Abstract
Agriculture affects both the quantity and the quality of water available for other purposes, which becomes problematic, especially during increasingly frequent severe droughts. This requires tapping into the resources that are typically neglected. One such resource is a by-product of anaerobic digestion, in which moisture content typically exceeds 90%. Application of hydrothermal carbonization process (HTC) to this residue could partially remove organic and inorganic material, improve dewatering, decrease the overall solid mass, sanitize the digestate, change its properties, and eliminate problems related with emissions of odors from the installation. However, a significant gap still exists in terms of the dewatering of the hydrochars and the composition of the effluents. This work presents results of experimental investigation focused on the removal of organic compounds from the HTC effluent. Results of qualitative and quantitative analysis of liquid by-products of HTC of the agricultural digestate showed that acetic acid, 3-pyridinol, 1-hydroxyacetone, and 1,3-propanediol were the main liquid organic products of the process. Application of ultrafiltration process with the use of 10 kDa membrane for liquid HTC by-product treatment allows for the reduction of chemical oxygen demand up to 30%, biological oxygen demand up to 10%, and dissolved organic carbon up to 21%.
1. Introduction
Given the growing demand from human activities and climate change issues, many regions, primarily in the south, face difficulties in providing enough freshwater to satisfy demand. It is estimated that in 2025, 5.5 billion people (2/3 of the population) will live in areas exposed to so-called water stress [1]. This means that the amount of renewable water resources (the so-called Falkenmark index) per person per year will be below 1700 m3. About 1.8 billion people will live in areas with a significant water shortage (Falkenmark’s value < 1000 m3 per person per year). Recently observed and experienced consequences of droughts in Europe make resolving the issues of the water resources even more urgent. For example, the drought in 2018 in Poland caused estimated losses of approximately 120 million EUR, with a significant impact on the livelihood of the inhabitants of 112,000 of small scale farms over an estimated area of two million hectares [2]. Agricultural irrigation is by far the largest application of reclaimed water worldwide. Therefore, increasingly unpredictable weather conditions, including severe droughts, may also affect the amount and quality of freshwater resources available for this sector. Irrigation of crops is one of the areas of agriculture in which significant improvement can be achieved through the introduction of new practices and strategies for the water recovery from treated wastewater. Sustainable Development Goals (SDG), proposed by the UN, are important drivers of the international research and development efforts in order to achieve the highest possible sustainability of human activities. In this context, SDG 6 “Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all” is especially relevant [1,3].
Land spreading is typically used to utilize digestate that is typically rich in nutrients [4]. However, European Nitrates Directive (91/676/EEC) introduces complications in the wide use of this practice [5]. Moreover, the state-of-the-art biogas plant has a substantial land requirement for the storage of digestate, typically 8 ha/MW of installed power, which introduces significant costs [6]. Thermal drying, along with a subsequent pelletizing, is considered as one of the management strategies, aiming at a decreased volume of digestate [7]. Moreover, the effluent after dewatering is stored in the lagoons and applied directly to the fields. This introduces significant water loss through evaporation. Few studies have been conducted so far, aiming at the recovery of water from anaerobic digestion (AD) using membranes [8].
Hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) is a thermal process performed in order to achieve valorization of a low-quality solid fuel [9]. It has been proposed for many different wet feedstocks, mostly residues of biological processes, such as sewage sludge [10], spent grain [11,12], fruit waste [13], algae before and after lipid extraction [14], as well as biomass problematic due to the content of inorganics (e.g., miscanthus) [9,15,16,17]. The typical temperatures of HTC range is between 200 °C to 260 °C. The process is performed under the water saturation pressure, i.e., water remains liquid [9,18]. HTC makes the higher heating value (HHV) of the produced hydrochar resemble that of coal [9,18,19,20].
HTC process involves a multitude of concurring reactions, especially when it is performed using biomass [9,18]. Hydrolysis is the first stage, when biomass is degraded to monomers and oligomers [18], with some intermediates (e.g., 5-(hydroxymethyl)furfural, 2-furfural) [18,20]. The rate of hydrolysis is diffusion-controlled [21]. Hydrolysis is followed by dehydration (loss of OH groups) [18,20], decarboxylation and decarbonylation, leading to loss of carboxyl (COOH) and carbonyl (C=O) groups, respectively [18,20,22,23]. Some works also state the importance of hydrodeoxygenation [23,24,25]. The aforementioned reactions, apart from decarbonylation, consequently cause a decrease in the O/C ratio of the solid product. The loss of functional groups, responsible for the hydrophilic nature of most biomasses not only promotes the formation of gases [9] but also makes hydrochars relatively more hydrophobic, thus leading to potential enhancement of its dewatering [9,26], leading to the energy savings when comparing to drying of unprocessed feedstock [27]. That, in turn, can improve the lower heating value (LHV) of the treated material. As part of inorganic matter is removed during HTC [9], it can be used for the recovery of nutrients, which is currently a problem with digestates from anaerobic digestion of various materials, such as sewage sludge [28,29]. Among liquid by-products, a wide variety of condensable compounds (liquid at ambient conditions) can be simultaneously produced.
The potential synergy between hydrothermal carbonization and anaerobic digestion has been suggested, so far, by plenty of published studies [20,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38]. This synergy can be achieved in many ways. Firstly it can enhance the dewatering of the digestate as suggested by Gao et al. [26] and Wang et al. [38]. Possible enhancement of the biogas production is also very appealing, as the problem of liquid by-products of hydrothermal carbonization does not have a viable technical solution for the commercial-scale reactors nowadays. Svensson et al. [30] determined that the thermal hydrolysis of digestate cake, from sewage sludge and food waste, can improve methane production and dewaterability of the digestates. Yields of methane as high as 0.25 dm3 per dm3 of the HTC liquid per day were reported by Wirth and Mumme [33]. Production potential of methane, using the liquid by-product from HTC of orange pomace, was determined by Erdogan et al. [31] to be between 213.6 cm3 and 195.3 cm3 of methane per gCOD (chemical oxygen demand (COD)), depending on the process parameters. Typical products such as acetic acid, formic acid, lactic acid, glucose, and saccharose were the most abundant in the liquid phase, reaching concentrations in the order of magnitude of 1 g/dm3 [31]. Moreover, Luz et al. [39] also reported the feasibility of the use of the soluble fraction from HTC of spent coffee grounds for anaerobic digestion.
The aim of this paper is to determine the organic compounds present in liquid by-products HTC of a digestate and possibilities of its subsequent purification. The liquid organic compounds obtained during the HTC process will be analyzed in order to assess the possibilities of their subsequent separation. This will be done by applying novel membrane separation technologies, that are currently a subject of intensive investigations [40]. Moreover, the determination of the basic fuel properties of hydrochars is also within the scope of this paper.
2. Materials and Methods
Samples were taken from a rural anaerobic digestion plant. Sampling procedure resembled the one specified in EN 14778:2011 “Solid biofuels—sampling” for the specific case of sampling from stationary stockpiles. Each sample was taken from different parts of the pile in order to achieve a representative sample.
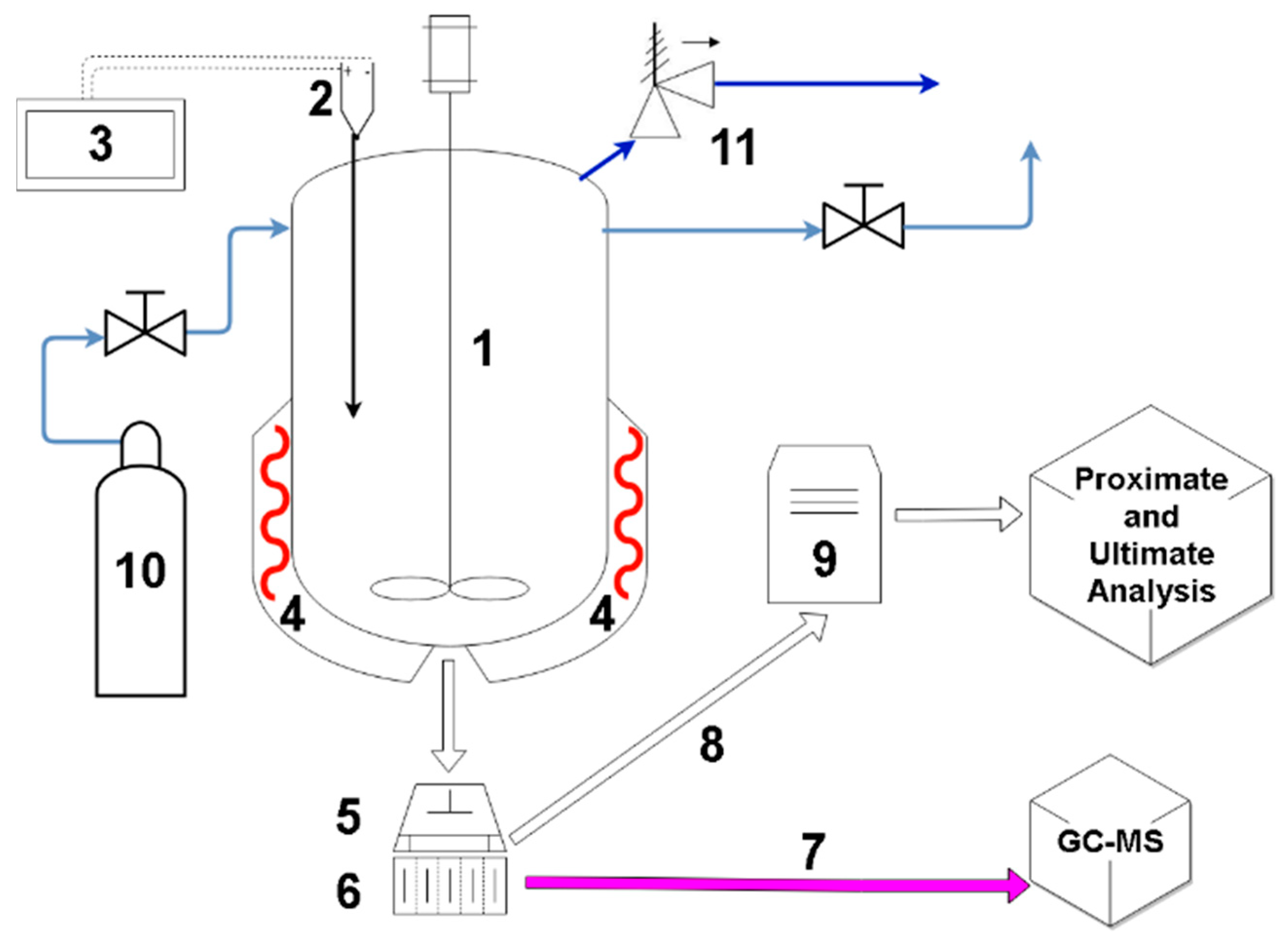
Diagram of the experimental setup (Figure 1) shows both autoclave rig as well as the hydraulic press. The press was used for the subsequent dewatering of the hydrochar. The autoclave was filled with dried digestate and distilled water, in order to achieve the water to dry biomass ratio of 12:1. The size of the processed sample was approximately 200 g of the dry mass of the agricultural digestate. Heating mantle, controlled by a PLC (Programmable Logic Controler), with band heaters, was used for heating up and maintaining the temperature of the autoclave vessel. The temperature was measured inside of the reactor by a K type thermocouple, inserted close to the center of the reactor. Setpoint temperature of 200 °C was chosen, as it is a reasonably typical temperature for the HTC process, with most of the literature results presented for the range of temperatures between 200 °C and 260 °C [9,15,41]. HTC pressure was measured by an analog gauge and during the experiment, it was close to the water vapor saturation pressure. The residence time in the reactor was 270 min. Time measurement started after the reactor reached the setpoint temperature. After 4.5 h of the heating, the mantle was turned off and the setup was left for cooling. The cooled material was drained using a clean colander and subsequently separated into sublots (approximately 20 g each). Some sublots were tested for the moisture content, whereas other sublots were taken to perform mechanical dewatering. This was performed using a hydraulic press with a custom-made piston and cellulose filter along with the filter casing. The sample was pressed using a pressure of 60 bar. The pressure was applied for 5 min to let all of the moisture be drained through the perforated bottom of the filter casing. The moisture content of the dewatered material was subsequently determined for further comparison.
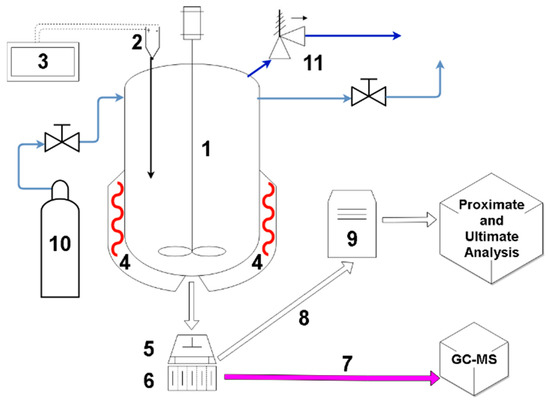
Figure 1.
Diagram of the test rig, used for hydrothermal carbonization of the digestate (1—autoclave; 2—type K thermocouple; 3—PLC controller; 4—heating mantle, with band heaters; 5—hydraulic press; 6—filter; 7—liquid, after mechanical dewatering; 8—hydrochar, after mechanical dewatering; 9—dryer; 10—nitrogen for purging; and 11—pressure relief valve).
The moisture content of the drained material was subsequently determined, at 105 °C, using the moisture analyzer Radwag MA.X2.A, with a scale resolution of 0.001 g and a maximum sample mass of 50 g. The mass of the sample was considered to be in equilibrium when the first derivative of the mass (dm/dt) was equal or smaller than 1 mg/min. Proximate analysis of both raw and hydrothermally carbonized digestate was performed using TGA/DTG (thermogravimetry/differential thermogravimetry) Pyris Diamond from Perkin Elmer, with programs outlined in the relevant standards: EN 15148:2009 (volatile matter content) and EN ISO 1822:2015 (ash content). The ultimate analysis was performed using a Perkin Elmer 2400 analyzer, according to the procedure set in the standard EN ISO 16948:2015. HHV of both feedstock and product was determined, according to the procedure from EN 14918:2009, using IKA C2000 calorimeter. LHV was calculated, based on HHV, moisture content after mechanical dewatering and hydrogen content of the fuel, using the formula from the same standard.
The sample of the liquid by-product of the HTC process was a subject of the investigation on membrane purification aiming at an increased recovery of water from the digestate. In the first step of experiments, the digestate was subjected to vacuum filtration using a 10 µm Buchner funnel and then, the filtrate was subjected to ultrafiltration process with the use of 10 kDa MWCO polyethersulphone membrane (Microdyn Nadir). Membrane separation was carried out using Millipore Amicon 8400 stirred cell in the dead-end mode. The transmembrane pressures (TMP) used in the experiments were in the range of 0.20–0.45 MPa. To estimate the separation and transport properties of the studied membrane, the following two parameters were used: Volume flux of the permeate (J) and organic substances retention coefficient (R). The concentration of organic substances in the permeates was determined based on chemical oxygen demand, biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in collected samples.
The sample of the drained liquid by-products of HTC was also analyzed using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) that consisted of the Agilent 7820-A chromatograph (manufactory, Agilent Technologies, Palo Alto, CA, USA) and the Agilent 5977B MSD spectrometer (Agilent Technologies, Palo Alto, CA, USA). In the chromatograph, the Stabilwax-DA column (Restek, Benner Circle, Bellefonte, PA, USA) was used. Helium was used as carrier gas (1.5 mL/min). A heating program was set to achieve 50 °C in 5 min, then subsequently heat up the column with a ramp of 10 °C/min until the temperature of 200 °C was reached, and hold for another 20 min.
Compound identification was automatically performed by comparing the mass spectra with the NIST-14 MS library (minimum match factor = 80%). The MS scanning range was m/z 10–450, with a frequency of 1.7 scans/s. The gain factor and EM (Electron Multiplier) Volts were 0.5 and 1348.5, respectively, and the MS source and quadrupole temperatures were 230 °C and 150 °C, respectively.
Major compounds, detected during the qualitative GC/MS analysis, were subjected to quantitative analysis. The analysis was performed according to an external standard method [42] and was based on the calibration curves for each individual compound. Four points of known compound concentration in an isopropanol-compound solution were used for each curve. Measurement for each point of the curve was repeated five times. References and isopropanol of chromatographic grade (supplied by Sigma Aldrich) were used for the calibration.
3. Results and Discussion
Obtained results, presented in Table 1, confirm the generally accepted consensus that the hydrothermal carbonization process increases the HHV of the processed material, increases carbon content, and leads to decreased oxygen content [9,11,12,20,26,43]. Additionally, the HTC process, performed at the particular process parameters, lead to a decrease in ash content. The improvement of the LHV is much more substantial when mechanically dewatered materials are compared in comparison to the increase of the HHV. This is caused by a combination of improved HHV and improved dewaterability of the treated material, which can be observed as the lower moisture content of the material after the press.

Table 1.
Results of the proximate and ultimate analysis of raw and hydrothermally treated hydrochar (moisture content (MC); wet material (wet); material after pressing (press); volatile matter content (VM); ash content (A); higher heating value (HHV); lower heating value (LHV); carbon content (C); hydrogen content (H); oxygen content (O); wet basis (wb); dry basis (db); and dry ash-free basis (daf)).
Undoubtedly that could enhance the efficiency along the lifecycle of the fuel, as thermal drying is usually much more energy-intensive than mechanical dewatering. The improved dewaterability also indicates, that a higher amount of water could be successfully recovered, without the need of a sizeable condensing heat exchanger, if the digestate is hydrothermally treated prior to pressing. The content of heavy metals and other inorganic elements, of the liquid by-product of the HTC process, along with properties fundamental from the water purification point of view, is presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
The composition of the liquid fraction obtained after hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) of a rural anaerobic digestion plant digestate.
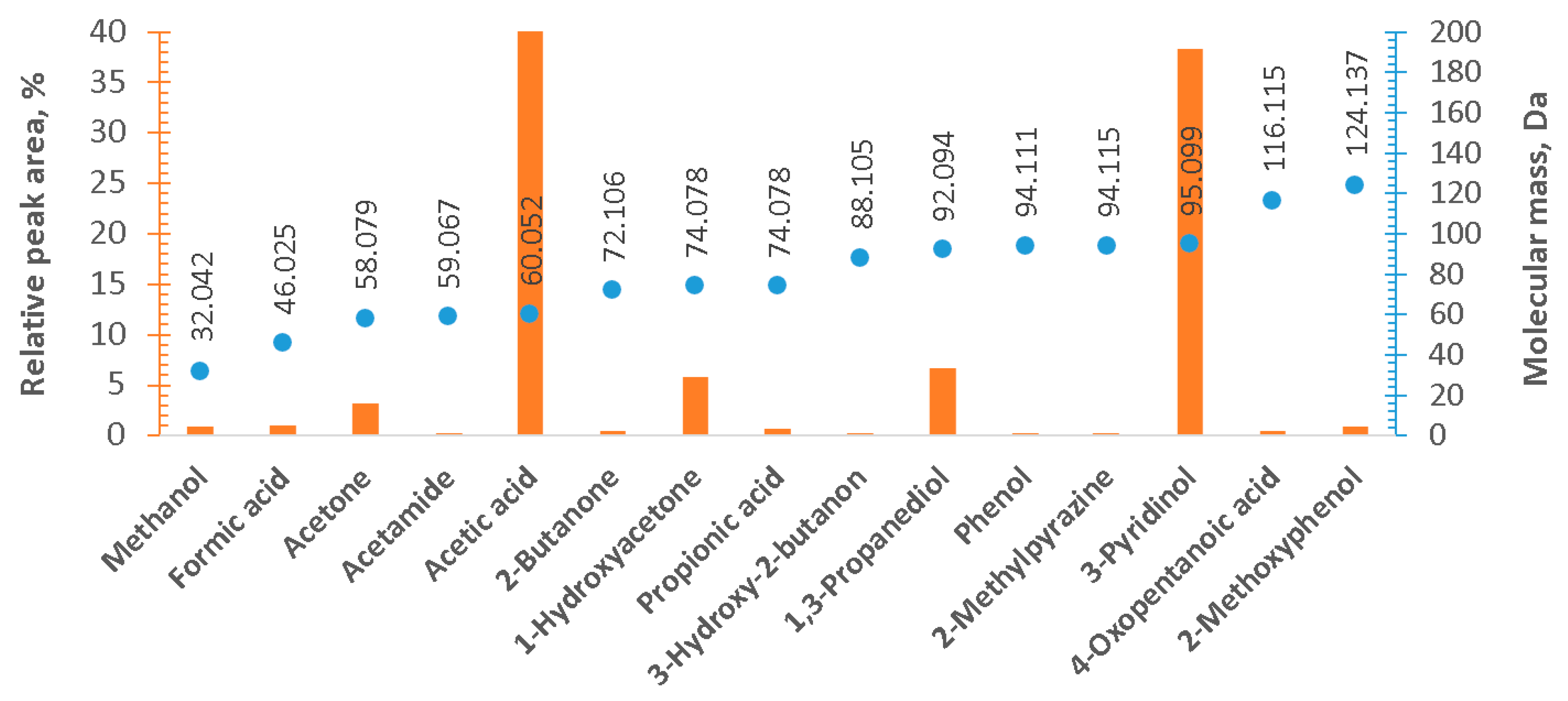
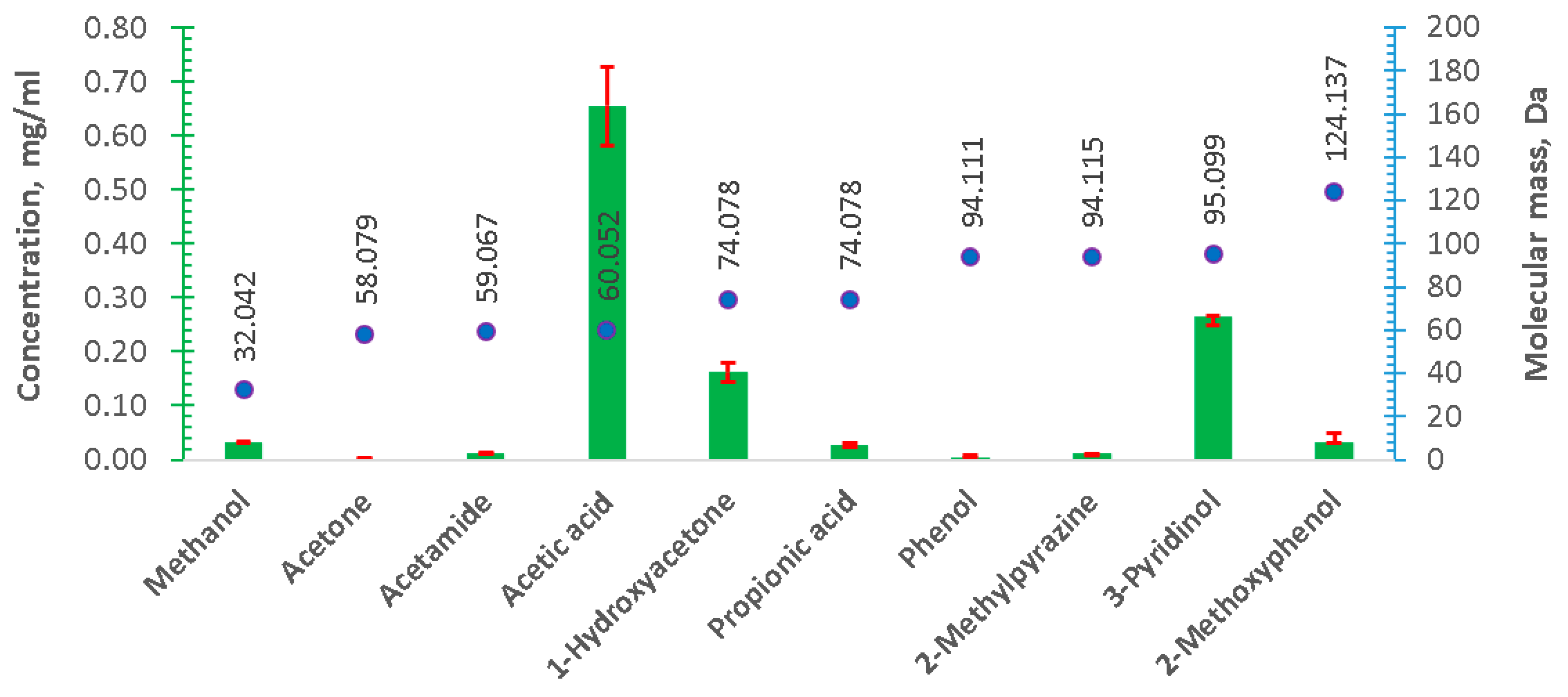
Qualitative results of the GC-MS analysis of the liquid by-products of HTC (Figure 2) show a variety of the organic compounds, with acetic acid being the most abundant. This has been confirmed by the results of the quantitative analysis (Figure 3). Acetic acid is a typical product of anaerobic digestion [9], and successful attempts of the use of HTC liquids containing acetic acid as a substrate for anaerobic digestion have been reported [31,33]. Moreover, the presence of significant amounts of 3-pyridinol is also worth noticing (Figure 2 and Figure 3). This compound was also reported in another study, focused on the liquid by-products of HTC (200 °C, residence time—150 min) of the residues from biological anaerobic decomposition processes (fermentation) [12]. Similarly, the presence of 1-hydroxyacetone and 1,3-propanediol was also reported in the aforementioned study [12]. Another study on HTC of fermentation by-products, by Arauzo et al., also reported acetic acid as a dominant organic compound in the liquid fraction [11]. Arauzo et al. also observed significant amounts of formic acid, lactic acid, and propionic acid [11], which were not detected in this study. The difference can be attributed mostly to the different types of fermentation processes for the production of the HTC feedstock. Arauzo et al. used spent grain from beer brewing, where the process is performed by yeast [11]. Whereas, in this study digestate from an agricultural anaerobic digestion plant was used, where the process is performed by bacteria. Danso-Boateng et al. also reported the presence of 3-pyridinol after HTC of primary sewage sludge at 180 °C and 200 °C for 240 min as well as the presence of 1,3-propanediol, but only for HTC at 200 °C for 240 min [44]. These compounds were not detected for short residence times [44], which suggests that the reactions responsible for the formation of these compounds are relatively slow, and compounds can be produced in relatively long residence times, which was the case in this study.
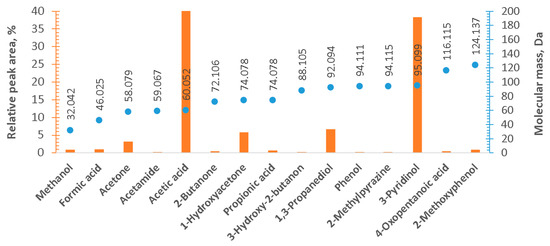
Figure 2.
Qualitative results of the gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) analysis. Relative peak area (area of an individual peak with respect to the total area of all peaks)—bar graph, with the axis on the left-hand side (orange). The molecular mass of each of the detected compound—axis on the right-hand side. Official IUPAC Names and respective masses from the Royal Society of Chemistry database.
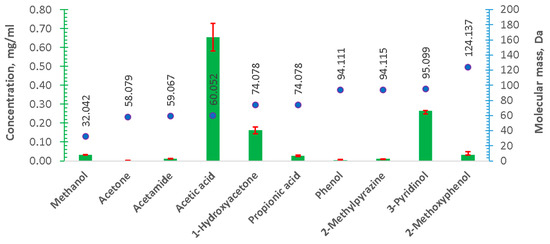
Figure 3.
Quantitative results of the GC-MS analysis. Concentration of each compound—bar graph, with the axis on the left-hand side (orange). The molecular mass of detected compound—axis on the right-hand side. Official IUPAC Names and respective masses from the Royal Society of Chemistry database.
It seems to be plausible to state that the liquid, with the content of such compounds, can be utilized effectively in the anaerobic digestion process, thus allowing the integration of the anaerobic digestion with HTC of its wet by-products, as already suggested by some authors [36,37,45]. Further research is needed to confirm this, assessing the influence of adding such a liquid to AD reactors and optimize the process, configured in such way (AD + HTC).
COD of the HTC liquid by-products, obtained within the scope of this study, was well in line with the values presented in the literature [35]. Values obtained by Aragón-Briceño et al. for HTC of digested sewage sludge were lower (approximately 12 g/dm3) [37], which could be attributed to the difference between two feedstocks Aragón-Briceño et al. [37]. The HTC residence time, used by Aragón-Briceño et al. (30 min) [37], was also much lower in comparison to the residence time in this study (270 min). However, the COD obtained in this study (Table 2) is very close to the one obtained for HTC of an agricultural digestate by Parmar and Ross (between 42.2 and 46.3 g/dm3) [36]. Overall, the spread of COD results presented in the literature, for effluents from HTC of by-products of fermentation processes, is quite wide (17.5 up to 105.6 g/dm3) in itself. This underlines that the COD from such processes is feedstock dependent and detailed determination is needed for each individual case.
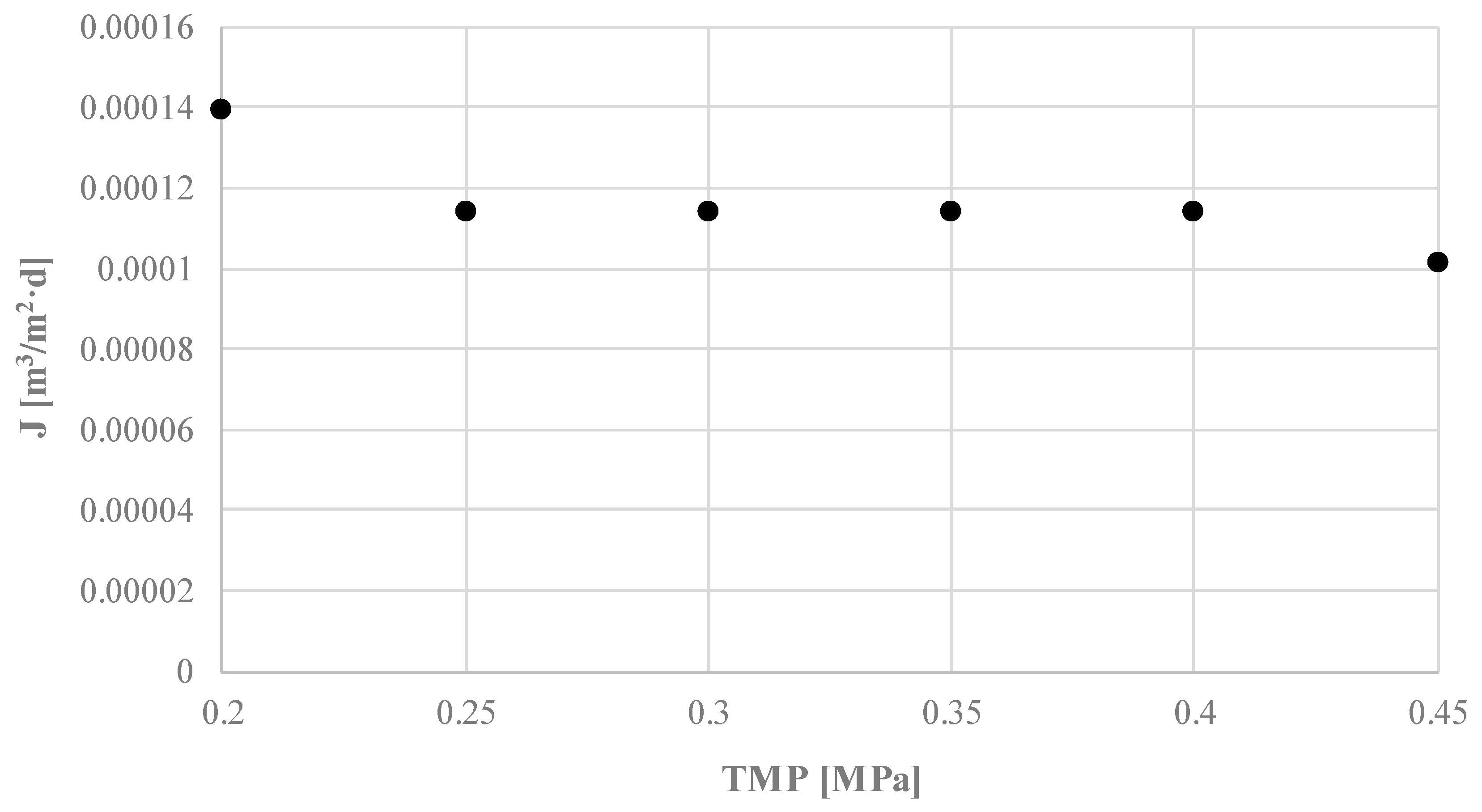
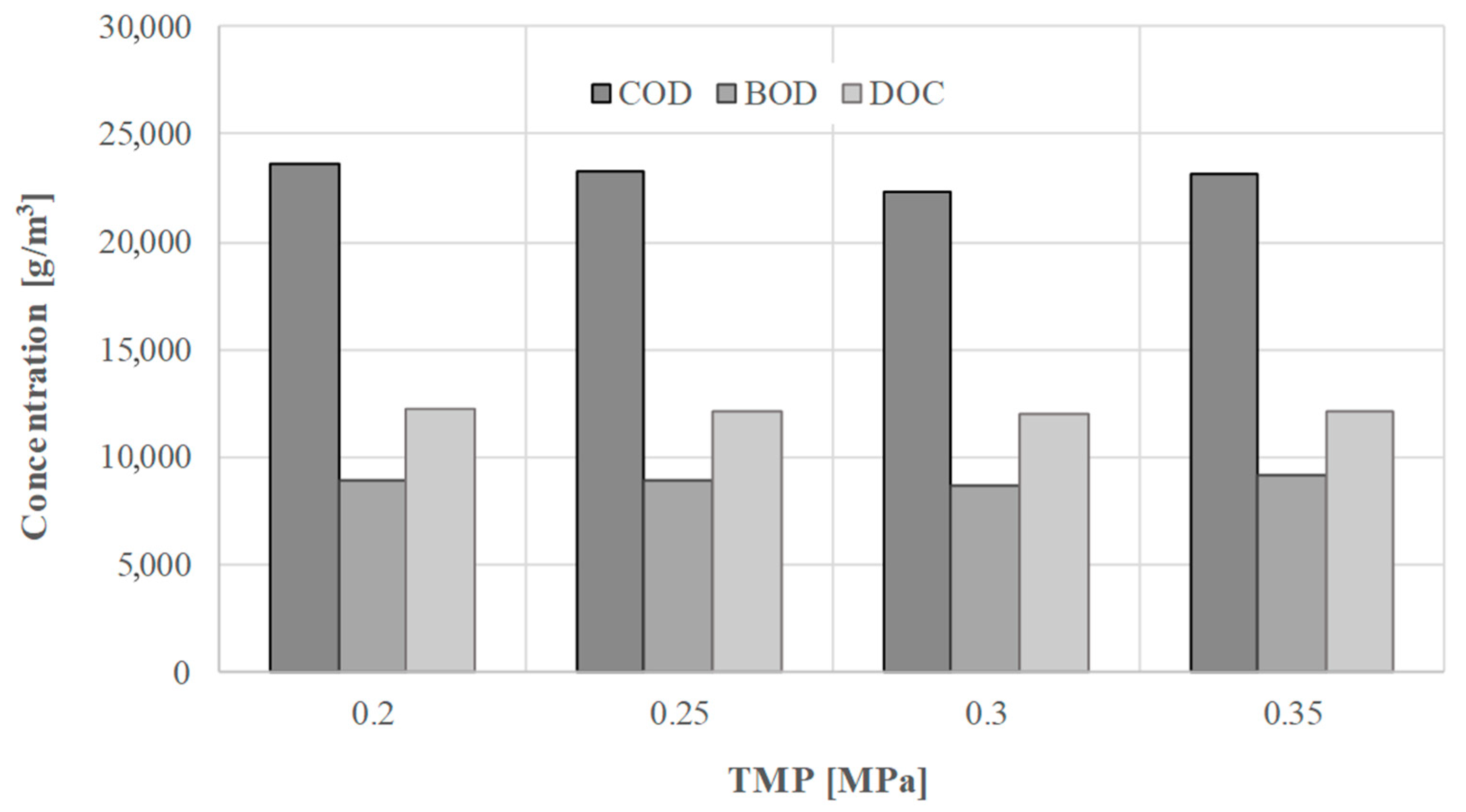
The use of HTC for treatment and enhanced dewatering of digestate would most certainly require some step that would recover at least a part of the water stream from the liquid phase, in order to maintain optimum solid loading in the AD reactor. The increase in water recovery from the liquid by-product of the HTC process may be achieved by its treatment with the use of ultrafiltration membranes. However, this requires determining the transport and separation properties of the membranes. On analyzing the results of transport tests (Figure 4), it was observed that the increase in transmembrane pressure resulted in a slight decrease in the flow rate of permeate.
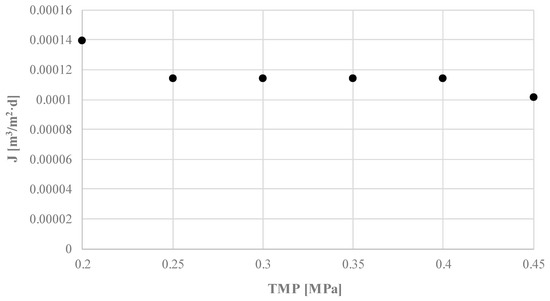
Figure 4.
The influence of transmembrane pressure on permeate volume flux of ultrafiltered liquid fraction of the digestate.
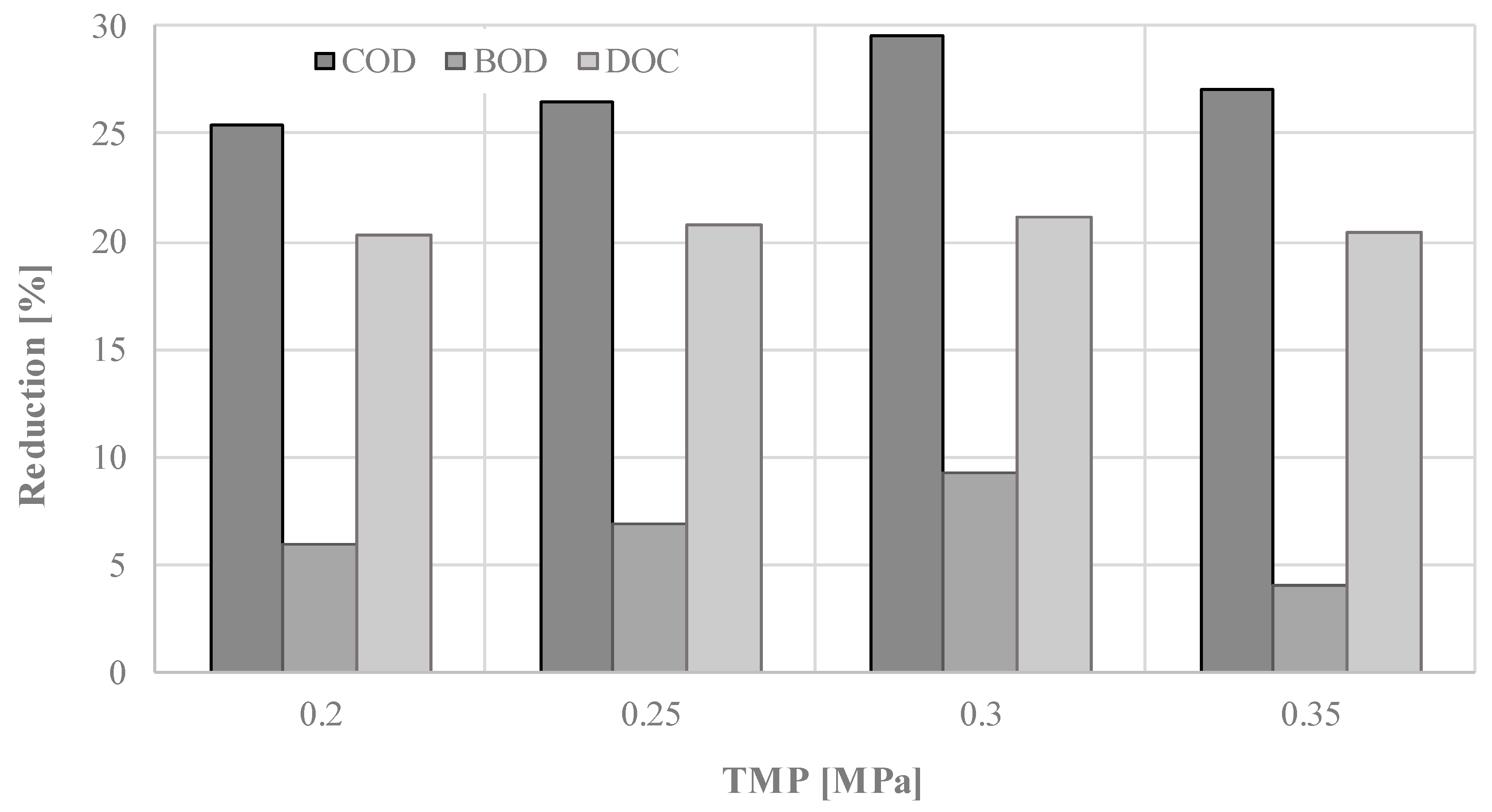
This finding may be attributed to the cake layer formation on the membrane surface (despite stirring of liquid in the cell) and its compaction with the increase with the TMP increase. As a result of the layer formation and compaction, membrane resistance increased. Removal of the organic substances from the liquid fraction of digestate by ultrafiltration with the use of 10 kDa membrane was investigated in terms of changes of COD, BOD, and DOC concentration (Figure 5 and Figure 6) in permeate samples. It can be concluded that TMP did not significantly influence the separation efficiency of the process and that the 10 kDa ultrafiltration membrane allowed the removal of only up to 30% of contaminants. When comparing the three parameters used for determination of organic substances in the samples, it can be concluded that the highest efficiency of separation was observed for COD (the measure of oxidizable pollutants amount in a sample) while the lowest was for BOD (the measure of biodegradable organic substances in a sample). Relatively low efficiency of contaminants separation obtained in ultrafiltration with the use of 10 kDa membrane points to the need to use a denser membrane in order to obtain better quality permeate. When comparing it with published data on the ultrafiltration of the digestate, obtained values are lower. For example, Chiumenti et al. reported a reduction of COD from 16.2 to 4.7 g/dm3, in the permeate from ultrafiltration of the clarified fraction, after centrifuge separation of the agricultural digestate [46].
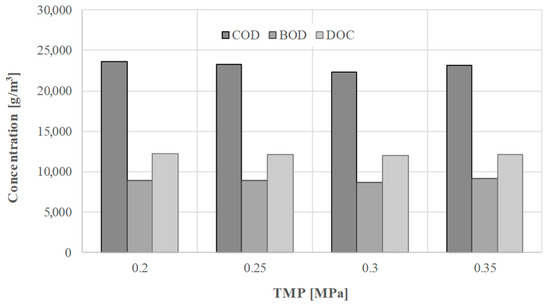
Figure 5.
The influence of transmembrane pressure on the concentration of organic substances in permeates of the liquid fraction of digestate, using 10 kDa ultrafiltration membrane (trans-membrane pressure (TMP); chemical oxygen demand (COD); biological oxygen demand (BOD); and dissolved organic carbon (DOC)).
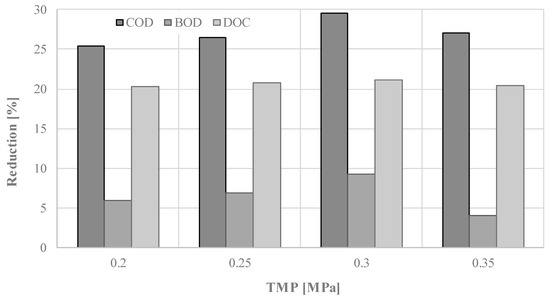
Figure 6.
Reduction of the organic substances in the liquid fraction of digestate, for different TMP, using 10 kDa ultrafiltration membrane.
This is not surprising as HTC changes the composition of organics—i.e., bacteria, as well as extracellular polymeric substances, are being decomposed, during HTC, into much simpler compounds. It could be reasonably expected that the use of other stages, such as micro and nanofiltration, should be included in HTC liquid cleaning systems. However, it should not be overlooked that ultrafiltration would most likely be needed anyway in membrane purification systems for HTC effluents. The reason is increased brittleness of the hydrochars, in comparison to the raw feedstock. This, in the form of improved grindability, has been reported by many studies [15,47,48]. This might result in an increased amount of suspended solids, depending on the HTC process parameters, which in turn could attribute to the formation of cake and fouling of the microfiltration and nanofiltration membranes. Therefore, the use of ultrafiltration upstream is justified and the ability to reduce the organic content in the HTC effluent could definitely be considered beneficial, from the installation maintenance perspective. Further research is needed on the performance of microfiltration and nanofiltration membranes with HTC effluents, as well as on the performance of the cascade systems.
4. Conclusions
Obtained results confirm that the hydrothermal carbonization process can be successfully applied for the digestate to improve its fuel properties, as it increases the HHV of the processed material, increases carbon content, and leads to decreased oxygen content. Especially, improvement of mechanical dewatering seems to be advantageous, both in the context of the use of hydrochar as a solid fuel and in the context of the recovery of agricultural water.
Results of the analysis of post-HTC liquid, suggests that it could potentially be recirculated to the anaerobic digestion process. However, care should be taken, as the organic compounds would appear in higher concentrations in the retentate. Application of ultrafiltration process with the use of 10 kDa membrane for liquid HTC by-product treatment allows for the reduction of COD up to 30%, BOD up to 10%, and DOC up to 21%.
The use of ultrafiltration upstream of micro and nanofiltration could be beneficial from the installation maintenance perspective. Further research is needed on the performance of microfiltration and nanofiltration membranes with HTC effluents, as well as on the performance of the cascade systems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: A.U., M.K.-K., H.P.-K. and P.S.; methodology: A.U., M.K.-K., M.W., and P.S.; validation: A.U. and M.W.; formal analysis: A.U. and M.W.; investigation: A.U., M.W., M.B., M.S.-T., K.K. and L.N.; resources: A.U., M.K.-K., H.P.-K., and P.S.; data curation: M.W., M.B., M.S.-T., K.K. and L.N.; Writing—original draft preparation: L.N. and A.U.; Writing—review and editing: L.N. and A.U.; visualization: L.N.; supervision: A.U., M.K.-K., H.P.-K. and P.S.; project administration: A.U., H.P.-K. and P.S.; funding acquisition: A.U., H.P.-K. and P.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Authors would like to thank the European Commission, the National Centre for Research and Development (Poland), Nederlandse Organisatie Voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek (Netherlands) and Swedish Research Council Formas for funding in the frame of the collaborative international consortium (RECOWATDIG) financed under the 2018 Joint call of the WaterWorks2017 ERA-NET Cofund. This ERA-NET is an integral part of the activities developed by the Water JPI. National Centre for Research and Development agreement number WATERWORKS2017/I/RECOWATDIG/01/2019.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Connor, R. The United Nations World Water Development Report 2015: Water for a Sustainable World; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015.
- Susza w Polsce: Straty Przekroczyły Już Pół Miliarda Złotych—EURACTIV.pl. Available online: https://www.euractiv.pl/section/rolnictwowpr/news/susza-w-polsce-straty-przekroczyly-juz-pol-miliarda-zlotych/ (accessed on 1 August 2018).
- Damkjaer, S.; Taylor, R. The measurement of water scarcity: Defining a meaningful indicator. Ambio 2017, 46, 513–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbanowska, A.; Kabsch-Korbutowicz, M. Analysis of the pre-treatment efficiency of digestate liquid fraction from a municipal waste biogas plant. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2019, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Rowe, I.; Golkowska, K.; Lebuf, V.; Vaneeckhaute, C.; Michels, E.; Meers, E.; Benetto, E.; Koster, D. Environmental assessment of digestate treatment technologies using LCA methodology. Waste Manag. 2015, 43, 442–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plana, P.V.; Noche, B. A review of the current digestate distribution models: Storage and transport. In Proceedings of the 8 International Conference on Waste Management and The Environment (WM 2016), Valencia, Spain, 7–9 June 2016; Volume 202, pp. 345–357. [Google Scholar]
- Monfet, E.; Aubry, G.; Ramirez, A.A. Nutrient removal and recovery from digestate: A review of the technology. Biofuels 2017, 9, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, O.; Kim, M.; Go, Y.; Hong, M.; Kim, B.; Shin, Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.G.; Joo, J.S.; Jeon, B.S.; et al. Selective Removal of Water Generated during Hydrogenotrophic Methanation from Culture Medium Using Membrane Distillation. Energies 2019, 12, 4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscicki, K.J.; Niedzwiecki, L.; Owczarek, P.; Wnukowski, M. Commoditization of wet and high ash biomass: Wet torrefaction—A review. J. Power Technol. 2017, 97, 354–369. [Google Scholar]
- Wilk, M.; Magdziarz, A.; Jayaraman, K.; Szymańska-Chargot, M.; Gokalp, I. Hydrothermal carbonization characteristics of sewage sludge and lignocellulosic biomass. A comparative study. Biomass Bioenergy 2019, 120, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arauzo, P.; Olszewski, M.; Kruse, A. Hydrothermal Carbonization Brewer’s Spent Grains with the Focus on Improving the Degradation of the Feedstock. Energies 2018, 11, 3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackowski, M.; Semba, D.; Trusek, A.; Wnukowski, M.; Niedzwiecki, L.; Baranowski, M.; Krochmalny, K.; Pawlak-Kruczek, H. Hydrothermal Carbonization of Brewery’s Spent Grains for the Production of Solid Biofuels. Beverages 2019, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Heidari, M.; Regmi, B.; Salaudeen, S.; Arku, P.; Thimmannagari, M.; Dutta, A. Hydrothermal carbonization of fruit wastes: A promising technique for generating hydrochar. Energies 2018, 11, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broch, A.; Jena, U.; Hoekman, S.K.; Langford, J. Analysis of solid and aqueous phase products from hydrothermal carbonization of whole and lipid-extracted algae. Energies 2014, 7, 62–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wnukowski, M.; Owczarek, P.; Niedźwiecki, Ł. Wet Torrefaction of Miscanthus—Characterization of Hydrochars in View of Handling, Storage and Combustion Properties. J. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 16, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk, M.; Magdziarz, A. Hydrothermal carbonization, torrefaction and slow pyrolysis of Miscanthus giganteus. Energy 2017, 140, 1292–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, M.T.; Lynam, J.G.; Uddin, M.H.; Coronella, C.J. Hydrothermal carbonization: Fate of inorganics. Biomass Bioenergy 2013, 49, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funke, A.; Ziegler, F. Hydrothermal carbonisation of biomass: A summary and discussion of chemical mechanisms for process engineering. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefining 2010, 4, 160–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, H.A.; Rodríguez-Jasso, R.M.; Fernandes, B.D.; Vicente, A.A.; Teixeira, J.A. Hydrothermal processing, as an alternative for upgrading agriculture residues and marine biomass according to the biorefinery concept: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 21, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, M.T.; Andert, J.; Wirth, B.; Busch, D.; Pielert, J.; Lynam, J.G.; Mumme, J. Hydrothermal Carbonization of Biomass for Energy and Crop Production. Appl. Bioenergy 2014, 1, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, M.T.; Yan, W.; Uddin, M.H.; Lynam, J.G.; Hoekman, S.K.; Coronella, C.J.; Vásquez, V.R. Reaction kinetics of hydrothermal carbonization of loblolly pine. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 139, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funke, A.; Ziegler, F. Heat of reaction measurements for hydrothermal carbonization of biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 7595–7598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilc, M.; Likozar, B.; Levec, J. Hydrotreatment of solvolytically liquefied lignocellulosic biomass over NiMo/Al2O3 catalyst: Reaction mechanism, hydrodeoxygenation kinetics and mass transfer model based on FTIR. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 63, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilc, M.; Likozar, B.; Levec, J. Simultaneous Liquefaction and Hydrodeoxygenation of Lignocellulosic Biomass over NiMo/Al2O3, Pd/Al2O3, and Zeolite y Catalysts in Hydrogen Donor Solvents. ChemCatChem 2016, 8, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faussone, G.C.; Grilc, M.; Likozar, B. Removal of inorganics from sludge and digestate: The BiAR process. Water Pract. Technol. 2017, 12, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Li, Z.; Quan, C.; Miskolczi, N.; Egedy, A. A new method combining hydrothermal carbonization and mechanical compression in-situ for sewage sludge dewatering: Bench-scale verification. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2019, 139, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Tang, C.; Li, C.; Yuan, J.; Tran, K.Q.; Bach, Q.V.; Qiu, R.; Yang, Y. Wet torrefaction of biomass for high quality solid fuel production: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 91, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubrowska-Sudol, M.; Walczak, J. Enhancing combined biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal from wastewater by applying mechanically disintegrated excess sludge. Water Res. 2015, 76, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubrowska-Sudol, M.; Walczak, J. Effects of mechanical disintegration of activated sludge on the activity of nitrifying and denitrifying bacteria and phosphorus accumulating organisms. Water Res. 2014, 61, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, K.; Kjørlaug, O.; Higgins, M.J.; Linjordet, R.; Horn, S.J. Post-anaerobic digestion thermal hydrolysis of sewage sludge and food waste: Effect on methane yields, dewaterability and solids reduction. Water Res. 2018, 132, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogan, E.; Atila, B.; Mumme, J.; Reza, M.T.; Toptas, A.; Elibol, M.; Yanik, J. Characterization of products from hydrothermal carbonization of orange pomace including anaerobic digestibility of process liquor. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 196, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funke, A.; Mumme, J.; Koon, M.; Diakité, M. Cascaded production of biogas and hydrochar from wheat straw: Energetic potential and recovery of carbon and plant nutrients. Biomass Bioenergy 2013, 58, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, B.; Mumme, J. Anaerobic Digestion of Waste Water from Hydrothermal Carbonization of Corn Silage. Appl. Bioenergy 2014, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedsadr, S.; Al Afif, R.; Pfeifer, C. Hydrothermal carbonization of agricultural residues: A case study of the farm residues -based biogas plants. Carbon Resour. Convers. 2018, 1, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Chen, H.; Chen, K.; Ren, S.; Clark, J.H.; Fan, J.; Luo, G.; Zhang, S. Characterization and utilization of aqueous products from hydrothermal conversion of biomass for bio-oil and hydro-char production: A review. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 1553–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, K.R.; Ross, A.B. Integration of hydrothermal carbonisation with anaerobic digestion; Opportunities for valorisation of digestate. Energies 2019, 12, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragón-Briceño, C.; Ross, A.B.; Camargo-Valero, M.A. Evaluation and comparison of product yields and bio-methane potential in sewage digestate following hydrothermal treatment. Appl. Energy 2017, 208, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, A.; Chang, Y. Hydrothermal treatment coupled with mechanical expression at increased temperature for excess sludge dewatering: Heavy metals, volatile organic compounds and combustion characteristics of hydrochar. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 297, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, F.C.; Cordiner, S.; Manni, A.; Mulone, V.; Rocco, V. Anaerobic digestion of coffee grounds soluble fraction at laboratory scale: Evaluation of the biomethane potential. Appl. Energy 2017, 207, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabsch-Korbutowicz, M.; Wisniewski, J.; Lakomska, S.; Urbanowska, A. Application of UF, NF and ED in natural organic matter removal from ion-exchange spent regenerant brine. Desalination 2011, 280, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Hastings, J.T.; Acharjee, T.C.; Coronella, C.J.; Vásquez, V.R. Mass and energy balances of wet torrefaction of lignocellulosic biomass. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 4738–4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, P.W. Introduction to Analytical Gas Chromatography, 2nd ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Persson, H.; Yang, W.; Jönsson, P.G. Pyrolysis study of hydrothermal carbonization-treated digested sewage sludge using a Py-GC/MS and a bench-scale pyrolyzer. Fuel 2019, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danso-Boateng, E.; Shama, G.; Wheatley, A.D.; Martin, S.J.; Holdich, R.G. Hydrothermal carbonisation of sewage sludge: Effect of process conditions on product characteristics and methane production. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 177, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamil, J.A.; Mohedano, A.F.; Rodríguez, J.J.; Borja, R.; De la Rubia, M.A. Anaerobic Co-digestion of the Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste and the Liquid Fraction From the Hydrothermal Carbonization of Industrial Sewage Sludge Under Thermophilic Conditions. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2018, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiumenti, A.; Da Borso, F.; Teri, F.; Chiumenti, R.; Piaia, B. Full-scale membrane filtration system for the treatment of digestate from a co-digestion plant. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2013, 29, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.B.; Panigrahi, S.; Dubey, B.K. Hydrothermal carbonization of yard waste for solid bio-fuel production: Study on combustion kinetic, energy properties, grindability and flowability of hydrochar. Waste Manag. 2019, 91, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kambo, H.S.; Dutta, A. Comparative evaluation of torrefaction and hydrothermal carbonization of lignocellulosic biomass for the production of solid biofuel. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 105, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).