Abstract
Through a numerical analytical approach based on piezoelectric analysis and meta-modeling, this study investigated the effect of the component design of an accelerometer sensor on sensitivity and resonance frequency. The results of the study confirmed that the resonance frequency obtained from the piezoelectric analysis was almost the same as the experimental value of the resonance frequency obtained from the fabricated sensing module and proved the validity of the piezoelectric analysis using a finite element method. Moreover, the results of examining the influence of the component design on the resonance frequency and electrical potential suggested that the diameter and height of the head (seismic mass) had the greatest influence. As the diameter and height of the head increased, the sensitivity increased, but the resonance frequency decreased, which indicates that it is necessary to select an appropriate mass to optimize the sensor performance. In addition, the increase in tail height and epoxy thickness had a positive effect on both the resonance frequency and electric potential, and the base diameter had a negative effect on both of them.
1. Introduction
Piezoelectric acceleration sensors, which have been used for structural health monitoring in a variety of applications, can be divided into flexural, compression, and shear types, etc. depending on the arrangement of the piezoelectric structures [1,2]. This structure can be designed according to the usage objective or usage band of the sensor. At the design stage, by applying analytical techniques, it is possible to reduce the labor and time required to go through a lot of trial-and-error process. One of the most important aspects of the sensor performance is sensitivity and resonance frequency. In general, there is a trade-off between the resonance frequency and sensitivity [3,4,5,6,7,8], such that a higher resonance frequency will provide a larger usable frequency range at the expense of reduced sensitivity.
The sensitivity and resonance frequency of the acceleration sensor are greatly affected by the dimensions, weight, mechanical properties, structure, and coupling configuration of each component of the sensor. It is thus important to determine and optimize the components of the sensor that are most sensitive to the working performance. However, it is difficult to experimentally optimize while changing all the factors affecting the sensitivity and resonance frequency. In this study, using a numerical analytic approach based on piezoelectric analysis and meta-modeling, we sought to determine the most influential factors for the sensitivity and resonance frequency of the acceleration sensor, as well as to reduce time-consuming and expensive experimental studies. To the best of our knowledge, numerical studies investigating sensor characteristics according to the component design that consider all the internal components in compression-type piezoelectric accelerometers are rare. This study is meaningful in that changes in sensor performance with component design are systematically investigated and the influencing parameters that should be considered important in the design trade-off are proposed.
A three-dimensional finite-element model was used for the piezoelectric elements and components of the compression-type accelerometer sensor. This enabled a complete description of the coupled fields in the piezoelectric materials and the solid structure. The finite element method was used for the analysis and design of the sensor, including the piezoelectric materials [9,10,11,12]. The accuracy of the finite element modeling of piezoelectric accelerometers has been proven in many cases through comparisons with experiments [13]. The impedance curve theoretically obtained by piezoelectric analysis was compared with the experimentally measured curve obtained from the fabricated sensor module with the same dimensions and material properties. Then, the Kriging meta-model, created using the design of experiment (DOE) method, was applied to investigate how each parameter affects the sensitivity and resonance frequency.
2. Materials and Methods
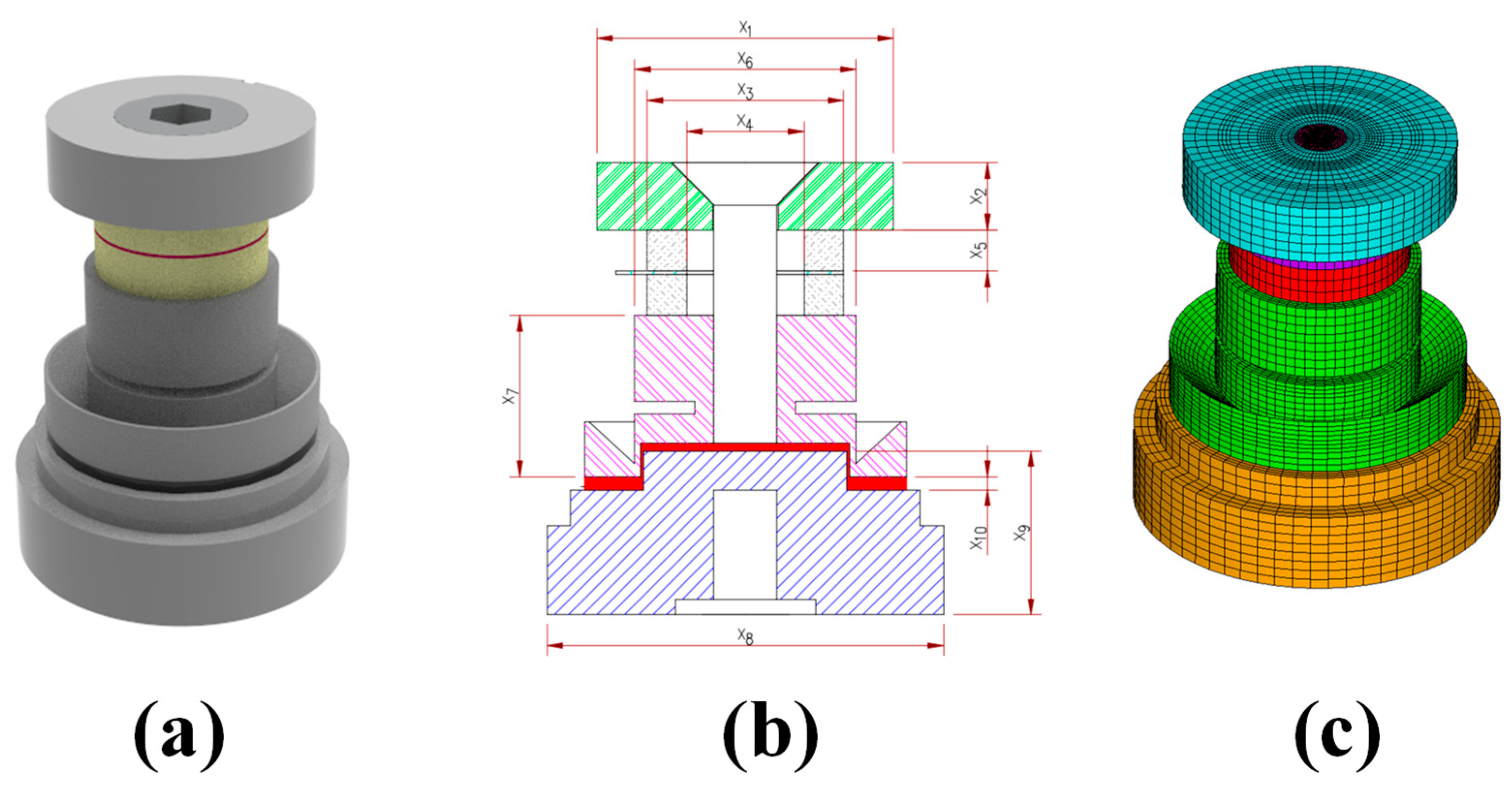
Figure 1a,b respectively show the three-dimensional model and cross-sectional design of the compression-type accelerometer sensor and the names and dimensions of each component are listed Table 1. The sensor module consists of two layers of piezo-elements connected electrically in parallel, forming a sandwich structure between the head (seismic mass) and the tail/base plates, which were tightened by a bolt. The gap between the tail and the base was electrically insulated using epoxy. The material type and the mechanical properties, namely, the density, Young’s Modulus, and Poisson’s ratio, for each component used in the analytical model are also listed in Table 1. The solver used for the finite element analysis was ANSYS V18, a commercial finite element program. The total number of elements was divided into 124,800 and the number of nodes was 134,977, as shown in Figure 1c.
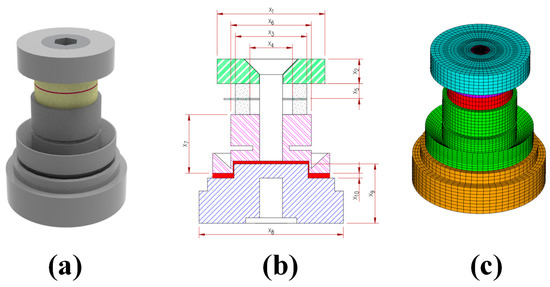
Figure 1.
(a) Three-dimensional model; (b) cross-section; (c) finite element model of the compression-type accelerometer sensor.

Table 1.
Dimensions, material type, and mechanical properties (i.e. density, Young’s modulus, and Poisson’s ratio) for each component.
The resonance frequency of the sensor module in Figure 1c was determined from the impedance curve as the result of the piezoelectric analysis combined with the finite element model in the free condition. For the experimental validation of the resonance frequency of the compression-type accelerometer, each component of the sensor module was fabricated with the same materials and dimensions that were used in the analytical model. When formulating a multilayer compression-mode sensor module, the resonance frequency was greatly affected by the tightening force (torque). It is generally known that a higher torque level causes a shift in resonance frequency to higher frequencies. On the other hand, if the torque value is too high, cracks or breakage may occur in the piezo-elements, thus it is important to provide an appropriate torque so that sufficient tightening can be achieved. In this study, as a result of examining the change of the resonance frequency with the torque value it was found that the resonance frequency was stabilized at a torque value of about 2.0 Nm, and accordingly the sensor module was assembled with a uniform torque value of 2.0 Nm using a digital torque wrench.
The impedance spectra of the fabricated sensor module were experimentally measured using a Solartron 1260 Impedance Analyzer (Solartron Analytical, Hampshire, UK) and compared with those of the analytical model. Moreover, to investigate how each parameter affects the sensitivity and resonance frequency, meta-modeling was performed by Incomplete Small Composite Design (ISCD-2), which was provided by a program called Easy Design.
3. Results
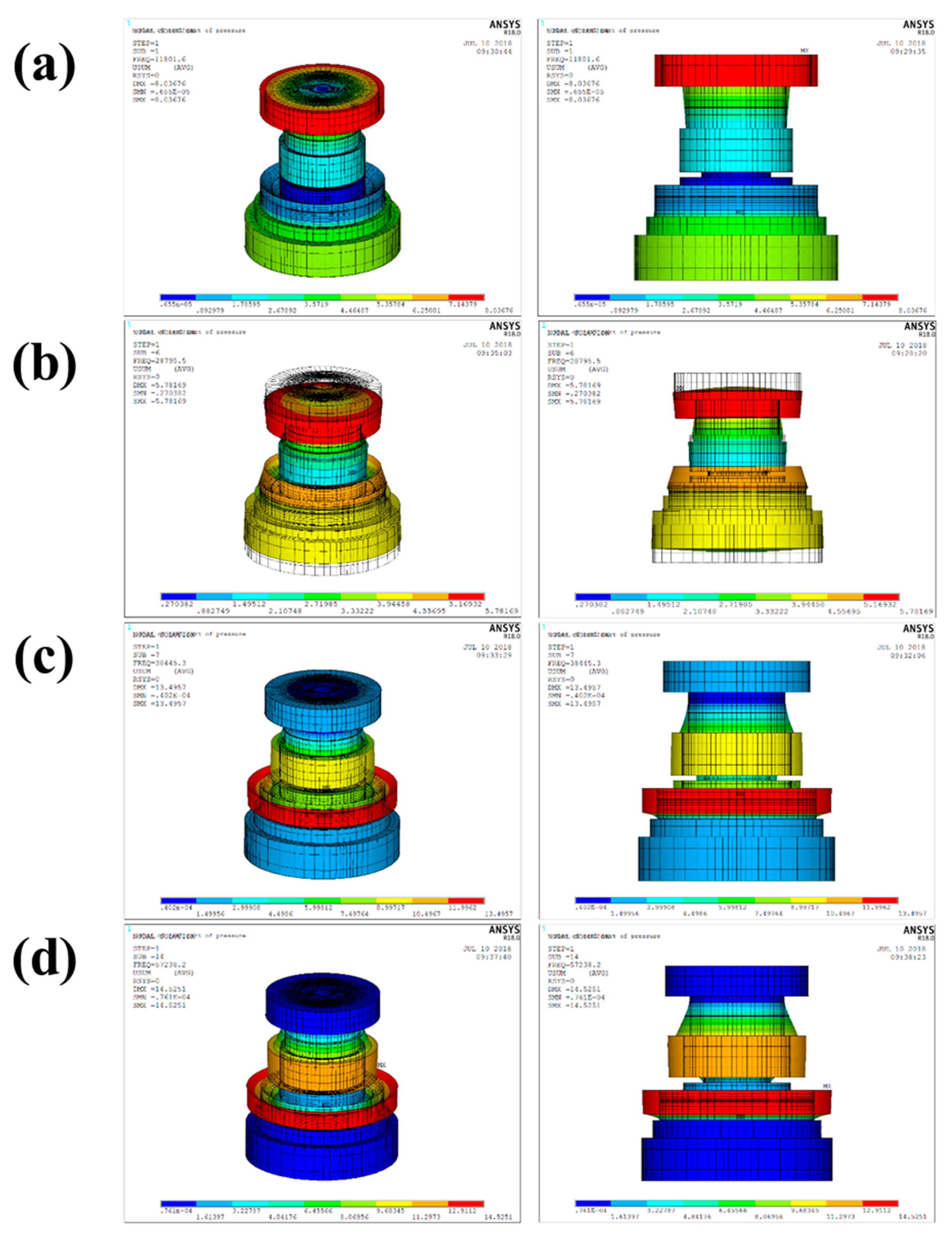
First, to confirm the structural resonance mode and to identify the effective frequency range for the piezoelectric analysis, a modal analysis was performed under free conditions for the whole model and the results are shown in Figure 2.
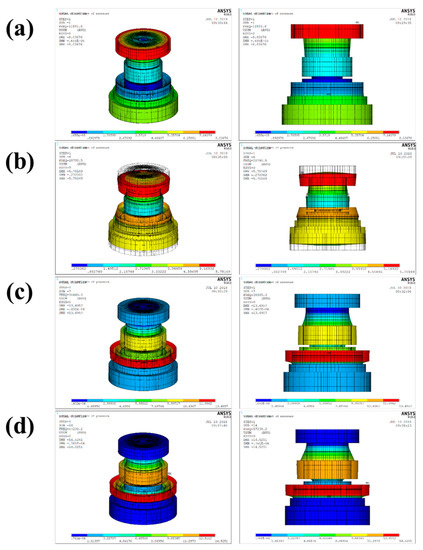
Figure 2.
Modal analysis results under a free condition for the sensor module in Figure 1: (a) the primary resonance mode; (b) the second resonance mode; (c) the third resonance mode; (d) the fourth resonance mode.
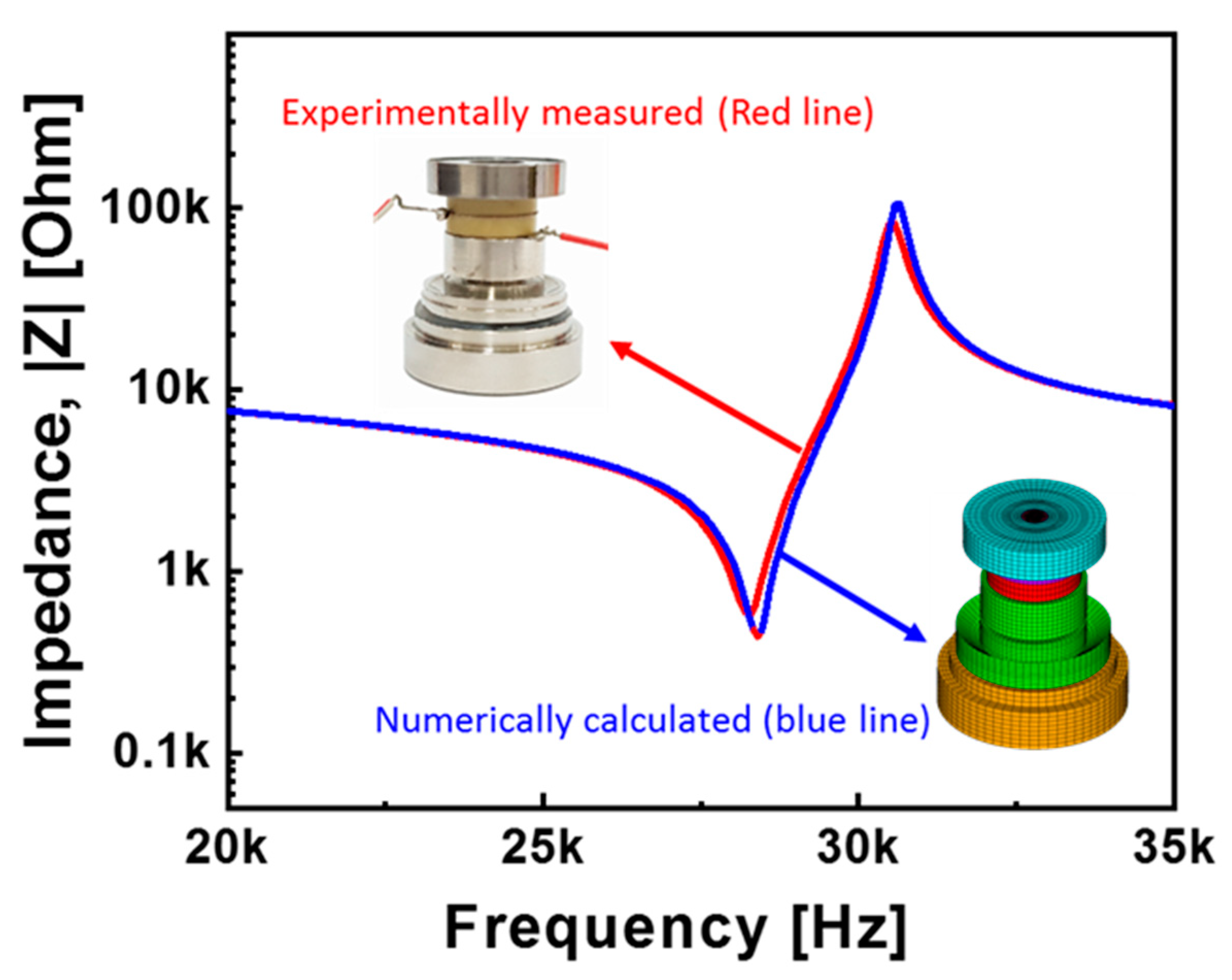
The results of the modal analysis gave a primary resonance frequency of 11.8 kHz, as shown in Figure 2a, and showed the circumferential translation of the head. The secondary resonance frequency, as shown in Figure 2b, was 28.8 kHz, which indicates bending of the head. The third resonance frequency, as shown in Figure 2c, was 38.4 kHz, which indicates the circumferential translation of the lower edge of the tail. The fourth order resonance frequency, as shown in Figure 2d, was 57.2 kHz, which indicates a translation in the circumferential direction of the lower edge of the tail. Based on the above results, the resonance frequency of the sensor module in Figure 1 can be verified by performing a piezoelectric analysis describing a situation where an electric voltage is applied to the piezoelectric elements. As shown in Figure 3 (blue line), the impedance curve related to the resonance characteristics was obtained and the resonance and anti-resonance frequencies were determined to be 28.7 kHz and 30.6 kHz, respectively. The resonance frequency of the piezoelectric analysis was almost the same as the secondary resonance frequency (28.8 kHz) of the modal analysis, indicating that the resonance mode correlated with the bending of the head due to the radial mode of the piezo-element.
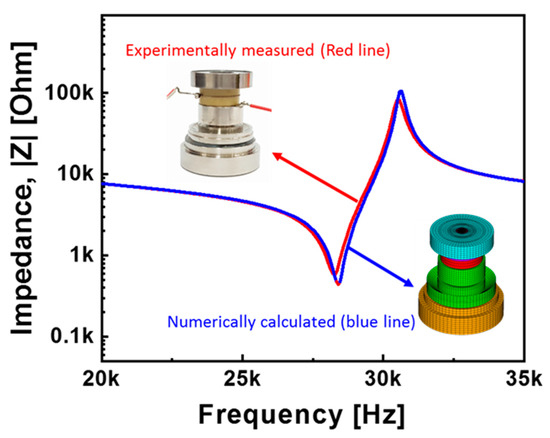
Figure 3.
The impedance curves obtained from the piezoelectric analysis (blue line) and experimentally measured on the fabricated sensor module (red line).
To prove how reliable the analytical results of the design model were, the sensor module was fabricated with the same materials and dimensions used in the analytical model. The experimentally measured impedance spectra of the fabricated sensor module are shown in Figure 3 (red line). The resonance and anti-resonance frequencies were experimentally determined to be 28.3 kHz and 30.5 kHz, respectively, which very nearly coincided with the theoretical values of the piezoelectric analysis (Table 2). These results confirm the validity of the piezoelectric analysis using a finite element model.

Table 2.
Analytical and experimental values of the resonance frequency, resonance impedance, anti-resonance frequency, and anti-resonance impedance for the sensor module.
It was necessary to investigate the factors that were most influential on sensor performance in order to achieve the desired sensitivity and resonance frequency of the accelerometer sensor. It is inefficient, time-consuming, and costly to find solutions through trial and error experimental studies to obtain the best solution for the design optimization. Thus, to optimize the design more effectively while reducing time and cost, we applied the design method using a meta-model. The meta-model technique has been developed in various engineering fields as a method to replace the actual analytical model, which requires much time and cost, by approximating the relationship between the response of the analytical model and the variable [14,15]. Since the sensor in this study includes many geometrical design variables and nonlinear characteristics, the Kriging model [16], which is a global approximation model, was adopted as a meta-model. The experimental design for the variables was applied according to the ISCD-2 provided by a program called Easy Design and the response was selected as the resonance frequency and electric potential of the piezo-element under 1 V of poling voltage and 1 g of gravitational acceleration at 159.2 Hz.
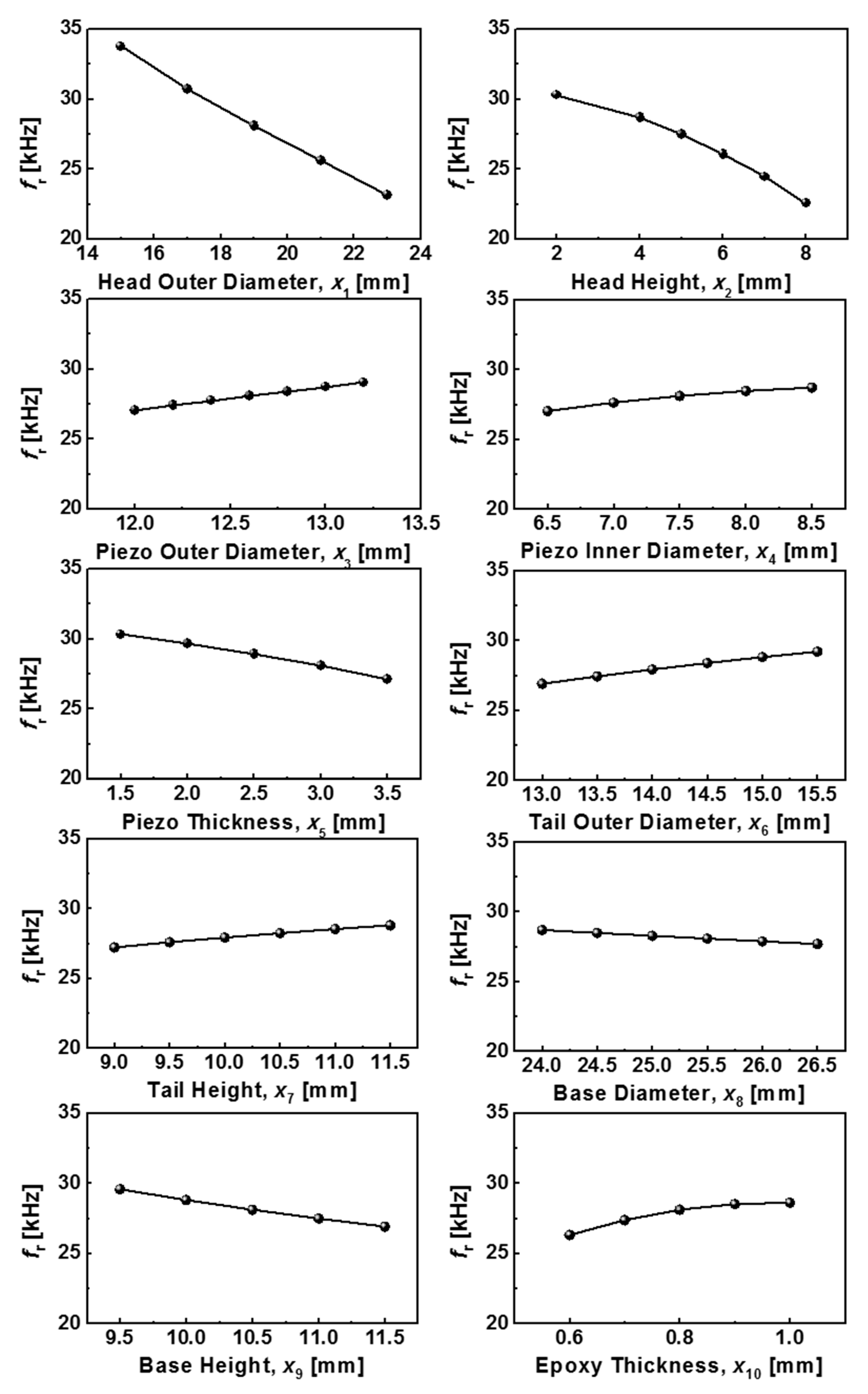
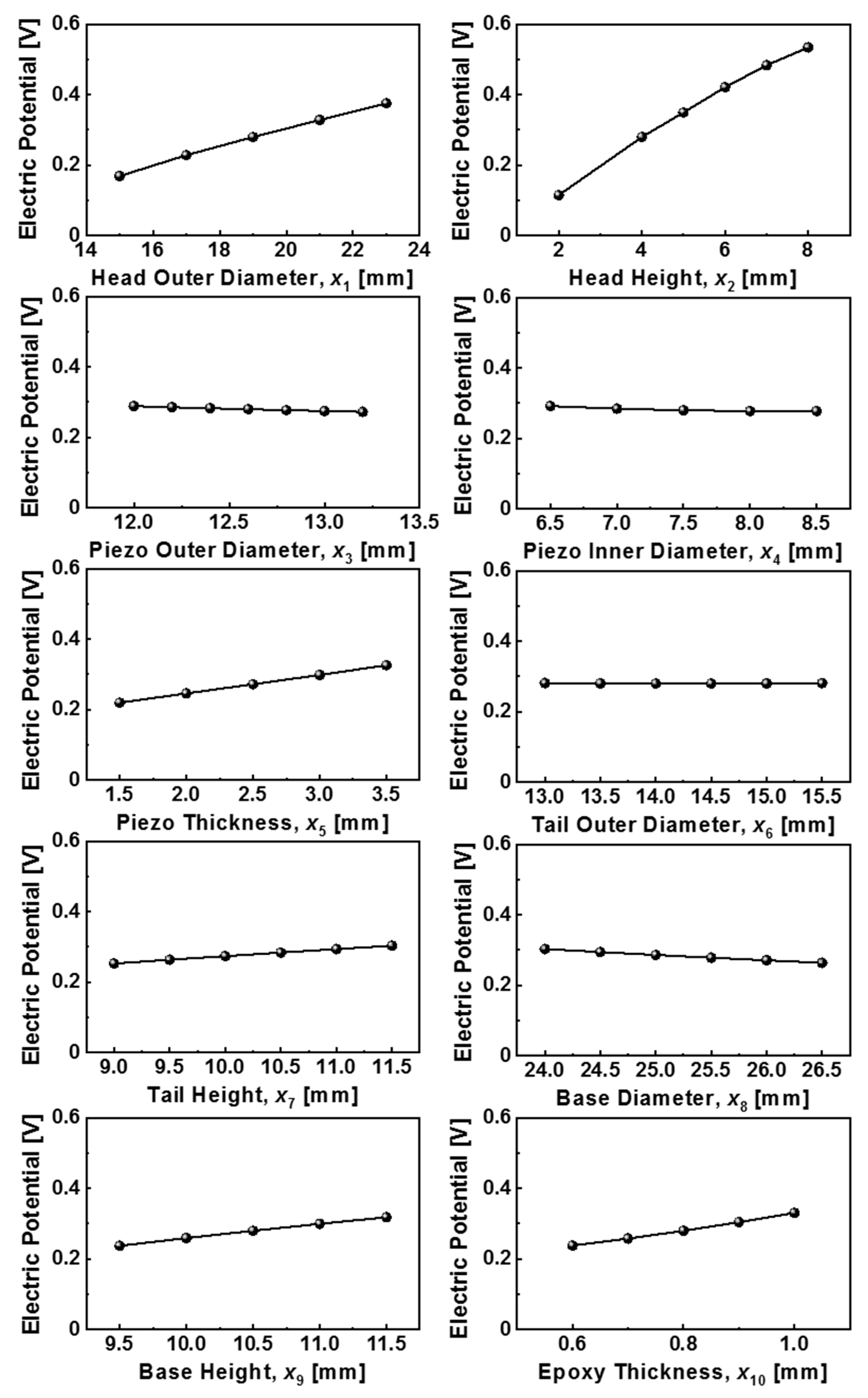
Table 3 summarizes the computation results of the resonance frequency and electric potential at 13 test points for ten variables. The meta-model (Kriging model), which is expressed by the sum of the global model and the localized deviation model, was obtained using the DOE [17,18] and the analytical results for each test point are shown in Table 3. In order to verify the reliability of the obtained Kriging model, we compared the difference between the ANSYS simulation result and the mathematical model (i.e., the Kriging meta-model) result using arbitrary values for ten variables. By confirming that the simulation and meta-model results were very similar to each other in the resonance frequency of 98.3% and with the electric potential of 92.4%, the reliability of the obtained Kriging model was proven. We examined the sensitivity of the ten selected variables x1 to x10 in affecting the resonance frequency and electrical potential using the obtained Kriging model. The resulting data values for the resonance frequency and electric potential with the change of design variables are listed in Table 4 and plotted with the same scale on the y-axis in Figure 4 and Figure 5 to more easily identify the sensitivity parameters.

Table 3.
Resonance frequency and electric potential for 13 selected test points.

Table 4.
Resonance frequency and electric potential calculated with the change of design variables x1 through x10 using the obtained Kriging meta-model.
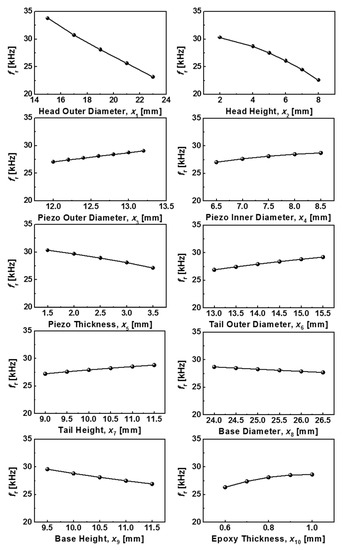
Figure 4.
The changes of resonance frequency according to the values of each component constituting the sensor module.
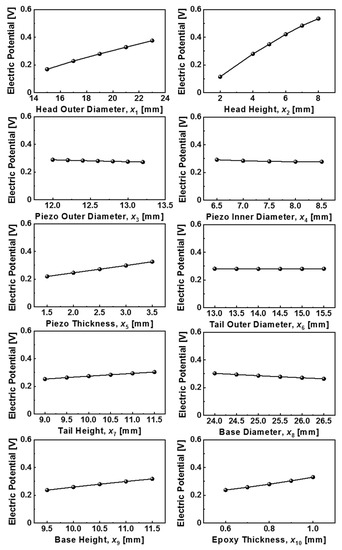
Figure 5.
The changes in the electric potential according to the values of each component constituting the sensor module.
Figure 4 shows the changes of the resonance frequency of the sensor module according to the values of each parameter. The variables x1 (head O.D.) and x2 (head height) had the greatest effect on the resonance frequency. As the values of x1 and x2 increased, the resonance frequency decreased. The variables x5 and x9 were also considered to be factors to some extent, as the values of x5 and x9 increased, the resonance frequency decreased. The other factors were found to be relatively insignificant compared to the variables x1, x2, x5, and x9. It is known that the resonance frequency fr is proportional to Dp/(ms tp)0.5. Here, ms, Dp, and tp represent the weight of the seismic mass, and the piezo-element diameter and thickness, respectively. Since ms increases in proportion to the square of x1 and in proportion to x2, the resonance frequency significantly decreased with increasing x1 and x2. Theoretically, Dp is a factor that greatly affects the resonance frequency. However, as the value of Dp increased, the size of the head or tail increased accordingly. Thus, the overall size and weight of the sensor increased, so there was a limit to the value that could change the Dp. Relatively, tp is a sensitive factor that changes the resonance frequency because it can have a large variation in dimensions without significantly changing the overall size of the sensor. As a result of evaluating the influence on the resonance frequency considering the change in width per variable, the variables x1, x2, x5, and x9 were found to be more sensitive than the other variables.
Figure 5 shows the changes in the electric potential of the sensor module, which is closely related to the voltage sensitivity, with the change of each parameter of x1 through x10. The electric potential is proportional to the piezoelectric voltage constant, which is defined as the electric field generated in a material per unit of mechanical stress applied to it. As shown in Figure 5, the electric potential was most sensitive to x1 and x2, and the value increased with increasing x1 and x2 values. From the above results of examining the resonance frequency and the electric potential change according to the change of ten variables, it was found that the diameter and height of the head were the most influential factors. As the diameter and height of the head increased, the resonance frequency decreased but the electric potential increased. Considering that resonance frequency and sensitivity have a trade-off relationship, it is important to find the optimal dimensions of the head. It should also be emphasized that the increase in tail height and epoxy thickness had a positive effect on both the resonance frequency and electric potential, and the base diameter had a negative effect on both of them. Based on the above results, we will continue to study the optimal sensor design to obtain the desired performance by taking into account not only the independent influence of each variable constituting the sensor module but also the correlation between the variables.
4. Conclusions
The degree of impact of each component on the resonance frequency and electrical potential was examined based on meta-modeling using the DOE for a problem of ten variables and two responses. We found that among the various components constituting the sensor module, the diameter and height of the head (seismic mass) had the most significant effects on the resonance frequency and electric potential. As the diameter and height of the head increased, the electric potential increased, but the resonance frequency decreased. Moreover, the increase in tail height and epoxy thickness positively affected both the resonance frequency and electric potential, and the base diameter had a negative effect on both of them. This result will be very useful for designing the sensor structure and selecting a suitable material to achieve the desired working performance of the acceleration sensor.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.-K.L. and G.-J.L.; methodology, W.-J.H. and J.-J.P.; validation, M.-K.L., W.-J.H. and G.-J.L.; formal analysis, W.-J.H. and J.-J.P.; investigation, M.-K.L. and G.-J.L.; writing—original draft preparation, G.-J.L.; writing—review and editing, M.-K.L.
Funding
This research was supported by the Korean Nuclear R&D program organized by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF). The grant was funded by the Korean government (MSIP) (NRF-2017M2A8A4017220) and by the Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute (KAERI) R&D program.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Serridge, M.; Licht, T.R. Piezoelectric Accelerometer and Vibration Preamplifiers. In Theory and Application Handbook; Brüel & Kjær: Nærum, Denmark, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Gautschi, G. Piezoelectric Sensorics: Force, Strain, Pressure, Acceleration and Acoustic Emission Sensors, Materials and Amplifiers; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Chow, K.S.; Du, H.; Wang, P.; Zhang, M.; Yu, S.; Liu, B. A ZnO thin-film driven microcantilever for nanoscale actuation and sensing. Int. J. Smart Nano Mater. 2013, 4, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koka, A.; Sodano, H.A. High-sensitivity accelerometer composed of ultra-long vertically aligned barium titanate nanowire arrays. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, Q.; Qiao, X.; Guo, T.; Bao, W.; Su, D.; Yang, H. Orientation-dependent fiber-optic accelerometer based on grating inscription over fiber cladding. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 6616–6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Peng, G.; Hu, Z.; Yang, H.; Hu, Y. Design and analysis of a high sensitivity FBG accelerometer based on local strain amplification. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 5442–5449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Bai, J.; Wang, K.; He, S. Design, optimization, and realization of a high-performance MOEMS accelerometer from a double-device-layer SOI wafer. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2017, 26, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Q.; Guo, T.; Bao, W.; Shao, Z.; Peng, G.D.; Qiao, X. Highly sensitive fiber-optic accelerometer by grating inscription in specific core dip fiber. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allik, H.; Hughes, T.J.R. Finite element method for piezoelectric vibration. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1970, 2, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerch, R. Finite element analysis of piezoelectric transducers. In IEEE 1988 Ultrasonics Symposium Proceedings; IEEE: Chicago, IL, USA, 1988; pp. 643–654. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Varadan, V.V.; Varadan, V.K. Finite element modelling of structures including piezoelectric active devices. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1997, 40, 817–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Yang, M. Optimal design of a double-vibrator ultrasonic motor using combination method of finite element method, sensitivity analysis and adaptive genetic algorithm. Sens. Actuators A 2017, 266, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Varadan, V.V.; Varadan, V.K.; Bao, X.Q. Finite-element modeling of a smart cantilever plate and comparison with experiments. Smart Mater. Struct. 1996, 5, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V. Optimization and modelling of process parameters involved in ultrasonic machining of glass using design of experiments and regression approach. Am. J. Mater. Eng. Technol. 2013, 1, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, J.P.N.; Kumar, S.J.; Jeyathilak, R.K.S.; Venkatesh, M.; Christopher, A.S.; Ganesh, K.C. Effect of design parameters on the static mechanical behavior of metal bellows using design of experiment and finite element analysis. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. 2017, 11, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Allen, T.T.; Notz, W.I.; Zeng, N. Global optimization of stochastic black-box systems via sequential Kriging meta-models. J. Global Optim. 2006, 34, 441–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, P. Taguchi Techniques for Quality Engineering; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, D.C. Design Analyses of Experiments, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).