Dual Solutions and Stability Analysis of Micropolar Nanofluid Flow with Slip Effect on Stretching/Shrinking Surfaces
Abstract
:1. Introduction
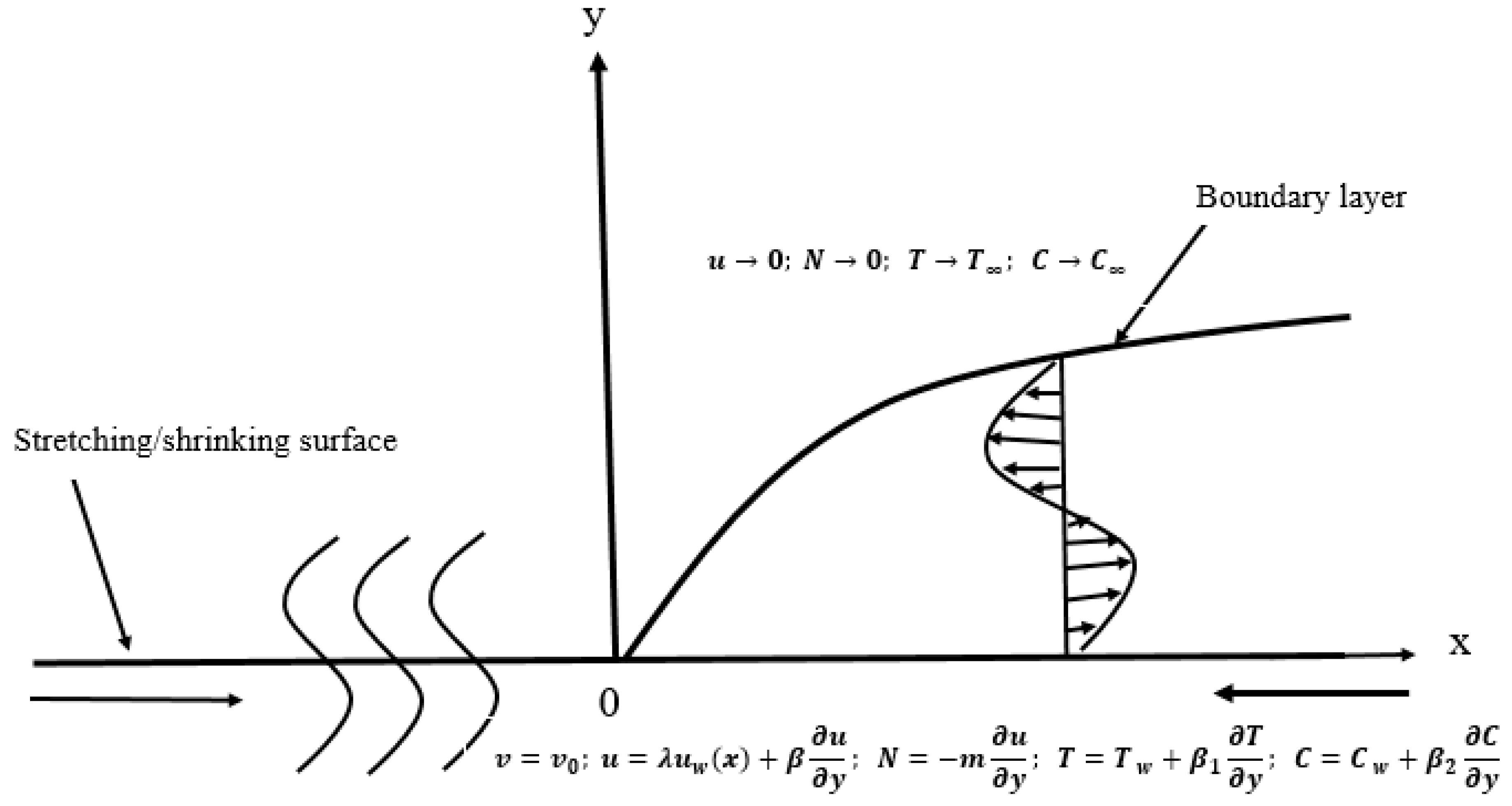
2. Flow Analysis
3. Stability Analysis
4. Result and Discussion
5. Conclusions
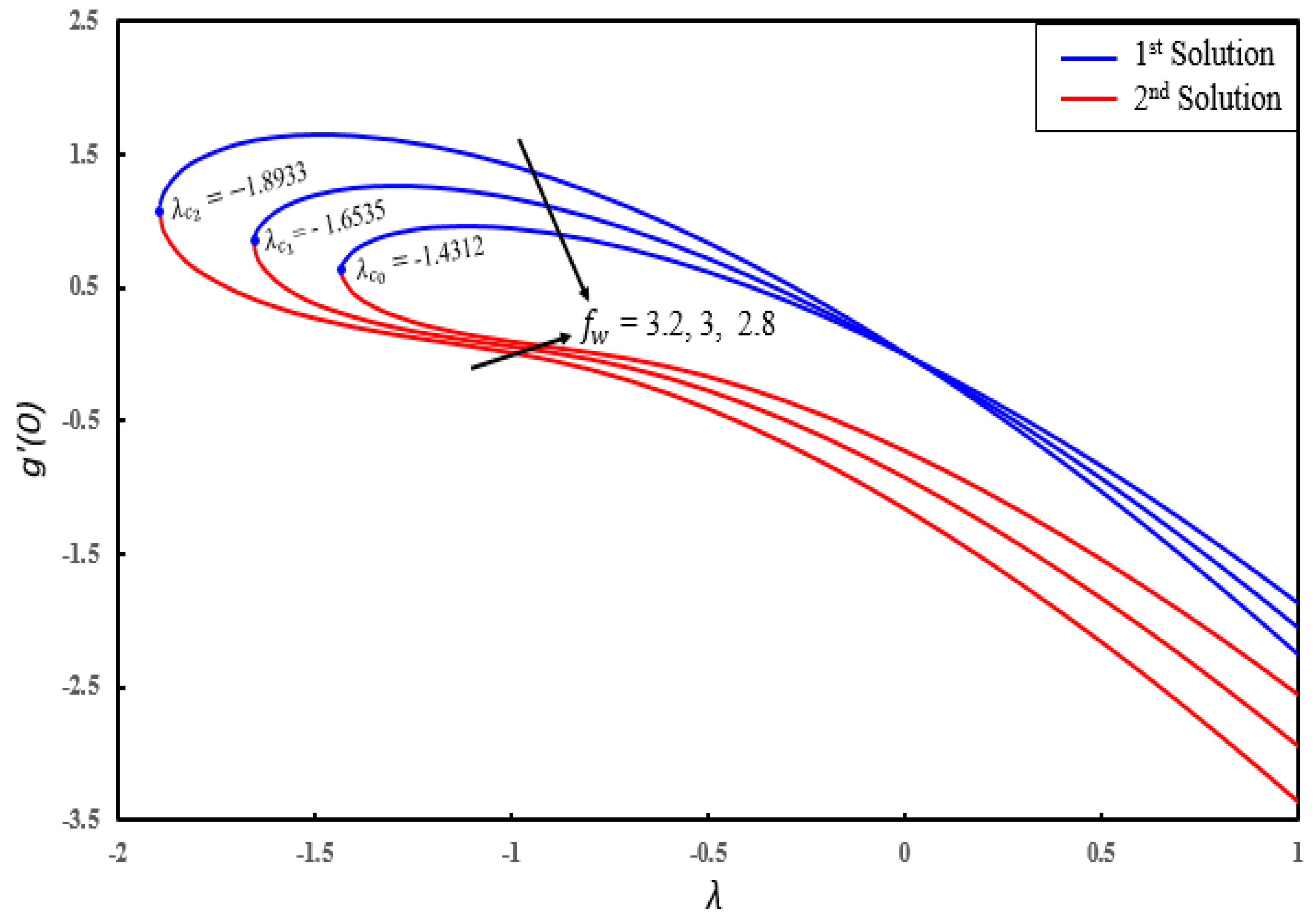
- Dual solutions exist for skin friction coefficient, couple stress coefficient, local Nusselt number and local Sherwood number for certain parameters.
- From stability analysis, it is examined that the first solution is stable and physically realizable, while the second solution is not stable so it is not physical realizable.
- There exist different ranges of dual similarity solutions. For (), dual solutions occur when () and no solution when .
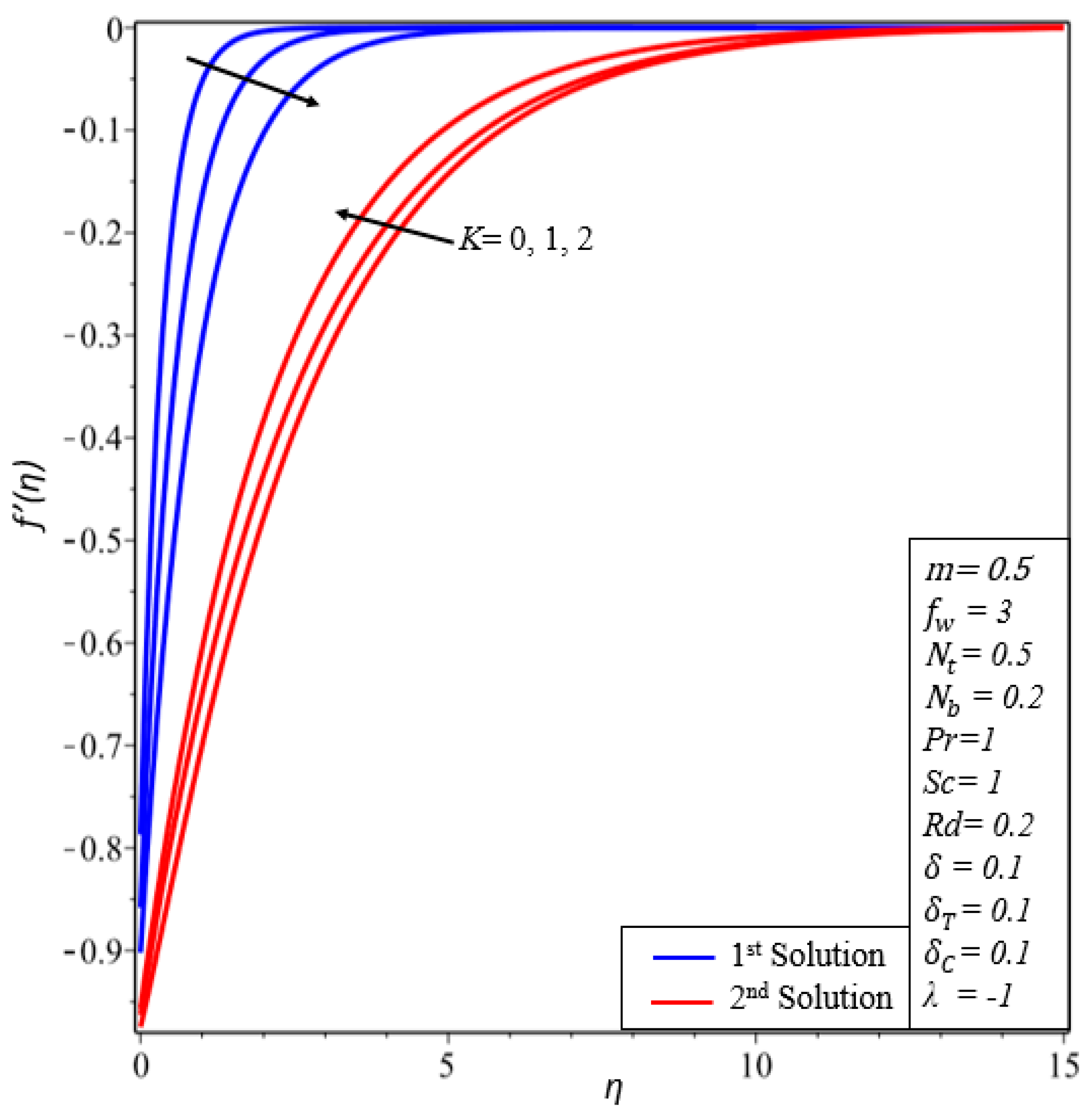
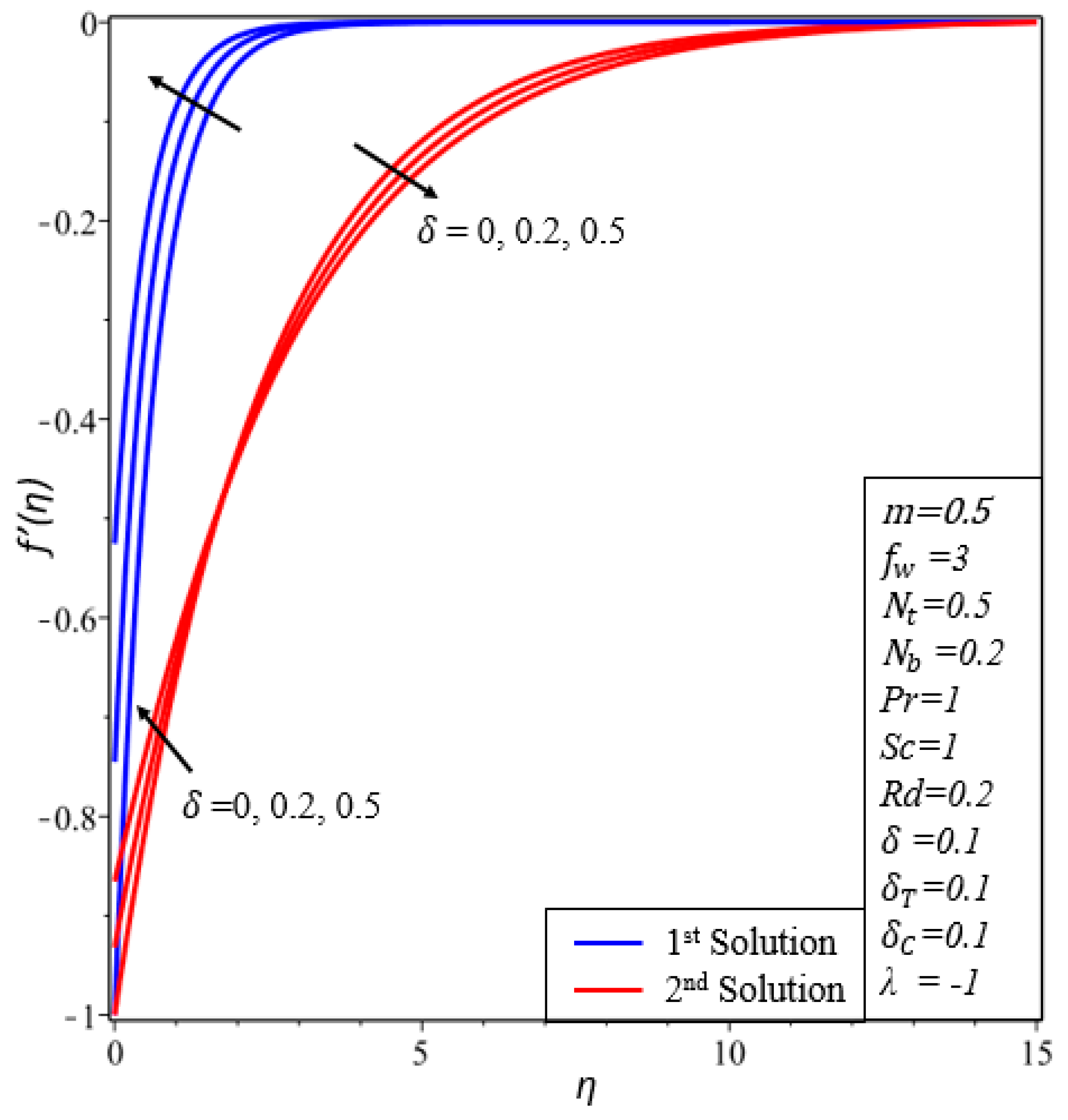
- The velocity profile declines in the first solution by increasing the values of the velocity slip parameter.
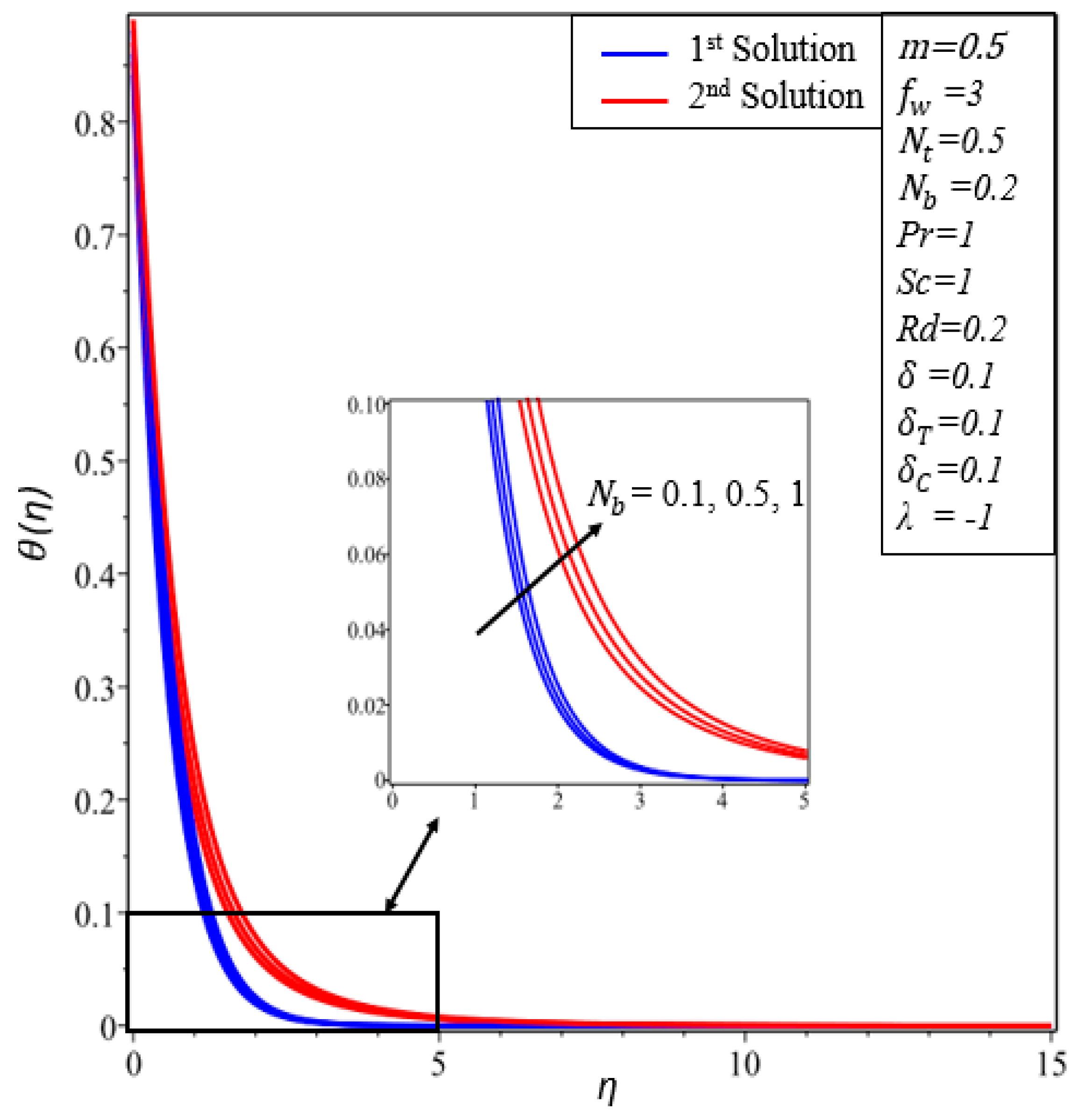
- The impact of and on microrotation profiles show that the microrotation boundary layer thicknesses and microrotation profiles decrease in both solutions.
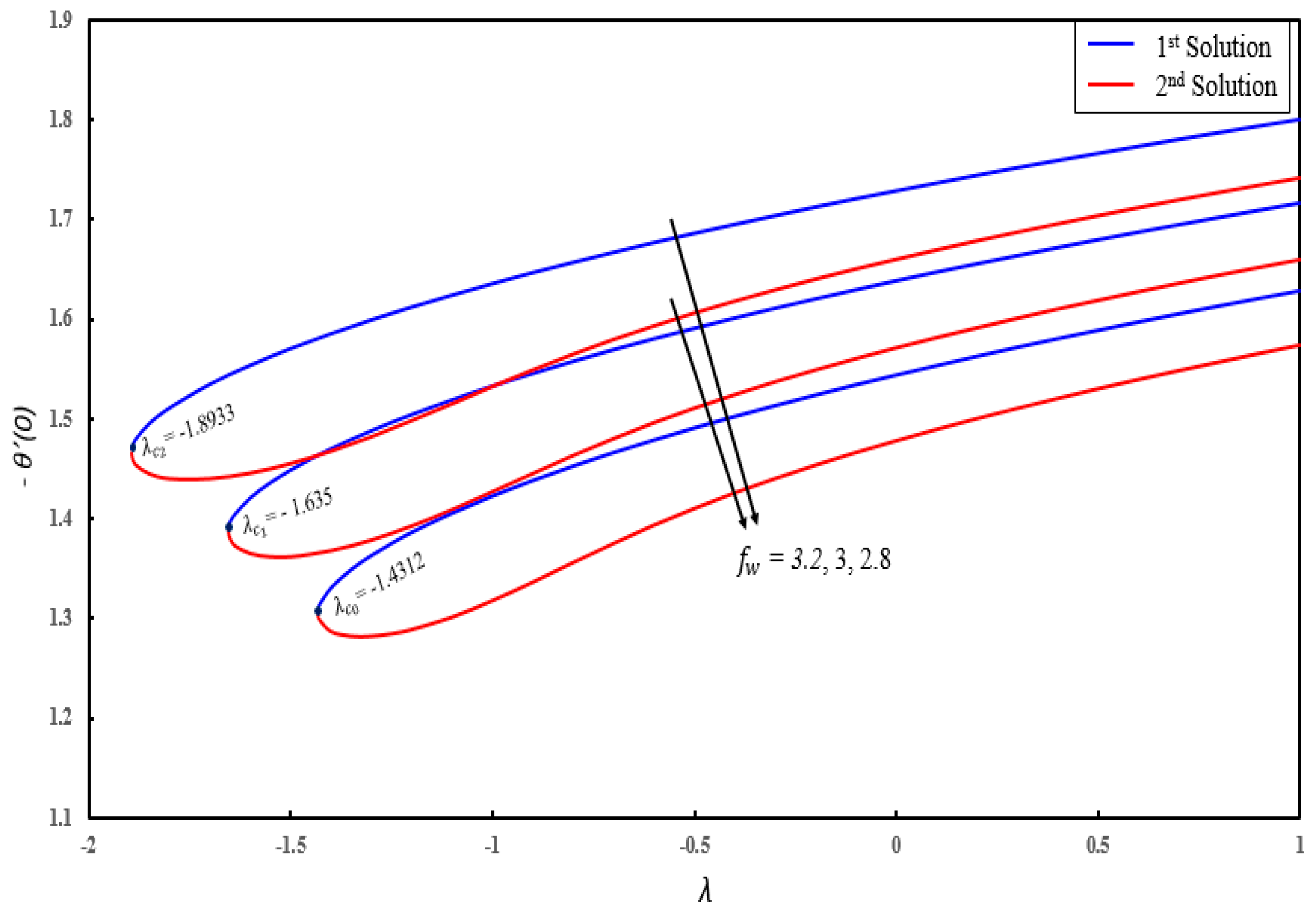
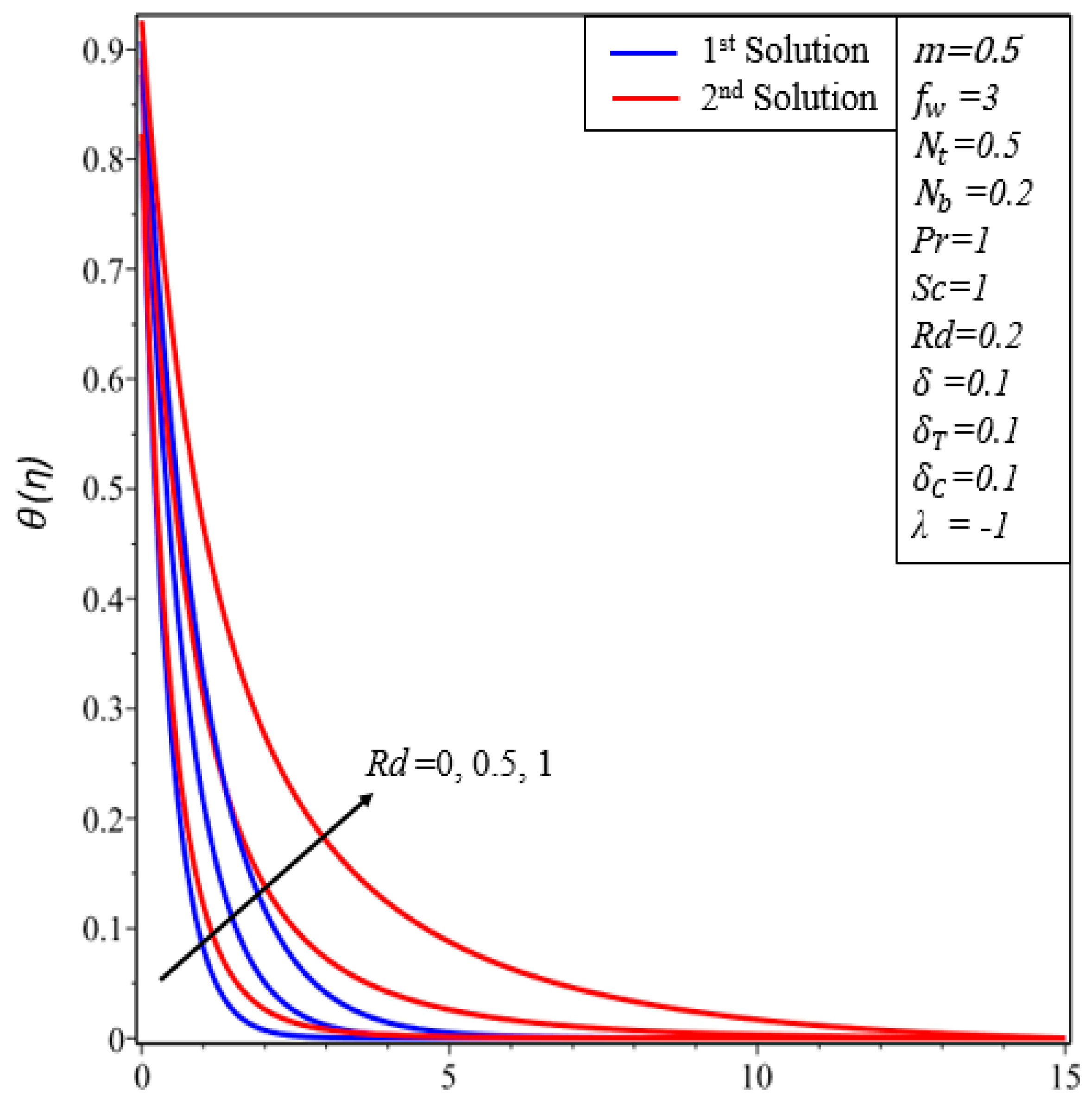
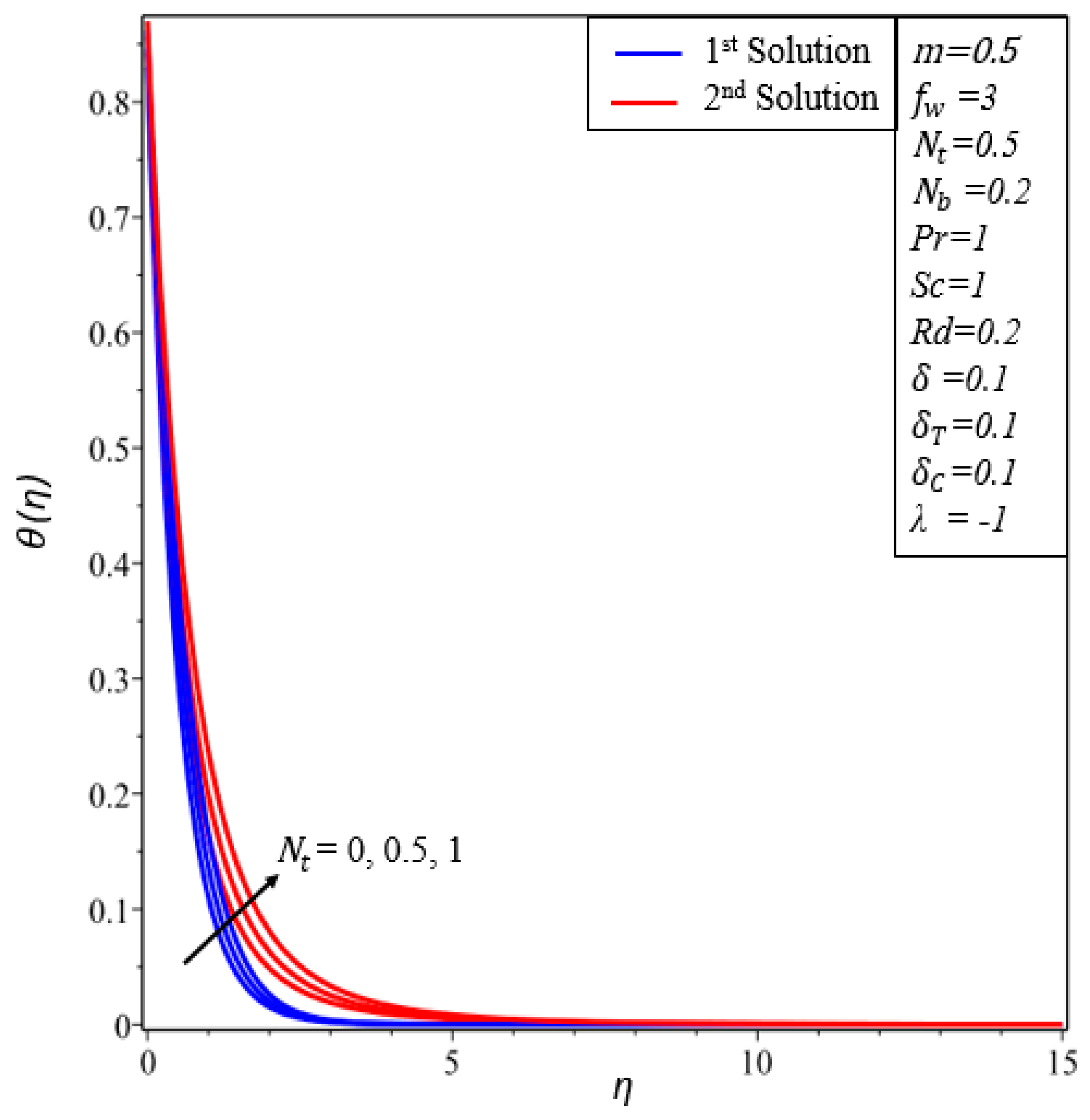
- Temperature profiles increase in both solutions when thermal radiation, thermophoresis and the Brownian motion parameters are enhanced.
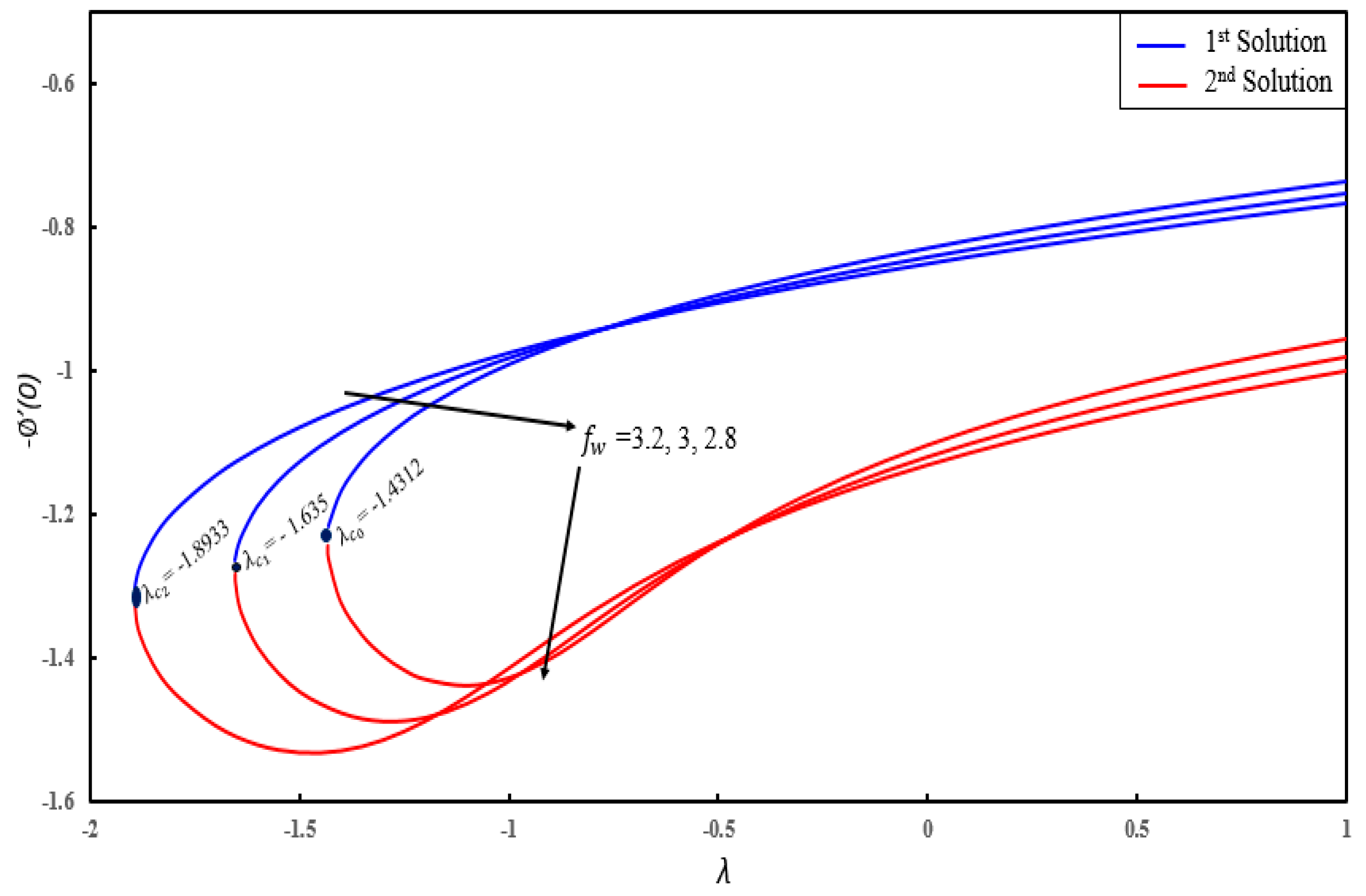
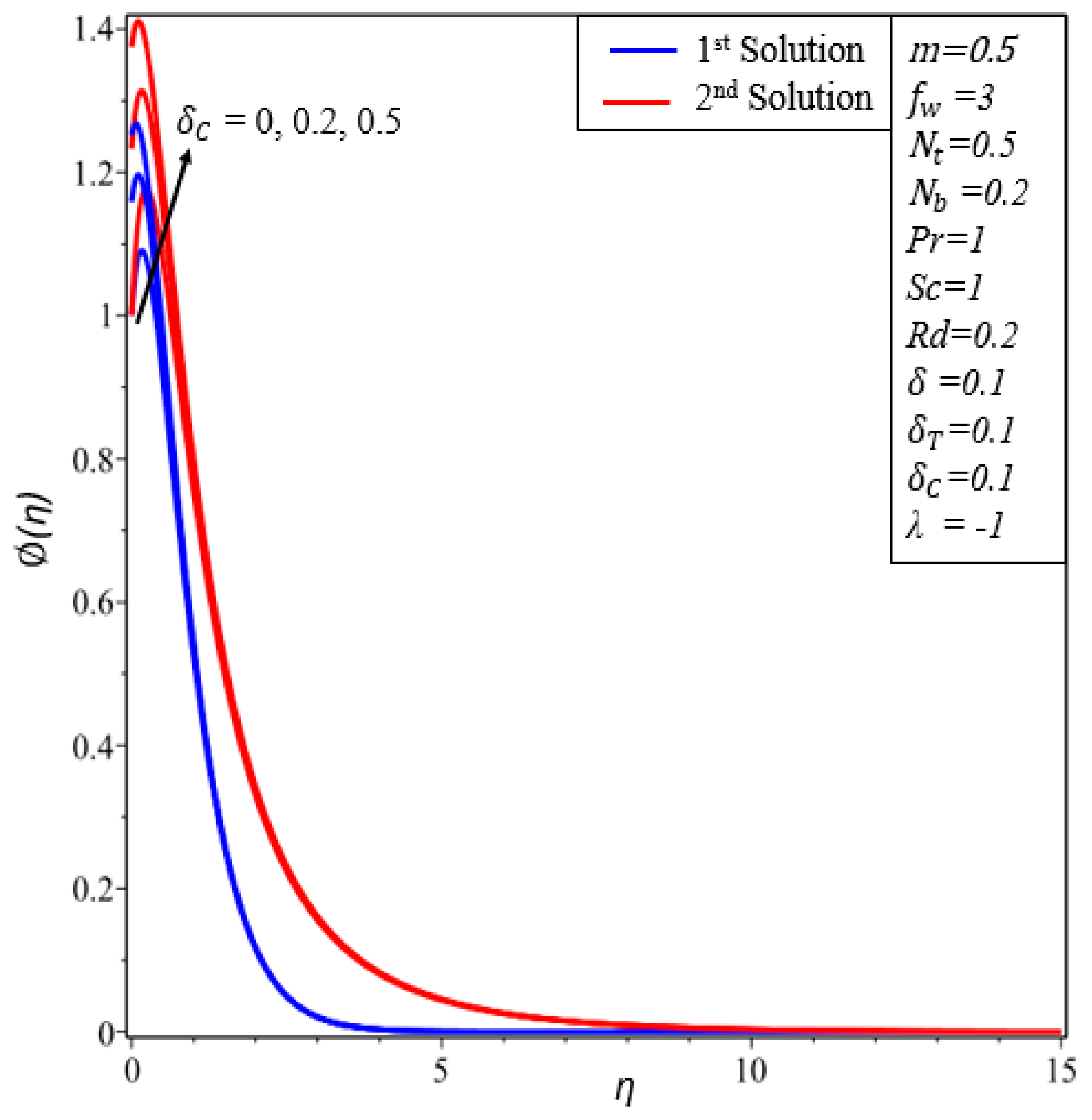
- The concentration of nanoparticles increases by increasing and decreases by increasing
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| u, v | velocity components (m/s) | concentration slip (mol/) | |
| N | Microrotation | thermal radiation | |
| shrinking velocity (m/s) | Pr | Prandtl number | |
| velocity slip (m/s) | thermophoresis parameter | ||
| K | material parameter | thermophoretic diffusion (/) | |
| m | a constant | variable concentration at the sheet (mol/) | |
| T | Temperature (K) | Brownian motion parameter (/) | |
| a constant | Brownian diffusion (/) | ||
| variable temperature at the sheet (K) | Schmidt number stretching/shrinking parameter | ||
| ambient temperature (K) | injunction/suction parameter | ||
| C | Concentration (mol/) | skin friction coefficient | |
| a constant | local Sherwood number | ||
| ambient concentration (mol/) | local Nusselt number | ||
| kinematic viscosity (/) | local Reynolds number | ||
| spin gradient viscosity (/) | ε | smallest eigenvalue | |
| vortex viscosity (/) | τ | Stability transformed variable | |
| microinertia per unit mass | thermal slip (K) | ||
| thermal diffusivity (/) | η | transformed variable | |
| thermal conductivity (W/m K) |
References
- Eringen, A.C. Theory of thermomicrofluids. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 1972, 38, 480–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chol, S.U.S.; Estman, J.A. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. ASME Publ. Fed. 1995, 231, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, R.K.; Das, M.K. Heat transfer augmentation in a two-sided lid-driven differentially heated square cavity utilizing nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2007, 50, 2002–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buongiorno, J. Convective transport in nanofluids. J. Heat Transf. 2006, 128, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleh, S.N.A.; Bachok, N.; Arifin, N.M.; Ali, F.M.; Pop, I. Magnetohydrodynamics Flow Past a Moving Vertical Thin Needle in a Nanofluid with Stability Analysis. Energies 2018, 11, 3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, K.-L. Micropolar nanofluid flow with MHD and viscous dissipation effects towards a stretching sheet with multimedia feature. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 112, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, L.A.; Omar, Z.; Khan, I.; Raza, J.; Bakouri, M.; Tlili, I. Stability Analysis of Darcy-Forchheimer Flow of Casson Type Nanofluid Over an Exponential Sheet: Investigation of Critical Points. Symmetry 2019, 11, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, L.A.; Omar, Z.; Khan, I.; Khan, I. Analysis of dual solution for MHD flow of Williamson fluid with slippage. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, H.; Namazian, Z.; Mehryan, S. Cu-water micropolar nanofluid natural convection within a porous enclosure with heat generation. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 236, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.T.; Nadeem, S.; Haq, R.U. Model-based analysis of micropolar nanofluid flow over a stretching surface. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2014, 129, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dero, S.; Uddin, M.J.; Rohni, A.M. Stefan Blowing and Slip Effects on Unsteady Nanofluid Transport Past a Shrinking Sheet: Multiple Solutions. Heat Transf. Asian Res. 2019, 48, 2047–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dero, S.; Rohni, A.M.; Saaban, A. MHD Micropolar Nanofluid Flow over an Exponentially Stretching/Shrinking Surface: Triple Solutions. J. Adv. Res. Fluid Mech. Therm. Sci. 2019, 56, 165–174. [Google Scholar]
- Dero, S.; Rohni, A.M.; Saaban, A. The Dual Solutions and Stability Analysis of Nanofluid Flow using Tiwari-Das Modelover a Permeable Exponentially Shrinking Surface with Partial Slip Conditions. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2019, 14, 4569–4582. [Google Scholar]
- Alarifi, I.M.; Alkouh, A.B.; Ali, V.; Nguyen, H.M.; Asadi, A. On the rheological properties of MWCNT-TiO2/oil hybrid nanofluid: An experimental investigation on the effects of shear rate, temperature, and solid concentration of nanoparticles. Powder Technol. 2019, 355, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourfattah, F.; Arani, A.A.A.; Babaie, M.R.; Nguyen, H.M.; Asadi, A. On the thermal characteristics of a manifold microchannel heat sink subjected to nanofluid using two-phase flow simulation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 143, 118518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsarraf, J.; Moradikazerouni, A.; Shahsavar, A.; Afrand, M.; Salehipour, H.; Tran, M.D. Hydrothermal analysis of turbulent boehmite alumina nanofluid flow with different nanoparticle shapes in a minichannel heat exchanger using two-phase mixture model. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2019, 520, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarimoghaddam, A. Two-phase modeling of magnetic nanofluids jets over a Stretching/shrinking wall. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2018, 8, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarimoghaddam, A.; Pop, I. Numerical modeling of Glauert type exponentially decaying wall jet flows of nanofluids using Tiwari and Das’ nanofluid model. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2019, 29, 1010–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, D.; Mandal, G. Thermal radiation and MHD effects on boundary layer flow of micropolar nanofluid past a stretching sheet with non-uniform heat source/sink. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2017, 126, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradikazerouni, A.; Hajizadeh, A.; Safaei, M.R.; Afrand, M.; Yarmand, H.; Zulkifli, N.W.B.M. Assessment of thermal conductivity enhancement of nano-antifreeze containing single-walled carbon nanotubes: Optimal artificial neural network and curve-fitting. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2019, 521, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, A.; Aberoumand, S.; Moradikazerouni, A.; Pourfattah, F.; Żyła, G.; Estellé, P.; Mahian, O.; Wongwises, S.; Nguyen, H.M.; Arabkoohsar, A. Recent advances in preparation methods and thermophysical properties of oil-based nanofluids: A state-of-the-art review. Powder Technol. 2019, 352, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, D.D.; Alsarraf, J.; Moradikazerouni, A.; Afrand, M.; Salehipour, H.; Qi, C. Numerical investigation of γ-AlOOH nano-fluid convection performance in a wavy channel considering various shapes of nanoadditives. Powder Technol. 2019, 345, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awais, M.; Hayat, T.; Ali, A.; Irum, S. Velocity, thermal and concentration slip effects on a magneto-hydrodynamic nanofluid flow. Alex. Eng. J. 2016, 55, 2107–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K. Slip effects on MHD mixed convection stagnation point flow of a micropolar fluid towards a shrinking vertical sheet. Comput. Math. Appl. 2012, 63, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramya, D.; Raju, R.S.; Rao, J.A.; Chamkha, A. Effects of velocity and thermal wall slip on magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) boundary layer viscous flow and heat transfer of a nanofluid over a non-linearly-stretching sheet: A numerical study. Propuls. Power Res. 2018, 7, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzan, M.; Chung, J.D.; Ullah, N. Partial slip effect in the flow of MHD micropolar nanofluid flow due to a rotating disk – A numerical approach. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 3557–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, J.; Zhao, P.; Cheng, Z.; Doi, M. Influence of particulate thermophoresis on convection heat and mass transfer in a slip flow of a viscoelasticity-based micropolar fluid. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 119, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzan, M.; Farooq, M.; Hayat, T.; Chung, J.D. Radiative and Joule heating effects in the MHD flow of a micropolar fluid with partial slip and convective boundary condition. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 221, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, L.A.; Omar, Z.; Khan, I. Mathematical analysis of magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) flow of micropolar nanofluid under buoyancy effects past a vertical shrinking surface: Dual solutions. Heliyon 2019, 5, 02432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Khan, M.I.; Waqas, M.; Alsaedi, A.; Khan, M.I. Radiative flow of micropolar nanofluid accounting thermophoresis and Brownian moment. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 16821–16833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzan, M.; Ullah, N.; Chung, J.D.; Lu, D.; Farooq, U. Buoyancy effects on the radiative magneto Micropolar nanofluid flow with double stratification, activation energy and binary chemical reaction. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidman, P.; Kubitschek, D.; Davis, A. The effect of transpiration on self-similar boundary layer flow over moving surfaces. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2006, 44, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roşca, N.C.; Pop, I. Mixed convection stagnation point flow past a vertical flat plate with a second order slip: Heat flux case. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 65, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roşca, A.V.; Pop, I. Mixed Convection Stagnation-Point Flow Past a Vertical Flat Plate with a Second Order Slip. J. Heat Transf. 2014, 136, 012501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.D.; Ingham, D.B.; Pop, I. Mixed convection boundary-layer flow near the stagnation point on a vertical surface in a porous medium: Brinkman model with slip. Transp. Porous Media 2009, 77, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, L.A.; Ching, D.L.C.; Omar, Z.; Khan, I.; Nisar, K.S.; Khan, I.; Khan, I. Triple Local Similarity Solutions of Darcy-Forchheimer Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) Flow of Micropolar Nanofluid Over an Exponential Shrinking Surface: Stability Analysis. Coatings 2019, 9, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lund, L.A.; Omar, Z.; Khan, I. Quadruple solutions of mixed convection flow of magnetohydrodynamic nanofluid over exponentially vertical shrinking and stretching surfaces: Stability analysis. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2019, 182, 105044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, L.A.; Omar, Z.; Khan, I.; Dero, S. Multiple solutions of Cu-C6H9NaO7 and Ag-C6H9NaO7 nanofluids flow over nonlinear shrinking surface. J. Cent. South Univ. 2019, 26, 1283–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Hayat et al., [30] | Present | Hayat et al., [30] | Present | |
| 0 | −1.00000 | −1.00000 | −1.00000 | −1.00000 |
| 1 | −1.367870 | 1.367996 | −1.224739 | −1.224819 |
| 2 | −1.621222 | −1.621570 | −1.414214 | −1.414479 |
| 4 | −2.004129 | −2.005420 | −1.732047 | −1.733292 |
| 1st solution | 2nd solution | ||
| 0 | 3 | 0.65232 | −1.04592 |
| 0 | 2.5 | 0.3938 | −0.77841 |
| 0 | 2 | 0.03269 | −0.13870 |
| 1 | 3 | 0.49827 | −0.85106 |
| 1 | 2.5 | 0.14281 | −0.49401 |
| 2 | 3 | 0.26092 | −0.52380 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dero, S.; Rohni, A.M.; Saaban, A.; Khan, I. Dual Solutions and Stability Analysis of Micropolar Nanofluid Flow with Slip Effect on Stretching/Shrinking Surfaces. Energies 2019, 12, 4529. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234529
Dero S, Rohni AM, Saaban A, Khan I. Dual Solutions and Stability Analysis of Micropolar Nanofluid Flow with Slip Effect on Stretching/Shrinking Surfaces. Energies. 2019; 12(23):4529. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234529
Chicago/Turabian StyleDero, Sumera, Azizah Mohd Rohni, Azizan Saaban, and Ilyas Khan. 2019. "Dual Solutions and Stability Analysis of Micropolar Nanofluid Flow with Slip Effect on Stretching/Shrinking Surfaces" Energies 12, no. 23: 4529. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234529
APA StyleDero, S., Rohni, A. M., Saaban, A., & Khan, I. (2019). Dual Solutions and Stability Analysis of Micropolar Nanofluid Flow with Slip Effect on Stretching/Shrinking Surfaces. Energies, 12(23), 4529. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12234529





