S to the next state can be described by
where and denote the next state of IoT devices i and j, respectively. In addition, and represent the current state for IoT devices i and j, respectively.
Meanwhile, and are influenced by the chosen action A, and these states are dependently changed with each other. In addition, is affected by . For example, when the task of IoT device j is processed in IoT device i, the processing speed of the task of IoT device i can decrease. Similarly, is influenced by . For example, when IoT device j does not process its own task, it can focus on processing the offloaded task from IoT device i, and therefore the offloaded task can be completed within a short duration. Meanwhile, when the task is processed in IoT device i, its energy level can decrease. That is, the transition of is influenced by . The timer for the deadline of the task operates only when the task occurs, and therefore the transition of is affected by and . Meanwhile, other states change independently of each other. Therefore, for the chosen action A, the transition probability from the current state of IoT device i, , to the next state of IoT device i, , can be described by
We assume that the inter-task occurrence time of IoT device i follows an exponential distribution with mean . Then, the probability that the task occurs in IoT device i during a decision epoch can be calculated as [27,31]. Therefore, can be represented by
Before receiving the result of the offloaded task, IoT device i does not generate the task. Therefore, can be defined as
Meanwhile, when the task occurs (i.e., ), IoT device i decides whether to offload to IoT device j or not and the offloaded portion (i.e., half of the task and all of the task). If IoT device i decides not to offload it (i.e., when ), the task state will change to 2 representing the situation where IoT device i processes all of the task by itself (i.e., ). On the other hand, when IoT device i decides to offload half of the task and all of the task (i.e., when and ), the next states of the occurrence and processing status for the task of IoT device i (i.e., ) become 3 and 4, respectively. Therefore, the corresponding transition probabilities can be represented as
and
respectively.
We assume that the processing time of IoT device i for its own task follows an exponential distribution with mean when it processes all of its own task and any task of IoT device j is not offloaded to IoT device i (i.e., and ). In this case, the probability that the task is completed during a decision epoch is [27,31]. Then, the probability that a task is not completed during a decision epoch is . On the other hand, if some portion of the task of IoT device j is offloaded to IoT device i (i.e., ), the processing speed of IoT device i for its own task decreases, and thus it is assumed that the processing time of IoT device i for its own task follows an exponential distribution with mean (). In this case, the probability that the task is completed (or not completed) during a decision epoch is (or ) [27,31]. Therefore, and can be derived as
and
Meanwhile, when offloading half of the task to IoT device j (i.e., ), the remained task can be completed with shorter time. It is assumed that the processing time of the remained task follows an exponential distribution with mean when any task of IoT device j is not offloaded to IoT device i (i.e., ), and then the probability that the remained task is completed during a decision epoch is [27,31]. On the other hand, when IoT device i offloads the half of its task to IoT device j and processes the offloaded task from IoT device j (i.e., and ), the processing time of the remained task of IoT device i follows an exponential distribution with mean . In this case, the probability that the remained task is completed during a decision epoch is [27,31]. Thus, the corresponding transition probabilities can be represented as
and
When the task does not occur, the processing status of the offloaded task of IoT device i does not change. Therefore, can be denoted as
Meanwhile, when the task occurs (i.e., ), the processing status of the offloaded task of IoT device i changes according to the chosen action A. Therefore, corresponding transition probabilities can be represented as
and
respectively.
When some portion of the task is offloaded (i.e., or ), it is processed by IoT device j. Meanwhile, the processing time of the offloaded task to IoT device j depends on the portion of the offloaded task (i.e., ) and whether IoT device j processes its own task or not (i.e., ). Specifically, when half of the task (or all of the task) of IoT device i is offloaded and IoT device j does not process its own task, we assume that the processing time of the offloaded task follows an exponential distribution with mean (). On the other hand, if half of the task (or all of the task) of IoT device i is offloaded and IoT device j processes its own task, the processing time of the offloaded task follows an exponential distribution with mean (). Then, the probabilities that the offloaded task is completed during a decision epoch for each case can be derived as , , , and , respectively [27,31]. Therefore, the corresponding transition probabilities can be denoted as
and
The IoT device can harvest energy only when its environments provide energy (e.g., when the wind blows above a certain speed). Therefore, the probability that IoT device i harvests one unit energy at an arbitrary decision epoch is modeled by a Bernoulli random process with the probability [32]. Then, when the IoT device i does not process any task (i.e., or ) and its battery is not fully charged (i.e., ), increases by one unit with the probability . If the battery of IoT device i is full (i.e., ), it cannot harvest energy anymore. Therefore, the corresponding transition probabilities can be represented as
and
When IoT device i processes the task (i.e., or ) and it has energy (i.e., ), it consumes one unit energy. On the other hand, if IoT device i does not have any energy, it cannot process for any task the sensed data, and thus no energy is consumed. In addition, its energy increases by one unit with the probability . Therefore, the corresponding transition probabilities can be expressed by
and
Meanwhile, when all of the tasks are offloaded to IoT device j (i.e., ), IoT device i does not consume its own energy. Therefore, the corresponding transition probability can be denoted as
When the task does not occur (i.e., or ), the timer for the deadline of the task does not start, and therefore it does not expire. Therefore, can be represented as
We assume that the timer for the deadline of the task of IoT device i follows an exponential distribution with mean [33,34]. Then, when the task is not completed (i.e., or ), the probability that the timer expires during a decision epoch is . Thus, the corresponding transition probabilities can be represented as
and
Meanwhile, when the task is completed (i.e., and ), the timer is reset and does not operate, which means that there is no expiration. Therefore, can be denoted as
If the timer expires (i.e., ) and the task is not completed (i.e., or ), the timer remains in the expired state. Therefore, the corresponding transition probabilities can be represented as
and
The transition probability for the states of IoT device j can be defined as similar to that of IoT device i. These are omitted in this paper due to the page limitation and for simple descriptions, which can be found in [30].
4.5. Cost and Constraint Functions
4.5.1. Cost Function
To define the cost function, we consider the energy outage of IoT devices. The energy outage occurs when batteries of IoT devices are empty. Therefore, the cost function can be defined as
4.5.2. Constraint Function
To prevent the situation where the task cannot be finished before the timer expiration, the constraint functions for the timer expiration of IoT devices i and j can be represented by
and
respectively.
4.6. Optimization Problem Formulation
Since means the number of energy outages, the average energy outage probability can be defined as
where lim denotes the value that a function approaches as the input approaches a specific value. In addition, sup (i.e., supremum) means the least upper bound.
Meanwhile, the average timer expiration probabilities of IoT devices i and j, denoted as, , and , respectively, can be defined as
and
Then, the optimization problem in the CMDP model can be formulated as
where and are the upper limits on the timer expiration probabilities of IoT devices i and j, respectively.
The formulated optimization problem can be transformed into an equivalent LP problem [28]. That is, when represents the stationary probability of state S and action A, the solution of the LP problem can be mapped to that of the CMDP-based optimization model. The equivalent LP model can be expressed as
The objective function in (51) is to minimize the energy outage probability of IoT devices. Meanwhile, the constraints in (52) and (53) are to maintain the timer expiration probabilities of IoT devices i and j below and , respectively. The constraint in (54) satisfies the Chapman–Kolmogorov equation. The constraints in (55) and (56) are for the probability properties.
The optimal policy , which is the probability of taking a particular action at a certain state, can be obtained from the solution of the above LP problem. The optimal policy can be derived from
Note that, if , which means that there is no solution to satisfy all constraints, IoT devices do not offload any task. LP problem can be solved in polynomial time [35,36,37]. Therefore, our proposed algorithm can be implemented to real systems without high computational power.
4.7. IoT Device Pairing Problem
The optimal offloading policy in the previous subsection is obtained given the paired IoT devices i and j. In this subsection, we formulate an IoT device pairing problem whose objective is to minimize the summation of energy outage probabilities of all IoT devices.
Let denote an individual energy outage probability of IoT device i when it is paired with IoT device j. can be calculated as (We assume that the individual energy outage probability of IoT device i when it is paired with IoT device j is lower than that when it is not paired (i.e., ). This assumption is reasonable because paired IoT devices operate by following the optimal policy obtained by CMDP:
Then, the optimization problem for pairing IoT devices can be defined as
where is a decision variable that is 1 if IoT devices i and j are paired and 0 otherwise. The objective function in (59) is to minimize the summation of energy outage probabilities of all IoT devices. Meanwhile, the constraint in (60) to ensure that all IoT devices are paired with only one IoT device. This optimization problem is solved in the controller by using several algorithms (e.g., brute-force approach, LP relaxation, and branch-and-bound algorithm), and therefore there is no burden in IoT devices.
5. Evaluation Results
For performance evaluation, we compare the proposed algorithm, EE-CCA, with the following four schemes: (1) ALL where IoT devices always offload all of the tasks; (2) HALF where IoT devices always offload half of the task; (3) NON where IoT devices do not offload any task (i.e., process their tasks by themselves); and (4) RAND where IoT devices randomly offload their tasks at each decision epoch. For pair comparison, IoT devices are paired based on the solution of the optimization problem in Section IV-G. Meanwhile, the objective of this paper is to minimize the energy outage probability while maintaining the probability that the task is completed before their deadline above a certain level. Therefore, the average energy outage probability, , and the average probabilities that the task of IoT device i and j are completed before their deadline, and , are used as performance measures of the EE-CCA. Note that and can be calculated by and , respectively.
To improve the reliability of the simulation results, we have conducted over 10,000 simulation runs with different seed values independently. The default number of IoT devices is set to 6. The other default parameter settings are summarized in Table 2, where denotes a random value between a and b.

Table 2.
Default parameter settings.
5.1. Effect of the Harvesting Probability
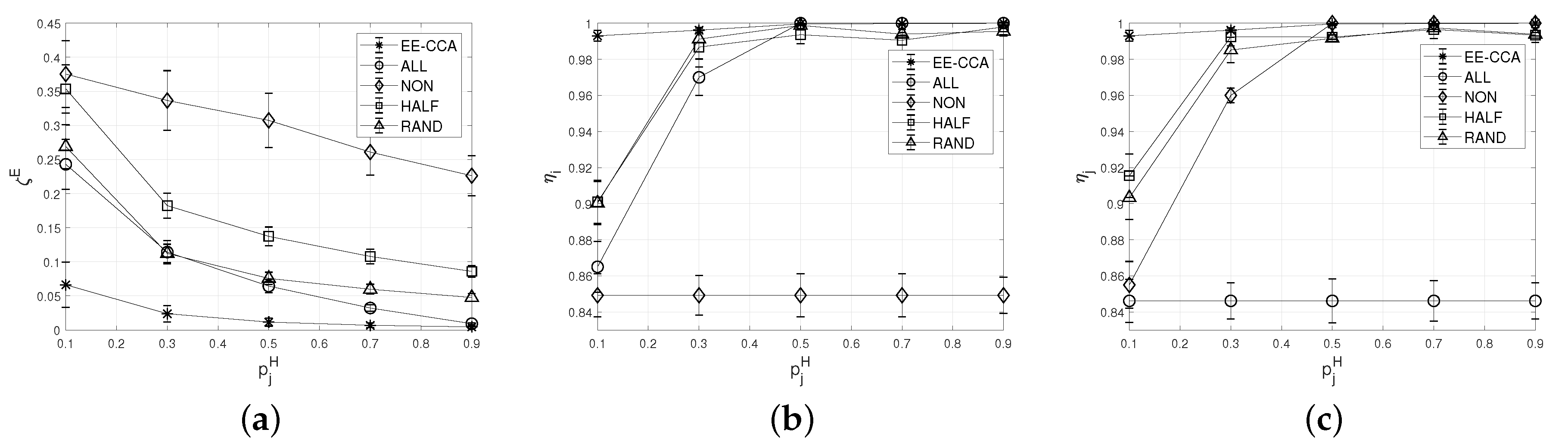
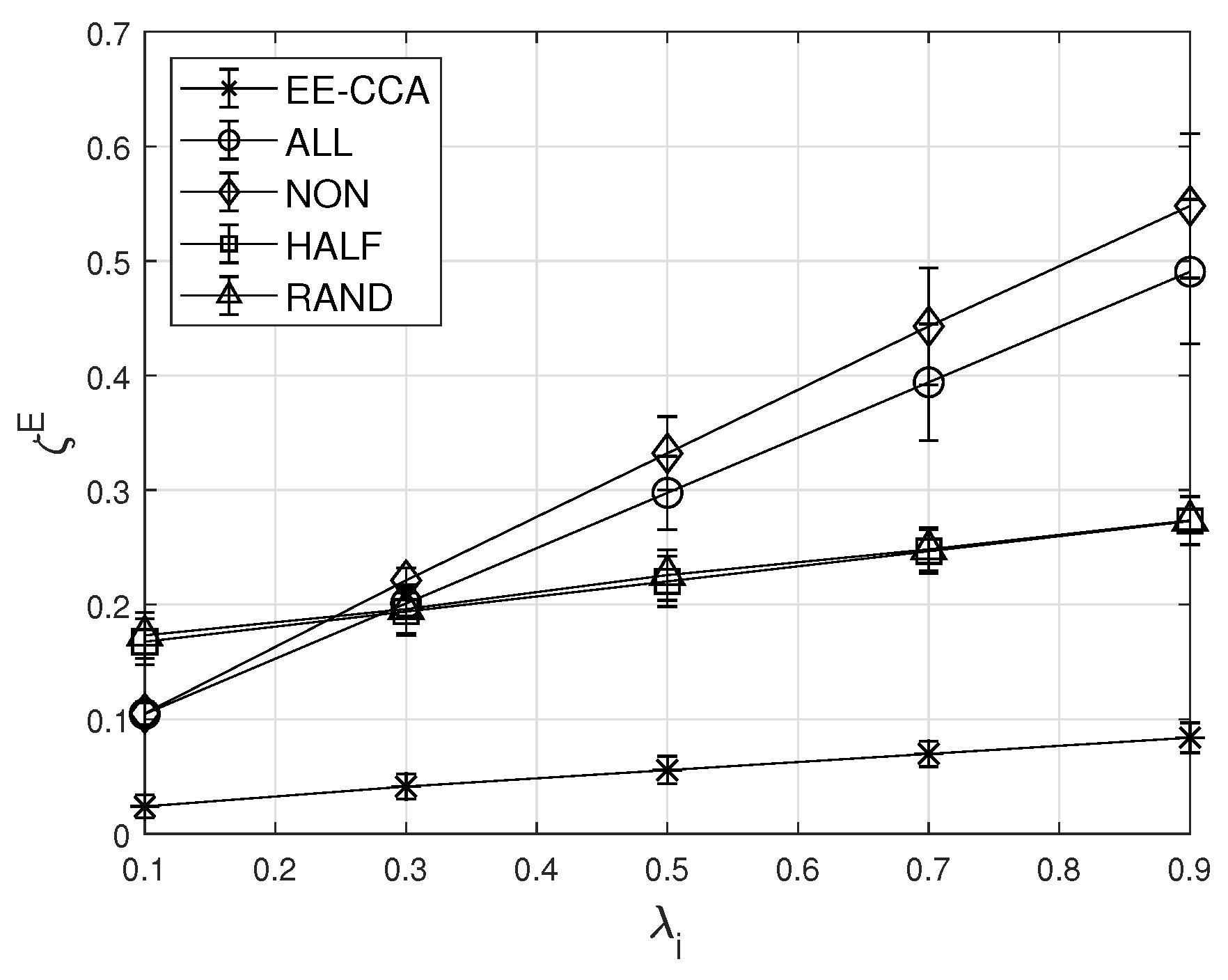
Figure 4 shows the effect of the harvesting probability of IoT device j on the average energy outage probability and the average probabilities that tasks of IoT devices i and j are completed before their deadlines. As shown in Figure 4, it can be found that the EE-CCA can reduce significantly the energy outage probability of IoT devices (see Figure 4a). For example, when is 0.1, EE-CCA can reduce the energy outage probability by compared to RAND. while maintaining the probability that the task is completed before the deadline (i.e., 0.99) (see Figure 4b,c). This is because IoT devices in the EE-CCA decide whether to offload some parts of the task to the opponent with the consideration of the energy harvesting probability, the task occurrence rate, and the current energy levels of IoT devices. For example, IoT device does not offload its task to the partner when the current energy level of the partner is low and predicted to be decreased due to low harvesting probability and high task occurrence rate.
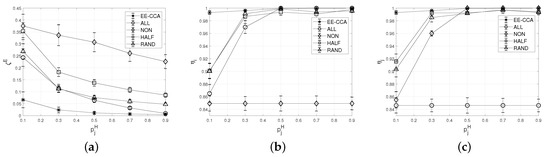
Figure 4.
Effect of the harvesting probability. (a) average energy outage probability; (b) average probability that the task of IoT device i is completed before the deadline; (c) average probability that the task of IoT device j is completed before the deadline.
From Figure 4a, it can be shown that the average energy outage probabilities of all schemes decrease as increases. This is because a high battery level of IoT device j can be maintained regardless of whether to offload or not when is high. Meanwhile, from Figure 4b,c, it can be seen that the probabilities that tasks of IoT devices i and j are completed before their deadlines increases with the increase of except specific cases (i.e., NON in Figure 4b and ALL in Figure 4c). This is because the tasks can be completed only when IoT devices have sufficient energy. In other words, IoT devices cannot complete their tasks within the deadline if they cannot harvest sufficiently energy. On the other hand, in NON, IoT device i does not offload its task to IoT device j. Therefore, the harvesting probability of IoT device j does not affect the probability that the task of IoT device i is completed within the deadline. Similarly, in ALL, all tasks of IoT device j are processed in IoT device i, and thus is not affected by .
5.2. Effect of the Inter-Task Occurrence Rate
Figure 5 shows the effect of the inter-task occurrence rate of IoT device i. From Figure 5, it can be found that the average energy outage probabilities of all schemes increase with the increase of the inter-task occurrence rate. This is because IoT devices consume more energy when tasks occur frequently. However, the incremental ratio of the EE-CCA is smallest among comparison schemes. This is because IoT devices in the EE-CCA operate adaptively even when the operating environment changes. Specifically, as the inter-task occurrence rate of IoT device i increases, it offloads more tasks to its opponent to avoid the energy depletion.
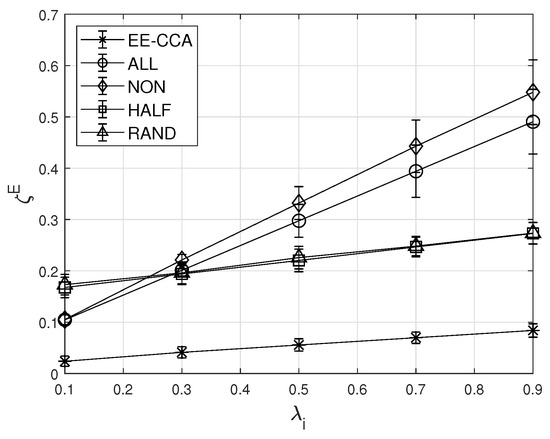
Figure 5.
Effect of the inter-task occurrence rate on the average energy outage probability.
5.3. Effect of the Average Deadline
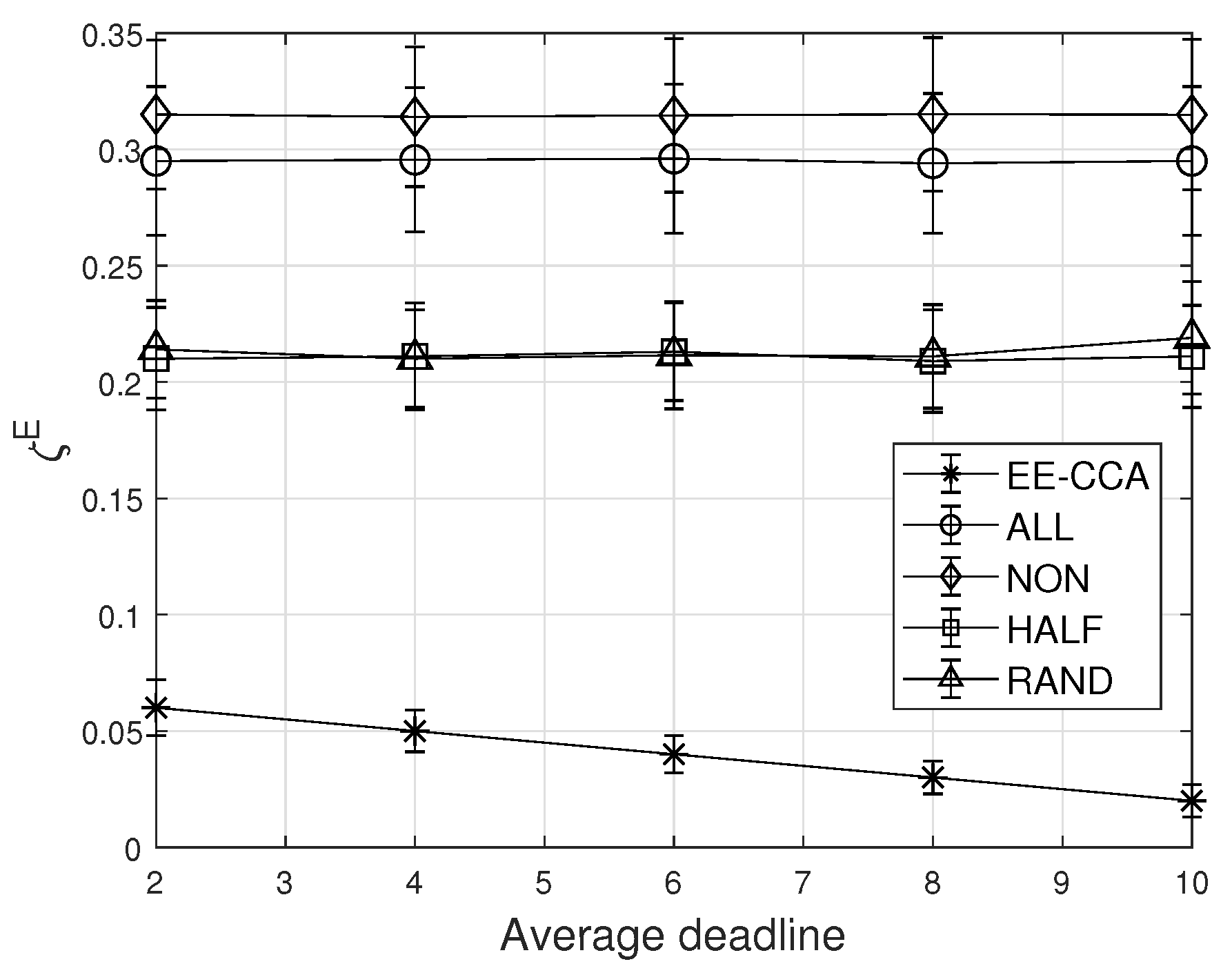
The effects of the average deadline of the task on the average energy outage probability are demonstrated in Figure 6. From Figure 6, it can be observed that the average energy outage probability of the EE-CCA decreases with the increase of the deadline. This is because, when a sufficient deadline is given, IoT devices in the EE-CCA can handle the task within the deadline by themselves even though they do not offload any tasks to energy-scarce opponents. On the other hand, the other schemes follow the fixed policy regardless of the deadline of the task, and thus their average energy outage probabilities do not change according to the deadline.
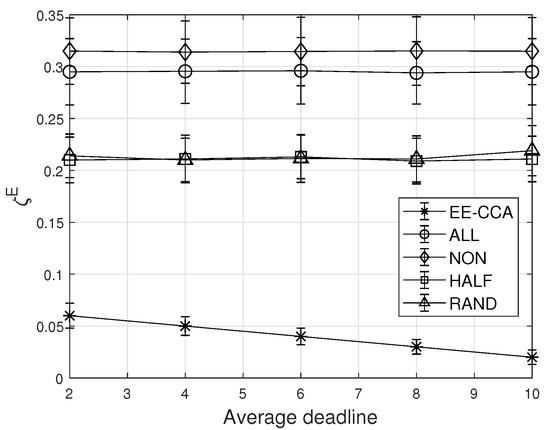
Figure 6.
Effect of the average deadline of the task.
5.4. Comparison between the Optimal IoT Device Pairing and the Random Pairing
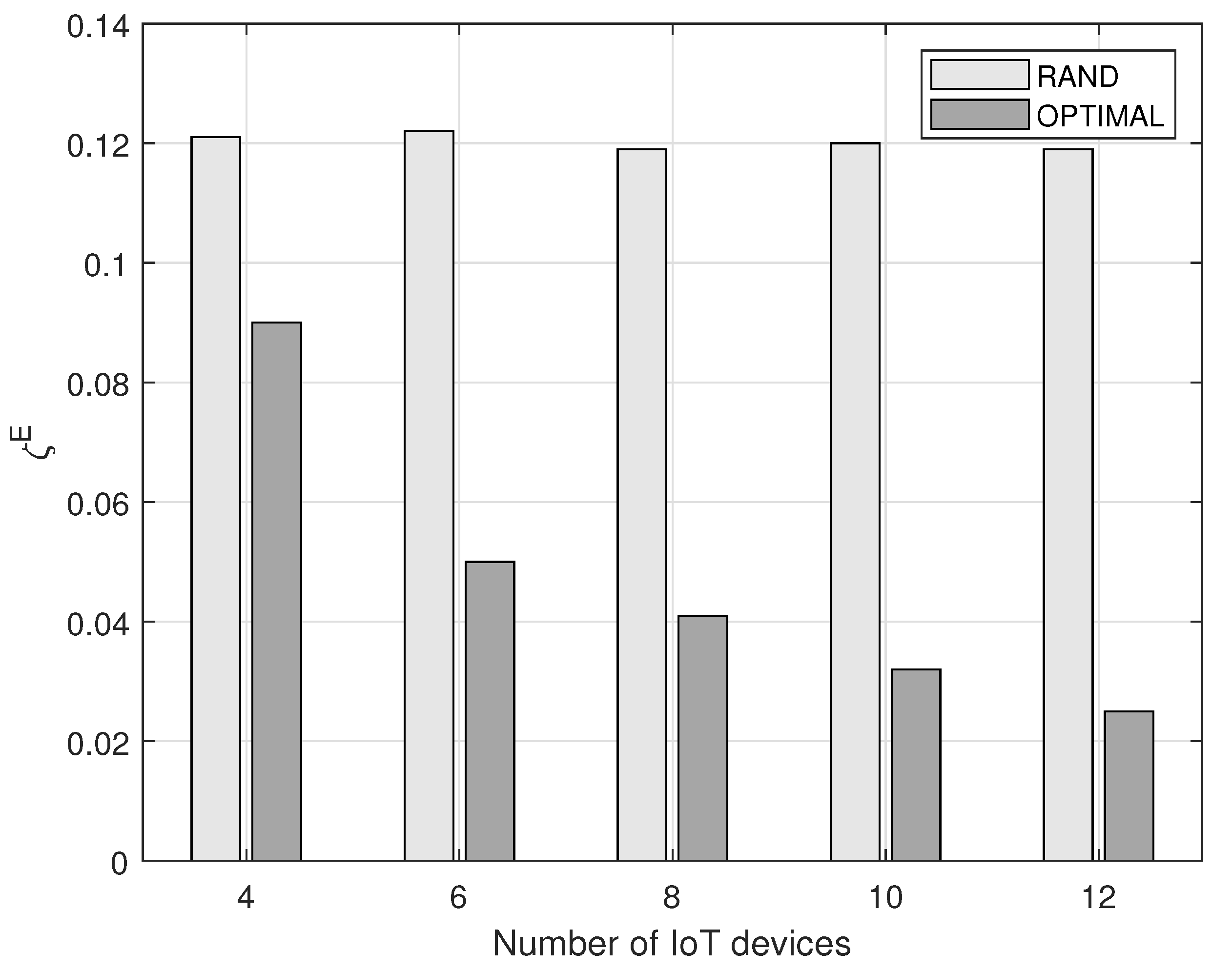
Figure 7 shows the average energy outage probabilities of the EE-CCA when pairing IoT devices based on the optimization problem (denoted by OPTIMAL) and pairing IoT devices randomly (denoted by RAND) as a function of the number of IoT devices. As shown in Figure 7, the average energy outage probability of OPTIMAL decreases as the number of IoT devices increases. This can be explained as follows: a large number of IoT devices means that there are lots of candidate IoT devices to be matched to a specific IoT device. In this situation, each IoT device can be paired to more appropriate IoT device. For example, an energy-scarce IoT device can be paired to more energy-abundant IoT device. On the other hand, since IoT devices are paired randomly in RAND regardless of the number of IoT devices, its energy outage probability is not affected by that number.
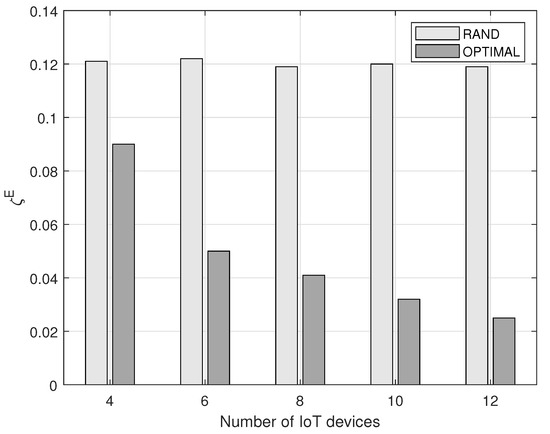
Figure 7.
Comparison between the optimal pairing and random pairing.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we proposed an energy efficient cooperative computation algorithm (EE-CCA), in which a pair of IoT devices decide whether to offload some parts of the task to the opponent with the consideration of their energy harvesting probabilities, task occurrence rates, and current energy levels. The optimal offloading decision can be obtained by means of a constraint Markov decision process (CMDP). Moreover, an optimization problem for IoT device pairing is formulated under the optimal offloading strategy. The evaluation results demonstrate that the EE-CCA offloads tasks appropriately, and thus the energy outage probability can be reduced by up to compared to the random offloading scheme while providing the desired probability that tasks are completed before the deadline. Moreover, it can be seen that the EE-CCA operates adaptively even when the operating environment (e.g., inter-task occurrence rate) is changed. In our future works, we will investigate an incentive mechanism to encourage IoT devices to process tasks. In addition, a study for the robustness of the proposed algorithm will be conducted for supporting heterogeneous functionality of IoT devices.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.K. and S.P.; methodology, S.J. and J.K.; software, J.L.; validation, H.K., S.J., J.K., and J.L.; investigation, S.P.; writing, original draft preparation, H.K.; review and editing, S.J., J.K., J.L., and S.P.; visualization, H.K.; supervision, S.P.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea Grant funded by the Korean Government (MSIP) (No. 2019R1C1C1004352).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the anonymous reviewers for their comments and valuable suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Arslan, M.; Singh, I.; Singh, S.; Madhyastha, H.; Sundaresan, K.; Krishnamurthy, S. Computing While Charging: Building a Distributed Computing Infrastructure Using Smartphones. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Emerging Network Experiment and Technology (CoNEXT), Nice, France, 10–12 December 2012; pp. 193–204. [Google Scholar]
- Saleem, U.; Jangsher, S.; Qureshi, H.; Hassan, S. Joint Subcarrier and Power Allocation in Energy Harvesting-Aided D2D Communication Sign in or Purchase. IEEE Tran. Ind. Inf. 2018, 14, 2608–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Qian, L.; Bi, S.; Xia, Z. Adaptive Scheduling in Energy Harvesting Sensor Networks for Green Cities. IEEE Tran. Ind. Inf. 2018, 14, 1575–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, R. Wireless Powered Communication Networks: An Overview. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2016, 23, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, L.; Chen, X.; Xu, J.; Fu, X. D2D Fogging: An Energy-Efficient and Incentive-Aware Task Offloading Framework via Network-Assisted D2D Collaboration. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2016, 34, 3887–3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Ren, J.; Yu, G.; Cai, Y. Joint Computation Offloading and Resource Allocation in D2D Enabled MEC Network. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Shanghai, China, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, S.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Luo, X. Alternate Distributed Allocation of Time Reuse Patterns in Fog-enabled Cooperative D2D Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Fog World Congress (FWC), Santa Clara, CA, USA, 30 October–1 November 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; Misra, S.; Wolfinger, B.; Obaidat, M. Temporal-Correlation-Aware Dynamic Self-Management of Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2016, 12, 2127–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Gkatzikis, L.; Fischione, C.; Xiao, M. On maximizing sensor network lifetime by energy- balancing. IEEE Trans. Control Netw. Syst. 2018, 5, 1206–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Deng, D.; Shu, L.; Wang, K.; Wang, S.; Tsai, I. On lifetime enhancement of dynamic wireless sensor networks with energy-harvesting sensors. In Proceedings of the 2016 EEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China (ICCC), Paris, France, 27 June–1 July; pp. 1206–1218.
- Wang, K.; Shen, M.; Cho, J.; Banerjee, A.; Merwe, J.; Webb, K. MobiScud: A Fast Moving Personal Cloud in the Mobile Network. In Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on All Things Cellular: Operations, Applications and Challenges, London, UK, 17–21 August 2015; pp. 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, L.; Li, Y.; Gao, W. A Hierarchical Edge Cloud Architecture for Mobile Computing. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications (ICC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 10–15 April 2016; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Taleb, T.; Ksentini, A. Follow Me Cloud: Interworking Federated Clouds and Distributed Mobile Networks. IEEE Netw. 2013, 27, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, T.; Zhou, S.; Cheng, Y.; Niu, Z. CONCERT: A Cloud-Based Architecture for Next-Generation Cellular Systems. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2014, 21, 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Puente, M.; Becvar, Z.; Rohlik, M.; Lobillo, F.; Strinati, E. A Seamless Integration of Computationally-Enhanced Base Stations into Mobile Networks towards 5G. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 81st Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Glasgow, Scotland, 11–14 May 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, R.; Munir, A. An Efficient Computation Offloading Architecture for the Internet of Things (IoT) Devices. In Proceedings of the The 14th Annual IEEE Consumer Communications & Networking Conference (CCNC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 8–11 January 2017; pp. 728–731. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, H.; Lee, J.; Pack, S. Spatial and Temporal Computation Offloading Decision Algorithm in Edge Cloud-Enabled Heterogeneous Networks. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 18920–18932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Zhou, S.; Guo, X.; Niu, Z. Tasks Scheduling and Resource Allocation in Heterogeneous Cloud for Delay-Bounded Mobile Edge Computing. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Paris, France, 21–25 May 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; Chen, X. An Efficient Social-Aware Computation Offloading Algorithm in Cloudlet System. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Washington, DC, USA, 4–8 December 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Jiao, L.; Li, W.; Fu, X. Efficient Multi-User Computation Offloading for Mobile-Edge Cloud Computing. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2016, 24, 2795–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Cai, Y.; Wu, Y.; Shen, X. Dynamic Computation Offloading for Mobile Cloud Computing: A Stochastic Game-Theoretic Approach. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2019, 18, 771–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Langar, R.; Fu, X.; Wang, L.; Han, Z. Computation Offloading With Data Caching Enhancement for Mobile Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 11098–11112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y. Resilient Multiscale Coordination Control against Adversarial Nodes. Energies 2018, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wen, Y.; Guan, K.; Kilper, D.; Luo, H.; Wu, D. Energy-Optimal Mobile Cloud Computing under Stochastic Wireless Channel. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2013, 12, 4569–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samteladze, N.; Christensen, K. DELTA: Delta Encoding for Less Traffic for Apps. In Proceedings of the 37th Annual IEEE Conference on Local Computer Networks, Clearwater, FL, USA, 22–25 October 2012; pp. 212–215. [Google Scholar]
- Alsheikh, N.; Hoang, D.; Niyato, D.; Tan, H.; Lin, S. Markov Decision Processes with Applications in Wireless Sensor Networks: A Survey. IEEE Comm. Surv. Tutor. 2015, 17, 1239–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H.; Pack, S. A Software-Defined Surveillance System with Energy Harvesting: Design and Performance Optimization. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puterman, M. Markov Decision Processes: Discrete Stochastic Dynamic Programming; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, Y. Vulnerability of networks: Fractional percolation on random graphs. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 89, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H.; Lee, J.; Jang, S.; Kim, J.; Pack, S. Energy Efficient Cooperative Computation Algorithm in Energy Harvesting Internet of Things. Available online: https://hoy.kr/B2KEm (accessed on 10 October 2019).
- Guo, T.; Wang, N.; Tafazolli, R. Local Mobility Management for Networked Femtocells Based on X2 Traffic Forwarding. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2013, 62, 326–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Cai, Y.; Shen, X.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, W. Green Energy Optimization in Energy Harvesting Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2015, 53, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Lin, P.; Lin, Y. Reducing Signaling Overhead for Femtocell/Macrocell Networks. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2013, 12, 1587–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H.; Lee, J.; Pack, S. Performance Optimization of Delayed WiFi Offloading in Heterogeneous Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 9436–9447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spielman, D.; Teng, S. Smoothed Analysis of Algorithms: Why the Simplex Algorithm Usually Takes Polynomial Time. IEEE J. ACM 2004, 51, 385–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, E. Constrained Markov Decision Processes; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Heyman, D.; Sobel, M. Stochastic Models in Operations Research: Stochastic Optimization; Courier Corporation: Chelmsford, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).